
Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

reproduction
The production by an organism of new individuals that contain some portion of their genetic material inherited from that organism.
chromosome organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level that results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of chromosomes, structures composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins that carries hereditary information.
M phase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the cell cycle comprising nuclear division.
metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
reproductive developmental process
A developmental process by which a progressive change in the state of some part of an organism specifically contributes to its ability to form offspring.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
DNA metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving deoxyribonucleic acid. This is one of the two main types of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from one, or more commonly, two, strands of linked deoxyribonucleotides.
DNA recombination
Any process by which a new genotype is formed by reassortment of genes resulting in gene combinations different from those that were present in the parents. In eukaryotes genetic recombination can occur by chromosome assortment, intrachromosomal recombination, or nonreciprocal interchromosomal recombination. Intrachromosomal recombination occurs by crossing over. In bacteria it may occur by genetic transformation, conjugation, transduction, or F-duction.
nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds; includes nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, assimilatory/dissimilatory nitrate reduction and the interconversion of nitrogenous organic matter and ammonium.
organelle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an organelle within a cell. An organelle is an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
cell cycle
The progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events. Canonically, the cell cycle comprises the replication and segregation of genetic material followed by the division of the cell, but in endocycles or syncytial cells nuclear replication or nuclear division may not be followed by cell division.
meiosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through the nuclear division phase of a meiotic cell cycle, the specialized nuclear and cell division in which a single diploid cell undergoes two nuclear divisions following a single round of DNA replication in order to produce four daughter cells that contain half the number of chromosomes as the diploid cell. Meiotic division occurs during the formation of gametes from diploid organisms and at the beginning of haplophase in those organisms that alternate between diploid and haploid generations.
meiosis I
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through the first phase of meiosis, in which cells divide and homologous chromosomes are paired and segregated from each other, producing two daughter cells.
synapsis
The cell cycle process whereby the side by side pairing and physical juxtaposition of homologous chromosomes is created at the metaphase plate.
reciprocal meiotic recombination
The cell cycle process whereby double strand breaks are formed and repaired through a double Holliday junction intermediate. This results in the equal exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids in a pair of homologous chromosomes. These reciprocal recombinant products ensure the proper segregation of homologous chromosomes during meiosis I and create genetic diversity.
gamete generation
The generation and maintenance of gametes in a multicellular organism. A gamete is a haploid reproductive cell.
spermatogenesis
The process of formation of spermatozoa, including spermatocytogenesis and spermiogenesis.
sex differentiation
The establishment of the sex of an organism by physical differentiation.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
cellular component organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a cellular component.
sexual reproduction
The regular alternation, in the life cycle of haplontic, diplontic and diplohaplontic organisms, of meiosis and fertilization which provides for the production offspring. In diplontic organisms there is a life cycle in which the products of meiosis behave directly as gametes, fusing to form a zygote from which the diploid, or sexually reproductive polyploid, adult organism will develop. In diplohaplontic organisms a haploid phase (gametophyte) exists in the life cycle between meiosis and fertilization (e.g. higher plants, many algae and Fungi); the products of meiosis are spores that develop as haploid individuals from which haploid gametes develop to form a diploid zygote; diplohaplontic organisms show an alternation of haploid and diploid generations. In haplontic organisms meiosis occurs in the zygote, giving rise to four haploid cells (e.g. many algae and protozoa), only the zygote is diploid and this may form a resistant spore, tiding organisms over hard times.
cell cycle process
A cellular process that is involved in the progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
cell cycle phase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through one of the biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
multicellular organism reproduction
The biological process by which new individuals are produced by one or two multicellular organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
male gamete generation
Generation of the male gamete; specialised haploid cells produced by meiosis and along with a female gamete takes part in sexual reproduction.
reproductive process in a multicellular organism
The process, occurring above the cellular level, that is pertinent to the reproductive function of a multicellular organism. This includes the integrated processes at the level of tissues and organs.
meiotic cell cycle
Progression through the phases of the meiotic cell cycle, in which canonically a cell replicates to produce four offspring with half the chromosomal content of the progenitor cell.
