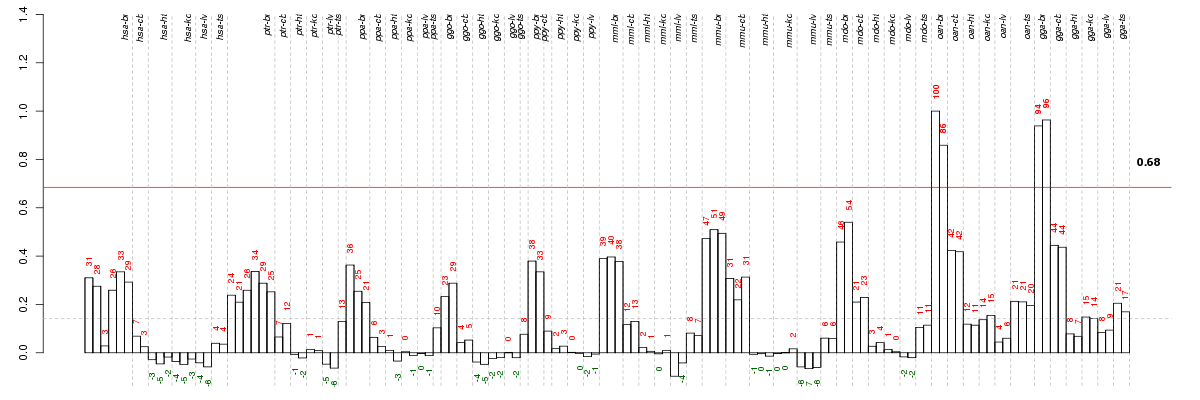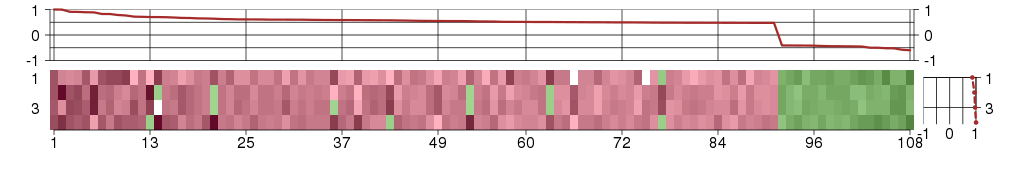

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

regulation of heart rate
Any process that modulates the frequency or rate of heart contraction.
system process
A multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system. An organ system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a biological objective.
circulatory system process
A organ system process carried out by any of the organs or tissues of the circulatory system. The circulatory system is an organ system that moves extracellular fluids to and from tissue within a multicellular organism.
heart process
A circulatory system process carried out by the heart. The heart is a hollow, muscular organ, which, by contracting rhythmically, keeps up the circulation of the blood. The heart is a hollow, muscular organ, which, by contracting rhythmically, keeps up the circulation of the blood.
signal transduction
The process whereby an activated receptor conveys information down the signaling pathway, resulting in a change in the function or state of a cell.
transport
The directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells, or within a multicellular organism by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
ion transport
The directed movement of charged atoms or small charged molecules into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
cell communication
Any process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
cell surface receptor linked signaling pathway
Any series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of an extracellular ligand to a receptor on the surface of the target cell.
G-protein coupled receptor protein signaling pathway
The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a G-protein coupled receptor binding to its physiological ligand.
G-protein signaling, coupled to cyclic nucleotide second messenger
The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a G-protein coupled receptor binding to its physiological ligand, followed by modulation of a nucleotide cyclase activity and a subsequent change in the concentration of a cyclic nucleotide.
cell-cell signaling
Any process that mediates the transfer of information from one cell to another.
synaptic transmission
The process of communication from a neuron to a target (neuron, muscle, or secretory cell) across a synapse.
neurological system process
A organ system process carried out by any of the organs or tissues of neurological system.
behavior
The specific actions or reactions of an organism in response to external or internal stimuli. Patterned activity of a whole organism in a manner dependent upon some combination of that organism's internal state and external conditions.
blood circulation
The flow of blood through the body of an animal, enabling the transport of nutrients to the tissues and the removal of waste products.
regulation of heart contraction
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of heart contraction. Heart contraction is the process by which the heart decreases in volume in a characteristic way to propel blood through the body.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
transmission of nerve impulse
The neurological system process by which a signal is transmitted through the nervous system by synaptic transmission and the sequential electrochemical polarization and depolarization that travels across the membrane of a nerve cell (neuron) in response to stimulation.
