
Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
carbohydrate metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving carbohydrates, any of a group of organic compounds based of the general formula Cx(H2O)y. Includes the formation of carbohydrate derivatives by the addition of a carbohydrate residue to another molecule.
monosaccharide metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving monosaccharides, the simplest carbohydrates. They are polyhydric alcohols containing either an aldehyde or a keto group and between three to ten or more carbon atoms. They form the constitutional repeating units of oligo- and polysaccharides.
alcohol metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving alcohols, any of a class of compounds containing one or more hydroxyl groups attached to a saturated carbon atom.
organic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
cellular amino acid and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, and compounds derived from amino acids, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular amino acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds; includes nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, assimilatory/dissimilatory nitrate reduction and the interconversion of nitrogenous organic matter and ammonium.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones.
amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
amine biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
response to toxin
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a toxin stimulus.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
hexose metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a hexose, any monosaccharide with a chain of six carbon atoms in the molecule.
carboxylic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving carboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (COOH) groups or anions (COO-).
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular ketone metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any of a class of organic compounds that contain the carbonyl group, CO, and in which the carbonyl group is bonded only to carbon atoms, as carried out by individual cells. The general formula for a ketone is RCOR, where R and R are alkyl or aryl groups.
response to chemical stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a chemical stimulus.
oxoacid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any oxoacid; an oxoacid is a compound which contains oxygen, at least one other element, and at least one hydrogen bound to oxygen, and which produces a conjugate base by loss of positive hydrogen ion(s) (hydrons).
cellular amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular carbohydrate metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving carbohydrates, any of a group of organic compounds based of the general formula Cx(H2O)y, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular nitrogen compound biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds.
small molecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
all
NA
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular amino acid and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, and compounds derived from amino acids, as carried out by individual cells.
organic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
cellular amino acid and derivative metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents, and compounds derived from amino acids, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular ketone metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any of a class of organic compounds that contain the carbonyl group, CO, and in which the carbonyl group is bonded only to carbon atoms, as carried out by individual cells. The general formula for a ketone is RCOR, where R and R are alkyl or aryl groups.
cellular amine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
cellular nitrogen compound biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds.
oxoacid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any oxoacid; an oxoacid is a compound which contains oxygen, at least one other element, and at least one hydrogen bound to oxygen, and which produces a conjugate base by loss of positive hydrogen ion(s) (hydrons).
cellular carbohydrate metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving carbohydrates, any of a group of organic compounds based of the general formula Cx(H2O)y, as carried out by individual cells.
monosaccharide metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving monosaccharides, the simplest carbohydrates. They are polyhydric alcohols containing either an aldehyde or a keto group and between three to ten or more carbon atoms. They form the constitutional repeating units of oligo- and polysaccharides.
cellular amino acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.
amine biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom.
cellular amino acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving amino acids, organic acids containing one or more amino substituents.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell fraction
A generic term for parts of cells prepared by disruptive biochemical techniques.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
apical plasma membrane
The region of the plasma membrane located at the apical end of the cell.
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
apical part of cell
The region of a polarized cell that forms a tip or is distal to a base. For example, in a polarized epithelial cell, the apical region has an exposed surface and lies opposite to the basal lamina that separates the epithelium from other tissue.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
apical plasma membrane
The region of the plasma membrane located at the apical end of the cell.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
catalytic activity
Catalysis of a biochemical reaction at physiological temperatures. In biologically catalyzed reactions, the reactants are known as substrates, and the catalysts are naturally occurring macromolecular substances known as enzymes. Enzymes possess specific binding sites for substrates, and are usually composed wholly or largely of protein, but RNA that has catalytic activity (ribozyme) is often also regarded as enzymatic.
aminopeptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of N-terminal amino acid residues from in a polypeptide chain.
metallopeptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of peptide bonds by a mechanism in which water acts as a nucleophile, one or two metal ions hold the water molecule in place, and charged amino acid side chains are ligands for the metal ions.
peptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of a peptide bond. A peptide bond is a covalent bond formed when the carbon atom from the carboxyl group of one amino acid shares electrons with the nitrogen atom from the amino group of a second amino acid.
methyltransferase activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a methyl group to an acceptor molecule.
