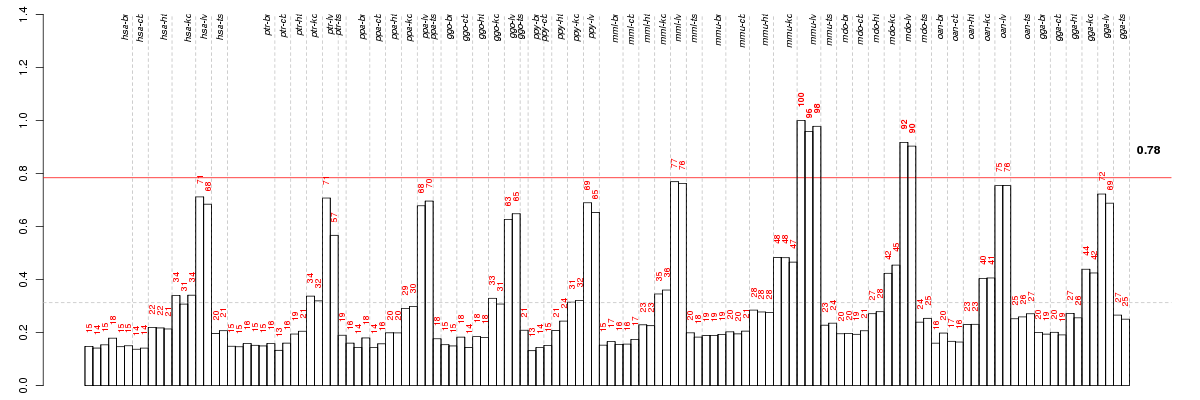

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
immune effector process
Any process of the immune system that occurs as part of an immune response.
activation of immune response
Any process that initiates an immune response.
immune system process
Any process involved in the development or functioning of the immune system, an organismal system for calibrated responses to potential internal or invasive threats.
acute inflammatory response
Inflammation which comprises a rapid, short-lived, relatively uniform response to acute injury or antigenic challenge and is characterized by accumulations of fluid, plasma proteins, and granulocytic leukocytes. An acute inflammatory response occurs within a matter of minutes or hours, and either resolves within a few days or becomes a chronic inflammatory response.
activation of plasma proteins involved in acute inflammatory response
Any process activating plasma proteins by proteolysis as part of an acute inflammatory response.
regulation of immune system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
positive regulation of immune system process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
response to unfolded protein
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an unfolded protein stimulus.
defense response
Reactions, triggered in response to the presence of a foreign body or the occurrence of an injury, which result in restriction of damage to the organism attacked or prevention/recovery from the infection caused by the attack.
blood coagulation
The sequential process by which the multiple coagulation factors of the blood interact, ultimately resulting in the formation of an insoluble fibrin clot; it may be divided into three stages: stage 1, the formation of intrinsic and extrinsic prothrombin converting principle; stage 2, the formation of thrombin; stage 3, the formation of stable fibrin polymers.
complement activation
Any process involved in the activation of any of the steps of the complement cascade, which allows for the direct killing of microbes, the disposal of immune complexes, and the regulation of other immune processes; the initial steps of complement activation involve one of three pathways, the classical pathway, the alternative pathway, and the lectin pathway, all of which lead to the terminal complement pathway.
alcohol metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving alcohols, any of a class of compounds containing one or more hydroxyl groups attached to a saturated carbon atom.
organic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
oxidation reduction
The process of removal or addition of one or more electrons with or without the concomitant removal or addition of a proton or protons.
protein maturation by peptide bond cleavage
The hydrolysis of a peptide bond or bonds within a protein as part of protein maturation, the process leading to the attainment of the full functional capacity of a protein.
cellular amino acid and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, and compounds derived from amino acids, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular amino acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
cellular amino acid derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving compounds derived from amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
cellular biogenic amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways occurring at the level of individual cells involving any of a group of naturally occurring, biologically active amines, such as norepinephrine, histamine, and serotonin, many of which act as neurotransmitters.
lipid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving lipids, compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent. Includes fatty acids; neutral fats, other fatty-acid esters, and soaps; long-chain (fatty) alcohols and waxes; sphingoids and other long-chain bases; glycolipids, phospholipids and sphingolipids; and carotenes, polyprenols, sterols, terpenes and other isoprenoids.
neutral lipid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving neutral lipids, lipids only soluble in solvents of very low polarity.
acylglycerol metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving acylglycerol, any mono-, di- or triester of glycerol with (one or more) fatty acids.
triglyceride metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving triglyceride, any triester of glycerol. The three fatty acid residues may all be the same or differ in any permutation. Triglycerides are important components of plant oils, animal fats and animal plasma lipoproteins.
glycerol ether metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving glycerol ethers, any anhydride formed between two organic hydroxy compounds, one of which is glycerol.
steroid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of steroids, compounds with a 1,2,cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene nucleus; includes de novo formation and steroid interconversion by modification.
cellular aromatic compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving aromatic compounds, any organic compound characterized by one or more planar rings, each of which contains conjugated double bonds and delocalized pi electrons, as carried out by individual cells.
coenzyme metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving coenzymes, any of various nonprotein organic cofactors that are required, in addition to an enzyme and a substrate, for an enzymatic reaction to proceed.
nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds; includes nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, assimilatory/dissimilatory nitrate reduction and the interconversion of nitrogenous organic matter and ammonium.
response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
inflammatory response
The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages.
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
humoral immune response
An immune response mediated through a body fluid.
organelle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an organelle within a cell. An organelle is an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
peroxisome organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a peroxisome. A peroxisome is a small, membrane-bounded organelle that uses dioxygen (O2) to oxidize organic molecules.
hemostasis
The stopping of bleeding (loss of body fluid) or the arrest of the circulation to an organ or part.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
steroid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving steroids, compounds with a 1,2,cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene nucleus.
cholesterol metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving cholesterol, cholest-5-en-3 beta-ol, the principal sterol of vertebrates and the precursor of many steroids, including bile acids and steroid hormones. It is a component of the plasma membrane lipid bilayer and of plasma lipoproteins and can be found in all animal tissues.
bile acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving bile acids, any of a group of steroid carboxylic acids occurring in bile, where they are present as the sodium salts of their amides with glycine or taurine.
androgen metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving androgens, C19 steroid hormones that can stimulate the development of male sexual characteristics.
lipid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of lipids, compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent.
catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of substances, including the breakdown of carbon compounds with the liberation of energy for use by the cell or organism.
biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones.
cellular amino acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
serine family amino acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids of the serine family, comprising cysteine, glycine, homoserine, selenocysteine and serine.
aromatic amino acid family metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving aromatic amino acid family, amino acids with aromatic ring (phenylalanine, tyrosine, tryptophan).
aromatic amino acid family catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of aromatic amino acid family, amino acids with aromatic ring (phenylalanine, tyrosine, tryptophan).
amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
amine catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
response to biotic stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a biotic stimulus, a stimulus caused or produced by a living organism.
response to wounding
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to the organism.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
response to organic substance
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an organic substance stimulus.
gene expression
The process by which a gene's sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
regulation of hormone levels
Any process that modulates the levels of hormone within an organism or a tissue. A hormone is any substance formed in very small amounts in one specialized organ or group of cells and carried (sometimes in the bloodstream) to another organ or group of cells in the same organism, upon which it has a specific regulatory action.
lipid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of lipids, compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent.
cellular component organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a cellular component.
organic acid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
organic acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
sterol metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving sterols, steroids with one or more hydroxyl groups and a hydrocarbon side-chain in the molecule.
protein processing
Any protein maturation process achieved by the cleavage of peptide bonds.
organic ether metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving organic ethers, any anhydride of the general formula R1-O-R2, formed between two identical or nonidentical organic hydroxy compounds.
aromatic compound biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of aromatic compounds, any substance containing an aromatic carbon ring.
aromatic compound catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of aromatic compounds, any substance containing an aromatic carbon ring.
protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general. Includes protein modification.
carboxylic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving carboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (COOH) groups or anions (COO-).
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
monocarboxylic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving monocarboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one carboxyl (COOH) group or anion (COO-).
