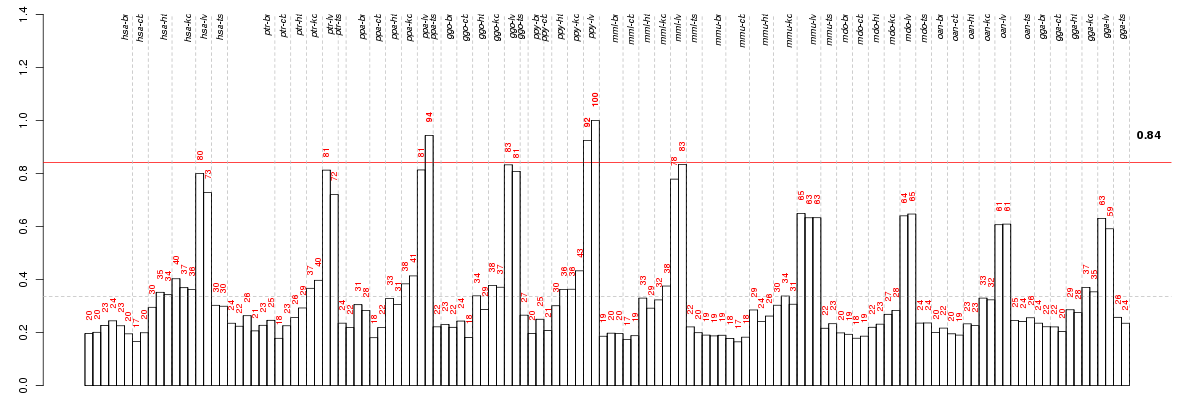

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
adaptive immune response
An immune response based on directed amplification of specific receptors for antigen produced through a somatic diversification process, and allowing for enhanced response to subsequent exposures to the same antigen (immunological memory).
immune effector process
Any process of the immune system that occurs as part of an immune response.
activation of immune response
Any process that initiates an immune response.
immune system process
Any process involved in the development or functioning of the immune system, an organismal system for calibrated responses to potential internal or invasive threats.
leukocyte mediated immunity
Any process involved in the carrying out of an immune response by a leukocyte.
lymphocyte mediated immunity
Any process involved in the carrying out of an immune response by a lymphocyte.
humoral immune response mediated by circulating immunoglobulin
An immune response dependent upon secreted immunoglobulin. An example of this process is found in Mus musculus.
adaptive immune response based on somatic recombination of immune receptors built from immunoglobulin superfamily domains
An immune response based on directed amplification of specific receptors for antigen produced through a somatic diversification process that includes somatic recombination of germline gene segments encoding immunoglobulin superfamily domains, and allowing for enhanced responses upon subsequent exposures to the same antigen (immunological memory). Recombined receptors for antigen encoded by immunoglobulin superfamily domains include T cell receptors and immunoglobulins (antibodies). An example of this is the adaptive immune response found in Mus musculus.
acute inflammatory response
Inflammation which comprises a rapid, short-lived, relatively uniform response to acute injury or antigenic challenge and is characterized by accumulations of fluid, plasma proteins, and granulocytic leukocytes. An acute inflammatory response occurs within a matter of minutes or hours, and either resolves within a few days or becomes a chronic inflammatory response.
activation of plasma proteins involved in acute inflammatory response
Any process activating plasma proteins by proteolysis as part of an acute inflammatory response.
regulation of immune system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
positive regulation of immune system process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
defense response
Reactions, triggered in response to the presence of a foreign body or the occurrence of an injury, which result in restriction of damage to the organism attacked or prevention/recovery from the infection caused by the attack.
blood coagulation
The sequential process by which the multiple coagulation factors of the blood interact, ultimately resulting in the formation of an insoluble fibrin clot; it may be divided into three stages: stage 1, the formation of intrinsic and extrinsic prothrombin converting principle; stage 2, the formation of thrombin; stage 3, the formation of stable fibrin polymers.
complement activation
Any process involved in the activation of any of the steps of the complement cascade, which allows for the direct killing of microbes, the disposal of immune complexes, and the regulation of other immune processes; the initial steps of complement activation involve one of three pathways, the classical pathway, the alternative pathway, and the lectin pathway, all of which lead to the terminal complement pathway.
signal transduction
The process whereby an activated receptor conveys information down the signaling pathway, resulting in a change in the function or state of a cell.
organic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
protein maturation by peptide bond cleavage
The hydrolysis of a peptide bond or bonds within a protein as part of protein maturation, the process leading to the attainment of the full functional capacity of a protein.
cellular amino acid and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, and compounds derived from amino acids, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular amino acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
histidine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving histidine, 2-amino-3-(1H-imidazol-4-yl)propanoic acid.
histidine catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of histidine, 2-amino-3-(1H-imidazol-4-yl)propanoic acid.
nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds; includes nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, assimilatory/dissimilatory nitrate reduction and the interconversion of nitrogenous organic matter and ammonium.
response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
inflammatory response
The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages.
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
complement activation, alternative pathway
Any process involved in the activation of any of the steps of the alternative pathway of the complement cascade which allows for the direct killing of microbes and the regulation of other immune processes.
complement activation, classical pathway
Any process involved in the activation of any of the steps of the classical pathway of the complement cascade which allows for the direct killing of microbes, the disposal of immune complexes, and the regulation of other immune processes.
humoral immune response
An immune response mediated through a body fluid.
intracellular protein kinase cascade
A series of reactions that occur within the cell, mediated by protein kinases, which occurs as a result of a single trigger reaction or compound.
