

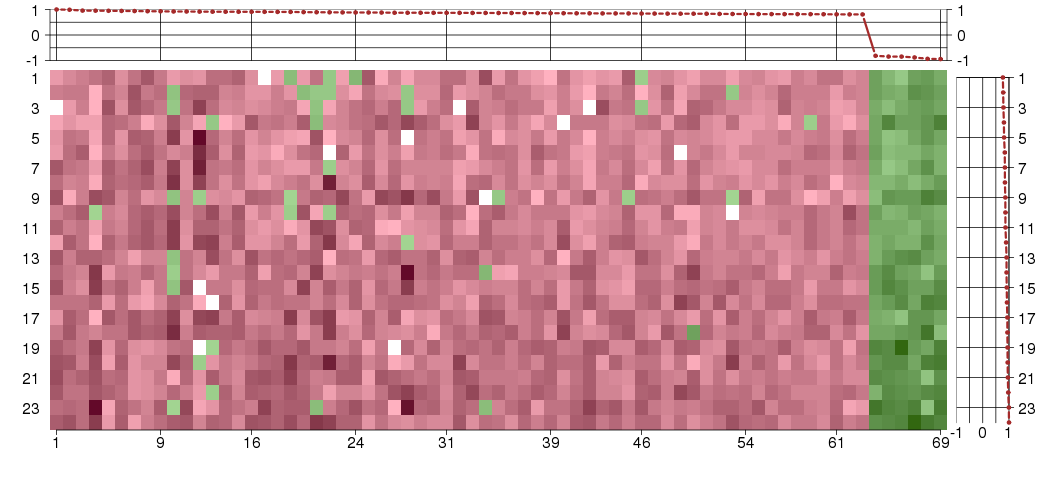

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
alcohol metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving alcohols, any of a class of compounds containing one or more hydroxyl groups attached to a saturated carbon atom.
organic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
cellular amino acid and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, and compounds derived from amino acids, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular amino acid derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving compounds derived from amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
cellular biogenic amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways occurring at the level of individual cells involving any of a group of naturally occurring, biologically active amines, such as norepinephrine, histamine, and serotonin, many of which act as neurotransmitters.
catecholamine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any of a group of physiologically important biogenic amines that possess a catechol (3,4-dihydroxyphenyl) nucleus and are derivatives of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylethylamine.
cellular aromatic compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving aromatic compounds, any organic compound characterized by one or more planar rings, each of which contains conjugated double bonds and delocalized pi electrons, as carried out by individual cells.
nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds; includes nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, assimilatory/dissimilatory nitrate reduction and the interconversion of nitrogenous organic matter and ammonium.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones.
amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
amine biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
catechol metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a compound containing a pyrocatechol (1,2-benzenediol) nucleus or substituent.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
phenol metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a phenol, any compound containing one or more hydroxyl groups directly attached to an aromatic carbon ring. The largest single use of phenol is in the production of plastics, but it is also used in the synthesis of caprolactam, a precursor for nylon 6 and other man-made fibers.
carboxylic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving carboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (COOH) groups or anions (COO-).
diol metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a diol, any alcohol containing two hydroxyl groups attached to saturated carbon atoms.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular ketone metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any of a class of organic compounds that contain the carbonyl group, CO, and in which the carbonyl group is bonded only to carbon atoms, as carried out by individual cells. The general formula for a ketone is RCOR, where R and R are alkyl or aryl groups.
cellular amino acid derivative biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of compounds derived from amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
cellular biogenic amine biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways occurring at the level of individual cells resulting in the formation of any of a group of naturally occurring, biologically active amines, such as norepinephrine, histamine, and serotonin, many of which act as neurotransmitters.
catecholamine biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of any of a group of physiologically important biogenic amines that possess a catechol (3,4-dihydroxyphenyl) nucleus and are derivatives of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylethylamine.
oxoacid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any oxoacid; an oxoacid is a compound which contains oxygen, at least one other element, and at least one hydrogen bound to oxygen, and which produces a conjugate base by loss of positive hydrogen ion(s) (hydrons).
cellular amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular nitrogen compound biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds.
small molecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
small molecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
all
NA
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular amino acid and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, and compounds derived from amino acids, as carried out by individual cells.
organic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
cellular amino acid and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, and compounds derived from amino acids, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular ketone metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any of a class of organic compounds that contain the carbonyl group, CO, and in which the carbonyl group is bonded only to carbon atoms, as carried out by individual cells. The general formula for a ketone is RCOR, where R and R are alkyl or aryl groups.
small molecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
cellular amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
cellular nitrogen compound biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds.
cellular amino acid derivative biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of compounds derived from amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
phenol metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a phenol, any compound containing one or more hydroxyl groups directly attached to an aromatic carbon ring. The largest single use of phenol is in the production of plastics, but it is also used in the synthesis of caprolactam, a precursor for nylon 6 and other man-made fibers.
