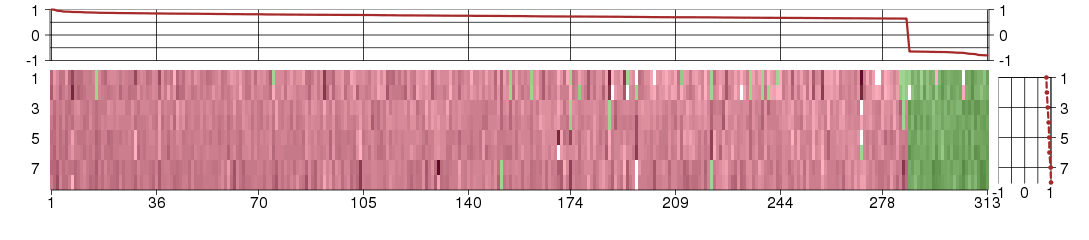

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

reproduction
The production by an organism of new individuals that contain some portion of their genetic material inherited from that organism.
chromosome segregation
The process by which genetic material, in the form of chromosomes, is organized into specific structures and then physically separated and apportioned to two or more sets.
chromosome organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level that results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of chromosomes, structures composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins that carries hereditary information.
cell cycle checkpoint
The cell cycle regulatory process by which progression through the cycle can be halted until conditions are suitable for the cell to proceed to the next stage.
M phase of mitotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the mitotic cell cycle during which mitosis takes place.
microtubule cytoskeleton organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising microtubules and their associated proteins.
mitotic cell cycle
Progression through the phases of the mitotic cell cycle, the most common eukaryotic cell cycle, which canonically comprises four successive phases called G1, S, G2, and M and includes replication of the genome and the subsequent segregation of chromosomes into daughter cells. In some variant cell cycles nuclear replication or nuclear division may not be followed by cell division, or G1 and G2 phases may be absent.
M phase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the cell cycle comprising nuclear division.
nuclear division
A process by which a cell nucleus is divided into two nuclei, with DNA and other nuclear contents distributed between the daughter nuclei.
metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
reproductive developmental process
A developmental process by which a progressive change in the state of some part of an organism specifically contributes to its ability to form offspring.
regulation of cell cycle
Any process that modulates the rate or extent of progression through the cell cycle.
cytoskeleton organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
DNA metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving deoxyribonucleic acid. This is one of the two main types of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from one, or more commonly, two, strands of linked deoxyribonucleotides.
DNA recombination
Any process by which a new genotype is formed by reassortment of genes resulting in gene combinations different from those that were present in the parents. In eukaryotes genetic recombination can occur by chromosome assortment, intrachromosomal recombination, or nonreciprocal interchromosomal recombination. Intrachromosomal recombination occurs by crossing over. In bacteria it may occur by genetic transformation, conjugation, transduction, or F-duction.
nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds; includes nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, assimilatory/dissimilatory nitrate reduction and the interconversion of nitrogenous organic matter and ammonium.
organelle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an organelle within a cell. An organelle is an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
microtubule-based process
Any cellular process that depends upon or alters the microtubule cytoskeleton, that part of the cytoskeleton comprising microtubules and their associated proteins.
microtubule-based movement
Movement of organelles, other microtubules and other particles along microtubules, mediated by motor proteins.
cell cycle
The progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events. Canonically, the cell cycle comprises the replication and segregation of genetic material followed by the division of the cell, but in endocycles or syncytial cells nuclear replication or nuclear division may not be followed by cell division.
spindle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of the spindle, the array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during DNA segregation and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
mitotic spindle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of the microtubule spindle during a mitotic cell cycle.
mitosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides; the process involves condensation of chromosomal DNA into a highly compacted form. Canonically, mitosis produces two daughter nuclei whose chromosome complement is identical to that of the mother cell.
meiosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through the nuclear division phase of a meiotic cell cycle, the specialized nuclear and cell division in which a single diploid cell undergoes two nuclear divisions following a single round of DNA replication in order to produce four daughter cells that contain half the number of chromosomes as the diploid cell. Meiotic division occurs during the formation of gametes from diploid organisms and at the beginning of haplophase in those organisms that alternate between diploid and haploid generations.
meiosis I
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through the first phase of meiosis, in which cells divide and homologous chromosomes are paired and segregated from each other, producing two daughter cells.
synapsis
The cell cycle process whereby the side by side pairing and physical juxtaposition of homologous chromosomes is created at the metaphase plate.
reciprocal meiotic recombination
The cell cycle process whereby double strand breaks are formed and repaired through a double Holliday junction intermediate. This results in the equal exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids in a pair of homologous chromosomes. These reciprocal recombinant products ensure the proper segregation of homologous chromosomes during meiosis I and create genetic diversity.
gamete generation
The generation and maintenance of gametes in a multicellular organism. A gamete is a haploid reproductive cell.
germ cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an immature germ cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure (gamete). A germ cell is any reproductive cell in a multicellular organism.
spermatogenesis
The process of formation of spermatozoa, including spermatocytogenesis and spermiogenesis.
regulation of mitotic cell cycle
Any process that modulates the rate or extent of progress through the mitotic cell cycle.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
fertilization
The union of gametes of opposite sexes during the process of sexual reproduction to form a zygote. It involves the fusion of the gametic nuclei (karyogamy) and cytoplasm (plasmogamy).
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
cellular component organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a cellular component.
RNA metabolic process
The cellular chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage.
sexual reproduction
The regular alternation, in the life cycle of haplontic, diplontic and diplohaplontic organisms, of meiosis and fertilization which provides for the production offspring. In diplontic organisms there is a life cycle in which the products of meiosis behave directly as gametes, fusing to form a zygote from which the diploid, or sexually reproductive polyploid, adult organism will develop. In diplohaplontic organisms a haploid phase (gametophyte) exists in the life cycle between meiosis and fertilization (e.g. higher plants, many algae and Fungi); the products of meiosis are spores that develop as haploid individuals from which haploid gametes develop to form a diploid zygote; diplohaplontic organisms show an alternation of haploid and diploid generations. In haplontic organisms meiosis occurs in the zygote, giving rise to four haploid cells (e.g. many algae and protozoa), only the zygote is diploid and this may form a resistant spore, tiding organisms over hard times.
cell cycle process
A cellular process that is involved in the progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
cell cycle phase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through one of the biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
cell differentiation
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
multicellular organism reproduction
The biological process by which new individuals are produced by one or two multicellular organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
piRNA metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving piRNAs, Piwi-associated RNAs, a class of 24- to 30-nucleotide RNA derived from repeat or complex DNA sequence elements and processed by a Dicer-independent mechanism.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
ncRNA metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving non-coding RNA transcripts (ncRNAs).