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular hormone metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any hormone, naturally occurring substances secreted by specialized cells that affects the metabolism or behavior of other cells possessing functional receptors for the hormone, as carried out by individual cells.
wound healing
The series of events that restore integrity to a damaged tissue, following an injury.
cellular ketone metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any of a class of organic compounds that contain the carbonyl group, CO, and in which the carbonyl group is bonded only to carbon atoms, as carried out by individual cells. The general formula for a ketone is RCOR, where R and R are alkyl or aryl groups.
response to chemical stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a chemical stimulus.
hormone metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any hormone, naturally occurring substances secreted by specialized cells that affects the metabolism or behavior of other cells possessing functional receptors for the hormone.
pteridine and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any compound containing pteridine (pyrazino(2,3-dipyrimidine)), e.g. pteroic acid, xanthopterin and folic acid.
homeostatic process
Any biological process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state.
cholesterol homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of cholesterol within an organism or cell.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
oxoacid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any oxoacid; an oxoacid is a compound which contains oxygen, at least one other element, and at least one hydrogen bound to oxygen, and which produces a conjugate base by loss of positive hydrogen ion(s) (hydrons).
cellular amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular lipid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving lipids, as carried out by individual cells.
small molecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
small molecule catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
small molecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
carboxylic acid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of carboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (-COOH) groups.
carboxylic acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of carboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (-COOH) groups.
heterocycle metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving heterocyclic compounds, those with a cyclic molecular structure and at least two different atoms in the ring (or rings).
glycerolipid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving glycerolipids, any lipid with a glycerol backbone. Diacylglycerol and phosphatidate are key lipid intermediates of glycerolipid biosynthesis.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
positive regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
chemical homeostasis
Any biological process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of a chemical.
regulation of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
positive regulation of immune response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
coagulation
The process by which a fluid solution, or part of it, changes into a solid or semisolid mass.
regulation of coagulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of coagulation, the process by which a fluid solution, or part of it, changes into a solid or semisolid mass.
positive regulation of coagulation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of coagulation.
regulation of body fluid levels
Any process that modulates the levels of body fluids.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
cofactor metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a cofactor, a substance that is required for the activity of an enzyme or other protein. Cofactors may be inorganic, such as the metal atoms zinc, iron, and copper in certain forms, or organic, in which case they are referred to as coenzymes. Cofactors may either be bound tightly to active sites or bind loosely with the substrate.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
positive regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of an organismal process, any of the processes pertinent to the function of an organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
protein maturation
Any process leading to the attainment of the full functional capacity of a protein.
response to protein stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a protein stimulus.
lipid homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of lipid within an organism or cell.
sterol homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of sterol within an organism or cell.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of biological quality
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological quality. A biological quality is a measurable attribute of an organism or part of an organism, such as size, mass, shape, color, etc.
all
NA
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
organelle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an organelle within a cell. An organelle is an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
positive regulation of immune system process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
positive regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of an organismal process, any of the processes pertinent to the function of an organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
regulation of immune system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
positive regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular hormone metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any hormone, naturally occurring substances secreted by specialized cells that affects the metabolism or behavior of other cells possessing functional receptors for the hormone, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular amino acid and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, and compounds derived from amino acids, as carried out by individual cells.
protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general. Includes protein modification.
organic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
cellular amino acid and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, and compounds derived from amino acids, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular ketone metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any of a class of organic compounds that contain the carbonyl group, CO, and in which the carbonyl group is bonded only to carbon atoms, as carried out by individual cells. The general formula for a ketone is RCOR, where R and R are alkyl or aryl groups.
small molecule catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
small molecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
complement activation
Any process involved in the activation of any of the steps of the complement cascade, which allows for the direct killing of microbes, the disposal of immune complexes, and the regulation of other immune processes; the initial steps of complement activation involve one of three pathways, the classical pathway, the alternative pathway, and the lectin pathway, all of which lead to the terminal complement pathway.
positive regulation of immune system process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
immune effector process
Any process of the immune system that occurs as part of an immune response.
regulation of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
positive regulation of immune response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
regulation of coagulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of coagulation, the process by which a fluid solution, or part of it, changes into a solid or semisolid mass.
positive regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of an organismal process, any of the processes pertinent to the function of an organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
positive regulation of coagulation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of coagulation.
positive regulation of immune response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
positive regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
response to unfolded protein
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an unfolded protein stimulus.
regulation of body fluid levels
Any process that modulates the levels of body fluids.
cellular amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
organic acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
organic acid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
protein maturation
Any process leading to the attainment of the full functional capacity of a protein.
organic acid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
organic acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
aromatic compound biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of aromatic compounds, any substance containing an aromatic carbon ring.
aromatic compound catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of aromatic compounds, any substance containing an aromatic carbon ring.
pteridine and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any compound containing pteridine (pyrazino(2,3-dipyrimidine)), e.g. pteroic acid, xanthopterin and folic acid.
oxoacid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any oxoacid; an oxoacid is a compound which contains oxygen, at least one other element, and at least one hydrogen bound to oxygen, and which produces a conjugate base by loss of positive hydrogen ion(s) (hydrons).
pteridine and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any compound containing pteridine (pyrazino(2,3-dipyrimidine)), e.g. pteroic acid, xanthopterin and folic acid.
lipid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of lipids, compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent.
lipid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of lipids, compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent.
cellular lipid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving lipids, as carried out by individual cells.
positive regulation of immune response
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
activation of immune response
Any process that initiates an immune response.
complement activation
Any process involved in the activation of any of the steps of the complement cascade, which allows for the direct killing of microbes, the disposal of immune complexes, and the regulation of other immune processes; the initial steps of complement activation involve one of three pathways, the classical pathway, the alternative pathway, and the lectin pathway, all of which lead to the terminal complement pathway.
positive regulation of coagulation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of coagulation.
blood coagulation
The sequential process by which the multiple coagulation factors of the blood interact, ultimately resulting in the formation of an insoluble fibrin clot; it may be divided into three stages: stage 1, the formation of intrinsic and extrinsic prothrombin converting principle; stage 2, the formation of thrombin; stage 3, the formation of stable fibrin polymers.
inflammatory response
The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages.
hormone metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any hormone, naturally occurring substances secreted by specialized cells that affects the metabolism or behavior of other cells possessing functional receptors for the hormone.
cellular amino acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
cellular amino acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
aromatic amino acid family metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving aromatic amino acid family, amino acids with aromatic ring (phenylalanine, tyrosine, tryptophan).
cellular biogenic amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways occurring at the level of individual cells involving any of a group of naturally occurring, biologically active amines, such as norepinephrine, histamine, and serotonin, many of which act as neurotransmitters.
aromatic amino acid family catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of aromatic amino acid family, amino acids with aromatic ring (phenylalanine, tyrosine, tryptophan).
acylglycerol metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving acylglycerol, any mono-, di- or triester of glycerol with (one or more) fatty acids.
steroid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of steroids, compounds with a 1,2,cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene nucleus; includes de novo formation and steroid interconversion by modification.
androgen metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving androgens, C19 steroid hormones that can stimulate the development of male sexual characteristics.
sterol metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving sterols, steroids with one or more hydroxyl groups and a hydrocarbon side-chain in the molecule.
acylglycerol metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving acylglycerol, any mono-, di- or triester of glycerol with (one or more) fatty acids.
blood coagulation
The sequential process by which the multiple coagulation factors of the blood interact, ultimately resulting in the formation of an insoluble fibrin clot; it may be divided into three stages: stage 1, the formation of intrinsic and extrinsic prothrombin converting principle; stage 2, the formation of thrombin; stage 3, the formation of stable fibrin polymers.
response to unfolded protein
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an unfolded protein stimulus.
aromatic amino acid family catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of aromatic amino acid family, amino acids with aromatic ring (phenylalanine, tyrosine, tryptophan).
cellular amino acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
cellular amino acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
carboxylic acid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of carboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (-COOH) groups.
carboxylic acid catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of carboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (-COOH) groups.
activation of plasma proteins involved in acute inflammatory response
Any process activating plasma proteins by proteolysis as part of an acute inflammatory response.
bile acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving bile acids, any of a group of steroid carboxylic acids occurring in bile, where they are present as the sodium salts of their amides with glycine or taurine.
complement activation
Any process involved in the activation of any of the steps of the complement cascade, which allows for the direct killing of microbes, the disposal of immune complexes, and the regulation of other immune processes; the initial steps of complement activation involve one of three pathways, the classical pathway, the alternative pathway, and the lectin pathway, all of which lead to the terminal complement pathway.

intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
cell fraction
A generic term for parts of cells prepared by disruptive biochemical techniques.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
mitochondrion
A semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration.
integral to membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer. When used to describe a protein, indicates that all or part of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
endoplasmic reticulum
The irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae. The ER takes two forms, rough (or granular), with ribosomes adhering to the outer surface, and smooth (with no ribosomes attached).
peroxisome
A small, membrane-bounded organelle that uses dioxygen (O2) to oxidize organic molecules; contains some enzymes that produce and others that degrade hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).
peroxisomal membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding a peroxisome.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cytoplasm
All of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
peroxisomal part
Any constituent part of a peroxisome, a small, membrane-bounded organelle that uses dioxygen (O2) to oxidize organic molecules; contains some enzymes that produce and others that degrade hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).
endoplasmic reticulum lumen
The volume enclosed by the membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum.
endoplasmic reticulum membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding the endoplasmic reticulum.
stored secretory granule
A small subcellular vesicle, surrounded by a membrane, that is formed from the Golgi apparatus and contains a highly concentrated protein destined for secretion. Secretory granules move towards the periphery of the cell and upon stimulation, their membranes fuse with the cell membrane, and their protein load is exteriorized. Processing of the contained protein may take place in secretory granules.
endomembrane system
A collection of membranous structures involved in transport within the cell. The main components of the endomembrane system are endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, vesicles, cell membrane and nuclear envelope. Members of the endomembrane system pass materials through each other or though the use of vesicles.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
platelet alpha granule
A secretory organelle found in blood platelets, which is unique in that it exhibits further compartmentalization and acquires its protein content via two distinct mechanisms: (1) biosynthesis predominantly at the megakaryocyte (MK) level (with some vestigial platelet synthesis) (e.g. platelet factor 4) and (2) endocytosis and pinocytosis at both the MK and circulating platelet levels (e.g. fibrinogen (Fg) and IgG).
platelet alpha granule lumen
The volume enclosed by the membrane of the platelet alpha granule.
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intrinsic to organelle membrane
Located in an organelle membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
integral to organelle membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of an organelle membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
microbody membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding a microbody.
membrane-enclosed lumen
The enclosed volume within a sealed membrane or between two sealed membranes. Encompasses the volume enclosed by the membranes of a particular organelle, e.g. endoplasmic reticulum lumen, or the space between the two lipid bilayers of a double membrane surrounding an organelle, e.g. nuclear envelope lumen.
vesicle
Any small, fluid-filled, spherical organelle enclosed by membrane or protein.
vesicle lumen
The volume enclosed by the membrane or protein that forms a vesicle.
membrane-bounded vesicle
Any small, fluid-filled, spherical organelle enclosed by a lipid bilayer.
nuclear membrane-endoplasmic reticulum network
The continuous network of membranes encompassing the outer nuclear membrane and the endoplasmic reticulum.
microbody
Cytoplasmic organelles, spherical or oval in shape, that are bounded by a single membrane and contain oxidative enzymes, especially those utilizing hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, and prokaryotic structures such as anammoxosomes and pirellulosomes. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
organelle lumen
The internal volume enclosed by the membranes of a particular organelle; includes the volume enclosed by a single organelle membrane, e.g. endoplasmic reticulum lumen, or the volume enclosed by the innermost of the two lipid bilayers of an organelle envelope, e.g. nuclear lumen.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
mitochondrial part
Any constituent part of a mitochondrion, a semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration.
endoplasmic reticulum part
Any constituent part of the endoplasmic reticulum, the irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae.
cytoplasmic vesicle part
Any constituent part of cytoplasmic vesicle, a vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
microbody part
Any constituent part of a microbody, a cytoplasmic organelle, spherical or oval in shape, that is bounded by a single membrane and contains oxidative enzymes, especially those utilizing hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle lumen
The volume enclosed by the membrane of a cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle.
intracellular organelle lumen
An organelle lumen that is part of an intracellular organelle.
subsynaptic reticulum
An elaborate tubulolamellar membrane system that underlies the postsynaptic cell membrane.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
organelle lumen
The internal volume enclosed by the membranes of a particular organelle; includes the volume enclosed by a single organelle membrane, e.g. endoplasmic reticulum lumen, or the volume enclosed by the innermost of the two lipid bilayers of an organelle envelope, e.g. nuclear lumen.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
intrinsic to organelle membrane
Located in an organelle membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intracellular organelle lumen
An organelle lumen that is part of an intracellular organelle.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
nuclear membrane-endoplasmic reticulum network
The continuous network of membranes encompassing the outer nuclear membrane and the endoplasmic reticulum.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
endoplasmic reticulum membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding the endoplasmic reticulum.
nuclear membrane-endoplasmic reticulum network
The continuous network of membranes encompassing the outer nuclear membrane and the endoplasmic reticulum.
cytoplasmic vesicle part
Any constituent part of cytoplasmic vesicle, a vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
vesicle lumen
The volume enclosed by the membrane or protein that forms a vesicle.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
endoplasmic reticulum lumen
The volume enclosed by the membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum.
endoplasmic reticulum membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding the endoplasmic reticulum.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle lumen
The volume enclosed by the membrane of a cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle.
endoplasmic reticulum membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding the endoplasmic reticulum.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
mitochondrion
A semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration.
endoplasmic reticulum
The irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae. The ER takes two forms, rough (or granular), with ribosomes adhering to the outer surface, and smooth (with no ribosomes attached).
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
microbody
Cytoplasmic organelles, spherical or oval in shape, that are bounded by a single membrane and contain oxidative enzymes, especially those utilizing hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).
mitochondrial part
Any constituent part of a mitochondrion, a semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration.
endoplasmic reticulum part
Any constituent part of the endoplasmic reticulum, the irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae.
cytoplasmic vesicle part
Any constituent part of cytoplasmic vesicle, a vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
microbody part
Any constituent part of a microbody, a cytoplasmic organelle, spherical or oval in shape, that is bounded by a single membrane and contains oxidative enzymes, especially those utilizing hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).
subsynaptic reticulum
An elaborate tubulolamellar membrane system that underlies the postsynaptic cell membrane.
intrinsic to organelle membrane
Located in an organelle membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle lumen
The volume enclosed by the membrane of a cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle.
mitochondrial part
Any constituent part of a mitochondrion, a semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration.
endoplasmic reticulum part
Any constituent part of the endoplasmic reticulum, the irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae.
microbody membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding a microbody.
microbody part
Any constituent part of a microbody, a cytoplasmic organelle, spherical or oval in shape, that is bounded by a single membrane and contains oxidative enzymes, especially those utilizing hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).
endoplasmic reticulum part
Any constituent part of the endoplasmic reticulum, the irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae.
peroxisomal membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding a peroxisome.
integral to organelle membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of an organelle membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
peroxisomal part
Any constituent part of a peroxisome, a small, membrane-bounded organelle that uses dioxygen (O2) to oxidize organic molecules; contains some enzymes that produce and others that degrade hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).
platelet alpha granule lumen
The volume enclosed by the membrane of the platelet alpha granule.

