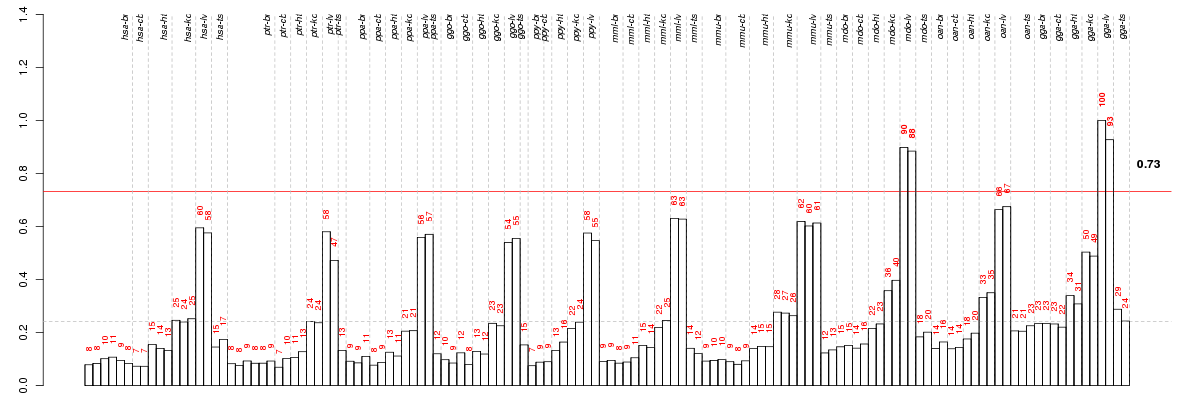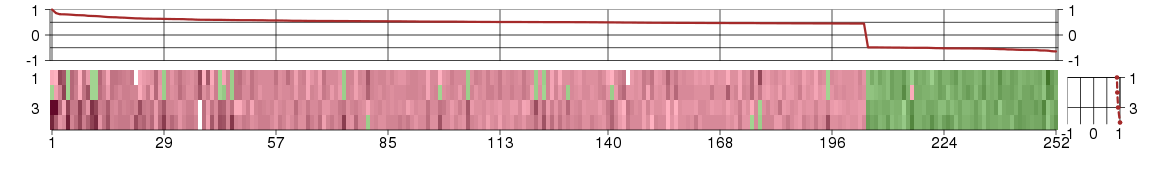

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
cell activation
A change in the morphology or behavior of a cell resulting from exposure to an activating factor such as a cellular or soluble ligand.
immune effector process
Any process of the immune system that occurs as part of an immune response.
activation of immune response
Any process that initiates an immune response.
immune system process
Any process involved in the development or functioning of the immune system, an organismal system for calibrated responses to potential internal or invasive threats.
acute inflammatory response
Inflammation which comprises a rapid, short-lived, relatively uniform response to acute injury or antigenic challenge and is characterized by accumulations of fluid, plasma proteins, and granulocytic leukocytes. An acute inflammatory response occurs within a matter of minutes or hours, and either resolves within a few days or becomes a chronic inflammatory response.
activation of plasma proteins involved in acute inflammatory response
Any process activating plasma proteins by proteolysis as part of an acute inflammatory response.
regulation of immune system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
positive regulation of immune system process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
regulation of leukocyte activation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte activation.
positive regulation of leukocyte activation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte activation.
regulation of immune effector process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune effector process.
regulation of response to biotic stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of a response to biotic stimulus.
defense response
Reactions, triggered in response to the presence of a foreign body or the occurrence of an injury, which result in restriction of damage to the organism attacked or prevention/recovery from the infection caused by the attack.
response to virus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a virus.
blood coagulation
The sequential process by which the multiple coagulation factors of the blood interact, ultimately resulting in the formation of an insoluble fibrin clot; it may be divided into three stages: stage 1, the formation of intrinsic and extrinsic prothrombin converting principle; stage 2, the formation of thrombin; stage 3, the formation of stable fibrin polymers.
complement activation
Any process involved in the activation of any of the steps of the complement cascade, which allows for the direct killing of microbes, the disposal of immune complexes, and the regulation of other immune processes; the initial steps of complement activation involve one of three pathways, the classical pathway, the alternative pathway, and the lectin pathway, all of which lead to the terminal complement pathway.
carbohydrate metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving carbohydrates, any of a group of organic compounds based of the general formula Cx(H2O)y. Includes the formation of carbohydrate derivatives by the addition of a carbohydrate residue to another molecule.
monosaccharide metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving monosaccharides, the simplest carbohydrates. They are polyhydric alcohols containing either an aldehyde or a keto group and between three to ten or more carbon atoms. They form the constitutional repeating units of oligo- and polysaccharides.
glucose metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving glucose, the aldohexose gluco-hexose. D-glucose is dextrorotatory and is sometimes known as dextrose; it is an important source of energy for living organisms and is found free as well as combined in homo- and hetero-oligosaccharides and polysaccharides.
alcohol metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving alcohols, any of a class of compounds containing one or more hydroxyl groups attached to a saturated carbon atom.
organic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
protein maturation by peptide bond cleavage
The hydrolysis of a peptide bond or bonds within a protein as part of protein maturation, the process leading to the attainment of the full functional capacity of a protein.
response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
inflammatory response
The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages.
