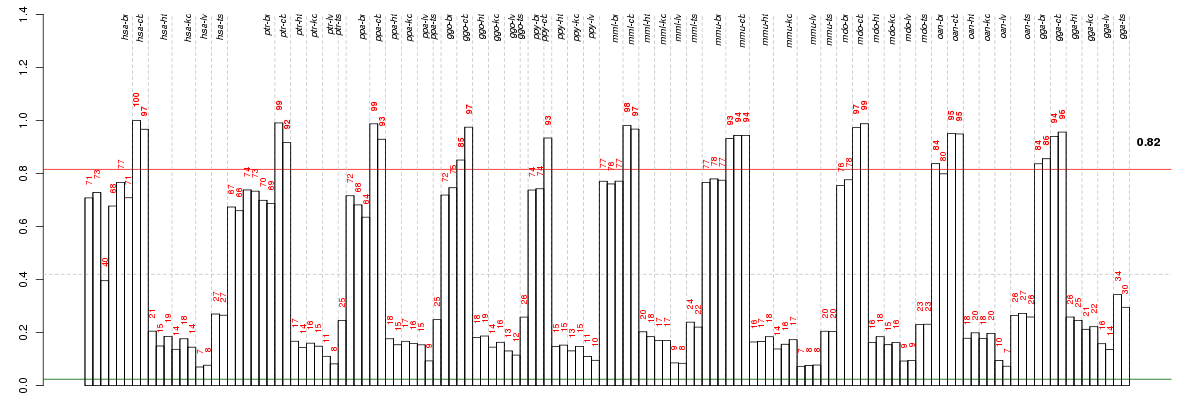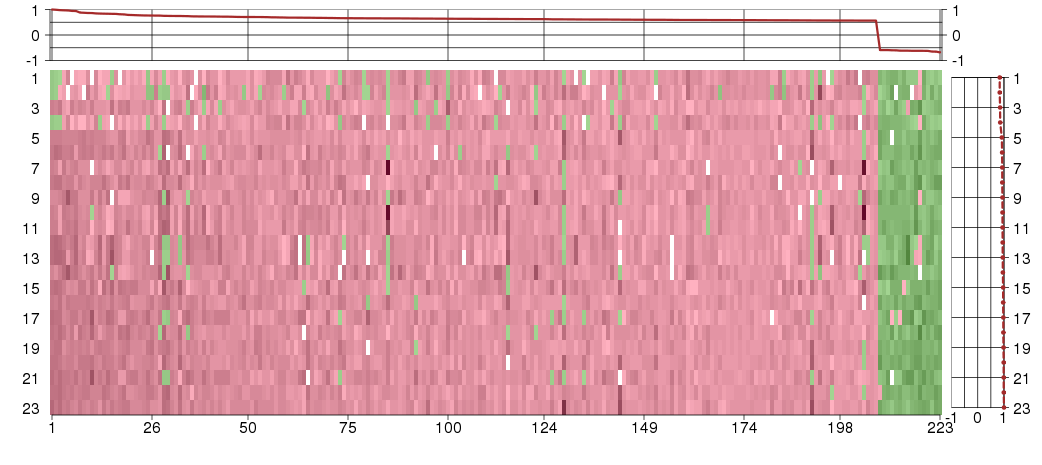

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

system process
A multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system. An organ system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a biological objective.
transport
The directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells, or within a multicellular organism by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
ion transport
The directed movement of charged atoms or small charged molecules into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
neurotransmitter transport
The directed movement of a neurotransmitter into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. Neurotransmitters are any chemical substance that is capable of transmitting (or inhibiting the transmission of) a nerve impulse from a neuron to another cell.
cellular ion homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of ions at the level of a cell.
cell communication
Any process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
cell-cell signaling
Any process that mediates the transfer of information from one cell to another.
synaptic transmission
The process of communication from a neuron to a target (neuron, muscle, or secretory cell) across a synapse.
nerve-nerve synaptic transmission
The process of communication from a neuron to another neuron across a synapse.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of nervous tissue over time, from its formation to its mature state.
neurological system process
A organ system process carried out by any of the organs or tissues of neurological system.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of cell communication
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell communication. Cell communication is the process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
transmission of nerve impulse
The neurological system process by which a signal is transmitted through the nervous system by synaptic transmission and the sequential electrochemical polarization and depolarization that travels across the membrane of a nerve cell (neuron) in response to stimulation.
cellular homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state at the level of the cell.
neurogenesis
Generation of cells within the nervous system.
signaling process
Any biological process involved in the generation, transmission, reception, or interpretation of a signal. A signal is an entity used to transmit or convey information.
signaling
The entirety of a process whereby information is transmitted. This process begins with the initiation of the signal and ends when a response has been triggered.
signal transmission
The process whereby a signal is released and/or conveyed from one location to another.
cell differentiation
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state.
neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron.
regulation of neurological system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a neurophysiological process, an organ system process carried out by any of the organs or tissues of neurological system.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
synaptic transmission, glutamatergic
The process of communication from a neuron to another neuron across a synapse using the neurotransmitter glutamate.