M phase of meiotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the meiotic cell cycle during which meiosis takes place.
chromosome organization involved in meiosis
A process of chromosome organization that is involved in meiosis.
nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleic acids.
all
NA
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
organelle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an organelle within a cell. An organelle is an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
multicellular organism reproduction
The biological process by which new individuals are produced by one or two multicellular organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
reproductive process in a multicellular organism
The process, occurring above the cellular level, that is pertinent to the reproductive function of a multicellular organism. This includes the integrated processes at the level of tissues and organs.
reproductive developmental process
A developmental process by which a progressive change in the state of some part of an organism specifically contributes to its ability to form offspring.
reproductive process in a multicellular organism
The process, occurring above the cellular level, that is pertinent to the reproductive function of a multicellular organism. This includes the integrated processes at the level of tissues and organs.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
cell cycle process
A cellular process that is involved in the progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
gamete generation
The generation and maintenance of gametes in a multicellular organism. A gamete is a haploid reproductive cell.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
chromosome organization involved in meiosis
A process of chromosome organization that is involved in meiosis.
DNA metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving deoxyribonucleic acid. This is one of the two main types of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from one, or more commonly, two, strands of linked deoxyribonucleotides.
meiosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through the nuclear division phase of a meiotic cell cycle, the specialized nuclear and cell division in which a single diploid cell undergoes two nuclear divisions following a single round of DNA replication in order to produce four daughter cells that contain half the number of chromosomes as the diploid cell. Meiotic division occurs during the formation of gametes from diploid organisms and at the beginning of haplophase in those organisms that alternate between diploid and haploid generations.
M phase of meiotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the meiotic cell cycle during which meiosis takes place.
meiosis I
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through the first phase of meiosis, in which cells divide and homologous chromosomes are paired and segregated from each other, producing two daughter cells.
chromosome organization involved in meiosis
A process of chromosome organization that is involved in meiosis.
synapsis
The cell cycle process whereby the side by side pairing and physical juxtaposition of homologous chromosomes is created at the metaphase plate.
reciprocal meiotic recombination
The cell cycle process whereby double strand breaks are formed and repaired through a double Holliday junction intermediate. This results in the equal exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids in a pair of homologous chromosomes. These reciprocal recombinant products ensure the proper segregation of homologous chromosomes during meiosis I and create genetic diversity.
