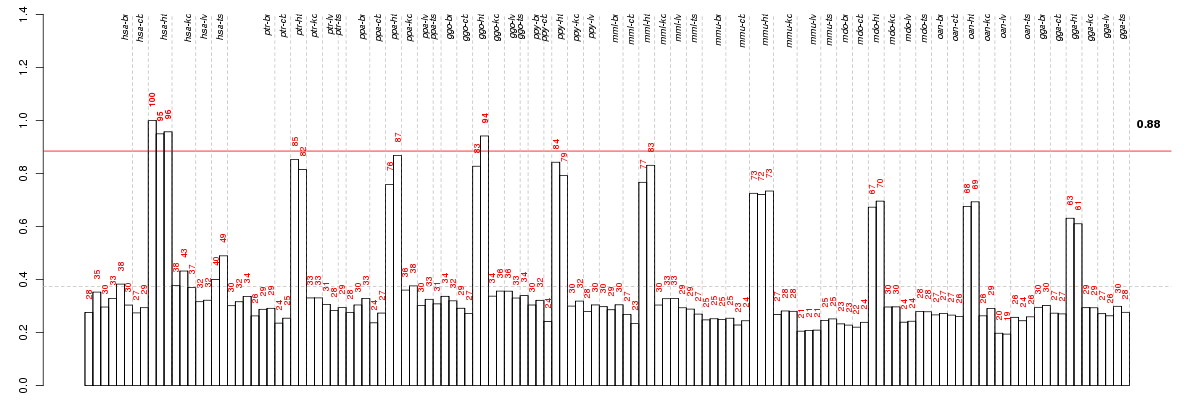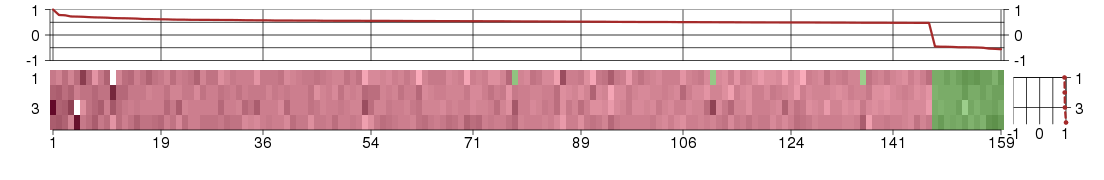

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
heart morphogenesis
The developmental process by which the heart is generated and organized. The heart is a hollow, muscular organ, which, by contracting rhythmically, keeps up the circulation of the blood.
system process
A multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system. An organ system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a biological objective.
muscle system process
A organ system process carried out at the level of a muscle. Muscle tissue is composed of contractile cells or fibers.
cardiac chamber development
The progression of a cardiac chamber over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A cardiac chamber is an enclosed cavity within the heart.
cardiac chamber morphogenesis
The process by which a cardiac chamber is generated and organized. A cardiac chamber is an enclosed cavity within the heart.
cardiac ventricle morphogenesis
The process by which the cardiac ventricle is generated and organized. A cardiac ventricle receives blood from a cardiac atrium and pumps it out of the heart.
ventricular cardiac muscle tissue development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of ventricular cardiac muscle over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
cardiac ventricle development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cardiac ventricle over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A cardiac ventricle receives blood from a cardiac atrium and pumps it out of the heart.
muscle contraction
A process whereby force is generated within muscle tissue, resulting in a change in muscle geometry. Force generation involves a chemo-mechanical energy conversion step that is carried out by the actin/myosin complex activity, which generates force through ATP hydrolysis.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of nucleotide metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleotides.
purine nucleotide metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a purine nucleotide, a compound consisting of nucleoside (a purine base linked to a deoxyribose or ribose sugar) esterified with a phosphate moiety at either the 3' or 5'-hydroxyl group of its glycose moiety.
