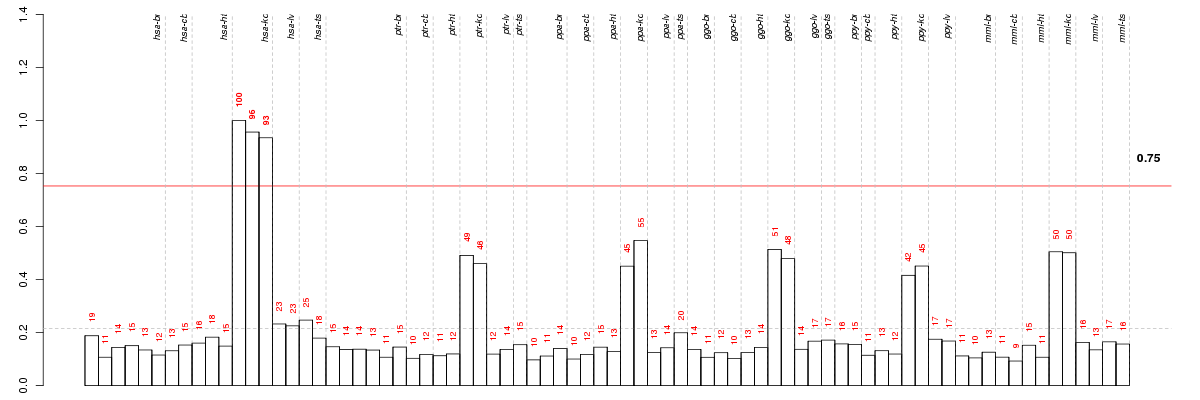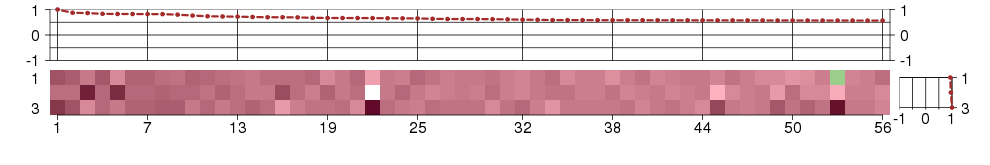

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

transition metal ion transport
The directed movement of transition metal ions into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. A transition metal is an element whose atom has an incomplete d-subshell of extranuclear electrons, or which gives rise to a cation or cations with an incomplete d-subshell. Transition metals often have more than one valency state. Biologically relevant transition metals include vanadium, manganese, iron, copper, cobalt, nickel, molybdenum and silver.
renal system process involved in regulation of blood volume
A slow mechanism of blood pressure regulation that responds to changes in pressure resulting from fluid and salt intake by modulating the quantity of blood in the circulatory system.
system process
A multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system. An organ system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a biological objective.
circulatory system process
A organ system process carried out by any of the organs or tissues of the circulatory system. The circulatory system is an organ system that moves extracellular fluids to and from tissue within a multicellular organism.
renal system process
A organ system process carried out by any of the organs or tissues of the renal system. The renal system is responsible for fluid volume regulation and detoxification in an organism.
renal system process involved in regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure
Renal process that modulates the force with which blood travels through the circulatory system. The process is controlled by a balance of processes that increase pressure and decrease pressure.
regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure
The process that modulates the force with which blood travels through the systemic arterial circulatory system. The process is controlled by a balance of processes that increase pressure and decrease pressure.
renal water transport
The directed movement of water (H2O) by the kidney.
transport
The directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells, or within a multicellular organism by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
ion transport
The directed movement of charged atoms or small charged molecules into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
cation transport
The directed movement of cations, atoms or small molecules with a net positive charge, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
metal ion transport
The directed movement of metal ions, any metal ion with an electric charge, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
zinc ion transport
The directed movement of zinc (Zn) ions into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
water transport
The directed movement of water (H2O) into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
blood circulation
The flow of blood through the body of an animal, enabling the transport of nutrients to the tissues and the removal of waste products.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
regulation of blood pressure
Any process that modulates the force with which blood travels through the circulatory system. The process is controlled by a balance of processes that increase pressure and decrease pressure.
carbohydrate transport
The directed movement of carbohydrate into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. Carbohydrates are any of a group of organic compounds based of the general formula Cx(H2O)y.
response to metal ion
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a metal ion stimulus.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
response to inorganic substance
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an inorganic substance stimulus.
polyol transport
The directed movement of polyols, any polyhydric alcohol, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
glycerol transport
The directed movement of glycerol into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. Glycerol is 1,2,3-propanetriol, a sweet, hygroscopic, viscous liquid, widely distributed in nature as a constituent of many lipids.