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
male gamete generation
Generation of the male gamete; specialised haploid cells produced by meiosis and along with a female gamete takes part in sexual reproduction.
organelle fission
The creation of two or more organelles by division of one organelle.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
reproductive process in a multicellular organism
The process, occurring above the cellular level, that is pertinent to the reproductive function of a multicellular organism. This includes the integrated processes at the level of tissues and organs.
reproductive cellular process
A process, occurring at the cellular level, that is involved in the reproductive function of a multicellular or single-celled organism.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
cell division
The process resulting in the physical partitioning and separation of a cell into daughter cells.
meiotic cell cycle
Progression through the phases of the meiotic cell cycle, in which canonically a cell replicates to produce four offspring with half the chromosomal content of the progenitor cell.
M phase of meiotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the meiotic cell cycle during which meiosis takes place.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
chromosome organization involved in meiosis
A process of chromosome organization that is involved in meiosis.
nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleic acids.
all
NA
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
organelle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an organelle within a cell. An organelle is an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
reproductive cellular process
A process, occurring at the cellular level, that is involved in the reproductive function of a multicellular or single-celled organism.
multicellular organism reproduction
The biological process by which new individuals are produced by one or two multicellular organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
reproductive process in a multicellular organism
The process, occurring above the cellular level, that is pertinent to the reproductive function of a multicellular organism. This includes the integrated processes at the level of tissues and organs.
reproductive developmental process
A developmental process by which a progressive change in the state of some part of an organism specifically contributes to its ability to form offspring.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
fertilization
The union of gametes of opposite sexes during the process of sexual reproduction to form a zygote. It involves the fusion of the gametic nuclei (karyogamy) and cytoplasm (plasmogamy).
reproductive process in a multicellular organism
The process, occurring above the cellular level, that is pertinent to the reproductive function of a multicellular organism. This includes the integrated processes at the level of tissues and organs.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
cell cycle process
A cellular process that is involved in the progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
regulation of cell cycle
Any process that modulates the rate or extent of progression through the cell cycle.
germ cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an immature germ cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure (gamete). A germ cell is any reproductive cell in a multicellular organism.
gamete generation
The generation and maintenance of gametes in a multicellular organism. A gamete is a haploid reproductive cell.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
germ cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an immature germ cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure (gamete). A germ cell is any reproductive cell in a multicellular organism.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
chromosome organization involved in meiosis
A process of chromosome organization that is involved in meiosis.
microtubule cytoskeleton organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising microtubules and their associated proteins.
mitotic spindle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of the microtubule spindle during a mitotic cell cycle.
regulation of mitotic cell cycle
Any process that modulates the rate or extent of progress through the mitotic cell cycle.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
germ cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an immature germ cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure (gamete). A germ cell is any reproductive cell in a multicellular organism.
DNA metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving deoxyribonucleic acid. This is one of the two main types of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from one, or more commonly, two, strands of linked deoxyribonucleotides.
RNA metabolic process
The cellular chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage.
mitosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides; the process involves condensation of chromosomal DNA into a highly compacted form. Canonically, mitosis produces two daughter nuclei whose chromosome complement is identical to that of the mother cell.
mitotic spindle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of the microtubule spindle during a mitotic cell cycle.
mitosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides; the process involves condensation of chromosomal DNA into a highly compacted form. Canonically, mitosis produces two daughter nuclei whose chromosome complement is identical to that of the mother cell.
meiosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through the nuclear division phase of a meiotic cell cycle, the specialized nuclear and cell division in which a single diploid cell undergoes two nuclear divisions following a single round of DNA replication in order to produce four daughter cells that contain half the number of chromosomes as the diploid cell. Meiotic division occurs during the formation of gametes from diploid organisms and at the beginning of haplophase in those organisms that alternate between diploid and haploid generations.
M phase of mitotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the mitotic cell cycle during which mitosis takes place.
spindle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of the spindle, the array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during DNA segregation and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
M phase of meiotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the meiotic cell cycle during which meiosis takes place.
meiosis I
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through the first phase of meiosis, in which cells divide and homologous chromosomes are paired and segregated from each other, producing two daughter cells.
chromosome organization involved in meiosis
A process of chromosome organization that is involved in meiosis.
synapsis
The cell cycle process whereby the side by side pairing and physical juxtaposition of homologous chromosomes is created at the metaphase plate.
reciprocal meiotic recombination
The cell cycle process whereby double strand breaks are formed and repaired through a double Holliday junction intermediate. This results in the equal exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids in a pair of homologous chromosomes. These reciprocal recombinant products ensure the proper segregation of homologous chromosomes during meiosis I and create genetic diversity.
reciprocal meiotic recombination
The cell cycle process whereby double strand breaks are formed and repaired through a double Holliday junction intermediate. This results in the equal exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids in a pair of homologous chromosomes. These reciprocal recombinant products ensure the proper segregation of homologous chromosomes during meiosis I and create genetic diversity.

nuclear chromosome
A chromosome found in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell.
condensed nuclear chromosome
A highly compacted molecule of DNA and associated proteins resulting in a cytologically distinct structure that remains in the nucleus.
condensed chromosome
A highly compacted molecule of DNA and associated proteins resulting in a cytologically distinct structure.
intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
chromosome, centromeric region
The region of a chromosome that includes the centromeric DNA and associated proteins. In monocentric chromosomes, this region corresponds to a single area of the chromosome, whereas in holocentric chromosomes, it is evenly distributed along the chromosome.
kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of DNA and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
condensed chromosome kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of a condensed chromosome and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
condensed chromosome, centromeric region
The region of a condensed chromosome that includes the centromere and associated proteins, including the kinetochore. In monocentric chromosomes, this region corresponds to a single area of the chromosome, whereas in holocentric chromosomes, it is evenly distributed along the chromosome.
spindle pole
Either of the ends of a spindle, where spindle microtubules are organized; usually contains a microtubule organizing center and accessory molecules, spindle microtubules and astral microtubules.
ribonucleoprotein complex
A macromolecular complex containing both protein and RNA molecules.
axoneme
The bundle of microtubules and associated proteins that forms the core of cilia and flagella in eukaryotic cells and is responsible for their movements.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
integral to membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer. When used to describe a protein, indicates that all or part of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
nucleus
A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent.
nuclear envelope
The double lipid bilayer enclosing the nucleus and separating its contents from the rest of the cytoplasm; includes the intermembrane space, a gap of width 20-40 nm (also called the perinuclear space).
nuclear pore
Any of the numerous similar discrete openings in the nuclear envelope of a eukaryotic cell, where the inner and outer nuclear membranes are joined.
cytoplasm
All of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
chromosome
A structure composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins (e.g. histones) that carries hereditary information.
centrosome
A structure comprised of a core structure (in most organisms, a pair of centrioles) and peripheral material from which a microtubule-based structure, such as a spindle apparatus, is organized. Centrosomes occur close to the nucleus during interphase in many eukaryotic cells, though in animal cells it changes continually during the cell-division cycle.