second-messenger-mediated signaling
A series of molecular signals in which an ion or small molecule is formed or released into the cytosol, thereby helping relay the signal within the cell.
cyclic-nucleotide-mediated signaling
A series of molecular signals in which a cell uses a cyclic nucleotide to convert an extracellular signal into a response.
signaling pathway
The series of molecular events whereby information is sent from one location to another within a living organism or between living organisms.
intracellular signaling pathway
The series of molecular events whereby information is sent from one location to another within a cell.
signaling process
Any biological process involved in the generation, transmission, reception, or interpretation of a signal. A signal is an entity used to transmit or convey information.
signaling
The entirety of a process whereby information is transmitted. This process begins with the initiation of the signal and ends when a response has been triggered.
signal transmission
The process whereby a signal is released and/or conveyed from one location to another.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
intracellular signal transduction
The process whereby a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell.
regulation of system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a system process, a multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
heart contraction
The multicellular organismal process by which the heart decreases in volume in a characteristic way to propel blood through the body.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of biological quality
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological quality. A biological quality is a measurable attribute of an organism or part of an organism, such as size, mass, shape, color, etc.
all
NA
signaling process
Any biological process involved in the generation, transmission, reception, or interpretation of a signal. A signal is an entity used to transmit or convey information.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
cell-cell signaling
Any process that mediates the transfer of information from one cell to another.
signal transduction
The process whereby an activated receptor conveys information down the signaling pathway, resulting in a change in the function or state of a cell.
transmission of nerve impulse
The neurological system process by which a signal is transmitted through the nervous system by synaptic transmission and the sequential electrochemical polarization and depolarization that travels across the membrane of a nerve cell (neuron) in response to stimulation.
regulation of system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a system process, a multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system.
synaptic transmission
The process of communication from a neuron to a target (neuron, muscle, or secretory cell) across a synapse.
intracellular signal transduction
The process whereby a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell.
transmission of nerve impulse
The neurological system process by which a signal is transmitted through the nervous system by synaptic transmission and the sequential electrochemical polarization and depolarization that travels across the membrane of a nerve cell (neuron) in response to stimulation.
heart contraction
The multicellular organismal process by which the heart decreases in volume in a characteristic way to propel blood through the body.
regulation of heart rate
Any process that modulates the frequency or rate of heart contraction.
regulation of heart contraction
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of heart contraction. Heart contraction is the process by which the heart decreases in volume in a characteristic way to propel blood through the body.
G-protein signaling, coupled to cyclic nucleotide second messenger
The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a G-protein coupled receptor binding to its physiological ligand, followed by modulation of a nucleotide cyclase activity and a subsequent change in the concentration of a cyclic nucleotide.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
integral to membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer. When used to describe a protein, indicates that all or part of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
ion channel complex
A protein complex that spans a membrane and forms a water-filled channel across the phospholipid bilayer allowing selective ion transport down its electrochemical gradient.
cation channel complex
An ion channel complex through which cations pass.
chloride channel complex
An ion channel complex through which chloride ions pass.
protein complex
Any macromolecular complex composed of two or more polypeptide subunits, which may or may not be identical. Protein complexes may have other associated non-protein prosthetic groups, such as nucleotides, metal ions or other small molecules.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
ion channel complex
A protein complex that spans a membrane and forms a water-filled channel across the phospholipid bilayer allowing selective ion transport down its electrochemical gradient.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
ion channel complex
A protein complex that spans a membrane and forms a water-filled channel across the phospholipid bilayer allowing selective ion transport down its electrochemical gradient.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.

peptide receptor activity
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular peptide to initiate a change in cell activity.
molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
signal transducer activity
Mediates the transfer of a signal from the outside to the inside of a cell by means other than the introduction of the signal molecule itself into the cell.
receptor activity
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell activity.
transmembrane receptor activity
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell activity, and spanning to the membrane of either the cell or an organelle.
