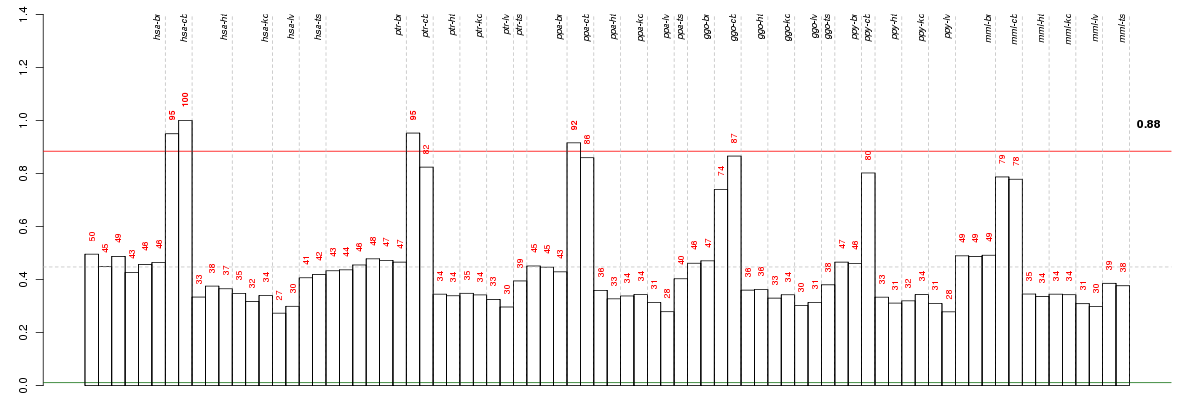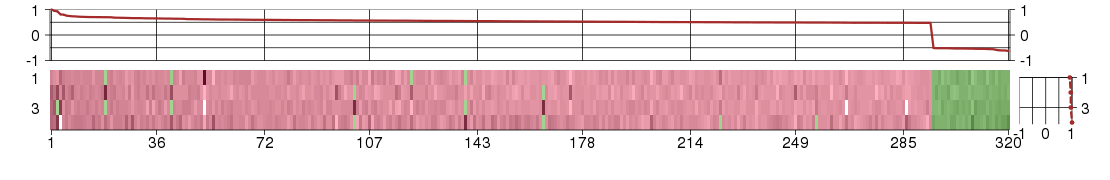

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

chromosome organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level that results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of chromosomes, structures composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins that carries hereditary information.
metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
chromatin organization
Any process that results in the specification, formation or maintenance of the physical structure of eukaryotic chromatin.
transcription
The cellular synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
transcription, DNA-dependent
The cellular synthesis of RNA on a template of DNA.
regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-dependent transcription.
regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter.
transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter
The synthesis of RNA from a DNA template by RNA polymerase II (Pol II), originating at a Pol II-specific promoter. Includes transcription of messenger RNA (mRNA) and certain small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs).
nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds; includes nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, assimilatory/dissimilatory nitrate reduction and the interconversion of nitrogenous organic matter and ammonium.
organelle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an organelle within a cell. An organelle is an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of nervous tissue over time, from its formation to its mature state.
central nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the central nervous system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The central nervous system is the core nervous system that serves an integrating and coordinating function. In vertebrates it consists of the brain, spinal cord and spinal nerves. In those invertebrates with a central nervous system it typically consists of a brain, cerebral ganglia and a nerve cord.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
positive regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
positive regulation of metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
gene expression
The process by which a gene's sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
regulation of gene expression
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
positive regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
positive regulation of gene expression
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
cellular component organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a cellular component.
RNA metabolic process
The cellular chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage.
positive regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
chromatin modification
The alteration of DNA or protein in chromatin, which may result in changing the chromatin structure.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
positive regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
RNA biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage. Includes polymerization of ribonucleotide monomers.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of gene expression, epigenetic
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression; the process is mitotically or meiotically heritable, or is stably self-propagated in the cytoplasm of a resting cell, and does not entail a change in DNA sequence.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
positive regulation of transcription
Any cellular process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nitrogen or nitrogenous compounds.
positive regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nitrogen or nitrogenous compounds.
regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of primary metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism involving those compounds formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleic acids.
all
NA
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
organelle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an organelle within a cell. An organelle is an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
positive regulation of metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
positive regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
positive regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nitrogen or nitrogenous compounds.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
positive regulation of metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nitrogen or nitrogenous compounds.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
regulation of primary metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism involving those compounds formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
positive regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nitrogen or nitrogenous compounds.
positive regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
positive regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
positive regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
positive regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
positive regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
positive regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of gene expression
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
positive regulation of gene expression
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
positive regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
positive regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
positive regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
positive regulation of transcription
Any cellular process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription.
transcription
The cellular synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
positive regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
positive regulation of transcription
Any cellular process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription.
positive regulation of transcription
Any cellular process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription.
positive regulation of gene expression
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
transcription, DNA-dependent
The cellular synthesis of RNA on a template of DNA.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
positive regulation of transcription
Any cellular process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription.