centriole
A cellular organelle, found close to the nucleus in many eukaryotic cells, consisting of a small cylinder with microtubular walls, 300-500 nm long and 150-250 nm in diameter. It contains nine short, parallel, peripheral microtubular fibrils, each fibril consisting of one complete microtubule fused to two incomplete microtubules. Cells usually have two centrioles, lying at right angles to each other. At division, each pair of centrioles generates another pair and the twin pairs form the pole of the mitotic spindle.
microtubule organizing center
A cytoplasmic structure that can catalyze gamma-tubulin-dependent microtubule nucleation and that can anchor microtubules by interacting with their minus ends, plus ends or sides.
spindle
The array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during mitosis or meiosis and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
cytoskeleton
Any of the various filamentous elements that form the internal framework of cells, and typically remain after treatment of the cells with mild detergent to remove membrane constituents and soluble components of the cytoplasm. The term embraces intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, the microtrabecular lattice, and other structures characterized by a polymeric filamentous nature and long-range order within the cell. The various elements of the cytoskeleton not only serve in the maintenance of cellular shape but also have roles in other cellular functions, including cellular movement, cell division, endocytosis, and movement of organelles.
microtubule
Any of the long, generally straight, hollow tubes of internal diameter 12-15 nm and external diameter 24 nm found in a wide variety of eukaryotic cells; each consists (usually) of 13 protofilaments of polymeric tubulin, staggered in such a manner that the tubulin monomers are arranged in a helical pattern on the microtubular surface, and with the alpha/beta axes of the tubulin subunits parallel to the long axis of the tubule; exist in equilibrium with pool of tubulin monomers and can be rapidly assembled or disassembled in response to physiological stimuli; concerned with force generation, e.g. in the spindle.
microtubule associated complex
Any multimeric complex connected to a microtubule.
spindle microtubule
Any microtubule that is part of a mitotic or meiotic spindle; anchored at one spindle pole.
endomembrane system
A collection of membranous structures involved in transport within the cell. The main components of the endomembrane system are endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, vesicles, cell membrane and nuclear envelope. Members of the endomembrane system pass materials through each other or though the use of vesicles.
pore complex
Any small opening in a membrane that allows the passage of gases and/or liquids.
microtubule cytoskeleton
The part of the cytoskeleton (the internal framework of a cell) composed of microtubules and associated proteins.
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
Ndc80 complex
A protein complex conserved among eukaryotes that forms part of the kinetochore and plays an essential role in forming stable kinetochore-microtubule attachments. The complex contains proteins known in several species, including budding and fission yeasts, as Ndc80p, Nuf2p, Spc24p, and Spc25p. In vertebrates it is part of the outer plate of the kinetochore.
organelle envelope
A double membrane structure enclosing an organelle, including two lipid bilayers and the region between them. In some cases, an organelle envelope may have more than two membranes.
envelope
A multilayered structure surrounding all or part of a cell; encompasses one or more lipid bilayers, and may include a cell wall layer; also includes the space between layers.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
chromatoid body
A ribonucleoprotein complex found in the cytoplasm of male germ cells, composed of exceedingly thin filaments that are consolidated into a compact mass or into dense strands of varying thickness that branch to form an irregular network. Contains mRNAs, miRNAs, and protein components involved in miRNA processing (such as Argonaute proteins and the endonuclease Dicer) and in RNA decay (such as the decapping enzyme DCP1a and GW182).
cell projection
A prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
P granule
A small cytoplasmic, non-membranous RNA/protein complex aggregates in the primordial germ cells of many higher eukaryotes.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, and prokaryotic structures such as anammoxosomes and pirellulosomes. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
protein complex
Any macromolecular complex composed of two or more polypeptide subunits, which may or may not be identical. Protein complexes may have other associated non-protein prosthetic groups, such as nucleotides, metal ions or other small molecules.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
chromosomal part
Any constituent part of a chromosome, a structure composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins (e.g. histones) that carries hereditary information.
nuclear part
Any constituent part of the nucleus, a membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
microtubule organizing center part
Any constituent part of a microtubule organizing center, a region in a eukaryotic cell, such as a centrosome or basal body, from which microtubules grow.
cell projection part
Any constituent part of a cell projection, a prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
pole plasm
Differentiated cytoplasm associated with a pole (animal, vegetal, anterior, or posterior) of an oocyte, egg or early embryo.
germ plasm
Differentiated cytoplasm associated with a pole of an oocyte, egg or early embryo that will be inherited by the cells that will give rise to the germ line.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
organelle envelope
A double membrane structure enclosing an organelle, including two lipid bilayers and the region between them. In some cases, an organelle envelope may have more than two membranes.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
organelle envelope
A double membrane structure enclosing an organelle, including two lipid bilayers and the region between them. In some cases, an organelle envelope may have more than two membranes.
cell projection part
Any constituent part of a cell projection, a prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
ribonucleoprotein complex
A macromolecular complex containing both protein and RNA molecules.
axoneme
The bundle of microtubules and associated proteins that forms the core of cilia and flagella in eukaryotic cells and is responsible for their movements.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
axoneme
The bundle of microtubules and associated proteins that forms the core of cilia and flagella in eukaryotic cells and is responsible for their movements.
Ndc80 complex
A protein complex conserved among eukaryotes that forms part of the kinetochore and plays an essential role in forming stable kinetochore-microtubule attachments. The complex contains proteins known in several species, including budding and fission yeasts, as Ndc80p, Nuf2p, Spc24p, and Spc25p. In vertebrates it is part of the outer plate of the kinetochore.
nuclear envelope
The double lipid bilayer enclosing the nucleus and separating its contents from the rest of the cytoplasm; includes the intermembrane space, a gap of width 20-40 nm (also called the perinuclear space).
axoneme
The bundle of microtubules and associated proteins that forms the core of cilia and flagella in eukaryotic cells and is responsible for their movements.
kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of DNA and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of DNA and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
Ndc80 complex
A protein complex conserved among eukaryotes that forms part of the kinetochore and plays an essential role in forming stable kinetochore-microtubule attachments. The complex contains proteins known in several species, including budding and fission yeasts, as Ndc80p, Nuf2p, Spc24p, and Spc25p. In vertebrates it is part of the outer plate of the kinetochore.
nuclear envelope
The double lipid bilayer enclosing the nucleus and separating its contents from the rest of the cytoplasm; includes the intermembrane space, a gap of width 20-40 nm (also called the perinuclear space).
nuclear pore
Any of the numerous similar discrete openings in the nuclear envelope of a eukaryotic cell, where the inner and outer nuclear membranes are joined.
spindle
The array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during mitosis or meiosis and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
microtubule
Any of the long, generally straight, hollow tubes of internal diameter 12-15 nm and external diameter 24 nm found in a wide variety of eukaryotic cells; each consists (usually) of 13 protofilaments of polymeric tubulin, staggered in such a manner that the tubulin monomers are arranged in a helical pattern on the microtubular surface, and with the alpha/beta axes of the tubulin subunits parallel to the long axis of the tubule; exist in equilibrium with pool of tubulin monomers and can be rapidly assembled or disassembled in response to physiological stimuli; concerned with force generation, e.g. in the spindle.
microtubule associated complex
Any multimeric complex connected to a microtubule.
nuclear pore
Any of the numerous similar discrete openings in the nuclear envelope of a eukaryotic cell, where the inner and outer nuclear membranes are joined.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
microtubule organizing center
A cytoplasmic structure that can catalyze gamma-tubulin-dependent microtubule nucleation and that can anchor microtubules by interacting with their minus ends, plus ends or sides.
