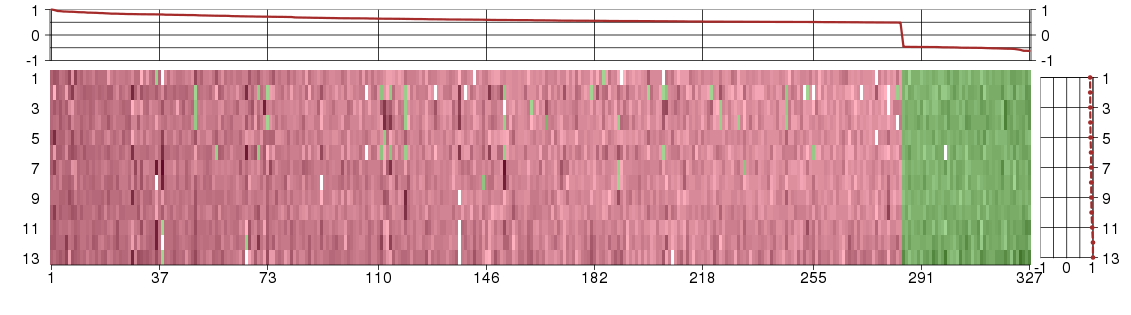

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

response to hypoxia
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating lowered oxygen tension. Hypoxia, defined as a decline in O2 levels below normoxic levels of 20.8 - 20.95%, results in metabolic adaptation at both the cellular and organismal level.
system process
A multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system. An organ system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a biological objective.
secretion
The controlled release of a substance by a cell, a group of cells, or a tissue.
transport
The directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells, or within a multicellular organism by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
ion transport
The directed movement of charged atoms or small charged molecules into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
cation transport
The directed movement of cations, atoms or small molecules with a net positive charge, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
sodium ion transport
The directed movement of sodium ions (Na+) into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
hydrogen transport
The directed movement of hydrogen (H2 or H+), into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
metal ion transport
The directed movement of metal ions, any metal ion with an electric charge, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
embryo development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an embryo from its formation until the end of its embryonic life stage. The end of the embryonic stage is organism-specific. For example, for mammals, the process would begin with zygote formation and end with birth. For insects, the process would begin at zygote formation and end with larval hatching. For plant zygotic embryos, this would be from zygote formation to the end of seed dormancy. For plant vegetative embryos, this would be from the initial determination of the cell or group of cells to form an embryo until the point when the embryo becomes independent of the parent plant.
organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis of an organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
excretion
The elimination by an organism of the waste products that arise as a result of metabolic activity. These products include water, carbon dioxide (CO2), and nitrogenous compounds.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
monovalent inorganic cation transport
The directed movement of inorganic cations with a valency of one into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. Inorganic cations are atoms or small molecules with a positive charge which do not contain carbon in covalent linkage.
proton transport
The directed movement of protons (hydrogen ions) into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
response to chemical stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a chemical stimulus.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
embryonic organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis, during the embryonic phase, of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
embryonic organ development
Development, taking place during the embryonic phase, of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
embryonic morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized during the embryonic phase. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. The embryonic phase begins with zygote formation. The end of the embryonic phase is organism-specific. For example, it would be at birth for mammals, larval hatching for insects and seed dormancy in plants.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
response to oxygen levels
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus reflecting the presence, absence, or concentration of oxygen.
all
NA
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
embryo development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an embryo from its formation until the end of its embryonic life stage. The end of the embryonic stage is organism-specific. For example, for mammals, the process would begin with zygote formation and end with birth. For insects, the process would begin at zygote formation and end with larval hatching. For plant zygotic embryos, this would be from zygote formation to the end of seed dormancy. For plant vegetative embryos, this would be from the initial determination of the cell or group of cells to form an embryo until the point when the embryo becomes independent of the parent plant.
embryonic morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized during the embryonic phase. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. The embryonic phase begins with zygote formation. The end of the embryonic phase is organism-specific. For example, it would be at birth for mammals, larval hatching for insects and seed dormancy in plants.
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
embryonic organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis, during the embryonic phase, of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
embryonic organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis, during the embryonic phase, of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis of an organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
embryonic organ development
Development, taking place during the embryonic phase, of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
response to hypoxia
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating lowered oxygen tension. Hypoxia, defined as a decline in O2 levels below normoxic levels of 20.8 - 20.95%, results in metabolic adaptation at both the cellular and organismal level.
excretion
The elimination by an organism of the waste products that arise as a result of metabolic activity. These products include water, carbon dioxide (CO2), and nitrogenous compounds.
sodium ion transport
The directed movement of sodium ions (Na+) into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
proton transport
The directed movement of protons (hydrogen ions) into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex
A large protein complex that catalyzes the synthesis or hydrolysis of ATP by a rotational mechanism, coupled to the transport of protons across a membrane. The complex comprises a membrane sector (F0, V0, or A0) that carries out proton transport and a cytoplasmic compartment sector (F1, V1, or A1) that catalyzes ATP synthesis or hydrolysis. Two major types have been characterized: V-type ATPases couple ATP hydrolysis to the transport of protons across a concentration gradient, whereas F-type ATPases, also known as ATP synthases, normally run in the reverse direction to utilize energy from a proton concentration or electrochemical gradient to synthesize ATP. A third type, A-type ATPases have been found in archaea, and are closely related to eukaryotic V-type ATPases but are reversible.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
integral to membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer. When used to describe a protein, indicates that all or part of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
extracellular space
That part of a multicellular organism outside the cells proper, usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
brush border
Dense covering of microvilli on the apical surface of epithelial cells in tissues such as the intestine, kidney, and choroid plexus; the microvilli aid absorption by increasing the surface area of the cell.
cell surface
The external part of the cell wall and/or plasma membrane.
apical plasma membrane
The region of the plasma membrane located at the apical end of the cell.
