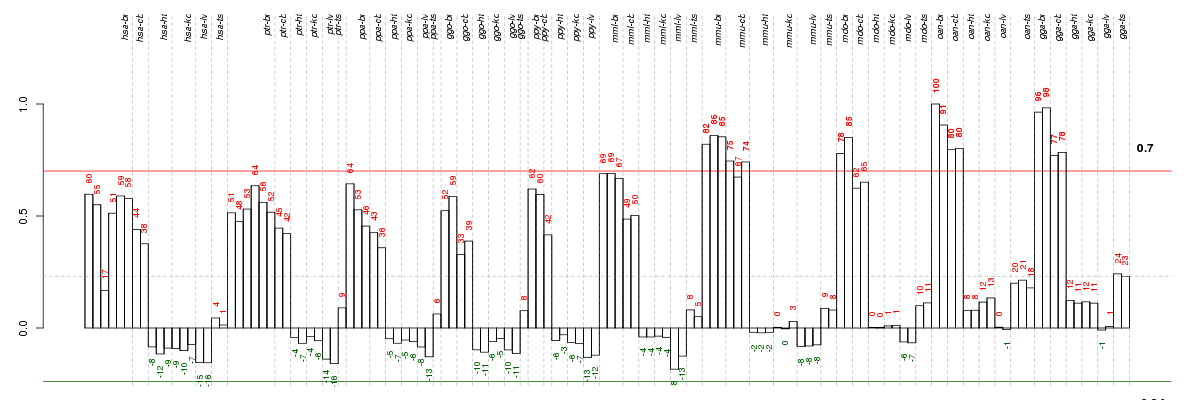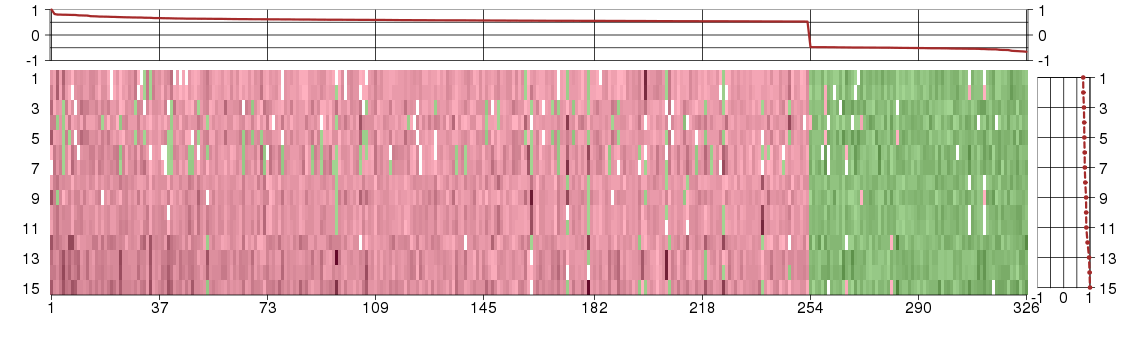

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

startle response
An action or movement due to the application of a sudden unexpected stimulus.
system process
A multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system. An organ system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a biological objective.
cell adhesion
The attachment of a cell, either to another cell or to an underlying substrate such as the extracellular matrix, via cell adhesion molecules.
transport
The directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells, or within a multicellular organism by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
ion transport
The directed movement of charged atoms or small charged molecules into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
cation transport
The directed movement of cations, atoms or small molecules with a net positive charge, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
calcium ion transport
The directed movement of calcium (Ca) ions into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
metal ion transport
The directed movement of metal ions, any metal ion with an electric charge, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
cellular ion homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of ions at the level of a cell.
cell communication
Any process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
cell surface receptor linked signaling pathway
Any series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of an extracellular ligand to a receptor on the surface of the target cell.
G-protein coupled receptor protein signaling pathway
The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a G-protein coupled receptor binding to its physiological ligand.
gamma-aminobutyric acid signaling pathway
The series of molecular signals generated by the binding of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA, 4-aminobutyrate), an amino acid which acts as a neurotransmitter in some organisms, to a cell surface receptor.
cell-cell signaling
Any process that mediates the transfer of information from one cell to another.
synaptic transmission
The process of communication from a neuron to a target (neuron, muscle, or secretory cell) across a synapse.
nerve-nerve synaptic transmission
The process of communication from a neuron to another neuron across a synapse.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of nervous tissue over time, from its formation to its mature state.
neurological system process
A organ system process carried out by any of the organs or tissues of neurological system.
behavior
The specific actions or reactions of an organism in response to external or internal stimuli. Patterned activity of a whole organism in a manner dependent upon some combination of that organism's internal state and external conditions.
locomotory behavior
The specific movement from place to place of an organism in response to external or internal stimuli. Locomotion of a whole organism in a manner dependent upon some combination of that organism's internal state and external conditions.
adult walking behavior
The actions or reactions of an adult relating to the progression of that organism along the ground by the process of lifting and setting down each leg.
adult behavior
Behavior in a fully developed and mature organism.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
adult locomotory behavior
Locomotory behavior in a fully developed and mature organism.
response to external stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an external stimulus.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
di-, tri-valent inorganic cation transport
The directed movement of inorganic cations with a valency of two or three into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. Inorganic cations are atoms or small molecules with a positive charge which do not contain carbon in covalent linkage.
transmission of nerve impulse
The neurological system process by which a signal is transmitted through the nervous system by synaptic transmission and the sequential electrochemical polarization and depolarization that travels across the membrane of a nerve cell (neuron) in response to stimulation.
cellular homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state at the level of the cell.
biological adhesion
The attachment of a cell or organism to a substrate or other organism.
signaling pathway
The series of molecular events whereby information is sent from one location to another within a living organism or between living organisms.
signaling process
Any biological process involved in the generation, transmission, reception, or interpretation of a signal. A signal is an entity used to transmit or convey information.
signaling
The entirety of a process whereby information is transmitted. This process begins with the initiation of the signal and ends when a response has been triggered.
signal transmission
The process whereby a signal is released and/or conveyed from one location to another.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of membrane potential
Any process that modulates the establishment or extent of a membrane potential, the electric potential existing across any membrane arising from charges in the membrane itself and from the charges present in the media on either side of the membrane.
homeostatic process
Any biological process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state.
ion homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of ions within an organism or cell.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
chemical homeostasis
Any biological process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of a chemical.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
neuromuscular process
Any process pertaining to the functions of the nervous and muscular systems of an organism.