P granule
A small cytoplasmic, non-membranous RNA/protein complex aggregates in the primordial germ cells of many higher eukaryotes.
microtubule organizing center part
Any constituent part of a microtubule organizing center, a region in a eukaryotic cell, such as a centrosome or basal body, from which microtubules grow.
nuclear part
Any constituent part of the nucleus, a membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated.
nuclear chromosome
A chromosome found in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell.
chromosomal part
Any constituent part of a chromosome, a structure composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins (e.g. histones) that carries hereditary information.
centriole
A cellular organelle, found close to the nucleus in many eukaryotic cells, consisting of a small cylinder with microtubular walls, 300-500 nm long and 150-250 nm in diameter. It contains nine short, parallel, peripheral microtubular fibrils, each fibril consisting of one complete microtubule fused to two incomplete microtubules. Cells usually have two centrioles, lying at right angles to each other. At division, each pair of centrioles generates another pair and the twin pairs form the pole of the mitotic spindle.
spindle pole
Either of the ends of a spindle, where spindle microtubules are organized; usually contains a microtubule organizing center and accessory molecules, spindle microtubules and astral microtubules.
spindle microtubule
Any microtubule that is part of a mitotic or meiotic spindle; anchored at one spindle pole.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of DNA and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
centrosome
A structure comprised of a core structure (in most organisms, a pair of centrioles) and peripheral material from which a microtubule-based structure, such as a spindle apparatus, is organized. Centrosomes occur close to the nucleus during interphase in many eukaryotic cells, though in animal cells it changes continually during the cell-division cycle.
microtubule organizing center part
Any constituent part of a microtubule organizing center, a region in a eukaryotic cell, such as a centrosome or basal body, from which microtubules grow.
centriole
A cellular organelle, found close to the nucleus in many eukaryotic cells, consisting of a small cylinder with microtubular walls, 300-500 nm long and 150-250 nm in diameter. It contains nine short, parallel, peripheral microtubular fibrils, each fibril consisting of one complete microtubule fused to two incomplete microtubules. Cells usually have two centrioles, lying at right angles to each other. At division, each pair of centrioles generates another pair and the twin pairs form the pole of the mitotic spindle.
pore complex
Any small opening in a membrane that allows the passage of gases and/or liquids.
condensed nuclear chromosome
A highly compacted molecule of DNA and associated proteins resulting in a cytologically distinct structure that remains in the nucleus.
condensed chromosome, centromeric region
The region of a condensed chromosome that includes the centromere and associated proteins, including the kinetochore. In monocentric chromosomes, this region corresponds to a single area of the chromosome, whereas in holocentric chromosomes, it is evenly distributed along the chromosome.
microtubule organizing center
A cytoplasmic structure that can catalyze gamma-tubulin-dependent microtubule nucleation and that can anchor microtubules by interacting with their minus ends, plus ends or sides.
spindle
The array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during mitosis or meiosis and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
microtubule
Any of the long, generally straight, hollow tubes of internal diameter 12-15 nm and external diameter 24 nm found in a wide variety of eukaryotic cells; each consists (usually) of 13 protofilaments of polymeric tubulin, staggered in such a manner that the tubulin monomers are arranged in a helical pattern on the microtubular surface, and with the alpha/beta axes of the tubulin subunits parallel to the long axis of the tubule; exist in equilibrium with pool of tubulin monomers and can be rapidly assembled or disassembled in response to physiological stimuli; concerned with force generation, e.g. in the spindle.
microtubule associated complex
Any multimeric complex connected to a microtubule.
condensed chromosome kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of a condensed chromosome and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
P granule
A small cytoplasmic, non-membranous RNA/protein complex aggregates in the primordial germ cells of many higher eukaryotes.

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
motor activity
Catalysis of movement along a polymeric molecule such as a microfilament or microtubule, coupled to the hydrolysis of a nucleoside triphosphate.
microtubule motor activity
Catalysis of movement along a microtubule, coupled to the hydrolysis of a nucleoside triphosphate (usually ATP).
catalytic activity
Catalysis of a biochemical reaction at physiological temperatures. In biologically catalyzed reactions, the reactants are known as substrates, and the catalysts are naturally occurring macromolecular substances known as enzymes. Enzymes possess specific binding sites for substrates, and are usually composed wholly or largely of protein, but RNA that has catalytic activity (ribozyme) is often also regarded as enzymatic.
nucleoside-triphosphatase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: a nucleoside triphosphate + H2O = nucleoside diphosphate + phosphate.
binding
The selective, non-covalent, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
pyrophosphatase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of a pyrophosphate bond between two phosphate groups, leaving one phosphate on each of the two fragments.
hydrolase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of various bonds, e.g. C-O, C-N, C-C, phosphoric anhydride bonds, etc. Hydrolase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 3.
hydrolase activity, acting on acid anhydrides
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of any acid anhydride.
hydrolase activity, acting on acid anhydrides, in phosphorus-containing anhydrides
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of any acid anhydride which contains phosphorus.
