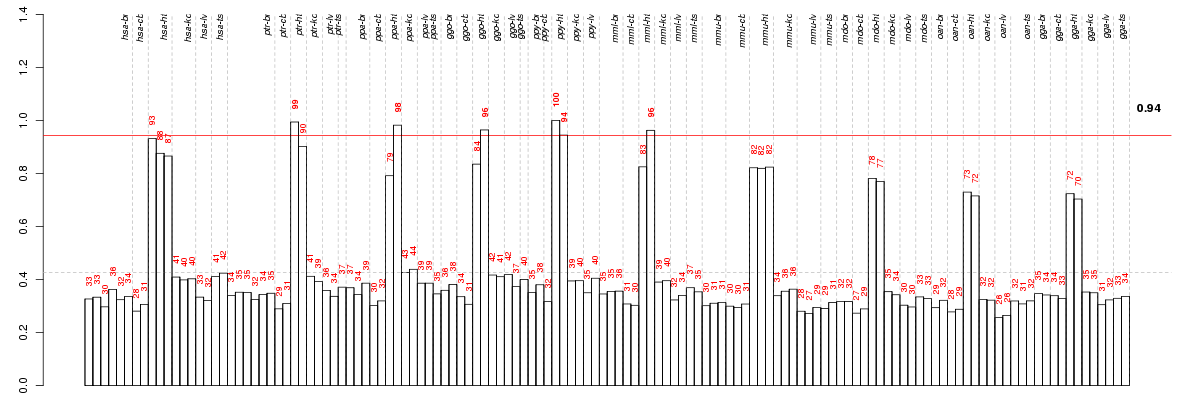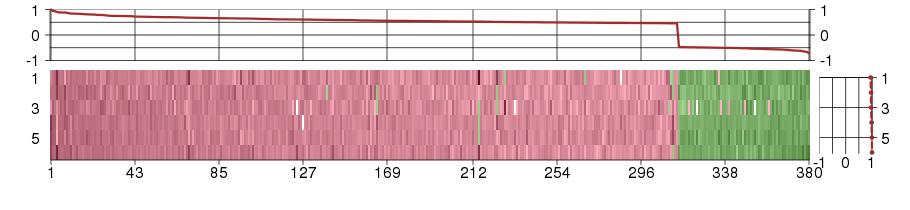

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
heart morphogenesis
The developmental process by which the heart is generated and organized. The heart is a hollow, muscular organ, which, by contracting rhythmically, keeps up the circulation of the blood.
system process
A multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system. An organ system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a biological objective.
muscle system process
A organ system process carried out at the level of a muscle. Muscle tissue is composed of contractile cells or fibers.
circulatory system process
A organ system process carried out by any of the organs or tissues of the circulatory system. The circulatory system is an organ system that moves extracellular fluids to and from tissue within a multicellular organism.
heart process
A circulatory system process carried out by the heart. The heart is a hollow, muscular organ, which, by contracting rhythmically, keeps up the circulation of the blood. The heart is a hollow, muscular organ, which, by contracting rhythmically, keeps up the circulation of the blood.
cardiac chamber development
The progression of a cardiac chamber over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A cardiac chamber is an enclosed cavity within the heart.
cardiac chamber morphogenesis
The process by which a cardiac chamber is generated and organized. A cardiac chamber is an enclosed cavity within the heart.
cardiac ventricle morphogenesis
The process by which the cardiac ventricle is generated and organized. A cardiac ventricle receives blood from a cardiac atrium and pumps it out of the heart.
ventricular cardiac muscle tissue development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of ventricular cardiac muscle over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
cardiac ventricle development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cardiac ventricle over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A cardiac ventricle receives blood from a cardiac atrium and pumps it out of the heart.
muscle contraction
A process whereby force is generated within muscle tissue, resulting in a change in muscle geometry. Force generation involves a chemo-mechanical energy conversion step that is carried out by the actin/myosin complex activity, which generates force through ATP hydrolysis.
generation of precursor metabolites and energy
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of precursor metabolites, substances from which energy is derived, and any process involved in the liberation of energy from these substances.
transport
The directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells, or within a multicellular organism by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis of an organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
tissue development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a tissue over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
heart development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the heart over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The heart is a hollow, muscular organ, which, by contracting rhythmically, keeps up the circulation of the blood.
muscle organ development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the muscle over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The muscle is an organ consisting of a tissue made up of various elongated cells that are specialized to contract and thus to produce movement and mechanical work.
blood circulation
The flow of blood through the body of an animal, enabling the transport of nutrients to the tissues and the removal of waste products.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
actin filament-based movement
Movement of organelles or other particles along actin filaments, or sliding of actin filaments past each other, mediated by motor proteins.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
striated muscle tissue development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a striated muscle over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Striated muscle contain fibers that are divided by transverse bands into striations, and cardiac and skeletal muscle are types of striated muscle. Skeletal muscle myoblasts fuse to form myotubes and eventually multinucleated muscle fibers. The fusion of cardiac cells is very rare and can only form binucleate cells.
energy derivation by oxidation of organic compounds
The chemical reactions and pathways by which a cell derives energy from organic compounds; results in the oxidation of the compounds from which energy is released.
actin filament-based process
Any cellular process that depends upon or alters the actin cytoskeleton, that part of the cytoskeleton comprising actin filaments and their associated proteins.
muscle filament sliding
The sliding of actin thin filaments and myosin thick filaments past each other in muscle contraction. This involves a process of interaction of myosin located on a thick filament with actin located on a thin filament. During this process ATP is split and forces are generated.
cytoskeleton-dependent intracellular transport
The directed movement of substances along cytoskeletal elements such as microfilaments or microtubules within a cell.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
actin-myosin filament sliding
The sliding movement of actin thin filaments and myosin thick filaments past each other.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cellular respiration
The enzymatic release of energy from organic compounds (especially carbohydrates and fats) which either requires oxygen (aerobic respiration) or does not (anaerobic respiration).
intracellular transport
The directed movement of substances within a cell.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
tissue morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a tissue are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
cardiac muscle tissue development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of cardiac muscle over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
cellular localization
Any process by which a substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in, a specific location within or in the membrane of a cell.
establishment of localization in cell
The directed movement of a substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location within, or in the membrane of, a cell.
cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of cardiac muscle tissue are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of cardiac ventricle muscle is generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
heart contraction
The multicellular organismal process by which the heart decreases in volume in a characteristic way to propel blood through the body.
muscle tissue morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of muscle tissue are generated and organized. Muscle tissue consists of a set of cells that are part of an organ and carry out a contractive function. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
muscle tissue development
The progression of muscle tissue over time, from its initial formation to its mature state. Muscle tissue is a contractile tissue made up of actin and myosin fibers.
muscle structure development
The progression of a muscle structure over time, from its formation to its mature state. Muscle structures are contractile cells, tissues or organs that are found in multicellular organisms.
actin-mediated cell contraction
The actin filament-based process by which cytoplasmic actin filaments slide past one another resulting in contraction of all or part of the cell body.
all
NA
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
cellular localization
Any process by which a substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in, a specific location within or in the membrane of a cell.
establishment of localization in cell
The directed movement of a substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location within, or in the membrane of, a cell.