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
cellular chemical homeostasis
Any biological process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of a chemical at the level of the cell.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of biological quality
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological quality. A biological quality is a measurable attribute of an organism or part of an organism, such as size, mass, shape, color, etc.
divalent metal ion transport
The directed movement of divalent metal cations, any metal ion with a +2 electric charge, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
all
NA
cell adhesion
The attachment of a cell, either to another cell or to an underlying substrate such as the extracellular matrix, via cell adhesion molecules.
signaling process
Any biological process involved in the generation, transmission, reception, or interpretation of a signal. A signal is an entity used to transmit or convey information.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
cell-cell signaling
Any process that mediates the transfer of information from one cell to another.
transmission of nerve impulse
The neurological system process by which a signal is transmitted through the nervous system by synaptic transmission and the sequential electrochemical polarization and depolarization that travels across the membrane of a nerve cell (neuron) in response to stimulation.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
adult behavior
Behavior in a fully developed and mature organism.
synaptic transmission
The process of communication from a neuron to a target (neuron, muscle, or secretory cell) across a synapse.
transmission of nerve impulse
The neurological system process by which a signal is transmitted through the nervous system by synaptic transmission and the sequential electrochemical polarization and depolarization that travels across the membrane of a nerve cell (neuron) in response to stimulation.
adult locomotory behavior
Locomotory behavior in a fully developed and mature organism.
cellular homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state at the level of the cell.
startle response
An action or movement due to the application of a sudden unexpected stimulus.
cellular chemical homeostasis
Any biological process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of a chemical at the level of the cell.
divalent metal ion transport
The directed movement of divalent metal cations, any metal ion with a +2 electric charge, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
cellular ion homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of ions at the level of a cell.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
integral to membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer. When used to describe a protein, indicates that all or part of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cytoplasm
All of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
synaptic vesicle
A secretory organelle, some 50 nm in diameter, of presynaptic nerve terminals; accumulates in high concentrations of neurotransmitters and is secreted these into the synaptic cleft by fusion with the 'active zone' of the presynaptic plasma membrane.
voltage-gated potassium channel complex
A protein complex that forms a transmembrane channel through which potassium ions may cross a cell membrane in response to changes in membrane potential.
ionotropic glutamate receptor complex
A multimeric assembly of four or five subunits which form a structure with an extracellular N-terminus and a large loop that together form the ligand binding domain. The C-terminus is intracellular. The ionotropic glutamate receptor complex itself acts as a ligand-gated ion channel; on binding glutamate, charged ions pass through a channel in the center of the receptor complex.
endomembrane system
A collection of membranous structures involved in transport within the cell. The main components of the endomembrane system are endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, vesicles, cell membrane and nuclear envelope. Members of the endomembrane system pass materials through each other or though the use of vesicles.
vesicle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding any membrane-bounded vesicle in the cell.
anchored to membrane
Tethered to a membrane by a covalently attached anchor, such as a lipid moiety, that is embedded in the membrane. When used to describe a protein, indicates that none of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
cell junction
A plasma membrane part that forms a specialized region of connection between two cells or between a cell and the extracellular matrix. At a cell junction, anchoring proteins extend through the plasma membrane to link cytoskeletal proteins in one cell to cytoskeletal proteins in neighboring cells or to proteins in the extracellular matrix.
coated vesicle
Small membrane-bounded organelle formed by pinching off of a coated region of membrane. Some coats are made of clathrin, whereas others are made from other proteins.
clathrin-coated vesicle
A vesicle with a coat formed of clathrin connected to the membrane via one of the clathrin adaptor complexes.
axon
The long process of a neuron that conducts nerve impulses, usually away from the cell body to the terminals and varicosities, which are sites of storage and release of neurotransmitter.
cytoplasmic vesicle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding a cytoplasmic vesicle.
coated vesicle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding a coated vesicle.
clathrin coated vesicle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding a clathrin-coated vesicle.
synaptic vesicle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding a synaptic vesicle.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
vesicle
Any small, fluid-filled, spherical organelle enclosed by membrane or protein.
membrane-bounded vesicle
Any small, fluid-filled, spherical organelle enclosed by a lipid bilayer.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
ion channel complex
A protein complex that spans a membrane and forms a water-filled channel across the phospholipid bilayer allowing selective ion transport down its electrochemical gradient.
cation channel complex
An ion channel complex through which cations pass.
potassium channel complex
An ion channel complex through which potassium ions pass.
chloride channel complex
An ion channel complex through which chloride ions pass.
cell projection
A prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
neuron projection
A prolongation or process extending from a nerve cell, e.g. an axon or dendrite.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, and prokaryotic structures such as anammoxosomes and pirellulosomes. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
protein complex
Any macromolecular complex composed of two or more polypeptide subunits, which may or may not be identical. Protein complexes may have other associated non-protein prosthetic groups, such as nucleotides, metal ions or other small molecules.
receptor complex
Any protein complex that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
cytoplasmic vesicle part
Any constituent part of cytoplasmic vesicle, a vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
synapse part
Any constituent part of a synapse, the junction between a nerve fiber of one neuron and another neuron or muscle fiber or glial cell.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
synapse
The junction between a nerve fiber of one neuron and another neuron or muscle fiber or glial cell; the site of interneuronal communication. As the nerve fiber approaches the synapse it enlarges into a specialized structure, the presynaptic nerve ending, which contains mitochondria and synaptic vesicles. At the tip of the nerve ending is the presynaptic membrane; facing it, and separated from it by a minute cleft (the synaptic cleft) is a specialized area of membrane on the receiving cell, known as the postsynaptic membrane. In response to the arrival of nerve impulses, the presynaptic nerve ending secretes molecules of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. These diffuse across the cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane.
postsynaptic membrane
A specialized area of membrane facing the presynaptic membrane on the tip of the nerve ending and separated from it by a minute cleft (the synaptic cleft). Neurotransmitters across the synaptic cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
synapse part
Any constituent part of a synapse, the junction between a nerve fiber of one neuron and another neuron or muscle fiber or glial cell.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
postsynaptic membrane
A specialized area of membrane facing the presynaptic membrane on the tip of the nerve ending and separated from it by a minute cleft (the synaptic cleft). Neurotransmitters across the synaptic cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane.
vesicle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding any membrane-bounded vesicle in the cell.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
ion channel complex
A protein complex that spans a membrane and forms a water-filled channel across the phospholipid bilayer allowing selective ion transport down its electrochemical gradient.