regulation of membrane potential
Any process that modulates the establishment or extent of a membrane potential, the electric potential existing across any membrane arising from charges in the membrane itself and from the charges present in the media on either side of the membrane.
homeostatic process
Any biological process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state.
regulation of system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a system process, a multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system.
ion homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of ions within an organism or cell.
generation of neurons
The process by which nerve cells are generated. This includes the production of neuroblasts and their differentiation into neurons.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
chemical homeostasis
Any biological process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of a chemical.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
regulation of transmission of nerve impulse
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transmission of a nerve impulse, the sequential electrochemical polarization and depolarization that travels across the membrane of a neuron in response to stimulation.
cellular chemical homeostasis
Any biological process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of a chemical at the level of the cell.
regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential
Any process that modulates the establishment or extent of the postsynaptic membrane potential, which is generated by changes in the membrane potential of the post synaptic neuron that receives information at a synapse. The presynaptic neuron releases neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft which bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron. After being bound by the neurotransmitters, these receptors can open or close an ion channel, allowing ions to enter or leave the cell and therefore altering the membrane potential of the postsynaptic neuron.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of biological quality
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological quality. A biological quality is a measurable attribute of an organism or part of an organism, such as size, mass, shape, color, etc.
all
NA
signaling process
Any biological process involved in the generation, transmission, reception, or interpretation of a signal. A signal is an entity used to transmit or convey information.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
cell-cell signaling
Any process that mediates the transfer of information from one cell to another.
regulation of cell communication
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell communication. Cell communication is the process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
transmission of nerve impulse
The neurological system process by which a signal is transmitted through the nervous system by synaptic transmission and the sequential electrochemical polarization and depolarization that travels across the membrane of a nerve cell (neuron) in response to stimulation.
regulation of system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a system process, a multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
synaptic transmission
The process of communication from a neuron to a target (neuron, muscle, or secretory cell) across a synapse.
regulation of transmission of nerve impulse
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transmission of a nerve impulse, the sequential electrochemical polarization and depolarization that travels across the membrane of a neuron in response to stimulation.
transmission of nerve impulse
The neurological system process by which a signal is transmitted through the nervous system by synaptic transmission and the sequential electrochemical polarization and depolarization that travels across the membrane of a nerve cell (neuron) in response to stimulation.
regulation of neurological system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a neurophysiological process, an organ system process carried out by any of the organs or tissues of neurological system.
cellular homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state at the level of the cell.
regulation of transmission of nerve impulse
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transmission of a nerve impulse, the sequential electrochemical polarization and depolarization that travels across the membrane of a neuron in response to stimulation.
neurogenesis
Generation of cells within the nervous system.
cellular chemical homeostasis
Any biological process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of a chemical at the level of the cell.
regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential
Any process that modulates the establishment or extent of the postsynaptic membrane potential, which is generated by changes in the membrane potential of the post synaptic neuron that receives information at a synapse. The presynaptic neuron releases neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft which bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron. After being bound by the neurotransmitters, these receptors can open or close an ion channel, allowing ions to enter or leave the cell and therefore altering the membrane potential of the postsynaptic neuron.
neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron.
cellular ion homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of ions at the level of a cell.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
integral to membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer. When used to describe a protein, indicates that all or part of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cytoplasm
All of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
cytoskeleton
Any of the various filamentous elements that form the internal framework of cells, and typically remain after treatment of the cells with mild detergent to remove membrane constituents and soluble components of the cytoplasm. The term embraces intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, the microtrabecular lattice, and other structures characterized by a polymeric filamentous nature and long-range order within the cell. The various elements of the cytoskeleton not only serve in the maintenance of cellular shape but also have roles in other cellular functions, including cellular movement, cell division, endocytosis, and movement of organelles.
synaptic vesicle
A secretory organelle, some 50 nm in diameter, of presynaptic nerve terminals; accumulates in high concentrations of neurotransmitters and is secreted these into the synaptic cleft by fusion with the 'active zone' of the presynaptic plasma membrane.
endomembrane system
A collection of membranous structures involved in transport within the cell. The main components of the endomembrane system are endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, vesicles, cell membrane and nuclear envelope. Members of the endomembrane system pass materials through each other or though the use of vesicles.
vesicle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding any membrane-bounded vesicle in the cell.
postsynaptic density
The post synaptic density is a region that lies adjacent to the cytoplasmic face of the postsynaptic membrane at excitatory synapse. It forms a disc that consists of a range of proteins with different functions, some of which contact the cytoplasmic domains of ion channels in the postsynaptic membrane. The proteins making up the disc include receptors, and structural proteins linked to the actin cytoskeleton. They also include signalling machinery, such as protein kinases and phosphatases.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
cell junction
A plasma membrane part that forms a specialized region of connection between two cells or between a cell and the extracellular matrix. At a cell junction, anchoring proteins extend through the plasma membrane to link cytoskeletal proteins in one cell to cytoskeletal proteins in neighboring cells or to proteins in the extracellular matrix.
coated vesicle
Small membrane-bounded organelle formed by pinching off of a coated region of membrane. Some coats are made of clathrin, whereas others are made from other proteins.