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
cell projection membrane
The portion of the plasma membrane surrounding a cell surface projection.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex
A proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex that couples ATP hydrolysis to the transport of protons across a concentration gradient. The resulting transmembrane electrochemical potential of H+ is used to drive a variety of (i) secondary active transport systems via H+-dependent symporters and antiporters and (ii) channel-mediated transport systems. The complex comprises a membrane sector (V0) that carries out proton transport and a cytoplasmic compartment sector (V1) that catalyzes ATP hydrolysis. V-type ATPases are found in the membranes of organelles such as vacuoles, endosomes, and lysosomes, and in the plasma membrane.
ion channel complex
A protein complex that spans a membrane and forms a water-filled channel across the phospholipid bilayer allowing selective ion transport down its electrochemical gradient.
cation channel complex
An ion channel complex through which cations pass.
sodium channel complex
An ion channel complex through which sodium ions pass.
cell projection
A prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
protein complex
Any macromolecular complex composed of two or more polypeptide subunits, which may or may not be identical. Protein complexes may have other associated non-protein prosthetic groups, such as nucleotides, metal ions or other small molecules.
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell projection part
Any constituent part of a cell projection, a prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
apical part of cell
The region of a polarized cell that forms a tip or is distal to a base. For example, in a polarized epithelial cell, the apical region has an exposed surface and lies opposite to the basal lamina that separates the epithelium from other tissue.
all
NA
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
cell projection part
Any constituent part of a cell projection, a prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex
A large protein complex that catalyzes the synthesis or hydrolysis of ATP by a rotational mechanism, coupled to the transport of protons across a membrane. The complex comprises a membrane sector (F0, V0, or A0) that carries out proton transport and a cytoplasmic compartment sector (F1, V1, or A1) that catalyzes ATP synthesis or hydrolysis. Two major types have been characterized: V-type ATPases couple ATP hydrolysis to the transport of protons across a concentration gradient, whereas F-type ATPases, also known as ATP synthases, normally run in the reverse direction to utilize energy from a proton concentration or electrochemical gradient to synthesize ATP. A third type, A-type ATPases have been found in archaea, and are closely related to eukaryotic V-type ATPases but are reversible.
ion channel complex
A protein complex that spans a membrane and forms a water-filled channel across the phospholipid bilayer allowing selective ion transport down its electrochemical gradient.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
apical plasma membrane
The region of the plasma membrane located at the apical end of the cell.
cell projection membrane
The portion of the plasma membrane surrounding a cell surface projection.
ion channel complex
A protein complex that spans a membrane and forms a water-filled channel across the phospholipid bilayer allowing selective ion transport down its electrochemical gradient.

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
catalytic activity
Catalysis of a biochemical reaction at physiological temperatures. In biologically catalyzed reactions, the reactants are known as substrates, and the catalysts are naturally occurring macromolecular substances known as enzymes. Enzymes possess specific binding sites for substrates, and are usually composed wholly or largely of protein, but RNA that has catalytic activity (ribozyme) is often also regarded as enzymatic.
serine-type peptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of peptide bonds in a polypeptide chain by a catalytic mechanism that involves a catalytic triad consisting of a serine nucleophile that is activated by a proton relay involving an acidic residue (e.g. aspartate or glutamate) and a basic residue (usually histidine).
peptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of a peptide bond. A peptide bond is a covalent bond formed when the carbon atom from the carboxyl group of one amino acid shares electrons with the nitrogen atom from the amino group of a second amino acid.
transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a substance from one side of a membrane to the other.
secondary active transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute from one side of a membrane to the other, up its concentration gradient. The transporter binds the solute and undergoes a series of conformational changes. Transport works equally well in either direction and is driven by a chemiosmotic source of energy. Chemiosmotic sources of energy include uniport, symport or antiport.
exopeptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of a peptide bond not more than three residues from the N- or C-terminus of a polypeptide chain, in a reaction that requires a free N-terminal amino group, C-terminal carboxyl group or both.
cation transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of cation from one side of the membrane to the other.
peptidase activity, acting on L-amino acid peptides
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of peptide bonds formed between L-amino acids.
ion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of an ion from one side of a membrane to the other.
hydrolase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of various bonds, e.g. C-O, C-N, C-C, phosphoric anhydride bonds, etc. Hydrolase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 3.
serine hydrolase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of a substrate by a catalytic mechanism that involves a catalytic triad consisting of a serine nucleophile that is activated by a proton relay involving an acidic residue (e.g. aspartate or glutamate) and a basic residue (usually histidine).
active transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a specific substance or related group of substances from one side of a membrane to the other, up the solute's concentration gradient. The transporter binds the solute and undergoes a series of conformational changes. Transport works equally well in either direction.
inorganic cation transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of inorganic cations from one side of a membrane to the other. Inorganic cations are atoms or small molecules with a positive charge that do not contain carbon in covalent linkage.