JAK-STAT cascade
Any process by which STAT proteins (Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription) are activated by members of the JAK (janus activated kinase) family of tyrosine kinases, following the binding of cytokines to their cognate receptor. Once activated, STATs dimerize and translocate to the nucleus and modulate the expression of target genes.
hemostasis
The stopping of bleeding (loss of body fluid) or the arrest of the circulation to an organ or part.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cell death
A biological process that results in permanent cessation of all vital functions of a cell.
cytolysis
The rupture of cell membranes and the loss of cytoplasm.
negative regulation of coagulation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of coagulation.
catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of substances, including the breakdown of carbon compounds with the liberation of energy for use by the cell or organism.
cellular amino acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
histidine family amino acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids of the histidine family.
histidine family amino acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of amino acids of the histidine family.
amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
amine catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
response to external stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an external stimulus.
response to biotic stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a biotic stimulus, a stimulus caused or produced by a living organism.
response to wounding
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to the organism.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
gene expression
The process by which a gene's sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
organic acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
immunoglobulin mediated immune response
An immune response mediated by immunoglobulins, whether cell-bound or in solution.
death
A permanent cessation of all vital functions: the end of life; can be applied to a whole organism or to a part of an organism.
protein processing
Any protein maturation process achieved by the cleavage of peptide bonds.
protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general. Includes protein modification.
B cell mediated immunity
Any process involved with the carrying out of an immune response by a B cell, through, for instance, the production of antibodies or cytokines, or antigen presentation to T cells.
carboxylic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving carboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (COOH) groups or anions (COO-).
signal transmission via phosphorylation event
The process whereby a signal is conveyed via the transfer of one or more phosphate groups.
signaling pathway
The series of molecular events whereby information is sent from one location to another within a living organism or between living organisms.
intracellular signaling pathway
The series of molecular events whereby information is sent from one location to another within a cell.
signaling process
Any biological process involved in the generation, transmission, reception, or interpretation of a signal. A signal is an entity used to transmit or convey information.
regulation of signaling process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a signaling process.
signaling
The entirety of a process whereby information is transmitted. This process begins with the initiation of the signal and ends when a response has been triggered.
negative regulation of signaling process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a signaling process.
signal transmission
The process whereby a signal is released and/or conveyed from one location to another.
regulation of blood coagulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of blood coagulation.
positive regulation of blood coagulation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of blood coagulation.
negative regulation of blood coagulation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of blood coagulation.
regulation of response to external stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to an external stimulus.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
intracellular signal transduction
The process whereby a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell.
wound healing
The series of events that restore integrity to a damaged tissue, following an injury.
cellular ketone metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any of a class of organic compounds that contain the carbonyl group, CO, and in which the carbonyl group is bonded only to carbon atoms, as carried out by individual cells. The general formula for a ketone is RCOR, where R and R are alkyl or aryl groups.
fibrinolysis
An ongoing process that solubilizes fibrin, chiefly by the proteolytic action of plasmin, resulting in the removal of small blood clots.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
oxoacid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any oxoacid; an oxoacid is a compound which contains oxygen, at least one other element, and at least one hydrogen bound to oxygen, and which produces a conjugate base by loss of positive hydrogen ion(s) (hydrons).
cellular amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of substances, carried out by individual cells.
small molecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
small molecule catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
innate immune response
Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens.
carboxylic acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of carboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (-COOH) groups.
heterocycle metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving heterocyclic compounds, those with a cyclic molecular structure and at least two different atoms in the ring (or rings).
heterocycle catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of heterocyclic compounds, those with a cyclic molecular structure and at least two different atoms in the ring (or rings).
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
positive regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
positive regulation of immune response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
coagulation
The process by which a fluid solution, or part of it, changes into a solid or semisolid mass.
regulation of coagulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of coagulation, the process by which a fluid solution, or part of it, changes into a solid or semisolid mass.
positive regulation of coagulation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of coagulation.
regulation of body fluid levels
Any process that modulates the levels of body fluids.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
positive regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of an organismal process, any of the processes pertinent to the function of an organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
negative regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of an organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of an organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
protein maturation
Any process leading to the attainment of the full functional capacity of a protein.
regulation of fibrinolysis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of fibrinolysis, an ongoing process that solubilizes fibrin, resulting in the removal of small blood clots.
negative regulation of fibrinolysis
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of fibrinolysis, an ongoing process that solubilizes fibrin, resulting in the removal of small blood clots.
regulation of wound healing
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency, or extent of the series of events that restore integrity to a damaged tissue, following an injury.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of biological quality
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological quality. A biological quality is a measurable attribute of an organism or part of an organism, such as size, mass, shape, color, etc.
regulation of response to stress
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to stress. Response to stress is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
all
NA
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cell death
A biological process that results in permanent cessation of all vital functions of a cell.
signaling process
Any biological process involved in the generation, transmission, reception, or interpretation of a signal. A signal is an entity used to transmit or convey information.
positive regulation of immune system process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
positive regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of an organismal process, any of the processes pertinent to the function of an organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
negative regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of an organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of an organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
regulation of immune system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
regulation of signaling process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a signaling process.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
positive regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular amino acid and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, and compounds derived from amino acids, as carried out by individual cells.
protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general. Includes protein modification.
organic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
cellular amino acid and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, and compounds derived from amino acids, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular ketone metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any of a class of organic compounds that contain the carbonyl group, CO, and in which the carbonyl group is bonded only to carbon atoms, as carried out by individual cells. The general formula for a ketone is RCOR, where R and R are alkyl or aryl groups.
small molecule catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
complement activation
Any process involved in the activation of any of the steps of the complement cascade, which allows for the direct killing of microbes, the disposal of immune complexes, and the regulation of other immune processes; the initial steps of complement activation involve one of three pathways, the classical pathway, the alternative pathway, and the lectin pathway, all of which lead to the terminal complement pathway.
positive regulation of immune system process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
immune effector process
Any process of the immune system that occurs as part of an immune response.
regulation of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
positive regulation of immune response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
signal transduction
The process whereby an activated receptor conveys information down the signaling pathway, resulting in a change in the function or state of a cell.
regulation of coagulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of coagulation, the process by which a fluid solution, or part of it, changes into a solid or semisolid mass.
positive regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of an organismal process, any of the processes pertinent to the function of an organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
negative regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of an organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of an organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
positive regulation of coagulation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of coagulation.
negative regulation of coagulation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of coagulation.
positive regulation of immune response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
positive regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
negative regulation of fibrinolysis
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of fibrinolysis, an ongoing process that solubilizes fibrin, resulting in the removal of small blood clots.