purine nucleotide catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a purine nucleotide, a compound consisting of nucleoside (a purine base linked to a deoxyribose or ribose sugar) esterified with a phosphate moiety at either the 3' or 5'-hydroxyl group of its glycose moiety.
nucleoside phosphate metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any phosphorylated nucleoside.
nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds; includes nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, assimilatory/dissimilatory nitrate reduction and the interconversion of nitrogenous organic matter and ammonium.
striated muscle contraction
A process whereby force is generated within striated muscle tissue, resulting in the shortening of the muscle. Force generation involves a chemo-mechanical energy conversion step that is carried out by the actin/myosin complex activity, which generates force through ATP hydrolysis. Striated muscle is a type of muscle in which the repeating units (sarcomeres) of the contractile myofibrils are arranged in registry throughout the cell, resulting in transverse or oblique striations observable at the level of the light microscope.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis of an organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
tissue development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a tissue over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
heart development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the heart over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The heart is a hollow, muscular organ, which, by contracting rhythmically, keeps up the circulation of the blood.
muscle organ development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the muscle over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The muscle is an organ consisting of a tissue made up of various elongated cells that are specialized to contract and thus to produce movement and mechanical work.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of substances, including the breakdown of carbon compounds with the liberation of energy for use by the cell or organism.
nucleotide metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a nucleotide, a nucleoside that is esterified with (ortho)phosphate or an oligophosphate at any hydroxyl group on the glycose moiety; may be mono-, di- or triphosphate; this definition includes cyclic nucleotides (nucleoside cyclic phosphates).
nucleotide catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of nucleotides, any nucleoside that is esterified with (ortho)phosphate or an oligophosphate at any hydroxyl group on the glycose moiety; may be mono-, di- or triphosphate; this definition includes cyclic-nucleotides (nucleoside cyclic phosphates).
regulation of catabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of substances.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
striated muscle tissue development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a striated muscle over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Striated muscle contain fibers that are divided by transverse bands into striations, and cardiac and skeletal muscle are types of striated muscle. Skeletal muscle myoblasts fuse to form myotubes and eventually multinucleated muscle fibers. The fusion of cardiac cells is very rare and can only form binucleate cells.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
regulation of nucleotide catabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of nucleotides.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular catabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of substances, carried out by individual cells.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of purine nucleotide catabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of purine nucleotides.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
nucleobase, nucleoside and nucleotide catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of nucleobases, nucleosides and nucleotides.
regulation of ATPase activity
Any process that modulates the rate of ATP hydrolysis by an ATPase.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular nitrogen compound catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds.
small molecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
small molecule catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
heterocycle metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving heterocyclic compounds, those with a cyclic molecular structure and at least two different atoms in the ring (or rings).
heterocycle catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of heterocyclic compounds, those with a cyclic molecular structure and at least two different atoms in the ring (or rings).
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
tissue morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a tissue are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
cardiac muscle tissue development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of cardiac muscle over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of catalytic activity
Any process that modulates the activity of an enzyme.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nitrogen or nitrogenous compounds.
regulation of hydrolase activity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of hydrolase activity, the catalysis of the hydrolysis of various bonds, e.g. C-O, C-N, C-C, phosphoric anhydride bonds, etc. Hydrolase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 3.
cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of cardiac muscle tissue are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of cardiac ventricle muscle is generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
nucleobase, nucleoside and nucleotide metabolic process
The cellular chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides and nucleotides.
muscle tissue morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of muscle tissue are generated and organized. Muscle tissue consists of a set of cells that are part of an organ and carry out a contractive function. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
muscle tissue development
The progression of muscle tissue over time, from its initial formation to its mature state. Muscle tissue is a contractile tissue made up of actin and myosin fibers.
muscle structure development
The progression of a muscle structure over time, from its formation to its mature state. Muscle structures are contractile cells, tissues or organs that are found in multicellular organisms.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of molecular function
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a molecular function, an elemental biological activity occurring at the molecular level, such as catalysis or binding.
regulation of primary metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism involving those compounds formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
all
NA
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of catabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of substances.
regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nitrogen or nitrogenous compounds.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of substances, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of primary metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism involving those compounds formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
small molecule catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
regulation of catalytic activity
Any process that modulates the activity of an enzyme.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of cellular catabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular nitrogen compound catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of cellular catabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of substances, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
heterocycle catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of heterocyclic compounds, those with a cyclic molecular structure and at least two different atoms in the ring (or rings).
