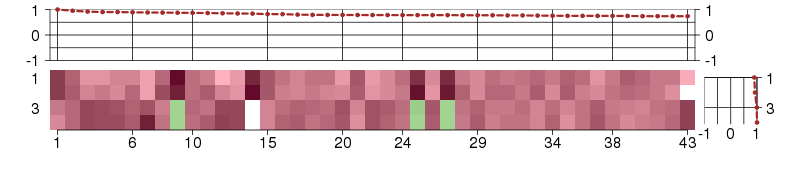

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

chromosome segregation
The process by which genetic material, in the form of chromosomes, is organized into specific structures and then physically separated and apportioned to two or more sets.
M phase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the cell cycle comprising nuclear division.
cell cycle
The progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events. Canonically, the cell cycle comprises the replication and segregation of genetic material followed by the division of the cell, but in endocycles or syncytial cells nuclear replication or nuclear division may not be followed by cell division.
meiosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through the nuclear division phase of a meiotic cell cycle, the specialized nuclear and cell division in which a single diploid cell undergoes two nuclear divisions following a single round of DNA replication in order to produce four daughter cells that contain half the number of chromosomes as the diploid cell. Meiotic division occurs during the formation of gametes from diploid organisms and at the beginning of haplophase in those organisms that alternate between diploid and haploid generations.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
cell cycle process
A cellular process that is involved in the progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
cell cycle phase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through one of the biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
meiotic chromosome segregation
The process by which genetic material, in the form of chromosomes, is organized into specific structures and then physically separated and apportioned to two or more sets during M phase of the meiotic cell cycle.
meiotic cell cycle
Progression through the phases of the meiotic cell cycle, in which canonically a cell replicates to produce four offspring with half the chromosomal content of the progenitor cell.
M phase of meiotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the meiotic cell cycle during which meiosis takes place.
all
NA
cell cycle process
A cellular process that is involved in the progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
meiosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through the nuclear division phase of a meiotic cell cycle, the specialized nuclear and cell division in which a single diploid cell undergoes two nuclear divisions following a single round of DNA replication in order to produce four daughter cells that contain half the number of chromosomes as the diploid cell. Meiotic division occurs during the formation of gametes from diploid organisms and at the beginning of haplophase in those organisms that alternate between diploid and haploid generations.
M phase of meiotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the meiotic cell cycle during which meiosis takes place.
meiotic chromosome segregation
The process by which genetic material, in the form of chromosomes, is organized into specific structures and then physically separated and apportioned to two or more sets during M phase of the meiotic cell cycle.

intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
nucleus
A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent.
chromosome
A structure composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins (e.g. histones) that carries hereditary information.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, and prokaryotic structures such as anammoxosomes and pirellulosomes. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
chromosomal part
Any constituent part of a chromosome, a structure composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins (e.g. histones) that carries hereditary information.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
chromosomal part
Any constituent part of a chromosome, a structure composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins (e.g. histones) that carries hereditary information.

