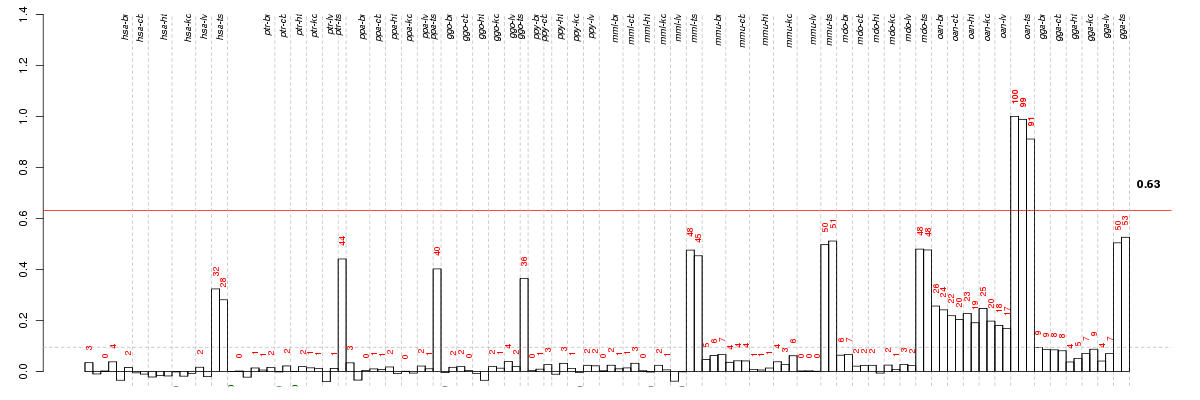

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

reproduction
The production by an organism of new individuals that contain some portion of their genetic material inherited from that organism.
DNA replication
The cellular metabolic process whereby new strands of DNA are synthesized. The template for replication can either be an existing DNA molecule or RNA.
chromosome segregation
The process by which genetic material, in the form of chromosomes, is organized into specific structures and then physically separated and apportioned to two or more sets.
chromosome organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level that results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of chromosomes, structures composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins that carries hereditary information.
M phase of mitotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the mitotic cell cycle during which mitosis takes place.
modification-dependent protein catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a protein or peptide by hydrolysis of its peptide bonds, initiated by the covalent modification of the target protein.
microtubule cytoskeleton organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising microtubules and their associated proteins.
mitotic cell cycle
Progression through the phases of the mitotic cell cycle, the most common eukaryotic cell cycle, which canonically comprises four successive phases called G1, S, G2, and M and includes replication of the genome and the subsequent segregation of chromosomes into daughter cells. In some variant cell cycles nuclear replication or nuclear division may not be followed by cell division, or G1 and G2 phases may be absent.
M phase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the cell cycle comprising nuclear division.
nuclear division
A process by which a cell nucleus is divided into two nuclei, with DNA and other nuclear contents distributed between the daughter nuclei.
metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
reproductive developmental process
A developmental process by which a progressive change in the state of some part of an organism specifically contributes to its ability to form offspring.
cytoskeleton organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
DNA metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving deoxyribonucleic acid. This is one of the two main types of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from one, or more commonly, two, strands of linked deoxyribonucleotides.
DNA packaging
Any process by which DNA and associated proteins are formed into a compact, orderly structure.
proteolysis
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a protein by the destruction of the native, active configuration, with the hydrolysis of peptide bonds.
proteolysis involved in cellular protein catabolic process
The hydrolysis of a peptide bond or bonds within a protein as part of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a protein by individual cells.
ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a protein or peptide by hydrolysis of its peptide bonds, initiated by the covalent attachment of a ubiquitin moiety, or multiple ubiquitin moieties, to the protein.
nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds; includes nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, assimilatory/dissimilatory nitrate reduction and the interconversion of nitrogenous organic matter and ammonium.
organelle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an organelle within a cell. An organelle is an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
microtubule-based process
Any cellular process that depends upon or alters the microtubule cytoskeleton, that part of the cytoskeleton comprising microtubules and their associated proteins.
cell cycle
The progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events. Canonically, the cell cycle comprises the replication and segregation of genetic material followed by the division of the cell, but in endocycles or syncytial cells nuclear replication or nuclear division may not be followed by cell division.
spindle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of the spindle, the array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during DNA segregation and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
mitotic spindle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of the microtubule spindle during a mitotic cell cycle.
mitosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides; the process involves condensation of chromosomal DNA into a highly compacted form. Canonically, mitosis produces two daughter nuclei whose chromosome complement is identical to that of the mother cell.
meiosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through the nuclear division phase of a meiotic cell cycle, the specialized nuclear and cell division in which a single diploid cell undergoes two nuclear divisions following a single round of DNA replication in order to produce four daughter cells that contain half the number of chromosomes as the diploid cell. Meiotic division occurs during the formation of gametes from diploid organisms and at the beginning of haplophase in those organisms that alternate between diploid and haploid generations.
gamete generation
The generation and maintenance of gametes in a multicellular organism. A gamete is a haploid reproductive cell.
germ cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an immature germ cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure (gamete). A germ cell is any reproductive cell in a multicellular organism.
spermatogenesis
The process of formation of spermatozoa, including spermatocytogenesis and spermiogenesis.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of substances, including the breakdown of carbon compounds with the liberation of energy for use by the cell or organism.
macromolecule catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
cellular component organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a cellular component.
protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general. Includes protein modification.
sexual reproduction
The regular alternation, in the life cycle of haplontic, diplontic and diplohaplontic organisms, of meiosis and fertilization which provides for the production offspring. In diplontic organisms there is a life cycle in which the products of meiosis behave directly as gametes, fusing to form a zygote from which the diploid, or sexually reproductive polyploid, adult organism will develop. In diplohaplontic organisms a haploid phase (gametophyte) exists in the life cycle between meiosis and fertilization (e.g. higher plants, many algae and Fungi); the products of meiosis are spores that develop as haploid individuals from which haploid gametes develop to form a diploid zygote; diplohaplontic organisms show an alternation of haploid and diploid generations. In haplontic organisms meiosis occurs in the zygote, giving rise to four haploid cells (e.g. many algae and protozoa), only the zygote is diploid and this may form a resistant spore, tiding organisms over hard times.
cell cycle process
A cellular process that is involved in the progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
cell cycle phase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through one of the biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
cell differentiation
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state.
protein catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a protein by the destruction of the native, active configuration, with or without the hydrolysis of peptide bonds.
chromosome condensation
The progressive compaction of dispersed interphase chromatin into threadlike chromosomes prior to mitotic or meiotic nuclear division, or during apoptosis, in eukaryotic cells.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
multicellular organism reproduction
The biological process by which new individuals are produced by one or two multicellular organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
modification-dependent macromolecule catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a macromolecule, initiated by covalent modification of the target molecule.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular protein catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a protein by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a macromolecule, any large molecule including proteins, nucleic acids and carbohydrates, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general, occurring at the level of an individual cell. Includes protein modification.
male gamete generation
Generation of the male gamete; specialised haploid cells produced by meiosis and along with a female gamete takes part in sexual reproduction.
organelle fission
The creation of two or more organelles by division of one organelle.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
reproductive process in a multicellular organism
The process, occurring above the cellular level, that is pertinent to the reproductive function of a multicellular organism. This includes the integrated processes at the level of tissues and organs.
reproductive cellular process
A process, occurring at the cellular level, that is involved in the reproductive function of a multicellular or single-celled organism.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
cell division
The process resulting in the physical partitioning and separation of a cell into daughter cells.
meiotic cell cycle
Progression through the phases of the meiotic cell cycle, in which canonically a cell replicates to produce four offspring with half the chromosomal content of the progenitor cell.