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
intracellular transport
The directed movement of substances within a cell.
actin-myosin filament sliding
The sliding movement of actin thin filaments and myosin thick filaments past each other.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
tissue morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a tissue are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
cardiac chamber morphogenesis
The process by which a cardiac chamber is generated and organized. A cardiac chamber is an enclosed cavity within the heart.
tissue morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a tissue are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis of an organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
tissue development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a tissue over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
muscle organ development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the muscle over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The muscle is an organ consisting of a tissue made up of various elongated cells that are specialized to contract and thus to produce movement and mechanical work.
muscle filament sliding
The sliding of actin thin filaments and myosin thick filaments past each other in muscle contraction. This involves a process of interaction of myosin located on a thick filament with actin located on a thin filament. During this process ATP is split and forces are generated.
heart contraction
The multicellular organismal process by which the heart decreases in volume in a characteristic way to propel blood through the body.
cardiac chamber morphogenesis
The process by which a cardiac chamber is generated and organized. A cardiac chamber is an enclosed cavity within the heart.
cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of cardiac muscle tissue are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
cardiac ventricle morphogenesis
The process by which the cardiac ventricle is generated and organized. A cardiac ventricle receives blood from a cardiac atrium and pumps it out of the heart.
heart morphogenesis
The developmental process by which the heart is generated and organized. The heart is a hollow, muscular organ, which, by contracting rhythmically, keeps up the circulation of the blood.
cardiac chamber development
The progression of a cardiac chamber over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A cardiac chamber is an enclosed cavity within the heart.
muscle tissue development
The progression of muscle tissue over time, from its initial formation to its mature state. Muscle tissue is a contractile tissue made up of actin and myosin fibers.
actin filament-based movement
Movement of organelles or other particles along actin filaments, or sliding of actin filaments past each other, mediated by motor proteins.
ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of cardiac ventricle muscle is generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
cardiac muscle tissue development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of cardiac muscle over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of cardiac muscle tissue are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of cardiac ventricle muscle is generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
contractile fiber
Fibers, composed of actin, myosin, and associated proteins, found in cells of smooth or striated muscle.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
mitochondrion
A semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration.
extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cytoplasm
All of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
mitochondrial envelope
The double lipid bilayer enclosing the mitochondrion and separating its contents from the cell cytoplasm; includes the intermembrane space.
mitochondrial inner membrane
The inner, i.e. lumen-facing, lipid bilayer of the mitochondrial envelope. It is highly folded to form cristae.
mitochondrial respiratory chain
The protein complexes that form the mitochondrial electron transport system (the respiratory chain), associated with the inner mitochondrial membrane. The respiratory chain complexes transfer electrons from an electron donor to an electron acceptor and are associated with a proton pump to create a transmembrane electrochemical gradient.
cytoskeleton
Any of the various filamentous elements that form the internal framework of cells, and typically remain after treatment of the cells with mild detergent to remove membrane constituents and soluble components of the cytoplasm. The term embraces intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, the microtrabecular lattice, and other structures characterized by a polymeric filamentous nature and long-range order within the cell. The various elements of the cytoskeleton not only serve in the maintenance of cellular shape but also have roles in other cellular functions, including cellular movement, cell division, endocytosis, and movement of organelles.
striated muscle thin filament
Filaments formed of actin and associated proteins; attached to Z discs at either end of sarcomeres in myofibrils.
adherens junction
A cell junction at which anchoring proteins (cadherins or integrins) extend through the plasma membrane and are attached to actin filaments.
actin cytoskeleton
The part of the cytoskeleton (the internal framework of a cell) composed of actin and associated proteins. Includes actin cytoskeleton-associated complexes.
organelle inner membrane
The inner, i.e. lumen-facing, lipid bilayer of an organelle envelope; usually highly selective to most ions and metabolites.
myofibril
The contractile element of skeletal and cardiac muscle; a long, highly organized bundle of actin, myosin, and other proteins that contracts by a sliding filament mechanism.
sarcomere
The repeating unit of a myofibril in a muscle cell, composed of an array of overlapping thick and thin filaments between two adjacent Z discs.
Z disc
Platelike region of a muscle sarcomere to which the plus ends of actin filaments are attached.
cell junction
A plasma membrane part that forms a specialized region of connection between two cells or between a cell and the extracellular matrix. At a cell junction, anchoring proteins extend through the plasma membrane to link cytoskeletal proteins in one cell to cytoskeletal proteins in neighboring cells or to proteins in the extracellular matrix.
extracellular matrix
A structure lying external to one or more cells, which provides structural support for cells or tissues; may be completely external to the cell (as in animals) or be part of the cell (as in plants).
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
pseudopodium
A temporary protrusion or retractile process of a cell, associated with flowing movements of the protoplasm, and serving for locomotion and feeding.
I band
A region of a sarcomere that appears as a light band on each side of the Z disc, comprising a region of the sarcomere where thin (actin) filaments are not overlapped by thick (myosin) filaments; contains actin, troponin, and tropomyosin; each sarcomere includes half of an I band at each end.
mitochondrial membrane
Either of the lipid bilayers that surround the mitochondrion and form the mitochondrial envelope.
organelle envelope
A double membrane structure enclosing an organelle, including two lipid bilayers and the region between them. In some cases, an organelle envelope may have more than two membranes.
envelope
A multilayered structure surrounding all or part of a cell; encompasses one or more lipid bilayers, and may include a cell wall layer; also includes the space between layers.
cell projection
A prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, and prokaryotic structures such as anammoxosomes and pirellulosomes. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
mitochondrial part
Any constituent part of a mitochondrion, a semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
contractile fiber part
Any constituent part of a contractile fiber, a fiber composed of actin, myosin, and associated proteins, found in cells of smooth or striated muscle.
mitochondrial membrane part
Any constituent part of a mitochondrial membrane, either of the lipid bilayers that surround the mitochondrion and form the mitochondrial envelope.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
anchoring junction
A cell junction that mechanically attaches a cell (and its cytoskeleton) to neighboring cells or to the extracellular matrix.