regulation of response to stress
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to stress. Response to stress is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
regulation of response to external stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to an external stimulus.
regulation of body fluid levels
Any process that modulates the levels of body fluids.
cellular amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
organic acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
protein maturation
Any process leading to the attainment of the full functional capacity of a protein.
organic acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
oxoacid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any oxoacid; an oxoacid is a compound which contains oxygen, at least one other element, and at least one hydrogen bound to oxygen, and which produces a conjugate base by loss of positive hydrogen ion(s) (hydrons).
heterocycle catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of heterocyclic compounds, those with a cyclic molecular structure and at least two different atoms in the ring (or rings).
positive regulation of immune response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
activation of immune response
Any process that initiates an immune response.
complement activation
Any process involved in the activation of any of the steps of the complement cascade, which allows for the direct killing of microbes, the disposal of immune complexes, and the regulation of other immune processes; the initial steps of complement activation involve one of three pathways, the classical pathway, the alternative pathway, and the lectin pathway, all of which lead to the terminal complement pathway.
complement activation, alternative pathway
Any process involved in the activation of any of the steps of the alternative pathway of the complement cascade which allows for the direct killing of microbes and the regulation of other immune processes.
intracellular signal transduction
The process whereby a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell.
negative regulation of blood coagulation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of blood coagulation.
negative regulation of coagulation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of coagulation.
regulation of blood coagulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of blood coagulation.
positive regulation of coagulation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of coagulation.
positive regulation of blood coagulation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of blood coagulation.
blood coagulation
The sequential process by which the multiple coagulation factors of the blood interact, ultimately resulting in the formation of an insoluble fibrin clot; it may be divided into three stages: stage 1, the formation of intrinsic and extrinsic prothrombin converting principle; stage 2, the formation of thrombin; stage 3, the formation of stable fibrin polymers.
regulation of blood coagulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of blood coagulation.
innate immune response
Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens.
inflammatory response
The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages.
cellular amino acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
cellular amino acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
histidine catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of histidine, 2-amino-3-(1H-imidazol-4-yl)propanoic acid.
B cell mediated immunity
Any process involved with the carrying out of an immune response by a B cell, through, for instance, the production of antibodies or cytokines, or antigen presentation to T cells.
complement activation, classical pathway
Any process involved in the activation of any of the steps of the classical pathway of the complement cascade which allows for the direct killing of microbes, the disposal of immune complexes, and the regulation of other immune processes.
intracellular protein kinase cascade
A series of reactions that occur within the cell, mediated by protein kinases, which occurs as a result of a single trigger reaction or compound.
positive regulation of blood coagulation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of blood coagulation.
negative regulation of blood coagulation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of blood coagulation.
negative regulation of fibrinolysis
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of fibrinolysis, an ongoing process that solubilizes fibrin, resulting in the removal of small blood clots.
regulation of blood coagulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of blood coagulation.
blood coagulation
The sequential process by which the multiple coagulation factors of the blood interact, ultimately resulting in the formation of an insoluble fibrin clot; it may be divided into three stages: stage 1, the formation of intrinsic and extrinsic prothrombin converting principle; stage 2, the formation of thrombin; stage 3, the formation of stable fibrin polymers.
regulation of wound healing
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency, or extent of the series of events that restore integrity to a damaged tissue, following an injury.
cellular amino acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
cellular amino acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
carboxylic acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of carboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (-COOH) groups.
histidine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving histidine, 2-amino-3-(1H-imidazol-4-yl)propanoic acid.
histidine family amino acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of amino acids of the histidine family.
regulation of fibrinolysis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of fibrinolysis, an ongoing process that solubilizes fibrin, resulting in the removal of small blood clots.
negative regulation of fibrinolysis
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of fibrinolysis, an ongoing process that solubilizes fibrin, resulting in the removal of small blood clots.
histidine catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of histidine, 2-amino-3-(1H-imidazol-4-yl)propanoic acid.
activation of plasma proteins involved in acute inflammatory response
Any process activating plasma proteins by proteolysis as part of an acute inflammatory response.
humoral immune response mediated by circulating immunoglobulin
An immune response dependent upon secreted immunoglobulin. An example of this process is found in Mus musculus.
complement activation
Any process involved in the activation of any of the steps of the complement cascade, which allows for the direct killing of microbes, the disposal of immune complexes, and the regulation of other immune processes; the initial steps of complement activation involve one of three pathways, the classical pathway, the alternative pathway, and the lectin pathway, all of which lead to the terminal complement pathway.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
integral to membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer. When used to describe a protein, indicates that all or part of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
endoplasmic reticulum
The irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae. The ER takes two forms, rough (or granular), with ribosomes adhering to the outer surface, and smooth (with no ribosomes attached).
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
membrane attack complex
A protein complex produced by sequentially activated components of the complement cascade inserted into a target cell membrane and forming a pore leading to cell lysis via ion and water flow.
extracellular space
That part of a multicellular organism outside the cells proper, usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cytoplasm
All of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
endoplasmic reticulum lumen
The volume enclosed by the membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum.
stored secretory granule
A small subcellular vesicle, surrounded by a membrane, that is formed from the Golgi apparatus and contains a highly concentrated protein destined for secretion. Secretory granules move towards the periphery of the cell and upon stimulation, their membranes fuse with the cell membrane, and their protein load is exteriorized. Processing of the contained protein may take place in secretory granules.
external side of plasma membrane
The side of the plasma membrane that is opposite to the side that faces the cytoplasm.
cell surface
The external part of the cell wall and/or plasma membrane.
pore complex
Any small opening in a membrane that allows the passage of gases and/or liquids.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
platelet alpha granule
A secretory organelle found in blood platelets, which is unique in that it exhibits further compartmentalization and acquires its protein content via two distinct mechanisms: (1) biosynthesis predominantly at the megakaryocyte (MK) level (with some vestigial platelet synthesis) (e.g. platelet factor 4) and (2) endocytosis and pinocytosis at both the MK and circulating platelet levels (e.g. fibrinogen (Fg) and IgG).
platelet alpha granule lumen
The volume enclosed by the membrane of the platelet alpha granule.