M phase of meiotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the meiotic cell cycle during which meiosis takes place.
DNA conformation change
A cellular process that results in a change in the spatial configuration of a DNA molecule. A conformation change can bend DNA, or alter the, twist, writhe, or linking number of a DNA molecule.
nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleic acids.
all
NA
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
organelle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an organelle within a cell. An organelle is an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
reproductive cellular process
A process, occurring at the cellular level, that is involved in the reproductive function of a multicellular or single-celled organism.
multicellular organism reproduction
The biological process by which new individuals are produced by one or two multicellular organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
reproductive process in a multicellular organism
The process, occurring above the cellular level, that is pertinent to the reproductive function of a multicellular organism. This includes the integrated processes at the level of tissues and organs.
reproductive developmental process
A developmental process by which a progressive change in the state of some part of an organism specifically contributes to its ability to form offspring.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
reproductive process in a multicellular organism
The process, occurring above the cellular level, that is pertinent to the reproductive function of a multicellular organism. This includes the integrated processes at the level of tissues and organs.
macromolecule catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general. Includes protein modification.
cell cycle process
A cellular process that is involved in the progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
DNA packaging
Any process by which DNA and associated proteins are formed into a compact, orderly structure.
germ cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an immature germ cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure (gamete). A germ cell is any reproductive cell in a multicellular organism.
gamete generation
The generation and maintenance of gametes in a multicellular organism. A gamete is a haploid reproductive cell.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
germ cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an immature germ cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure (gamete). A germ cell is any reproductive cell in a multicellular organism.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
cellular macromolecule catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a macromolecule, any large molecule including proteins, nucleic acids and carbohydrates, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
protein catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a protein by the destruction of the native, active configuration, with or without the hydrolysis of peptide bonds.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a macromolecule, any large molecule including proteins, nucleic acids and carbohydrates, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general, occurring at the level of an individual cell. Includes protein modification.
chromosome condensation
The progressive compaction of dispersed interphase chromatin into threadlike chromosomes prior to mitotic or meiotic nuclear division, or during apoptosis, in eukaryotic cells.
microtubule cytoskeleton organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising microtubules and their associated proteins.
mitotic spindle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of the microtubule spindle during a mitotic cell cycle.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
germ cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an immature germ cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure (gamete). A germ cell is any reproductive cell in a multicellular organism.
cellular protein catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a protein by individual cells.
cellular protein catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a protein by individual cells.
DNA replication
The cellular metabolic process whereby new strands of DNA are synthesized. The template for replication can either be an existing DNA molecule or RNA.
DNA metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving deoxyribonucleic acid. This is one of the two main types of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from one, or more commonly, two, strands of linked deoxyribonucleotides.
mitosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides; the process involves condensation of chromosomal DNA into a highly compacted form. Canonically, mitosis produces two daughter nuclei whose chromosome complement is identical to that of the mother cell.
mitotic spindle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of the microtubule spindle during a mitotic cell cycle.
mitosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides; the process involves condensation of chromosomal DNA into a highly compacted form. Canonically, mitosis produces two daughter nuclei whose chromosome complement is identical to that of the mother cell.
meiosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through the nuclear division phase of a meiotic cell cycle, the specialized nuclear and cell division in which a single diploid cell undergoes two nuclear divisions following a single round of DNA replication in order to produce four daughter cells that contain half the number of chromosomes as the diploid cell. Meiotic division occurs during the formation of gametes from diploid organisms and at the beginning of haplophase in those organisms that alternate between diploid and haploid generations.
M phase of mitotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the mitotic cell cycle during which mitosis takes place.
spindle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of the spindle, the array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during DNA segregation and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
M phase of meiotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the meiotic cell cycle during which meiosis takes place.
proteolysis involved in cellular protein catabolic process
The hydrolysis of a peptide bond or bonds within a protein as part of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a protein by individual cells.
modification-dependent protein catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a protein or peptide by hydrolysis of its peptide bonds, initiated by the covalent modification of the target protein.

condensed chromosome
A highly compacted molecule of DNA and associated proteins resulting in a cytologically distinct structure.
intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
chromosome, centromeric region
The region of a chromosome that includes the centromeric DNA and associated proteins. In monocentric chromosomes, this region corresponds to a single area of the chromosome, whereas in holocentric chromosomes, it is evenly distributed along the chromosome.
kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of DNA and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
condensed chromosome kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of a condensed chromosome and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
condensed chromosome, centromeric region
The region of a condensed chromosome that includes the centromere and associated proteins, including the kinetochore. In monocentric chromosomes, this region corresponds to a single area of the chromosome, whereas in holocentric chromosomes, it is evenly distributed along the chromosome.
outer kinetochore of condensed chromosome
The region of a condensed chromosome kinetochore most external to centromeric DNA; this outer region mediates kinetochore-microtubule interactions.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
nucleus
A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent.
cytoplasm
All of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
chromosome
A structure composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins (e.g. histones) that carries hereditary information.
spindle
The array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during mitosis or meiosis and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
cytoskeleton
Any of the various filamentous elements that form the internal framework of cells, and typically remain after treatment of the cells with mild detergent to remove membrane constituents and soluble components of the cytoplasm. The term embraces intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, the microtrabecular lattice, and other structures characterized by a polymeric filamentous nature and long-range order within the cell. The various elements of the cytoskeleton not only serve in the maintenance of cellular shape but also have roles in other cellular functions, including cellular movement, cell division, endocytosis, and movement of organelles.
microtubule cytoskeleton
The part of the cytoskeleton (the internal framework of a cell) composed of microtubules and associated proteins.