respiratory chain
The protein complexes that form the electron transport system (the respiratory chain), associated with a cell membrane, usually the plasma membrane (in prokaryotes) or the inner mitochondrial membrane (on eukaryotes). The respiratory chain complexes transfer electrons from an electron donor to an electron acceptor and are associated with a proton pump to create a transmembrane electrochemical gradient.
all
NA
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
organelle envelope
A double membrane structure enclosing an organelle, including two lipid bilayers and the region between them. In some cases, an organelle envelope may have more than two membranes.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
organelle envelope
A double membrane structure enclosing an organelle, including two lipid bilayers and the region between them. In some cases, an organelle envelope may have more than two membranes.
organelle inner membrane
The inner, i.e. lumen-facing, lipid bilayer of an organelle envelope; usually highly selective to most ions and metabolites.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
organelle inner membrane
The inner, i.e. lumen-facing, lipid bilayer of an organelle envelope; usually highly selective to most ions and metabolites.
mitochondrial inner membrane
The inner, i.e. lumen-facing, lipid bilayer of the mitochondrial envelope. It is highly folded to form cristae.
mitochondrial membrane part
Any constituent part of a mitochondrial membrane, either of the lipid bilayers that surround the mitochondrion and form the mitochondrial envelope.
mitochondrial envelope
The double lipid bilayer enclosing the mitochondrion and separating its contents from the cell cytoplasm; includes the intermembrane space.
mitochondrial membrane
Either of the lipid bilayers that surround the mitochondrion and form the mitochondrial envelope.
mitochondrial membrane part
Any constituent part of a mitochondrial membrane, either of the lipid bilayers that surround the mitochondrion and form the mitochondrial envelope.
striated muscle thin filament
Filaments formed of actin and associated proteins; attached to Z discs at either end of sarcomeres in myofibrils.
striated muscle thin filament
Filaments formed of actin and associated proteins; attached to Z discs at either end of sarcomeres in myofibrils.
I band
A region of a sarcomere that appears as a light band on each side of the Z disc, comprising a region of the sarcomere where thin (actin) filaments are not overlapped by thick (myosin) filaments; contains actin, troponin, and tropomyosin; each sarcomere includes half of an I band at each end.
Z disc
Platelike region of a muscle sarcomere to which the plus ends of actin filaments are attached.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
contractile fiber
Fibers, composed of actin, myosin, and associated proteins, found in cells of smooth or striated muscle.
mitochondrion
A semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration.
mitochondrial part
Any constituent part of a mitochondrion, a semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration.
contractile fiber part
Any constituent part of a contractile fiber, a fiber composed of actin, myosin, and associated proteins, found in cells of smooth or striated muscle.
mitochondrial respiratory chain
The protein complexes that form the mitochondrial electron transport system (the respiratory chain), associated with the inner mitochondrial membrane. The respiratory chain complexes transfer electrons from an electron donor to an electron acceptor and are associated with a proton pump to create a transmembrane electrochemical gradient.
mitochondrial membrane
Either of the lipid bilayers that surround the mitochondrion and form the mitochondrial envelope.
mitochondrial part
Any constituent part of a mitochondrion, a semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration.
contractile fiber part
Any constituent part of a contractile fiber, a fiber composed of actin, myosin, and associated proteins, found in cells of smooth or striated muscle.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
mitochondrial respiratory chain
The protein complexes that form the mitochondrial electron transport system (the respiratory chain), associated with the inner mitochondrial membrane. The respiratory chain complexes transfer electrons from an electron donor to an electron acceptor and are associated with a proton pump to create a transmembrane electrochemical gradient.
sarcomere
The repeating unit of a myofibril in a muscle cell, composed of an array of overlapping thick and thin filaments between two adjacent Z discs.
striated muscle thin filament
Filaments formed of actin and associated proteins; attached to Z discs at either end of sarcomeres in myofibrils.

protein binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any protein or protein complex (a complex of two or more proteins that may include other nonprotein molecules).
molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
actin binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with monomeric or multimeric forms of actin, including actin filaments.
structural molecule activity
The action of a molecule that contributes to the structural integrity of a complex or assembly within or outside a cell.
binding
The selective, non-covalent, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
cytoskeletal protein binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any protein component of any cytoskeleton (actin, microtubule, or intermediate filament cytoskeleton).
structural constituent of muscle
The action of a molecule that contributes to the structural integrity of a muscle fiber.
all
NA
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 04260 | 1.942e-04 | 1.628 | 10 | 25 | Cardiac muscle contraction |