all
NA
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 04110 | 1.056e-04 | 1.443 | 10 | 46 | Cell cycle |
| 04114 | 8.708e-03 | 1.223 | 7 | 39 | Oocyte meiosis |
ACBD6acyl-CoA binding domain containing 6 (ENSG00000135847), score: 0.72 ADAD1adenosine deaminase domain containing 1 (testis-specific) (ENSG00000164113), score: 0.84 ADSSadenylosuccinate synthase (ENSG00000035687), score: 0.67 AGBL3ATP/GTP binding protein-like 3 (ENSG00000146856), score: 0.84 AGBL5ATP/GTP binding protein-like 5 (ENSG00000084693), score: 0.7 AGFG1ArfGAP with FG repeats 1 (ENSG00000173744), score: 0.66 AK7adenylate kinase 7 (ENSG00000140057), score: 0.87 ANAPC10anaphase promoting complex subunit 10 (ENSG00000164162), score: 0.68 ANGEL1angel homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000013523), score: 0.65 ANKFN1ankyrin-repeat and fibronectin type III domain containing 1 (ENSG00000153930), score: 0.66 ANKRD5ankyrin repeat domain 5 (ENSG00000132623), score: 0.86 ANUBL1AN1, ubiquitin-like, homolog (Xenopus laevis) (ENSG00000172671), score: 0.75 ANXA6annexin A6 (ENSG00000197043), score: -0.67 ANXA7annexin A7 (ENSG00000138279), score: -0.74 ARID2AT rich interactive domain 2 (ARID, RFX-like) (ENSG00000189079), score: 0.8 ARID3BAT rich interactive domain 3B (BRIGHT-like) (ENSG00000179361), score: 0.75 ARL13BADP-ribosylation factor-like 13B (ENSG00000169379), score: 0.79 ARL9ADP-ribosylation factor-like 9 (ENSG00000196503), score: 0.64 ARMC3armadillo repeat containing 3 (ENSG00000165309), score: 0.83 ARMC4armadillo repeat containing 4 (ENSG00000169126), score: 0.82 ASPHaspartate beta-hydroxylase (ENSG00000198363), score: -0.7 ASPMasp (abnormal spindle) homolog, microcephaly associated (Drosophila) (ENSG00000066279), score: 0.78 AURKAaurora kinase A (ENSG00000087586), score: 0.83 BAZ1Abromodomain adjacent to zinc finger domain, 1A (ENSG00000198604), score: 0.68 BHLHE40basic helix-loop-helix family, member e40 (ENSG00000134107), score: -0.68 BLMBloom syndrome, RecQ helicase-like (ENSG00000197299), score: 0.65 BOLLbol, boule-like (Drosophila) (ENSG00000152430), score: 0.84 BRAPBRCA1 associated protein (ENSG00000089234), score: 0.7 BRCA2breast cancer 2, early onset (ENSG00000139618), score: 0.73 BRIP1BRCA1 interacting protein C-terminal helicase 1 (ENSG00000136492), score: 0.82 BTG4B-cell translocation gene 4 (ENSG00000137707), score: 0.68 BUB1budding uninhibited by benzimidazoles 1 homolog (yeast) (ENSG00000169679), score: 0.78 BUB1Bbudding uninhibited by benzimidazoles 1 homolog beta (yeast) (ENSG00000156970), score: 0.72 C10orf46chromosome 10 open reading frame 46 (ENSG00000151893), score: 0.68 C10orf96chromosome 10 open reading frame 96 (ENSG00000182645), score: 0.8 C11orf70chromosome 11 open reading frame 70 (ENSG00000137691), score: 0.79 C11orf82chromosome 11 open reading frame 82 (ENSG00000165490), score: 0.76 C12orf50chromosome 12 open reading frame 50 (ENSG00000165805), score: 0.79 C12orf63chromosome 12 open reading frame 63 (ENSG00000188596), score: 0.86 C13orf34chromosome 13 open reading frame 34 (ENSG00000136122), score: 0.77 C14orf166Bchromosome 14 open reading frame 166B (ENSG00000100565), score: 0.86 C14orf38chromosome 14 open reading frame 38 (ENSG00000151838), score: 0.66 C14orf39chromosome 14 open reading frame 39 (ENSG00000179008), score: 0.72 C14orf50chromosome 14 open reading frame 50 (ENSG00000165807), score: 0.82 C15orf26chromosome 15 open reading frame 26 (ENSG00000156206), score: 0.88 C17orf104chromosome 17 open reading frame 104 (ENSG00000180336), score: 0.79 C19orf45chromosome 19 open reading frame 45 (ENSG00000198723), score: 0.91 C1orf100chromosome 1 open reading frame 100 (ENSG00000173728), score: 0.83 C1orf111chromosome 1 open reading frame 111 (ENSG00000171722), score: 0.81 C1orf158chromosome 1 open reading frame 158 (ENSG00000157330), score: 0.83 C1orf228chromosome 1 open reading frame 228 (ENSG00000198520), score: 0.73 C1orf59chromosome 1 open reading frame 59 (ENSG00000162639), score: 0.66 C1orf88chromosome 1 open reading frame 88 (ENSG00000173947), score: 0.66 C20orf85chromosome 20 open reading frame 85 (ENSG00000124237), score: 0.86 C2orf65chromosome 2 open reading frame 65 (ENSG00000159374), score: 0.79 C2orf71chromosome 2 open reading frame 71 (ENSG00000179270), score: 0.76 C3orf38chromosome 3 open reading frame 38 (ENSG00000179021), score: 0.7 C4orf47chromosome 4 open reading frame 47 (ENSG00000205129), score: 0.67 C6orf204chromosome 6 open reading frame 204 (ENSG00000111860), score: 0.73 C6orf64chromosome 6 open reading frame 64 (ENSG00000112167), score: 0.67 C7orf31chromosome 7 open reading frame 31 (ENSG00000153790), score: 0.8 C7orf45chromosome 7 open reading frame 45 (ENSG00000165120), score: 0.9 C7orf57chromosome 7 open reading frame 57 (ENSG00000164746), score: 0.66 C7orf62chromosome 7 open reading frame 62 (ENSG00000164645), score: 0.85 C9orf96chromosome 9 open reading frame 96 (ENSG00000198870), score: 0.76 C9orf98chromosome 9 open reading frame 98 (ENSG00000165695), score: 0.75 CALR3calreticulin 3 (ENSG00000141979), score: 0.81 CASC1cancer susceptibility candidate 1 (ENSG00000118307), score: 0.72 CCDC108coiled-coil domain containing 108 (ENSG00000181378), score: 0.85 CCDC122coiled-coil domain containing 122 (ENSG00000151773), score: 0.73 CCDC135coiled-coil domain containing 135 (ENSG00000159625), score: 0.75 CCDC146coiled-coil domain containing 146 (ENSG00000135205), score: 0.8 CCDC27coiled-coil domain containing 27 (ENSG00000162592), score: 0.81 CCDC30coiled-coil domain containing 30 (ENSG00000186409), score: 0.76 CCDC37coiled-coil domain containing 37 (ENSG00000163885), score: 0.77 CCDC40coiled-coil domain containing 40 (ENSG00000141519), score: 0.8 CCDC41coiled-coil domain containing 41 (ENSG00000173588), score: 0.69 