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
membrane-enclosed lumen
The enclosed volume within a sealed membrane or between two sealed membranes. Encompasses the volume enclosed by the membranes of a particular organelle, e.g. endoplasmic reticulum lumen, or the space between the two lipid bilayers of a double membrane surrounding an organelle, e.g. nuclear envelope lumen.
vesicle
Any small, fluid-filled, spherical organelle enclosed by membrane or protein.
vesicle lumen
The volume enclosed by the membrane or protein that forms a vesicle.
membrane-bounded vesicle
Any small, fluid-filled, spherical organelle enclosed by a lipid bilayer.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, and prokaryotic structures such as anammoxosomes and pirellulosomes. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
organelle lumen
The internal volume enclosed by the membranes of a particular organelle; includes the volume enclosed by a single organelle membrane, e.g. endoplasmic reticulum lumen, or the volume enclosed by the innermost of the two lipid bilayers of an organelle envelope, e.g. nuclear lumen.
protein complex
Any macromolecular complex composed of two or more polypeptide subunits, which may or may not be identical. Protein complexes may have other associated non-protein prosthetic groups, such as nucleotides, metal ions or other small molecules.
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
endoplasmic reticulum part
Any constituent part of the endoplasmic reticulum, the irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae.
cytoplasmic vesicle part
Any constituent part of cytoplasmic vesicle, a vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle lumen
The volume enclosed by the membrane of a cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle.
intracellular organelle lumen
An organelle lumen that is part of an intracellular organelle.
subsynaptic reticulum
An elaborate tubulolamellar membrane system that underlies the postsynaptic cell membrane.
all
NA
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
organelle lumen
The internal volume enclosed by the membranes of a particular organelle; includes the volume enclosed by a single organelle membrane, e.g. endoplasmic reticulum lumen, or the volume enclosed by the innermost of the two lipid bilayers of an organelle envelope, e.g. nuclear lumen.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle lumen
An organelle lumen that is part of an intracellular organelle.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
cytoplasmic vesicle part
Any constituent part of cytoplasmic vesicle, a vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
vesicle lumen
The volume enclosed by the membrane or protein that forms a vesicle.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
endoplasmic reticulum lumen
The volume enclosed by the membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle lumen
The volume enclosed by the membrane of a cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
endoplasmic reticulum
The irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae. The ER takes two forms, rough (or granular), with ribosomes adhering to the outer surface, and smooth (with no ribosomes attached).
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
endoplasmic reticulum part
Any constituent part of the endoplasmic reticulum, the irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae.
cytoplasmic vesicle part
Any constituent part of cytoplasmic vesicle, a vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
subsynaptic reticulum
An elaborate tubulolamellar membrane system that underlies the postsynaptic cell membrane.
membrane attack complex
A protein complex produced by sequentially activated components of the complement cascade inserted into a target cell membrane and forming a pore leading to cell lysis via ion and water flow.
external side of plasma membrane
The side of the plasma membrane that is opposite to the side that faces the cytoplasm.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle lumen
The volume enclosed by the membrane of a cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle.
endoplasmic reticulum part
Any constituent part of the endoplasmic reticulum, the irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae.
endoplasmic reticulum part
Any constituent part of the endoplasmic reticulum, the irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae.
pore complex
Any small opening in a membrane that allows the passage of gases and/or liquids.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
membrane attack complex
A protein complex produced by sequentially activated components of the complement cascade inserted into a target cell membrane and forming a pore leading to cell lysis via ion and water flow.
platelet alpha granule lumen
The volume enclosed by the membrane of the platelet alpha granule.

protein binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any protein or protein complex (a complex of two or more proteins that may include other nonprotein molecules).
molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
protein disulfide isomerase activity
Catalysis of the rearrangement of both intrachain and interchain disulfide bonds in proteins.
catalytic activity
Catalysis of a biochemical reaction at physiological temperatures. In biologically catalyzed reactions, the reactants are known as substrates, and the catalysts are naturally occurring macromolecular substances known as enzymes. Enzymes possess specific binding sites for substrates, and are usually composed wholly or largely of protein, but RNA that has catalytic activity (ribozyme) is often also regarded as enzymatic.
enzyme inhibitor activity
Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of an enzyme.
endopeptidase inhibitor activity
Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of an endopeptidase, any enzyme that hydrolyzes nonterminal peptide bonds in polypeptides.
serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity
Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of serine-type endopeptidases, enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of nonterminal peptide bonds in a polypeptide chain; a serine residue (and a histidine residue) are at the active center of the enzyme.
signal transducer activity
Mediates the transfer of a signal from the outside to the inside of a cell by means other than the introduction of the signal molecule itself into the cell.
receptor activity
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell activity.
transmembrane receptor activity
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell activity, and spanning to the membrane of either the cell or an organelle.
cytokine receptor activity
Combining with a cytokine to initiate a change in cell activity.
interleukin-1 receptor activity
Combining with interleukin-1 to initiate a change in cell activity. Interleukin-1 is produced mainly by activated macrophages and is involved in the inflammatory response.
growth factor binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any growth factor, proteins or polypeptides that stimulate a cell or organism to grow or proliferate.
binding
The selective, non-covalent, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
endopeptidase regulator activity
Modulates the activity of a peptidase, any enzyme that hydrolyzes nonterminal peptide bonds in polypeptides.
isomerase activity
Catalysis of the geometric or structural changes within one molecule. Isomerase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 5.
intramolecular oxidoreductase activity
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which the hydrogen donor and acceptor are the same molecule, and no oxidized product appears.
intramolecular oxidoreductase activity, interconverting keto- and enol-groups
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which the hydrogen donor and acceptor, which is a keto- or an enol-group, are the same molecule, and no oxidized product appears.
intramolecular oxidoreductase activity, transposing S-S bonds
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which the hydrogen donor and acceptor are the same molecule, one or more sulfur-sulfur bonds in the molecule are rearranged, and no oxidized product appears.