G-protein coupled receptor activity
A receptor that binds an extracellular ligand and transmits the signal to a heterotrimeric G-protein complex. These receptors are characteristically seven-transmembrane receptors and are made up of hetero- or homodimers.
transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
ion channel activity
Catalysis of facilitated diffusion of an ion (by an energy-independent process) by passage through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel without evidence for a carrier-mediated mechanism.
extracellular ligand-gated ion channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a channel that opens when a specific extracellular ligand has been bound by the channel complex or one of its constituent parts.
anion channel activity
Catalysis of the energy-independent passage of anions across a lipid bilayer down a concentration gradient.
chloride channel activity
Catalysis of facilitated diffusion of a chloride (by an energy-independent process) involving passage through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel without evidence for a carrier-mediated mechanism.
transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a substance from one side of a membrane to the other.
binding
The selective, non-covalent, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
neuropeptide receptor activity
Combining with a neuropeptide to initiate a change in cell activity.
anion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a negatively charged ion from one side of a membrane to the other.
peptide receptor activity, G-protein coupled
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular peptide to initiate a G-protein mediated change in cell activity. A G-protein is a signal transduction molecule that alternates between an inactive GDP-bound and an active GTP-bound state.
ion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of an ion from one side of a membrane to the other.
channel activity
Catalysis of energy-independent facilitated diffusion, mediated by passage of a solute through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel. Stereospecificity is not exhibited but this transport may be specific for a particular molecular species or class of molecules.
ligand-gated ion channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a channel that opens when a specific ligand has been bound by the channel complex or one of its constituent parts.
passive transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute from one side of the membrane to the other, down the solute's concentration gradient.
ligand-gated channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a solute by a channel that opens when a specific ligand has been bound by the channel complex or one of its constituent parts.
gated channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a solute by a channel that opens in response to a specific stimulus.
substrate-specific channel activity
Catalysis of energy-independent facilitated diffusion, mediated by passage of a specific solute through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel. Stereospecificity is not exhibited but this transport may be specific for a particular molecular species or class of molecules.
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
substrate-specific transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of a specific substance or group of related substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
neurotransmitter receptor activity
Combining with a neurotransmitter to initiate a change in cell activity.
neurotransmitter binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a neurotransmitter, any chemical substance that is capable of transmitting (or inhibiting the transmission of) a nerve impulse from a neuron to another cell.
peptide binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with peptides, any of a group of organic compounds comprising two or more amino acids linked by peptide bonds.
neuropeptide binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently and stoichiometrically with neuropeptides, peptides with direct synaptic effects (peptide neurotransmitters) or indirect modulatory effects on the nervous system (peptide neuromodulators).
molecular transducer activity
The molecular function that accepts an input of one form and creates an output of a different form.
all
NA
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
neuropeptide receptor activity
Combining with a neuropeptide to initiate a change in cell activity.
peptide receptor activity
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular peptide to initiate a change in cell activity.
neurotransmitter receptor activity
Combining with a neurotransmitter to initiate a change in cell activity.
substrate-specific channel activity
Catalysis of energy-independent facilitated diffusion, mediated by passage of a specific solute through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel. Stereospecificity is not exhibited but this transport may be specific for a particular molecular species or class of molecules.
ion channel activity
Catalysis of facilitated diffusion of an ion (by an energy-independent process) by passage through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel without evidence for a carrier-mediated mechanism.
neuropeptide receptor activity
Combining with a neuropeptide to initiate a change in cell activity.
anion channel activity
Catalysis of the energy-independent passage of anions across a lipid bilayer down a concentration gradient.
peptide receptor activity, G-protein coupled
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular peptide to initiate a G-protein mediated change in cell activity. A G-protein is a signal transduction molecule that alternates between an inactive GDP-bound and an active GTP-bound state.
ligand-gated ion channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a channel that opens when a specific ligand has been bound by the channel complex or one of its constituent parts.