cytoplasmic vesicle part
Any constituent part of cytoplasmic vesicle, a vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
vesicle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding any membrane-bounded vesicle in the cell.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
cytoplasmic vesicle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding a cytoplasmic vesicle.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
cytoplasmic vesicle part
Any constituent part of cytoplasmic vesicle, a vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
ionotropic glutamate receptor complex
A multimeric assembly of four or five subunits which form a structure with an extracellular N-terminus and a large loop that together form the ligand binding domain. The C-terminus is intracellular. The ionotropic glutamate receptor complex itself acts as a ligand-gated ion channel; on binding glutamate, charged ions pass through a channel in the center of the receptor complex.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
cytoplasmic vesicle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding a cytoplasmic vesicle.
ion channel complex
A protein complex that spans a membrane and forms a water-filled channel across the phospholipid bilayer allowing selective ion transport down its electrochemical gradient.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
voltage-gated potassium channel complex
A protein complex that forms a transmembrane channel through which potassium ions may cross a cell membrane in response to changes in membrane potential.
coated vesicle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding a coated vesicle.
voltage-gated potassium channel complex
A protein complex that forms a transmembrane channel through which potassium ions may cross a cell membrane in response to changes in membrane potential.
ionotropic glutamate receptor complex
A multimeric assembly of four or five subunits which form a structure with an extracellular N-terminus and a large loop that together form the ligand binding domain. The C-terminus is intracellular. The ionotropic glutamate receptor complex itself acts as a ligand-gated ion channel; on binding glutamate, charged ions pass through a channel in the center of the receptor complex.
synaptic vesicle
A secretory organelle, some 50 nm in diameter, of presynaptic nerve terminals; accumulates in high concentrations of neurotransmitters and is secreted these into the synaptic cleft by fusion with the 'active zone' of the presynaptic plasma membrane.
clathrin coated vesicle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding a clathrin-coated vesicle.
synaptic vesicle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding a synaptic vesicle.

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
signal transducer activity
Mediates the transfer of a signal from the outside to the inside of a cell by means other than the introduction of the signal molecule itself into the cell.
receptor activity
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell activity.
transmembrane receptor activity
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell activity, and spanning to the membrane of either the cell or an organelle.
GABA-A receptor activity
Combining with the amino acid gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA, 4-aminobutyrate) to initiate a change in cell activity. GABA-A receptors function as chloride channels.
ionotropic glutamate receptor activity
Combining with glutamate to initiate a change in cell activity through the regulation of ion channels.
transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
ion channel activity
Catalysis of facilitated diffusion of an ion (by an energy-independent process) by passage through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel without evidence for a carrier-mediated mechanism.
extracellular ligand-gated ion channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a channel that opens when a specific extracellular ligand has been bound by the channel complex or one of its constituent parts.
excitatory extracellular ligand-gated ion channel activity
NA
extracellular-glutamate-gated ion channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a channel that opens when extracellular glutamate has been bound by the channel complex or one of its constituent parts.
voltage-gated ion channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a voltage-gated channel. An ion is an atom or group of atoms carrying an electric charge by virtue of having gained or lost one or more electrons.
voltage-gated potassium channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a potassium ion by a voltage-gated channel.
anion channel activity
Catalysis of the energy-independent passage of anions across a lipid bilayer down a concentration gradient.
chloride channel activity
Catalysis of facilitated diffusion of a chloride (by an energy-independent process) involving passage through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel without evidence for a carrier-mediated mechanism.
cation channel activity
Catalysis of the energy-independent passage of cations across a lipid bilayer down a concentration gradient.
calcium channel activity
Catalysis of facilitated diffusion of a calcium ion (by an energy-independent process) involving passage through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel without evidence for a carrier-mediated mechanism.
potassium channel activity
Catalysis of facilitated diffusion of a potassium ion (by an energy-independent process) involving passage through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel without evidence for a carrier-mediated mechanism.
transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a substance from one side of a membrane to the other.
binding
The selective, non-covalent, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
glutamate receptor activity
Combining with glutamate to initiate a change in cell activity.
cation transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of cation from one side of the membrane to the other.
glycine binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with glycine, aminoethanoic acid.
anion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a negatively charged ion from one side of a membrane to the other.
ion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of an ion from one side of a membrane to the other.
channel activity
Catalysis of energy-independent facilitated diffusion, mediated by passage of a solute through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel. Stereospecificity is not exhibited but this transport may be specific for a particular molecular species or class of molecules.
ligand-gated ion channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a channel that opens when a specific ligand has been bound by the channel complex or one of its constituent parts.
amino acid binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with an amino acid, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
GABA receptor activity
Combining with gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA, 4-aminobutyrate), an amino acid which acts as a neurotransmitter in some organisms, to initiate a change in cell activity.
passive transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute from one side of the membrane to the other, down the solute's concentration gradient.
voltage-gated channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a solute by a channel whose open state is dependent on the voltage across the membrane in which it is embedded.
ligand-gated channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a solute by a channel that opens when a specific ligand has been bound by the channel complex or one of its constituent parts.
gated channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a solute by a channel that opens in response to a specific stimulus.
substrate-specific channel activity
Catalysis of energy-independent facilitated diffusion, mediated by passage of a specific solute through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel. Stereospecificity is not exhibited but this transport may be specific for a particular molecular species or class of molecules.
voltage-gated cation channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a cation by a voltage-gated channel. A cation is a positively charged ion.
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
substrate-specific transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of a specific substance or group of related substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
carboxylic acid binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a carboxylic acid, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (COOH) groups or anions (COO-).
neurotransmitter binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a neurotransmitter, any chemical substance that is capable of transmitting (or inhibiting the transmission of) a nerve impulse from a neuron to another cell.
amine binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group.
molecular transducer activity
The molecular function that accepts an input of one form and creates an output of a different form.
all
NA
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
amino acid binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with an amino acid, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
substrate-specific channel activity
Catalysis of energy-independent facilitated diffusion, mediated by passage of a specific solute through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel. Stereospecificity is not exhibited but this transport may be specific for a particular molecular species or class of molecules.
ion channel activity
Catalysis of facilitated diffusion of an ion (by an energy-independent process) by passage through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel without evidence for a carrier-mediated mechanism.
cation channel activity
Catalysis of the energy-independent passage of cations across a lipid bilayer down a concentration gradient.
anion channel activity
Catalysis of the energy-independent passage of anions across a lipid bilayer down a concentration gradient.
voltage-gated ion channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a voltage-gated channel. An ion is an atom or group of atoms carrying an electric charge by virtue of having gained or lost one or more electrons.
ligand-gated ion channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a channel that opens when a specific ligand has been bound by the channel complex or one of its constituent parts.
voltage-gated cation channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a cation by a voltage-gated channel. A cation is a positively charged ion.
voltage-gated potassium channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a potassium ion by a voltage-gated channel.