peptidase inhibitor activity
Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of a peptidase, any enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis peptide bonds.
cytokine binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a cytokine, any of a group of proteins that function to control the survival, growth and differentiation of tissues and cells, and which have autocrine and paracrine activity.
interleukin-1 binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with interleukin-1.
enzyme regulator activity
Modulates the activity of an enzyme.
molecular transducer activity
The molecular function that accepts an input of one form and creates an output of a different form.
peptidase regulator activity
Modulates the activity of a peptidase, any enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis peptide bonds.
all
NA
peptidase inhibitor activity
Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of a peptidase, any enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis peptide bonds.
interleukin-1 binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with interleukin-1.
endopeptidase inhibitor activity
Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of an endopeptidase, any enzyme that hydrolyzes nonterminal peptide bonds in polypeptides.
protein disulfide isomerase activity
Catalysis of the rearrangement of both intrachain and interchain disulfide bonds in proteins.
interleukin-1 receptor activity
Combining with interleukin-1 to initiate a change in cell activity. Interleukin-1 is produced mainly by activated macrophages and is involved in the inflammatory response.
cytokine receptor activity
Combining with a cytokine to initiate a change in cell activity.
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 04610 | 4.622e-10 | 1.305 | 14 | 21 | Complement and coagulation cascades |
| 04060 | 1.261e-02 | 4.908 | 14 | 79 | Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction |
| 05020 | 2.983e-02 | 0.8076 | 5 | 13 | Prion diseases |
ABCB11ATP-binding cassette, sub-family B (MDR/TAP), member 11 (ENSG00000073734), score: 0.49 ABCG5ATP-binding cassette, sub-family G (WHITE), member 5 (ENSG00000138075), score: 0.6 ACOT12acyl-CoA thioesterase 12 (ENSG00000172497), score: 0.54 ACSL1acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 1 (ENSG00000151726), score: 0.48 AGXTalanine-glyoxylate aminotransferase (ENSG00000172482), score: 0.52 AKR1D1aldo-keto reductase family 1, member D1 (delta 4-3-ketosteroid-5-beta-reductase) (ENSG00000122787), score: 0.53 ALBalbumin (ENSG00000163631), score: 0.55 ALG9asparagine-linked glycosylation 9, alpha-1,2-mannosyltransferase homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000086848), score: 0.66 ALOX5AParachidonate 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein (ENSG00000132965), score: 0.48 ALPK1alpha-kinase 1 (ENSG00000073331), score: 0.59 AMBPalpha-1-microglobulin/bikunin precursor (ENSG00000106927), score: 0.62 AMDHD1amidohydrolase domain containing 1 (ENSG00000139344), score: 0.49 ANK3ankyrin 3, node of Ranvier (ankyrin G) (ENSG00000151150), score: -0.51 ANKRD22ankyrin repeat domain 22 (ENSG00000152766), score: 0.68 AOAHacyloxyacyl hydrolase (neutrophil) (ENSG00000136250), score: 0.49 APBB1IPamyloid beta (A4) precursor protein-binding, family B, member 1 interacting protein (ENSG00000077420), score: 0.6 AQP8aquaporin 8 (ENSG00000103375), score: 0.63 ATF3activating transcription factor 3 (ENSG00000162772), score: 0.57 ATF6activating transcription factor 6 (ENSG00000118217), score: 0.56 BHLHE40basic helix-loop-helix family, member e40 (ENSG00000134107), score: 0.48 BMP10bone morphogenetic protein 10 (ENSG00000163217), score: 0.68 BMPERBMP binding endothelial regulator (ENSG00000164619), score: 0.66 BMXBMX non-receptor tyrosine kinase (ENSG00000102010), score: 0.52 BPIL3bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein-like 3 (ENSG00000167104), score: 0.93 BST1bone marrow stromal cell antigen 1 (ENSG00000109743), score: 0.62 C12orf45chromosome 12 open reading frame 45 (ENSG00000151131), score: 0.52 C18orf8chromosome 18 open reading frame 8 (ENSG00000141452), score: 0.48 C5complement component 5 (ENSG00000106804), score: 0.6 C5orf33chromosome 5 open reading frame 33 (ENSG00000152620), score: 0.5 C8Acomplement component 8, alpha polypeptide (ENSG00000157131), score: 0.65 C8Bcomplement component 8, beta polypeptide (ENSG00000021852), score: 0.66 C8Gcomplement component 8, gamma polypeptide (ENSG00000176919), score: 0.58 C8orf80chromosome 8 open reading frame 80 (ENSG00000189233), score: 0.57 C9orf72chromosome 9 open reading frame 72 (ENSG00000147894), score: 0.63 C9orf95chromosome 9 open reading frame 95 (ENSG00000106733), score: 0.48 CASD1CAS1 domain containing 1 (ENSG00000127995), score: -0.49 CCNIcyclin I (ENSG00000118816), score: -0.6 CCNL1cyclin L1 (ENSG00000163660), score: 0.66 CDC37L1cell division cycle 37 homolog (S. cerevisiae)-like 1 (ENSG00000106993), score: 0.55 CLDN14claudin 14 (ENSG00000159261), score: 0.73 CLUclusterin (ENSG00000120885), score: 0.54 CMTM6CKLF-like MARVEL transmembrane domain containing 6 (ENSG00000091317), score: 0.52 CNGA1cyclic nucleotide gated channel alpha 1 (ENSG00000198515), score: 0.62 COG3component of oligomeric golgi complex 3 (ENSG00000136152), score: 0.49 COLEC10collectin sub-family member 10 (C-type