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
substrate-specific transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of a specific substance or group of related substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
all
NA
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
serine-type peptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of peptide bonds in a polypeptide chain by a catalytic mechanism that involves a catalytic triad consisting of a serine nucleophile that is activated by a proton relay involving an acidic residue (e.g. aspartate or glutamate) and a basic residue (usually histidine).
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 05110 | 9.104e-03 | 0.9228 | 6 | 15 | Vibrio cholerae infection |
| 04966 | 1.996e-02 | 0.4306 | 4 | 7 | Collecting duct acid secretion |
| 04145 | 4.710e-02 | 1.784 | 7 | 29 | Phagosome |
ABCC4ATP-binding cassette, sub-family C (CFTR/MRP), member 4 (ENSG00000125257), score: 0.55 ACE2angiotensin I converting enzyme (peptidyl-dipeptidase A) 2 (ENSG00000130234), score: 0.61 ACMSDaminocarboxymuconate semialdehyde decarboxylase (ENSG00000153086), score: 0.65 ACOT11acyl-CoA thioesterase 11 (ENSG00000162390), score: 0.58 ACPPacid phosphatase, prostate (ENSG00000014257), score: 0.92 ACTN4actinin, alpha 4 (ENSG00000130402), score: 0.54 ADMadrenomedullin (ENSG00000148926), score: 0.62 AGR2anterior gradient homolog 2 (Xenopus laevis) (ENSG00000106541), score: 0.64 AIM1absent in melanoma 1 (ENSG00000112297), score: 0.63 AKR1A1aldo-keto reductase family 1, member A1 (aldehyde reductase) (ENSG00000117448), score: 0.51 ALPK1alpha-kinase 1 (ENSG00000073331), score: 0.55 ANXA13annexin A13 (ENSG00000104537), score: 0.51 AQP3aquaporin 3 (Gill blood group) (ENSG00000165272), score: 0.58 ARHGAP24Rho GTPase activating protein 24 (ENSG00000138639), score: 0.61 ARMC7armadillo repeat containing 7 (ENSG00000125449), score: 0.54 ATP10DATPase, class V, type 10D (ENSG00000145246), score: 0.56 ATP2C2ATPase, Ca++ transporting, type 2C, member 2 (ENSG00000064270), score: 0.53 ATP6V0A4ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal V0 subunit a4 (ENSG00000105929), score: 0.81 ATP6V0D2ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 38kDa, V0 subunit d2 (ENSG00000147614), score: 0.77 ATP6V0E1ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 9kDa, V0 subunit e1 (ENSG00000113732), score: 0.56 ATP6V1C2ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 42kDa, V1 subunit C2 (ENSG00000143882), score: 0.51 AXIN2axin 2 (ENSG00000168646), score: -0.47 B4GALNT3beta-1,4-N-acetyl-galactosaminyl transferase 3 (ENSG00000139044), score: 0.54 BACE2beta-site APP-cleaving enzyme 2 (ENSG00000182240), score: 0.55 BARX2BARX homeobox 2 (ENSG00000043039), score: 0.76 BBOX1butyrobetaine (gamma), 2-oxoglutarate dioxygenase (gamma-butyrobetaine hydroxylase) 1 (ENSG00000129151), score: 0.67 BCAP29B-cell receptor-associated protein 29 (ENSG00000075790), score: -0.55 BDKRB2bradykinin receptor B2 (ENSG00000168398), score: 0.72 BNC2basonuclin 2 (ENSG00000173068), score: 0.65 BSPRYB-box and SPRY domain containing (ENSG00000119411), score: 0.49 C11orf54chromosome 11 open reading frame 54 (ENSG00000182919), score: 0.5 C18orf1chromosome 18 open reading frame 1 (ENSG00000168675), score: -0.62 C19orf28chromosome 19 open reading frame 28 (ENSG00000161091), score: 0.53 C20orf118chromosome 20 open reading frame 118 (ENSG00000101342), score: 0.51 C4orf31chromosome 4 open reading frame 31 (ENSG00000173376), score: 0.52 C8orf84chromosome 8 open reading frame 84 (ENSG00000164764), score: 0.71 C9orf72chromosome 9 open reading frame 72 (ENSG00000147894), score: -0.62 CA12carbonic anhydrase XII (ENSG00000074410), score: 0.9 CALB1calbindin 1, 28kDa (ENSG00000104327), score: 0.51 CAMK1Dcalcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase ID (ENSG00000183049), score: -0.49 CAPN13calpain 13 (ENSG00000162949), score: 0.55 CAPN2calpain 2, (m/II) large subunit (ENSG00000162909), score: 0.52 CASRcalcium-sensing receptor (ENSG00000036828), score: 0.75 CDCP1CUB domain containing protein 1 (ENSG00000163814), score: 0.6 CDH6cadherin 6, type 2, K-cadherin (fetal kidney) (ENSG00000113361), score: 0.68 CDK10cyclin-dependent kinase 10 (ENSG00000185324), score: 0.5 CDO1cysteine dioxygenase, type I (ENSG00000129596), score: -0.48 CLCN5chloride channel 5 (ENSG00000171365), score: 0.5 CLDN16claudin 16 (ENSG00000113946), score: 0.85 CLDN19claudin 19 (ENSG00000164007), score: 0.55 CLIC5chloride intracellular channel 5 (ENSG00000112782), score: 0.51 CLPTM1LCLPTM1-like (ENSG00000049656), score: 0.56 CMTM4CKLF-like MARVEL transmembrane domain containing 4 (ENSG00000183723), score: 0.51 COL4A3collagen, type IV, alpha 3 (Goodpasture antigen) (ENSG00000169031), score: 0.73 COL4A4collagen, type IV, alpha 4 (ENSG00000081052), score: 0.54 COMTD1catechol-O-methyltransferase domain containing 1 (ENSG00000165644), score: 0.5 CPEB3cytoplasmic polyadenylation element binding protein 3 (ENSG00000107864), score: -0.5 CPMcarboxypeptidase M (ENSG00000135678), score: 0.62 CRTAPcartilage associated protein (ENSG00000170275), score: 0.49 CRYAAcrystallin, alpha A (ENSG00000160202), score: 0.78 CRYL1crystallin, lambda 1 (ENSG00000165475), score: 0.67 CTGFconnective tissue growth factor (ENSG00000118523), score: 0.52 CTNND1catenin (cadherin-associated protein), delta 1 (ENSG00000198561), score: 0.56 CTSHcathepsin H (ENSG00000103811), score: 0.66 CUBNcubilin (intrinsic factor-cobalamin receptor) (ENSG00000107611), score: 0.8 CUX2cut-like homeobox 2 (ENSG00000111249), score: -0.52 CXCL14chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 14 (ENSG00000145824), score: 0.67 D2HGDHD-2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase (ENSG00000180902), score: 0.52 DAAM1dishevelled associated activator of morphogenesis 1 (ENSG00000100592), score: -0.58 DAB2disabled homolog 2, mitogen-responsive phosphoprotein (Drosophila) (ENSG00000153071), score: 0.71 DDCdopa decarboxylase (aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase) (ENSG00000132437), score: 0.77 DDHD1DDHD domain containing 1 (ENSG00000100523), score: -0.47 DENND2DDENN/MADD domain containing 2D (ENSG00000162777), score: 0.6 DENND5BDENN/MADD domain containing 5B (ENSG00000170456), score: -0.51 DEPDC6DEP domain containing 6 (ENSG00000155792), score: 0.55 DGKEdiacylglycerol kinase, epsilon 64kDa (ENSG00000153933), score: -0.47 DHDPSLdihydrodipicolinate synthase-like, mitochondrial (ENSG00000241935), score: 0.51 DOK4docking protein 4 (ENSG00000125170), score: 0.55 DPEP1dipeptidase 1 (renal) (ENSG00000015413), score: 0.85 DPP4dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 (ENSG00000197635), score: 0.61 DSG2desmoglein 2 (ENSG00000046604), score: 0.52 EBNA1BP2EBNA1 binding protein 2 (ENSG00000117395), score: 0.49 EGFepidermal growth factor (ENSG00000138798), score: 0.71 EHFets homologous factor (ENSG00000135373), score: 0.67 ELF3E74-like factor 3 (ets domain transcription factor, epithelial-specific ) (ENSG00000163435), score: 0.74 ELF5E74-like factor 5 (ets domain transcription factor) (ENSG00000135374), score: 0.91 ELMO3engulfment and cell motility 3 (ENSG00000102890), score: 0.52 ENPEPglutamyl aminopeptidase (aminopeptidase A) (ENSG00000138792), score: 0.68 EPCAMepithelial cell adhesion molecule (ENSG00000119888), score: 0.75 ERBB2v-erb-b2 erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene homolog 2, neuro/glioblastoma derived oncogene homolog (avian) (ENSG00000141736), score: 0.67 ESRP1epithelial splicing regulatory protein 1 (ENSG00000104413), score: 0.79 EVCEllis van Creveld syndrome (ENSG00000072840), score: 0.59 F2RL1coagulation factor II (thrombin) receptor-like 1 (ENSG00000164251), score: 0.88 F2RL3coagulation factor II (thrombin) receptor-like 3 (ENSG00000127533), score: 0.54 FAM107Bfamily with sequence similarity 107, member B (ENSG00000065809), score: 0.5 FAM110Cfamily with sequence similarity 110, member C (ENSG00000184731), score: 0.52 FAM150Bfamily with sequence similarity 150, member B (ENSG00000189292), score: 0.64 FAM3Bfamily with sequence similarity 3, member B (ENSG00000183844), score: 0.65 FAM55Cfamily with sequence similarity 55, member C (ENSG00000144815), score: -0.47 FAM60Afamily with sequence similarity 60, member A (ENSG00000139146), score: 0.54 FAM83Bfamily with sequence similarity 83, member B (ENSG00000168143), score: 0.52 FAM83Hfamily with sequence similarity 83, member H (ENSG00000180921), score: 0.51 FARP1FERM, RhoGEF (ARHGEF) and pleckstrin domain protein 1 (chondrocyte-derived) (ENSG00000152767), score: 0.6 FBXL5F-box and leucine-rich repeat protein 5 (ENSG00000118564), score: 0.51 FBXW7F-box and WD repeat domain containing 7 (ENSG00000109670), score: -0.53 FGFBP1fibroblast growth factor binding protein 1 (ENSG00000137440), score: 0.61 FGFR4fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (ENSG00000160867), score: 0.49 FOXI1forkhead box I1 (ENSG00000168269), score: 0.94 FRMD6FERM domain containing 6 (ENSG00000139926), score: -0.5 FUCA2fucosidase, alpha-L- 2, plasma (ENSG00000001036), score: 0.52 GALNT10UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 10 (GalNAc-T10) (ENSG00000164574), score: 0.56 GALNT11UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 11 (GalNAc-T11) (ENSG00000178234), score: 0.57 GALNT14UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 14 (GalNAc-T14) (ENSG00000158089), score: 0.64 GATA3GATA binding protein 3 (ENSG00000107485), score: 0.83 GCNT3glucosaminyl (N-acetyl) transferase 3, mucin type (ENSG00000140297), score: 0.67 GHRHRgrowth hormone releasing hormone receptor (ENSG00000106128), score: 0.81 GJA5gap junction protein, alpha 5, 40kDa (ENSG00000143140), score: 0.53 GLB1galactosidase, beta 1 (ENSG00000170266), score: 0.49 GLT1D1glycosyltransferase 1 domain containing 1 (ENSG00000151948), score: -0.5 GPR160G protein-coupled receptor 160 (ENSG00000173890), score: 0.55 GPR56G protein-coupled receptor 56 (ENSG00000205336), score: 0.61 GRHL2grainyhead-like 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000083307), score: 0.81 HAO2hydroxyacid oxidase 2 (long chain) (ENSG00000116882), score: 0.58 HNF1AHNF1 homeobox A (ENSG00000135100), score: 0.58 HNF4Ahepatocyte nuclear factor 4, alpha (ENSG00000101076), score: 0.53 HOXA10homeobox A10 (ENSG00000153807), score: 0.89 HOXB7homeobox B7 (ENSG00000120087), score: 0.82 HOXD10homeobox D10 (ENSG00000128710), score: 0.79 HOXD4homeobox D4 (ENSG00000170166), score: 0.88 HSD11B2hydroxysteroid (11-beta) dehydrogenase 2 (ENSG00000176387), score: 0.89 IGFBP7insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 (ENSG00000163453), score: 0.57 IL1RL1interleukin 1 receptor-like 1 (ENSG00000115602), score: 0.72 ILDR1immunoglobulin-like domain containing receptor 1 (ENSG00000145103), score: 0.76 IMPA2inositol(myo)-1(or 4)-monophosphatase 2 (ENSG00000141401), score: 0.82 IRX2iroquois homeobox 2 (ENSG00000170561), score: 0.49 ITGB3integrin, beta 3 (platelet glycoprotein IIIa, antigen CD61) (ENSG00000056345), score: 0.72 ITGB6integrin, beta 6 (ENSG00000115221), score: 0.5 ITM2Bintegral membrane protein 2B (ENSG00000136156), score: 0.5 ITPKAinositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase A (ENSG00000137825), score: -0.5 KCNJ1potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 1 (ENSG00000151704), score: 0.92 KCNJ16potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 16 (ENSG00000153822), score: 0.63 KCNK5potassium channel, subfamily K, member 5 (ENSG00000164626), score: 0.66 KCNQ1potassium voltage-gated channel, KQT-like subfamily, member 1 (ENSG00000053918), score: 0.62 KIAA0174KIAA0174 (ENSG00000182149), score: 0.49 KIAA1522KIAA1522 (ENSG00000162522), score: 0.52 KIF12kinesin family member 12 (ENSG00000136883), score: 0.69 KIF13Bkinesin family member 13B (ENSG00000197892), score: 0.66 KIRRELkin of IRRE like (Drosophila) (ENSG00000183853), score: 0.53 KLklotho (ENSG00000133116), score: 0.76 KLHDC7Akelch domain containing 7A (ENSG00000179023), score: 0.74 KLHL11kelch-like 11 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000178502), score: -0.47 KLHL28kelch-like 28 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000179454), score: -0.47 LAD1ladinin 1 (ENSG00000159166), score: 0.65 LAMB1laminin, beta 1 (ENSG00000091136), score: 0.52 LGALS2lectin, galactoside-binding, soluble, 2 (ENSG00000100079), score: 0.79 LGALS3lectin, galactoside-binding, soluble, 3 (ENSG00000131981), score: 0.5 LIFleukemia inhibitory factor (cholinergic differentiation factor) (ENSG00000128342), score: 0.72 LLGL2lethal giant larvae homolog 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000073350), score: 0.63 LMBRD2LMBR1 domain containing 2 (ENSG00000164187), score: -0.48 LMX1BLIM homeobox transcription factor 1, beta (ENSG00000136944), score: 0.9 LPIN3lipin 3 (ENSG00000132793), score: 0.58 MALmal, T-cell differentiation protein (ENSG00000172005), score: 0.62 MARVELD3MARVEL domain containing 3 (ENSG00000140832), score: 0.56 METRNLmeteorin, glial cell differentiation regulator-like (ENSG00000176845), score: 