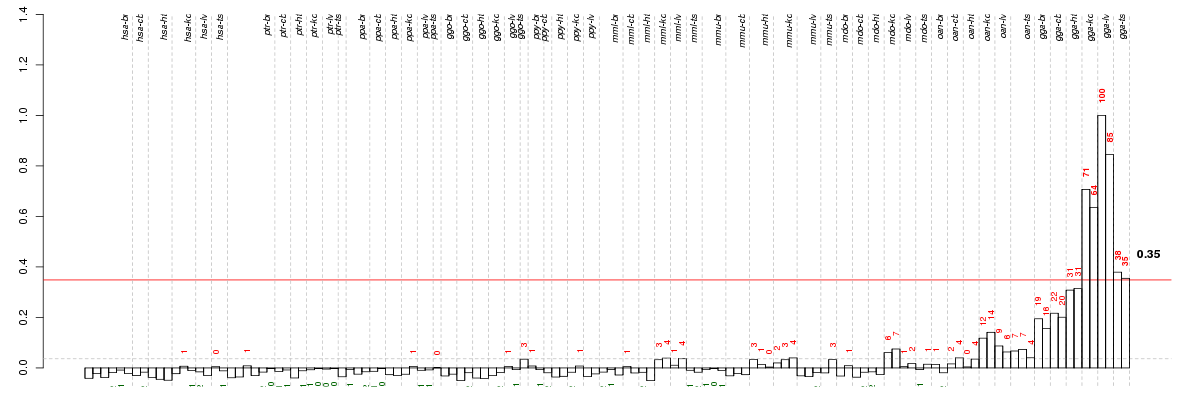

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
cytokine production
The appearance of a cytokine due to biosynthesis or secretion following a cellular stimulus, resulting in an increase in its intracellular or extracellular levels.
regulation of cytokine production
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of production of a cytokine.
response to tumor cell
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a tumor cell.
immune system process
Any process involved in the development or functioning of the immune system, an organismal system for calibrated responses to potential internal or invasive threats.
immune response to tumor cell
An immune system process that functions in the response of an organism to a tumor cell.
immune system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system whose objective is to provide calibrated responses by an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat, over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
leukocyte differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized hemopoietic precursor cell acquires the specialized features of a plasmacytoid dendritic cell or any cell of the myeloid leukocyte or lymphocyte lineages.
regulation of immune system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
positive regulation of immune system process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
regulation of response to biotic stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of a response to biotic stimulus.
positive regulation of response to biotic stimulus
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of a response to biotic stimulus.
regulation of response to tumor cell
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of a response to tumor cell.
positive regulation of response to tumor cell
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of a response to tumor cell.
regulation of immune response to tumor cell
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune response to tumor cell.
positive regulation of immune response to tumor cell
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune response to tumor cell.
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
response to biotic stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a biotic stimulus, a stimulus caused or produced by a living organism.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
positive regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
positive regulation of metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
positive regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
hemopoiesis
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the myeloid and lymphoid derived organ/tissue systems of the blood and other parts of the body over time, from formation to the mature structure. The site of hemopoiesis is variable during development, but occurs primarily in bone marrow or kidney in many adult vertebrates.
cell differentiation
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
positive regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of cytokine biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of cytokines.
cytokine biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of cytokines, any of a group of proteins that function to control the survival, growth and differentiation of tissues and cells, and which have autocrine and paracrine activity.
cytokine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving cytokines, any of a group of proteins or glycoproteins that function to control the survival, growth and differentiation of tissues and cells, and which have autocrine and paracrine activity.
positive regulation of cytokine biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of cytokines.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
hemopoietic or lymphoid organ development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of any organ involved in hemopoiesis or lymphoid cell activation over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Such development includes differentiation of resident cell types (stromal cells) and of migratory cell types dependent on the unique microenvironment afforded by the organ for their proper differentiation.
regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
positive regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
positive regulation of immune response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
all
NA
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
positive regulation of immune system process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
positive regulation of metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of immune system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
positive regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
positive regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
positive regulation of metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
positive regulation of immune system process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
regulation of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
positive regulation of immune response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of cytokine production
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of production of a cytokine.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
positive regulation of immune response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
positive regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
regulation of response to biotic stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of a response to biotic stimulus.
positive regulation of response to biotic stimulus
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of a response to biotic stimulus.
positive regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
positive regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
positive regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
positive regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
positive regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
cytokine biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of cytokines, any of a group of proteins that function to control the survival, growth and differentiation of tissues and cells, and which have autocrine and paracrine activity.
positive regulation of immune response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
regulation of immune response to tumor cell
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune response to tumor cell.
positive regulation of immune response to tumor cell
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune response to tumor cell.
regulation of cytokine biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of cytokines.