S-methyltransferase activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a methyl group to the sulfur atom of an acceptor molecule.
exopeptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of a peptide bond not more than three residues from the N- or C-terminus of a polypeptide chain, in a reaction that requires a free N-terminal amino group, C-terminal carboxyl group or both.
acyltransferase activity
Catalysis of the generalized reaction: acyl-carrier + reactant = acyl-reactant + carrier.
S-adenosylmethionine-dependent methyltransferase activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a methyl group from S-adenosyl-L-methionine to a substrate.
homocysteine S-methyltransferase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: S-adenosyl-L-methionine + L-homocysteine = S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + L-methionine.
peptidase activity, acting on L-amino acid peptides
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of peptide bonds formed between L-amino acids.
N-acyltransferase activity
Catalysis of the transfer of an acyl group to a nitrogen atom on the acceptor molecule.
transferase activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a group, e.g. a methyl group, glycosyl group, acyl group, phosphorus-containing, or other groups, from one compound (generally regarded as the donor) to another compound (generally regarded as the acceptor). Transferase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 2.
transferase activity, transferring one-carbon groups
Catalysis of the transfer of a one-carbon group from one compound (donor) to another (acceptor).
transferase activity, transferring acyl groups
Catalysis of the transfer of an acyl group from one compound (donor) to another (acceptor).
transferase activity, transferring acyl groups other than amino-acyl groups
Catalysis of the transfer of an acyl group, other than amino-acyl, from one compound (donor) to another (acceptor).
hydrolase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of various bonds, e.g. C-O, C-N, C-C, phosphoric anhydride bonds, etc. Hydrolase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 3.
betaine-homocysteine S-methyltransferase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: homocysteine + betaine = L-methionine + dimethylglycine.
glycine N-acyltransferase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: acyl-CoA + glycine = CoA + N-acylglycine.
all
NA
homocysteine S-methyltransferase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: S-adenosyl-L-methionine + L-homocysteine = S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + L-methionine.
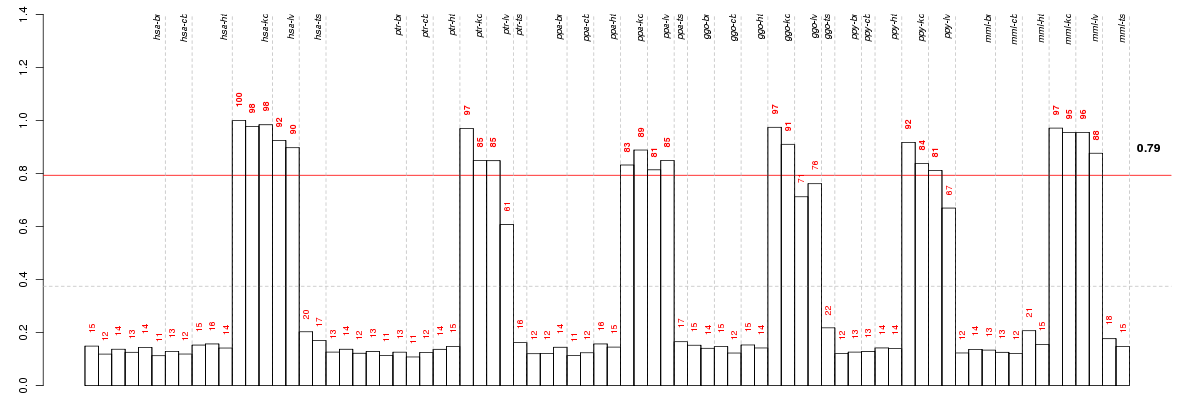
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00010 | 4.214e-04 | 0.3066 | 5 | 42 | Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis |
| 04950 | 4.278e-03 | 0.1095 | 3 | 15 | Maturity onset diabetes of the young |