| 05414 | 5.196e-04 | 2.215 | 11 | 34 | Dilated cardiomyopathy |
| 05410 | 2.665e-03 | 2.215 | 10 | 34 | Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) |
ABI3BPABI family, member 3 (NESH) binding protein (ENSG00000154175), score: 0.46 ABLIM1actin binding LIM protein 1 (ENSG00000099204), score: 0.61 ABRAactin-binding Rho activating protein (ENSG00000174429), score: 0.7 ACTN2actinin, alpha 2 (ENSG00000077522), score: 0.66 ADALadenosine deaminase-like (ENSG00000168803), score: 0.49 ADAMTS15ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 15 (ENSG00000166106), score: 0.48 ADAMTSL5ADAMTS-like 5 (ENSG00000185761), score: 0.65 ADCY5adenylate cyclase 5 (ENSG00000173175), score: 0.52 ADSSadenylosuccinate synthase (ENSG00000035687), score: -0.48 ADSSL1adenylosuccinate synthase like 1 (ENSG00000185100), score: 0.55 AFAP1L1actin filament associated protein 1-like 1 (ENSG00000157510), score: 0.57 AFTPHaftiphilin (ENSG00000119844), score: -0.57 AKAP13A kinase (PRKA) anchor protein 13 (ENSG00000170776), score: 0.61 AMBRA1autophagy/beclin-1 regulator 1 (ENSG00000110497), score: -0.48 AMDHD2amidohydrolase domain containing 2 (ENSG00000162066), score: -0.48 ANAPC16anaphase promoting complex subunit 16 (ENSG00000166295), score: 0.56 ANGPTL2angiopoietin-like 2 (ENSG00000136859), score: 0.5 ANGPTL7angiopoietin-like 7 (ENSG00000171819), score: 0.56 ANKRD1ankyrin repeat domain 1 (cardiac muscle) (ENSG00000148677), score: 0.85 ANKRD2ankyrin repeat domain 2 (stretch responsive muscle) (ENSG00000165887), score: 0.47 ANO5anoctamin 5 (ENSG00000171714), score: 0.49 ANTXR2anthrax toxin receptor 2 (ENSG00000163297), score: 0.46 ANXA1annexin A1 (ENSG00000135046), score: 0.51 APOBEC2apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme, catalytic polypeptide-like 2 (ENSG00000124701), score: 0.72 APPBP2amyloid beta precursor protein (cytoplasmic tail) binding protein 2 (ENSG00000062725), score: -0.52 APPL2adaptor protein, phosphotyrosine interaction, PH domain and leucine zipper containing 2 (ENSG00000136044), score: -0.49 AQP11aquaporin 11 (ENSG00000178301), score: -0.48 ARHGAP10Rho GTPase activating protein 10 (ENSG00000071205), score: 0.62 ARHGEF6Rac/Cdc42 guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 6 (ENSG00000129675), score: 0.58 ARL6IP1ADP-ribosylation factor-like 6 interacting protein 1 (ENSG00000170540), score: -0.71 ARL6IP5ADP-ribosylation-like factor 6 interacting protein 5 (ENSG00000144746), score: 0.48 ART3ADP-ribosyltransferase 3 (ENSG00000156219), score: 0.47 ASAH1N-acylsphingosine amidohydrolase (acid ceramidase) 1 (ENSG00000104763), score: 0.53 ASB11ankyrin repeat and SOCS box-containing 11 (ENSG00000165192), score: 0.83 ASB14ankyrin repeat and SOCS box-containing 14 (ENSG00000239388), score: 0.57 ASB15ankyrin repeat and SOCS box-containing 15 (ENSG00000146809), score: 0.77 ASB2ankyrin repeat and SOCS box-containing 2 (ENSG00000100628), score: 0.63 ASPNasporin (ENSG00000106819), score: 0.48 ATF3activating transcription factor 3 (ENSG00000162772), score: 0.48 ATP13A1ATPase type 13A1 (ENSG00000105726), score: -0.55 ATP2A2ATPase, Ca++ transporting, cardiac muscle, slow twitch 2 (ENSG00000174437), score: 0.52 ATPIF1ATPase inhibitory factor 1 (ENSG00000130770), score: 0.61 B3GALTLbeta 1,3-galactosyltransferase-like (ENSG00000187676), score: 0.54 BAG3BCL2-associated athanogene 3 (ENSG00000151929), score: 0.5 BAIAP2BAI1-associated protein 2 (ENSG00000175866), score: -0.54 BRI3BPBRI3 binding protein (ENSG00000184992), score: -0.67 C10orf76chromosome 10 open reading frame 76 (ENSG00000120029), score: 0.51 C15orf41chromosome 15 open reading frame 41 (ENSG00000186073), score: 0.7 C18orf55chromosome 18 open reading frame 55 (ENSG00000075336), score: 0.57 C1orf151chromosome 1 open reading frame 151 (ENSG00000173436), score: 0.7 C6orf142chromosome 6 open reading frame 142 (ENSG00000146147), score: 0.7 C7orf30chromosome 7 open reading frame 30 (ENSG00000156928), score: 0.48 C9orf16chromosome 9 open reading frame 16 (ENSG00000171159), score: -0.52 CA1carbonic anhydrase I (ENSG00000133742), score: 0.53 CABLES1Cdk5 and Abl enzyme substrate 1 (ENSG00000134508), score: -0.53 CAMK2Dcalcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II delta (ENSG00000145349), score: 0.49 CAPZA2capping protein (actin filament) muscle Z-line, alpha 2 (ENSG00000198898), score: 0.6 CASTcalpastatin (ENSG00000153113), score: 0.63 CBLBCas-Br-M (murine) ecotropic retroviral transforming sequence b (ENSG00000114423), score: 0.59 CCDC76coiled-coil domain containing 76 (ENSG00000122435), score: 0.53 CCDC80coiled-coil domain containing 80 (ENSG00000091986), score: 0.64 CCND2cyclin D2 (ENSG00000118971), score: 0.61 CD274CD274 molecule (ENSG00000120217), score: 0.68 CD34CD34 molecule (ENSG00000174059), score: 0.49 CDC42EP3CDC42 effector protein (Rho GTPase binding) 3 (ENSG00000163171), score: 0.51 CDH13cadherin 13, H-cadherin (heart) (ENSG00000140945), score: 0.58 CDH2cadherin 2, type 1, N-cadherin (neuronal) (ENSG00000170558), score: 0.64 CDH5cadherin 5, type 2 (vascular endothelium) (ENSG00000179776), score: 0.47 CDS1CDP-diacylglycerol synthase (phosphatidate cytidylyltransferase) 1 (ENSG00000163624), score: -0.54 CFLARCASP8 and FADD-like apoptosis regulator (ENSG00000003402), score: 0.58 CHN2chimerin (chimaerin) 2 (ENSG00000106069), score: -0.51 CHPF2chondroitin polymerizing factor 2 (ENSG00000033100), score: -0.48 CLIC5chloride intracellular channel 5 (ENSG00000112782), score: 0.64 CMYA5cardiomyopathy associated 5 (ENSG00000164309), score: 0.75 CNNM2cyclin M2 (ENSG00000148842), score: -0.58 COL15A1collagen, type XV, alpha 1 (ENSG00000204291), score: 0.6 COL6A3collagen, type VI, alpha 3 (ENSG00000163359), score: 0.56 COMMD3COMM domain containing 3 (ENSG00000148444), score: 0.54 COQ5coenzyme Q5 homolog, methyltransferase (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000110871), score: 0.5 COQ9coenzyme