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
complement activation, alternative pathway
Any process involved in the activation of any of the steps of the alternative pathway of the complement cascade which allows for the direct killing of microbes and the regulation of other immune processes.
humoral immune response
An immune response mediated through a body fluid.
hemostasis
The stopping of bleeding (loss of body fluid) or the arrest of the circulation to an organ or part.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cell proliferation
The multiplication or reproduction of cells, resulting in the expansion of a cell population.
positive regulation of cell proliferation
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of cell proliferation.
negative regulation of coagulation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of coagulation.
response to biotic stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a biotic stimulus, a stimulus caused or produced by a living organism.
response to wounding
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to the organism.
response to other organism
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from another living organism.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
gene expression
The process by which a gene's sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
protein processing
Any protein maturation process achieved by the cleavage of peptide bonds.
hexose metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a hexose, any monosaccharide with a chain of six carbon atoms in the molecule.
protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general. Includes protein modification.
carboxylic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving carboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (COOH) groups or anions (COO-).
regulation of defense response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a defense response.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
mononuclear cell proliferation
The expansion of a mononuclear cell population by cell division. A mononuclear cell is a leukocyte with a single non-segmented nucleus in the mature form.
regulation of mononuclear cell proliferation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of mononuclear cell proliferation.
positive regulation of mononuclear cell proliferation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of mononuclear cell proliferation.
wound healing
The series of events that restore integrity to a damaged tissue, following an injury.
T cell proliferation
The expansion of a T cell population by cell division. Follows T cell activation.
positive regulation of T cell proliferation
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of T cell proliferation.
T cell activation
The change in morphology and behavior of a mature or immature T cell resulting from exposure to a mitogen, cytokine, chemokine, cellular ligand, or an antigen for which it is specific.
regulation of cell proliferation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell proliferation.
regulation of T cell proliferation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of T cell proliferation.
cellular ketone metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any of a class of organic compounds that contain the carbonyl group, CO, and in which the carbonyl group is bonded only to carbon atoms, as carried out by individual cells. The general formula for a ketone is RCOR, where R and R are alkyl or aryl groups.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
oxoacid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any oxoacid; an oxoacid is a compound which contains oxygen, at least one other element, and at least one hydrogen bound to oxygen, and which produces a conjugate base by loss of positive hydrogen ion(s) (hydrons).
regulation of multi-organism process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multi-organism process, a process by which an organism has an effect on another organism of the same or different species.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular carbohydrate metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving carbohydrates, any of a group of organic compounds based of the general formula Cx(H2O)y, as carried out by individual cells.
small molecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
innate immune response
Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens.
leukocyte activation
A change in morphology and behavior of a leukocyte resulting from exposure to a specific antigen, mitogen, cytokine, cellular ligand, or soluble factor.
lymphocyte activation
A change in morphology and behavior of a lymphocyte resulting from exposure to a specific antigen, mitogen, cytokine, chemokine, cellular ligand, or soluble factor.
lymphocyte proliferation
The expansion of a lymphocyte population by cell division.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
positive regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of lymphocyte proliferation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of lymphocyte proliferation.
positive regulation of lymphocyte proliferation
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of lymphocyte proliferation.
regulation of defense response to virus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the antiviral response of a cell or organism.
regulation of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
positive regulation of immune response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
coagulation
The process by which a fluid solution, or part of it, changes into a solid or semisolid mass.
regulation of coagulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of coagulation, the process by which a fluid solution, or part of it, changes into a solid or semisolid mass.
regulation of T cell activation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of T cell activation.
regulation of cell activation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell activation, the change in the morphology or behavior of a cell resulting from exposure to an activating factor such as a cellular or soluble ligand.
positive regulation of cell activation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of activation.
positive regulation of T cell activation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of T cell activation.
regulation of body fluid levels
Any process that modulates the levels of body fluids.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
cofactor metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a cofactor, a substance that is required for the activity of an enzyme or other protein. Cofactors may be inorganic, such as the metal atoms zinc, iron, and copper in certain forms, or organic, in which case they are referred to as coenzymes. Cofactors may either be bound tightly to active sites or bind loosely with the substrate.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
negative regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of an organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of an organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
regulation of lymphocyte activation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of lymphocyte activation.
positive regulation of lymphocyte activation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of lymphocyte activation.
protein maturation
Any process leading to the attainment of the full functional capacity of a protein.
defense response to virus
Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a virus that act to protect the cell or organism.
multi-organism process
Any process by which an organism has an effect on another organism of the same or different species.
cellular response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of biological quality
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological quality. A biological quality is a measurable attribute of an organism or part of an organism, such as size, mass, shape, color, etc.
leukocyte proliferation
The expansion of a leukocyte population by cell division.
regulation of leukocyte proliferation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of leukocyte proliferation.
positive regulation of leukocyte proliferation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of leukocyte proliferation.
cellular response to biotic stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a biotic stimulus, a stimulus caused or produced by a living organism.
regulation of response to stress
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to stress. Response to stress is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
all
NA
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of immune system process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
negative regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of an organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of an organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
regulation of immune system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
positive regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
cellular response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of multi-organism process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multi-organism process, a process by which an organism has an effect on another organism of the same or different species.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general. Includes protein modification.