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 04080 | 4.502e-07 | 6.152 | 24 | 102 | Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction |
| 00601 | 1.890e-02 | 0.4222 | 4 | 7 | Glycosphingolipid biosynthesis - lacto and neolacto series |
| 04360 | 2.755e-02 | 3.076 | 10 | 51 | Axon guidance |
ABCG4ATP-binding cassette, sub-family G (WHITE), member 4 (ENSG00000172350), score: 0.54 ABHD3abhydrolase domain containing 3 (ENSG00000158201), score: 0.6 ACCN4amiloride-sensitive cation channel 4, pituitary (ENSG00000072182), score: 0.6 ADAM22ADAM metallopeptidase domain 22 (ENSG00000008277), score: 0.61 ADCYAP1adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide 1 (pituitary) (ENSG00000141433), score: 0.58 AIFM2apoptosis-inducing factor, mitochondrion-associated, 2 (ENSG00000042286), score: -0.51 AK2adenylate kinase 2 (ENSG00000004455), score: -0.54 AKAP1A kinase (PRKA) anchor protein 1 (ENSG00000121057), score: -0.5 AMZ1archaelysin family metallopeptidase 1 (ENSG00000174945), score: 0.54 ANKRA2ankyrin repeat, family A (RFXANK-like), 2 (ENSG00000164331), score: 0.65 ANKRD46ankyrin repeat domain 46 (ENSG00000186106), score: 0.55 ANO3anoctamin 3 (ENSG00000134343), score: 0.69 ANXA1annexin A1 (ENSG00000135046), score: -0.49 APCadenomatous polyposis coli (ENSG00000134982), score: 0.54 APEHN-acylaminoacyl-peptide hydrolase (ENSG00000164062), score: -0.56 ARFGAP2ADP-ribosylation factor GTPase activating protein 2 (ENSG00000149182), score: -0.48 ARPP21cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein, 21kDa (ENSG00000172995), score: 0.64 ARRDC4arrestin domain containing 4 (ENSG00000140450), score: -0.52 ASTN1astrotactin 1 (ENSG00000152092), score: 0.54 ATP13A5ATPase type 13A5 (ENSG00000187527), score: 0.64 ATP6V0E1ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 9kDa, V0 subunit e1 (ENSG00000113732), score: -0.51 AURKAIP1aurora kinase A interacting protein 1 (ENSG00000175756), score: -0.52 AVPR1Barginine vasopressin receptor 1B (ENSG00000198049), score: 0.55 B3GALT1UDP-Gal:betaGlcNAc beta 1,3-galactosyltransferase, polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000172318), score: 0.62 B3GALT5UDP-Gal:betaGlcNAc beta 1,3-galactosyltransferase, polypeptide 5 (ENSG00000183778), score: 0.8 B4GALT1UDP-Gal:betaGlcNAc beta 1,4- galactosyltransferase, polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000086062), score: -0.53 B4GALT6UDP-Gal:betaGlcNAc beta 1,4- galactosyltransferase, polypeptide 6 (ENSG00000118276), score: 0.58 BAI1brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor 1 (ENSG00000181790), score: 0.53 BAT2L2HLA-B associated transcript 2-like 2 (ENSG00000117523), score: 0.53 BCANbrevican (ENSG00000132692), score: 0.55 BCL11BB-cell CLL/lymphoma 11B (zinc finger protein) (ENSG00000127152), score: 0.56 BICD1bicaudal D homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000151746), score: 0.55 BMP3bone morphogenetic protein 3 (ENSG00000152785), score: 0.68 BRS3bombesin-like receptor 3 (ENSG00000102239), score: 0.54 BTBD8BTB (POZ) domain containing 8 (ENSG00000189195), score: 0.57 C11orf41chromosome 11 open reading frame 41 (ENSG00000110427), score: 0.54 C14orf159chromosome 14 open reading frame 159 (ENSG00000133943), score: -0.51 C14orf37chromosome 14 open reading frame 37 (ENSG00000139971), score: 0.62 C18orf55chromosome 18 open reading frame 55 (ENSG00000075336), score: -0.65 C20orf103chromosome 20 open reading frame 103 (ENSG00000125869), score: 0.63 C5orf24chromosome 5 open reading frame 24 (ENSG00000181904), score: 0.54 C6orf154chromosome 6 open reading frame 154 (ENSG00000204052), score: 0.53 C6orf72chromosome 6 open reading frame 72 (ENSG00000055211), score: -0.51 C8orf34chromosome 8 open reading frame 34 (ENSG00000165084), score: 0.64 C9orf4chromosome 9 open reading frame 4 (ENSG00000136805), score: 0.62 CA10carbonic anhydrase X (ENSG00000154975), score: 0.54 CACHD1cache domain containing 1 (ENSG00000158966), score: 0.58 CACNA1Ecalcium channel, voltage-dependent, R type, alpha 1E subunit (ENSG00000198216), score: 0.63 CACNB4calcium channel, voltage-dependent, beta 4 subunit (ENSG00000182389), score: 0.62 CACNG2calcium channel, voltage-dependent, gamma subunit 2 (ENSG00000166862), score: 0.62 CACNG3calcium channel, voltage-dependent, gamma subunit 3 (ENSG00000006116), score: 0.54 CADM2cell adhesion molecule 2 (ENSG00000175161), score: 0.53 CASD1CAS1 domain containing 1 (ENSG00000127995), score: 0.59 CASKcalcium/calmodulin-dependent serine protein kinase (MAGUK family) (ENSG00000147044), score: 0.53 CASP7caspase 7, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase (ENSG00000165806), score: -0.52 CASTcalpastatin (ENSG00000153113), score: -0.59 CCBL2cysteine conjugate-beta lyase 2 (ENSG00000137944), score: -0.49 CCDC111coiled-coil domain containing 111 (ENSG00000164306), score: -0.51 CD44CD44 molecule (Indian blood group) (ENSG00000026508), score: -0.54 CDC42BPACDC42 binding protein kinase alpha (DMPK-like) (ENSG00000143776), score: 0.54 CDH10cadherin 10, type 2 (T2-cadherin) (ENSG00000040731), score: 0.53 CDH12cadherin 12, type 2 (N-cadherin 2) (ENSG00000154162), score: 0.56 CDH20cadherin 20, type 2 (ENSG00000101542), score: 0.54 CDH7cadherin 7, type 2 (ENSG00000081138), score: 0.56 CDK17cyclin-dependent kinase 17 (ENSG00000059758), score: 0.72 