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
nucleobase, nucleoside and nucleotide metabolic process
The cellular chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides and nucleotides.
nucleobase, nucleoside and nucleotide catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of nucleobases, nucleosides and nucleotides.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
tissue morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a tissue are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
cardiac chamber morphogenesis
The process by which a cardiac chamber is generated and organized. A cardiac chamber is an enclosed cavity within the heart.
tissue morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a tissue are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis of an organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
tissue development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a tissue over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
muscle organ development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the muscle over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The muscle is an organ consisting of a tissue made up of various elongated cells that are specialized to contract and thus to produce movement and mechanical work.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
purine nucleotide catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a purine nucleotide, a compound consisting of nucleoside (a purine base linked to a deoxyribose or ribose sugar) esterified with a phosphate moiety at either the 3' or 5'-hydroxyl group of its glycose moiety.
nucleobase, nucleoside and nucleotide catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of nucleobases, nucleosides and nucleotides.
cardiac chamber morphogenesis
The process by which a cardiac chamber is generated and organized. A cardiac chamber is an enclosed cavity within the heart.
cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of cardiac muscle tissue are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
cardiac ventricle morphogenesis
The process by which the cardiac ventricle is generated and organized. A cardiac ventricle receives blood from a cardiac atrium and pumps it out of the heart.
heart morphogenesis
The developmental process by which the heart is generated and organized. The heart is a hollow, muscular organ, which, by contracting rhythmically, keeps up the circulation of the blood.
cardiac chamber development
The progression of a cardiac chamber over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A cardiac chamber is an enclosed cavity within the heart.
muscle tissue development
The progression of muscle tissue over time, from its initial formation to its mature state. Muscle tissue is a contractile tissue made up of actin and myosin fibers.
regulation of nucleotide catabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of nucleotides.
regulation of purine nucleotide catabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of purine nucleotides.
purine nucleotide catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a purine nucleotide, a compound consisting of nucleoside (a purine base linked to a deoxyribose or ribose sugar) esterified with a phosphate moiety at either the 3' or 5'-hydroxyl group of its glycose moiety.
regulation of nucleotide catabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of nucleotides.
regulation of nucleotide metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleotides.
purine nucleotide metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a purine nucleotide, a compound consisting of nucleoside (a purine base linked to a deoxyribose or ribose sugar) esterified with a phosphate moiety at either the 3' or 5'-hydroxyl group of its glycose moiety.
nucleotide catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of nucleotides, any nucleoside that is esterified with (ortho)phosphate or an oligophosphate at any hydroxyl group on the glycose moiety; may be mono-, di- or triphosphate; this definition includes cyclic-nucleotides (nucleoside cyclic phosphates).
ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of cardiac ventricle muscle is generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
cardiac muscle tissue development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of cardiac muscle over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of cardiac muscle tissue are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
regulation of ATPase activity
Any process that modulates the rate of ATP hydrolysis by an ATPase.
ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of cardiac ventricle muscle is generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
contractile fiber
Fibers, composed of actin, myosin, and associated proteins, found in cells of smooth or striated muscle.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
proteinaceous extracellular matrix
A layer consisting mainly of proteins (especially collagen) and glycosaminoglycans (mostly as proteoglycans) that forms a sheet underlying or overlying cells such as endothelial and epithelial cells. The proteins are secreted by cells in the vicinity. An example of this component is found in Mus musculus.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cytoplasm
All of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
cytoskeleton
Any of the various filamentous elements that form the internal framework of cells, and typically remain after treatment of the cells with mild detergent to remove membrane constituents and soluble components of the cytoplasm. The term embraces intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, the microtrabecular lattice, and other structures characterized by a polymeric filamentous nature and long-range order within the cell. The various elements of the cytoskeleton not only serve in the maintenance of cellular shape but also have roles in other cellular functions, including cellular movement, cell division, endocytosis, and movement of organelles.
adherens junction
A cell junction at which anchoring proteins (cadherins or integrins) extend through the plasma membrane and are attached to actin filaments.
cell-substrate adherens junction
An adherens junction which connects a cell to the extracellular matrix.
actin cytoskeleton
The part of the cytoskeleton (the internal framework of a cell) composed of actin and associated proteins. Includes actin cytoskeleton-associated complexes.
basolateral plasma membrane
The region of the plasma membrane that includes the basal end and sides of the cell. Often used in reference to animal polarized epithelial membranes, where the basal membrane is the part attached to the extracellular matrix, or in plant cells, where the basal membrane is defined with respect to the zygotic axis.
myofibril
The contractile element of skeletal and cardiac muscle; a long, highly organized bundle of actin, myosin, and other proteins that contracts by a sliding filament mechanism.
sarcomere
The repeating unit of a myofibril in a muscle cell, composed of an array of overlapping thick and thin filaments between two adjacent Z discs.
Z disc
Platelike region of a muscle sarcomere to which the plus ends of actin filaments are attached.
cell junction
A plasma membrane part that forms a specialized region of connection between two cells or between a cell and the extracellular matrix. At a cell junction, anchoring proteins extend through the plasma membrane to link cytoskeletal proteins in one cell to cytoskeletal proteins in neighboring cells or to proteins in the extracellular matrix.
cell-substrate junction
A cell junction that forms a connection between a cell and the extracellular matrix.
extracellular matrix
A structure lying external to one or more cells, which provides structural support for cells or tissues; may be completely external to the cell (as in animals) or be part of the cell (as in plants).
pseudopodium
A temporary protrusion or retractile process of a cell, associated with flowing movements of the protoplasm, and serving for locomotion and feeding.
A band
The dark-staining region of a sarcomere, in which myosin thick filaments are present; the center is traversed by the paler H zone, which in turn contains the M line.
I band
A region of a sarcomere that appears as a light band on each side of the Z disc, comprising a region of the sarcomere where thin (actin) filaments are not overlapped by thick (myosin) filaments; contains actin, troponin, and tropomyosin; each sarcomere includes half of an I band at each end.
cell projection
A prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, and prokaryotic structures such as anammoxosomes and pirellulosomes. Excludes the plasma membrane.
non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
contractile fiber part
Any constituent part of a contractile fiber, a fiber composed of actin, myosin, and associated proteins, found in cells of smooth or striated muscle.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
anchoring junction
A cell junction that mechanically attaches a cell (and its cytoskeleton) to neighboring cells or to the extracellular matrix.
all
NA
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
A band
The dark-staining region of a sarcomere, in which myosin thick filaments are present; the center is traversed by the paler H zone, which in turn contains the M line.
I band
A region of a sarcomere that appears as a light band on each side of the Z disc, comprising a region of the sarcomere where thin (actin) filaments are not overlapped by thick (myosin) filaments; contains actin, troponin, and tropomyosin; each sarcomere includes half of an I band at each end.
Z disc
Platelike region of a muscle sarcomere to which the plus ends of actin filaments are attached.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
contractile fiber
Fibers, composed of actin, myosin, and associated proteins, found in cells of smooth or striated muscle.
contractile fiber part
Any constituent part of a contractile fiber, a fiber composed of actin, myosin, and associated proteins, found in cells of smooth or striated muscle.
contractile fiber part
Any constituent part of a contractile fiber, a fiber composed of actin, myosin, and associated proteins, found in cells of smooth or striated muscle.
cell-substrate junction
A cell junction that forms a connection between a cell and the extracellular matrix.
sarcomere
The repeating unit of a myofibril in a muscle cell, composed of an array of overlapping thick and thin filaments between two adjacent Z discs.
cell-substrate adherens junction
An adherens junction which connects a cell to the extracellular matrix.