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 04080 | 7.535e-09 | 2.399 | 17 | 102 | Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction |
ACCN4amiloride-sensitive cation channel 4, pituitary (ENSG00000072182), score: 0.5 ACVR2Aactivin A receptor, type IIA (ENSG00000121989), score: 0.49 ALX4ALX homeobox 4 (ENSG00000052850), score: 0.48 ANKFN1ankyrin-repeat and fibronectin type III domain containing 1 (ENSG00000153930), score: 0.48 ANKRA2ankyrin repeat, family A (RFXANK-like), 2 (ENSG00000164331), score: 0.48 ANKRD27ankyrin repeat domain 27 (VPS9 domain) (ENSG00000105186), score: -0.5 APEHN-acylaminoacyl-peptide hydrolase (ENSG00000164062), score: -0.41 AVPR1Barginine vasopressin receptor 1B (ENSG00000198049), score: 0.7 B3GALT5UDP-Gal:betaGlcNAc beta 1,3-galactosyltransferase, polypeptide 5 (ENSG00000183778), score: 0.48 BCL11BB-cell CLL/lymphoma 11B (zinc finger protein) (ENSG00000127152), score: 0.58 BMP3bone morphogenetic protein 3 (ENSG00000152785), score: 0.62 BRS3bombesin-like receptor 3 (ENSG00000102239), score: 0.89 C18orf55chromosome 18 open reading frame 55 (ENSG00000075336), score: -0.44 C20orf186chromosome 20 open reading frame 186 (ENSG00000186191), score: 0.65 C5orf24chromosome 5 open reading frame 24 (ENSG00000181904), score: 0.48 C6orf106chromosome 6 open reading frame 106 (ENSG00000196821), score: -0.5 CDC40cell division cycle 40 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000168438), score: 0.51 CLCN3chloride channel 3 (ENSG00000109572), score: 0.53 CNGB1cyclic nucleotide gated channel beta 1 (ENSG00000070729), score: 0.6 CNTN3contactin 3 (plasmacytoma associated) (ENSG00000113805), score: 0.61 CNTN5contactin 5 (ENSG00000149972), score: 0.78 COL25A1collagen, type XXV, alpha 1 (ENSG00000188517), score: 0.51 CPLX4complexin 4 (ENSG00000166569), score: 0.51 CPSF4cleavage and polyadenylation specific factor 4, 30kDa (ENSG00000160917), score: -0.43 CSMD2CUB and Sushi multiple domains 2 (ENSG00000121904), score: 0.48 CTNND1catenin (cadherin-associated protein), delta 1 (ENSG00000198561), score: -0.52 CUL4Acullin 4A (ENSG00000139842), score: -0.58 DCLK3doublecortin-like kinase 3 (ENSG00000163673), score: 0.48 DCTN4dynactin 4 (p62) (ENSG00000132912), score: 0.5 DGKIdiacylglycerol kinase, iota (ENSG00000157680), score: 0.57 DLX6distal-less homeobox 6 (ENSG00000006377), score: 0.59 DRD2dopamine receptor D2 (ENSG00000149295), score: 0.48 DUSP19dual specificity phosphatase 19 (ENSG00000162999), score: 0.5 EPHA3EPH receptor A3 (ENSG00000044524), score: 0.55 EPHA5EPH receptor A5 (ENSG00000145242), score: 0.62 FAM120Bfamily with sequence similarity 120B (ENSG00000112584), score: -0.41 FIBCD1fibrinogen C domain containing 1 (ENSG00000130720), score: 0.6 FUT11fucosyltransferase 11 (alpha (1,3) fucosyltransferase) (ENSG00000196968), score: -0.41 GAAglucosidase, alpha; acid (ENSG00000171298), score: -0.44 GABRA2gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, alpha 2 (ENSG00000151834), score: 0.55 GABRA4gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, alpha 4 (ENSG00000109158), score: 0.51 GABREgamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, epsilon (ENSG00000102287), score: 0.59 GALNTL6UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase-like 6 (ENSG00000174473), score: 0.59 GALR1galanin receptor 1 (ENSG00000166573), score: 0.76 GBX2gastrulation brain homeobox 2 (ENSG00000168505), score: 0.52 GDPD5glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase domain containing 5 (ENSG00000158555), score: 0.48 GLRA2glycine receptor, alpha 2 (ENSG00000101958), score: 0.48 GLRA3glycine receptor, alpha 3 (ENSG00000145451), score: 0.51 GPR139G protein-coupled receptor 139 (ENSG00000180269), score: 0.82 GRIN2Bglutamate receptor, ionotropic, N-methyl D-aspartate 2B (ENSG00000150086), score: 0.6 HBP1HMG-box transcription factor 1 (ENSG00000105856), score: -0.41 HHLA1HERV-H LTR-associating 1 (ENSG00000132297), score: 0.59 HTR1D5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 1D (ENSG00000179546), score: 0.67 HTR45-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 4 (ENSG00000164270), score: 0.72 IL1RAPL1interleukin 1 receptor accessory protein-like 1 (ENSG00000169306), score: 0.61 IL1RAPL2interleukin 1 receptor accessory protein-like 2 (ENSG00000189108), score: 1 ITFG1integrin