organic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
cellular ketone metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any of a class of organic compounds that contain the carbonyl group, CO, and in which the carbonyl group is bonded only to carbon atoms, as carried out by individual cells. The general formula for a ketone is RCOR, where R and R are alkyl or aryl groups.
complement activation
Any process involved in the activation of any of the steps of the complement cascade, which allows for the direct killing of microbes, the disposal of immune complexes, and the regulation of other immune processes; the initial steps of complement activation involve one of three pathways, the classical pathway, the alternative pathway, and the lectin pathway, all of which lead to the terminal complement pathway.
positive regulation of immune system process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
immune effector process
Any process of the immune system that occurs as part of an immune response.
regulation of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
positive regulation of immune response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
regulation of leukocyte activation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte activation.
positive regulation of leukocyte activation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte activation.
positive regulation of cell proliferation
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of cell proliferation.
regulation of leukocyte proliferation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of leukocyte proliferation.
positive regulation of leukocyte proliferation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of leukocyte proliferation.
leukocyte activation
A change in morphology and behavior of a leukocyte resulting from exposure to a specific antigen, mitogen, cytokine, cellular ligand, or soluble factor.
positive regulation of cell proliferation
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of cell proliferation.
positive regulation of cell activation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of activation.
regulation of cell proliferation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell proliferation.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of cell activation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell activation, the change in the morphology or behavior of a cell resulting from exposure to an activating factor such as a cellular or soluble ligand.
regulation of coagulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of coagulation, the process by which a fluid solution, or part of it, changes into a solid or semisolid mass.
negative regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of an organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of an organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
negative regulation of coagulation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of coagulation.
positive regulation of immune response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
positive regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
regulation of response to stress
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to stress. Response to stress is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
regulation of response to biotic stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of a response to biotic stimulus.
response to other organism
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from another living organism.
cellular response to biotic stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a biotic stimulus, a stimulus caused or produced by a living organism.
regulation of body fluid levels
Any process that modulates the levels of body fluids.
protein maturation
Any process leading to the attainment of the full functional capacity of a protein.
oxoacid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any oxoacid; an oxoacid is a compound which contains oxygen, at least one other element, and at least one hydrogen bound to oxygen, and which produces a conjugate base by loss of positive hydrogen ion(s) (hydrons).
cellular carbohydrate metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving carbohydrates, any of a group of organic compounds based of the general formula Cx(H2O)y, as carried out by individual cells.
monosaccharide metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving monosaccharides, the simplest carbohydrates. They are polyhydric alcohols containing either an aldehyde or a keto group and between three to ten or more carbon atoms. They form the constitutional repeating units of oligo- and polysaccharides.
regulation of defense response to virus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the antiviral response of a cell or organism.
regulation of defense response to virus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the antiviral response of a cell or organism.
positive regulation of leukocyte activation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte activation.
regulation of immune effector process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune effector process.
positive regulation of immune response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
activation of immune response
Any process that initiates an immune response.
complement activation
Any process involved in the activation of any of the steps of the complement cascade, which allows for the direct killing of microbes, the disposal of immune complexes, and the regulation of other immune processes; the initial steps of complement activation involve one of three pathways, the classical pathway, the alternative pathway, and the lectin pathway, all of which lead to the terminal complement pathway.
complement activation, alternative pathway
Any process involved in the activation of any of the steps of the alternative pathway of the complement cascade which allows for the direct killing of microbes and the regulation of other immune processes.
regulation of lymphocyte activation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of lymphocyte activation.
positive regulation of lymphocyte activation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of lymphocyte activation.
positive regulation of leukocyte proliferation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of leukocyte proliferation.
regulation of mononuclear cell proliferation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of mononuclear cell proliferation.
positive regulation of mononuclear cell proliferation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of mononuclear cell proliferation.
lymphocyte proliferation
The expansion of a lymphocyte population by cell division.
regulation of leukocyte activation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte activation.
positive regulation of cell activation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of activation.
positive regulation of leukocyte activation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte activation.
negative regulation of coagulation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of coagulation.
blood coagulation
The sequential process by which the multiple coagulation factors of the blood interact, ultimately resulting in the formation of an insoluble fibrin clot; it may be divided into three stages: stage 1, the formation of intrinsic and extrinsic prothrombin converting principle; stage 2, the formation of thrombin; stage 3, the formation of stable fibrin polymers.
regulation of defense response to virus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the antiviral response of a cell or organism.
regulation of defense response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a defense response.
innate immune response
Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens.
defense response to virus
Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a virus that act to protect the cell or organism.
inflammatory response
The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages.
defense response to virus
Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a virus that act to protect the cell or organism.
positive regulation of lymphocyte activation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of lymphocyte activation.
regulation of T cell activation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of T cell activation.
positive regulation of T cell activation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of T cell activation.
