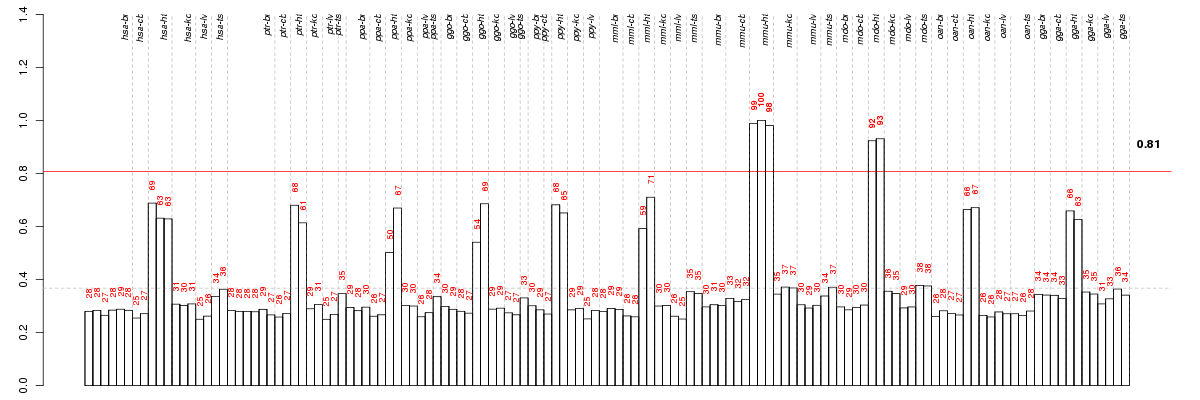

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
generation of precursor metabolites and energy
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of precursor metabolites, substances from which energy is derived, and any process involved in the liberation of energy from these substances.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
energy derivation by oxidation of organic compounds
The chemical reactions and pathways by which a cell derives energy from organic compounds; results in the oxidation of the compounds from which energy is released.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cellular respiration
The enzymatic release of energy from organic compounds (especially carbohydrates and fats) which either requires oxygen (aerobic respiration) or does not (anaerobic respiration).
all
NA
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
contractile fiber
Fibers, composed of actin, myosin, and associated proteins, found in cells of smooth or striated muscle.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
mitochondrion
A semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration.
endoplasmic reticulum
The irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae. The ER takes two forms, rough (or granular), with ribosomes adhering to the outer surface, and smooth (with no ribosomes attached).
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cytoplasm
All of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
mitochondrial envelope
The double lipid bilayer enclosing the mitochondrion and separating its contents from the cell cytoplasm; includes the intermembrane space.
mitochondrial inner membrane
The inner, i.e. lumen-facing, lipid bilayer of the mitochondrial envelope. It is highly folded to form cristae.
sarcoplasm
The cytoplasm of a muscle cell; includes the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
sarcoplasmic reticulum
A fine reticular network of membrane-limited elements that pervades the sarcoplasm of a muscle cell; continuous over large portions of the cell and with the nuclear envelope; that part of the endoplasmic reticulum specialized for calcium release, uptake and storage.
organelle inner membrane
The inner, i.e. lumen-facing, lipid bilayer of an organelle envelope; usually highly selective to most ions and metabolites.
myofibril
The contractile element of skeletal and cardiac muscle; a long, highly organized bundle of actin, myosin, and other proteins that contracts by a sliding filament mechanism.
sarcomere
The repeating unit of a myofibril in a muscle cell, composed of an array of overlapping thick and thin filaments between two adjacent Z discs.
T-tubule
Invagination of the plasma membrane of a muscle cell that extends inward from the cell surface around each myofibril. The ends of T-tubules make contact with the sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
mitochondrial membrane
Either of the lipid bilayers that surround the mitochondrion and form the mitochondrial envelope.
organelle envelope
A double membrane structure enclosing an organelle, including two lipid bilayers and the region between them. In some cases, an organelle envelope may have more than two membranes.
envelope
A multilayered structure surrounding all or part of a cell; encompasses one or more lipid bilayers, and may include a cell wall layer; also includes the space between layers.
sarcolemma
The outer membrane of a muscle cell, consisting of the plasma membrane, a covering basement membrane (about 100 nm thick and sometimes common to more than one fiber), and the associated loose network of collagen fibers.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, and prokaryotic structures such as anammoxosomes and pirellulosomes. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
mitochondrial part
Any constituent part of a mitochondrion, a semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
contractile fiber part
Any constituent part of a contractile fiber, a fiber composed of actin, myosin, and associated proteins, found in cells of smooth or striated muscle.