reciprocal meiotic recombination
The cell cycle process whereby double strand breaks are formed and repaired through a double Holliday junction intermediate. This results in the equal exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids in a pair of homologous chromosomes. These reciprocal recombinant products ensure the proper segregation of homologous chromosomes during meiosis I and create genetic diversity.


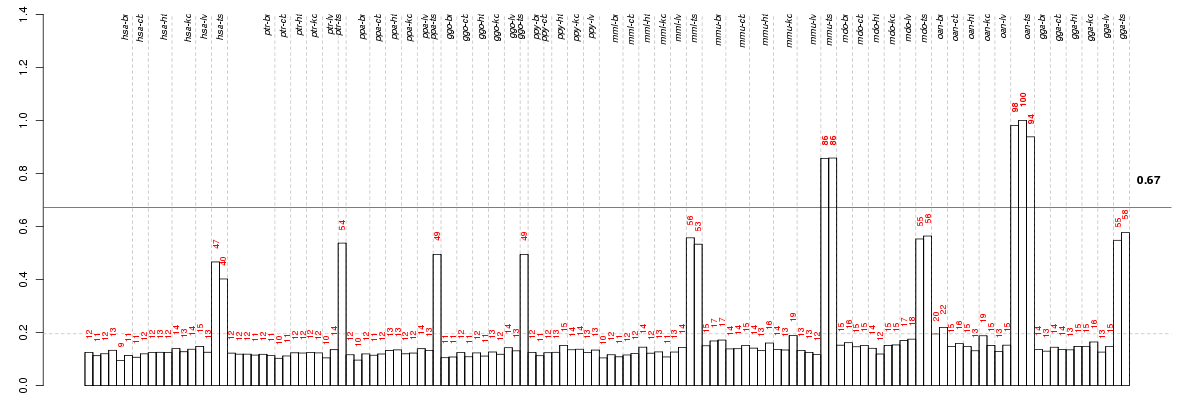
ASPMasp (abnormal spindle) homolog, microcephaly associated (Drosophila) (ENSG00000066279), score: 0.68 BRCA2breast cancer 2, early onset (ENSG00000139618), score: 0.67 C10orf96chromosome 10 open reading frame 96 (ENSG00000182645), score: 0.68 C12orf48chromosome 12 open reading frame 48 (ENSG00000185480), score: 0.78 C13orf34chromosome 13 open reading frame 34 (ENSG00000136122), score: 0.69 C1orf174chromosome 1 open reading frame 174 (ENSG00000198912), score: 0.76 C3orf38chromosome 3 open reading frame 38 (ENSG00000179021), score: 0.7 CNGA2cyclic nucleotide gated channel alpha 2 (ENSG00000183862), score: 0.68 CPA6carboxypeptidase A6 (ENSG00000165078), score: 0.78 CYP11A1cytochrome P450, family 11, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000140459), score: 0.64 DMRT3doublesex and mab-3 related transcription factor 3 (ENSG00000064218), score: 0.7 DNAH8dynein, axonemal, heavy chain 8 (ENSG00000124721), score: 0.7 EPYCepiphycan (ENSG00000083782), score: 0.72 EXOSC10exosome component 10 (ENSG00000171824), score: 0.71 FANCBFanconi anemia, complementation group B (ENSG00000181544), score: 0.75 FBXO47F-box protein 47 (ENSG00000204952), score: 0.67 KIF14kinesin family member 14 (ENSG00000118193), score: 0.68 LHCGRluteinizing hormone/choriogonadotropin receptor (ENSG00000138039), score: 0.67 LRRC18leucine rich repeat containing 18 (ENSG00000165383), score: 0.7 LRRC52leucine rich repeat containing 52 (ENSG00000162763), score: 0.67 LRRIQ4leucine-rich repeats and IQ motif containing 4 (ENSG00000188306), score: 0.68 NR5A1nuclear receptor subfamily 5, group A, member 1 (ENSG00000136931), score: 0.64 PAX5paired box 5 (ENSG00000196092), score: 0.81 PAX9paired box 9 (ENSG00000198807), score: 0.86 RAD54BRAD54 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000197275), score: 0.71 RASEFRAS and EF-hand domain containing (ENSG00000165105), score: 0.69 RBP2retinol binding protein 2, cellular (ENSG00000114113), score: 0.7 RPAP2RNA polymerase II associated protein 2 (ENSG00000122484), score: 0.66 SLC6A14solute carrier family 6 (amino acid transporter), member 14 (ENSG00000087916), score: 1 SPO11SPO11 meiotic protein covalently bound to DSB homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000054796), score: 0.77 STRA8stimulated by retinoic acid gene 8 homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000146857), score: 0.71 SYCP1synaptonemal complex protein 1 (ENSG00000198765), score: 0.65 TBX4T-box 4 (ENSG00000121075), score: 0.67 TDRD1tudor domain containing 1 (ENSG00000095627), score: 0.69 WDR64WD repeat domain 64 (ENSG00000162843), score: 0.67 WDR78WD repeat domain 78 (ENSG00000152763), score: 0.65 ZNF438zinc finger protein 438 (ENSG00000183621), score: 0.77
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mmu_ts_m1_ca1 | mmu | ts | m | 1 |
| mmu_ts_m2_ca1 | mmu | ts | m | 2 |
| oan_ts_m2_ca1 | oan | ts | m | 2 |
| oan_ts_m3_ca1 | oan | ts | m | 3 |
| oan_ts_m1_ca1 | oan | ts | m | 1 |