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
serine-type endopeptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of internal, alpha-peptide bonds in a polypeptide chain by a catalytic mechanism that involves a catalytic triad consisting of a serine nucleophile that is activated by a proton relay involving an acidic residue (e.g. aspartate or glutamate) and a basic residue (usually histidine).
catalytic activity
Catalysis of a biochemical reaction at physiological temperatures. In biologically catalyzed reactions, the reactants are known as substrates, and the catalysts are naturally occurring macromolecular substances known as enzymes. Enzymes possess specific binding sites for substrates, and are usually composed wholly or largely of protein, but RNA that has catalytic activity (ribozyme) is often also regarded as enzymatic.
endopeptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of internal, alpha-peptide bonds in a polypeptide chain.
serine-type peptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of peptide bonds in a polypeptide chain by a catalytic mechanism that involves a catalytic triad consisting of a serine nucleophile that is activated by a proton relay involving an acidic residue (e.g. aspartate or glutamate) and a basic residue (usually histidine).
peptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of a peptide bond. A peptide bond is a covalent bond formed when the carbon atom from the carboxyl group of one amino acid shares electrons with the nitrogen atom from the amino group of a second amino acid.
binding
The selective, non-covalent, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
folic acid binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with folic acid, pteroylglutamic acid. Folic acid is widely distributed as a member of the vitamin B complex and is essential for the synthesis of purine and pyrimidines.
oxidoreductase activity
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction, a reversible chemical reaction in which the oxidation state of an atom or atoms within a molecule is altered. One substrate acts as a hydrogen or electron donor and becomes oxidized, while the other acts as hydrogen or electron acceptor and becomes reduced.
lipid binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a lipid.
peptidase activity, acting on L-amino acid peptides
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of peptide bonds formed between L-amino acids.
amino acid binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with an amino acid, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
hydrolase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of various bonds, e.g. C-O, C-N, C-C, phosphoric anhydride bonds, etc. Hydrolase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 3.
lyase activity
Catalysis of the cleavage of C-C, C-O, C-N and other bonds by other means than by hydrolysis or oxidation, or conversely adding a group to a double bond. They differ from other enzymes in that two substrates are involved in one reaction direction, but only one in the other direction. When acting on the single substrate, a molecule is eliminated and this generates either a new double bond or a new ring.
carbon-sulfur lyase activity
Catalysis of the elimination of H2S or substituted H2S.
serine hydrolase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of a substrate by a catalytic mechanism that involves a catalytic triad consisting of a serine nucleophile that is activated by a proton relay involving an acidic residue (e.g. aspartate or glutamate) and a basic residue (usually histidine).
vitamin binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a vitamin, one of a number of unrelated organic substances that occur in many foods in small amounts and that are necessary in trace amounts for the normal metabolic functioning of the body.
pyridoxal phosphate binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with pyridoxal 5' phosphate, 3-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methyl4-pyridine carboxaldehyde 5' phosphate, the biologically active form of vitamin B6.
carboxylic acid binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a carboxylic acid, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (COOH) groups or anions (COO-).
amine binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group.
cofactor binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a cofactor, a substance that is required for the activity of an enzyme or other protein. Cofactors may be inorganic, such as the metal atoms zinc, iron, and copper in certain forms, or organic, in which case they are referred to as coenzymes. Cofactors may either be bound tightly to active sites or bind loosely with the substrate.
coenzyme binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a coenzyme, any of various nonprotein organic cofactors that are required, in addition to an enzyme and a substrate, for an enzymatic reaction to proceed.
vitamin B6 binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any of the vitamin B6 compounds: pyridoxal, pyridoxamine and pyridoxine and the active form, pyridoxal phosphate.
all
NA
amino acid binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with an amino acid, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
pyridoxal phosphate binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with pyridoxal 5' phosphate, 3-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methyl4-pyridine carboxaldehyde 5' phosphate, the biologically active form of vitamin B6.
folic acid binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with folic acid, pteroylglutamic acid. Folic acid is widely distributed as a member of the vitamin B complex and is essential for the synthesis of purine and pyrimidines.
serine-type peptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of peptide bonds in a polypeptide chain by a catalytic mechanism that involves a catalytic triad consisting of a serine nucleophile that is activated by a proton relay involving an acidic residue (e.g. aspartate or glutamate) and a basic residue (usually histidine).
serine-type endopeptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of internal, alpha-peptide bonds in a polypeptide chain by a catalytic mechanism that involves a catalytic triad consisting of a serine nucleophile that is activated by a proton relay involving an acidic residue (e.g. aspartate or glutamate) and a basic residue (usually histidine).
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 04610 | 6.417e-07 | 2.343 | 14 | 21 | Complement and coagulation cascades |
| 04146 | 2.245e-05 | 3.347 | 15 | 30 | Peroxisome |
| 01100 | 3.454e-04 | 39.39 | 65 | 353 | Metabolic pathways |
| 00120 | 4.692e-02 | 0.3347 | 3 | 3 | Primary bile acid biosynthesis |