| 04614 | 5.062e-03 | 0.1168 | 3 | 16 | Renin-angiotensin system |
| 01100 | 1.322e-02 | 5.876 | 14 | 805 | Metabolic pathways |
| 00260 | 1.401e-02 | 0.1752 | 3 | 24 | Glycine, serine and threonine metabolism |
ACMSDaminocarboxymuconate semialdehyde decarboxylase (ENSG00000153086), score: 0.92 ACSF2acyl-CoA synthetase family member 2 (ENSG00000167107), score: 0.91 ACY1aminoacylase 1 (ENSG00000243989), score: 0.92 AGMATagmatine ureohydrolase (agmatinase) (ENSG00000116771), score: 0.94 AGXT2alanine--glyoxylate aminotransferase 2 (ENSG00000113492), score: 0.98 AKR1A1aldo-keto reductase family 1, member A1 (aldehyde reductase) (ENSG00000117448), score: 0.91 ALDOBaldolase B, fructose-bisphosphate (ENSG00000136872), score: 0.95 ANKS4Bankyrin repeat and sterile alpha motif domain containing 4B (ENSG00000175311), score: 0.94 ANPEPalanyl (membrane) aminopeptidase (ENSG00000166825), score: 0.95 BHMTbetaine--homocysteine S-methyltransferase (ENSG00000145692), score: 0.92 BHMT2betaine--homocysteine S-methyltransferase 2 (ENSG00000132840), score: 0.91 C11orf54chromosome 11 open reading frame 54 (ENSG00000182919), score: 0.94 CDH1cadherin 1, type 1, E-cadherin (epithelial) (ENSG00000039068), score: 0.92 CDHR5cadherin-related family member 5 (ENSG00000099834), score: 1 CLCN5chloride channel 5 (ENSG00000171365), score: 0.92 CRB3crumbs homolog 3 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000130545), score: 0.92 DDCdopa decarboxylase (aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase) (ENSG00000132437), score: 0.98 DEFB1defensin, beta 1 (ENSG00000164825), score: 0.91 DHDPSLdihydrodipicolinate synthase-like, mitochondrial (ENSG00000241935), score: 0.91 DIO1deiodinase, iodothyronine, type I (ENSG00000211452), score: 0.96 DMGDHdimethylglycine dehydrogenase (ENSG00000132837), score: 0.91 DPP4dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 (ENSG00000197635), score: 0.94 DPYSdihydropyrimidinase (ENSG00000147647), score: 0.91 ENPEPglutamyl aminopeptidase (aminopeptidase A) (ENSG00000138792), score: 0.92 FBP1fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1 (ENSG00000165140), score: 0.92 FGFR4fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (ENSG00000160867), score: 0.9 FMO4flavin containing monooxygenase 4 (ENSG00000076258), score: 0.94 GALMgalactose mutarotase (aldose 1-epimerase) (ENSG00000143891), score: 0.93 GLYATglycine-N-acyltransferase (ENSG00000149124), score: 0.91 GLYATL1glycine-N-acyltransferase-like 1 (ENSG00000166840), score: 0.98 HAO2hydroxyacid oxidase 2 (long chain) (ENSG00000116882), score: 0.95 HNF1AHNF1 homeobox A (ENSG00000135100), score: 0.93 HNF4Ahepatocyte nuclear factor 4, alpha (ENSG00000101076), score: 0.94 IYDiodotyrosine deiodinase (ENSG00000009765), score: 0.97 KCNK5potassium channel, subfamily K, member 5 (ENSG00000164626), score: 0.97 KIF12kinesin family member 12 (ENSG00000136883), score: 0.93 KLHDC7Akelch domain containing 7A (ENSG00000179023), score: 0.99 KNG1kininogen 1 (ENSG00000113889), score: 0.9 LAD1ladinin 1 (ENSG00000159166), score: 0.93 MMEmembrane metallo-endopeptidase (ENSG00000196549), score: 0.98 PEPDpeptidase D (ENSG00000124299), score: 0.92 PIGRpolymeric immunoglobulin receptor (ENSG00000162896), score: 0.96 PKHD1polycystic kidney and hepatic disease 1 (autosomal recessive) (ENSG00000170927), score: 0.92 PKLRpyruvate kinase, liver and RBC (ENSG00000143627), score: 0.9 PLCG2phospholipase C, gamma 2 (phosphatidylinositol-specific) (ENSG00000197943), score: 0.91 RAB17RAB17, member RAS oncogene family (ENSG00000124839), score: 0.93 RBP5retinol binding protein 5, cellular (ENSG00000139194), score: 0.92 SDC1syndecan 1 (ENSG00000115884), score: 0.91 SLC17A1solute carrier family 17 (sodium phosphate), member 1 (ENSG00000124568), score: 1 SLC17A3solute carrier family 17 (sodium phosphate), member 3 (ENSG00000124564), score: 0.96 SLC23A1solute carrier family 23 (nucleobase transporters), member 1 (ENSG00000170482), score: 0.97 SLC27A2solute carrier family 27 (fatty acid transporter), member 2 (ENSG00000140284), score: 0.93 SLC37A4solute carrier family 37 (glucose-6-phosphate transporter), member 4 (ENSG00000137700), score: 0.92 SLC5A9solute carrier family 5 (sodium/glucose cotransporter), member 9 (ENSG00000117834), score: 0.91 SLC7A9solute carrier family 7 (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system), member 9 (ENSG00000021488), score: 0.95 SLCO4C1solute carrier organic anion transporter family, member 4C1 (ENSG00000173930), score: 0.95 TMEM27transmembrane protein 27 (ENSG00000147003), score: 0.94 TMEM37transmembrane protein 37 (ENSG00000171227), score: 0.92 TMEM45Btransmembrane protein 45B (ENSG00000151715), score: 0.91 TMEM82transmembrane protein 82 (ENSG00000162460), score: 0.94 TMPRSS2transmembrane protease, serine 2 (ENSG00000184012), score: 0.96 TRPV4transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily V, member 4 (ENSG00000111199), score: 0.92 TTC22tetratricopeptide repeat domain 22 (ENSG00000006555), score: 0.9 VIL1villin 1 (ENSG00000127831), score: 0.94
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ppy_lv_m_ca1 | ppy | lv | m | _ |
| ppa_lv_m_ca1 | ppa | lv | m | _ |
| ppa_kd_m_ca1 | ppa | kd | m | _ |
| ppy_kd_f_ca1 | ppy | kd | f | _ |
| ptr_lv_m_ca1 | ptr | lv | m | _ |
| ppa_lv_f_ca1 | ppa | lv | f | _ |
| ptr_kd_f_ca1 | ptr | kd | f | _ |
| mml_lv_f_ca1 | mml | lv | f | _ |
| ppa_kd_f_ca1 | ppa | kd | f | _ |
| hsa_lv_m2_ca1 | hsa | lv | m | 2 |
| ggo_kd_f_ca1 | ggo | kd | f | _ |
| ppy_kd_m_ca1 | ppy | kd | m | _ |
| hsa_lv_m1_ca1 | hsa | lv | m | 1 |
| mml_kd_f_ca1 | mml | kd | f | _ |
| mml_lv_m_ca1 | mml | lv | m | _ |
| ptr_kd_m_ca1 | ptr | kd | m | _ |
| mml_kd_m_ca1 | mml | kd | m | _ |
| ggo_kd_m_ca1 | ggo | kd | m | _ |
| hsa_kd_m2_ca1 | hsa | kd | m | 2 |
| hsa_kd_f_ca1 | hsa | kd | f | _ |
| hsa_kd_m1_ca1 | hsa | kd | m | 1 |