clathrin-coated vesicle
A vesicle with a coat formed of clathrin connected to the membrane via one of the clathrin adaptor complexes.
dendrite
A neuron projection that has a short, tapering, often branched, morphology, receives and integrates signals from other neurons or from sensory stimuli, and conducts a nerve impulse towards the axon or the cell body. In most neurons, the impulse is conveyed from dendrites to axon via the cell body, but in some types of unipolar neuron, the impulse does not travel via the cell body.
cytoplasmic vesicle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding a cytoplasmic vesicle.
coated vesicle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding a coated vesicle.
clathrin coated vesicle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding a clathrin-coated vesicle.
synaptic vesicle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding a synaptic vesicle.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
vesicle
Any small, fluid-filled, spherical organelle enclosed by membrane or protein.
membrane-bounded vesicle
Any small, fluid-filled, spherical organelle enclosed by a lipid bilayer.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
ion channel complex
A protein complex that spans a membrane and forms a water-filled channel across the phospholipid bilayer allowing selective ion transport down its electrochemical gradient.
cation channel complex
An ion channel complex through which cations pass.
cell projection
A prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
neuron projection
A prolongation or process extending from a nerve cell, e.g. an axon or dendrite.
neuronal cell body
The portion of a neuron that includes the nucleus, but excludes all cell projections such as axons and dendrites.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, and prokaryotic structures such as anammoxosomes and pirellulosomes. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
protein complex
Any macromolecular complex composed of two or more polypeptide subunits, which may or may not be identical. Protein complexes may have other associated non-protein prosthetic groups, such as nucleotides, metal ions or other small molecules.
cell body
The portion of a cell bearing surface projections such as axons, dendrites, cilia, or flagella that includes the nucleus, but excludes all cell projections.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
cytoplasmic vesicle part
Any constituent part of cytoplasmic vesicle, a vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
synapse part
Any constituent part of a synapse, the junction between a nerve fiber of one neuron and another neuron or muscle fiber or glial cell.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
synapse
The junction between a nerve fiber of one neuron and another neuron or muscle fiber or glial cell; the site of interneuronal communication. As the nerve fiber approaches the synapse it enlarges into a specialized structure, the presynaptic nerve ending, which contains mitochondria and synaptic vesicles. At the tip of the nerve ending is the presynaptic membrane; facing it, and separated from it by a minute cleft (the synaptic cleft) is a specialized area of membrane on the receiving cell, known as the postsynaptic membrane. In response to the arrival of nerve impulses, the presynaptic nerve ending secretes molecules of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. These diffuse across the cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane.
postsynaptic membrane
A specialized area of membrane facing the presynaptic membrane on the tip of the nerve ending and separated from it by a minute cleft (the synaptic cleft). Neurotransmitters across the synaptic cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
synapse part
Any constituent part of a synapse, the junction between a nerve fiber of one neuron and another neuron or muscle fiber or glial cell.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
postsynaptic membrane
A specialized area of membrane facing the presynaptic membrane on the tip of the nerve ending and separated from it by a minute cleft (the synaptic cleft). Neurotransmitters across the synaptic cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane.
vesicle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding any membrane-bounded vesicle in the cell.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
ion channel complex
A protein complex that spans a membrane and forms a water-filled channel across the phospholipid bilayer allowing selective ion transport down its electrochemical gradient.
cytoplasmic vesicle part
Any constituent part of cytoplasmic vesicle, a vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
vesicle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding any membrane-bounded vesicle in the cell.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
postsynaptic density
The post synaptic density is a region that lies adjacent to the cytoplasmic face of the postsynaptic membrane at excitatory synapse. It forms a disc that consists of a range of proteins with different functions, some of which contact the cytoplasmic domains of ion channels in the postsynaptic membrane. The proteins making up the disc include receptors, and structural proteins linked to the actin cytoskeleton. They also include signalling machinery, such as protein kinases and phosphatases.
cytoplasmic vesicle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding a cytoplasmic vesicle.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
cytoplasmic vesicle part
Any constituent part of cytoplasmic vesicle, a vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
cytoplasmic vesicle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding a cytoplasmic vesicle.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
ion channel complex
A protein complex that spans a membrane and forms a water-filled channel across the phospholipid bilayer allowing selective ion transport down its electrochemical gradient.
coated vesicle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding a coated vesicle.
synaptic vesicle
A secretory organelle, some 50 nm in diameter, of presynaptic nerve terminals; accumulates in high concentrations of neurotransmitters and is secreted these into the synaptic cleft by fusion with the 'active zone' of the presynaptic plasma membrane.
clathrin coated vesicle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding a clathrin-coated vesicle.
synaptic vesicle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding a synaptic vesicle.