RNA biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage. Includes polymerization of ribonucleotide monomers.
regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
transcription
The cellular synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
RNA metabolic process
The cellular chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage.
central nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the central nervous system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The central nervous system is the core nervous system that serves an integrating and coordinating function. In vertebrates it consists of the brain, spinal cord and spinal nerves. In those invertebrates with a central nervous system it typically consists of a brain, cerebral ganglia and a nerve cord.
regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-dependent transcription.
positive regulation of transcription
Any cellular process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription.
regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-dependent transcription.
regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter.

intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
nucleus
A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent.
nucleoplasm
That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus.
nuclear body
Extra-nucleolar nuclear domains usually visualized by confocal microscopy and fluorescent antibodies to specific proteins.
membrane-enclosed lumen
The enclosed volume within a sealed membrane or between two sealed membranes. Encompasses the volume enclosed by the membranes of a particular organelle, e.g. endoplasmic reticulum lumen, or the space between the two lipid bilayers of a double membrane surrounding an organelle, e.g. nuclear envelope lumen.
nuclear lumen
The volume enclosed by the nuclear inner membrane.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, and prokaryotic structures such as anammoxosomes and pirellulosomes. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
organelle lumen
The internal volume enclosed by the membranes of a particular organelle; includes the volume enclosed by a single organelle membrane, e.g. endoplasmic reticulum lumen, or the volume enclosed by the innermost of the two lipid bilayers of an organelle envelope, e.g. nuclear lumen.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
nuclear part
Any constituent part of the nucleus, a membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
nucleoplasm part
Any constituent part of the nucleoplasm, that part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
intracellular organelle lumen
An organelle lumen that is part of an intracellular organelle.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
organelle lumen
The internal volume enclosed by the membranes of a particular organelle; includes the volume enclosed by a single organelle membrane, e.g. endoplasmic reticulum lumen, or the volume enclosed by the innermost of the two lipid bilayers of an organelle envelope, e.g. nuclear lumen.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle lumen
An organelle lumen that is part of an intracellular organelle.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
nuclear lumen
The volume enclosed by the nuclear inner membrane.
nucleoplasm
That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus.
nuclear part
Any constituent part of the nucleus, a membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated.
nucleoplasm part
Any constituent part of the nucleoplasm, that part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus.

protein binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any protein or protein complex (a complex of two or more proteins that may include other nonprotein molecules).
molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
nucleic acid binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any nucleic acid.
DNA binding
Any molecular function by which a gene product interacts selectively with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid).
chromatin binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with chromatin, the network of fibers of DNA and protein that make up the chromosomes of the eukaryotic nucleus during interphase.
sequence-specific DNA binding transcription factor activity
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a specific DNA sequence in order to modulate transcription. The transcription factor may or may not also interact selectively with a protein or macromolecular complex.
transcription cofactor activity
The function that links a sequence-specific transcription factor to the core RNA polymerase II complex but does not bind DNA itself.
transcription coactivator activity
The function of a transcription cofactor that activates transcription from a RNA polymerase II promoter; does not bind DNA itself.
receptor binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with one or more specific sites on a receptor molecule, a macromolecule that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function.
binding
The selective, non-covalent, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
transcription factor binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a transcription factor, any protein required to initiate or regulate transcription.
transcription activator activity
Any transcription regulator activity required for initiation or upregulation of transcription.
transcription regulator activity
Plays a role in regulating transcription; may bind a promoter or enhancer DNA sequence or interact with a DNA-binding transcription factor.
chromatin DNA binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with DNA that is assembled into chromatin.
nuclear hormone receptor binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a nuclear hormone receptor, a ligand-dependent receptor found in the nucleus of the cell.
steroid hormone receptor binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a steroid hormone receptor.
glucocorticoid receptor binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a glucocorticoid receptor.
sequence-specific DNA binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with DNA of a specific nucleotide composition, e.g. GC-rich DNA binding, or with a specific sequence motif or type of DNA e.g. promotor binding or rDNA binding.
structure-specific DNA binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with DNA of a specific structure or configuration e.g. triplex DNA binding or bent DNA binding.