ACER1alkaline ceramidase 1 (ENSG00000167769), score: 0.9 AIREautoimmune regulator (ENSG00000160224), score: 0.85 APTXaprataxin (ENSG00000137074), score: 0.9 C12orf63chromosome 12 open reading frame 63 (ENSG00000188596), score: 0.78 C17orf104chromosome 17 open reading frame 104 (ENSG00000180336), score: 0.74 CCDC37coiled-coil domain containing 37 (ENSG00000163885), score: 0.74 CCDC67coiled-coil domain containing 67 (ENSG00000165325), score: 0.75 CENPIcentromere protein I (ENSG00000102384), score: 0.75 CNOT8CCR4-NOT transcription complex, subunit 8 (ENSG00000155508), score: 0.77 CRYBA1crystallin, beta A1 (ENSG00000108255), score: 0.78 CXorf22chromosome X open reading frame 22 (ENSG00000165164), score: 1 CXorf30chromosome X open reading frame 30 (ENSG00000205081), score: 0.82 E2F8E2F transcription factor 8 (ENSG00000129173), score: 0.95 ENO4enolase family member 4 (ENSG00000188316), score: 0.8 ENPP4ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 4 (putative) (ENSG00000001561), score: 0.77 FAM54Afamily with sequence similarity 54, member A (ENSG00000146410), score: 0.75 FKBP14FK506 binding protein 14, 22 kDa (ENSG00000106080), score: 0.77 FOXN1forkhead box N1 (ENSG00000109101), score: 0.88 GEMC1geminin coiled-coil domain-containing protein 1 (ENSG00000205835), score: 0.78 GPR1G protein-coupled receptor 1 (ENSG00000183671), score: 0.78 HEATR6HEAT repeat containing 6 (ENSG00000068097), score: 0.78 KIAA1609KIAA1609 (ENSG00000140950), score: 0.74 KIF18Bkinesin family member 18B (ENSG00000186185), score: 0.88 KIF24kinesin family member 24 (ENSG00000186638), score: 0.87 MYBv-myb myeloblastosis viral oncogene homolog (avian) (ENSG00000118513), score: 0.92 MYF5myogenic factor 5 (ENSG00000111049), score: 0.87 NUP54nucleoporin 54kDa (ENSG00000138750), score: 0.79 ORC1Lorigin recognition complex, subunit 1-like (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000085840), score: 0.78 PUS3pseudouridylate synthase 3 (ENSG00000110060), score: 0.89 RFX6regulatory factor X, 6 (ENSG00000185002), score: 0.84 RPE65retinal pigment epithelium-specific protein 65kDa (ENSG00000116745), score: 0.78 SGOL1shugoshin-like 1 (S. pombe) (ENSG00000129810), score: 0.79 SMC1Bstructural maintenance of chromosomes 1B (ENSG00000077935), score: 0.76 STILSCL/TAL1 interrupting locus (ENSG00000123473), score: 0.78 STRA8stimulated by retinoic acid gene 8 homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000146857), score: 0.76 TERTtelomerase reverse transcriptase (ENSG00000164362), score: 0.84 TLX1T-cell leukemia homeobox 1 (ENSG00000107807), score: 0.78 TMEM26transmembrane protein 26 (ENSG00000196932), score: 0.75 TP53TG5TP53 target 5 (ENSG00000124251), score: 0.77 UHRF1ubiquitin-like with PHD and ring finger domains 1 (ENSG00000034063), score: 0.82 VASH2vasohibin 2 (ENSG00000143494), score: 0.74
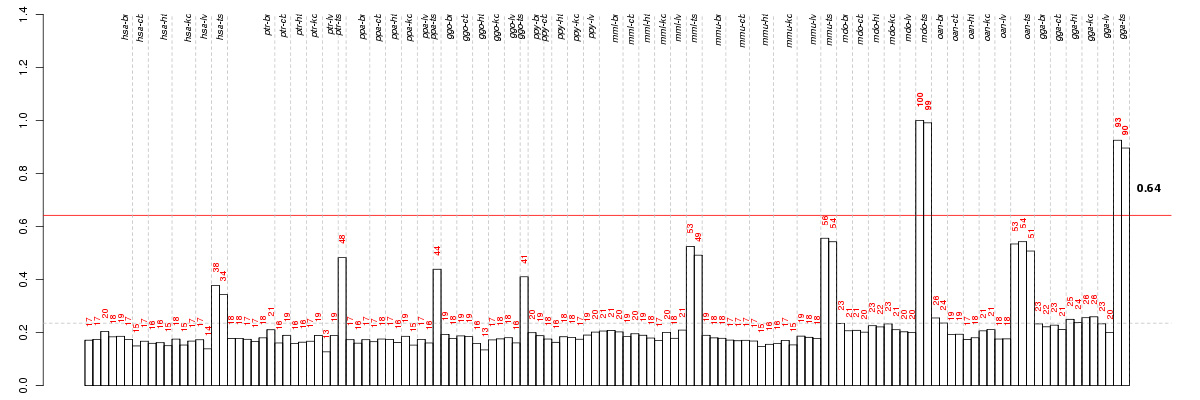
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| gga_ts_m2_ca1 | gga | ts | m | 2 |
| gga_ts_m1_ca1 | gga | ts | m | 1 |
| mdo_ts_m1_ca1 | mdo | ts | m | 1 |
| mdo_ts_m2_ca1 | mdo | ts | m | 2 |