protein binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any protein or protein complex (a complex of two or more proteins that may include other nonprotein molecules).
molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
actin binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with monomeric or multimeric forms of actin, including actin filaments.
structural molecule activity
The action of a molecule that contributes to the structural integrity of a complex or assembly within or outside a cell.
binding
The selective, non-covalent, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
cytoskeletal protein binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any protein component of any cytoskeleton (actin, microtubule, or intermediate filament cytoskeleton).
structural constituent of muscle
The action of a molecule that contributes to the structural integrity of a muscle fiber.
titin binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with titin, any of a family of giant proteins found in striated and smooth muscle. In striated muscle, single titin molecules span half the sarcomere, with their N- and C-termini in the Z-disc and M-line, respectively.
all
NA
ABLIM1actin binding LIM protein 1 (ENSG00000099204), score: 0.49 ABRAactin-binding Rho activating protein (ENSG00000174429), score: 0.5 ACTN2actinin, alpha 2 (ENSG00000077522), score: 0.51 ADAMTS15ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 15 (ENSG00000166106), score: 0.54 ADSSadenylosuccinate synthase (ENSG00000035687), score: -0.46 ADSSL1adenylosuccinate synthase like 1 (ENSG00000185100), score: 0.49 AFAP1L1actin filament associated protein 1-like 1 (ENSG00000157510), score: 0.48 AFTPHaftiphilin (ENSG00000119844), score: -0.56 AKAP13A kinase (PRKA) anchor protein 13 (ENSG00000170776), score: 0.54 ANAPC16anaphase promoting complex subunit 16 (ENSG00000166295), score: 0.66 ANGPTL2angiopoietin-like 2 (ENSG00000136859), score: 0.55 ANKRD1ankyrin repeat domain 1 (cardiac muscle) (ENSG00000148677), score: 0.57 ANKRD2ankyrin repeat domain 2 (stretch responsive muscle) (ENSG00000165887), score: 0.66 ANO2anoctamin 2 (ENSG00000047617), score: 0.49 APOBEC2apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme, catalytic polypeptide-like 2 (ENSG00000124701), score: 0.56 APPBP2amyloid beta precursor protein (cytoplasmic tail) binding protein 2 (ENSG00000062725), score: -0.53 ARHGAP10Rho GTPase activating protein 10 (ENSG00000071205), score: 0.5 ARHGDIGRho GDP dissociation inhibitor (GDI) gamma (ENSG00000167930), score: 0.48 ARIH2ariadne homolog 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000177479), score: 0.5 ASB11ankyrin repeat and SOCS box-containing 11 (ENSG00000165192), score: 0.61 C10orf76chromosome 10 open reading frame 76 (ENSG00000120029), score: 0.71 C15orf41chromosome 15 open reading frame 41 (ENSG00000186073), score: 0.77 C1orf151chromosome 1 open reading frame 151 (ENSG00000173436), score: 0.48 C1QTNF1C1q and tumor necrosis factor related protein 1 (ENSG00000173918), score: 0.5 C6orf142chromosome 6 open reading frame 142 (ENSG00000146147), score: 0.53 CALHM2calcium homeostasis modulator 2 (ENSG00000138172), score: 0.59 CBLBCas-Br-M (murine) ecotropic retroviral transforming sequence b (ENSG00000114423), score: 0.57 CD151CD151 molecule (Raph blood group) (ENSG00000177697), score: 0.54 CD79BCD79b molecule, immunoglobulin-associated beta (ENSG00000007312), score: 0.6 CDH19cadherin 19, type 2 (ENSG00000071991), score: 0.53 CFLARCASP8 and FADD-like apoptosis regulator (ENSG00000003402), score: 0.51 CHRNA10cholinergic receptor, nicotinic, alpha 10 (ENSG00000129749), score: 0.52 CMYA5cardiomyopathy associated 5 (ENSG00000164309), score: 0.55 COL15A1collagen, type XV, alpha 1 (ENSG00000204291), score: 0.48 COL23A1collagen, type XXIII, alpha 1 (ENSG00000050767), score: 0.58 COL6A2collagen, type VI, alpha 2 (ENSG00000142173), score: 0.55 COL6A3collagen, type VI, alpha 3 (ENSG00000163359), score: 0.54 CREB3L1cAMP responsive element binding protein 3-like 1 (ENSG00000157613), score: 0.55 CSRP3cysteine and glycine-rich protein 3 (cardiac LIM protein) (ENSG00000129170), score: 0.54 DHX35DEAH (Asp-Glu-Ala-His) box polypeptide 35 (ENSG00000101452), score: 0.5 DUSP27dual specificity phosphatase 27 (putative) (ENSG00000198842), score: 0.63 EMILIN3elastin microfibril interfacer 3 (ENSG00000183798), score: 0.51 EXOSC7exosome component 7 (ENSG00000075914), score: 0.49 EYA4eyes absent homolog 4 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000112319), score: 0.52 F2RL3coagulation factor II (thrombin) receptor-like 3 (ENSG00000127533), score: 0.5 FAM129Afamily with sequence similarity 129, member A (ENSG00000135842), score: 0.54 FAM54Bfamily with sequence similarity 54, member B (ENSG00000117640), score: 0.49 FBLN2fibulin 2 (ENSG00000163520), score: 0.54 FBXO33F-box protein 33 (ENSG00000165355), score: -0.48 FBXO40F-box protein 40 (ENSG00000163833), score: 0.5 FGF18fibroblast growth factor 18 (ENSG00000156427), score: 0.6 FHL2four and a half LIM domains 2 (ENSG00000115641), score: 0.55 FHOD3formin homology 2 domain containing 3 (ENSG00000134775), score: 0.48 FIGFc-fos induced growth factor (vascular endothelial growth factor D) (ENSG00000165197), score: 0.73 FITM2fat storage-inducing transmembrane protein 2 (ENSG00000197296), score: 0.54 FKBP10FK506 binding protein 10, 65 kDa (ENSG00000141756), score: 0.49 GAB3GRB2-associated binding protein 3 (ENSG00000160219), score: 0.52 GAS6growth arrest-specific 6 (ENSG00000183087), score: 0.53 GCOM1GRINL1A complex locus (ENSG00000137878), score: 0.57 GJA3gap junction protein, alpha 3, 46kDa (ENSG00000121743), score: 0.59 GLP1Rglucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (ENSG00000112164), score: 0.72 GPR133G protein-coupled receptor 133 (ENSG00000111452), score: 0.69 GRK5G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 (ENSG00000198873), score: 0.58 GRXCR2glutaredoxin, cysteine rich 2 (ENSG00000204928), score: 0.48 HAPLN3hyaluronan and proteoglycan link protein 3 (ENSG00000140511), score: 0.56 HEY2hairy/enhancer-of-split related with YRPW motif 2 (ENSG00000135547), score: 0.6 HHATLhedgehog acyltransferase-like (ENSG00000010282), score: 0.49 HMGCR3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase (ENSG00000113161), score: -0.48 HSF1heat shock transcription factor 1 (ENSG00000185122), score: 0.51 IL18R1interleukin 18 receptor 1 (ENSG00000115604), score: 0.56 KBTBD10kelch repeat and BTB (POZ) domain containing 10 (ENSG00000239474), score: 