lectin) (ENSG00000184374), score: 0.67 COLEC11collectin sub-family member 11 (ENSG00000118004), score: 0.52 CPB2carboxypeptidase B2 (plasma) (ENSG00000080618), score: 0.67 CSF3Rcolony stimulating factor 3 receptor (granulocyte) (ENSG00000119535), score: 0.59 CXCR4chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4 (ENSG00000121966), score: 0.57 CYB5Acytochrome b5 type A (microsomal) (ENSG00000166347), score: 0.48 CYTIPcytohesin 1 interacting protein (ENSG00000115165), score: 0.66 DBHdopamine beta-hydroxylase (dopamine beta-monooxygenase) (ENSG00000123454), score: 0.65 DDX6DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 6 (ENSG00000110367), score: -0.52 DECR22,4-dienoyl CoA reductase 2, peroxisomal (ENSG00000242612), score: 0.48 DHODHdihydroorotate dehydrogenase (ENSG00000102967), score: 0.86 DNAJC1DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 1 (ENSG00000136770), score: 0.52 DNAJC18DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 18 (ENSG00000170464), score: -0.53 DSEdermatan sulfate epimerase (ENSG00000111817), score: 0.48 DUSP1dual specificity phosphatase 1 (ENSG00000120129), score: 0.48 EDEM1ER degradation enhancer, mannosidase alpha-like 1 (ENSG00000134109), score: 0.5 ELF3E74-like factor 3 (ets domain transcription factor, epithelial-specific ) (ENSG00000163435), score: 0.56 EPHX1epoxide hydrolase 1, microsomal (xenobiotic) (ENSG00000143819), score: 0.49 ERP44endoplasmic reticulum protein 44 (ENSG00000023318), score: 0.51 F10coagulation factor X (ENSG00000126218), score: 0.58 F2coagulation factor II (thrombin) (ENSG00000180210), score: 0.58 F9coagulation factor IX (ENSG00000101981), score: 0.57 FAM176Afamily with sequence similarity 176, member A (ENSG00000115363), score: 0.48 FAM20Afamily with sequence similarity 20, member A (ENSG00000108950), score: 0.57 FAM76Bfamily with sequence similarity 76, member B (ENSG00000077458), score: 0.55 FAM83Afamily with sequence similarity 83, member A (ENSG00000147689), score: 1 FAM96Afamily with sequence similarity 96, member A (ENSG00000166797), score: 0.47 FESfeline sarcoma oncogene (ENSG00000182511), score: 0.5 FETUBfetuin B (ENSG00000090512), score: 0.53 FGBfibrinogen beta chain (ENSG00000171564), score: 0.66 FGGfibrinogen gamma chain (ENSG00000171557), score: 0.66 FOXF1forkhead box F1 (ENSG00000103241), score: 0.63 FRRS1ferric-chelate reductase 1 (ENSG00000156869), score: 0.5 FSTfollistatin (ENSG00000134363), score: 0.78 GADD45Bgrowth arrest and DNA-damage-inducible, beta (ENSG00000099860), score: 0.64 GALK1galactokinase 1 (ENSG00000108479), score: 0.53 GAS2growth arrest-specific 2 (ENSG00000148935), score: 0.57 GDF2growth differentiation factor 2 (ENSG00000128802), score: 0.59 GFRA1GDNF family receptor alpha 1 (ENSG00000151892), score: 0.54 GNL3guanine nucleotide binding protein-like 3 (nucleolar) (ENSG00000163938), score: 0.5 GPR183G protein-coupled receptor 183 (ENSG00000169508), score: 0.75 GPR97G protein-coupled receptor 97 (ENSG00000182885), score: 0.93 GRAMD1BGRAM domain containing 1B (ENSG00000023171), score: -0.49 GRAP2GRB2-related adaptor protein 2 (ENSG00000100351), score: 0.78 GRHL1grainyhead-like 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000134317), score: 0.55 HALhistidine ammonia-lyase (ENSG00000084110), score: 0.63 HAO1hydroxyacid oxidase (glycolate oxidase) 1 (ENSG00000101323), score: 0.59 HCLS1hematopoietic cell-specific Lyn substrate 1 (ENSG00000180353), score: 0.48 HDAC11histone deacetylase 11 (ENSG00000163517), score: -0.56 HGDhomogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase (ENSG00000113924), score: 0.48 HGFhepatocyte growth factor (hepapoietin A; scatter factor) (ENSG00000019991), score: 0.67 HPXhemopexin (ENSG00000110169), score: 0.61 HRGhistidine-rich glycoprotein (ENSG00000113905), score: 0.58 HSPA5heat shock 70kDa protein 5 (glucose-regulated protein, 78kDa) (ENSG00000044574), score: 0.55 IFNAR1interferon (alpha, beta and omega) receptor 1 (ENSG00000142166), score: 0.49 IFNGR1interferon gamma receptor 1 (ENSG00000027697), score: 0.62 IFT20intraflagellar transport 20 homolog (Chlamydomonas) (ENSG00000109083), score: 0.56 IGF1insulin-like growth factor 1 (somatomedin C) (ENSG00000017427), score: 0.51 IGFBP1insulin-like growth factor binding protein 1 (ENSG00000146678), score: 0.62 IGFBP3insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 (ENSG00000146674), score: 0.55 IGSF6immunoglobulin superfamily, member 6 (ENSG00000140749), score: 0.53 IHHIndian hedgehog (ENSG00000163501), score: 0.58 IKZF1IKAROS family zinc finger 1 (Ikaros) (ENSG00000185811), score: 0.54 IL10RAinterleukin 10 receptor, alpha (ENSG00000110324), score: 0.51 IL18RAPinterleukin 18 receptor accessory protein (ENSG00000115607), score: 0.98 IL1R1interleukin 1 receptor, type I (ENSG00000115594), score: 0.56 IL1R2interleukin 1 receptor, type II (ENSG00000115590), score: 0.81 IL1RAPinterleukin 1 receptor accessory protein (ENSG00000196083), score: 0.52 IL1RL1interleukin 1 receptor-like 1 (ENSG00000115602), score: 0.54 IL2RBinterleukin 2 receptor, beta (ENSG00000100385), score: 0.65 IL7Rinterleukin 7 receptor (ENSG00000168685), score: 0.67 IP6K1inositol hexakisphosphate kinase 1 (ENSG00000176095), score: -0.57 IRF4interferon regulatory factor 4 (ENSG00000137265), score: 0.68 ITKIL2-inducible T-cell kinase (ENSG00000113263), score: 0.79 KCNE4potassium voltage-gated