T cell proliferation
The expansion of a T cell population by cell division. Follows T cell activation.
regulation of lymphocyte proliferation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of lymphocyte proliferation.
positive regulation of lymphocyte proliferation
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of lymphocyte proliferation.
positive regulation of lymphocyte proliferation
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of lymphocyte proliferation.
positive regulation of mononuclear cell proliferation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of mononuclear cell proliferation.
regulation of lymphocyte proliferation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of lymphocyte proliferation.
regulation of defense response to virus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the antiviral response of a cell or organism.
blood coagulation
The sequential process by which the multiple coagulation factors of the blood interact, ultimately resulting in the formation of an insoluble fibrin clot; it may be divided into three stages: stage 1, the formation of intrinsic and extrinsic prothrombin converting principle; stage 2, the formation of thrombin; stage 3, the formation of stable fibrin polymers.
positive regulation of lymphocyte proliferation
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of lymphocyte proliferation.
regulation of T cell proliferation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of T cell proliferation.
positive regulation of T cell activation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of T cell activation.
positive regulation of T cell proliferation
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of T cell proliferation.
positive regulation of T cell proliferation
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of T cell proliferation.
regulation of T cell proliferation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of T cell proliferation.
activation of plasma proteins involved in acute inflammatory response
Any process activating plasma proteins by proteolysis as part of an acute inflammatory response.
positive regulation of T cell proliferation
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of T cell proliferation.
complement activation
Any process involved in the activation of any of the steps of the complement cascade, which allows for the direct killing of microbes, the disposal of immune complexes, and the regulation of other immune processes; the initial steps of complement activation involve one of three pathways, the classical pathway, the alternative pathway, and the lectin pathway, all of which lead to the terminal complement pathway.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
integral to membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer. When used to describe a protein, indicates that all or part of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
membrane attack complex
A protein complex produced by sequentially activated components of the complement cascade inserted into a target cell membrane and forming a pore leading to cell lysis via ion and water flow.
extracellular space
That part of a multicellular organism outside the cells proper, usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
pore complex
Any small opening in a membrane that allows the passage of gases and/or liquids.
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
protein complex
Any macromolecular complex composed of two or more polypeptide subunits, which may or may not be identical. Protein complexes may have other associated non-protein prosthetic groups, such as nucleotides, metal ions or other small molecules.
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
all
NA
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
membrane attack complex
A protein complex produced by sequentially activated components of the complement cascade inserted into a target cell membrane and forming a pore leading to cell lysis via ion and water flow.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
pore complex
Any small opening in a membrane that allows the passage of gases and/or liquids.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
membrane attack complex
A protein complex produced by sequentially activated components of the complement cascade inserted into a target cell membrane and forming a pore leading to cell lysis via ion and water flow.

| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 04610 | 3.061e-04 | 1.368 | 9 | 21 | Complement and coagulation cascades |
| 00565 | 1.198e-02 | 0.6514 | 5 | 10 | Ether lipid metabolism |
| 00120 | 1.460e-02 | 0.1954 | 3 | 3 | Primary bile acid biosynthesis |
| 00270 | 1.828e-02 | 0.7165 | 5 | 11 | Cysteine and methionine metabolism |
| 01100 | 3.381e-02 | 22.99 | 37 | 353 | Metabolic pathways |
