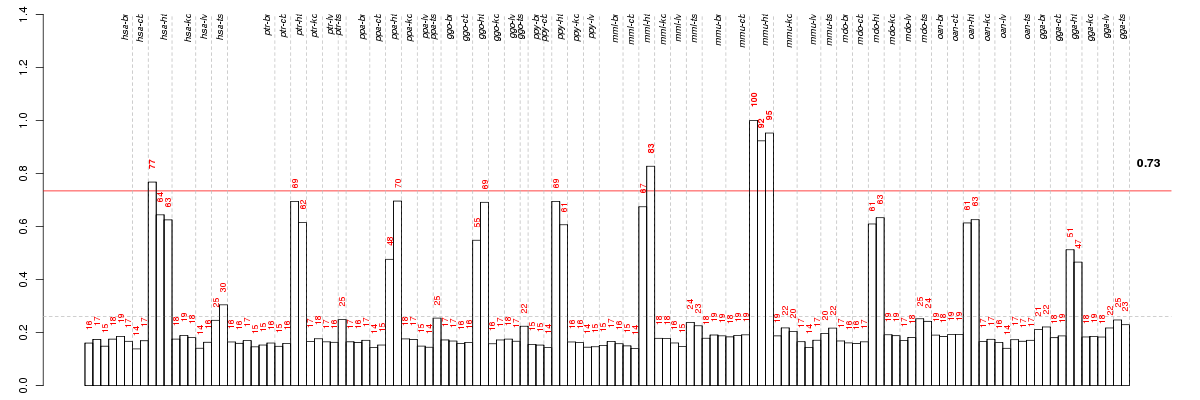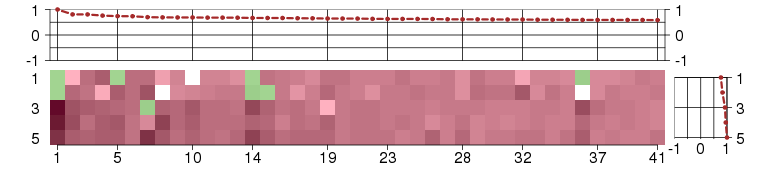

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

system process
A multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system. An organ system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a biological objective.
muscle system process
A organ system process carried out at the level of a muscle. Muscle tissue is composed of contractile cells or fibers.
circulatory system process
A organ system process carried out by any of the organs or tissues of the circulatory system. The circulatory system is an organ system that moves extracellular fluids to and from tissue within a multicellular organism.
heart process
A circulatory system process carried out by the heart. The heart is a hollow, muscular organ, which, by contracting rhythmically, keeps up the circulation of the blood. The heart is a hollow, muscular organ, which, by contracting rhythmically, keeps up the circulation of the blood.
muscle contraction
A process whereby force is generated within muscle tissue, resulting in a change in muscle geometry. Force generation involves a chemo-mechanical energy conversion step that is carried out by the actin/myosin complex activity, which generates force through ATP hydrolysis.
striated muscle contraction
A process whereby force is generated within striated muscle tissue, resulting in the shortening of the muscle. Force generation involves a chemo-mechanical energy conversion step that is carried out by the actin/myosin complex activity, which generates force through ATP hydrolysis. Striated muscle is a type of muscle in which the repeating units (sarcomeres) of the contractile myofibrils are arranged in registry throughout the cell, resulting in transverse or oblique striations observable at the level of the light microscope.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
muscle organ development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the muscle over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The muscle is an organ consisting of a tissue made up of various elongated cells that are specialized to contract and thus to produce movement and mechanical work.
blood circulation
The flow of blood through the body of an animal, enabling the transport of nutrients to the tissues and the removal of waste products.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
heart contraction
The multicellular organismal process by which the heart decreases in volume in a characteristic way to propel blood through the body.
cardiac muscle contraction
Muscle contraction of cardiac muscle tissue.
muscle structure development
The progression of a muscle structure over time, from its formation to its mature state. Muscle structures are contractile cells, tissues or organs that are found in multicellular organisms.
all
NA
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
muscle organ development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the muscle over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The muscle is an organ consisting of a tissue made up of various elongated cells that are specialized to contract and thus to produce movement and mechanical work.
heart contraction
The multicellular organismal process by which the heart decreases in volume in a characteristic way to propel blood through the body.
cardiac muscle contraction
Muscle contraction of cardiac muscle tissue.

intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
contractile fiber
Fibers, composed of actin, myosin, and associated proteins, found in cells of smooth or striated muscle.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cytoplasm
All of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
cytoskeleton
Any of the various filamentous elements that form the internal framework of cells, and typically remain after treatment of the cells with mild detergent to remove membrane constituents and soluble components of the cytoplasm. The term embraces intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, the microtrabecular lattice, and other structures characterized by a polymeric filamentous nature and long-range order within the cell. The various elements of the cytoskeleton not only serve in the maintenance of cellular shape but also have roles in other cellular functions, including cellular movement, cell division, endocytosis, and movement of organelles.
muscle myosin complex
A filament of myosin found in a muscle cell of any type.
actin cytoskeleton
The part of the cytoskeleton (the internal framework of a cell) composed of actin and associated proteins. Includes actin cytoskeleton-associated complexes.
myosin complex
A protein complex, formed of one or more myosin heavy chains plus associated light chains and other proteins, that functions as a molecular motor; uses the energy of ATP hydrolysis to move actin filaments or to move vesicles or other cargo on fixed actin filaments; has magnesium-ATPase activity and binds actin. Myosin classes are distinguished based on sequence features of the motor, or head, domain, but also have distinct tail regions that are believed to bind specific cargoes.
myosin II complex
A myosin complex containing two class II myosin heavy chains, two myosin essential light chains and two myosin regulatory light chains. Also known as classical myosin or conventional myosin, the myosin II class includes the major muscle myosin of vertebrate and invertebrate muscle, and is characterized by alpha-helical coiled coil tails that self assemble to form a variety of filament structures.
myofibril
The contractile element of skeletal and cardiac muscle; a long, highly organized bundle of actin, myosin, and other proteins that contracts by a sliding filament mechanism.
sarcomere
The repeating unit of a myofibril in a muscle cell, composed of an array of overlapping thick and thin filaments between two adjacent Z discs.
I band
A region of a sarcomere that appears as a light band on each side of the Z disc, comprising a region of the sarcomere where thin (actin) filaments are not overlapped by thick (myosin) filaments; contains actin, troponin, and tropomyosin; each sarcomere includes half of an I band at each end.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, and prokaryotic structures such as anammoxosomes and pirellulosomes. Excludes the plasma membrane.
non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
protein complex
Any macromolecular complex composed of two or more polypeptide subunits, which may or may not be identical. Protein complexes may have other associated non-protein prosthetic groups, such as nucleotides, metal ions or other small molecules.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
contractile fiber part
Any constituent part of a contractile fiber, a fiber composed of actin, myosin, and associated proteins, found in cells of smooth or striated muscle.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
myosin complex
A protein complex, formed of one or more myosin heavy chains plus associated light chains and other proteins, that functions as a molecular motor; uses the energy of ATP hydrolysis to move actin filaments or to move vesicles or other cargo on fixed actin filaments; has magnesium-ATPase activity and binds actin. Myosin classes are distinguished based on sequence features of the motor, or head, domain, but also have distinct tail regions that are believed to bind specific cargoes.
I band
A region of a sarcomere that appears as a light band on each side of the Z disc, comprising a region of the sarcomere where thin (actin) filaments are not overlapped by thick (myosin) filaments; contains actin, troponin, and tropomyosin; each sarcomere includes half of an I band at each end.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
contractile fiber
Fibers, composed of actin, myosin, and associated proteins, found in cells of smooth or striated muscle.
contractile fiber part
Any constituent part of a contractile fiber, a fiber composed of actin, myosin, and associated proteins, found in cells of smooth or striated muscle.
muscle myosin complex
A filament of myosin found in a muscle cell of any type.
contractile fiber part
Any constituent part of a contractile fiber, a fiber composed of actin, myosin, and associated proteins, found in cells of smooth or striated muscle.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
sarcomere
The repeating unit of a myofibril in a muscle cell, composed of an array of overlapping thick and thin filaments between two adjacent Z discs.
myosin complex
A protein complex, formed of one or more myosin heavy chains plus associated light chains and other proteins, that functions as a molecular motor; uses the energy of ATP hydrolysis to move actin filaments or to move vesicles or other cargo on fixed actin filaments; has magnesium-ATPase activity and binds actin. Myosin classes are distinguished based on sequence features of the motor, or head, domain, but also have distinct tail regions that are believed to bind specific cargoes.