channel, Isk-related family, member 4 (ENSG00000152049), score: 0.5 KCNJ8potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 8 (ENSG00000121361), score: 0.53 KCTD1potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 1 (ENSG00000134504), score: -0.5 KCTD2potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 2 (ENSG00000180901), score: -0.7 KIAA0146KIAA0146 (ENSG00000164808), score: 0.62 KIAA1462KIAA1462 (ENSG00000165757), score: -0.52 KLBklotho beta (ENSG00000134962), score: 0.51 KLF6Kruppel-like factor 6 (ENSG00000067082), score: 0.5 LAP3leucine aminopeptidase 3 (ENSG00000002549), score: 0.48 LCP1lymphocyte cytosolic protein 1 (L-plastin) (ENSG00000136167), score: 0.51 LCP2lymphocyte cytosolic protein 2 (SH2 domain containing leukocyte protein of 76kDa) (ENSG00000043462), score: 0.52 LEAP2liver expressed antimicrobial peptide 2 (ENSG00000164406), score: 0.51 LECT2leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin 2 (ENSG00000145826), score: 0.61 LNX2ligand of numb-protein X 2 (ENSG00000139517), score: 0.48 LOC100292202similar to solute carrier family 25, member 25 (ENSG00000148339), score: 0.67 LPIN2lipin 2 (ENSG00000101577), score: 0.56 LYVE1lymphatic vessel endothelial hyaluronan receptor 1 (ENSG00000133800), score: 0.57 MARK1MAP/microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 1 (ENSG00000116141), score: -0.5 MASP2mannan-binding lectin serine peptidase 2 (ENSG00000009724), score: 0.51 MAT1Amethionine adenosyltransferase I, alpha (ENSG00000151224), score: 0.55 MED17mediator complex subunit 17 (ENSG00000042429), score: 0.48 MGST2microsomal glutathione S-transferase 2 (ENSG00000085871), score: 0.49 MMAAmethylmalonic aciduria (cobalamin deficiency) cblA type (ENSG00000151611), score: 0.55 MMABmethylmalonic aciduria (cobalamin deficiency) cblB type (ENSG00000139428), score: 0.58 MOCOSmolybdenum cofactor sulfurase (ENSG00000075643), score: 0.51 MORN4MORN repeat containing 4 (ENSG00000171160), score: -0.52 MSI2musashi homolog 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000153944), score: -0.52 MTHFD2Lmethylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (NADP+ dependent) 2-like (ENSG00000163738), score: 0.91 MXD1MAX dimerization protein 1 (ENSG00000059728), score: 0.65 MYO1Bmyosin IB (ENSG00000128641), score: 0.62 MYO1Fmyosin IF (ENSG00000142347), score: 0.7 NCF2neutrophil cytosolic factor 2 (ENSG00000116701), score: 0.6 NCF4neutrophil cytosolic factor 4, 40kDa (ENSG00000100365), score: 0.66 NFKBIAnuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, alpha (ENSG00000100906), score: 0.52 NFKBIZnuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, zeta (ENSG00000144802), score: 0.59 NMT2N-myristoyltransferase 2 (ENSG00000152465), score: 0.56 NR1H4nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group H, member 4 (ENSG00000012504), score: 0.51 NR5A2nuclear receptor subfamily 5, group A, member 2 (ENSG00000116833), score: 0.61 NRBF2nuclear receptor binding factor 2 (ENSG00000148572), score: 0.76 NT5M5',3'-nucleotidase, mitochondrial (ENSG00000205309), score: -0.68 NTF3neurotrophin 3 (ENSG00000185652), score: 0.58 NUCB2nucleobindin 2 (ENSG00000070081), score: 0.48 OIT3oncoprotein induced transcript 3 (ENSG00000138315), score: 0.71 ONECUT1one cut homeobox 1 (ENSG00000169856), score: 0.54 OSMRoncostatin M receptor (ENSG00000145623), score: 0.48 OTCornithine carbamoyltransferase (ENSG00000036473), score: 0.51 P4HA1prolyl 4-hydroxylase, alpha polypeptide I (ENSG00000122884), score: 0.49 PARVGparvin, gamma (ENSG00000138964), score: 0.55 PCSK9proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (ENSG00000169174), score: 0.48 PCTPphosphatidylcholine transfer protein (ENSG00000141179), score: 0.56 PDIA3protein disulfide isomerase family A, member 3 (ENSG00000167004), score: 0.56 PDIA5protein disulfide isomerase family A, member 5 (ENSG00000065485), score: 0.52 PDIA6protein disulfide isomerase family A, member 6 (ENSG00000143870), score: 0.55 PHLPP2PH domain and leucine rich repeat protein phosphatase 2 (ENSG00000040199), score: -0.5 PIGSphosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis, class S (ENSG00000087111), score: -0.49 PPIBpeptidylprolyl isomerase B (cyclophilin B) (ENSG00000166794), score: 0.58 PRDM1PR domain containing 1, with ZNF domain (ENSG00000057657), score: 0.73 PROZprotein Z, vitamin K-dependent plasma glycoprotein (ENSG00000126231), score: 0.58 PTRH2peptidyl-tRNA hydrolase 2 (ENSG00000141378), score: 0.5 R3HDMLR3H domain containing-like (ENSG00000101074), score: 0.59 RAB32RAB32, member RAS oncogene family (ENSG00000118508), score: 0.49 RBP4retinol binding protein 4, plasma (ENSG00000138207), score: 0.54 RHOHras homolog gene family, member H (ENSG00000168421), score: 0.63 RND3Rho family GTPase 3 (ENSG00000115963), score: 0.67 RNF130ring finger protein 130 (ENSG00000113269), score: 0.52 RUNX3runt-related transcription factor 3 (ENSG00000020633), score: 0.51 S1PR4sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 4 (ENSG00000125910), score: 0.75 SAMD3sterile alpha motif domain containing 3 (ENSG00000164483), score: 0.55 SAMSN1SAM domain, SH3 domain and nuclear localization signals 1 (ENSG00000155307), score: 0.86 SBNO2strawberry notch homolog 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000064932), score: 0.48 SDC4syndecan 4 (ENSG00000124145), score: 0.48 SEBOXSEBOX