A1CFAPOBEC1 complementation factor (ENSG00000148584), score: 0.51 A2LD1AIG2-like domain 1 (ENSG00000134864), score: 0.5 AARS2alanyl-tRNA synthetase 2, mitochondrial (putative) (ENSG00000124608), score: 0.48 ABCA1ATP-binding cassette, sub-family A (ABC1), member 1 (ENSG00000165029), score: 0.52 ABCA12ATP-binding cassette, sub-family A (ABC1), member 12 (ENSG00000144452), score: 0.74 ABCB11ATP-binding cassette, sub-family B (MDR/TAP), member 11 (ENSG00000073734), score: 0.47 ABCG1ATP-binding cassette, sub-family G (WHITE), member 1 (ENSG00000160179), score: -0.53 ABHD5abhydrolase domain containing 5 (ENSG00000011198), score: 0.64 ACAD9acyl-CoA dehydrogenase family, member 9 (ENSG00000177646), score: 0.56 ACBD5acyl-CoA binding domain containing 5 (ENSG00000107897), score: 0.5 ACO1aconitase 1, soluble (ENSG00000122729), score: 0.45 ACSL5acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 5 (ENSG00000197142), score: 0.52 ACSM5acyl-CoA synthetase medium-chain family member 5 (ENSG00000183549), score: 0.47 ADRA1Badrenergic, alpha-1B-, receptor (ENSG00000170214), score: 0.46 ADSLadenylosuccinate lyase (ENSG00000239900), score: 0.59 AGXTalanine-glyoxylate aminotransferase (ENSG00000172482), score: 0.53 AHRaryl hydrocarbon receptor (ENSG00000106546), score: 0.62 AKAP12A kinase (PRKA) anchor protein 12 (ENSG00000131016), score: -0.54 AKR1D1aldo-keto reductase family 1, member D1 (delta 4-3-ketosteroid-5-beta-reductase) (ENSG00000122787), score: 0.56 ALBalbumin (ENSG00000163631), score: 0.57 AMBPalpha-1-microglobulin/bikunin precursor (ENSG00000106927), score: 0.49 AMDHD1amidohydrolase domain containing 1 (ENSG00000139344), score: 0.54 ANXA5annexin A5 (ENSG00000164111), score: 0.46 AP1S3adaptor-related protein complex 1, sigma 3 subunit (ENSG00000152056), score: 0.6 AP2B1adaptor-related protein complex 2, beta 1 subunit (ENSG00000006125), score: -0.52 APBB2amyloid beta (A4) precursor protein-binding, family B, member 2 (ENSG00000163697), score: -0.57 ARCN1archain 1 (ENSG00000095139), score: 0.46 ARHGEF38Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 38 (ENSG00000138784), score: 0.6 ARL14ADP-ribosylation factor-like 14 (ENSG00000179674), score: 0.54 ARL3ADP-ribosylation factor-like 3 (ENSG00000138175), score: -0.59 ARL5BADP-ribosylation factor-like 5B (ENSG00000165997), score: 0.46 ASPGasparaginase homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000166183), score: 0.46 ASXL2additional sex combs like 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000143970), score: 0.45 ATMINATM interactor (ENSG00000166454), score: -0.64 ATP2C1ATPase, Ca++ transporting, type 2C, member 1 (ENSG00000017260), score: -0.55 BCMO1beta-carotene 15,15'-monooxygenase 1 (ENSG00000135697), score: 0.66 C12orf66chromosome 12 open reading frame 66 (ENSG00000174206), score: 0.54 C13orf15chromosome 13 open reading frame 15 (ENSG00000102760), score: -0.5 C1orf116chromosome 1 open reading frame 116 (ENSG00000182795), score: 0.64 C2orf54chromosome 2 open reading frame 54 (ENSG00000172478), score: 0.64 C5complement component 5 (ENSG00000106804), score: 0.52 C8Acomplement component 8, alpha polypeptide (ENSG00000157131), score: 0.6 C8Gcomplement component 8, gamma polypeptide (ENSG00000176919), score: 0.52 CA6carbonic anhydrase VI (ENSG00000131686), score: 0.52 CAMSAP1calmodulin regulated spectrin-associated protein 1 (ENSG00000130559), score: -0.5 CAPRIN2caprin family member 2 (ENSG00000110888), score: -0.53 CCDC92coiled-coil domain containing 92 (ENSG00000119242), score: -0.59 CD28CD28 molecule (ENSG00000178562), score: 0.59 CDCP2CUB domain containing protein 2 (ENSG00000157211), score: 0.45 CDH1cadherin 1, type 1, E-cadherin (epithelial) (ENSG00000039068), score: 0.46 CDO1cysteine dioxygenase, type I (ENSG00000129596), score: 0.48 CDR2Lcerebellar degeneration-related protein 2-like (ENSG00000109089), score: -0.51 CEPT1choline/ethanolamine phosphotransferase 1 (ENSG00000134255), score: 0.61 CHPT1choline phosphotransferase 1 (ENSG00000111666), score: -0.5 CLDN1claudin 1 (ENSG00000163347), score: 0.58 CNGA2cyclic nucleotide gated channel alpha 2 (ENSG00000183862), score: 0.48 COLEC10collectin sub-family member 10 (C-type lectin) (ENSG00000184374), score: 0.51 COMTD1catechol-O-methyltransferase domain containing 1 (ENSG00000165644), score: 0.46 CPB2carboxypeptidase B2 (plasma) (ENSG00000080618), score: 0.51 CREB3L3cAMP responsive element binding protein 3-like 3 (ENSG00000060566), score: 0.55 CRYABcrystallin, alpha B (ENSG00000109846), score: -0.49 CRYGNcrystallin, gamma N (ENSG00000127377), score: 0.75 CTBSchitobiase, di-N-acetyl- (ENSG00000117151), score: 0.51 CTHcystathionase (cystathionine gamma-lyase) (ENSG00000116761), score: 0.51 CUEDC2CUE domain containing 2 (ENSG00000107874), score: -0.61 CYB5R2cytochrome b5 reductase 2 (ENSG00000166394), score: 0.52 CYBASC3cytochrome b, ascorbate dependent 3 (ENSG00000162144), score: 0.46 CYP39A1cytochrome P450, family 39, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000146233), score: 0.77 