alpha FG-GAP repeat containing 1 (ENSG00000129636), score: 0.56 KCNA4potassium voltage-gated channel, shaker-related subfamily, member 4 (ENSG00000182255), score: 0.55 KCNG3potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily G, member 3 (ENSG00000171126), score: 0.53 KCNQ3potassium voltage-gated channel, KQT-like subfamily, member 3 (ENSG00000184156), score: 0.48 KCNS2potassium voltage-gated channel, delayed-rectifier, subfamily S, member 2 (ENSG00000156486), score: 0.67 KCTD4potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 4 (ENSG00000180332), score: 0.51 KIAA2022KIAA2022 (ENSG00000050030), score: 0.52 LHX8LIM homeobox 8 (ENSG00000162624), score: 0.49 LMO1LIM domain only 1 (rhombotin 1) (ENSG00000166407), score: 0.53 LOC100133692similar to cell division cycle 2-like 1 (PITSLRE proteins) (ENSG00000008128), score: -0.45 LOC100291726similar to family with sequence similarity 70, member A (ENSG00000125355), score: 0.6 LRMPlymphoid-restricted membrane protein (ENSG00000118308), score: 0.61 LRRC41leucine rich repeat containing 41 (ENSG00000132128), score: -0.44 LRRC7leucine rich repeat containing 7 (ENSG00000033122), score: 0.61 MAN2C1mannosidase, alpha, class 2C, member 1 (ENSG00000140400), score: -0.42 MCF2MCF.2 cell line derived transforming sequence (ENSG00000101977), score: 0.55 MDGA2MAM domain containing glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor 2 (ENSG00000139915), score: 0.58 MLXIPMLX interacting protein (ENSG00000175727), score: -0.6 MYOGmyogenin (myogenic factor 4) (ENSG00000122180), score: 0.58 NDST4N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase (heparan glucosaminyl) 4 (ENSG00000138653), score: 0.58 NFKB1nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 1 (ENSG00000109320), score: -0.45 NPY2Rneuropeptide Y receptor Y2 (ENSG00000185149), score: 0.91 NPY5Rneuropeptide Y receptor Y5 (ENSG00000164129), score: 0.49 NTSneurotensin (ENSG00000133636), score: 0.82 NTSR1neurotensin receptor 1 (high affinity) (ENSG00000101188), score: 0.48 OFCC1orofacial cleft 1 candidate 1 (ENSG00000181355), score: 0.54 OLIG3oligodendrocyte transcription factor 3 (ENSG00000177468), score: 1 OPRK1opioid receptor, kappa 1 (ENSG00000082556), score: 0.65 OTOFotoferlin (ENSG00000115155), score: 0.55 P2RY1purinergic receptor P2Y, G-protein coupled, 1 (ENSG00000169860), score: 0.5 PLCB1phospholipase C, beta 1 (phosphoinositide-specific) (ENSG00000182621), score: 0.48 POU1F1POU class 1 homeobox 1 (ENSG00000064835), score: 0.7 RPE65retinal pigment epithelium-specific protein 65kDa (ENSG00000116745), score: 0.58 RSPO3R-spondin 3 homolog (Xenopus laevis) (ENSG00000146374), score: 0.5 RXFP3relaxin/insulin-like family peptide receptor 3 (ENSG00000182631), score: 0.48 SEMA3Asema domain, immunoglobulin domain (Ig), short basic domain, secreted, (semaphorin) 3A (ENSG00000075213), score: 0.58 SLC25A37solute carrier family 25, member 37 (ENSG00000147454), score: -0.52 SLC5A7solute carrier family 5 (choline transporter), member 7 (ENSG00000115665), score: 0.91 SV2Csynaptic vesicle glycoprotein 2C (ENSG00000122012), score: 0.71 TAC1tachykinin, precursor 1 (ENSG00000006128), score: 0.7 TFAP2Dtranscription factor AP-2 delta (activating enhancer binding protein 2 delta) (ENSG00000008197), score: 0.89 THSD7Athrombospondin, type I, domain containing 7A (ENSG00000005108), score: 0.59 TMEM117transmembrane protein 117 (ENSG00000139173), score: 0.49 TMEM200Atransmembrane protein 200A (ENSG00000164484), score: 0.5 TPBGtrophoblast glycoprotein (ENSG00000146242), score: 0.57 TRPC1transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily C, member 1 (ENSG00000144935), score: 0.49 TRPC5transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily C, member 5 (ENSG00000072315), score: 0.69 VWC2Lvon Willebrand factor C domain-containing protein 2-like (ENSG00000174453), score: 0.51 WNT3Awingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 3A (ENSG00000154342), score: 0.64 WNT4wingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 4 (ENSG00000162552), score: 0.6 ZNF326zinc finger protein 326 (ENSG00000162664), score: 0.48
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| oan_br_f_ca1 | oan | br | f | _ |
| gga_br_m_ca1 | gga | br | m | _ |
| gga_br_f_ca1 | gga | br | f | _ |
| oan_br_m_ca1 | oan | br | m | _ |