0.52 METTL9methyltransferase like 9 (ENSG00000197006), score: 0.66 MMDmonocyte to macrophage differentiation-associated (ENSG00000108960), score: -0.52 MMP7matrix metallopeptidase 7 (matrilysin, uterine) (ENSG00000137673), score: 0.98 MOBKL2BMOB1, Mps One Binder kinase activator-like 2B (yeast) (ENSG00000120162), score: 0.56 MPP5membrane protein, palmitoylated 5 (MAGUK p55 subfamily member 5) (ENSG00000072415), score: 0.55 MSNmoesin (ENSG00000147065), score: 0.5 MSRAmethionine sulfoxide reductase A (ENSG00000175806), score: 0.49 MYO19myosin XIX (ENSG00000141140), score: 0.54 MYO1Dmyosin ID (ENSG00000176658), score: 0.49 MYO6myosin VI (ENSG00000196586), score: 0.59 NDRG4NDRG family member 4 (ENSG00000103034), score: -0.5 NHSNance-Horan syndrome (congenital cataracts and dental anomalies) (ENSG00000188158), score: 0.56 NOX4NADPH oxidase 4 (ENSG00000086991), score: 0.81 NPHS2nephrosis 2, idiopathic, steroid-resistant (podocin) (ENSG00000116218), score: 1 NPNTnephronectin (ENSG00000168743), score: 0.69 NPR3natriuretic peptide receptor C/guanylate cyclase C (atrionatriuretic peptide receptor C) (ENSG00000113389), score: 0.65 NTN4netrin 4 (ENSG00000074527), score: 0.56 NUAK2NUAK family, SNF1-like kinase, 2 (ENSG00000163545), score: 0.62 OGG18-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase (ENSG00000114026), score: 0.51 OLFM4olfactomedin 4 (ENSG00000102837), score: 0.59 ORC6Lorigin recognition complex, subunit 6 like (yeast) (ENSG00000091651), score: -0.52 OVCH2ovochymase 2 (gene/pseudogene) (ENSG00000183378), score: 0.63 PAPPApregnancy-associated plasma protein A, pappalysin 1 (ENSG00000182752), score: 0.73 PAPPA2pappalysin 2 (ENSG00000116183), score: 0.81 PAQR5progestin and adipoQ receptor family member V (ENSG00000137819), score: 0.64 PCGF2polycomb group ring finger 2 (ENSG00000056661), score: 0.52 PEPDpeptidase D (ENSG00000124299), score: 0.71 PGPEP1pyroglutamyl-peptidase I (ENSG00000130517), score: 0.55 PHLPP1PH domain and leucine rich repeat protein phosphatase 1 (ENSG00000081913), score: -0.54 PICALMphosphatidylinositol binding clathrin assembly protein (ENSG00000073921), score: 0.51 PLA2R1phospholipase A2 receptor 1, 180kDa (ENSG00000153246), score: 0.82 PLATplasminogen activator, tissue (ENSG00000104368), score: 0.52 PLAUplasminogen activator, urokinase (ENSG00000122861), score: 0.66 PLCG2phospholipase C, gamma 2 (phosphatidylinositol-specific) (ENSG00000197943), score: 0.86 PLEK2pleckstrin 2 (ENSG00000100558), score: 0.66 PLEKHJ1pleckstrin homology domain containing, family J member 1 (ENSG00000104886), score: 0.56 PNPLA1patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 1 (ENSG00000180316), score: 0.82 PPM1Bprotein phosphatase, Mg2+/Mn2+ dependent, 1B (ENSG00000138032), score: -0.5 PPP4R4protein phosphatase 4, regulatory subunit 4 (ENSG00000119698), score: -0.47 PRCPprolylcarboxypeptidase (angiotensinase C) (ENSG00000137509), score: 0.51 PRKAB1protein kinase, AMP-activated, beta 1 non-catalytic subunit (ENSG00000111725), score: 0.68 PROM2prominin 2 (ENSG00000155066), score: 0.94 PROX1prospero homeobox 1 (ENSG00000117707), score: -0.56 PRSS23protease, serine, 23 (ENSG00000150687), score: 0.58 PSKH1protein serine kinase H1 (ENSG00000159792), score: 0.5 PSMD12proteasome (prosome, macropain) 26S subunit, non-ATPase, 12 (ENSG00000197170), score: -0.48 PTGER4prostaglandin E receptor 4 (subtype EP4) (ENSG00000171522), score: 0.53 PTPN1protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 1 (ENSG00000196396), score: 0.51 QARSglutaminyl-tRNA synthetase (ENSG00000172053), score: 0.52 R3HDM1R3H domain containing 1 (ENSG00000048991), score: -0.47 R3HDMLR3H domain containing-like (ENSG00000101074), score: 0.64 RAB11FIP1RAB11 family interacting protein 1 (class I) (ENSG00000156675), score: 0.61 RAB11FIP3RAB11 family interacting protein 3 (class II) (ENSG00000090565), score: 0.61 RAB17RAB17, member RAS oncogene family (ENSG00000124839), score: 0.65 RAB38RAB38, member RAS oncogene family (ENSG00000123892), score: 0.5 RAB7L1RAB7, member RAS oncogene family-like 1 (ENSG00000117280), score: 0.68 RAB9BRAB9B, member RAS oncogene family (ENSG00000123570), score: -0.47 RASL11ARAS-like, family 11, member A (ENSG00000122035), score: 0.51 RBKSribokinase (ENSG00000171174), score: 0.49 RHCGRh family, C glycoprotein (ENSG00000140519), score: 0.84 RIPK4receptor-interacting