oxoacid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any oxoacid; an oxoacid is a compound which contains oxygen, at least one other element, and at least one hydrogen bound to oxygen, and which produces a conjugate base by loss of positive hydrogen ion(s) (hydrons).
amine biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
cellular biogenic amine biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways occurring at the level of individual cells resulting in the formation of any of a group of naturally occurring, biologically active amines, such as norepinephrine, histamine, and serotonin, many of which act as neurotransmitters.
cellular biogenic amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways occurring at the level of individual cells involving any of a group of naturally occurring, biologically active amines, such as norepinephrine, histamine, and serotonin, many of which act as neurotransmitters.
cellular amino acid derivative biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of compounds derived from amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
catechol metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a compound containing a pyrocatechol (1,2-benzenediol) nucleus or substituent.
catecholamine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any of a group of physiologically important biogenic amines that possess a catechol (3,4-dihydroxyphenyl) nucleus and are derivatives of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylethylamine.
cellular biogenic amine biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways occurring at the level of individual cells resulting in the formation of any of a group of naturally occurring, biologically active amines, such as norepinephrine, histamine, and serotonin, many of which act as neurotransmitters.
catecholamine biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of any of a group of physiologically important biogenic amines that possess a catechol (3,4-dihydroxyphenyl) nucleus and are derivatives of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylethylamine.


ACMSDaminocarboxymuconate semialdehyde decarboxylase (ENSG00000153086), score: 0.96 AIM1absent in melanoma 1 (ENSG00000112297), score: 0.81 ALPK1alpha-kinase 1 (ENSG00000073331), score: 0.87 ANXA13annexin A13 (ENSG00000104537), score: 0.89 ATP6V0E1ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 9kDa, V0 subunit e1 (ENSG00000113732), score: 0.83 BBOX1butyrobetaine (gamma), 2-oxoglutarate dioxygenase (gamma-butyrobetaine hydroxylase) 1 (ENSG00000129151), score: 0.82 C8orf80chromosome 8 open reading frame 80 (ENSG00000189233), score: 0.9 CLDN14claudin 14 (ENSG00000159261), score: 0.95 CLPTM1LCLPTM1-like (ENSG00000049656), score: 0.85 COLEC11collectin sub-family member 11 (ENSG00000118004), score: 0.84 CRYAAcrystallin, alpha A (ENSG00000160202), score: 0.92 CRYL1crystallin, lambda 1 (ENSG00000165475), score: 0.93 CYB5Acytochrome b5 type A (microsomal) (ENSG00000166347), score: 0.86 DBHdopamine beta-hydroxylase (dopamine beta-monooxygenase) (ENSG00000123454), score: 1 DDCdopa decarboxylase (aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase) (ENSG00000132437), score: 0.91 DECR22,4-dienoyl CoA reductase 2, peroxisomal (ENSG00000242612), score: 0.83 DNAJC18DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 18 (ENSG00000170464), score: -0.94 DNM1Ldynamin 1-like (ENSG00000087470), score: -0.85 ELF3E74-like factor 3 (ets domain transcription factor, epithelial-specific ) (ENSG00000163435), score: 0.95 ENPEPglutamyl aminopeptidase (aminopeptidase A) (ENSG00000138792), score: 0.87 FAM110Cfamily with sequence similarity 110, member C (ENSG00000184731), score: 0.85 FAM176Afamily with sequence similarity 176, member A (ENSG00000115363), score: 0.85 FGFR4fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (ENSG00000160867), score: 0.82 GALK1galactokinase 1 (ENSG00000108479), score: 0.91 GLYCTKglycerate kinase (ENSG00000168237), score: 0.92 HAO2hydroxyacid oxidase 2 (long chain) (ENSG00000116882), score: 0.91 HGDhomogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase (ENSG00000113924), score: 0.82 HNF4Ahepatocyte nuclear factor 4, alpha (ENSG00000101076), score: 