CCDC63coiled-coil domain containing 63 (ENSG00000173093), score: 0.92 CCDC67coiled-coil domain containing 67 (ENSG00000165325), score: 0.84 CCDC83coiled-coil domain containing 83 (ENSG00000150676), score: 0.92 CCNA1cyclin A1 (ENSG00000133101), score: 0.74 CCR4chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 4 (ENSG00000183813), score: 0.72 CDC14ACDC14 cell division cycle 14 homolog A (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000079335), score: 0.7 CDC25Acell division cycle 25 homolog A (S. pombe) (ENSG00000164045), score: 0.66 CDKN3cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 3 (ENSG00000100526), score: 0.83 CENPFcentromere protein F, 350/400kDa (mitosin) (ENSG00000117724), score: 0.74 CENPKcentromere protein K (ENSG00000123219), score: 0.74 CEP152centrosomal protein 152kDa (ENSG00000103995), score: 0.68 CEP350centrosomal protein 350kDa (ENSG00000135837), score: 0.7 CEP55centrosomal protein 55kDa (ENSG00000138180), score: 0.76 CEP57centrosomal protein 57kDa (ENSG00000166037), score: 0.66 CGRRF1cell growth regulator with ring finger domain 1 (ENSG00000100532), score: 0.72 CHRNB3cholinergic receptor, nicotinic, beta 3 (ENSG00000147432), score: 0.73 CLCA2chloride channel accessory 2 (ENSG00000137975), score: 0.71 CLSPNclaspin (ENSG00000092853), score: 0.69 CNOT1CCR4-NOT transcription complex, subunit 1 (ENSG00000125107), score: 0.78 CNOT4CCR4-NOT transcription complex, subunit 4 (ENSG00000080802), score: 0.84 CREMcAMP responsive element modulator (ENSG00000095794), score: 0.67 CTBP1C-terminal binding protein 1 (ENSG00000159692), score: -0.7 CUL3cullin 3 (ENSG00000036257), score: 0.7 CXorf22chromosome X open reading frame 22 (ENSG00000165164), score: 0.79 CXorf30chromosome X open reading frame 30 (ENSG00000205081), score: 0.69 DDX20DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 20 (ENSG00000064703), score: 0.76 DDX4DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 4 (ENSG00000152670), score: 0.79 DMC1DMC1 dosage suppressor of mck1 homolog, meiosis-specific homologous recombination (yeast) (ENSG00000100206), score: 0.68 DMRT3doublesex and mab-3 related transcription factor 3 (ENSG00000064218), score: 0.69 DNAH8dynein, axonemal, heavy chain 8 (ENSG00000124721), score: 0.95 DNAI1dynein, axonemal, intermediate chain 1 (ENSG00000122735), score: 0.69 DNAI2dynein, axonemal, intermediate chain 2 (ENSG00000171595), score: 0.87 DNAJC5BDnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 5 beta (ENSG00000147570), score: 0.73 DNALI1dynein, axonemal, light intermediate chain 1 (ENSG00000163879), score: 0.66 DR1down-regulator of transcription 1, TBP-binding (negative cofactor 2) (ENSG00000117505), score: 0.69 DTLdenticleless homolog (Drosophila) (ENSG00000143476), score: 0.78 DYDC1DPY30 domain containing 1 (ENSG00000170788), score: 0.89 DYMdymeclin (ENSG00000141627), score: 0.78 E2F8E2F transcription factor 8 (ENSG00000129173), score: 0.76 EFCAB1EF-hand calcium binding domain 1 (ENSG00000034239), score: 0.65 EFCAB5EF-hand calcium binding domain 5 (ENSG00000176927), score: 0.83 EFHC1EF-hand domain (C-terminal) containing 1 (ENSG00000096093), score: 0.73 ERCC8excision repair cross-complementing rodent repair deficiency, complementation group 8 (ENSG00000049167), score: 0.65 ESAMendothelial cell adhesion molecule (ENSG00000149564), score: -0.65 FAM161Afamily with sequence similarity 161, member A (ENSG00000170264), score: 0.72 FAM194Afamily with sequence similarity 194, member A (ENSG00000163645), score: 0.85 FAM46Cfamily with sequence similarity 46, member C (ENSG00000183508), score: 0.65 FAM48Afamily with sequence similarity 48, member A (ENSG00000102710), score: 0.71 FAM73Bfamily with sequence similarity 73, member B (ENSG00000148343), score: -0.7 FAM81Bfamily with sequence similarity 81, member B (ENSG00000153347), score: 0.74 FBXO43F-box protein 43 (ENSG00000156509), score: 0.85 FBXO47F-box protein 47 (ENSG00000204952), score: 0.81 FEM1Cfem-1 homolog c (C. elegans) (ENSG00000145780), score: 0.64 FLOT2flotillin 2 (ENSG00000132589), score: -0.65 FOXJ1forkhead box J1 (ENSG00000129654), score: 0.65 GKAP1G kinase anchoring protein 1 (ENSG00000165113), score: 0.82 GLT8D1glycosyltransferase 8 domain containing 1 (ENSG00000016864), score: 0.7 GMPSguanine monphosphate synthetase (ENSG00000163655), score: 0.87 GPATCH2G patch domain containing 2 (ENSG00000092978), score: 0.69 GRB2growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 (ENSG00000177885), score: -0.79 GSG1germ cell associated 1 (ENSG00000111305), score: 0.88 GTSF1gametocyte specific factor 1 (ENSG00000170627), score: 0.72 HIAT1hippocampus abundant transcript 1 (ENSG00000156875), score: 0.84 HORMAD1HORMA domain containing 1 (ENSG00000143452), score: 0.82 HSF2BPheat shock transcription factor 2 binding protein (ENSG00000160207), score: 0.8 IFT74intraflagellar transport 74 homolog (Chlamydomonas) (ENSG00000096872), score: 0.67 IFT88intraflagellar transport 88 homolog (Chlamydomonas) (ENSG00000032742), score: 0.75 IGF2BP1insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 1 (ENSG00000159217), score: 0.68 IQCHIQ motif containing H (ENSG00000103599), score: 0.86 IQUBIQ motif and ubiquitin domain containing (ENSG00000164675), score: 0.77 ISG20L2interferon stimulated exonuclease gene 20kDa-like 2 (ENSG00000143319), score: 0.79 KATNAL2katanin p60 subunit A-like 2 (ENSG00000167216), score: 0.73 KIAA0586KIAA0586 (ENSG00000100578), score: 0.87 KIF11kinesin family member 11 (ENSG00000138160), score: 0.8 KIF14kinesin family member 14 (ENSG00000118193), score: 0.74 KIF15kinesin family member 15 (ENSG00000163808), score: 0.79 KIF18Akinesin family member 18A (ENSG00000121621), score: 0.94 KIF18Bkinesin family member 18B (ENSG00000186185), score: 0.84 KIF23kinesin family member 23 (ENSG00000137807), score: 