Ndc80 complex
A protein complex conserved among eukaryotes that forms part of the kinetochore and plays an essential role in forming stable kinetochore-microtubule attachments. The complex contains proteins known in several species, including budding and fission yeasts, as Ndc80p, Nuf2p, Spc24p, and Spc25p. In vertebrates it is part of the outer plate of the kinetochore.
membrane-enclosed lumen
The enclosed volume within a sealed membrane or between two sealed membranes. Encompasses the volume enclosed by the membranes of a particular organelle, e.g. endoplasmic reticulum lumen, or the space between the two lipid bilayers of a double membrane surrounding an organelle, e.g. nuclear envelope lumen.
nuclear lumen
The volume enclosed by the nuclear inner membrane.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
P granule
A small cytoplasmic, non-membranous RNA/protein complex aggregates in the primordial germ cells of many higher eukaryotes.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, and prokaryotic structures such as anammoxosomes and pirellulosomes. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
organelle lumen
The internal volume enclosed by the membranes of a particular organelle; includes the volume enclosed by a single organelle membrane, e.g. endoplasmic reticulum lumen, or the volume enclosed by the innermost of the two lipid bilayers of an organelle envelope, e.g. nuclear lumen.
protein complex
Any macromolecular complex composed of two or more polypeptide subunits, which may or may not be identical. Protein complexes may have other associated non-protein prosthetic groups, such as nucleotides, metal ions or other small molecules.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
chromosomal part
Any constituent part of a chromosome, a structure composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins (e.g. histones) that carries hereditary information.
nuclear part
Any constituent part of the nucleus, a membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
pole plasm
Differentiated cytoplasm associated with a pole (animal, vegetal, anterior, or posterior) of an oocyte, egg or early embryo.
germ plasm
Differentiated cytoplasm associated with a pole of an oocyte, egg or early embryo that will be inherited by the cells that will give rise to the germ line.
intracellular organelle lumen
An organelle lumen that is part of an intracellular organelle.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
organelle lumen
The internal volume enclosed by the membranes of a particular organelle; includes the volume enclosed by a single organelle membrane, e.g. endoplasmic reticulum lumen, or the volume enclosed by the innermost of the two lipid bilayers of an organelle envelope, e.g. nuclear lumen.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle lumen
An organelle lumen that is part of an intracellular organelle.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
Ndc80 complex
A protein complex conserved among eukaryotes that forms part of the kinetochore and plays an essential role in forming stable kinetochore-microtubule attachments. The complex contains proteins known in several species, including budding and fission yeasts, as Ndc80p, Nuf2p, Spc24p, and Spc25p. In vertebrates it is part of the outer plate of the kinetochore.
kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of DNA and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of DNA and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
outer kinetochore of condensed chromosome
The region of a condensed chromosome kinetochore most external to centromeric DNA; this outer region mediates kinetochore-microtubule interactions.
Ndc80 complex
A protein complex conserved among eukaryotes that forms part of the kinetochore and plays an essential role in forming stable kinetochore-microtubule attachments. The complex contains proteins known in several species, including budding and fission yeasts, as Ndc80p, Nuf2p, Spc24p, and Spc25p. In vertebrates it is part of the outer plate of the kinetochore.
nuclear lumen
The volume enclosed by the nuclear inner membrane.
spindle
The array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during mitosis or meiosis and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
P granule
A small cytoplasmic, non-membranous RNA/protein complex aggregates in the primordial germ cells of many higher eukaryotes.
outer kinetochore of condensed chromosome
The region of a condensed chromosome kinetochore most external to centromeric DNA; this outer region mediates kinetochore-microtubule interactions.
nuclear part
Any constituent part of the nucleus, a membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated.
chromosomal part
Any constituent part of a chromosome, a structure composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins (e.g. histones) that carries hereditary information.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of DNA and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
condensed chromosome, centromeric region
The region of a condensed chromosome that includes the centromere and associated proteins, including the kinetochore. In monocentric chromosomes, this region corresponds to a single area of the chromosome, whereas in holocentric chromosomes, it is evenly distributed along the chromosome.
spindle
The array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during mitosis or meiosis and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
condensed chromosome kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of a condensed chromosome and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
P granule
A small cytoplasmic, non-membranous RNA/protein complex aggregates in the primordial germ cells of many higher eukaryotes.

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
nucleic acid binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any nucleic acid.
binding
The selective, non-covalent, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
all
NA