CYP7B1cytochrome P450, family 7, subfamily B, polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000172817), score: 0.61 DAKdihydroxyacetone kinase 2 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000149476), score: 0.48 DECR22,4-dienoyl CoA reductase 2, peroxisomal (ENSG00000242612), score: 0.45 DENND5ADENN/MADD domain containing 5A (ENSG00000184014), score: -0.49 DERL3Der1-like domain family, member 3 (ENSG00000099958), score: 0.47 DFNA5deafness, autosomal dominant 5 (ENSG00000105928), score: -0.5 DHTKD1dehydrogenase E1 and transketolase domain containing 1 (ENSG00000181192), score: 0.45 DLL1delta-like 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000198719), score: 0.47 DNAJC22DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 22 (ENSG00000178401), score: 0.45 EEDembryonic ectoderm development (ENSG00000074266), score: -0.51 EGFRepidermal growth factor receptor (ENSG00000146648), score: 0.46 EHHADHenoyl-CoA, hydratase/3-hydroxyacyl CoA dehydrogenase (ENSG00000113790), score: 0.47 EIF2AK3eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2-alpha kinase 3 (ENSG00000172071), score: 0.52 EIF4EBP1eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E binding protein 1 (ENSG00000187840), score: 0.5 EPT1ethanolaminephosphotransferase 1 (CDP-ethanolamine-specific) (ENSG00000138018), score: 0.55 ERN1endoplasmic reticulum to nucleus signaling 1 (ENSG00000178607), score: 0.48 ESR1estrogen receptor 1 (ENSG00000091831), score: 0.48 F2coagulation factor II (thrombin) (ENSG00000180210), score: 0.5 F9coagulation factor IX (ENSG00000101981), score: 0.68 FAF2Fas associated factor family member 2 (ENSG00000113194), score: 0.51 FAM3Dfamily with sequence similarity 3, member D (ENSG00000198643), score: 0.47 FAM82Bfamily with sequence similarity 82, member B (ENSG00000176623), score: 0.46 FERMT1fermitin family member 1 (ENSG00000101311), score: 0.55 FETUBfetuin B (ENSG00000090512), score: 0.7 FGBfibrinogen beta chain (ENSG00000171564), score: 0.5 FGFR4fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (ENSG00000160867), score: 0.46 FGGfibrinogen gamma chain (ENSG00000171557), score: 0.51 FZD5frizzled homolog 5 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000163251), score: 0.54 GAS6growth arrest-specific 6 (ENSG00000183087), score: -0.57 GBE1glucan (1,4-alpha-), branching enzyme 1 (ENSG00000114480), score: 0.53 GCH1GTP cyclohydrolase 1 (ENSG00000131979), score: 0.46 GCNT7glucosaminyl (N-acetyl) transferase family member 7 (ENSG00000124091), score: 0.53 GJB1gap junction protein, beta 1, 32kDa (ENSG00000169562), score: 0.45 GK5glycerol kinase 5 (putative) (ENSG00000175066), score: 0.58 GPR114G protein-coupled receptor 114 (ENSG00000159618), score: 0.51 GPR146G protein-coupled receptor 146 (ENSG00000164849), score: 0.54 HABP2hyaluronan binding protein 2 (ENSG00000148702), score: 0.48 HALhistidine ammonia-lyase (ENSG00000084110), score: 0.7 HAO1hydroxyacid oxidase (glycolate oxidase) 1 (ENSG00000101323), score: 0.52 HPGDShematopoietic prostaglandin D synthase (ENSG00000163106), score: 0.59 HPXhemopexin (ENSG00000110169), score: 0.57 HRGhistidine-rich glycoprotein (ENSG00000113905), score: 0.54 ICOSLGinducible T-cell co-stimulator ligand (ENSG00000160223), score: 0.64 IDH3Aisocitrate dehydrogenase 3 (NAD+) alpha (ENSG00000166411), score: -0.52 IFT27intraflagellar transport 27 homolog (Chlamydomonas) (ENSG00000100360), score: -0.52 IFT46intraflagellar transport 46 homolog (Chlamydomonas) (ENSG00000118096), score: -0.53 IGF1insulin-like growth factor 1 (somatomedin C) (ENSG00000017427), score: 0.51 IHHIndian hedgehog (ENSG00000163501), score: 0.5 IKZF3IKAROS family zinc finger 3 (Aiolos) (ENSG00000161405), score: 0.68 IL12Binterleukin 12B (natural killer cell stimulatory factor 2, cytotoxic lymphocyte maturation factor 2, p40) (ENSG00000113302), score: 0.86 IL15interleukin 15 (ENSG00000164136), score: 0.47 IL1RAPinterleukin 1 receptor accessory protein (ENSG00000196083), score: 0.52 IL20RAinterleukin 20 receptor, alpha (ENSG00000016402), score: 0.5 IL22RA2interleukin 22 receptor, alpha 2 (ENSG00000164485), score: 1 IL28RAinterleukin 28 receptor, alpha (interferon, lambda receptor) (ENSG00000185436), score: 0.51 IL6STinterleukin 6 signal transducer (gp130, oncostatin M receptor) (ENSG00000134352), score: 0.58 IMPAD1inositol monophosphatase domain containing 1 (ENSG00000104331), score: -0.61 IMPG2interphotoreceptor matrix proteoglycan 2 (ENSG00000081148), score: 0.47 INHBAinhibin, beta A (ENSG00000122641), score: 0.64 INTS2integrator complex subunit 2 (ENSG00000108506), score: 0.57 IRF8interferon regulatory factor 8 (ENSG00000140968), score: 0.55 IYDiodotyrosine deiodinase (ENSG00000009765), score: 0.53 KCTD7potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 7 (ENSG00000154710), score: -0.5 KIAA1958KIAA1958 (ENSG00000165185), score: 0.49 KLBklotho beta (ENSG00000134962), score: 0.58 KLHL25kelch-like 25 