0.75 KIF24kinesin family member 24 (ENSG00000186638), score: 0.79 KIF27kinesin family member 27 (ENSG00000165115), score: 0.81 KIF2Bkinesin family member 2B (ENSG00000141200), score: 0.84 KIF6kinesin family member 6 (ENSG00000164627), score: 0.71 KLHL10kelch-like 10 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000161594), score: 0.85 KNTC1kinetochore associated 1 (ENSG00000184445), score: 0.82 KPNA6karyopherin alpha 6 (importin alpha 7) (ENSG00000025800), score: 0.67 LASS3LAG1 homolog, ceramide synthase 3 (ENSG00000154227), score: 0.99 LETM2leucine zipper-EF-hand containing transmembrane protein 2 (ENSG00000165046), score: 0.67 LGSNlengsin, lens protein with glutamine synthetase domain (ENSG00000146166), score: 0.64 LIG3ligase III, DNA, ATP-dependent (ENSG00000005156), score: 0.68 LIN28Blin-28 homolog B (C. elegans) (ENSG00000187772), score: 0.71 LOC100133760similar to Jumonji, AT rich interactive domain 1B (RBP2-like) (ENSG00000117139), score: 0.68 LOC81691exonuclease NEF-sp (ENSG00000005189), score: 0.68 LRGUKleucine-rich repeats and guanylate kinase domain containing (ENSG00000155530), score: 0.76 LRP2BPLRP2 binding protein (ENSG00000109771), score: 0.7 LRRC18leucine rich repeat containing 18 (ENSG00000165383), score: 0.7 LRRC43leucine rich repeat containing 43 (ENSG00000158113), score: 0.84 LRRC48leucine rich repeat containing 48 (ENSG00000171962), score: 0.72 LRRC50leucine rich repeat containing 50 (ENSG00000154099), score: 0.72 LRRC52leucine rich repeat containing 52 (ENSG00000162763), score: 0.75 LRRC6leucine rich repeat containing 6 (ENSG00000129295), score: 0.71 LRRC67leucine rich repeat containing 67 (ENSG00000178125), score: 0.9 LRRC8Aleucine rich repeat containing 8 family, member A (ENSG00000136802), score: -0.67 LRRCC1leucine rich repeat and coiled-coil domain containing 1 (ENSG00000133739), score: 0.84 LRRIQ1leucine-rich repeats and IQ motif containing 1 (ENSG00000133640), score: 0.71 LRRIQ4leucine-rich repeats and IQ motif containing 4 (ENSG00000188306), score: 0.86 MAELmaelstrom homolog (Drosophila) (ENSG00000143194), score: 0.77 MAKmale germ cell-associated kinase (ENSG00000111837), score: 0.71 MARCH11membrane-associated ring finger (C3HC4) 11 (ENSG00000183654), score: 0.78 MC2Rmelanocortin 2 receptor (adrenocorticotropic hormone) (ENSG00000185231), score: 0.69 MDH1Bmalate dehydrogenase 1B, NAD (soluble) (ENSG00000138400), score: 0.81 MELKmaternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase (ENSG00000165304), score: 0.76 MLF2myeloid leukemia factor 2 (ENSG00000089693), score: -0.65 MORN3MORN repeat containing 3 (ENSG00000139714), score: 0.81 MOV10L1Mov10l1, Moloney leukemia virus 10-like 1, homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000073146), score: 0.69 MPP1membrane protein, palmitoylated 1, 55kDa (ENSG00000130830), score: -0.67 MTF1metal-regulatory transcription factor 1 (ENSG00000188786), score: 0.67 MYBL1v-myb myeloblastosis viral oncogene homolog (avian)-like 1 (ENSG00000185697), score: 0.77 MYF6myogenic factor 6 (herculin) (ENSG00000111046), score: 0.72 NCAPGnon-SMC condensin I complex, subunit G (ENSG00000109805), score: 0.79 NCBP1nuclear cap binding protein subunit 1, 80kDa (ENSG00000136937), score: 0.8 NDC80NDC80 homolog, kinetochore complex component (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000080986), score: 0.7 NEK2NIMA (never in mitosis gene a)-related kinase 2 (ENSG00000117650), score: 0.88 NFIBnuclear factor I/B (ENSG00000147862), score: -0.8 NMBRneuromedin B receptor (ENSG00000135577), score: 0.85 NRD1nardilysin (N-arginine dibasic convertase) (ENSG00000078618), score: 0.75 NSUN4NOP2/Sun domain family, member 4 (ENSG00000117481), score: 0.64 NUF2NUF2, NDC80 kinetochore complex component, homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000143228), score: 0.77 NUP153nucleoporin 153kDa (ENSG00000124789), score: 0.69 NUP214nucleoporin 214kDa (ENSG00000126883), score: 0.65 ORC1Lorigin recognition complex, subunit 1-like (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000085840), score: 0.72 OSCP1organic solute carrier partner 1 (ENSG00000116885), score: 0.65 PACRGLPARK2 co-regulated-like (ENSG00000163138), score: 0.65 PASKPAS domain containing serine/threonine kinase (ENSG00000115687), score: 0.67 PDZD8PDZ domain containing 8 (ENSG00000165650), score: 0.66 PFN4profilin family, member 4 (ENSG00000176732), score: 0.75 PHF13PHD finger protein 13 (ENSG00000116273), score: 0.68 PIAS1protein inhibitor of activated STAT, 1 (ENSG00000033800), score: 0.67 PIAS4protein inhibitor of activated STAT, 4 (ENSG00000105229), score: 0.68 PIH1D2PIH1 domain containing 2 (ENSG00000150773), score: 0.72 PIWIL1piwi-like 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000125207), score: 0.8 POLKpolymerase (DNA directed) kappa (ENSG00000122008), score: 0.7 PPEF1protein phosphatase, EF-hand calcium binding domain 1 (ENSG00000086717), score: 0.67 PPM1Gprotein phosphatase, Mg2+/Mn2+ dependent, 1G (ENSG00000115241), score: 0.74 PTGES2prostaglandin E synthase 2 (ENSG00000148334), score: -0.66 PVRL3poliovirus receptor-related 3 (ENSG00000177707), score: 0.66 RAB14RAB14, member RAS oncogene family (ENSG00000119396), score: -0.65 RABGGTBRab geranylgeranyltransferase, beta subunit (ENSG00000137955), score: -0.65 RAE1RAE1 RNA export 1 homolog (S. pombe) (ENSG00000101146), score: 0.72 RAG2recombination activating gene 2 (ENSG00000175097), score: 0.9 RAGErenal tumor antigen (ENSG00000080823), score: 0.66 RANBP17RAN binding protein 17 (ENSG00000204764), score: 0.68 RANBP9RAN binding protein 9 (ENSG00000010017), score: 0.7 RBM27RNA binding motif protein 27 (ENSG00000091009), score: 0.74 RBM46RNA binding motif protein 46 (ENSG00000151962), score: 0.79 RFX2regulatory factor X, 2 (influences HLA class