AAGABalpha- and gamma-adaptin binding protein (ENSG00000103591), score: 0.38 AASDHaminoadipate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase (ENSG00000157426), score: 0.47 ABHD12abhydrolase domain containing 12 (ENSG00000100997), score: -0.4 ACTN4actinin, alpha 4 (ENSG00000130402), score: -0.45 ADAD1adenosine deaminase domain containing 1 (testis-specific) (ENSG00000164113), score: 0.44 ADALadenosine deaminase-like (ENSG00000168803), score: 0.39 AFF4AF4/FMR2 family, member 4 (ENSG00000072364), score: -0.44 AGBL3ATP/GTP binding protein-like 3 (ENSG00000146856), score: 0.47 AK7adenylate kinase 7 (ENSG00000140057), score: 0.49 ALG9asparagine-linked glycosylation 9, alpha-1,2-mannosyltransferase homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000086848), score: 0.42 AMHanti-Mullerian hormone (ENSG00000104899), score: 0.45 ANKRD5ankyrin repeat domain 5 (ENSG00000132623), score: 0.44 APPamyloid beta (A4) precursor protein (ENSG00000142192), score: -0.39 APTXaprataxin (ENSG00000137074), score: 0.38 ARHGAP40Rho GTPase activating protein 40 (ENSG00000124143), score: 0.41 ARHGAP42Rho GTPase activating protein 42 (ENSG00000165895), score: 0.4 ARHGEF18Rho/Rac guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 18 (ENSG00000104880), score: -0.41 ARHGEF3Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 3 (ENSG00000163947), score: -0.44 ARIH2ariadne homolog 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000177479), score: -0.49 ARL6IP5ADP-ribosylation-like factor 6 interacting protein 5 (ENSG00000144746), score: -0.39 ARMC4armadillo repeat containing 4 (ENSG00000169126), score: 0.41 ARRDC1arrestin domain containing 1 (ENSG00000197070), score: -0.49 ASB1ankyrin repeat and SOCS box-containing 1 (ENSG00000065802), score: -0.42 ASF1AASF1 anti-silencing function 1 homolog A (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000111875), score: 0.61 ASPMasp (abnormal spindle) homolog, microcephaly associated (Drosophila) (ENSG00000066279), score: 0.61 ATAD2ATPase family, AAA domain containing 2 (ENSG00000156802), score: 0.58 ATP6V0A2ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal V0 subunit a2 (ENSG00000185344), score: 0.42 ATP9AATPase, class II, type 9A (ENSG00000054793), score: -0.39 B3GNT5UDP-GlcNAc:betaGal beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 5 (ENSG00000176597), score: 0.39 BAT2L2HLA-B associated transcript 2-like 2 (ENSG00000117523), score: -0.41 BCDIN3DBCDIN3 domain containing (ENSG00000186666), score: -0.41 BICD2bicaudal D homolog 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000185963), score: -0.53 BMP3bone morphogenetic protein 3 (ENSG00000152785), score: 0.39 BOLLbol, boule-like (Drosophila) (ENSG00000152430), score: 0.42 BRCA2breast cancer 2, early onset (ENSG00000139618), score: 0.44 BRS3bombesin-like receptor 3 (ENSG00000102239), score: 0.56 BTBD1BTB (POZ) domain containing 1 (ENSG00000064726), score: 0.48 BUB1Bbudding uninhibited by benzimidazoles 1 homolog beta (yeast) (ENSG00000156970), score: 0.39 C10orf96chromosome 10 open reading frame 96 (ENSG00000182645), score: 0.52 C11orf30chromosome 11 open reading frame 30 (ENSG00000158636), score: 0.48 C12orf48chromosome 12 open reading frame 48 (ENSG00000185480), score: 0.62 C12orf50chromosome 12 open reading frame 50 (ENSG00000165805), score: 0.45 C13orf34chromosome 13 open reading frame 34 (ENSG00000136122), score: 0.53 C14orf126chromosome 14 open reading frame 126 (ENSG00000129480), score: 0.44 C14orf39chromosome 14 open reading frame 39 (ENSG00000179008), score: 0.65 C14orf50chromosome 14 open reading frame 50 (ENSG00000165807), score: 0.47 C17orf71chromosome 17 open reading frame 71 (ENSG00000167447), score: 0.53 C19orf12chromosome 19 open reading frame 12 (ENSG00000131943), score: -0.45 C1orf100chromosome 1 open reading frame 100 (ENSG00000173728), score: 0.42 C1orf111chromosome 1 open reading frame 111 (ENSG00000171722), score: 0.45 C1orf114chromosome 1 open reading frame 114 (ENSG00000117477), score: 0.43 C1orf158chromosome 1 open reading frame 158 (ENSG00000157330), score: 0.5 C1orf174chromosome 1 open reading frame 174 (ENSG00000198912), score: 0.73 C1orf88chromosome 1 open reading frame 88 (ENSG00000173947), score: 0.46 C1orf9chromosome 1 open reading frame 9 (ENSG00000094975), score: 0.58 C1QTNF7C1q and tumor necrosis factor related protein 7 (ENSG00000163145), score: 0.4 C20orf85chromosome 20 open reading frame 85 (ENSG00000124237), score: 0.39 C3orf38chromosome 3 open reading frame 38 (ENSG00000179021), score: 0.44 C4orf47chromosome 4 open reading frame 47 (ENSG00000205129), score: 0.5 C5orf22chromosome 5 open reading frame 22 (ENSG00000082213), score: -0.42 C5orf51chromosome 5 open reading frame 51 (ENSG00000205765), score: 0.69 C7orf57chromosome 7 open reading frame 57 (ENSG00000164746), score: 0.49 C7orf60chromosome 7 open reading frame 60 (ENSG00000164603), score: 0.55 C7orf62chromosome 7 open reading frame 62 (ENSG00000164645), score: 0.4 C8orf42chromosome 8 open reading frame 42 (ENSG00000180190), score: 0.43 C9orf9chromosome 9 open reading frame 9 (ENSG00000165698), score: 0.4 CAPN13calpain 13 (ENSG00000162949), score: 0.56 CASC1cancer susceptibility candidate 1 (ENSG00000118307), score: 0.49 CASP2caspase 2, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase (ENSG00000106144), score: 0.62 CCDC108coiled-coil domain containing 108 (ENSG00000181378), score: 0.4 CCDC113coiled-coil domain containing 113 (ENSG00000103021), score: 0.45 CCDC122coiled-coil domain containing 122 (ENSG00000151773), score: 0.5 CCDC124coiled-coil domain containing 124 (ENSG00000007080), score: -0.5 CCDC127coiled-coil domain containing 127 (ENSG00000164366), score: -0.44 CCDC27coiled-coil domain containing 27 (ENSG00000162592), score: 0.45 CCDC45coiled-coil domain containing 45 (ENSG00000141325), score: 0.41 CCDC67coiled-coil domain containing 67 (ENSG00000165325), score: 0.43 CCDC93coiled-coil domain containing 93 (ENSG00000125633), score: 0.4 CCNA1cyclin A1 (ENSG00000133101), score: 0.42 CCNYcyclin Y (ENSG00000108100), score: -0.39 CDK13cyclin-dependent kinase 13 (ENSG00000065883), score: 0.41 CENPFcentromere protein F, 350/400kDa (mitosin) (ENSG00000117724), score: 0.42 CENPIcentromere protein I (ENSG00000102384), score: 0.63 CENPKcentromere protein K (ENSG00000123219), score: 0.47 CENPTcentromere protein T (ENSG00000102901), score: 0.48 CEP152centrosomal protein 152kDa (ENSG00000103995), score: 0.39 CEP55centrosomal protein 55kDa (ENSG00000138180), score: 0.4 CERKLceramide kinase-like (ENSG00000188452), score: 0.49 CFLARCASP8 and FADD-like apoptosis regulator (ENSG00000003402), score: -0.4 CHAF1Bchromatin assembly factor 1, subunit B (p60) (ENSG00000159259), score: 0.59 CHERPcalcium homeostasis endoplasmic reticulum protein (ENSG00000085872), score: -0.51 CIAO1cytosolic iron-sulfur protein assembly 1 (ENSG00000144021), score: 0.4 CIRBPcold inducible RNA binding protein (ENSG00000099622), score: -0.47 