A1CFAPOBEC1 complementation factor (ENSG00000148584), score: 0.48 ABCA1ATP-binding cassette, sub-family A (ABC1), member 1 (ENSG00000165029), score: 0.63 ABCB11ATP-binding cassette, sub-family B (MDR/TAP), member 11 (ENSG00000073734), score: 0.61 ABCC1ATP-binding cassette, sub-family C (CFTR/MRP), member 1 (ENSG00000103222), score: -0.53 ABCC2ATP-binding cassette, sub-family C (CFTR/MRP), member 2 (ENSG00000023839), score: 0.49 ABCD3ATP-binding cassette, sub-family D (ALD), member 3 (ENSG00000117528), score: 0.74 ABCG5ATP-binding cassette, sub-family G (WHITE), member 5 (ENSG00000138075), score: 0.64 ABHD3abhydrolase domain containing 3 (ENSG00000158201), score: 0.43 ABI2abl-interactor 2 (ENSG00000138443), score: -0.56 ACAA2acetyl-CoA acyltransferase 2 (ENSG00000167315), score: 0.41 ACBD5acyl-CoA binding domain containing 5 (ENSG00000107897), score: 0.65 ACER2alkaline ceramidase 2 (ENSG00000177076), score: 0.48 ACO1aconitase 1, soluble (ENSG00000122729), score: 0.48 ACOT12acyl-CoA thioesterase 12 (ENSG00000172497), score: 0.6 ACSL5acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 5 (ENSG00000197142), score: 0.58 ACSM5acyl-CoA synthetase medium-chain family member 5 (ENSG00000183549), score: 0.42 ACYP2acylphosphatase 2, muscle type (ENSG00000170634), score: -0.51 ADAP2ArfGAP with dual PH domains 2 (ENSG00000184060), score: 0.5 ADRA1Badrenergic, alpha-1B-, receptor (ENSG00000170214), score: 0.44 AFMIDarylformamidase (ENSG00000183077), score: 0.42 AGPHD1aminoglycoside phosphotransferase domain containing 1 (ENSG00000188266), score: 0.4 AGXTalanine-glyoxylate aminotransferase (ENSG00000172482), score: 0.52 AHRaryl hydrocarbon receptor (ENSG00000106546), score: 0.44 AK2adenylate kinase 2 (ENSG00000004455), score: 0.51 AKR1D1aldo-keto reductase family 1, member D1 (delta 4-3-ketosteroid-5-beta-reductase) (ENSG00000122787), score: 0.55 ALAS1aminolevulinate, delta-, synthase 1 (ENSG00000023330), score: 0.56 ALBalbumin (ENSG00000163631), score: 0.56 ALDH2aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 family (mitochondrial) (ENSG00000111275), score: 0.43 ALDH8A1aldehyde dehydrogenase 8 family, member A1 (ENSG00000118514), score: 0.46 ALG5asparagine-linked glycosylation 5, dolichyl-phosphate beta-glucosyltransferase homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000120697), score: 0.42 AMBPalpha-1-microglobulin/bikunin precursor (ENSG00000106927), score: 0.5 AMDHD1amidohydrolase domain containing 1 (ENSG00000139344), score: 0.54 AMMECR1LAMME chromosomal region gene 1-like (ENSG00000144233), score: 0.51 ANKS4Bankyrin repeat and sterile alpha motif domain containing 4B (ENSG00000175311), score: 0.47 AP2B1adaptor-related protein complex 2, beta 1 subunit (ENSG00000006125), score: -0.48 AQP8aquaporin 8 (ENSG00000103375), score: 0.49 ARCN1archain 1 (ENSG00000095139), score: 0.52 ARHGAP42Rho GTPase activating protein 42 (ENSG00000165895), score: 0.44 ARHGEF38Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 38 (ENSG00000138784), score: 0.45 ASPGasparaginase homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000166183), score: 0.5 ATL2atlastin GTPase 2 (ENSG00000119787), score: 0.56 ATMINATM interactor (ENSG00000166454), score: -0.52 ATP13A3ATPase type 13A3 (ENSG00000133657), score: 0.48 ATP2B4ATPase, Ca++ transporting, plasma membrane 4 (ENSG00000058668), score: -0.57 ATP2C1ATPase, Ca++ transporting, type 2C, member 1 (ENSG00000017260), score: -0.5 ATP8B1ATPase, aminophospholipid transporter, class I, type 8B, member 1 (ENSG00000081923), score: 0.46 AVPR1Aarginine vasopressin receptor 1A (ENSG00000166148), score: 0.57 B3GALTLbeta 1,3-galactosyltransferase-like (ENSG00000187676), score: -0.52 B4GALT2UDP-Gal:betaGlcNAc beta 1,4- galactosyltransferase, polypeptide 2 (ENSG00000117411), score: -0.5 BACH1BTB and CNC homology 1, basic leucine zipper transcription factor 1 (ENSG00000156273), score: 0.42 BBS2Bardet-Biedl syndrome 2 (ENSG00000125124), score: -0.61 BCHEbutyrylcholinesterase (ENSG00000114200), score: 0.43 BCKDHBbranched chain keto acid dehydrogenase E1, beta polypeptide (ENSG00000083123), score: 0.43 BCMO1beta-carotene 15,15'-monooxygenase 1 (ENSG00000135697), score: 0.54 BMP2bone morphogenetic protein 2 (ENSG00000125845), score: 0.45 BPNT13'(2'), 5'-bisphosphate nucleotidase 1 (ENSG00000162813), score: 0.45 C11orf54chromosome 11 open reading frame 54 (ENSG00000182919), score: 0.42 C12orf72chromosome 12 open reading frame 72 (ENSG00000139160), score: 0.45 C13orf15chromosome 13 open reading frame 15 (ENSG00000102760), score: -0.57 C16orf70chromosome 16 open reading frame 70 (ENSG00000125149), score: 0.48 C5complement component 5 (ENSG00000106804), score: 0.61 C5orf33chromosome 5 open reading frame 33 (ENSG00000152620), score: 0.45 C7orf23chromosome 7 open reading frame 23 (ENSG00000135185), score: 0.44 C8Acomplement component 8, alpha polypeptide (ENSG00000157131), score: 0.59 C8Gcomplement component 8, gamma polypeptide (ENSG00000176919), score: 0.53 C9orf150chromosome 9 open reading frame 150 (ENSG00000153714), score: 0.56 CA1carbonic anhydrase I (ENSG00000133742), score: 0.68 CAPRIN2caprin family member 2 (ENSG00000110888), score: -0.59 CASP6caspase 6, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase (ENSG00000138794), score: 0.43 CASP8caspase 8, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase (ENSG00000064012), score: 0.42 CCBL1cysteine conjugate-beta lyase, cytoplasmic (ENSG00000171097), score: 0.43 CCBL2cysteine conjugate-beta lyase 2 (ENSG00000137944), score: 0.62 CCDC92coiled-coil domain containing 92 (ENSG00000119242), score: -0.64 CCRL1chemokine (C-C motif) receptor-like 1 (ENSG00000129048), score: 0.62 CDK14cyclin-dependent kinase 14 (ENSG00000058091), score: -0.48 CDK8cyclin-dependent kinase 8 (ENSG00000132964), score: 0.45 CDO1cysteine dioxygenase, type I (ENSG00000129596), score: 0.53 CEPT1choline/ethanolamine phosphotransferase 1 (ENSG00000134255), score: 0.43 CHUKconserved helix-loop-helix ubiquitous kinase (ENSG00000213341), score: 0.52 CIB3calcium and integrin binding family member 3 (ENSG00000141977), score: 0.48 CMTM8CKLF-like MARVEL transmembrane domain containing 8 (ENSG00000170293), score: 0.45 CNR2cannabinoid receptor 2 (macrophage) (ENSG00000188822), score: 1 COLEC10collectin sub-family member 10 (C-type lectin) (ENSG00000184374), score: 0.46 COPB2coatomer protein complex, subunit beta 2 (beta prime) (ENSG00000184432), score: 0.5 CPB2carboxypeptidase B2 (plasma) (ENSG00000080618), score: 0.56 CPOXcoproporphyrinogen oxidase (ENSG00000080819), score: 0.46 CRCPCGRP receptor component (ENSG00000241258), score: 0.41 CREB3L3cAMP responsive element binding protein 3-like 3 (ENSG00000060566), score: 0.63 CREG1cellular repressor of E1A-stimulated genes 1 (ENSG00000143162), score: 0.49 CROTcarnitine O-octanoyltransferase (ENSG00000005469), score: 0.46 CRYGNcrystallin, gamma N (ENSG00000127377), score: 0.53 CTHcystathionase (cystathionine gamma-lyase) (ENSG00000116761), score: 0.57 CYP39A1cytochrome P450, family 39, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000146233), score: 0.57 CYP7B1cytochrome P450, family 7, subfamily B, polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000172817), score: 0.65 DAAM2dishevelled associated activator of morphogenesis 2 (ENSG00000146122), score: -0.49 DAKdihydroxyacetone kinase 2 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000149476), score: 0.42 DARSaspartyl-tRNA synthetase (ENSG00000115866), score: 0.48 DCLRE1ADNA cross-link repair 1A (ENSG00000198924), score: 0.41 DERL1Der1-like domain family, member 1 (ENSG00000136986), score: 0.53 DHCR77-dehydrocholesterol reductase (ENSG00000172893), score: 0.42 DHDPSLdihydrodipicolinate synthase-like, mitochondrial (ENSG00000241935), score: 0.42 DHTKD1dehydrogenase E1 and transketolase domain containing 1 (ENSG00000181192), score: 0.41 DIP2ADIP2 disco-interacting protein 2 homolog A (Drosophila) (ENSG00000160305), score: -0.53 DMGDHdimethylglycine dehydrogenase (ENSG00000132837), score: 0.49 DNAJC22DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 22 (ENSG00000178401), score: 0.56 DNAJC3DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 3 (ENSG00000102580), score: 0.51 DNAJC9DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 9 (ENSG00000213551), score: -0.49 DNTTdeoxynucleotidyltransferase, terminal (ENSG00000107447), score: 0.57 EDEM1ER degradation enhancer, mannosidase alpha-like 1 (ENSG00000134109), score: 0.49 EDEM2ER degradation enhancer, mannosidase alpha-like 2 (ENSG00000088298), score: 0.42 EEA1early endosome antigen 1 (ENSG00000102189), score: 0.48 EGFRepidermal growth factor receptor (ENSG00000146648), score: 0.64 EHHADHenoyl-CoA, hydratase/3-hydroxyacyl CoA dehydrogenase (ENSG00000113790), score: 0.43 ELK4ELK4, ETS-domain protein (SRF accessory protein 1) (ENSG00000158711), score: 0.42 EPB41L4Berythrocyte membrane protein band 4.1 like 4B (ENSG00000095203), score: 0.42 EPHA1EPH receptor A1 (ENSG00000146904), score: 0.45 EPN2epsin 2 (ENSG00000072134), score: -0.49 ERN1endoplasmic reticulum to nucleus signaling 1 (ENSG00000178607), score: 0.62 ERP44endoplasmic reticulum protein 44 (ENSG00000023318), score: 0.41 ESR1estrogen receptor 1 (ENSG00000091831), score: 0.44 ETFDHelectron-transferring-flavoprotein dehydrogenase (ENSG00000171503), score: 0.41 ETNK2ethanolamine kinase 2 (ENSG00000143845), score: 0.42 EVI5ecotropic viral integration site 5 (ENSG00000067208), score: 0.5 F10coagulation factor X (ENSG00000126218), score: 0.42 F2coagulation factor II (thrombin) (ENSG00000180210), score: 0.54 F9coagulation factor IX (ENSG00000101981), score: 0.55 FABP2fatty acid binding protein 2, intestinal (ENSG00000145384), score: 0.95 FAM105Bfamily with sequence similarity 105, member B (ENSG00000154124), score: 0.54 FAM160B1family with sequence similarity 160, member B1 (ENSG00000151553), score: 0.58 FAM175Bfamily with sequence similarity 175, member B (ENSG00000165660), score: 0.43 FAM176Afamily with sequence similarity 176, member A (ENSG00000115363), score: 0.46 FAM59Afamily with sequence similarity 59, member A (ENSG00000141441), score: 0.45 FAM69Bfamily with sequence similarity 69, member B (ENSG00000165716), score: -0.56 FAM82A2family with sequence similarity 82, member A2 (ENSG00000137824), score: 0.47 FAR1fatty acyl CoA reductase 1 (ENSG00000197601), score: -0.57 FBXO3F-box protein 3 (ENSG00000110429), score: 0.52 FDXRferredoxin reductase (ENSG00000161513), score: 0.41 FETUBfetuin B (ENSG00000090512), score: 0.7 FEZ1fasciculation and elongation protein zeta 1 (zygin I) (ENSG00000149557), score: -0.49 FGBfibrinogen beta chain (ENSG00000171564), score: 0.51 FGD6FYVE, RhoGEF and PH domain containing 6 (ENSG00000180263), score: 0.47 FGGfibrinogen gamma chain (ENSG00000171557), score: 0.51 FN1fibronectin 1 (ENSG00000115414), score: 0.56 GAS2growth arrest-specific 2 (ENSG00000148935), score: 0.43 GBE1glucan (1,4-alpha-), branching enzyme 1 (ENSG00000114480), score: 0.49 GCH1GTP cyclohydrolase 1 (ENSG00000131979), score: 0.53 GCLMglutamate-cysteine ligase, modifier subunit (ENSG00000023909), score: 0.5 GDF2growth differentiation factor 2 (ENSG00000128802), score: 0.52 GFRA1GDNF family receptor alpha 1 (ENSG00000151892), score: 0.44 GGPS1geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase 1 (ENSG00000152904), score: -0.53 GJB1gap junction protein, beta 1, 32kDa (ENSG00000169562), score: 0.48 GJB2gap junction protein, beta 2, 26kDa (ENSG00000165474), score: 0.53 GLO1glyoxalase I (ENSG00000124767), score: 0.46 GLT25D1glycosyltransferase 25 domain containing 1 (ENSG00000130309), score: 0.47 GMPRguanosine monophosphate reductase (ENSG00000137198), score: -0.63 GNAI1guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), alpha inhibiting activity polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000127955), score: -0.54 GNB5guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), beta 5 (ENSG00000069966), score: -0.53 GNEglucosamine (UDP-N-acetyl)-2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase (ENSG00000159921), score: 0.66 GNMTglycine N-methyltransferase (ENSG00000124713), score: 0.63 GPLD1glycosylphosphatidylinositol specific phospholipase D1 (ENSG00000112293), score: 0.61 GPR146G protein-coupled receptor 146 (ENSG00000164849), score: 0.49 GPR180G protein-coupled receptor 180 (ENSG00000152749), score: 0.44 GXYLT1glucoside xylosyltransferase 1 (ENSG00000151233), score: 0.51 H6PDhexose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (glucose 1-dehydrogenase) (ENSG00000049239), score: 0.56 HALhistidine ammonia-lyase (ENSG00000084110), score: 0.74 HAO1hydroxyacid oxidase (glycolate oxidase) 1 (ENSG00000101323), score: 0.57 HDGFRP3hepatoma-derived growth factor, related protein 3 (ENSG00000166503), score: -0.51 HEBP1heme binding protein 1 (ENSG00000013583), score: 0.5 HERPUD1homocysteine-inducible, endoplasmic reticulum stress-inducible, ubiquitin-like domain member 1 (ENSG00000051108), score: 0.49 HGDhomogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase (ENSG00000113924), score: 0.46 HGFhepatocyte growth factor (hepapoietin A; scatter factor) (ENSG00000019991), score: 0.51 HM13histocompatibility (minor) 13 (ENSG00000101294), score: 0.42 HMGCR3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase (ENSG00000113161), score: 0.42 HNF4Ahepatocyte nuclear factor 4, alpha (ENSG00000101076), score: 0.44 HNRNPRheterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein R (ENSG00000125944), score: -0.57 HPXhemopexin (ENSG00000110169), score: 0.53 HRGhistidine-rich glycoprotein (ENSG00000113905), score: 0.51 HTRA1HtrA serine peptidase 1 (ENSG00000166033), score: -0.72 IDH1isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (NADP+), soluble (ENSG00000138413), score: 0.43 IFIH1interferon induced with helicase C domain 1 (ENSG00000115267), score: 0.42 IGF1insulin-like growth factor 1 (somatomedin C) (ENSG00000017427), score: 0.72 IGF1Rinsulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (ENSG00000140443), score: -0.51 IGFBP1insulin-like growth factor binding protein 1 (ENSG00000146678), score: 0.45 IL1RAPinterleukin 1 receptor accessory protein (ENSG00000196083), score: 0.49 IL6STinterleukin 6 signal transducer (gp130, oncostatin M receptor) (ENSG00000134352), score: 0.56 INHBAinhibin, beta A (ENSG00000122641), score: 0.43 ITCHitchy E3 ubiquitin protein ligase homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000078747), score: 0.43 IYDiodotyrosine deiodinase (ENSG00000009765), score: 0.56 JAG2jagged 2 (ENSG00000184916), score: -0.54 JAM3junctional adhesion molecule 3 (ENSG00000166086), score: -0.58 KIAA1370KIAA1370 (ENSG00000047346), score: 0.47 KIFAP3kinesin-associated protein 3 (ENSG00000075945), score: -0.62 KLBklotho beta (ENSG00000134962), score: 0.65 KLF15Kruppel-like factor 15 (ENSG00000163884), score: 0.46 KMOkynurenine 3-monooxygenase (kynurenine 3-hydroxylase) (ENSG00000117009), score: 0.47 LARP4BLa ribonucleoprotein domain family, member 4B (ENSG00000107929), score: 0.49 LCLAT1lysocardiolipin acyltransferase 1 (ENSG00000172954), score: 0.44 LEAP2liver expressed antimicrobial peptide 2 (ENSG00000164406), score: 0.41 LECT2leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin 2 (ENSG00000145826), score: 0.7 LIFRleukemia inhibitory factor receptor alpha (ENSG00000113594), score: 0.67 LIPClipase, hepatic (ENSG00000166035), score: 0.52 LMBRD2LMBR1 domain containing 2 (ENSG00000164187), score: 0.4 LOC100292202similar to solute carrier family 25, member 25 (ENSG00000148339), score: 0.53 LPGAT1lysophosphatidylglycerol acyltransferase 1 (ENSG00000123684), score: 0.46 LPIN1lipin 1 (ENSG00000134324), score: 0.57 LPIN2lipin 2 (ENSG00000101577), score: 0.58 LRATlecithin retinol acyltransferase (phosphatidylcholine--retinol O-acyltransferase) (ENSG00000121207), score: 0.57 LRIT2leucine-rich repeat, immunoglobulin-like and transmembrane domains 2 (ENSG00000204033), score: 0.52 LYSMD3LysM, putative peptidoglycan-binding, domain containing 3 (ENSG00000176018), score: 0.52 MAN2A1mannosidase, alpha, class 2A, member 1 (ENSG00000112893), score: 0.53 MASP1mannan-binding lectin serine peptidase 1 (C4/C2 activating component of Ra-reactive factor) (ENSG00000127241), score: 0.41 MASP2mannan-binding lectin serine peptidase 2 (ENSG00000009724), score: 0.47 MAT1Amethionine adenosyltransferase I, alpha (ENSG00000151224), score: 0.6 MCM10minichromosome maintenance complex component 10 (ENSG00000065328), score: 0.66 ME3malic enzyme 3, NADP(+)-dependent, mitochondrial (ENSG00000151376), score: -0.55 MFSD2Amajor facilitator superfamily domain containing 2A (ENSG00000168389), score: 0.41 MGAT4Amannosyl (alpha-1,3-)-glycoprotein beta-1,4-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase, isozyme A (ENSG00000071073), score: -0.57 MIA3melanoma inhibitory activity family, member 3 (ENSG00000154305), score: 0.62 MINPP1multiple inositol-polyphosphate phosphatase 1 (ENSG00000107789), score: 0.49 MKS1Meckel syndrome, type 1 (ENSG00000011143), score: -0.51 MOCOSmolybdenum cofactor sulfurase (ENSG00000075643), score: 0.44 MOCS1molybdenum cofactor synthesis 1 (ENSG00000124615), score: 0.42 MOSPD2motile sperm domain containing 2 (ENSG00000130150), score: 0.45 MPZL2myelin protein zero-like 2 (ENSG00000149573), score: 0.48 MPZL3myelin protein zero-like 3 (ENSG00000160588), score: 0.44 MRASmuscle RAS oncogene homolog (ENSG00000158186), score: -0.48 MTTPmicrosomal triglyceride transfer protein (ENSG00000138823), score: 0.56 MYH10myosin, heavy chain 10, non-muscle (ENSG00000133026), score: -0.56 MYO1Bmyosin IB (ENSG00000128641), score: 0.48 NADKNAD kinase (ENSG00000008130), score: 0.47 NAPEPLDN-acyl phosphatidylethanolamine phospholipase D (ENSG00000161048), score: -0.62 NDUFA6NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 alpha subcomplex, 6, 14kDa (ENSG00000184983), score: 0.43 NECAB3N-terminal EF-hand calcium binding protein 3 (ENSG00000125967), score: -0.6 NPC1Niemann-Pick disease, type C1 (ENSG00000141458), score: 0.51 NR0B2nuclear receptor subfamily 0, group B, member 2 (ENSG00000131910), score: 0.41 NR1H3nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group H, member 3 (ENSG00000025434), score: 0.42 NR1H4nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group H, member 4 (ENSG00000012504), score: 0.54 NR5A2nuclear receptor subfamily 5, group A, member 2 (ENSG00000116833), score: 0.61 NRBF2nuclear receptor binding factor 2 (ENSG00000148572), score: 0.46 NUDT12nudix (nucleoside diphosphate linked moiety X)-type motif 12 (ENSG00000112874), score: 0.5 NUDT19nudix (nucleoside diphosphate linked moiety X)-type motif 19 (ENSG00000213965), score: 0.42 NUP93nucleoporin 93kDa (ENSG00000102900), score: -0.48 OAZ2ornithine decarboxylase antizyme 2 (ENSG00000180304), score: -0.53 OGDHLoxoglutarate dehydrogenase-like (ENSG00000197444), score: -0.5 OIT3oncoprotein induced transcript 3 (ENSG00000138315), score: 0.4 ONECUT1one cut homeobox 1 (ENSG00000169856), score: 0.58 OSCP1organic solute carrier partner 1 (ENSG00000116885), score: -0.49 OTCornithine carbamoyltransferase (ENSG00000036473), score: 0.71 P2RX4purinergic receptor P2X, ligand-gated ion channel, 4 (ENSG00000135124), score: 0.44 P4HTMprolyl 4-hydroxylase, transmembrane (endoplasmic reticulum) (ENSG00000178467), score: -0.68 PAFAH2platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase 2, 40kDa (ENSG00000158006), score: 0.51 PAHphenylalanine hydroxylase (ENSG00000171759), score: 0.51 PAK1IP1PAK1 interacting protein 1 (ENSG00000111845), score: 0.42 PANK1pantothenate kinase 1 (ENSG00000152782), score: 0.55 PAPSS23'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate synthase 2 (ENSG00000198682), score: 0.47 PAQR9progestin and adipoQ receptor family member IX (ENSG00000188582), score: 0.41 PARD3par-3 partitioning defective 3 homolog (C. elegans) (ENSG00000148498), score: 0.43 PCBD2pterin-4 alpha-carbinolamine dehydratase/dimerization cofactor of hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 alpha (TCF1) 2 (ENSG00000132570), score: 0.41 PCK1phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase 1 (soluble) (ENSG00000124253), score: 0.47 PCSK9proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (ENSG00000169174), score: 0.41 PDCD4programmed cell death 4 (neoplastic transformation inhibitor) (ENSG00000150593), score: 0.53 PDE3Bphosphodiesterase 3B, cGMP-inhibited (ENSG00000152270), score: 0.45 PDE7Aphosphodiesterase 7A (ENSG00000205268), score: -0.5 PDIA5protein disulfide isomerase family A, member 5 (ENSG00000065485), score: 0.43 PDP1pyruvate dehyrogenase phosphatase catalytic subunit 1 (ENSG00000164951), score: -0.59 PDP2pyruvate dehyrogenase phosphatase catalytic subunit 2 (ENSG00000172840), score: 0.58 PEMTphosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase (ENSG00000133027), score: 0.5 PEX11Aperoxisomal biogenesis factor 11 alpha (ENSG00000166821), score: 0.55 PEX11Gperoxisomal biogenesis factor 11 gamma (ENSG00000104883), score: 0.41 PEX16peroxisomal biogenesis factor 16 (ENSG00000121680), score: 0.59 PEX7peroxisomal biogenesis factor 7 (ENSG00000112357), score: 0.56 PIK3R3phosphoinositide-3-kinase, regulatory subunit 3 (gamma) (ENSG00000117461), score: -0.49 PIP5K1Bphosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase, type I, beta (ENSG00000107242), score: -0.48 PLA2G12Bphospholipase A2, group XIIB (ENSG00000138308), score: 0.52 PLAAphospholipase A2-activating protein (ENSG00000137055), score: 0.54 PLATplasminogen activator, tissue (ENSG00000104368), score: -0.55 PLK3polo-like kinase 3 (ENSG00000173846), score: 0.58 PM20D1peptidase M20 domain containing 1 (ENSG00000162877), score: 0.55 POLR2Cpolymerase (RNA) II (DNA directed) polypeptide C, 33kDa (ENSG00000102978), score: -0.5 PPEF2protein phosphatase, EF-hand calcium binding domain 2 (ENSG00000156194), score: 0.44 PPP1R15Bprotein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 15B (ENSG00000158615), score: 0.65 PPP1R3Dprotein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 3D (ENSG00000132825), score: -0.51 PPP2R5Aprotein phosphatase 2, regulatory subunit B', alpha (ENSG00000066027), score: 0.59 PRKD1protein kinase D1 (ENSG00000184304), score: -0.5 PRKD3protein kinase D3 (ENSG00000115825), score: 0.59 PRLRprolactin receptor (ENSG00000113494), score: 0.63 PROX1prospero homeobox 1 (ENSG00000117707), score: 0.4 PROZprotein Z, vitamin K-dependent plasma glycoprotein (ENSG00000126231), score: 0.53 PSEN2presenilin 2 (Alzheimer disease 4) (ENSG00000143801), score: 0.65 PSMD12proteasome (prosome, macropain) 26S subunit, non-ATPase, 12 (ENSG00000197170), score: 0.41 PYGLphosphorylase, glycogen, liver (ENSG00000100504), score: 0.56 RAPH1Ras association (RalGDS/AF-6) and pleckstrin homology domains 1 (ENSG00000173166), score: 0.47 RASL11ARAS-like, family 11, member A (ENSG00000122035), score: -0.49 RASL12RAS-like, family 12 (ENSG00000103710), score: -0.49 RASSF6Ras association (RalGDS/AF-6) domain family member 6 (ENSG00000169435), score: 0.5 RBP4retinol binding protein 4, plasma (ENSG00000138207), score: 0.46 RCN2reticulocalbin 2, EF-hand calcium binding domain (ENSG00000117906), score: -0.59 RER1RER1 retention in endoplasmic reticulum 1 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000157916), score: 0.42 RGNregucalcin (senescence marker protein-30) (ENSG00000130988), score: 0.5 RNF144Bring finger protein 144B (ENSG00000137393), score: 0.49 RRAGCRas-related GTP binding C (ENSG00000116954), score: 0.41 RRBP1ribosome binding protein 1 homolog 180kDa (dog) (ENSG00000125844), score: 0.44 RXRAretinoid X receptor, alpha (ENSG00000186350), score: 0.43 SAP30BPSAP30 binding protein (ENSG00000161526), score: -0.5 SARDHsarcosine dehydrogenase (ENSG00000123453), score: 0.55 SCARB1scavenger receptor class B, member 1 (ENSG00000073060), score: 0.52 SCCPDHsaccharopine dehydrogenase (putative) (ENSG00000143653), score: -0.5 SCLYselenocysteine lyase (ENSG00000132330), score: 0.46 SCRN1secernin 1 (ENSG00000136193), score: -0.49 SDR42E1short chain dehydrogenase/reductase family 42E, member 1 (ENSG00000184860), score: 0.55 SEBOXSEBOX homeobox (ENSG00000109072), score: 0.47 SEC16ASEC16 homolog A (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000148396), score: 0.42 SEC16BSEC16 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000120341), score: 0.52 