II expression) (ENSG00000087903), score: 0.77 RFX6regulatory factor X, 6 (ENSG00000185002), score: 0.65 RIBC2RIB43A domain with coiled-coils 2 (ENSG00000128408), score: 0.74 RNF17ring finger protein 17 (ENSG00000132972), score: 0.9 RNF32ring finger protein 32 (ENSG00000105982), score: 0.79 RNF38ring finger protein 38 (ENSG00000137075), score: 0.79 ROPN1Lropporin 1-like (ENSG00000145491), score: 0.77 RPS6KA3ribosomal protein S6 kinase, 90kDa, polypeptide 3 (ENSG00000177189), score: -0.65 RSBN1round spermatid basic protein 1 (ENSG00000081019), score: 0.7 RSPH1radial spoke head 1 homolog (Chlamydomonas) (ENSG00000160188), score: 0.76 RTKN2rhotekin 2 (ENSG00000182010), score: 0.75 SASS6spindle assembly 6 homolog (C. elegans) (ENSG00000156876), score: 0.65 SCARB2scavenger receptor class B, member 2 (ENSG00000138760), score: -0.78 SEPT11septin 11 (ENSG00000138758), score: -0.69 SH3GLB1SH3-domain GRB2-like endophilin B1 (ENSG00000097033), score: 0.69 SHCBP1SHC SH2-domain binding protein 1 (ENSG00000171241), score: 0.85 SLC26A8solute carrier family 26, member 8 (ENSG00000112053), score: 0.75 SLC37A3solute carrier family 37 (glycerol-3-phosphate transporter), member 3 (ENSG00000157800), score: -0.74 SMC1Bstructural maintenance of chromosomes 1B (ENSG00000077935), score: 0.76 SMC5structural maintenance of chromosomes 5 (ENSG00000198887), score: 0.69 SPACA1sperm acrosome associated 1 (ENSG00000118434), score: 0.88 SPATA17spermatogenesis associated 17 (ENSG00000162814), score: 0.79 SPATA18spermatogenesis associated 18 homolog (rat) (ENSG00000163071), score: 0.82 SPATA4spermatogenesis associated 4 (ENSG00000150628), score: 0.83 SPC25SPC25, NDC80 kinetochore complex component, homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000152253), score: 0.73 SPO11SPO11 meiotic protein covalently bound to DSB homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000054796), score: 0.79 SSH2slingshot homolog 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000141298), score: 0.69 STRA8stimulated by retinoic acid gene 8 homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000146857), score: 0.67 STX7syntaxin 7 (ENSG00000079950), score: -0.75 SYCP1synaptonemal complex protein 1 (ENSG00000198765), score: 0.83 TAS1R1taste receptor, type 1, member 1 (ENSG00000173662), score: 0.67 TDP1tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1 (ENSG00000042088), score: 0.82 TDRD1tudor domain containing 1 (ENSG00000095627), score: 0.73 TDRD5tudor domain containing 5 (ENSG00000162782), score: 0.76 TDRD6tudor domain containing 6 (ENSG00000180113), score: 0.76 TEKT2tektin 2 (testicular) (ENSG00000092850), score: 0.69 TEKT3tektin 3 (ENSG00000125409), score: 0.83 TEKT5tektin 5 (ENSG00000153060), score: 0.74 TEX10testis expressed 10 (ENSG00000136891), score: 0.72 TMC1transmembrane channel-like 1 (ENSG00000165091), score: 0.73 TMC5transmembrane channel-like 5 (ENSG00000103534), score: 0.82 TMC7transmembrane channel-like 7 (ENSG00000170537), score: 0.68 TMEM63Btransmembrane protein 63B (ENSG00000137216), score: -0.66 TMF1TATA element modulatory factor 1 (ENSG00000144747), score: 0.79 TOP2Atopoisomerase (DNA) II alpha 170kDa (ENSG00000131747), score: 0.77 TP53TG5TP53 target 5 (ENSG00000124251), score: 0.77 TP63tumor protein p63 (ENSG00000073282), score: 0.71 TPX2TPX2, microtubule-associated, homolog (Xenopus laevis) (ENSG00000088325), score: 0.66 TRIM24tripartite motif-containing 24 (ENSG00000122779), score: 0.67 TRIM36tripartite motif-containing 36 (ENSG00000152503), score: 0.76 TRIM8tripartite motif-containing 8 (ENSG00000171206), score: -0.8 TRIP12thyroid hormone receptor interactor 12 (ENSG00000153827), score: 0.75 TSC22D3TSC22 domain family, member 3 (ENSG00000157514), score: -0.72 TSGA14testis specific, 14 (ENSG00000106477), score: 0.73 TSPAN9tetraspanin 9 (ENSG00000011105), score: -0.67 TTC16tetratricopeptide repeat domain 16 (ENSG00000167094), score: 0.79 TTC25tetratricopeptide repeat domain 25 (ENSG00000204815), score: 0.81 TTC29tetratricopeptide repeat domain 29 (ENSG00000137473), score: 0.81 TTKTTK protein kinase (ENSG00000112742), score: 0.79 TTLL9tubulin tyrosine ligase-like family, member 9 (ENSG00000131044), score: 0.73 UBN2ubinuclein 2 (ENSG00000157741), score: 0.65 UHRF1ubiquitin-like with PHD and ring finger domains 1 (ENSG00000034063), score: 0.72 USP7ubiquitin specific peptidase 7 (herpes virus-associated) (ENSG00000187555), score: 0.8 VASH2vasohibin 2 (ENSG00000143494), score: 0.79 VEGFAvascular endothelial growth factor A (ENSG00000112715), score: -0.66 VPRBPVpr (HIV-1) binding protein (ENSG00000145041), score: 0.78 VPS13Avacuolar protein sorting 13 homolog A (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000197969), score: 0.65 WDR16WD repeat domain 16 (ENSG00000166596), score: 0.78 WDR64WD repeat domain 64 (ENSG00000162843), score: 0.79 WDR78WD repeat domain 78 (ENSG00000152763), score: 0.71 YWHABtyrosine 3-monooxygenase/tryptophan 5-monooxygenase activation protein, beta polypeptide (ENSG00000166913), score: -0.67 ZMYND10zinc finger, MYND-type containing 10 (ENSG00000004838), score: 0.67 ZNF318zinc finger protein 318 (ENSG00000171467), score: 0.72 ZNRF4zinc and ring finger 4 (ENSG00000105428), score: 0.87 ZPBPzona pellucida binding protein (ENSG00000042813), score: 0.86 ZPBP2zona pellucida binding protein 2 (ENSG00000186075), score: 0.8 ZRANB3zinc finger, RAN-binding domain containing 3 (ENSG00000121988), score: 0.65
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| gga_ts_m1_ca1 | gga | ts | m | 1 |
| gga_ts_m2_ca1 | gga | ts | m | 2 |
| ppa_ts_m_ca1 | ppa | ts | m | _ |
| ptr_ts_m_ca1 | ptr | ts | m | _ |
| mml_ts_m1_ca1 | mml | ts | m | 1 |
| mml_ts_m2_ca1 | mml | ts | m | 2 |
| mmu_ts_m1_ca1 | mmu | ts | m | 1 |
| mmu_ts_m2_ca1 | mmu | ts | m | 2 |