CDS2CDP-diacylglycerol synthase (phosphatidate cytidylyltransferase) 2 (ENSG00000101290), score: 0.74 CHCHD8coiled-coil-helix-coiled-coil-helix domain containing 8 (ENSG00000181924), score: -0.64 CLCN3chloride channel 3 (ENSG00000109572), score: 0.61 CLVS1clavesin 1 (ENSG00000177182), score: 0.6 CLVS2clavesin 2 (ENSG00000146352), score: 0.63 CNKSR2connector enhancer of kinase suppressor of Ras 2 (ENSG00000149970), score: 0.59 CNNM1cyclin M1 (ENSG00000119946), score: 0.54 CNR1cannabinoid receptor 1 (brain) (ENSG00000118432), score: 0.6 CNTN3contactin 3 (plasmacytoma associated) (ENSG00000113805), score: 0.55 CNTN4contactin 4 (ENSG00000144619), score: 0.54 CNTN5contactin 5 (ENSG00000149972), score: 0.79 COL25A1collagen, type XXV, alpha 1 (ENSG00000188517), score: 0.82 CPSF4cleavage and polyadenylation specific factor 4, 30kDa (ENSG00000160917), score: -0.58 CRTAPcartilage associated protein (ENSG00000170275), score: -0.5 CSMD2CUB and Sushi multiple domains 2 (ENSG00000121904), score: 0.66 CTNND1catenin (cadherin-associated protein), delta 1 (ENSG00000198561), score: -0.66 CTTNBP2cortactin binding protein 2 (ENSG00000077063), score: 0.59 CUL4Acullin 4A (ENSG00000139842), score: -0.55 D2HGDHD-2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase (ENSG00000180902), score: -0.53 DAB1disabled homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000173406), score: 0.54 DBC1deleted in bladder cancer 1 (ENSG00000078725), score: 0.56 DCLK3doublecortin-like kinase 3 (ENSG00000163673), score: 0.59 DCNdecorin (ENSG00000011465), score: -0.52 DCTDdCMP deaminase (ENSG00000129187), score: -0.51 DGKIdiacylglycerol kinase, iota (ENSG00000157680), score: 0.79 DNAJC27DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 27 (ENSG00000115137), score: 0.59 DOPEY2dopey family member 2 (ENSG00000142197), score: 0.57 DRD2dopamine receptor D2 (ENSG00000149295), score: 0.57 DRP2dystrophin related protein 2 (ENSG00000102385), score: 0.58 DSCAMDown syndrome cell adhesion molecule (ENSG00000171587), score: 0.58 DSCAML1Down syndrome cell adhesion molecule like 1 (ENSG00000177103), score: 0.53 DUSP19dual specificity phosphatase 19 (ENSG00000162999), score: 0.62 ECE2endothelin converting enzyme 2 (ENSG00000145194), score: 0.54 EFR3BEFR3 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000084710), score: 0.55 EIF2B4eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2B, subunit 4 delta, 67kDa (ENSG00000115211), score: -0.48 ELAVL4ELAV (embryonic lethal, abnormal vision, Drosophila)-like 4 (Hu antigen D) (ENSG00000162374), score: 0.55 ELMOD1ELMO/CED-12 domain containing 1 (ENSG00000110675), score: 0.61 ELOVL4elongation of very long chain fatty acids (FEN1/Elo2, SUR4/Elo3, yeast)-like 4 (ENSG00000118402), score: 0.58 EPHA3EPH receptor A3 (ENSG00000044524), score: 0.55 EPHA5EPH receptor A5 (ENSG00000145242), score: 0.8 EPHA7EPH receptor A7 (ENSG00000135333), score: 0.56 EPHA8EPH receptor A8 (ENSG00000070886), score: 0.62 EPHX4epoxide hydrolase 4 (ENSG00000172031), score: 0.7 EPS15epidermal growth factor receptor pathway substrate 15 (ENSG00000085832), score: 0.54 ERBB2v-erb-b2 erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene homolog 2, neuro/glioblastoma derived oncogene homolog (avian) (ENSG00000141736), score: -0.5 FADDFas (TNFRSF6)-associated via death domain (ENSG00000168040), score: -0.63 FAM164Afamily with sequence similarity 164, member A (ENSG00000104427), score: 0.6 FAM5Cfamily with sequence similarity 5, member C (ENSG00000162670), score: 0.54 FBLIM1filamin binding LIM protein 1 (ENSG00000162458), score: -0.48 FHDC1FH2 domain containing 1 (ENSG00000137460), score: 0.56 FIBCD1fibrinogen C domain containing 1 (ENSG00000130720), score: 0.62 FPGSfolylpolyglutamate synthase (ENSG00000136877), score: -0.5 FRMPD4FERM and PDZ domain containing 4 (ENSG00000169933), score: 0.65 FUT9fucosyltransferase 9 (alpha (1,3) fucosyltransferase) (ENSG00000172461), score: 0.57 GABRA1gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, alpha 1 (ENSG00000022355), score: 0.57 GABRA2gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, alpha 2 (ENSG00000151834), score: 0.71 GABRA4gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, alpha 4 (ENSG00000109158), score: 0.72 GABRB2gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, beta 2 (ENSG00000145864), score: 0.56 GABRG2gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, gamma 2 (ENSG00000113327), score: 0.53 GAD2glutamate decarboxylase 2 (pancreatic islets and brain, 65kDa) (ENSG00000136750), score: 0.72 GALNTL6UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase-like 6 (ENSG00000174473), score: 0.66 GAMTguanidinoacetate N-methyltransferase (ENSG00000130005), score: -0.48 GDPD1glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase domain containing 1 (ENSG00000153982), score: 0.54 GLRA1glycine receptor, alpha 1 (ENSG00000145888), score: 0.55 GLRA2glycine receptor, alpha 2 (ENSG00000101958), score: 0.59 GLRBglycine receptor, beta (ENSG00000109738), score: 0.54 GNALguanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), alpha activating activity polypeptide, olfactory type (ENSG00000141404), score: 0.59 GNG13guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), gamma 13 (ENSG00000127588), score: 0.55 GPM6Bglycoprotein M6B (ENSG00000046653), score: 0.58 GPR139G