protein binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any protein or protein complex (a complex of two or more proteins that may include other nonprotein molecules).
molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
structural molecule activity
The action of a molecule that contributes to the structural integrity of a complex or assembly within or outside a cell.
binding
The selective, non-covalent, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
cytoskeletal protein binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any protein component of any cytoskeleton (actin, microtubule, or intermediate filament cytoskeleton).
structural constituent of muscle
The action of a molecule that contributes to the structural integrity of a muscle fiber.
myosin binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any part of a myosin complex; myosins are any of a superfamily of molecular motor proteins that bind to actin and use the energy of ATP hydrolysis to generate force and movement along actin filaments.
myosin heavy chain binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a heavy chain of a myosin complex.
all
NA
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 05410 | 1.614e-03 | 0.1846 | 4 | 34 | Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) |
| 05414 | 1.614e-03 | 0.1846 | 4 | 34 | Dilated cardiomyopathy |
| 05412 | 2.148e-02 | 0.1683 | 3 | 31 | Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC) |
ABRAactin-binding Rho activating protein (ENSG00000174429), score: 0.63 ADAMTSL5ADAMTS-like 5 (ENSG00000185761), score: 0.63 ANKRD1ankyrin repeat domain 1 (cardiac muscle) (ENSG00000148677), score: 0.58 ASB11ankyrin repeat and SOCS box-containing 11 (ENSG00000165192), score: 0.81 ATP2A2ATPase, Ca++ transporting, cardiac muscle, slow twitch 2 (ENSG00000174437), score: 0.69 BMP10bone morphogenetic protein 10 (ENSG00000163217), score: 0.7 CACNA1Scalcium channel, voltage-dependent, L type, alpha 1S subunit (ENSG00000081248), score: 0.59 CHRNA10cholinergic receptor, nicotinic, alpha 10 (ENSG00000129749), score: 0.74 CYTL1cytokine-like 1 (ENSG00000170891), score: 0.69 EHD4EH-domain containing 4 (ENSG00000103966), score: 0.61 FBXO40F-box protein 40 (ENSG00000163833), score: 0.61 FITM2fat storage-inducing transmembrane protein 2 (ENSG00000197296), score: 0.61 FSD2fibronectin type III and SPRY domain containing 2 (ENSG00000186628), score: 0.6 FYCO1FYVE and coiled-coil domain containing 1 (ENSG00000163820), score: 0.59 GJA3gap junction protein, alpha 3, 46kDa (ENSG00000121743), score: 0.63 KBTBD5kelch repeat and BTB (POZ) domain containing 5 (ENSG00000157119), score: 0.61 KCNJ5potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 5 (ENSG00000120457), score: 0.68 KCNV2potassium channel, subfamily V, member 2 (ENSG00000168263), score: 0.67 KIF13Akinesin family member 13A (ENSG00000137177), score: 0.6 LMOD2leiomodin 2 (cardiac) (ENSG00000170807), score: 0.61 LMOD3leiomodin 3 (fetal) (ENSG00000163380), score: 0.76 LRRC10leucine rich repeat containing 10 (ENSG00000198812), score: 0.65 LRRC2leucine rich repeat containing 2 (ENSG00000163827), score: 0.63 LRRC39leucine rich repeat containing 39 (ENSG00000122477), score: 0.62 LRTM1leucine-rich repeats and transmembrane domains 1 (ENSG00000144771), score: 1 MURCmuscle-related coiled-coil protein (ENSG00000170681), score: 0.59 MYBPC3myosin binding protein C, cardiac (ENSG00000134571), score: 0.59 MYL1myosin, light chain 1, alkali; skeletal, fast (ENSG00000168530), score: 0.74 MYL4myosin, light chain 4, alkali; atrial, embryonic (ENSG00000198336), score: 0.65 MYLK3myosin light chain kinase 3 (ENSG00000140795), score: 0.63 MYLK4myosin light chain kinase family, member 4 (ENSG00000145949), score: 0.81 MYOCDmyocardin (ENSG00000141052), score: 0.68 MYPNmyopalladin (ENSG00000138347), score: 0.65 OGDHoxoglutarate (alpha-ketoglutarate) dehydrogenase (lipoamide) (ENSG00000105953), score: 0.66 PHTF2putative homeodomain transcription factor 2 (ENSG00000006576), score: 0.69 PPP1R3Aprotein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 3A (ENSG00000154415), score: 0.67 RAPSNreceptor-associated protein of the synapse (ENSG00000165917), score: 0.67 SGCGsarcoglycan, gamma (35kDa dystrophin-associated glycoprotein) (ENSG00000102683), score: 0.64 TEAD1TEA domain family member 1 (SV40 transcriptional enhancer factor) (ENSG00000187079), score: 0.59 TMEM182transmembrane protein 182 (ENSG00000170417), score: 0.6 TXLNBtaxilin beta (ENSG00000164440), score: 0.68
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa_ht_m1_ca1 | hsa | ht | m | 1 |
| mml_ht_f_ca1 | mml | ht | f | _ |
| mmu_ht_m1_ca1 | mmu | ht | m | 1 |
| mmu_ht_f_ca1 | mmu | ht | f | _ |
| mmu_ht_m2_ca1 | mmu | ht | m | 2 |