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000183655), score: 0.46 LEAP2liver expressed antimicrobial peptide 2 (ENSG00000164406), score: 0.5 LHX8LIM homeobox 8 (ENSG00000162624), score: 0.75 LOC100292021similar to thioredoxin peroxidase (ENSG00000123131), score: 0.46 LRATlecithin retinol acyltransferase (phosphatidylcholine--retinol O-acyltransferase) (ENSG00000121207), score: 0.58 LRP11low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 11 (ENSG00000120256), score: -0.54 LY75lymphocyte antigen 75 (ENSG00000054219), score: 0.62 LYSMD3LysM, putative peptidoglycan-binding, domain containing 3 (ENSG00000176018), score: 0.58 MAST4microtubule associated serine/threonine kinase family member 4 (ENSG00000069020), score: -0.49 MAT1Amethionine adenosyltransferase I, alpha (ENSG00000151224), score: 0.54 MAT2Bmethionine adenosyltransferase II, beta (ENSG00000038274), score: -0.53 MED13mediator complex subunit 13 (ENSG00000108510), score: 0.45 MFSD10major facilitator superfamily domain containing 10 (ENSG00000109736), score: -0.59 MTMR14myotubularin related protein 14 (ENSG00000163719), score: 0.49 MTTPmicrosomal triglyceride transfer protein (ENSG00000138823), score: 0.55 MUTYHmutY homolog (E. coli) (ENSG00000132781), score: 0.51 NFIAnuclear factor I/A (ENSG00000162599), score: 0.5 NR0B1nuclear receptor subfamily 0, group B, member 1 (ENSG00000169297), score: 0.65 NR5A2nuclear receptor subfamily 5, group A, member 2 (ENSG00000116833), score: 0.63 NRBF2nuclear receptor binding factor 2 (ENSG00000148572), score: 0.48 NTSR1neurotensin receptor 1 (high affinity) (ENSG00000101188), score: 0.52 NUDT3nudix (nucleoside diphosphate linked moiety X)-type motif 3 (ENSG00000112664), score: -0.49 OIT3oncoprotein induced transcript 3 (ENSG00000138315), score: 0.47 ONECUT1one cut homeobox 1 (ENSG00000169856), score: 0.47 ORC2Lorigin recognition complex, subunit 2-like (yeast) (ENSG00000115942), score: -0.49 ORC5Lorigin recognition complex, subunit 5-like (yeast) (ENSG00000164815), score: -0.64 OSTalphaorganic solute transporter alpha (ENSG00000163959), score: 0.55 PAFAH2platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase 2, 40kDa (ENSG00000158006), score: 0.51 PAIP1poly(A) binding protein interacting protein 1 (ENSG00000172239), score: -0.49 PANK1pantothenate kinase 1 (ENSG00000152782), score: 0.51 PANK3pantothenate kinase 3 (ENSG00000120137), score: 0.49 PCGF2polycomb group ring finger 2 (ENSG00000056661), score: -0.55 PCK2phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase 2 (mitochondrial) (ENSG00000100889), score: 0.51 PDCD1LG2programmed cell death 1 ligand 2 (ENSG00000197646), score: 0.5 PDE6Dphosphodiesterase 6D, cGMP-specific, rod, delta (ENSG00000156973), score: -0.5 PDE7Aphosphodiesterase 7A (ENSG00000205268), score: -0.49 PDIA5protein disulfide isomerase family A, member 5 (ENSG00000065485), score: 0.47 PDP2pyruvate dehyrogenase phosphatase catalytic subunit 2 (ENSG00000172840), score: 0.79 PEMTphosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase (ENSG00000133027), score: 0.47 PHKA2phosphorylase kinase, alpha 2 (liver) (ENSG00000044446), score: 0.51 PIK3CGphosphoinositide-3-kinase, catalytic, gamma polypeptide (ENSG00000105851), score: 0.5 PLA2G12Bphospholipase A2, group XIIB (ENSG00000138308), score: 0.53 PLXDC2plexin domain containing 2 (ENSG00000120594), score: -0.49 PM20D1peptidase M20 domain containing 1 (ENSG00000162877), score: 0.47 PPEF2protein phosphatase, EF-hand calcium binding domain 2 (ENSG00000156194), score: 0.81 PPP1R15Bprotein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 15B (ENSG00000158615), score: 0.45 PSMD1proteasome (prosome, macropain) 26S subunit, non-ATPase, 1 (ENSG00000173692), score: 0.49 PTPRGprotein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, G (ENSG00000144724), score: 0.48 PYGLphosphorylase, glycogen, liver (ENSG00000100504), score: 0.5 RAB30RAB30, member RAS oncogene family (ENSG00000137502), score: 0.54 RAD52RAD52 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000002016), score: -0.55 RAP2CRAP2C, member of RAS oncogene family (ENSG00000123728), score: 0.47 RCAN1regulator of calcineurin 1 (ENSG00000159200), score: -0.59 RGNregucalcin (senescence marker protein-30) (ENSG00000130988), score: 0.47 RGS18regulator of G-protein signaling 18 (ENSG00000150681), score: 0.73 RPIAribose 5-phosphate isomerase A (ENSG00000153574), score: 0.7 RRM1ribonucleotide reductase M1 (ENSG00000167325), score: -0.52 SDC2syndecan 2 (ENSG00000169439), score: 0.56 SEBOXSEBOX homeobox (ENSG00000109072), score: 0.54 SERPINA10serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade A (alpha-1 antiproteinase, antitrypsin), member 10 (ENSG00000140093), score: 0.48 SERPINC1serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade C (antithrombin), member 1 (ENSG00000117601), score: 0.54 SGPL1sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase 1 (ENSG00000166224), score: 0.47 SGSM2small G protein signaling modulator 2 (ENSG00000141258), score: -0.52 SIKE1suppressor of IKBKE 1 (ENSG00000052723), score: 0.63 SLC16A10solute carrier family 16, member 10 (aromatic amino acid transporter) (ENSG00000112394), score: 0.57 SLC24A6solute carrier family 24 (sodium/potassium/calcium exchanger), member 6 (ENSG00000089060), score: 0.5 SLC25A38solute carrier family 25, member 38 (ENSG00000144659), score: -0.52 SLC26A5solute carrier family 26, member 5 (prestin) (ENSG00000170615), score: 0.78 SLC2A10solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 10 (ENSG00000197496), score: 0.51 SLC2A2solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 2 (ENSG00000163581), score: 0.5 SLC2A9solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 9 (ENSG00000109667), score: 0.59 SLC30A1solute carrier family 30 (zinc transporter), member 1 (ENSG00000170385), score: 0.55 SLC30A7solute carrier family 30 (zinc transporter), member 7 (ENSG00000162695), score: 0.55 SLC33A1solute carrier family 33 (acetyl-CoA transporter), member 1 (ENSG00000169359), score: 0.54 SLC35D1solute carrier family 35 (UDP-glucuronic acid/UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine dual transporter), member D1 (ENSG00000116704), score: 0.51 SLC38A4solute carrier family 38, member 4 (ENSG00000139209), score: 0.62 SLC7A2solute carrier family 7 (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system), member 2 (ENSG00000003989), score: 0.48 SLIT3slit homolog 3 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000184347), score: -0.5 SPINK4serine peptidase inhibitor, Kazal type 4 (ENSG00000122711), score: 0.8 SPP2secreted phosphoprotein 2, 24kDa (ENSG00000072080), score: 0.72 SSR3signal sequence receptor, gamma (translocon-associated protein gamma) (ENSG00000114850), score: 0.45 ST6GAL1ST6 beta-galactosamide alpha-2,6-sialyltranferase 1 (ENSG00000073849), score: 0.48 STOML3stomatin (EPB72)-like 3 (ENSG00000133115), score: 0.63 STT3BSTT3, subunit of the oligosaccharyltransferase complex, homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000163527), score: 0.49 TAAR1trace amine associated receptor 1 (ENSG00000146399), score: 0.55 TATtyrosine aminotransferase (ENSG00000198650), score: 0.56 TBC1D8BTBC1 domain family, member 8B (with GRAM domain) (ENSG00000133138), score: 0.55 TBCELtubulin folding cofactor E-like (ENSG00000154114), score: 0.52 TBX3T-box 3 (ENSG00000135111), score: 0.49 TDO2tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (ENSG00000151790), score: 0.59 TEX264testis expressed 264 (ENSG00000164081), score: 0.45 TM7SF4transmembrane 7 superfamily member 4 (ENSG00000164935), score: 0.51 TMCO3transmembrane and coiled-coil domains 3 (ENSG00000150403), score: -0.5 TMCO7transmembrane and coiled-coil domains 7 (ENSG00000103047), score: 0.47 TMED5transmembrane emp24 protein transport domain containing 5 (ENSG00000117500), score: 0.55 TMEM135transmembrane protein 135 (ENSG00000166575), score: 0.54 TMEM41Atransmembrane protein 41A (ENSG00000163900), score: 0.67 TMEM9transmembrane protein 9 (ENSG00000116857), score: -0.53 TNMDtenomodulin (ENSG00000000005), score: 0.46 TOMM40Ltranslocase of outer mitochondrial membrane 40 homolog (yeast)-like (ENSG00000158882), score: 0.53 TOR1Btorsin family 1, member B (torsin B) (ENSG00000136816), score: 0.48 TRAT1T cell receptor associated transmembrane adaptor 1 (ENSG00000163519), score: 0.56 TRPA1transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily A, member 1 (ENSG00000104321), score: 0.59 TTPAtocopherol (alpha) transfer protein (ENSG00000137561), score: 0.58 TWSG1twisted gastrulation homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000128791), score: -0.53 TXNDC12thioredoxin domain containing 12 (endoplasmic reticulum) (ENSG00000117862), score: 0.51 UNC119unc-119 homolog (C. elegans) (ENSG00000109103), score: -0.58 USO1USO1 vesicle docking protein homolog (yeast) (ENSG00000138768), score: 0.57 VPS39vacuolar protein sorting 39 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000166887), score: -0.58 VSIG4V-set and immunoglobulin domain containing 4 (ENSG00000155659), score: 0.55 WDFY2WD repeat and FYVE domain containing 2 (ENSG00000139668), score: 0.78 WDFY4WDFY family member 4 (ENSG00000128815), score: 0.46 WDR41WD repeat domain 41 (ENSG00000164253), score: -0.61 XCR1chemokine (C motif) receptor 1 (ENSG00000173578), score: 0.81 YOD1YOD1 OTU deubiquinating enzyme 1 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000180667), score: 0.5 ZBTB2zinc finger and BTB domain containing 2 (ENSG00000181472), score: 0.51 ZCCHC11zinc finger, CCHC domain containing 11 (ENSG00000134744), score: 0.58 ZDHHC13zinc finger, DHHC-type containing 13 (ENSG00000177054), score: 0.6 ZP1zona pellucida glycoprotein 1 (sperm receptor) (ENSG00000149506), score: 0.65
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mdo_lv_f_ca1 | mdo | lv | f | _ |
| mdo_lv_m_ca1 | mdo | lv | m | _ |
| gga_lv_f_ca1 | gga | lv | f | _ |
| gga_lv_m_ca1 | gga | lv | m | _ |