protein-coupled receptor 139 (ENSG00000180269), score: 1 GPR149G protein-coupled receptor 149 (ENSG00000174948), score: 0.56 GPR37L1G protein-coupled receptor 37 like 1 (ENSG00000170075), score: 0.55 GPR85G protein-coupled receptor 85 (ENSG00000164604), score: 0.56 GRB10growth factor receptor-bound protein 10 (ENSG00000106070), score: -0.54 GRIA1glutamate receptor, ionotropic, AMPA 1 (ENSG00000155511), score: 0.6 GRIA2glutamate receptor, ionotropic, AMPA 2 (ENSG00000120251), score: 0.55 GRIA4glutamate receptor, ionotrophic, AMPA 4 (ENSG00000152578), score: 0.55 GRID2glutamate receptor, ionotropic, delta 2 (ENSG00000152208), score: 0.59 GRIN2Bglutamate receptor, ionotropic, N-methyl D-aspartate 2B (ENSG00000150086), score: 0.58 GRIN3Aglutamate receptor, ionotropic, N-methyl-D-aspartate 3A (ENSG00000198785), score: 0.6 GRM1glutamate receptor, metabotropic 1 (ENSG00000152822), score: 0.56 GRM3glutamate receptor, metabotropic 3 (ENSG00000198822), score: 0.53 GSG1LGSG1-like (ENSG00000169181), score: 0.57 H6PDhexose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (glucose 1-dehydrogenase) (ENSG00000049239), score: -0.48 HEATR2HEAT repeat containing 2 (ENSG00000164818), score: -0.49 HEATR5BHEAT repeat containing 5B (ENSG00000008869), score: 0.58 HHLA1HERV-H LTR-associating 1 (ENSG00000132297), score: 0.54 HMHA1histocompatibility (minor) HA-1 (ENSG00000180448), score: -0.5 HMP19HMP19 protein (ENSG00000170091), score: 0.54 HS2ST1heparan sulfate 2-O-sulfotransferase 1 (ENSG00000153936), score: 0.53 HTR45-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 4 (ENSG00000164270), score: 0.59 IAH1isoamyl acetate-hydrolyzing esterase 1 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000134330), score: -0.56 IL1RAPL1interleukin 1 receptor accessory protein-like 1 (ENSG00000169306), score: 0.71 IL1RAPL2interleukin 1 receptor accessory protein-like 2 (ENSG00000189108), score: 0.68 ILDR2immunoglobulin-like domain containing receptor 2 (ENSG00000143195), score: 0.54 INPPL1inositol polyphosphate phosphatase-like 1 (ENSG00000165458), score: -0.49 ITFG1integrin alpha FG-GAP repeat containing 1 (ENSG00000129636), score: 0.68 ITPRIPinositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor interacting protein (ENSG00000148841), score: -0.49 KCNA1potassium voltage-gated channel, shaker-related subfamily, member 1 (episodic ataxia with myokymia) (ENSG00000111262), score: 0.57 KCNA3potassium voltage-gated channel, shaker-related subfamily, member 3 (ENSG00000177272), score: 0.53 KCNA4potassium voltage-gated channel, shaker-related subfamily, member 4 (ENSG00000182255), score: 0.61 KCNA6potassium voltage-gated channel, shaker-related subfamily, member 6 (ENSG00000151079), score: 0.58 KCNH7potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily H (eag-related), member 7 (ENSG00000184611), score: 0.62 KCNJ13potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 13 (ENSG00000115474), score: 0.53 KCNJ6potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 6 (ENSG00000157542), score: 0.76 KCNK2potassium channel, subfamily K, member 2 (ENSG00000082482), score: 0.64 KCNQ3potassium voltage-gated channel, KQT-like subfamily, member 3 (ENSG00000184156), score: 0.63 KCNS2potassium voltage-gated channel, delayed-rectifier, subfamily S, member 2 (ENSG00000156486), score: 0.55 KCTD4potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 4 (ENSG00000180332), score: 0.6 KIAA0146KIAA0146 (ENSG00000164808), score: -0.48 KIAA0391KIAA0391 (ENSG00000100890), score: -0.62 KIAA1279KIAA1279 (ENSG00000198954), score: 0.58 KIAA1467KIAA1467 (ENSG00000084444), score: 0.61 KIAA2022KIAA2022 (ENSG00000050030), score: 0.69 KRT9keratin 9 (ENSG00000171403), score: 0.53 LGI2leucine-rich repeat LGI family, member 2 (ENSG00000153012), score: 0.73 LMO1LIM domain only 1 (rhombotin 1) (ENSG00000166407), score: 0.56 LOC100291726similar to family with sequence similarity 70, member A (ENSG00000125355), score: 0.72 LOC100293817similar to hCG1811893 (ENSG00000144460), score: 0.62 LPPR4lipid phosphate phosphatase-related protein type 4 (ENSG00000117600), score: 0.63 LRFN2leucine rich repeat and fibronectin type III domain containing 2 (ENSG00000156564), score: 0.55 LRFN3leucine rich repeat and fibronectin type III domain containing 3 (ENSG00000126243), score: 0.55 LRFN5leucine rich repeat and fibronectin type III domain containing 5 (ENSG00000165379), score: 0.61 LRP12low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 12 (ENSG00000147650), score: 0.57 LRRC26leucine rich repeat containing 26 (ENSG00000184709), score: 0.54 LRRC4Cleucine rich repeat containing 4C (ENSG00000148948), score: 0.58 LRRC7leucine rich repeat containing 7 (ENSG00000033122), score: 0.61 LRRN1leucine rich repeat neuronal 1 (ENSG00000175928), score: 0.6 LRRTM3leucine rich repeat transmembrane neuronal 3 (ENSG00000198739), score: 0.55 LRTM2leucine-rich repeats and transmembrane domains 2 (ENSG00000166159), score: 0.54 LSAMPlimbic system-associated membrane protein (ENSG00000185565), score: 0.57 LSM10LSM10, U7 small nuclear RNA associated (ENSG00000181817), score: -0.56 MAD2L1BPMAD2L1 binding protein (ENSG00000124688), score: -0.51 MAML1mastermind-like 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000161021), score: -0.49 MAP3K3mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 