mitochondrial membrane part
Any constituent part of a mitochondrial membrane, either of the lipid bilayers that surround the mitochondrion and form the mitochondrial envelope.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
subsynaptic reticulum
An elaborate tubulolamellar membrane system that underlies the postsynaptic cell membrane.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
organelle envelope
A double membrane structure enclosing an organelle, including two lipid bilayers and the region between them. In some cases, an organelle envelope may have more than two membranes.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
organelle envelope
A double membrane structure enclosing an organelle, including two lipid bilayers and the region between them. In some cases, an organelle envelope may have more than two membranes.
organelle inner membrane
The inner, i.e. lumen-facing, lipid bilayer of an organelle envelope; usually highly selective to most ions and metabolites.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
organelle inner membrane
The inner, i.e. lumen-facing, lipid bilayer of an organelle envelope; usually highly selective to most ions and metabolites.
mitochondrial inner membrane
The inner, i.e. lumen-facing, lipid bilayer of the mitochondrial envelope. It is highly folded to form cristae.
mitochondrial membrane part
Any constituent part of a mitochondrial membrane, either of the lipid bilayers that surround the mitochondrion and form the mitochondrial envelope.
mitochondrial envelope
The double lipid bilayer enclosing the mitochondrion and separating its contents from the cell cytoplasm; includes the intermembrane space.
mitochondrial membrane
Either of the lipid bilayers that surround the mitochondrion and form the mitochondrial envelope.
mitochondrial membrane part
Any constituent part of a mitochondrial membrane, either of the lipid bilayers that surround the mitochondrion and form the mitochondrial envelope.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
contractile fiber
Fibers, composed of actin, myosin, and associated proteins, found in cells of smooth or striated muscle.
mitochondrion
A semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration.
endoplasmic reticulum
The irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae. The ER takes two forms, rough (or granular), with ribosomes adhering to the outer surface, and smooth (with no ribosomes attached).
mitochondrial part
Any constituent part of a mitochondrion, a semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration.
contractile fiber part
Any constituent part of a contractile fiber, a fiber composed of actin, myosin, and associated proteins, found in cells of smooth or striated muscle.
subsynaptic reticulum
An elaborate tubulolamellar membrane system that underlies the postsynaptic cell membrane.
mitochondrial membrane
Either of the lipid bilayers that surround the mitochondrion and form the mitochondrial envelope.
mitochondrial part
Any constituent part of a mitochondrion, a semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration.
sarcoplasmic reticulum
A fine reticular network of membrane-limited elements that pervades the sarcoplasm of a muscle cell; continuous over large portions of the cell and with the nuclear envelope; that part of the endoplasmic reticulum specialized for calcium release, uptake and storage.
contractile fiber part
Any constituent part of a contractile fiber, a fiber composed of actin, myosin, and associated proteins, found in cells of smooth or striated muscle.
T-tubule
Invagination of the plasma membrane of a muscle cell that extends inward from the cell surface around each myofibril. The ends of T-tubules make contact with the sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane.
sarcoplasmic reticulum
A fine reticular network of membrane-limited elements that pervades the sarcoplasm of a muscle cell; continuous over large portions of the cell and with the nuclear envelope; that part of the endoplasmic reticulum specialized for calcium release, uptake and storage.
sarcomere
The repeating unit of a myofibril in a muscle cell, composed of an array of overlapping thick and thin filaments between two adjacent Z discs.

| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 05010 | 7.656e-03 | 0.5308 | 5 | 44 | Alzheimer's disease |
| 00020 | 2.294e-02 | 0.1689 | 3 | 14 | Citrate cycle (TCA cycle) |
| 05410 | 2.510e-02 | 0.4101 | 4 | 34 | Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) |
| 05414 | 2.510e-02 | 0.4101 | 4 | 34 | Dilated cardiomyopathy |