0.56 KCNJ8potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 8 (ENSG00000121361), score: 0.49 KLHDC8Bkelch domain containing 8B (ENSG00000185909), score: 0.48 KLHL31kelch-like 31 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000124743), score: 0.57 KLHL38kelch-like 38 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000175946), score: 0.63 LAMB2laminin, beta 2 (laminin S) (ENSG00000172037), score: 0.56 LDB3LIM domain binding 3 (ENSG00000122367), score: 0.53 LIMS2LIM and senescent cell antigen-like domains 2 (ENSG00000072163), score: 0.59 LMOD2leiomodin 2 (cardiac) (ENSG00000170807), score: 0.56 LMOD3leiomodin 3 (fetal) (ENSG00000163380), score: 0.78 LRRC14Bleucine rich repeat containing 14B (ENSG00000185028), score: 0.54 LRRC2leucine rich repeat containing 2 (ENSG00000163827), score: 0.53 LRRC39leucine rich repeat containing 39 (ENSG00000122477), score: 0.52 MAFKv-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog K (avian) (ENSG00000198517), score: 0.56 MAGI3membrane associated guanylate kinase, WW and PDZ domain containing 3 (ENSG00000081026), score: -0.5 MALLmal, T-cell differentiation protein-like (ENSG00000144063), score: 0.53 MAP3K3mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 3 (ENSG00000198909), score: 0.56 MAP7microtubule-associated protein 7 (ENSG00000135525), score: -0.49 MAPKAPK3mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 3 (ENSG00000114738), score: 0.68 METTL6methyltransferase like 6 (ENSG00000206562), score: -0.54 MFN2mitofusin 2 (ENSG00000116688), score: 0.5 MLPHmelanophilin (ENSG00000115648), score: 0.48 MMP2matrix metallopeptidase 2 (gelatinase A, 72kDa gelatinase, 72kDa type IV collagenase) (ENSG00000087245), score: 0.53 MRPL21mitochondrial ribosomal protein L21 (ENSG00000197345), score: 0.52 MURCmuscle-related coiled-coil protein (ENSG00000170681), score: 0.48 MYBPC3myosin binding protein C, cardiac (ENSG00000134571), score: 0.59 MYL3myosin, light chain 3, alkali; ventricular, skeletal, slow (ENSG00000160808), score: 0.58 MYLK3myosin light chain kinase 3 (ENSG00000140795), score: 0.49 MYOCDmyocardin (ENSG00000141052), score: 0.5 MYOM2myomesin (M-protein) 2, 165kDa (ENSG00000036448), score: 0.55 MYOM3myomesin family, member 3 (ENSG00000142661), score: 0.7 MYOZ2myozenin 2 (ENSG00000172399), score: 0.57 MYPNmyopalladin (ENSG00000138347), score: 0.62 NEURL1Bneuralized homolog 1B (Drosophila) (ENSG00000214357), score: 0.58 NRAPnebulin-related anchoring protein (ENSG00000197893), score: 0.51 NRTNneurturin (ENSG00000171119), score: 0.49 PARVBparvin, beta (ENSG00000188677), score: 0.49 PBX3pre-B-cell leukemia homeobox 3 (ENSG00000167081), score: 0.59 PDE3Aphosphodiesterase 3A, cGMP-inhibited (ENSG00000172572), score: 0.52 PDGFRBplatelet-derived growth factor receptor, beta polypeptide (ENSG00000113721), score: 0.51 PDZRN3PDZ domain containing ring finger 3 (ENSG00000121440), score: 0.51 PPP1R14Cprotein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 14C (ENSG00000198729), score: 0.51 PPP1R3Aprotein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 3A (ENSG00000154415), score: 0.59 PRELPproline/arginine-rich end leucine-rich repeat protein (ENSG00000188783), score: 0.52 PTCD1pentatricopeptide repeat domain 1 (ENSG00000106246), score: 