CLSPNclaspin (ENSG00000092853), score: 0.45 CNGA2cyclic nucleotide gated channel alpha 2 (ENSG00000183862), score: 0.9 CNGB1cyclic nucleotide gated channel beta 1 (ENSG00000070729), score: 0.51 COCHcoagulation factor C homolog, cochlin (Limulus polyphemus) (ENSG00000100473), score: 0.39 COG2component of oligomeric golgi complex 2 (ENSG00000135775), score: 0.43 COG4component of oligomeric golgi complex 4 (ENSG00000103051), score: -0.41 COL17A1collagen, type XVII, alpha 1 (ENSG00000065618), score: 0.63 COPAcoatomer protein complex, subunit alpha (ENSG00000122218), score: -0.5 COQ3coenzyme Q3 homolog, methyltransferase (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000132423), score: 0.41 CPA1carboxypeptidase A1 (pancreatic) (ENSG00000091704), score: 0.67 CPA6carboxypeptidase A6 (ENSG00000165078), score: 0.73 CPEB2cytoplasmic polyadenylation element binding protein 2 (ENSG00000137449), score: 0.39 CPLX4complexin 4 (ENSG00000166569), score: 0.52 CPZcarboxypeptidase Z (ENSG00000109625), score: 0.39 CRADDCASP2 and RIPK1 domain containing adaptor with death domain (ENSG00000169372), score: -0.4 CRBNcereblon (ENSG00000113851), score: -0.41 CREB1cAMP responsive element binding protein 1 (ENSG00000118260), score: -0.38 CREB3cAMP responsive element binding protein 3 (ENSG00000107175), score: -0.49 CRKv-crk sarcoma virus CT10 oncogene homolog (avian) (ENSG00000167193), score: -0.42 CRY2cryptochrome 2 (photolyase-like) (ENSG00000121671), score: -0.5 CTCFCCCTC-binding factor (zinc finger protein) (ENSG00000102974), score: -0.39 CTNNB1catenin (cadherin-associated protein), beta 1, 88kDa (ENSG00000168036), score: -0.41 CUL3cullin 3 (ENSG00000036257), score: 0.43 CXorf23chromosome X open reading frame 23 (ENSG00000173681), score: 0.49 CXorf30chromosome X open reading frame 30 (ENSG00000205081), score: 0.53 CYHR1cysteine/histidine-rich 1 (ENSG00000187954), score: 0.47 CYLDcylindromatosis (turban tumor syndrome) (ENSG00000083799), score: 0.43 CYP11A1cytochrome P450, family 11, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000140459), score: 0.63 DAZAP1DAZ associated protein 1 (ENSG00000071626), score: -0.4 DCLRE1CDNA cross-link repair 1C (ENSG00000152457), score: 0.61 DCTN4dynactin 4 (p62) (ENSG00000132912), score: 0.43 DDAH1dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase 1 (ENSG00000153904), score: -0.39 DDHD1DDHD domain containing 1 (ENSG00000100523), score: 0.41 DDX4DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 4 (ENSG00000152670), score: 0.47 DHRS11dehydrogenase/reductase (SDR family) member 11 (ENSG00000108272), score: -0.48 DMC1DMC1 dosage suppressor of mck1 homolog, meiosis-specific homologous recombination (yeast) (ENSG00000100206), score: 0.49 DMRT3doublesex and mab-3 related transcription factor 3 (ENSG00000064218), score: 0.61 DNAH8dynein, axonemal, heavy chain 8 (ENSG00000124721), score: 0.44 DNAI1dynein, axonemal, intermediate chain 1 (ENSG00000122735), score: 0.46 DNTTIP1deoxynucleotidyltransferase, terminal, interacting protein 1 (ENSG00000101457), score: 0.42 DSCC1defective in sister chromatid cohesion 1 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000136982), score: 0.54 DSELdermatan sulfate epimerase-like (ENSG00000171451), score: 0.46 DTLdenticleless homolog (Drosophila) (ENSG00000143476), score: 0.42 DTX2deltex homolog 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000091073), score: 0.39 E2F4E2F transcription factor 4, p107/p130-binding (ENSG00000205250), score: -0.57 E2F7E2F transcription factor 7 (ENSG00000165891), score: 0.5 EFCAB1EF-hand calcium binding domain 1 (ENSG00000034239), score: 0.59 EFCAB5EF-hand calcium binding domain 5 (ENSG00000176927), score: 0.43 EIF2S1eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2, subunit 1 alpha, 35kDa (ENSG00000134001), score: 0.47 ENPP7ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 7 (ENSG00000182156), score: 0.41 EPC2enhancer of polycomb homolog 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000135999), score: 0.45 EPYCepiphycan (ENSG00000083782), score: 0.41 ERCC6Lexcision repair cross-complementing rodent repair deficiency, complementation group 6-like (ENSG00000186871), score: 0.66 ERLEC1endoplasmic reticulum lectin 1 (ENSG00000068912), score: 0.49 ESYT2extended synaptotagmin-like protein 2 (ENSG00000117868), score: -0.51 EXO1exonuclease 1 (ENSG00000174371), score: 0.52 EXOSC1exosome component 1 (ENSG00000171311), score: 0.55 EXOSC10exosome component 10 (ENSG00000171824), score: 0.74 EXOSC2exosome component 2 (ENSG00000130713), score: 0.48 FAM163Afamily with sequence similarity 163, member A (ENSG00000143340), score: 0.42 FAM194Afamily with sequence similarity 194, member A (ENSG00000163645), score: 0.43 FAM20Bfamily with sequence similarity 20, member B (ENSG00000116199), score: -0.46 FAM54Afamily with sequence similarity 54, member A (ENSG00000146410), score: 0.38 FAM57Afamily with sequence similarity 57, member A (ENSG00000167695), score: 0.39 FAM65Afamily with sequence similarity 65, member A (ENSG00000039523), score: -0.4 FAM81Bfamily with sequence similarity 81, member B (ENSG00000153347), score: 0.4 FANCBFanconi anemia, complementation group B (ENSG00000181544), score: 1 FBRSL1fibrosin-like 1 (ENSG00000112787), score: -0.4 FBXO21F-box protein 21 (ENSG00000135108), score: -0.52 FBXO42F-box protein 42 (ENSG00000037637), score: 0.43 FBXO47F-box protein 47 (ENSG00000204952), score: 0.56 FIG4FIG4 homolog, SAC1 lipid phosphatase domain containing (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000112367), score: 0.39 FLNBfilamin B, beta (ENSG00000136068), score: -0.47 FOXJ1forkhead box J1 (ENSG00000129654), score: 0.45 FOXP1forkhead box P1 (ENSG00000114861), score: -0.5 GABPB1GA binding protein transcription factor, beta subunit 1 (ENSG00000104064), score: 0.49 GAMTguanidinoacetate N-methyltransferase (ENSG00000130005), score: -0.39 GCM1glial cells missing homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000137270), score: 0.56 GDPD4glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase domain containing 4 (ENSG00000178795), score: 0.45 GEMC1geminin coiled-coil domain-containing protein 1 (ENSG00000205835), score: 0.51 GFOD2glucose-fructose oxidoreductase domain containing 2 (ENSG00000141098), score: -0.4 GGCTgamma-glutamylcyclotransferase (ENSG00000006625), score: 0.39 GNL2guanine nucleotide binding protein-like 2 (nucleolar) (ENSG00000134697), score: 0.46 GNL3guanine nucleotide binding protein-like 3 (nucleolar) (ENSG00000163938), score: -0.39 GPATCH2G patch domain containing 2 (ENSG00000092978), score: 0.53 GPN3GPN-loop GTPase 3 (ENSG00000111231), score: -0.47 GPR12G protein-coupled receptor 12 (ENSG00000132975), score: 0.39 GPR20G protein-coupled receptor 20 (ENSG00000204882), score: 0.78 GRXCR1glutaredoxin, cysteine rich 1 (ENSG00000215203), score: 0.72 GTPBP5GTP binding protein 5 (putative) (ENSG00000101181), score: -0.42 HDXhighly divergent homeobox (ENSG00000165259), score: 0.41 HELQhelicase, POLQ-like (ENSG00000163312), score: 0.56 HERPUD2HERPUD family member 2 (ENSG00000122557), score: 0.44 HMOX2heme oxygenase (decycling) 2 (ENSG00000103415), score: 0.41 HOOK1hook homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000134709), score: 0.41 HORMAD1HORMA domain containing 1 (ENSG00000143452), score: 0.51 HORMAD2HORMA domain containing 2 (ENSG00000176635), score: 0.54 HRH4histamine receptor H4 (ENSG00000134489), score: 0.5 HSCBHscB iron-sulfur cluster co-chaperone homolog (E. coli) (ENSG00000100209), score: 0.45 ING3inhibitor of growth family, member 3 (ENSG00000071243), score: 0.53 INTS12integrator complex subunit 12 (ENSG00000138785), score: 0.42 IP6K3inositol hexakisphosphate kinase 3 (ENSG00000161896), score: 0.41 IQCHIQ motif containing H (ENSG00000103599), score: 0.42 IQUBIQ motif and ubiquitin domain containing (ENSG00000164675), score: 0.5 ISG20L2interferon stimulated exonuclease gene 20kDa-like 2 (ENSG00000143319), score: 0.45 ITIH5inter-alpha (globulin) inhibitor H5 (ENSG00000123243), score: 0.42 ITM2Bintegral membrane protein 2B (ENSG00000136156), score: -0.4 JMJD1Cjumonji domain containing 1C (ENSG00000171988), score: -0.4 KDELC1KDEL (Lys-Asp-Glu-Leu) containing 1 (ENSG00000134901), score: 0.39 KIAA0892KIAA0892 (ENSG00000129933), score: -0.57 KIAA1407KIAA1407 (ENSG00000163617), score: 0.48 KIAA1712KIAA1712 (ENSG00000164118), score: 0.4 KIF11kinesin family member 11 (ENSG00000138160), score: 0.51 KIF14kinesin family member 14 (ENSG00000118193), score: 0.54 KIF2Bkinesin family member 2B (ENSG00000141200), score: 0.48 KIF6kinesin family member 6 (ENSG00000164627), score: 0.49 KLF11Kruppel-like factor 11 (ENSG00000172059), score: 0.46 KLF15Kruppel-like factor 15 (ENSG00000163884), score: -0.41 KLHL10kelch-like 10 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000161594), score: 0.44 KLHL22kelch-like 22 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000099910), score: -0.4 LBRlamin B receptor (ENSG00000143815), score: 0.43 LCORLligand dependent nuclear receptor corepressor-like (ENSG00000178177), score: 0.67 LCTlactase (ENSG00000115850), score: 0.73 LHCGRluteinizing hormone/choriogonadotropin receptor (ENSG00000138039), score: 0.73 LIN28Blin-28 homolog B (C. elegans) (ENSG00000187772), score: 0.61 LMO2LIM domain only 2 (rhombotin-like 1) (ENSG00000135363), score: -0.4 LOH12CR1loss of heterozygosity, 12, chromosomal region 1 (ENSG00000165714), score: 0.4 LPIN1lipin 1 (ENSG00000134324), score: -0.41 LRGUKleucine-rich repeats and guanylate kinase domain containing (ENSG00000155530), score: 0.53 LRP2BPLRP2 binding protein (ENSG00000109771), score: 0.39 LRRC18leucine rich repeat containing 18 (ENSG00000165383), score: 0.56 LRRC43leucine rich repeat containing 43 (ENSG00000158113), score: 0.47 LRRC52leucine rich repeat containing 52 (ENSG00000162763), score: 0.62 LRRC67leucine rich repeat containing 67 (ENSG00000178125), score: 0.49 LRRIQ1leucine-rich repeats and IQ motif containing 1 (ENSG00000133640), score: 0.39 LRRIQ4leucine-rich repeats and IQ motif containing 4 (ENSG00000188306), score: 0.55 LTA4Hleukotriene A4 hydrolase (ENSG00000111144), score: -0.41 LYPD2LY6/PLAUR domain containing 2 (ENSG00000197353), score: 0.53 MAP1LC3Amicrotubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 alpha (ENSG00000101460), score: -0.42 MAP2K6mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 6 (ENSG00000108984), score: 0.44 MAP3K5mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 5 (ENSG00000197442), score: -0.5 MAP9microtubule-associated protein 9 (ENSG00000164114), score: 0.48 MAPK15mitogen-activated protein kinase 15 (ENSG00000181085), score: 0.47 MBOAT1membrane bound O-acyltransferase domain containing 1 (ENSG00000172197), score: 0.39 MCM5minichromosome maintenance complex component 5 (ENSG00000100297), score: 0.39 MCM6minichromosome maintenance complex component 6 (ENSG00000076003), score: 0.4 MED14mediator complex subunit 14 (ENSG00000180182), score: 0.38 MED17mediator complex subunit 17 (ENSG00000042429), score: 0.43 MED7mediator complex subunit 7 (ENSG00000155868), score: 0.51 MELKmaternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase (ENSG00000165304), score: 0.54 MKKSMcKusick-Kaufman syndrome (ENSG00000125863), score: -0.39 MKRN2makorin ring finger protein 2 (ENSG00000075975), score: 0.4 MLLT1myeloid/lymphoid or mixed-lineage leukemia (trithorax homolog, Drosophila); translocated to, 1 (ENSG00000130382), score: -0.5 MLLT6myeloid/lymphoid or mixed-lineage leukemia (trithorax homolog, Drosophila); translocated to, 6 (ENSG00000108292), score: -0.45 MND1meiotic nuclear divisions 1 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000121211), score: 0.4 MOV10L1Mov10l1, Moloney leukemia virus 10-like 1, homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000073146), score: 0.45 MRPL12mitochondrial ribosomal protein L12 (ENSG00000183093), score: -0.43 MSH6mutS homolog 6 (E. coli) (ENSG00000116062), score: 0.38 MTF1metal-regulatory transcription factor 1 (ENSG00000188786), score: 0.5 MTF2metal response element binding transcription factor 2 (ENSG00000143033), score: 0.69 MTMR12myotubularin related protein 12 (ENSG00000150712), score: -0.44 MYBL1v-myb myeloblastosis viral oncogene homolog (avian)-like 1 (ENSG00000185697), score: 0.5 MYO10myosin X (ENSG00000145555), score: -0.43 MYO18Amyosin XVIIIA (ENSG00000196535), score: -0.58 NBR1neighbor of BRCA1 gene 1 (ENSG00000188554), score: 0.53 NCAPD2non-SMC condensin I complex, subunit D2 (ENSG00000010292), score: 0.43 NCAPGnon-SMC condensin I complex, subunit G (ENSG00000109805), score: 0.43 NCAPG2non-SMC condensin II complex, subunit G2 (ENSG00000146918), score: 0.39 NDC80NDC80 homolog, kinetochore complex component (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000080986), score: 0.5 NEK9NIMA (never in mitosis gene a)- related kinase 9 (ENSG00000119638), score: -0.4 NIPAL4NIPA-like domain containing 4 (ENSG00000172548), score: 0.54 NISCHnischarin (ENSG00000010322), score: -0.43 NPATnuclear