organic alcohol transport
The directed movement of organic alcohols into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. An organic alcohol is any carbon-containing compound containing a hydroxyl group.
response to mercury ion
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a mercury ion stimulus.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
fluid transport
The directed movement of substances that are in liquid form in normal living conditions into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
response to chemical stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a chemical stimulus.
response to copper ion
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a copper ion stimulus.
regulation of body fluid levels
Any process that modulates the levels of body fluids.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
cellular response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
transmembrane transport
The process whereby a solute is transported from one side of a membrane to the other. This process includes the actual movement of the solute, and any regulation and preparatory steps, such as reduction of the solute.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of biological quality
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological quality. A biological quality is a measurable attribute of an organism or part of an organism, such as size, mass, shape, color, etc.
cellular response to chemical stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a chemical stimulus.
cellular response to inorganic substance
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an inorganic substance stimulus.
cellular response to metal ion
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a metal ion stimulus.
cellular response to copper ion
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a copper ion stimulus.
cellular response to mercury ion
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a mercury ion stimulus.
all
NA
cellular response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
cellular response to chemical stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a chemical stimulus.
transmembrane transport
The process whereby a solute is transported from one side of a membrane to the other. This process includes the actual movement of the solute, and any regulation and preparatory steps, such as reduction of the solute.
regulation of body fluid levels
Any process that modulates the levels of body fluids.
renal water transport
The directed movement of water (H2O) by the kidney.
cellular response to inorganic substance
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an inorganic substance stimulus.
regulation of blood pressure
Any process that modulates the force with which blood travels through the circulatory system. The process is controlled by a balance of processes that increase pressure and decrease pressure.
renal system process involved in regulation of blood volume
A slow mechanism of blood pressure regulation that responds to changes in pressure resulting from fluid and salt intake by modulating the quantity of blood in the circulatory system.
cellular response to metal ion
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a metal ion stimulus.
glycerol transport
The directed movement of glycerol into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. Glycerol is 1,2,3-propanetriol, a sweet, hygroscopic, viscous liquid, widely distributed in nature as a constituent of many lipids.
renal water transport
The directed movement of water (H2O) by the kidney.
renal system process involved in regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure
Renal process that modulates the force with which blood travels through the circulatory system. The process is controlled by a balance of processes that increase pressure and decrease pressure.
cellular response to mercury ion
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a mercury ion stimulus.
cellular response to copper ion
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a copper ion stimulus.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
integral to membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer. When used to describe a protein, indicates that all or part of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
apical plasma membrane
The region of the plasma membrane located at the apical end of the cell.
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
apical part of cell
The region of a polarized cell that forms a tip or is distal to a base. For example, in a polarized epithelial cell, the apical region has an exposed surface and lies opposite to the basal lamina that separates the epithelium from other tissue.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
apical plasma membrane
The region of the plasma membrane located at the apical end of the cell.

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
metal ion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of metal ions from one side of a membrane to the other.
transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a substance from one side of a membrane to the other.
cation transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of cation from one side of the membrane to the other.
ion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of an ion from one side of a membrane to the other.
polyol transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a polyol from one side of the membrane to the other. A polyol is any polyhydric alcohol.
glycerol transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of glycerol from one side of the membrane to the other. Glycerol is 1,2,3-propanetriol, a sweet, hygroscopic, viscous liquid, widely distributed in nature as a constituent of many lipids.
alcohol transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of an alcohol from one side of the membrane to the other. An alcohol is any carbon compound that contains a hydroxyl group.