immune system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system whose objective is to provide calibrated responses by an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat, over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
hemopoietic or lymphoid organ development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of any organ involved in hemopoiesis or lymphoid cell activation over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Such development includes differentiation of resident cell types (stromal cells) and of migratory cell types dependent on the unique microenvironment afforded by the organ for their proper differentiation.
positive regulation of response to biotic stimulus
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of a response to biotic stimulus.
immune response to tumor cell
An immune system process that functions in the response of an organism to a tumor cell.
regulation of response to tumor cell
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of a response to tumor cell.
positive regulation of response to tumor cell
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of a response to tumor cell.
positive regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of cytokine biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of cytokines.
positive regulation of cytokine biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of cytokines.
positive regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of cytokine biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of cytokines.
positive regulation of cytokine biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of cytokines.
leukocyte differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized hemopoietic precursor cell acquires the specialized features of a plasmacytoid dendritic cell or any cell of the myeloid leukocyte or lymphocyte lineages.
positive regulation of immune response to tumor cell
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune response to tumor cell.
positive regulation of cytokine biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of cytokines.
positive regulation of immune response to tumor cell
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune response to tumor cell.
positive regulation of response to tumor cell
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of a response to tumor cell.
regulation of immune response to tumor cell
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune response to tumor cell.


| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 05330 | 7.963e-04 | 0.04825 | 3 | 5 | Allograft rejection |
| 04672 | 1.392e-02 | 0.1351 | 3 | 14 | Intestinal immune network for IgA production |
| 04940 | 4.529e-02 | 0.0579 | 2 | 6 | Type I diabetes mellitus |
ABCA12ATP-binding cassette, sub-family A (ABC1), member 12 (ENSG00000144452), score: 0.84 AP1S3adaptor-related protein complex 1, sigma 3 subunit (ENSG00000152056), score: 0.67 APBB3amyloid beta (A4) precursor protein-binding, family B, member 3 (ENSG00000113108), score: -0.76 C13orf39chromosome 13 open reading frame 39 (ENSG00000139780), score: 0.67 C2orf54chromosome 2 open reading frame 54 (ENSG00000172478), score: 0.72 CA6carbonic anhydrase VI (ENSG00000131686), score: 0.81 CD28CD28 molecule (ENSG00000178562), score: 0.69 CD40LGCD40 ligand (ENSG00000102245), score: 0.67 CDCP2CUB domain containing protein 2 (ENSG00000157211), score: 0.8 EREGepiregulin (ENSG00000124882), score: 0.77 ESR2estrogen receptor 2 (ER beta) (ENSG00000140009), score: 0.7 FBXL18F-box and leucine-rich repeat protein 18 (ENSG00000155034), score: 0.69 HPGDShematopoietic prostaglandin D synthase (ENSG00000163106), score: 0.92 ICOSinducible T-cell co-stimulator (ENSG00000163600), score: 0.75 IL12Binterleukin 12B (natural killer cell stimulatory factor 2, cytotoxic lymphocyte maturation factor 2, p40) (ENSG00000113302), score: 0.93 IL22RA2interleukin 22 receptor, alpha 2 (ENSG00000164485), score: 0.86 LAPTM4Blysosomal protein transmembrane 4 beta (ENSG00000104341), score: -0.64 LCMT1leucine carboxyl methyltransferase 1 (ENSG00000205629), score: -0.68 LHX8LIM homeobox 8 (ENSG00000162624), score: 0.75 PANX3pannexin 3 (ENSG00000154143), score: 0.7 PDX1pancreatic and duodenal homeobox 1 (ENSG00000139515), score: 0.71 RPIAribose 5-phosphate isomerase A (ENSG00000153574), score: 0.78 SLC26A5solute carrier family 26, member 5 (prestin) (ENSG00000170615), score: 0.86 SPINK4serine peptidase inhibitor, Kazal type 4 (ENSG00000122711), score: 1 TAAR1trace amine associated receptor 1 (ENSG00000146399), score: 0.67 TM7SF4transmembrane 7 superfamily member 4 (ENSG00000164935), score: 0.66 TMPRSS13transmembrane protease, serine 13 (ENSG00000137747), score: 0.66 TNFRSF11Atumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 11a, NFKB activator (ENSG00000141655), score: 0.73 TRPA1transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily A, member 1 (ENSG00000104321), score: 0.68 WDR41WD repeat domain 41 (ENSG00000164253), score: -0.71 ZBTB8Bzinc finger and BTB domain containing 8B (ENSG00000215897), score: 0.65 ZNF704zinc finger protein 704 (ENSG00000164684), score: 0.65
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| gga_ts_m2_ca1 | gga | ts | m | 2 |
| gga_ts_m1_ca1 | gga | ts | m | 1 |
| gga_kd_f_ca1 | gga | kd | f | _ |
| gga_kd_m_ca1 | gga | kd | m | _ |
| gga_lv_f_ca1 | gga | lv | f | _ |
| gga_lv_m_ca1 | gga | lv | m | _ |