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
signal transducer activity
Mediates the transfer of a signal from the outside to the inside of a cell by means other than the introduction of the signal molecule itself into the cell.
receptor activity
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell activity.
transmembrane receptor activity
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell activity, and spanning to the membrane of either the cell or an organelle.
ionotropic glutamate receptor activity
Combining with glutamate to initiate a change in cell activity through the regulation of ion channels.
transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
ion channel activity
Catalysis of facilitated diffusion of an ion (by an energy-independent process) by passage through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel without evidence for a carrier-mediated mechanism.
extracellular ligand-gated ion channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a channel that opens when a specific extracellular ligand has been bound by the channel complex or one of its constituent parts.
excitatory extracellular ligand-gated ion channel activity
NA
extracellular-glutamate-gated ion channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a channel that opens when extracellular glutamate has been bound by the channel complex or one of its constituent parts.
voltage-gated ion channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a voltage-gated channel. An ion is an atom or group of atoms carrying an electric charge by virtue of having gained or lost one or more electrons.
cation channel activity
Catalysis of the energy-independent passage of cations across a lipid bilayer down a concentration gradient.
potassium channel activity
Catalysis of facilitated diffusion of a potassium ion (by an energy-independent process) involving passage through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel without evidence for a carrier-mediated mechanism.
transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a substance from one side of a membrane to the other.
glutamate receptor activity
Combining with glutamate to initiate a change in cell activity.
cation transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of cation from one side of the membrane to the other.
ion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of an ion from one side of a membrane to the other.
channel activity
Catalysis of energy-independent facilitated diffusion, mediated by passage of a solute through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel. Stereospecificity is not exhibited but this transport may be specific for a particular molecular species or class of molecules.
ligand-gated ion channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a channel that opens when a specific ligand has been bound by the channel complex or one of its constituent parts.
passive transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute from one side of the membrane to the other, down the solute's concentration gradient.
voltage-gated channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a solute by a channel whose open state is dependent on the voltage across the membrane in which it is embedded.
ligand-gated channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a solute by a channel that opens when a specific ligand has been bound by the channel complex or one of its constituent parts.
gated channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a solute by a channel that opens in response to a specific stimulus.
substrate-specific channel activity
Catalysis of energy-independent facilitated diffusion, mediated by passage of a specific solute through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel. Stereospecificity is not exhibited but this transport may be specific for a particular molecular species or class of molecules.
voltage-gated cation channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a cation by a voltage-gated channel. A cation is a positively charged ion.
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
substrate-specific transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of a specific substance or group of related substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
molecular transducer activity
The molecular function that accepts an input of one form and creates an output of a different form.
all
NA
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
substrate-specific channel activity
Catalysis of energy-independent facilitated diffusion, mediated by passage of a specific solute through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel. Stereospecificity is not exhibited but this transport may be specific for a particular molecular species or class of molecules.