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
substrate-specific transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of a specific substance or group of related substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
all
NA
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
ACPPacid phosphatase, prostate (ENSG00000014257), score: 0.58 ALDH3B1aldehyde dehydrogenase 3 family, member B1 (ENSG00000006534), score: 0.58 APCDD1Ladenomatosis polyposis coli down-regulated 1-like (ENSG00000198768), score: 0.6 AQP2aquaporin 2 (collecting duct) (ENSG00000167580), score: 0.58 ATP12AATPase, H+/K+ transporting, nongastric, alpha polypeptide (ENSG00000075673), score: 0.71 B3GNT3UDP-GlcNAc:betaGal beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 3 (ENSG00000179913), score: 0.87 B4GALNT2beta-1,4-N-acetyl-galactosaminyl transferase 2 (ENSG00000167080), score: 0.57 C1orf186chromosome 1 open reading frame 186 (ENSG00000196533), score: 1 CHP2calcineurin B homologous protein 2 (ENSG00000166869), score: 0.65 CLDN19claudin 19 (ENSG00000164007), score: 0.57 CTRCchymotrypsin C (caldecrin) (ENSG00000162438), score: 0.57 CYP27B1cytochrome P450, family 27, subfamily B, polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000111012), score: 0.65 ERP27endoplasmic reticulum protein 27 (ENSG00000139055), score: 0.73 FAM151Afamily with sequence similarity 151, member A (ENSG00000162391), score: 0.57 FOLR1folate receptor 1 (adult) (ENSG00000110195), score: 0.58 FUT3fucosyltransferase 3 (galactoside 3(4)-L-fucosyltransferase, Lewis blood group) (ENSG00000171124), score: 0.72 GGT6gamma-glutamyltransferase 6 (ENSG00000167741), score: 0.73 GPR114G protein-coupled receptor 114 (ENSG00000159618), score: 0.82 HHLA2HERV-H LTR-associating 2 (ENSG00000114455), score: 0.67 IL17RBinterleukin 17 receptor B (ENSG00000056736), score: 0.58 INMTindolethylamine N-methyltransferase (ENSG00000106125), score: 0.63 KCNE3potassium voltage-gated channel, Isk-related family, member 3 (ENSG00000175538), score: 0.67 KCNH6potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily H (eag-related), member 6 (ENSG00000173826), score: 0.82 LYG1lysozyme G-like 1 (ENSG00000144214), score: 0.62 MCCD1mitochondrial coiled-coil domain 1 (ENSG00000204511), score: 0.69 MUC13mucin 13, cell surface associated (ENSG00000173702), score: 0.7 NCCRP1non-specific cytotoxic cell receptor protein 1 homolog (zebrafish) (ENSG00000188505), score: 0.76 PAPPA2pappalysin 2 (ENSG00000116183), score: 0.66 PTH2Rparathyroid hormone 2 receptor (ENSG00000144407), score: 0.58 RBP2retinol binding protein 2, cellular (ENSG00000114113), score: 0.82 RDH8retinol dehydrogenase 8 (all-trans) (ENSG00000080511), score: 0.57 RENrenin (ENSG00000143839), score: 0.57 S100A2S100 calcium binding protein A2 (ENSG00000196754), score: 0.6 SLC22A13solute carrier family 22 (organic anion transporter), member 13 (ENSG00000172940), score: 0.7 SLC30A2solute carrier family 30 (zinc transporter), member 2 (ENSG00000158014), score: 0.58 SLC39A4solute carrier family 39 (zinc transporter), member 4 (ENSG00000147804), score: 0.57 SLC39A5solute carrier family 39 (metal ion transporter), member 5 (ENSG00000139540), score: 0.58 SLC5A10solute carrier family 5 (sodium/glucose cotransporter), member 10 (ENSG00000154025), score: 0.57 SLC5A8solute carrier family 5 (iodide transporter), member 8 (ENSG00000139357), score: 0.57 SLC6A19solute carrier family 6 (neutral amino acid transporter), member 19 (ENSG00000174358), score: 0.57 SLC9A4solute carrier family 9 (sodium/hydrogen exchanger), member 4 (ENSG00000180251), score: 0.57 SMPDL3Bsphingomyelin phosphodiesterase, acid-like 3B (ENSG00000130768), score: 0.64 SOSTsclerostin (ENSG00000167941), score: 0.57 SUSD2sushi domain containing 2 (ENSG00000099994), score: 0.66 TACSTD2tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (ENSG00000184292), score: 0.58 TMC4transmembrane channel-like 4 (ENSG00000167608), score: 0.58 TMED4transmembrane emp24 protein transport domain containing 4 (ENSG00000158604), score: 0.61 TMEM150Btransmembrane protein 150B (ENSG00000180061), score: 0.67 TMEM79transmembrane protein 79 (ENSG00000163472), score: 0.63 TMPRSS4transmembrane protease, serine 4 (ENSG00000137648), score: 0.63 TRIM10tripartite motif-containing 10 (ENSG00000204613), score: 0.8 TRIM15tripartite motif-containing 15 (ENSG00000204610), score: 0.82 TRPC7transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily C, member 7 (ENSG00000069018), score: 0.86 TSPO2translocator protein 2 (ENSG00000112212), score: 0.58 TUBAL3tubulin, alpha-like 3 (ENSG00000178462), score: 0.83 VGLL1vestigial like 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000102243), score: 0.66
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa_kd_f_ca1 | hsa | kd | f | _ |
| hsa_kd_m2_ca1 | hsa | kd | m | 2 |
| hsa_kd_m1_ca1 | hsa | kd | m | 1 |