serine-threonine kinase 4 (ENSG00000183421), score: 0.62 RLFrearranged L-myc fusion (ENSG00000117000), score: -0.5 RNF152ring finger protein 152 (ENSG00000176641), score: 0.63 RPS6KA1ribosomal protein S6 kinase, 90kDa, polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000117676), score: 0.52 SAMD8sterile alpha motif domain containing 8 (ENSG00000156671), score: -0.48 SAP30Sin3A-associated protein, 30kDa (ENSG00000164105), score: -0.53 SCINscinderin (ENSG00000006747), score: 0.74 SCNN1Asodium channel, nonvoltage-gated 1 alpha (ENSG00000111319), score: 0.81 SCNN1Bsodium channel, nonvoltage-gated 1, beta (ENSG00000168447), score: 0.78 SCNN1Gsodium channel, nonvoltage-gated 1, gamma (ENSG00000166828), score: 0.79 SCRN2secernin 2 (ENSG00000141295), score: 0.58 SDC4syndecan 4 (ENSG00000124145), score: 0.53 SEC23ASec23 homolog A (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000100934), score: -0.54 SESN1sestrin 1 (ENSG00000080546), score: -0.49 SFXN2sideroflexin 2 (ENSG00000156398), score: 0.56 SGK2serum/glucocorticoid regulated kinase 2 (ENSG00000101049), score: 0.56 SGPP2sphingosine-1-phosphate phosphatase 2 (ENSG00000163082), score: 0.52 SH3RF1SH3 domain containing ring finger 1 (ENSG00000154447), score: 0.51 SH3YL1SH3 domain containing, Ysc84-like 1 (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000035115), score: 0.71 SHFSrc homology 2 domain containing F (ENSG00000138606), score: -0.49 SIM1single-minded homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000112246), score: 0.73 SIM2single-minded homolog 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000159263), score: 0.81 SLC10A2solute carrier family 10 (sodium/bile acid cotransporter family), member 2 (ENSG00000125255), score: 0.59 SLC13A1solute carrier family 13 (sodium/sulfate symporters), member 1 (ENSG00000081800), score: 0.78 SLC13A3solute carrier family 13 (sodium-dependent dicarboxylate transporter), member 3 (ENSG00000158296), score: 0.72 SLC15A2solute carrier family 15 (H+/peptide transporter), member 2 (ENSG00000163406), score: 0.55 SLC16A12solute carrier family 16, member 12 (monocarboxylic acid transporter 12) (ENSG00000152779), score: 0.55 SLC16A4solute carrier family 16, member 4 (monocarboxylic acid transporter 5) (ENSG00000168679), score: 0.76 SLC22A7solute carrier family 22 (organic anion transporter), member 7 (ENSG00000137204), score: 0.51 SLC25A10solute carrier family 25 (mitochondrial carrier; dicarboxylate transporter), member 10 (ENSG00000183048), score: 0.52 SLC26A7solute carrier family 26, member 7 (ENSG00000147606), score: 0.91 SLC34A1solute carrier family 34 (sodium phosphate), member 1 (ENSG00000131183), score: 0.78 SLC35F2solute carrier family 35, member F2 (ENSG00000110660), score: 0.57 SLC39A13solute carrier family 39 (zinc transporter), member 13 (ENSG00000165915), score: 0.51 SLC3A1solute carrier family 3 (cystine, dibasic and neutral amino acid transporters, activator of cystine, dibasic and neutral amino acid transport), member 1 (ENSG00000138079), score: 0.65 SLC44A3solute carrier family 44, member 3 (ENSG00000143036), score: 0.73 SLC5A12solute carrier family 5 (sodium/glucose cotransporter), member 12 (ENSG00000148942), score: 0.87 SLC5A9solute carrier family 5 (sodium/glucose cotransporter), member 9 (ENSG00000117834), score: 0.59 SLC6A19solute carrier family 6 (neutral amino acid transporter), member 19 (ENSG00000174358), score: 0.81 SLC7A9solute carrier family 7 (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system), member 9 (ENSG00000021488), score: 0.77 SLC9A3solute carrier family 9 (sodium/hydrogen exchanger), member 3 (ENSG00000066230), score: 0.71 SLC9A3R1solute carrier family 9 (sodium/hydrogen exchanger), member 3 regulator 1 (ENSG00000109062), score: 0.54 SLC9A4solute carrier family 9 (sodium/hydrogen exchanger), member 4 (ENSG00000180251), score: 0.81 SLIT2slit homolog 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000145147), score: 0.51 SMOsmoothened homolog (Drosophila) (ENSG00000128602), score: 0.56 SNX29sorting nexin 29 (ENSG00000048471), score: 0.6 SNX5sorting nexin 5 (ENSG00000089006), score: 0.63 SOSTDC1sclerostin domain containing 1 (ENSG00000171243), score: 0.58 SOX13SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 13 (ENSG00000143842), score: 0.53 SPASTspastin (ENSG00000021574), score: -0.54 