ion channel activity
Catalysis of facilitated diffusion of an ion (by an energy-independent process) by passage through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel without evidence for a carrier-mediated mechanism.
cation channel activity
Catalysis of the energy-independent passage of cations across a lipid bilayer down a concentration gradient.
voltage-gated ion channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a voltage-gated channel. An ion is an atom or group of atoms carrying an electric charge by virtue of having gained or lost one or more electrons.
ligand-gated ion channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a channel that opens when a specific ligand has been bound by the channel complex or one of its constituent parts.
voltage-gated cation channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a cation by a voltage-gated channel. A cation is a positively charged ion.
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 04080 | 6.635e-04 | 4.122 | 15 | 102 | Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction |
| 04720 | 2.862e-03 | 1.01 | 7 | 25 | Long-term potentiation |
| 04730 | 7.875e-03 | 1.212 | 7 | 30 | Long-term depression |
ABCG4ATP-binding cassette, sub-family G (WHITE), member 4 (ENSG00000172350), score: 0.65 ACAA2acetyl-CoA acyltransferase 2 (ENSG00000167315), score: -0.59 ADAM22ADAM metallopeptidase domain 22 (ENSG00000008277), score: 0.73 ADCY8adenylate cyclase 8 (brain) (ENSG00000155897), score: 0.57 AKAP13A kinase (PRKA) anchor protein 13 (ENSG00000170776), score: -0.65 AP3B2adaptor-related protein complex 3, beta 2 subunit (ENSG00000103723), score: 0.59 APPL2adaptor protein, phosphotyrosine interaction, PH domain and leucine zipper containing 2 (ENSG00000136044), score: 0.57 AQP4aquaporin 4 (ENSG00000171885), score: 0.59 ARPC2actin related protein 2/3 complex, subunit 2, 34kDa (ENSG00000163466), score: -0.62 ARPP21cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein, 21kDa (ENSG00000172995), score: 0.65 ATP6V0E1ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 9kDa, V0 subunit e1 (ENSG00000113732), score: -0.59 B4GALT6UDP-Gal:betaGlcNAc beta 1,4- galactosyltransferase, polypeptide 6 (ENSG00000118276), score: 0.57 BCANbrevican (ENSG00000132692), score: 0.57 BICD1bicaudal D homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000151746), score: 0.73 BPTFbromodomain PHD finger transcription factor (ENSG00000171634), score: 0.61 BRP44brain protein 44 (ENSG00000143158), score: -0.6 BTBD3BTB (POZ) domain containing 3 (ENSG00000132640), score: 0.65 C11orf41chromosome 11 open reading frame 41 (ENSG00000110427), score: 0.57 C15orf27chromosome 15 open reading frame 27 (ENSG00000169758), score: 0.77 C17orf28chromosome 17 open reading frame 28 (ENSG00000167861), score: 0.58 C6orf115chromosome 6 open reading frame 115 (ENSG00000146386), score: -0.62 C6orf174chromosome 6 open reading frame 174 (ENSG00000214338), score: 0.61 C7orf16chromosome 7 open reading frame 16 (ENSG00000106341), score: 0.75 C8orf79chromosome 8 open reading frame 79 (ENSG00000170941), score: 0.79 C9orf4chromosome 9 open reading frame 4 (ENSG00000136805), score: 0.64 CA10carbonic anhydrase X (ENSG00000154975), score: 0.7 CA8carbonic anhydrase VIII (ENSG00000178538), score: 0.73 CACNA1Gcalcium channel, voltage-dependent, T type, alpha 1G subunit (ENSG00000006283), score: 0.59 CACNA1Icalcium channel, voltage-dependent, T type, alpha 1I subunit (ENSG00000100346), score: 0.62 CACNB4calcium channel, voltage-dependent, beta 4 subunit (ENSG00000182389), score: 0.71 CACNG2calcium channel, voltage-dependent, gamma subunit 2 (ENSG00000166862), score: 0.68 CAMKK2calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2, beta (ENSG00000110931), score: 0.64 CASP7caspase 7, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase (ENSG00000165806), score: -0.61 CBLN1cerebellin 1 precursor (ENSG00000102924), score: 0.94 CCDC109Acoiled-coil domain containing 109A (ENSG00000156026), score: 0.61 CDH18cadherin 18, type 2 (ENSG00000145526), score: 0.58 CDH7cadherin 7, type 2 (ENSG00000081138), score: 0.86 CDS2CDP-diacylglycerol synthase (phosphatidate cytidylyltransferase) 2 (ENSG00000101290), score: 0.64 CERKLceramide kinase-like (ENSG00000188452), score: 0.58 CHD9chromodomain helicase DNA binding protein 9 (ENSG00000177200), score: 0.59 CHGBchromogranin B (secretogranin 1) (ENSG00000089199), score: 0.71 CHN2chimerin (chimaerin) 2 (ENSG00000106069), score: 0.69 CHRNA3cholinergic receptor, nicotinic, alpha 3 (ENSG00000080644), score: 0.6 CLVS1clavesin 1 (ENSG00000177182), score: 0.63 CLVS2clavesin 2 (ENSG00000146352), score: 0.76 CNKSR2connector enhancer of kinase suppressor of Ras 2 (ENSG00000149970), score: 0.65 CNNM1cyclin M1 (ENSG00000119946), score: 0.59 CNR1cannabinoid receptor 