Q9 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000088682), score: 0.55 COX10COX10 homolog, cytochrome c oxidase assembly protein, heme A: farnesyltransferase (yeast) (ENSG00000006695), score: 0.47 COX4I1cytochrome c oxidase subunit IV isoform 1 (ENSG00000131143), score: 0.53 CPEB4cytoplasmic polyadenylation element binding protein 4 (ENSG00000113742), score: 0.46 CRISPLD2cysteine-rich secretory protein LCCL domain containing 2 (ENSG00000103196), score: 0.47 CRYABcrystallin, alpha B (ENSG00000109846), score: 0.5 CSRP3cysteine and glycine-rich protein 3 (cardiac LIM protein) (ENSG00000129170), score: 0.79 CTNNAL1catenin (cadherin-associated protein), alpha-like 1 (ENSG00000119326), score: 0.5 CUL4Acullin 4A (ENSG00000139842), score: 0.5 DCAF10DDB1 and CUL4 associated factor 10 (ENSG00000122741), score: -0.47 DCAF6DDB1 and CUL4 associated factor 6 (ENSG00000143164), score: 0.47 DCNdecorin (ENSG00000011465), score: 0.49 DCP1BDCP1 decapping enzyme homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000151065), score: -0.48 DCUN1D2DCN1, defective in cullin neddylation 1, domain containing 2 (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000150401), score: 0.63 DDR2discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinase 2 (ENSG00000162733), score: 0.51 DDX1DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000079785), score: 0.61 DECR12,4-dienoyl CoA reductase 1, mitochondrial (ENSG00000104325), score: 0.47 DLDdihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase (ENSG00000091140), score: 0.59 DNAJC12DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 12 (ENSG00000108176), score: -0.6 DPTdermatopontin (ENSG00000143196), score: 0.59 DSPdesmoplakin (ENSG00000096696), score: 0.59 DTWD2DTW domain containing 2 (ENSG00000169570), score: 0.48 DUSP13dual specificity phosphatase 13 (ENSG00000079393), score: 0.56 DUSP27dual specificity phosphatase 27 (putative) (ENSG00000198842), score: 0.77 DYRK1Adual-specificity tyrosine-(Y)-phosphorylation regulated kinase 1A (ENSG00000157540), score: 0.46 EDNRAendothelin receptor type A (ENSG00000151617), score: 0.59 EEF2Keukaryotic elongation factor-2 kinase (ENSG00000103319), score: 0.6 EIF3Aeukaryotic translation initiation factor 3, subunit A (ENSG00000107581), score: 0.65 EIF5Beukaryotic translation initiation factor 5B (ENSG00000158417), score: 0.52 EMILIN2elastin microfibril interfacer 2 (ENSG00000132205), score: 0.59 EMP1epithelial membrane protein 1 (ENSG00000134531), score: 0.53 ESYT2extended synaptotagmin-like protein 2 (ENSG00000117868), score: 0.61 ETV5ets variant 5 (ENSG00000244405), score: -0.56 FAAHfatty acid amide hydrolase (ENSG00000117480), score: -0.54 FAM129Afamily with sequence similarity 129, member A (ENSG00000135842), score: 0.7 FAM198Bfamily with sequence similarity 198, member B (ENSG00000164125), score: 0.58 FAM36Afamily with sequence similarity 36, member A (ENSG00000203667), score: 0.55 FAPfibroblast activation protein, alpha (ENSG00000078098), score: 0.65 FASTKD2FAST kinase domains 2 (ENSG00000118246), score: 0.53 FBLIM1filamin binding LIM protein 1 (ENSG00000162458), score: 0.47 FBN1fibrillin 1 (ENSG00000166147), score: 0.57 FBXO30F-box protein 30 (ENSG00000118496), score: 0.49 FBXO32F-box protein 32 (ENSG00000156804), score: 0.67 FBXO33F-box protein 33 (ENSG00000165355), score: -0.52 FBXO40F-box protein 40 (ENSG00000163833), score: 0.8 FBXO9F-box protein 9 (ENSG00000112146), score: -0.5 FGF12fibroblast growth factor 12 (ENSG00000114279), score: 0.55 FGF18fibroblast growth factor 18 (ENSG00000156427), score: 0.72 FGFR2fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (ENSG00000066468), score: -0.57 FHL2four and a half LIM domains 2 (ENSG00000115641), score: 0.62 FHOD3formin homology 2 domain containing 3 (ENSG00000134775), score: 0.66 FICDFIC domain containing (ENSG00000198855), score: -0.61 FILIP1filamin A interacting protein 1 (ENSG00000118407), score: 0.68 FITM2fat storage-inducing transmembrane protein 2 (ENSG00000197296), score: 0.71 FLT1fms-related tyrosine kinase 1 (vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor receptor) (ENSG00000102755), score: 0.49 FNBP1Lformin binding protein 1-like (ENSG00000137942), score: 0.48 FSD2fibronectin type III and SPRY domain containing 2 (ENSG00000186628), score: 0.7 FXR1fragile X mental retardation, autosomal homolog 1 (ENSG00000114416), score: 0.55 FYCO1FYVE and coiled-coil domain containing 1 (ENSG00000163820), score: 0.56 FYTTD1forty-two-three domain containing 1 (ENSG00000122068), score: 0.47 GAB1GRB2-associated binding protein 1 (ENSG00000109458), score: 0.48 GATA4GATA binding protein 4 (ENSG00000136574), score: 0.55 GATA6GATA binding protein 6 (ENSG00000141448), score: 0.5 GCOM1GRINL1A complex locus (ENSG00000137878), score: 0.75 GEMGTP binding protein overexpressed in skeletal muscle (ENSG00000164949), score: 0.65 GFM2G elongation factor, mitochondrial 2 (ENSG00000164347), score: 0.57 GGHgamma-glutamyl hydrolase (conjugase, folylpolygammaglutamyl hydrolase) (ENSG00000137563), score: -0.62 GHITMgrowth hormone inducible transmembrane protein (ENSG00000165678), score: 0.66 GJA3gap junction protein, alpha 3, 46kDa (ENSG00000121743), score: 0.66 GJA5gap junction protein, alpha 5, 40kDa (ENSG00000143140), score: 0.47 GJB1gap junction protein, beta 1, 32kDa (ENSG00000169562), score: -0.5 GLDCglycine dehydrogenase (decarboxylating) (ENSG00000178445), score: -0.49 GLT8D2glycosyltransferase 8 domain containing 2 (ENSG00000120820), score: 0.68 GMPRguanosine monophosphate reductase (ENSG00000137198), score: 0.52 GRIP2glutamate receptor interacting protein 2 (ENSG00000144596), score: 0.64 GRK5G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 (ENSG00000198873), score: 0.61 HAT1histone acetyltransferase 1 (ENSG00000128708), score: 0.49 HBEGFheparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (ENSG00000113070), score: 