protein, ataxia-telangiectasia locus (ENSG00000149308), score: 0.42 NPRL2nitrogen permease regulator-like 2 (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000114388), score: -0.58 NR5A1nuclear receptor subfamily 5, group A, member 1 (ENSG00000136931), score: 0.57 NSMAFneutral sphingomyelinase (N-SMase) activation associated factor (ENSG00000035681), score: -0.42 NUB1negative regulator of ubiquitin-like proteins 1 (ENSG00000013374), score: 0.42 NUF2NUF2, NDC80 kinetochore complex component, homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000143228), score: 0.43 NUFIP1nuclear fragile X mental retardation protein interacting protein 1 (ENSG00000083635), score: 0.38 NUP133nucleoporin 133kDa (ENSG00000069248), score: 0.4 ORC3Lorigin recognition complex, subunit 3-like (yeast) (ENSG00000135336), score: 0.7 ORC4Lorigin recognition complex, subunit 4-like (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000115947), score: 0.46 OSBPL2oxysterol binding protein-like 2 (ENSG00000130703), score: -0.46 OSGIN2oxidative stress induced growth inhibitor family member 2 (ENSG00000164823), score: 0.42 OXTRoxytocin receptor (ENSG00000180914), score: 0.69 PAX5paired box 5 (ENSG00000196092), score: 0.67 PAX9paired box 9 (ENSG00000198807), score: 0.71 PDCD2Lprogrammed cell death 2-like (ENSG00000126249), score: 0.44 PFKFB26-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 2 (ENSG00000123836), score: 0.42 PHEXphosphate regulating endopeptidase homolog, X-linked (ENSG00000102174), score: 0.55 PHF6PHD finger protein 6 (ENSG00000156531), score: 0.44 PHTF1putative homeodomain transcription factor 1 (ENSG00000116793), score: 0.4 PI15peptidase inhibitor 15 (ENSG00000137558), score: 0.59 PIH1D2PIH1 domain containing 2 (ENSG00000150773), score: 0.48 PIK3C3phosphoinositide-3-kinase, class 3 (ENSG00000078142), score: 0.51 PIWIL1piwi-like 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000125207), score: 0.48 PLDNpallidin homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000104164), score: 0.39 PLEKHM2pleckstrin homology domain containing, family M (with RUN domain) member 2 (ENSG00000116786), score: -0.5 PNPLA6patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 6 (ENSG00000032444), score: -0.46 POC5POC5 centriolar protein homolog (Chlamydomonas) (ENSG00000152359), score: 0.39 POLD3polymerase (DNA-directed), delta 3, accessory subunit (ENSG00000077514), score: 0.4 POLGpolymerase (DNA directed), gamma (ENSG00000140521), score: -0.42 POLR3Fpolymerase (RNA) III (DNA directed) polypeptide F, 39 kDa (ENSG00000132664), score: 0.44 POMGNT1protein O-linked mannose beta1,2-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (ENSG00000085998), score: -0.43 PPARGC1Bperoxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma, coactivator 1 beta (ENSG00000155846), score: 0.39 PPEF2protein phosphatase, EF-hand calcium binding domain 2 (ENSG00000156194), score: 0.6 PPM1Mprotein phosphatase, Mg2+/Mn2+ dependent, 1M (ENSG00000164088), score: -0.44 PPYR1pancreatic polypeptide receptor 1 (ENSG00000204174), score: 0.65 PRKAA1protein kinase, AMP-activated, alpha 1 catalytic subunit (ENSG00000132356), score: 0.4 PSKH1protein serine kinase H1 (ENSG00000159792), score: -0.38 PSMC2proteasome (prosome, macropain) 26S subunit, ATPase, 2 (ENSG00000161057), score: 0.41 PSMD6proteasome (prosome, macropain) 26S subunit, non-ATPase, 6 (ENSG00000163636), score: -0.53 PTHLHparathyroid hormone-like hormone (ENSG00000087494), score: 0.46 PUS7pseudouridylate synthase 7 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000091127), score: 0.47 PVRL3poliovirus receptor-related 3 (ENSG00000177707), score: 0.39 RAB11ARAB11A, member RAS oncogene family (ENSG00000103769), score: 0.44 RAD54BRAD54 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000197275), score: 0.67 RANBP3RAN binding protein 3 (ENSG00000031823), score: -0.46 RAPSNreceptor-associated protein of the synapse (ENSG00000165917), score: 0.44 RASEFRAS and EF-hand domain containing (ENSG00000165105), score: 0.54 RAVER2ribonucleoprotein, PTB-binding 2 (ENSG00000162437), score: 0.47 RBM46RNA binding motif protein 46 (ENSG00000151962), score: 0.56 RBP2retinol binding protein 2, cellular (ENSG00000114113), score: 0.9 RCHY1ring finger and CHY zinc finger domain containing 1 (ENSG00000163743), score: 0.47 RCOR3REST corepressor 3 (ENSG00000117625), score: -0.41 RECKreversion-inducing-cysteine-rich protein with kazal motifs (ENSG00000122707), score: 0.42 RHOT1ras homolog gene family, member T1 (ENSG00000126858), score: -0.39 RHOT2ras homolog gene family, member T2 (ENSG00000140983), score: -0.41 RIBC2RIB43A domain with coiled-coils 2 (ENSG00000128408), score: 0.51 RIOK2RIO kinase 2 (yeast) (ENSG00000058729), score: 0.5 RNF17ring finger protein 17 (ENSG00000132972), score: 0.4 RNF182ring finger protein 182 (ENSG00000180537), score: 0.42 RNF20ring finger protein 20 (ENSG00000155827), score: -0.45 RNF32ring finger protein 32 (ENSG00000105982), score: 0.4 RPAP2RNA polymerase II associated protein 2 (ENSG00000122484), score: 0.61 RRM1ribonucleotide reductase M1 (ENSG00000167325), score: 0.4 RRP9ribosomal RNA processing 9, small subunit (SSU) processome component, homolog (yeast) (ENSG00000114767), score: -0.49 RSPH9radial spoke head 9 homolog (Chlamydomonas) (ENSG00000172426), score: 0.46 RUSC2RUN and SH3 domain containing 2 (ENSG00000198853), score: -0.41 SASH1SAM and SH3 domain containing 1 (ENSG00000111961), score: -0.45 SDC4syndecan 4 (ENSG00000124145), score: -0.47 SEC13SEC13 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000157020), score: -0.47 SEPT11septin 11 (ENSG00000138758), score: -0.39 SEPT6septin 6 (ENSG00000125354), score: -0.41 SGCZsarcoglycan, zeta (ENSG00000185053), score: 0.47 SGOL1shugoshin-like 1 (S. pombe) (ENSG00000129810), score: 0.62 SLAIN2SLAIN motif family, member 2 (ENSG00000109171), score: 0.43 SLC1A7solute carrier family 1 (glutamate transporter), member 7 (ENSG00000162383), score: 0.4 SLC26A8solute carrier family 26, member 8 (ENSG00000112053), score: 0.44 SLC41A2solute carrier family 41, member 2 (ENSG00000136052), score: 0.43 SLC6A14solute carrier family 6 (amino acid transporter), member 14 (ENSG00000087916), score: 0.97 SMC1Bstructural maintenance of chromosomes 1B (ENSG00000077935), score: 0.47 SNX16sorting nexin 16 (ENSG00000104497), score: 0.46 SNX2sorting nexin 2 (ENSG00000205302), score: -0.42 SOS1son of sevenless homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000115904), score: -0.46 SPACA1sperm acrosome