0.52 PTGES2prostaglandin E synthase 2 (ENSG00000148334), score: 0.48 PTGFRNprostaglandin F2 receptor negative regulator (ENSG00000134247), score: 0.51 PTX3pentraxin 3, long (ENSG00000163661), score: 0.66 RBM24RNA binding motif protein 24 (ENSG00000112183), score: 0.49 RBPMS2RNA binding protein with multiple splicing 2 (ENSG00000166831), score: 0.48 RPL3Lribosomal protein L3-like (ENSG00000140986), score: 0.56 RRADRas-related associated with diabetes (ENSG00000166592), score: 0.55 RSPO1R-spondin homolog (Xenopus laevis) (ENSG00000169218), score: 0.53 SGCGsarcoglycan, gamma (35kDa dystrophin-associated glycoprotein) (ENSG00000102683), score: 0.56 SH3RF2SH3 domain containing ring finger 2 (ENSG00000156463), score: 0.49 SLC25A17solute carrier family 25 (mitochondrial carrier; peroxisomal membrane protein, 34kDa), member 17 (ENSG00000100372), score: -0.47 SLC26A9solute carrier family 26, member 9 (ENSG00000174502), score: 0.59 SLC35B4solute carrier family 35, member B4 (ENSG00000205060), score: -0.48 SLC41A1solute carrier family 41, member 1 (ENSG00000133065), score: 0.65 SMPXsmall muscle protein, X-linked (ENSG00000091482), score: 0.54 SMYD1SET and MYND domain containing 1 (ENSG00000115593), score: 0.56 SMYD2SET and MYND domain containing 2 (ENSG00000143499), score: 0.49 SNX10sorting nexin 10 (ENSG00000086300), score: -0.46 SORBS1sorbin and SH3 domain containing 1 (ENSG00000095637), score: 0.5 SYNMsynemin, intermediate filament protein (ENSG00000182253), score: 0.56 SYNPO2synaptopodin 2 (ENSG00000172403), score: 0.57 TBC1D8TBC1 domain family, member 8 (with GRAM domain) (ENSG00000204634), score: 0.54 TBX18T-box 18 (ENSG00000112837), score: 0.5 TBX20T-box 20 (ENSG00000164532), score: 0.54 TBX5T-box 5 (ENSG00000089225), score: 0.55 TECRLtrans-2,3-enoyl-CoA reductase-like (ENSG00000205678), score: 0.58 TMC6transmembrane channel-like 6 (ENSG00000141524), score: 0.55 TMEM182transmembrane protein 182 (ENSG00000170417), score: 0.51 TNNC1troponin C type 1 (slow) (ENSG00000114854), score: 0.55 TPM1tropomyosin 1 (alpha) (ENSG00000140416), score: 0.6 TPOthyroid peroxidase (ENSG00000115705), score: 1 TRIM63tripartite motif-containing 63 (ENSG00000158022), score: 0.52 TSPAN18tetraspanin 18 (ENSG00000157570), score: 0.48 TUBB6tubulin, beta 6 (ENSG00000176014), score: 0.49 TXLNBtaxilin beta (ENSG00000164440), score: 0.48 TYRP1tyrosinase-related protein 1 (ENSG00000107165), score: 0.64 UHRF1BP1LUHRF1 binding protein 1-like (ENSG00000111647), score: -0.45 UQCRC1ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase core protein I (ENSG00000010256), score: 0.48 VIPR2vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor 2 (ENSG00000106018), score: 0.56 VITvitrin (ENSG00000205221), score: 0.69 WISP2WNT1 inducible signaling pathway protein 2 (ENSG00000064205), score: 0.51 WNT11wingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 11 (ENSG00000085741), score: 0.5 ZAKsterile alpha motif and leucine zipper containing kinase AZK (ENSG00000091436), score: 0.49 ZNF330zinc finger protein 330 (ENSG00000109445), score: 0.61
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ggo_ht_f_ca1 | ggo | ht | f | _ |
| hsa_ht_m2_ca1 | hsa | ht | m | 2 |
| hsa_ht_f_ca1 | hsa | ht | f | _ |
| hsa_ht_m1_ca1 | hsa | ht | m | 1 |