0.51 HCCSholocytochrome c synthase (ENSG00000004961), score: 0.53 HEY2hairy/enhancer-of-split related with YRPW motif 2 (ENSG00000135547), score: 0.61 HGShepatocyte growth factor-regulated tyrosine kinase substrate (ENSG00000185359), score: -0.51 HHATLhedgehog acyltransferase-like (ENSG00000010282), score: 0.58 HIF1ANhypoxia inducible factor 1, alpha subunit inhibitor (ENSG00000166135), score: 0.63 HMCN1hemicentin 1 (ENSG00000143341), score: 0.51 HMGCR3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase (ENSG00000113161), score: -0.56 IL6interleukin 6 (interferon, beta 2) (ENSG00000136244), score: 0.51 IP6K1inositol hexakisphosphate kinase 1 (ENSG00000176095), score: -0.58 ITGB1BP1integrin beta 1 binding protein 1 (ENSG00000119185), score: 0.5 ITPRIPinositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor interacting protein (ENSG00000148841), score: 0.48 JMJD6jumonji domain containing 6 (ENSG00000070495), score: 0.51 KBTBD10kelch repeat and BTB (POZ) domain containing 10 (ENSG00000239474), score: 0.8 KBTBD5kelch repeat and BTB (POZ) domain containing 5 (ENSG00000157119), score: 0.88 KCNJ2potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 2 (ENSG00000123700), score: 0.61 KCNJ8potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 8 (ENSG00000121361), score: 0.55 KIAA0232KIAA0232 (ENSG00000170871), score: 0.55 KIAA1598KIAA1598 (ENSG00000187164), score: -0.61 KIF13Akinesin family member 13A (ENSG00000137177), score: 0.55 KIF5Bkinesin family member 5B (ENSG00000170759), score: 0.53 KLHL24kelch-like 24 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000114796), score: 0.66 KLHL25kelch-like 25 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000183655), score: -0.57 KLHL31kelch-like 31 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000124743), score: 0.83 KLHL38kelch-like 38 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000175946), score: 0.94 KLHL7kelch-like 7 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000122550), score: 0.7 LAMA4laminin, alpha 4 (ENSG00000112769), score: 0.64 LAPTM4Blysosomal protein transmembrane 4 beta (ENSG00000104341), score: 0.47 LBHlimb bud and heart development homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000213626), score: 0.54 LDB3LIM domain binding 3 (ENSG00000122367), score: 0.75 LIMS2LIM and senescent cell antigen-like domains 2 (ENSG00000072163), score: 0.52 LMOD2leiomodin 2 (cardiac) (ENSG00000170807), score: 0.8 LOC100291405similar to protein tyrosine phosphatase-like A domain containing 1 (ENSG00000074696), score: -0.55 LOC100291671similar to SH3-binding domain and glutamic acid-rich protein (ENSG00000185437), score: 0.68 LPAR3lysophosphatidic acid receptor 3 (ENSG00000171517), score: 0.47 LPIN2lipin 2 (ENSG00000101577), score: -0.5 LRRC10leucine rich repeat containing 10 (ENSG00000198812), score: 0.72 LRRC14Bleucine rich repeat containing 14B (ENSG00000185028), score: 0.71 LRRC2leucine rich repeat containing 2 (ENSG00000163827), score: 0.71 LRRC39leucine rich repeat containing 39 (ENSG00000122477), score: 0.88 LRRFIP2leucine rich repeat (in FLII) interacting protein 2 (ENSG00000093167), score: 0.49 LTBP1latent transforming growth factor beta binding protein 1 (ENSG00000049323), score: 0.54 LUMlumican (ENSG00000139329), score: 0.55 MALLmal, T-cell differentiation protein-like (ENSG00000144063), score: 0.5 MAMDC2MAM domain containing 2 (ENSG00000165072), score: 0.51 MAP7microtubule-associated protein 7 (ENSG00000135525), score: -0.53 MAPKAPK2mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2 (ENSG00000162889), score: 0.62 MAPKAPK3mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 3 (ENSG00000114738), score: 0.74 ME2malic enzyme 2, NAD(+)-dependent, mitochondrial (ENSG00000082212), score: 0.59 MEGF9multiple EGF-like-domains 9 (ENSG00000106780), score: -0.59 MEOX2mesenchyme homeobox 2 (ENSG00000106511), score: 0.7 METRNLmeteorin, glial cell differentiation regulator-like (ENSG00000176845), score: 0.46 METTL11Bmethyltransferase like 11B (ENSG00000203740), score: 1 MFN2mitofusin 2 (ENSG00000116688), score: 0.67 MFSD2Amajor facilitator superfamily domain containing 2A (ENSG00000168389), score: -0.52 MLPHmelanophilin (ENSG00000115648), score: 0.61 MMP2matrix metallopeptidase 2 (gelatinase A, 72kDa gelatinase, 72kDa type IV collagenase) (ENSG00000087245), score: 0.48 MPDZmultiple PDZ domain protein (ENSG00000107186), score: 0.53 MRPL15mitochondrial ribosomal protein L15 (ENSG00000137547), score: 0.55 MRPL16mitochondrial ribosomal protein L16 (ENSG00000166902), score: 0.46 MRPL21mitochondrial ribosomal protein L21 (ENSG00000197345), score: 0.53 MRPL22mitochondrial ribosomal protein L22 (ENSG00000082515), score: 0.47 MRPL51mitochondrial ribosomal protein L51 (ENSG00000111639), score: 0.47 MRPS23mitochondrial ribosomal protein S23 (ENSG00000181610), score: 0.48 MRPS9mitochondrial ribosomal protein S9 (ENSG00000135972), score: 0.84 MTIF2mitochondrial translational initiation factor 2 (ENSG00000085760), score: 0.47 MURCmuscle-related coiled-coil protein (ENSG00000170681), score: 0.68 MYBPC3myosin binding protein C, cardiac (ENSG00000134571), score: 0.74 MYCT1myc target 1 (ENSG00000120279), score: 0.48 MYL3myosin, light chain 3, alkali; ventricular, skeletal, slow (ENSG00000160808), score: 0.71 MYLK3myosin light chain kinase 3 (ENSG00000140795), score: 0.6 MYLK4myosin light chain kinase family, member 4 (ENSG00000145949), score: 0.81 MYOCmyocilin, trabecular meshwork inducible glucocorticoid response (ENSG00000034971), score: 0.68 MYOCDmyocardin (ENSG00000141052), score: 0.65 MYOM2myomesin (M-protein) 2, 165kDa (ENSG00000036448), score: 0.69 MYOM3myomesin family, member 3 (ENSG00000142661), score: 0.88 MYOZ1myozenin 1 (ENSG00000177791), score: 0.9 MYOZ2myozenin 2 (ENSG00000172399), score: 0.81 MYPNmyopalladin (ENSG00000138347), score: 0.84 NARS2asparaginyl-tRNA synthetase 