SEC23ASec23 homolog A (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000100934), score: 0.43 SEC24DSEC24 family, member D (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000150961), score: 0.48 SEC63SEC63 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000025796), score: 0.47 SEPSECSSep (O-phosphoserine) tRNA:Sec (selenocysteine) tRNA synthase (ENSG00000109618), score: 0.54 SERPINA10serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade A (alpha-1 antiproteinase, antitrypsin), member 10 (ENSG00000140093), score: 0.55 SERPINC1serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade C (antithrombin), member 1 (ENSG00000117601), score: 0.57 SERPINF2serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade F (alpha-2 antiplasmin, pigment epithelium derived factor), member 2 (ENSG00000167711), score: 0.44 SETBP1SET binding protein 1 (ENSG00000152217), score: -0.55 SFXN3sideroflexin 3 (ENSG00000107819), score: -0.56 SGCBsarcoglycan, beta (43kDa dystrophin-associated glycoprotein) (ENSG00000163069), score: -0.55 SGPL1sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase 1 (ENSG00000166224), score: 0.45 SLC16A10solute carrier family 16, member 10 (aromatic amino acid transporter) (ENSG00000112394), score: 0.72 SLC16A12solute carrier family 16, member 12 (monocarboxylic acid transporter 12) (ENSG00000152779), score: 0.48 SLC17A8solute carrier family 17 (sodium-dependent inorganic phosphate cotransporter), member 8 (ENSG00000179520), score: 0.89 SLC19A2solute carrier family 19 (thiamine transporter), member 2 (ENSG00000117479), score: 0.6 SLC25A16solute carrier family 25 (mitochondrial carrier; Graves disease autoantigen), member 16 (ENSG00000122912), score: 0.47 SLC25A17solute carrier family 25 (mitochondrial carrier; peroxisomal membrane protein, 34kDa), member 17 (ENSG00000100372), score: 0.43 SLC25A47solute carrier family 25, member 47 (ENSG00000140107), score: 0.65 SLC2A2solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 2 (ENSG00000163581), score: 0.52 SLC2A9solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 9 (ENSG00000109667), score: 0.57 SLC30A7solute carrier family 30 (zinc transporter), member 7 (ENSG00000162695), score: 0.46 SLC33A1solute carrier family 33 (acetyl-CoA transporter), member 1 (ENSG00000169359), score: 0.45 SLC35D1solute carrier family 35 (UDP-glucuronic acid/UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine dual transporter), member D1 (ENSG00000116704), score: 0.62 SLC38A4solute carrier family 38, member 4 (ENSG00000139209), score: 0.68 SLC39A8solute carrier family 39 (zinc transporter), member 8 (ENSG00000138821), score: 0.41 SLC46A1solute carrier family 46 (folate transporter), member 1 (ENSG00000076351), score: 0.51 SLC7A2solute carrier family 7 (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system), member 2 (ENSG00000003989), score: 0.65 SLC7A6solute carrier family 7 (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system), member 6 (ENSG00000103064), score: -0.72 SLIT3slit homolog 3 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000184347), score: -0.58 SMARCA1SWI/SNF related, matrix associated, actin dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily a, member 1 (ENSG00000102038), score: -0.67 SMYD4SET and MYND domain containing 4 (ENSG00000186532), score: -0.55 SPIRE1spire homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000134278), score: -0.57 SPP2secreted phosphoprotein 2, 24kDa (ENSG00000072080), score: 0.57 SRD5A2steroid-5-alpha-reductase, alpha polypeptide 2 (3-oxo-5 alpha-steroid delta 4-dehydrogenase alpha 2) (ENSG00000049319), score: 0.56 SSR3signal sequence receptor, gamma (translocon-associated protein gamma) (ENSG00000114850), score: 0.44 STAB2stabilin 2 (ENSG00000136011), score: 0.51 STARD5StAR-related lipid transfer (START) domain containing 5 (ENSG00000172345), score: 0.65 STAU2staufen, RNA binding protein, homolog 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000040341), score: -0.52 TATtyrosine aminotransferase (ENSG00000198650), score: 0.66 TBC1D8BTBC1 domain family, member 8B (with GRAM domain) (ENSG00000133138), score: 0.53 TBCELtubulin folding cofactor E-like (ENSG00000154114), score: 0.5 TCEA2transcription elongation factor A (SII), 2 (ENSG00000171703), score: -0.48 TDO2tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (ENSG00000151790), score: 0.67 TEX2testis expressed 2 (ENSG00000136478), score: 0.47 TGDSTDP-glucose 4,6-dehydratase (ENSG00000088451), score: 0.42 TLCD1TLC domain containing 1 (ENSG00000160606), score: 0.41 TMEM106Btransmembrane protein 106B (ENSG00000106460), score: 0.42 TMEM135transmembrane protein 135 (ENSG00000166575), score: 0.59 TMEM20transmembrane protein 20 (ENSG00000176273), score: 0.52 TMEM231transmembrane protein 231 (ENSG00000205084), score: -0.59 TMEM56transmembrane protein 56 (ENSG00000152078), score: 0.51 TOB1transducer of ERBB2, 1 (ENSG00000141232), score: 0.47 TOMM70Atranslocase of outer mitochondrial membrane 70 homolog A (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000154174), score: 0.42 TOR1Atorsin family 1, member A (torsin A) (ENSG00000136827), score: 0.58 TOR1Btorsin family 1, member B (torsin B) (ENSG00000136816), score: 0.46 TP53BP1tumor protein p53 binding protein 1 (ENSG00000067369), score: -0.54 TRIB2tribbles homolog 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000071575), score: -0.59 TRPC1transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily C, member 1 (ENSG00000144935), score: -0.52 TSPAN3tetraspanin 3 (ENSG00000140391), score: -0.78 TSR1TSR1, 20S rRNA accumulation, homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000167721), score: 0.48 TTC36tetratricopeptide repeat domain 36 (ENSG00000172425), score: 0.51 TTC39Ctetratricopeptide repeat domain 39C (ENSG00000168234), score: 0.61 TTPAtocopherol (alpha) transfer protein (ENSG00000137561), score: 0.6 TUBGCP5tubulin, gamma complex associated protein 5 (ENSG00000153575), score: -0.59 TULP3tubby like protein 3 (ENSG00000078246), score: -0.6 TXNDC15thioredoxin domain containing 15 (ENSG00000113621), score: 0.41 TXNL1thioredoxin-like 1 (ENSG00000091164), score: 0.41 TXNRD1thioredoxin reductase 1 (ENSG00000198431), score: 0.54 TYW3tRNA-yW synthesizing protein 3 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000162623), score: -0.54 UBR2ubiquitin protein ligase E3 component n-recognin 2 (ENSG00000024048), score: 0.55 UPB1ureidopropionase, beta (ENSG00000100024), score: 0.42 USO1USO1 vesicle docking protein homolog (yeast) (ENSG00000138768), score: 0.42 VPS54vacuolar protein sorting 54 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000143952), score: 0.51 VSIG4V-set and immunoglobulin domain containing 4 (ENSG00000155659), score: 0.45 WDFY2WD repeat and FYVE domain containing 2 (ENSG00000139668), score: 0.42 WDR36WD repeat domain 36 (ENSG00000134987), score: 0.44 WDR37WD repeat domain 37 (ENSG00000047056), score: -0.52 WDR89WD repeat domain 89 (ENSG00000140006), score: 0.41 WRBtryptophan rich basic protein (ENSG00000182093), score: -0.52 XCR1chemokine (C motif) receptor 1 (ENSG00000173578), score: 0.58 XKR9XK, Kell blood group complex subunit-related family, member 9 (ENSG00000221947), score: 0.76 YOD1YOD1 OTU deubiquinating enzyme 1 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000180667), score: 0.4 ZAP70zeta-chain (TCR) associated protein kinase 70kDa (ENSG00000115085), score: 0.46 ZC3H7Azinc finger CCCH-type containing 7A (ENSG00000122299), score: 0.43 ZNF750zinc finger protein 750 (ENSG00000141579), score: 0.69
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mdo_lv_f_ca1 | mdo | lv | f | _ |
| mdo_lv_m_ca1 | mdo | lv | m | _ |
| mmu_lv_m1_ca1 | mmu | lv | m | 1 |
| mmu_lv_f_ca1 | mmu | lv | f | _ |
| mmu_lv_m2_ca1 | mmu | lv | m | 2 |