associated 1 (ENSG00000118434), score: 0.45 SPATA5L1spermatogenesis associated 5-like 1 (ENSG00000171763), score: 0.39 SPATS2spermatogenesis associated, serine-rich 2 (ENSG00000123352), score: 0.42 SPC25SPC25, NDC80 kinetochore complex component, homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000152253), score: 0.54 SPHK1sphingosine kinase 1 (ENSG00000176170), score: 0.43 SPO11SPO11 meiotic protein covalently bound to DSB homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000054796), score: 0.39 SPRY4sprouty homolog 4 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000187678), score: -0.41 SPTBN1spectrin, beta, non-erythrocytic 1 (ENSG00000115306), score: -0.41 SQSTM1sequestosome 1 (ENSG00000161011), score: -0.45 SRSF4serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 4 (ENSG00000116350), score: -0.43 SRSF5serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 5 (ENSG00000100650), score: -0.48 SS18synovial sarcoma translocation, chromosome 18 (ENSG00000141380), score: 0.46 SSH1slingshot homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000084112), score: -0.4 ST6GALNAC6ST6 (alpha-N-acetyl-neuraminyl-2,3-beta-galactosyl-1,3)-N-acetylgalactosaminide alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase 6 (ENSG00000160408), score: -0.43 STIM2stromal interaction molecule 2 (ENSG00000109689), score: 0.4 STOML2stomatin (EPB72)-like 2 (ENSG00000165283), score: -0.47 STOML3stomatin (EPB72)-like 3 (ENSG00000133115), score: 0.46 STRA8stimulated by retinoic acid gene 8 homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000146857), score: 0.63 STRADASTE20-related kinase adaptor alpha (ENSG00000125695), score: 0.48 SUFUsuppressor of fused homolog (Drosophila) (ENSG00000107882), score: 0.44 SWAP70SWAP switching B-cell complex 70kDa subunit (ENSG00000133789), score: -0.42 SYCP1synaptonemal complex protein 1 (ENSG00000198765), score: 0.51 TAAR2trace amine associated receptor 2 (ENSG00000146378), score: 0.58 TACC2transforming, acidic coiled-coil containing protein 2 (ENSG00000138162), score: -0.4 TADA3transcriptional adaptor 3 (ENSG00000171148), score: -0.39 TATDN3TatD DNase domain containing 3 (ENSG00000203705), score: -0.46 TBX4T-box 4 (ENSG00000121075), score: 0.81 TDRD1tudor domain containing 1 (ENSG00000095627), score: 0.53 TDRD5tudor domain containing 5 (ENSG00000162782), score: 0.44 TDRD6tudor domain containing 6 (ENSG00000180113), score: 0.44 TEKT3tektin 3 (ENSG00000125409), score: 0.46 TEKT5tektin 5 (ENSG00000153060), score: 0.46 TEX9testis expressed 9 (ENSG00000151575), score: 0.5 THAP11THAP domain containing 11 (ENSG00000168286), score: -0.49 TIMM44translocase of inner mitochondrial membrane 44 homolog (yeast) (ENSG00000104980), score: -0.45 TMEM168transmembrane protein 168 (ENSG00000146802), score: 0.44 TMEM60transmembrane protein 60 (ENSG00000135211), score: 0.4 TNKStankyrase, TRF1-interacting ankyrin-related ADP-ribose polymerase (ENSG00000173273), score: 0.39 TOP2Atopoisomerase (DNA) II alpha 170kDa (ENSG00000131747), score: 0.49 TPRA1transmembrane protein, adipocyte asscociated 1 (ENSG00000163870), score: -0.54 TPRG1Ltumor protein p63 regulated 1-like (ENSG00000158109), score: -0.48 TPX2TPX2, microtubule-associated, homolog (Xenopus laevis) (ENSG00000088325), score: 0.44 TRMT61AtRNA methyltransferase 61 homolog A (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000166166), score: 0.38 TRPC6transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily C, member 6 (ENSG00000137672), score: 0.62 TSGA14testis specific, 14 (ENSG00000106477), score: 0.43 TTC25tetratricopeptide repeat domain 25 (ENSG00000204815), score: 0.48 TTC27tetratricopeptide repeat domain 27 (ENSG00000018699), score: 0.62 TTKTTK protein kinase (ENSG00000112742), score: 0.54 TUBGCP2tubulin, gamma complex associated protein 2 (ENSG00000130640), score: -0.46 TXNRD1thioredoxin reductase 1 (ENSG00000198431), score: -0.5 UBA6ubiquitin-like modifier activating enzyme 6 (ENSG00000033178), score: 0.48 UBE2R2ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2R 2 (ENSG00000107341), score: 0.51 UBE4Aubiquitination factor E4A (UFD2 homolog, yeast) (ENSG00000110344), score: 0.64 UBXN4UBX domain protein 4 (ENSG00000144224), score: 0.45 UGCGUDP-glucose ceramide glucosyltransferase (ENSG00000148154), score: -0.41 USP3ubiquitin specific peptidase 3 (ENSG00000140455), score: -0.43 USP49ubiquitin specific peptidase 49 (ENSG00000164663), score: 0.54 USP8ubiquitin specific peptidase 8 (ENSG00000138592), score: 0.44 UTP15UTP15, U3 small nucleolar ribonucleoprotein, homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000164338), score: 0.4 VGLL1vestigial like 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000102243), score: 0.4 VPS4Bvacuolar protein sorting 4 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000119541), score: 0.46 WDHD1WD repeat and HMG-box DNA binding protein 1 (ENSG00000198554), score: 0.45 WDR16WD repeat domain 16 (ENSG00000166596), score: 0.45 WDR3WD repeat domain 3 (ENSG00000065183), score: 0.44 WDR64WD repeat domain 64 (ENSG00000162843), score: 0.47 WDR76WD repeat domain 76 (ENSG00000092470), score: 0.52 WDR78WD repeat domain 78 (ENSG00000152763), score: 0.57 WHSC2Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome candidate 2 (ENSG00000185049), score: 0.49 XRCC6BP1XRCC6 binding protein 1 (ENSG00000166896), score: 0.42 YAF2YY1 associated factor 2 (ENSG00000015153), score: 0.39 YOD1YOD1 OTU deubiquinating enzyme 1 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000180667), score: 0.51 ZBTB40zinc finger and BTB domain containing 40 (ENSG00000184677), score: 0.54 ZC3H7Bzinc finger CCCH-type containing 7B (ENSG00000100403), score: -0.48 ZC3HC1zinc finger, C3HC-type containing 1 (ENSG00000091732), score: 0.39 ZDHHC7zinc finger, DHHC-type containing 7 (ENSG00000153786), score: -0.48 ZHX3zinc fingers and homeoboxes 3 (ENSG00000174306), score: -0.48 ZNF366zinc finger protein 366 (ENSG00000178175), score: 0.61 ZNF438zinc finger protein 438 (ENSG00000183621), score: 0.7 ZNF507zinc finger protein 507 (ENSG00000168813), score: 0.44 ZNF644zinc finger protein 644 (ENSG00000122482), score: 0.59 ZNRF4zinc and ring finger 4 (ENSG00000105428), score: 0.41 ZPBPzona pellucida binding protein (ENSG00000042813), score: 0.47 ZPBP2zona pellucida binding protein 2 (ENSG00000186075), score: 0.41
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| oan_ts_m2_ca1 | oan | ts | m | 2 |
| oan_ts_m1_ca1 | oan | ts | m | 1 |
| oan_ts_m3_ca1 | oan | ts | m | 3 |