0.82 HRGhistidine-rich glycoprotein (ENSG00000113905), score: 0.85 IHHIndian hedgehog (ENSG00000163501), score: 0.87 IL13RA1interleukin 13 receptor, alpha 1 (ENSG00000131724), score: 0.85 IL1R1interleukin 1 receptor, type I (ENSG00000115594), score: 0.87 IL1R2interleukin 1 receptor, type II (ENSG00000115590), score: 0.87 IL22RA1interleukin 22 receptor, alpha 1 (ENSG00000142677), score: 0.91 IMPA2inositol(myo)-1(or 4)-monophosphatase 2 (ENSG00000141401), score: 0.94 LPIN3lipin 3 (ENSG00000132793), score: 0.86 MARK1MAP/microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 1 (ENSG00000116141), score: -0.85 MGST2microsomal glutathione S-transferase 2 (ENSG00000085871), score: 0.82 MMP7matrix metallopeptidase 7 (matrilysin, uterine) (ENSG00000137673), score: 0.92 NFKBIZnuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, zeta (ENSG00000144802), score: 0.83 NR0B2nuclear receptor subfamily 0, group B, member 2 (ENSG00000131910), score: 0.88 NR1H4nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group H, member 4 (ENSG00000012504), score: 0.84 PAHphenylalanine hydroxylase (ENSG00000171759), score: 0.81 PEPDpeptidase D (ENSG00000124299), score: 0.85 PLCG2phospholipase C, gamma 2 (phosphatidylinositol-specific) (ENSG00000197943), score: 0.93 PPIBpeptidylprolyl isomerase B (cyclophilin B) (ENSG00000166794), score: 0.88 PRRG4proline rich Gla (G-carboxyglutamic acid) 4 (transmembrane) (ENSG00000135378), score: 0.82 RAB17RAB17, member RAS oncogene family (ENSG00000124839), score: 0.99 RAB32RAB32, member RAS oncogene family (ENSG00000118508), score: 0.87 RIPK4receptor-interacting serine-threonine kinase 4 (ENSG00000183421), score: 0.86 SAMD8sterile alpha motif domain containing 8 (ENSG00000156671), score: -0.81 SERPINF2serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade F (alpha-2 antiplasmin, pigment epithelium derived factor), member 2 (ENSG00000167711), score: 0.91 SH2D4ASH2 domain containing 4A (ENSG00000104611), score: 0.89 SLC15A1solute carrier family 15 (oligopeptide transporter), member 1 (ENSG00000088386), score: 0.89 SLC22A7solute carrier family 22 (organic anion transporter), member 7 (ENSG00000137204), score: 0.94 SLC25A38solute carrier family 25, member 38 (ENSG00000144659), score: 0.84 SLC5A9solute carrier family 5 (sodium/glucose cotransporter), member 9 (ENSG00000117834), score: 0.86 SLC7A9solute carrier family 7 (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system), member 9 (ENSG00000021488), score: 0.85 SNX5sorting nexin 5 (ENSG00000089006), score: 0.81 SPG21spastic paraplegia 21 (autosomal recessive, Mast syndrome) (ENSG00000090487), score: 0.87 SPTLC3serine palmitoyltransferase, long chain base subunit 3 (ENSG00000172296), score: 0.87 SUMF1sulfatase modifying factor 1 (ENSG00000144455), score: 0.84 TAOK1TAO kinase 1 (ENSG00000160551), score: -0.88 TFPItissue factor pathway inhibitor (lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor) (ENSG00000003436), score: 0.91 TMPRSS2transmembrane protease, serine 2 (ENSG00000184012), score: 0.88 TNRC6Ctrinucleotide repeat containing 6C (ENSG00000078687), score: -0.93 TOM1L1target of myb1 (chicken)-like 1 (ENSG00000141198), score: 0.81 WDR72WD repeat domain 72 (ENSG00000166415), score: 0.91 ZNF395zinc finger protein 395 (ENSG00000186918), score: 0.82
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mml_kd_f_ca1 | mml | kd | f | _ |
| ppy_kd_m_ca1 | ppy | kd | m | _ |
| ppy_kd_f_ca1 | ppy | kd | f | _ |
| ptr_lv_f_ca1 | ptr | lv | f | _ |
| ppa_kd_m_ca1 | ppa | kd | m | _ |
| ggo_kd_f_ca1 | ggo | kd | f | _ |
| ppa_kd_f_ca1 | ppa | kd | f | _ |
| ptr_kd_f_ca1 | ptr | kd | f | _ |
| ppy_lv_f_ca1 | ppy | lv | f | _ |
| ggo_kd_m_ca1 | ggo | kd | m | _ |
| ptr_kd_m_ca1 | ptr | kd | m | _ |
| hsa_kd_f_ca1 | hsa | kd | f | _ |
| ggo_lv_m_ca1 | ggo | lv | m | _ |
| mml_lv_f_ca1 | mml | lv | f | _ |
| ppy_lv_m_ca1 | ppy | lv | m | _ |
| ppa_lv_m_ca1 | ppa | lv | m | _ |
| hsa_kd_m2_ca1 | hsa | kd | m | 2 |
| hsa_kd_m1_ca1 | hsa | kd | m | 1 |
| ptr_lv_m_ca1 | ptr | lv | m | _ |
| hsa_lv_m2_ca1 | hsa | lv | m | 2 |
| ggo_lv_f_ca1 | ggo | lv | f | _ |
| ppa_lv_f_ca1 | ppa | lv | f | _ |
| mml_lv_m_ca1 | mml | lv | m | _ |
| hsa_lv_m1_ca1 | hsa | lv | m | 1 |