2, mitochondrial (putative) (ENSG00000137513), score: 0.64 NDUFA12NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 alpha subcomplex, 12 (ENSG00000184752), score: 0.7 NDUFA8NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 alpha subcomplex, 8, 19kDa (ENSG00000119421), score: 0.56 NDUFB10NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 beta subcomplex, 10, 22kDa (ENSG00000140990), score: 0.49 NDUFS3NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) Fe-S protein 3, 30kDa (NADH-coenzyme Q reductase) (ENSG00000213619), score: 0.54 NEBLnebulette (ENSG00000078114), score: 0.55 NEK9NIMA (never in mitosis gene a)- related kinase 9 (ENSG00000119638), score: 0.6 NFU1NFU1 iron-sulfur cluster scaffold homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000169599), score: 0.49 NGEFneuronal guanine nucleotide exchange factor (ENSG00000066248), score: -0.51 NHLRC2NHL repeat containing 2 (ENSG00000196865), score: 0.65 NINninein (GSK3B interacting protein) (ENSG00000100503), score: 0.54 NOD1nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing 1 (ENSG00000106100), score: 0.49 NRAPnebulin-related anchoring protein (ENSG00000197893), score: 0.7 NT5C1A5'-nucleotidase, cytosolic IA (ENSG00000116981), score: 0.54 P2RY2purinergic receptor P2Y, G-protein coupled, 2 (ENSG00000175591), score: 0.53 P4HA2prolyl 4-hydroxylase, alpha polypeptide II (ENSG00000072682), score: 0.47 PAIP1poly(A) binding protein interacting protein 1 (ENSG00000172239), score: 0.47 PALMDpalmdelphin (ENSG00000099260), score: 0.61 PAMpeptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase (ENSG00000145730), score: 0.56 PARVBparvin, beta (ENSG00000188677), score: 0.54 PBX3pre-B-cell leukemia homeobox 3 (ENSG00000167081), score: 0.5 PDAP1PDGFA associated protein 1 (ENSG00000106244), score: 0.46 PDE3Aphosphodiesterase 3A, cGMP-inhibited (ENSG00000172572), score: 0.67 PDE7Aphosphodiesterase 7A (ENSG00000205268), score: 0.67 PDHBpyruvate dehydrogenase (lipoamide) beta (ENSG00000168291), score: 0.55 PDLIM5PDZ and LIM domain 5 (ENSG00000163110), score: 0.67 PDZRN3PDZ domain containing ring finger 3 (ENSG00000121440), score: 0.67 PEX16peroxisomal biogenesis factor 16 (ENSG00000121680), score: -0.49 PFKFB46-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 4 (ENSG00000114268), score: -0.48 PLAAphospholipase A2-activating protein (ENSG00000137055), score: 0.51 PLCL1phospholipase C-like 1 (ENSG00000115896), score: 0.61 PLCXD2phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C, X domain containing 2 (ENSG00000144824), score: 0.53 PLEKHA2pleckstrin homology domain containing, family A (phosphoinositide binding specific) member 2 (ENSG00000169499), score: 0.47 PLNphospholamban (ENSG00000198523), score: 0.72 POF1Bpremature ovarian failure, 1B (ENSG00000124429), score: 0.56 POSTNperiostin, osteoblast specific factor (ENSG00000133110), score: 0.75 PPARGC1Aperoxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma, coactivator 1 alpha (ENSG00000109819), score: 0.51 PPICpeptidylprolyl isomerase C (cyclophilin C) (ENSG00000168938), score: 0.46 PPP1R13Bprotein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 13B (ENSG00000088808), score: 0.46 PPP1R14Cprotein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 14C (ENSG00000198729), score: 0.65 PPP1R1Cprotein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 1C (ENSG00000150722), score: 0.84 PPP1R3Aprotein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 3A (ENSG00000154415), score: 0.93 PPTC7PTC7 protein phosphatase homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000196850), score: 0.6 PRKCHprotein kinase C, eta (ENSG00000027075), score: 0.46 PRMT3protein arginine methyltransferase 3 (ENSG00000185238), score: 0.46 PTCD2pentatricopeptide repeat domain 2 (ENSG00000049883), score: 0.57 PTDSS1phosphatidylserine synthase 1 (ENSG00000156471), score: 0.75 PTGFRNprostaglandin F2 receptor negative regulator (ENSG00000134247), score: 0.56 PTGR2prostaglandin reductase 2 (ENSG00000140043), score: 0.48 PTRFpolymerase I and transcript release factor (ENSG00000177469), score: 0.57 RBM20RNA binding motif protein 20 (ENSG00000203867), score: 0.72 RBM24RNA binding motif protein 24 (ENSG00000112183), score: 0.76 RBPMS2RNA binding protein with multiple splicing 2 (ENSG00000166831), score: 0.53 REXO2REX2, RNA exonuclease 2 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000076043), score: 0.54 RHOBTB3Rho-related BTB domain containing 3 (ENSG00000164292), score: 0.48 RILPL1Rab interacting lysosomal protein-like 1 (ENSG00000188026), score: 0.53 ROCK1Rho-associated, coiled-coil containing protein kinase 1 (ENSG00000067900), score: 0.53 RPF1ribosome production factor 1 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000117133), score: 0.49 RPL3Lribosomal protein L3-like (ENSG00000140986), score: 0.7 RRADRas-related associated with diabetes (ENSG00000166592), score: 0.61 RYR2ryanodine receptor 2 (cardiac) (ENSG00000198626), score: 0.66 SALL1sal-like 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000103449), score: -0.54 SEC16ASEC16 homolog A (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000148396), score: -0.49 SEMA3Csema domain, immunoglobulin domain (Ig), short basic domain, secreted, (semaphorin) 3C (ENSG00000075223), score: 0.56 SGCGsarcoglycan, gamma (35kDa dystrophin-associated glycoprotein) (ENSG00000102683), score: 0.79 SGPP1sphingosine-1-phosphate phosphatase 1 (ENSG00000126821), score: -0.49 SH3RF2SH3 domain containing ring finger 2 (ENSG00000156463), score: 0.53 SHROOM2shroom family member 2 (ENSG00000146950), score: -0.5 SIPA1L1signal-induced proliferation-associated 1 like 1 (ENSG00000197555), score: -0.65 SIRT5sirtuin 5 (ENSG00000124523), score: 0.56 SLC16A1solute carrier family 16, member 1 (monocarboxylic acid transporter 1) (ENSG00000155380), score: 0.57 SLC19A1solute carrier family 19 (folate transporter), member 