SPP1secreted phosphoprotein 1 (ENSG00000118785), score: 0.6 SPTLC3serine palmitoyltransferase, long chain base subunit 3 (ENSG00000172296), score: 0.75 ST14suppression of tumorigenicity 14 (colon carcinoma) (ENSG00000149418), score: 0.65 STC1stanniocalcin 1 (ENSG00000159167), score: 0.56 STK24serine/threonine kinase 24 (ENSG00000102572), score: 0.5 STK32Bserine/threonine kinase 32B (ENSG00000152953), score: 0.86 SULF2sulfatase 2 (ENSG00000196562), score: 0.57 SUMF1sulfatase modifying factor 1 (ENSG00000144455), score: 0.63 SUSD1sushi domain containing 1 (ENSG00000106868), score: 0.59 SUSD2sushi domain containing 2 (ENSG00000099994), score: 0.6 SUSD3sushi domain containing 3 (ENSG00000157303), score: 0.56 TAOK1TAO kinase 1 (ENSG00000160551), score: -0.5 TBC1D1TBC1 (tre-2/USP6, BUB2, cdc16) domain family, member 1 (ENSG00000065882), score: 0.64 TBC1D13TBC1 domain family, member 13 (ENSG00000107021), score: 0.58 TBX2T-box 2 (ENSG00000121068), score: 0.75 TCF21transcription factor 21 (ENSG00000118526), score: 0.58 TCN2transcobalamin II (ENSG00000185339), score: 0.58 TFAP2Atranscription factor AP-2 alpha (activating enhancer binding protein 2 alpha) (ENSG00000137203), score: 0.54 TFAP2Btranscription factor AP-2 beta (activating enhancer binding protein 2 beta) (ENSG00000008196), score: 0.51 TFCP2L1transcription factor CP2-like 1 (ENSG00000115112), score: 0.87 THBS1thrombospondin 1 (ENSG00000137801), score: 0.54 TINAGtubulointerstitial nephritis antigen (ENSG00000137251), score: 0.84 TM7SF3transmembrane 7 superfamily member 3 (ENSG00000064115), score: 0.62 TMCO4transmembrane and coiled-coil domains 4 (ENSG00000162542), score: 0.52 TMEM171transmembrane protein 171 (ENSG00000157111), score: 0.63 TMEM27transmembrane protein 27 (ENSG00000147003), score: 0.68 TMEM51transmembrane protein 51 (ENSG00000171729), score: 0.6 TMEM56transmembrane protein 56 (ENSG00000152078), score: -0.47 TMIGD1transmembrane and immunoglobulin domain containing 1 (ENSG00000182271), score: 0.59 TMPRSS2transmembrane protease, serine 2 (ENSG00000184012), score: 0.79 TMPRSS3transmembrane protease, serine 3 (ENSG00000160183), score: 0.54 TMPRSS4transmembrane protease, serine 4 (ENSG00000137648), score: 0.72 TNFSF15tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 15 (ENSG00000181634), score: 0.73 TNKStankyrase, TRF1-interacting ankyrin-related ADP-ribose polymerase (ENSG00000173273), score: -0.52 TNRC6Ctrinucleotide repeat containing 6C (ENSG00000078687), score: -0.62 TOM1L1target of myb1 (chicken)-like 1 (ENSG00000141198), score: 0.54 TRIM23tripartite motif-containing 23 (ENSG00000113595), score: -0.46 TRIM8tripartite motif-containing 8 (ENSG00000171206), score: 0.5 TRPV4transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily V, member 4 (ENSG00000111199), score: 0.83 TULP3tubby like protein 3 (ENSG00000078246), score: 0.53 VCAM1vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (ENSG00000162692), score: 0.71 WARS2tryptophanyl tRNA synthetase 2, mitochondrial (ENSG00000116874), score: 0.49 WDR72WD repeat domain 72 (ENSG00000166415), score: 0.84 WDR91WD repeat domain 91 (ENSG00000105875), score: 0.5 WISP1WNT1 inducible signaling pathway protein 1 (ENSG00000104415), score: 0.49 WNT8Bwingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 8B (ENSG00000075290), score: 0.64 XPCxeroderma pigmentosum, complementation group C (ENSG00000154767), score: 0.59 XPNPEP2X-prolyl aminopeptidase (aminopeptidase P) 2, membrane-bound (ENSG00000122121), score: 0.79 ZDHHC6zinc finger, DHHC-type containing 6 (ENSG00000023041), score: 0.57 ZFATzinc finger and AT hook domain containing (ENSG00000066827), score: 0.59 ZFPM2zinc finger protein, multitype 2 (ENSG00000169946), score: -0.47 ZNF395zinc finger protein 395 (ENSG00000186918), score: 0.52 ZNF618zinc finger protein 618 (ENSG00000157657), score: 0.61
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ptr_kd_f_ca1 | ptr | kd | f | _ |
| mml_kd_m_ca1 | mml | kd | m | _ |
| ppy_kd_f_ca1 | ppy | kd | f | _ |
| ppy_kd_m_ca1 | ppy | kd | m | _ |
| ppa_kd_m_ca1 | ppa | kd | m | _ |
| mml_kd_f_ca1 | mml | kd | f | _ |
| ggo_kd_f_ca1 | ggo | kd | f | _ |
| ggo_kd_m_ca1 | ggo | kd | m | _ |
| ptr_kd_m_ca1 | ptr | kd | m | _ |
| ppa_kd_f_ca1 | ppa | kd | f | _ |
| hsa_kd_f_ca1 | hsa | kd | f | _ |
| hsa_kd_m2_ca1 | hsa | kd | m | 2 |
| hsa_kd_m1_ca1 | hsa | kd | m | 1 |