homeobox (ENSG00000109072), score: 0.55 SEC16BSEC16 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000120341), score: 0.49 SERPINA10serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade A (alpha-1 antiproteinase, antitrypsin), member 10 (ENSG00000140093), score: 0.71 SERPINC1serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade C (antithrombin), member 1 (ENSG00000117601), score: 0.6 SERPINF1serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade F (alpha-2 antiplasmin, pigment epithelium derived factor), member 1 (ENSG00000132386), score: 0.49 SERPINF2serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade F (alpha-2 antiplasmin, pigment epithelium derived factor), member 2 (ENSG00000167711), score: 0.49 SH2D2ASH2 domain containing 2A (ENSG00000027869), score: 0.61 SH2D4ASH2 domain containing 4A (ENSG00000104611), score: 0.5 SIK1salt-inducible kinase 1 (ENSG00000142178), score: 0.63 SLASrc-like-adaptor (ENSG00000155926), score: 0.48 SLC11A1solute carrier family 11 (proton-coupled divalent metal ion transporters), member 1 (ENSG00000018280), score: 0.57 SLC13A5solute carrier family 13 (sodium-dependent citrate transporter), member 5 (ENSG00000141485), score: 0.71 SLC20A1solute carrier family 20 (phosphate transporter), member 1 (ENSG00000144136), score: 0.63 SLC22A3solute carrier family 22 (extraneuronal monoamine transporter), member 3 (ENSG00000146477), score: 0.49 SLC25A38solute carrier family 25, member 38 (ENSG00000144659), score: 0.58 SLC25A47solute carrier family 25, member 47 (ENSG00000140107), score: 0.51 SLC2A12solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 12 (ENSG00000146411), score: -0.53 SLC30A10solute carrier family 30, member 10 (ENSG00000196660), score: 0.53 SLC38A4solute carrier family 38, member 4 (ENSG00000139209), score: 0.48 SLC41A2solute carrier family 41, member 2 (ENSG00000136052), score: 0.55 SLC45A4solute carrier family 45, member 4 (ENSG00000022567), score: -0.52 SLC6A2solute carrier family 6 (neurotransmitter transporter, noradrenalin), member 2 (ENSG00000103546), score: 0.55 SLCO2B1solute carrier organic anion transporter family, member 2B1 (ENSG00000137491), score: 0.5 SOCS3suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (ENSG00000184557), score: 0.51 SPON2spondin 2, extracellular matrix protein (ENSG00000159674), score: 0.48 SPP2secreted phosphoprotein 2, 24kDa (ENSG00000072080), score: 0.54 ST6GAL1ST6 beta-galactosamide alpha-2,6-sialyltranferase 1 (ENSG00000073849), score: 0.57 STAB2stabilin 2 (ENSG00000136011), score: 0.58 STAT3signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (acute-phase response factor) (ENSG00000168610), score: 0.5 STX11syntaxin 11 (ENSG00000135604), score: 0.48 TATtyrosine aminotransferase (ENSG00000198650), score: 0.64 TBXAS1thromboxane A synthase 1 (platelet) (ENSG00000059377), score: 0.55 TC2Ntandem C2 domains, nuclear (ENSG00000165929), score: 0.56 TDO2tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (ENSG00000151790), score: 0.66 TEFthyrotrophic embryonic factor (ENSG00000167074), score: -0.64 TFPItissue factor pathway inhibitor (lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor) (ENSG00000003436), score: 0.56 TGDSTDP-glucose 4,6-dehydratase (ENSG00000088451), score: 0.71 TM4SF4transmembrane 4 L six family member 4 (ENSG00000169903), score: 0.61 TMED6transmembrane emp24 protein transport domain containing 6 (ENSG00000157315), score: 0.76 TMEM131transmembrane protein 131 (ENSG00000075568), score: -0.58 TMEM201transmembrane protein 201 (ENSG00000188807), score: -0.51 TMEM41Btransmembrane protein 41B (ENSG00000166471), score: 0.5 TNFAIP3tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 3 (ENSG00000118503), score: 0.55 TNFSF13Btumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 13b (ENSG00000102524), score: 0.52 TNRC6Ctrinucleotide repeat containing 6C (ENSG00000078687), score: -0.5 TOB1transducer of ERBB2, 1 (ENSG00000141232), score: 0.78 TOM1L2target of myb1-like 2 (chicken) (ENSG00000175662), score: -0.57 TRAT1T cell receptor associated transmembrane adaptor 1 (ENSG00000163519), score: 0.68 TRIB1tribbles homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000173334), score: 0.61 TRPM8transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily M, member 8 (ENSG00000144481), score: 0.68 TSC22D3TSC22 domain family, member 3 (ENSG00000157514), score: 0.56 TSTA3tissue specific transplantation antigen P35B (ENSG00000104522), score: 0.6 TTPALtocopherol (alpha) transfer protein-like (ENSG00000124120), score: 0.67 TULP4tubby like protein 4 (ENSG00000130338), score: -0.5 TXNDC12thioredoxin domain containing 12 (endoplasmic reticulum) (ENSG00000117862), score: 0.58 USP2ubiquitin specific peptidase 2 (ENSG00000036672), score: -0.71 WISP1WNT1 inducible signaling pathway protein 1 (ENSG00000104415), score: 0.55 ZBTB24zinc finger and BTB domain containing 24 (ENSG00000112365), score: -0.52 ZFAND5zinc finger, AN1-type domain 5 (ENSG00000107372), score: 0.54 ZFYVE20zinc finger, FYVE domain containing 20 (ENSG00000131381), score: -0.58 ZGPATzinc finger, CCCH-type with G patch domain (ENSG00000197114), score: 0.49 ZNF827zinc finger protein 827 (ENSG00000151612), score: -0.59
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ppy_lv_m_ca1 | ppy | lv | m | _ |
| ppa_lv_f_ca1 | ppa | lv | f | _ |
| ppy_lv_f_ca1 | ppy | lv | f | _ |