1 (ENSG00000173638), score: -0.49 SLC25A17solute carrier family 25 (mitochondrial carrier; peroxisomal membrane protein, 34kDa), member 17 (ENSG00000100372), score: -0.64 SLC25A3solute carrier family 25 (mitochondrial carrier; phosphate carrier), member 3 (ENSG00000075415), score: 0.54 SLC25A30solute carrier family 25, member 30 (ENSG00000174032), score: 0.61 SLC25A33solute carrier family 25, member 33 (ENSG00000171612), score: -0.62 SLC26A9solute carrier family 26, member 9 (ENSG00000174502), score: 0.79 SLC35B4solute carrier family 35, member B4 (ENSG00000205060), score: -0.49 SLC41A1solute carrier family 41, member 1 (ENSG00000133065), score: 0.78 SLC8A1solute carrier family 8 (sodium/calcium exchanger), member 1 (ENSG00000183023), score: 0.69 SLC9A3R1solute carrier family 9 (sodium/hydrogen exchanger), member 3 regulator 1 (ENSG00000109062), score: -0.48 SMPXsmall muscle protein, X-linked (ENSG00000091482), score: 0.74 SMYD1SET and MYND domain containing 1 (ENSG00000115593), score: 0.69 SMYD2SET and MYND domain containing 2 (ENSG00000143499), score: 0.59 SNAPC4small nuclear RNA activating complex, polypeptide 4, 190kDa (ENSG00000165684), score: -0.5 SNX10sorting nexin 10 (ENSG00000086300), score: -0.61 SNX3sorting nexin 3 (ENSG00000112335), score: 0.61 SORBS1sorbin and SH3 domain containing 1 (ENSG00000095637), score: 0.66 SPIRE2spire homolog 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000204991), score: -0.5 SQLEsqualene epoxidase (ENSG00000104549), score: -0.51 SSBP1single-stranded DNA binding protein 1 (ENSG00000106028), score: 0.54 STX11syntaxin 11 (ENSG00000135604), score: 0.64 SUCLG1succinate-CoA ligase, alpha subunit (ENSG00000163541), score: 0.47 SWAP70SWAP switching B-cell complex 70kDa subunit (ENSG00000133789), score: 0.47 SYF2SYF2 homolog, RNA splicing factor (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000117614), score: 0.47 SYNMsynemin, intermediate filament protein (ENSG00000182253), score: 0.73 SYNPO2synaptopodin 2 (ENSG00000172403), score: 0.65 TACC2transforming, acidic coiled-coil containing protein 2 (ENSG00000138162), score: 0.59 TAF15TAF15 RNA polymerase II, TATA box binding protein (TBP)-associated factor, 68kDa (ENSG00000172660), score: 0.49 TARSL2threonyl-tRNA synthetase-like 2 (ENSG00000185418), score: 0.49 TBX20T-box 20 (ENSG00000164532), score: 0.75 TBX5T-box 5 (ENSG00000089225), score: 0.66 TEAD1TEA domain family member 1 (SV40 transcriptional enhancer factor) (ENSG00000187079), score: 0.63 TECRLtrans-2,3-enoyl-CoA reductase-like (ENSG00000205678), score: 0.82 TIMM44translocase of inner mitochondrial membrane 44 homolog (yeast) (ENSG00000104980), score: 0.5 TINAGL1tubulointerstitial nephritis antigen-like 1 (ENSG00000142910), score: 0.46 TLCD1TLC domain containing 1 (ENSG00000160606), score: -0.55 TMEM182transmembrane protein 182 (ENSG00000170417), score: 0.89 TMEM57transmembrane protein 57 (ENSG00000204178), score: -0.49 TMOD1tropomodulin 1 (ENSG00000136842), score: 0.52 TNFRSF19tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 19 (ENSG00000127863), score: 0.54 TNNC1troponin C type 1 (slow) (ENSG00000114854), score: 0.74 TNNT2troponin T type 2 (cardiac) (ENSG00000118194), score: 0.74 TOP2Btopoisomerase (DNA) II beta 180kDa (ENSG00000077097), score: 0.5 TOR2Atorsin family 2, member A (ENSG00000160404), score: -0.54 TPM1tropomyosin 1 (alpha) (ENSG00000140416), score: 0.83 TPST1tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase 1 (ENSG00000169902), score: -0.55 TRAF2TNF receptor-associated factor 2 (ENSG00000127191), score: -0.57 TRIM55tripartite motif-containing 55 (ENSG00000147573), score: 0.6 TRIM63tripartite motif-containing 63 (ENSG00000158022), score: 0.7 TSTD2thiosulfate sulfurtransferase (rhodanese)-like domain containing 2 (ENSG00000136925), score: 0.58 TXLNBtaxilin beta (ENSG00000164440), score: 0.72 TYRP1tyrosinase-related protein 1 (ENSG00000107165), score: 0.46 UQCRC1ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase core protein I (ENSG00000010256), score: 0.55 UQCRC2ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase core protein II (ENSG00000140740), score: 0.65 USP28ubiquitin specific peptidase 28 (ENSG00000048028), score: 0.58 VEZTvezatin, adherens junctions transmembrane protein (ENSG00000028203), score: 0.51 VIPR2vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor 2 (ENSG00000106018), score: 0.67 VLDLRvery low density lipoprotein receptor (ENSG00000147852), score: 0.5 WDR26WD repeat domain 26 (ENSG00000162923), score: 0.49 WDR91WD repeat domain 91 (ENSG00000105875), score: -0.52 WISP2WNT1 inducible signaling pathway protein 2 (ENSG00000064205), score: 0.51 WNT11wingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 11 (ENSG00000085741), score: 0.53 WTIPWilms tumor 1 interacting protein (ENSG00000142279), score: 0.6 XPO4exportin 4 (ENSG00000132953), score: 0.61 YME1L1YME1-like 1 (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000136758), score: 0.49 YRDCyrdC domain containing (E. coli) (ENSG00000196449), score: -0.5 ZAKsterile alpha motif and leucine zipper containing kinase AZK (ENSG00000091436), score: 0.81 ZBTB24zinc finger and BTB domain containing 24 (ENSG00000112365), score: -0.5 ZBTB43zinc finger and BTB domain containing 43 (ENSG00000169155), score: 0.59 ZEB1zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1 (ENSG00000148516), score: 0.66 ZNF330zinc finger protein 330 (ENSG00000109445), score: 0.87 ZNF821zinc finger protein 821 (ENSG00000102984), score: -0.56 ZNHIT6zinc finger, HIT type 6 (ENSG00000117174), score: 0.46 ZNRF3zinc and ring finger 3 (ENSG00000183579), score: -0.51
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ppy_ht_f_ca1 | ppy | ht | f | _ |
| mml_ht_f_ca1 | mml | ht | f | _ |
| ggo_ht_f_ca1 | ggo | ht | f | _ |
| ppa_ht_f_ca1 | ppa | ht | f | _ |
| ptr_ht_m_ca1 | ptr | ht | m | _ |
| ppy_ht_m_ca1 | ppy | ht | m | _ |