1 (brain) (ENSG00000118432), score: 0.72 CNTN6contactin 6 (ENSG00000134115), score: 0.68 CNTNAP1contactin associated protein 1 (ENSG00000108797), score: 0.63 CORO2Bcoronin, actin binding protein, 2B (ENSG00000103647), score: 0.57 CRHR1corticotropin releasing hormone receptor 1 (ENSG00000120088), score: 0.73 CRTAMcytotoxic and regulatory T cell molecule (ENSG00000109943), score: 0.75 DAB1disabled homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000173406), score: 0.61 DBC1deleted in bladder cancer 1 (ENSG00000078725), score: 0.58 DGKIdiacylglycerol kinase, iota (ENSG00000157680), score: 0.59 DNM3dynamin 3 (ENSG00000197959), score: 0.67 DOPEY2dopey family member 2 (ENSG00000142197), score: 0.67 DPP6dipeptidyl-peptidase 6 (ENSG00000130226), score: 0.59 EBF1early B-cell factor 1 (ENSG00000164330), score: 0.58 ECE2endothelin converting enzyme 2 (ENSG00000145194), score: 0.7 EFR3BEFR3 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000084710), score: 0.62 ELF1E74-like factor 1 (ets domain transcription factor) (ENSG00000120690), score: -0.61 ELMOD1ELMO/CED-12 domain containing 1 (ENSG00000110675), score: 0.56 ELOVL4elongation of very long chain fatty acids (FEN1/Elo2, SUR4/Elo3, yeast)-like 4 (ENSG00000118402), score: 0.6 EPC1enhancer of polycomb homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000120616), score: 0.67 EPHA8EPH receptor A8 (ENSG00000070886), score: 0.63 FAIM2Fas apoptotic inhibitory molecule 2 (ENSG00000135472), score: 0.56 FAM131Bfamily with sequence similarity 131, member B (ENSG00000159784), score: 0.61 FAT2FAT tumor suppressor homolog 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000086570), score: 1 FGF14fibroblast growth factor 14 (ENSG00000102466), score: 0.6 FGF5fibroblast growth factor 5 (ENSG00000138675), score: 0.86 FGFR1fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (ENSG00000077782), score: 0.57 FHDC1FH2 domain containing 1 (ENSG00000137460), score: 0.65 FUT9fucosyltransferase 9 (alpha (1,3) fucosyltransferase) (ENSG00000172461), score: 0.62 FZD7frizzled homolog 7 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000155760), score: 0.6 GABRA1gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, alpha 1 (ENSG00000022355), score: 0.64 GABRB2gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, beta 2 (ENSG00000145864), score: 0.66 GABRG2gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, gamma 2 (ENSG00000113327), score: 0.58 GAD2glutamate decarboxylase 2 (pancreatic islets and brain, 65kDa) (ENSG00000136750), score: 0.58 GALNT7UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 7 (GalNAc-T7) (ENSG00000109586), score: 0.71 GDF10growth differentiation factor 10 (ENSG00000107623), score: 0.63 GHITMgrowth hormone inducible transmembrane protein (ENSG00000165678), score: -0.62 GLRA1glycine receptor, alpha 1 (ENSG00000145888), score: 0.57 GLRA2glycine receptor, alpha 2 (ENSG00000101958), score: 0.66 GNG13guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), gamma 13 (ENSG00000127588), score: 0.72 GPM6Aglycoprotein M6A (ENSG00000150625), score: 0.61 GPR37L1G protein-coupled receptor 37 like 1 (ENSG00000170075), score: 0.62 GRIA1glutamate receptor, ionotropic, AMPA 1 (ENSG00000155511), score: 0.62 GRIA2glutamate receptor, ionotropic, AMPA 2 (ENSG00000120251), score: 0.58 GRIA4glutamate receptor, ionotrophic, AMPA 4 (ENSG00000152578), score: 0.75 GRID2glutamate receptor, ionotropic, delta 2 (ENSG00000152208), score: 0.94 GRIK1glutamate receptor, ionotropic, kainate 1 (ENSG00000171189), score: 0.62 GRIN1glutamate receptor, ionotropic, N-methyl D-aspartate 1 (ENSG00000176884), score: 0.58 GRM1glutamate receptor, metabotropic 1 (ENSG00000152822), score: 0.83 HCN1hyperpolarization activated cyclic nucleotide-gated potassium channel 1 (ENSG00000164588), score: 0.6 IGSF21immunoglobin superfamily, member 21 (ENSG00000117154), score: 0.57 JAKMIP2janus kinase and microtubule interacting protein 2 (ENSG00000176049), score: 0.58 JARID2jumonji, AT rich interactive domain 2 (ENSG00000008083), score: 0.63 KCNA1potassium voltage-gated channel, shaker-related subfamily, member 1 (episodic ataxia with myokymia) (ENSG00000111262), score: 0.72 KCNC1potassium voltage-gated channel, Shaw-related subfamily, member 1 (ENSG00000129159), score: 0.77 KCND3potassium voltage-gated channel, Shal-related subfamily, member 3 (ENSG00000171385), score: 0.6 KCNJ6potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 6 (ENSG00000157542), score: 0.66 KCNK10potassium channel, subfamily K, member 10 (ENSG00000100433), score: 0.76 KCNK9potassium channel, subfamily K, member 9 (ENSG00000169427), score: 0.81 KCNT1potassium channel, subfamily T, member 1 (ENSG00000107147), score: 0.64 KIAA1409KIAA1409 (ENSG00000133958), score: 0.62 KIF1Bkinesin family member 1B (ENSG00000054523), score: 0.58 