ABRAactin-binding Rho activating protein (ENSG00000174429), score: 0.64 ACSL3acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 3 (ENSG00000123983), score: -0.69 ART3ADP-ribosyltransferase 3 (ENSG00000156219), score: 0.6 ASB14ankyrin repeat and SOCS box-containing 14 (ENSG00000239388), score: 0.72 ATP2A2ATPase, Ca++ transporting, cardiac muscle, slow twitch 2 (ENSG00000174437), score: 0.8 CACNA1Scalcium channel, voltage-dependent, L type, alpha 1S subunit (ENSG00000081248), score: 0.88 CADM1cell adhesion molecule 1 (ENSG00000182985), score: -0.73 COQ5coenzyme Q5 homolog, methyltransferase (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000110871), score: 0.6 DAPP1dual adaptor of phosphotyrosine and 3-phosphoinositides (ENSG00000070190), score: 0.75 DTNBP1dystrobrevin binding protein 1 (ENSG00000047579), score: 0.6 EDNRAendothelin receptor type A (ENSG00000151617), score: 0.63 EGLN1egl nine homolog 1 (C. elegans) (ENSG00000135766), score: 0.71 EHD4EH-domain containing 4 (ENSG00000103966), score: 0.6 FAAHfatty acid amide hydrolase (ENSG00000117480), score: -0.67 FAM160A1family with sequence similarity 160, member A1 (ENSG00000164142), score: 0.72 FAM174Bfamily with sequence similarity 174, member B (ENSG00000185442), score: 0.6 FBLIM1filamin binding LIM protein 1 (ENSG00000162458), score: 0.61 FBP2fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 2 (ENSG00000130957), score: 0.74 FSD2fibronectin type III and SPRY domain containing 2 (ENSG00000186628), score: 0.71 FYCO1FYVE and coiled-coil domain containing 1 (ENSG00000163820), score: 0.62 GJA3gap junction protein, alpha 3, 46kDa (ENSG00000121743), score: 0.66 HIPK3homeodomain interacting protein kinase 3 (ENSG00000110422), score: 0.61 IDH3Aisocitrate dehydrogenase 3 (NAD+) alpha (ENSG00000166411), score: 0.65 IVNS1ABPinfluenza virus NS1A binding protein (ENSG00000116679), score: 0.74 KCNJ5potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 5 (ENSG00000120457), score: 0.75 KCNV2potassium channel, subfamily V, member 2 (ENSG00000168263), score: 0.67 LBHlimb bud and heart development homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000213626), score: 0.6 LMOD2leiomodin 2 (cardiac) (ENSG00000170807), score: 0.61 LRRC10leucine rich repeat containing 10 (ENSG00000198812), score: 0.81 LRTM1leucine-rich repeats and transmembrane domains 1 (ENSG00000144771), score: 1 MFN1mitofusin 1 (ENSG00000171109), score: 0.77 MURCmuscle-related coiled-coil protein (ENSG00000170681), score: 0.63 MYBPC3myosin binding protein C, cardiac (ENSG00000134571), score: 0.62 MYLK3myosin light chain kinase 3 (ENSG00000140795), score: 0.72 MYLK4myosin light chain kinase family, member 4 (ENSG00000145949), score: 0.72 MYOTmyotilin (ENSG00000120729), score: 0.75 MYPNmyopalladin (ENSG00000138347), score: 0.63 NDUFA10NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 alpha subcomplex, 10, 42kDa (ENSG00000130414), score: 0.65 NDUFA6NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 alpha subcomplex, 6, 14kDa (ENSG00000184983), score: 0.61 NIPSNAP1nipsnap homolog 1 (C. elegans) (ENSG00000184117), score: -0.72 OGDHoxoglutarate (alpha-ketoglutarate) dehydrogenase (lipoamide) (ENSG00000105953), score: 0.65 PCGF5polycomb group ring finger 5 (ENSG00000180628), score: 0.64 PDHBpyruvate dehydrogenase (lipoamide) beta (ENSG00000168291), score: 0.73 PHTF2putative homeodomain transcription factor 2 (ENSG00000006576), score: 0.69 PPIP5K2diphosphoinositol pentakisphosphate kinase 2 (ENSG00000145725), score: 0.68 RAPSNreceptor-associated protein of the synapse (ENSG00000165917), score: 0.68 RPL3Lribosomal protein L3-like (ENSG00000140986), score: 0.63 SGCGsarcoglycan, gamma (35kDa dystrophin-associated glycoprotein) (ENSG00000102683), score: 0.62 SMYD1SET and MYND domain containing 1 (ENSG00000115593), score: 0.6 TBX20T-box 20 (ENSG00000164532), score: 0.62 TCP11L2t-complex 11 (mouse)-like 2 (ENSG00000166046), score: 0.67 TIMM17Atranslocase of inner mitochondrial membrane 17 homolog A (yeast) (ENSG00000134375), score: 0.68 TMEM38Atransmembrane protein 38A (ENSG00000072954), score: 0.62 TXLNBtaxilin beta (ENSG00000164440), score: 0.74 UCP3uncoupling protein 3 (mitochondrial, proton carrier) (ENSG00000175564), score: 0.85 UQCRC1ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase core protein I (ENSG00000010256), score: 0.61 USP28ubiquitin specific peptidase 28 (ENSG00000048028), score: 0.64
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mdo_ht_m_ca1 | mdo | ht | m | _ |
| mdo_ht_f_ca1 | mdo | ht | f | _ |
| mmu_ht_f_ca1 | mmu | ht | f | _ |
| mmu_ht_m2_ca1 | mmu | ht | m | 2 |
| mmu_ht_m1_ca1 | mmu | ht | m | 1 |