3 (ENSG00000198909), score: -0.56 MAP7D2MAP7 domain containing 2 (ENSG00000184368), score: 0.56 MAPK8mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 (ENSG00000107643), score: 0.6 MAPKAP1mitogen-activated protein kinase associated protein 1 (ENSG00000119487), score: -0.55 MAPKAPK2mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2 (ENSG00000162889), score: -0.53 MDGA2MAM domain containing glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor 2 (ENSG00000139915), score: 0.76 MLXIPMLX interacting protein (ENSG00000175727), score: -0.5 MMP16matrix metallopeptidase 16 (membrane-inserted) (ENSG00000156103), score: 0.58 MRPL21mitochondrial ribosomal protein L21 (ENSG00000197345), score: -0.53 MRPL51mitochondrial ribosomal protein L51 (ENSG00000111639), score: -0.49 MYO16myosin XVI (ENSG00000041515), score: 0.77 NCKAP1NCK-associated protein 1 (ENSG00000061676), score: 0.58 NDST4N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase (heparan glucosaminyl) 4 (ENSG00000138653), score: 0.6 NECAB1N-terminal EF-hand calcium binding protein 1 (ENSG00000123119), score: 0.53 NECAP2NECAP endocytosis associated 2 (ENSG00000157191), score: -0.49 NEK9NIMA (never in mitosis gene a)- related kinase 9 (ENSG00000119638), score: -0.51 NELL2NEL-like 2 (chicken) (ENSG00000184613), score: 0.53 NFKB1nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 1 (ENSG00000109320), score: -0.48 NKAIN4Na+/K+ transporting ATPase interacting 4 (ENSG00000101198), score: 0.58 NPY2Rneuropeptide Y receptor Y2 (ENSG00000185149), score: 0.7 NPY5Rneuropeptide Y receptor Y5 (ENSG00000164129), score: 0.56 NRSN1neurensin 1 (ENSG00000152954), score: 0.57 NSMCE1non-SMC element 1 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000169189), score: -0.51 NTRK3neurotrophic tyrosine kinase, receptor, type 3 (ENSG00000140538), score: 0.58 NTSneurotensin (ENSG00000133636), score: 0.79 OLIG3oligodendrocyte transcription factor 3 (ENSG00000177468), score: 0.6 OPCMLopioid binding protein/cell adhesion molecule-like (ENSG00000183715), score: 0.57 OSTF1osteoclast stimulating factor 1 (ENSG00000134996), score: -0.59 OTOFotoferlin (ENSG00000115155), score: 0.62 P2RY12purinergic receptor P2Y, G-protein coupled, 12 (ENSG00000169313), score: 0.57 PAFAH1B2platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase 1b, catalytic subunit 2 (30kDa) (ENSG00000168092), score: 0.59 PAK7p21 protein (Cdc42/Rac)-activated kinase 7 (ENSG00000101349), score: 0.55 PCDH19protocadherin 19 (ENSG00000165194), score: 0.56 PCDH20protocadherin 20 (ENSG00000197991), score: 0.58 PCSK2proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 2 (ENSG00000125851), score: 0.61 PDE10Aphosphodiesterase 10A (ENSG00000112541), score: 0.62 PDS5BPDS5, regulator of cohesion maintenance, homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000083642), score: 0.55 PENKproenkephalin (ENSG00000181195), score: 0.56 PEX5Lperoxisomal biogenesis factor 5-like (ENSG00000114757), score: 0.63 PLBD1phospholipase B domain containing 1 (ENSG00000121316), score: -0.49 PLCB1phospholipase C, beta 1 (phosphoinositide-specific) (ENSG00000182621), score: 0.56 PNOCprepronociceptin (ENSG00000168081), score: 0.6 PPM1Eprotein phosphatase, Mg2+/Mn2+ dependent, 1E (ENSG00000175175), score: 0.59 PPP3CAprotein phosphatase 3, catalytic subunit, alpha isozyme (ENSG00000138814), score: 0.63 PQLC1PQ loop repeat containing 1 (ENSG00000122490), score: -0.52 PRCPprolylcarboxypeptidase (angiotensinase C) (ENSG00000137509), score: -0.59 PRMT8protein arginine methyltransferase 8 (ENSG00000111218), score: 0.55 PSKH1protein serine kinase H1 (ENSG00000159792), score: -0.52 PTP4A2protein tyrosine phosphatase type IVA, member 2 (ENSG00000184007), score: -0.5 PTPRRprotein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, R (ENSG00000153233), score: 0.57 QARSglutaminyl-tRNA synthetase (ENSG00000172053), score: -0.63 R3HDM1R3H domain containing 1 (ENSG00000048991), score: 0.53 RAB3GAP2RAB3 GTPase activating protein subunit 2 (non-catalytic) (ENSG00000118873), score: 0.7 RALGAPA1Ral GTPase activating protein, alpha subunit 1 (catalytic) (ENSG00000174373), score: 0.55 RASGEF1ARasGEF domain family, member 1A (ENSG00000198915), score: 0.57 RBM45RNA binding motif protein 45 (ENSG00000155636), score: 0.54 RGS7BPregulator of G-protein signaling 7 binding protein (ENSG00000186479), score: 0.64 RGS8regulator of G-protein signaling 8 (ENSG00000135824), score: 0.69 RPS6KC1ribosomal protein S6 kinase, 52kDa, polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000136643), score: 0.57 RTN1reticulon 1 (ENSG00000139970), score: 0.56 SACSspastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay (sacsin) (ENSG00000151835), score: 0.56 SCAMP1secretory carrier membrane protein 1 (ENSG00000085365), score: 0.66 SCG2secretogranin II (ENSG00000171951), score: 0.66 SEMA3Asema domain, immunoglobulin domain (Ig), short basic domain, secreted, (semaphorin) 3A (ENSG00000075213), score: 0.77 SEMA3Esema domain, immunoglobulin domain (Ig), short basic domain, secreted, (semaphorin) 3E (ENSG00000170381), score: 0.6 SERPINB2serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade B (ovalbumin), member 2 (ENSG00000197632), score: 0.56 SGCZsarcoglycan, zeta (ENSG00000185053), score: 0.59 SGTBsmall glutamine-rich tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR)-containing, beta (ENSG00000197860), score: 0.6 SLC12A5solute carrier family 12 (potassium/chloride transporter), member 5 (ENSG00000124140), score: 0.55 SLC25A37solute carrier family 25, member 37 (ENSG00000147454), score: -0.54 SLC32A1solute carrier family 32 (GABA vesicular transporter), member 1 (ENSG00000101438), score: 0.69 SLC39A12solute carrier family 39 (zinc transporter), member 12 (ENSG00000148482), score: 0.55 SLC39A13solute carrier family 39 (zinc transporter), member 13 (ENSG00000165915), score: -0.48 SLC4A10solute carrier family 4, sodium bicarbonate transporter, member 10 (ENSG00000144290), score: 0.59 SLC5A7solute carrier family 5 (choline transporter), member 7 (ENSG00000115665), score: 0.79 SLC6A11solute carrier family 6 (neurotransmitter transporter, GABA), member 11 (ENSG00000132164), score: 0.67 SLC6A9solute carrier family 6 (neurotransmitter transporter, glycine), member 9 (ENSG00000196517), score: 0.56 SLC7A14solute carrier family 7 (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system), member 14 (ENSG00000013293), score: 0.58 SNAP23synaptosomal-associated protein, 23kDa (ENSG00000092531), score: -0.53 SNX25sorting nexin 25 (ENSG00000109762), score: 0.56 SPHKAPSPHK1 interactor, AKAP domain containing (ENSG00000153820), score: 0.55 SPON1spondin 1, extracellular matrix protein (ENSG00000152268), score: 0.57 SPRED1sprouty-related, EVH1 domain containing 1 (ENSG00000166068), score: 0.57 SRGAP3SLIT-ROBO Rho GTPase activating protein 3 (ENSG00000196220), score: 0.53 SSTsomatostatin (ENSG00000157005), score: 0.54 STIM2stromal interaction molecule 2 (ENSG00000109689), score: 0.56 STK40serine/threonine kinase 40 (ENSG00000196182), score: -0.48 STX12syntaxin 12 (ENSG00000117758), score: 0.61 STXBP4syntaxin binding protein 4 (ENSG00000166263), score: 0.63 SV2Csynaptic vesicle glycoprotein 2C (ENSG00000122012), score: 0.65 SYNGR3synaptogyrin 3 (ENSG00000127561), score: 0.53 SYNJ1synaptojanin 1 (ENSG00000159082), score: 0.69 SYT11synaptotagmin XI (ENSG00000132718), score: 0.56 TAC1tachykinin, precursor 1 (ENSG00000006128), score: 0.64 TBC1D19TBC1 domain family, member 19 (ENSG00000109680), score: 0.59 TBC1D30TBC1 domain family, member 30 (ENSG00000111490), score: 0.58 TFAP2Dtranscription factor AP-2 delta (activating enhancer binding protein 2 delta) (ENSG00000008197), score: 0.66 TGM2transglutaminase 2 (C polypeptide, protein-glutamine-gamma-glutamyltransferase) (ENSG00000198959), score: -0.54 THSD7Athrombospondin, type I, domain containing 7A (ENSG00000005108), score: 0.73 THY1Thy-1 cell surface antigen (ENSG00000154096), score: 0.57 TLN1talin 1 (ENSG00000137076), score: -0.54 TMEFF2transmembrane protein with EGF-like and two follistatin-like domains 2 (ENSG00000144339), score: 0.61 TMEM117transmembrane protein 117 (ENSG00000139173), score: 0.54 TMEM200Atransmembrane protein 200A (ENSG00000164484), score: 0.64 TMEM22transmembrane protein 22 (ENSG00000168917), score: 0.55 TNFAIP2tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 2 (ENSG00000185215), score: -0.5 TNFRSF1Atumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 1A (ENSG00000067182), score: -0.48 TNRtenascin R (restrictin, janusin) (ENSG00000116147), score: 0.53 TPBGtrophoblast glycoprotein (ENSG00000146242), score: 0.61 TRAM2translocation associated membrane protein 2 (ENSG00000065308), score: -0.52 TRHRthyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor (ENSG00000174417), score: 0.56 TRPC1transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily C, member 1 (ENSG00000144935), score: 0.64 TRPC3transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily C, member 3 (ENSG00000138741), score: 0.54 TRPC5transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily C, member 5 (ENSG00000072315), score: 0.79 TRPM2transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily M, member 2 (ENSG00000142185), score: 0.54 TSPAN2tetraspanin 2 (ENSG00000134198), score: 0.68 TSTA3tissue specific transplantation antigen P35B (ENSG00000104522), score: -0.49 UBAP1ubiquitin associated protein 1 (ENSG00000165006), score: -0.49 UNC80unc-80 homolog (C. elegans) (ENSG00000144406), score: 0.53 USP45ubiquitin specific peptidase 45 (ENSG00000123552), score: 0.61 VSTM2AV-set and transmembrane domain containing 2A (ENSG00000170419), score: 0.58 WDFY3WD repeat and FYVE domain containing 3 (ENSG00000163625), score: 0.64 WNT4wingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 4 (ENSG00000162552), score: 0.65 ZC3H12Bzinc finger CCCH-type containing 12B (ENSG00000102053), score: 0.62 ZFYVE21zinc finger, FYVE domain containing 21 (ENSG00000100711), score: -0.49 ZNF828zinc finger protein 828 (ENSG00000198824), score: 0.55
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mmu_cb_f_ca1 | mmu | cb | f | _ |
| mmu_cb_m1_ca1 | mmu | cb | m | 1 |
| gga_cb_m_ca1 | gga | cb | m | _ |
| mdo_br_m_ca1 | mdo | br | m | _ |
| gga_cb_f_ca1 | gga | cb | f | _ |
| oan_cb_m_ca1 | oan | cb | m | _ |
| oan_cb_f_ca1 | oan | cb | f | _ |
| mmu_br_m2_ca1 | mmu | br | m | 2 |
| mdo_br_f_ca1 | mdo | br | f | _ |
| mmu_br_f_ca1 | mmu | br | f | _ |
| mmu_br_m1_ca1 | mmu | br | m | 1 |
| oan_br_f_ca1 | oan | br | f | _ |
| gga_br_m_ca1 | gga | br | m | _ |
| gga_br_f_ca1 | gga | br | f | _ |
| oan_br_m_ca1 | oan | br | m | _ |