KIF5Ckinesin family member 5C (ENSG00000168280), score: 0.58 KRT222keratin 222 (ENSG00000213424), score: 0.59 LGI2leucine-rich repeat LGI family, member 2 (ENSG00000153012), score: 0.68 LOC100131509similar to inward rectifying K+ channel negative regulator Kir2.2v (ENSG00000184185), score: 0.65 LOC100134209similar to IQ motif and Sec7 domain-containing protein 3 (ENSG00000120645), score: 0.59 LOC100293817similar to hCG1811893 (ENSG00000144460), score: 0.6 LRCH1leucine-rich repeats and calponin homology (CH) domain containing 1 (ENSG00000136141), score: 0.7 LRP8low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 8, apolipoprotein e receptor (ENSG00000157193), score: 0.6 LRRC26leucine rich repeat containing 26 (ENSG00000184709), score: 0.57 LRRC38leucine rich repeat containing 38 (ENSG00000162494), score: 0.73 LRRC3Bleucine rich repeat containing 3B (ENSG00000179796), score: 0.66 LRRN1leucine rich repeat neuronal 1 (ENSG00000175928), score: 0.61 LRRTM3leucine rich repeat transmembrane neuronal 3 (ENSG00000198739), score: 0.6 LSAMPlimbic system-associated membrane protein (ENSG00000185565), score: 0.57 MAB21L1mab-21-like 1 (C. elegans) (ENSG00000180660), score: 0.99 MAML3mastermind-like 3 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000196782), score: 0.83 MAN2A1mannosidase, alpha, class 2A, member 1 (ENSG00000112893), score: -0.62 MCTP1multiple C2 domains, transmembrane 1 (ENSG00000175471), score: 0.65 MDGA1MAM domain containing glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor 1 (ENSG00000112139), score: 0.75 MEIS1Meis homeobox 1 (ENSG00000143995), score: 0.72 MLC1megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts 1 (ENSG00000100427), score: 0.6 MLLmyeloid/lymphoid or mixed-lineage leukemia (trithorax homolog, Drosophila) (ENSG00000118058), score: 0.63 MYT1myelin transcription factor 1 (ENSG00000196132), score: 0.84 NKX6-3NK6 homeobox 3 (ENSG00000165066), score: 0.57 NMNAT2nicotinamide nucleotide adenylyltransferase 2 (ENSG00000157064), score: 0.65 NRG2neuregulin 2 (ENSG00000158458), score: 0.78 NRP1neuropilin 1 (ENSG00000099250), score: -0.68 NTMneurotrimin (ENSG00000182667), score: 0.64 NTRK3neurotrophic tyrosine kinase, receptor, type 3 (ENSG00000140538), score: 0.64 OLFM3olfactomedin 3 (ENSG00000118733), score: 0.6 PAG1phosphoprotein associated with glycosphingolipid microdomains 1 (ENSG00000076641), score: 0.62 PAK7p21 protein (Cdc42/Rac)-activated kinase 7 (ENSG00000101349), score: 0.65 PAX3paired box 3 (ENSG00000135903), score: 0.64 PAX6paired box 6 (ENSG00000007372), score: 0.87 PIK3R3phosphoinositide-3-kinase, regulatory subunit 3 (gamma) (ENSG00000117461), score: 0.6 PKDCCprotein kinase domain containing, cytoplasmic homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000162878), score: -0.59 PLCB4phospholipase C, beta 4 (ENSG00000101333), score: 0.73 PLCXD3phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C, X domain containing 3 (ENSG00000182836), score: 0.67 PLD5phospholipase D family, member 5 (ENSG00000180287), score: 0.66 PPM1Hprotein phosphatase, Mg2+/Mn2+ dependent, 1H (ENSG00000111110), score: 0.58 PPP3CAprotein phosphatase 3, catalytic subunit, alpha isozyme (ENSG00000138814), score: 0.62 PRDM10PR domain containing 10 (ENSG00000170325), score: 0.63 PSD2pleckstrin and Sec7 domain containing 2 (ENSG00000146005), score: 0.66 PTCH1patched 1 (ENSG00000185920), score: 0.66 PTCHD1patched domain containing 1 (ENSG00000165186), score: 0.85 PTP4A2protein tyrosine phosphatase type IVA, member 2 (ENSG00000184007), score: -0.62 PTPRRprotein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, R (ENSG00000153233), score: 0.72 PVALBparvalbumin (ENSG00000100362), score: 0.71 PYGO1pygopus homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000171016), score: 0.58 QARSglutaminyl-tRNA synthetase (ENSG00000172053), score: -0.6 RASGEF1CRasGEF domain family, member 1C (ENSG00000146090), score: 0.59 RCAN3RCAN family member 3 (ENSG00000117602), score: 0.61 RGS7BPregulator of G-protein signaling 7 binding protein (ENSG00000186479), score: 0.57 RGS8regulator of G-protein signaling 8 (ENSG00000135824), score: 0.74 RIMS4regulating synaptic membrane exocytosis 4 (ENSG00000101098), score: 0.58 RIT2Ras-like without CAAX 2 (ENSG00000152214), score: 0.67 RNF182ring finger protein 182 (ENSG00000180537), score: 0.57 RTN1reticulon 1 (ENSG00000139970), score: 0.59 RUNX1T1runt-related transcription factor 1; translocated to, 1 (cyclin D-related) (ENSG00000079102), score: 0.59 SART3squamous cell carcinoma antigen recognized by T cells 3 (ENSG00000075856), score: 0.57 SEL1L3sel-1 suppressor of lin-12-like 3 (C. elegans) (ENSG00000091490), score: 0.61 SGSM1small G protein signaling modulator 1 (ENSG00000167037), score: 0.65 SHFSrc homology 2 domain containing F (ENSG00000138606), score: 0.7 SKIv-ski sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (avian) (ENSG00000157933), score: 0.64 SKOR1SKI family transcriptional corepressor 1 (ENSG00000188779), score: 0.76 SLC12A5solute carrier family 12 (potassium/chloride transporter), member 5 (ENSG00000124140), score: 0.64 SLC1A3solute carrier family 1 (glial high affinity glutamate transporter), member 3 (ENSG00000079215), score: 0.62 SLC32A1solute carrier family 32 (GABA vesicular transporter), member 1 (ENSG00000101438), score: 0.64 SLC35F4solute carrier family 35, member F4 (ENSG00000151812), score: 0.83 SLC4A10solute carrier family 4, sodium bicarbonate transporter, member 10 (ENSG00000144290), score: 0.58 SLC6A5solute carrier family 6 (neurotransmitter transporter, glycine), member 5 (ENSG00000165970), score: 0.65 SLC7A14solute carrier family 7 (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system), member 14 (ENSG00000013293), score: 0.68 SLC9A5solute carrier family 9 (sodium/hydrogen exchanger), member 5 (ENSG00000135740), score: 0.68 SLITRK4SLIT and NTRK-like family, member 4 (ENSG00000179542), score: 0.63 SNAP23synaptosomal-associated protein, 23kDa (ENSG00000092531), score: -0.62 SNAP25synaptosomal-associated protein, 25kDa (ENSG00000132639), score: 0.63 SNAP91synaptosomal-associated protein, 91kDa homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000065609), score: 0.61 SNRKSNF related kinase (ENSG00000163788), score: 0.61 SNX25sorting nexin 25 (ENSG00000109762), score: 0.68 SPHKAPSPHK1 interactor, AKAP domain containing (ENSG00000153820), score: 0.74 SRCIN1SRC kinase signaling inhibitor 1 (ENSG00000017373), score: 0.63 SRGAP3SLIT-ROBO Rho GTPase activating protein 3 (ENSG00000196220), score: 0.63 SRRM4serine/arginine repetitive matrix 4 (ENSG00000139767), score: 0.69 STACSH3 and cysteine rich domain (ENSG00000144681), score: 0.65 STXBP1syntaxin binding protein 1 (ENSG00000136854), score: 0.6 SYBUsyntabulin (syntaxin-interacting) (ENSG00000147642), score: 0.61 SYNPRsynaptoporin (ENSG00000163630), score: 0.56 SYT11synaptotagmin XI (ENSG00000132718), score: 0.58 SYT12synaptotagmin XII (ENSG00000173227), score: 0.59 SYT4synaptotagmin IV (ENSG00000132872), score: 0.71 TAGLN3transgelin 3 (ENSG00000144834), score: 0.57 TBC1D30TBC1 domain family, member 30 (ENSG00000111490), score: 0.57 TBC1D9TBC1 domain family, member 9 (with GRAM domain) (ENSG00000109436), score: 0.64 TIAM1T-cell lymphoma invasion and metastasis 1 (ENSG00000156299), score: 0.81 TLL1tolloid-like 1 (ENSG00000038295), score: 0.96 TMEM22transmembrane protein 22 (ENSG00000168917), score: 0.65 TMEM63Ctransmembrane protein 63C (ENSG00000165548), score: 0.69 TNFAIP2tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 2 (ENSG00000185215), score: -0.65 TNRtenascin R (restrictin, janusin) (ENSG00000116147), score: 0.59 TRIM3tripartite motif-containing 3 (ENSG00000110171), score: 0.66 TRIM67tripartite motif-containing 67 (ENSG00000119283), score: 0.97 TRIM9tripartite motif-containing 9 (ENSG00000100505), score: 0.6 TRPC3transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily C, member 3 (ENSG00000138741), score: 0.76 UNC80unc-80 homolog (C. elegans) (ENSG00000144406), score: 0.68 UPF0639UPF0639 protein (ENSG00000175985), score: 0.84 VAT1Lvesicle amine transport protein 1 homolog (T. californica)-like (ENSG00000171724), score: 0.69 VSX1visual system homeobox 1 (ENSG00000100987), score: 0.61 WDFY3WD repeat and FYVE domain containing 3 (ENSG00000163625), score: 0.59 WSCD1WSC domain containing 1 (ENSG00000179314), score: 0.64 YPEL4yippee-like 4 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000166793), score: 0.57 ZFPM2zinc finger protein, multitype 2 (ENSG00000169946), score: 0.75 ZIC4Zic family member 4 (ENSG00000174963), score: 0.97 ZNF238zinc finger protein 238 (ENSG00000179456), score: 0.78 ZNF521zinc finger protein 521 (ENSG00000198795), score: 0.88 ZNF536zinc finger protein 536 (ENSG00000198597), score: 0.63
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| gga_br_m_ca1 | gga | br | m | _ |
| oan_br_m_ca1 | oan | br | m | _ |
| ggo_cb_m_ca1 | ggo | cb | m | _ |
| gga_br_f_ca1 | gga | br | f | _ |
| ptr_cb_f_ca1 | ptr | cb | f | _ |
| ppa_cb_f_ca1 | ppa | cb | f | _ |
| mmu_cb_m1_ca1 | mmu | cb | m | 1 |
| ppy_cb_f_ca1 | ppy | cb | f | _ |
| gga_cb_m_ca1 | gga | cb | m | _ |
| mmu_cb_f_ca1 | mmu | cb | f | _ |
| mmu_cb_m2_ca1 | mmu | cb | m | 2 |
| oan_cb_f_ca1 | oan | cb | f | _ |
| oan_cb_m_ca1 | oan | cb | m | _ |
| gga_cb_f_ca1 | gga | cb | f | _ |
| hsa_cb_f_ca1 | hsa | cb | f | _ |
| mml_cb_f_ca1 | mml | cb | f | _ |
| mdo_cb_m_ca1 | mdo | cb | m | _ |
| ggo_cb_f_ca1 | ggo | cb | f | _ |
| mml_cb_m_ca1 | mml | cb | m | _ |
| ppa_cb_m_ca1 | ppa | cb | m | _ |
| mdo_cb_f_ca1 | mdo | cb | f | _ |
| ptr_cb_m_ca1 | ptr | cb | m | _ |
| hsa_cb_m_ca1 | hsa | cb | m | _ |