SMAD binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a SMAD signaling protein.
hormone receptor binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a receptor for hormones.
all
NA
transcription coactivator activity
The function of a transcription cofactor that activates transcription from a RNA polymerase II promoter; does not bind DNA itself.
transcription cofactor activity
The function that links a sequence-specific transcription factor to the core RNA polymerase II complex but does not bind DNA itself.
chromatin DNA binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with DNA that is assembled into chromatin.
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-129/129-5p | 4.941e-05 | 8.227 | 29 | 275 |
| miR-495/1192 | 4.140e-02 | 12.98 | 29 | 434 |
ACVR2Bactivin A receptor, type IIB (ENSG00000114739), score: 0.56 ADARB1adenosine deaminase, RNA-specific, B1 (ENSG00000197381), score: 0.49 AFAP1L2actin filament associated protein 1-like 2 (ENSG00000169129), score: 0.53 AFF2AF4/FMR2 family, member 2 (ENSG00000155966), score: 0.51 ANKLE1ankyrin repeat and LEM domain containing 1 (ENSG00000160117), score: 0.7 ANKS6ankyrin repeat and sterile alpha motif domain containing 6 (ENSG00000165138), score: 0.54 ARID1BAT rich interactive domain 1B (SWI1-like) (ENSG00000049618), score: 0.54 ARSJarylsulfatase family, member J (ENSG00000180801), score: 0.51 ARVCFarmadillo repeat gene deleted in velocardiofacial syndrome (ENSG00000099889), score: 0.52 ATF7activating transcription factor 7 (ENSG00000170653), score: 0.55 ATP2A3ATPase, Ca++ transporting, ubiquitous (ENSG00000074370), score: 0.54 AXIN1axin 1 (ENSG00000103126), score: 0.51 B3GALTLbeta 1,3-galactosyltransferase-like (ENSG00000187676), score: -0.61 B3GNT2UDP-GlcNAc:betaGal beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 2 (ENSG00000170340), score: -0.59 BACH2BTB and CNC homology 1, basic leucine zipper transcription factor 2 (ENSG00000112182), score: 0.61 BAHCC1BAH domain and coiled-coil containing 1 (ENSG00000171282), score: 0.58 BARHL1BarH-like homeobox 1 (ENSG00000125492), score: 0.65 BARHL2BarH-like homeobox 2 (ENSG00000143032), score: 0.72 BCL6B-cell CLL/lymphoma 6 (ENSG00000113916), score: 0.49 BCL9LB-cell CLL/lymphoma 9-like (ENSG00000186174), score: 0.49 BCORL1BCL6 corepressor-like 1 (ENSG00000085185), score: 0.5 BEST4bestrophin 4 (ENSG00000142959), score: 0.49 BICD1bicaudal D homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000151746), score: 0.55 BTN2A1butyrophilin, subfamily 2, member A1 (ENSG00000112763), score: 0.61 C12orf51chromosome 12 open reading frame 51 (ENSG00000173064), score: 0.49 C15orf27chromosome 15 open reading frame 27 (ENSG00000169758), score: 0.56 C16orf11chromosome 16 open reading frame 11 (ENSG00000161992), score: 0.62 C1orf127chromosome 1 open reading frame 127 (ENSG00000175262), score: 0.57 C20orf117chromosome 20 open reading frame 117 (ENSG00000149639), score: 0.59 C2orf44chromosome 2 open reading frame 44 (ENSG00000163026), score: 0.48 C6orf15chromosome 6 open reading frame 15 (ENSG00000204542), score: 0.49 C7orf16chromosome 7 open reading frame 16 (ENSG00000106341), score: 0.65 C8orf79chromosome 8 open reading frame 79 (ENSG00000170941), score: 0.5 CA8carbonic anhydrase VIII (ENSG00000178538), score: 0.58 CACNA1Acalcium channel, voltage-dependent, P/Q type, alpha 1A subunit (ENSG00000141837), score: 0.49 CADM1cell adhesion molecule 1 (ENSG00000182985), score: 0.49 CBLN1cerebellin 1 precursor (ENSG00000102924), score: 0.59 CBLN3cerebellin 3 precursor (ENSG00000139899), score: 0.6 CCDC109Acoiled-coil domain containing 109A (ENSG00000156026), score: 0.56 CCDC120coiled-coil domain containing 120 (ENSG00000147144), score: 0.51 CCDC14coiled-coil domain containing 14 (ENSG00000175455), score: -0.52 CCDC78coiled-coil domain containing 78 (ENSG00000162004), score: 0.48 CCNJLcyclin J-like (ENSG00000135083), score: 0.54 CDC25Bcell division cycle 25 homolog B (S. pombe) (ENSG00000101224), score: 0.48 CDC42BPGCDC42 binding protein kinase gamma (DMPK-like) (ENSG00000171219), score: 0.49 CDH15cadherin 15, type 1, M-cadherin (myotubule) (ENSG00000129910), score: 0.71 CDH7cadherin 7, type 2 (ENSG00000081138), score: 0.55 CDKN1Bcyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B (p27, Kip1) (ENSG00000111276), score: 0.53 CDONCdon homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000064309), score: 0.57 CDR2Lcerebellar degeneration-related protein 2-like (ENSG00000109089), score: 0.49 CDS2CDP-diacylglycerol synthase (phosphatidate cytidylyltransferase) 2 (ENSG00000101290), score: 0.49 CECR2cat eye syndrome chromosome region, candidate 2 (ENSG00000099954), score: 0.52 CELF1CUGBP, Elav-like family member 1 (ENSG00000149187), score: 0.59 CERKLceramide kinase-like (ENSG00000188452), score: 0.62 CHD7chromodomain helicase DNA binding protein 7 (ENSG00000171316), score: 0.6 CHN2chimerin (chimaerin) 2 (ENSG00000106069), score: 0.53 CHRNA3cholinergic receptor, nicotinic, alpha 3 (ENSG00000080644), score: 0.75 CHTF18CTF18, chromosome transmission fidelity factor 18 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000127586), score: 0.48 CLVS2clavesin 2 (ENSG00000146352), score: 0.5 CNOT2CCR4-NOT transcription complex, subunit 2 (ENSG00000111596), score: 0.53 CNOT6CCR4-NOT transcription complex, subunit 6 (ENSG00000113300), score: 0.54 CNPY1canopy 1 homolog (zebrafish) (ENSG00000146910), score: 0.5 COL13A1collagen, type XIII, alpha 1 (ENSG00000197467), score: 0.64 COL19A1collagen, type XIX, alpha 1 (ENSG00000082293), score: 0.49 COL5A2collagen, type V, alpha 2 (ENSG00000204262), score: -0.53 COL8A2collagen, type VIII, alpha 2 (ENSG00000171812), score: 0.48 CPLX4complexin 4 (ENSG00000166569), score: 0.8 CPSF6cleavage and polyadenylation specific factor 6, 68kDa (ENSG00000111605), score: 0.55 CRAMP1LCrm, cramped-like (Drosophila) (ENSG00000007545), score: 0.5 CREBBPCREB binding protein (ENSG00000005339), score: 0.54 CRKLv-crk sarcoma virus CT10 oncogene homolog (avian)-like (ENSG00000099942), score: 0.48 CRTAMcytotoxic and regulatory T cell molecule (ENSG00000109943), score: 0.73 CTCFCCCTC-binding factor (zinc finger protein) (ENSG00000102974), score: 0.58 CTNNB1catenin (cadherin-associated protein), beta 1, 88kDa (ENSG00000168036), score: 0.62 DAB2IPDAB2 interacting protein (ENSG00000136848), score: 0.52 DACT1dapper, antagonist of beta-catenin, homolog 1 (Xenopus laevis) (ENSG00000165617), score: 0.57 DCLRE1BDNA cross-link repair 1B (ENSG00000118655), score: 0.52 DCP1ADCP1 decapping enzyme homolog A (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000162290), score: 0.55 DGCR8DiGeorge syndrome critical region gene 8 (ENSG00000128191), score: 0.61 DHRS13dehydrogenase/reductase (SDR family) member 13 (ENSG00000167536), score: 0.56 DNMT1DNA (cytosine-5-)-methyltransferase 1 (ENSG00000130816), score: 0.5 DNMT3ADNA (cytosine-5-)-methyltransferase 3 alpha (ENSG00000119772), score: 0.52 DPF3D4, zinc and double PHD fingers, family 3 (ENSG00000205683), score: 0.5 DUOX1dual oxidase 1 (ENSG00000137857), score: 0.59 EBF1early B-cell factor 1 (ENSG00000164330), score: 0.48 ECE1endothelin converting enzyme 1 (ENSG00000117298), score: -0.54 EFTUD2elongation factor Tu GTP binding domain containing 2 (ENSG00000108883), score: -0.54 EN2engrailed homeobox 2 (ENSG00000164778), score: 0.68 EOMESeomesodermin (ENSG00000163508), score: 0.62 EP300E1A binding protein p300 (ENSG00000100393), score: 0.48 EPB41erythrocyte membrane protein band 4.1 (elliptocytosis 1, RH-linked) (ENSG00000159023), score: 0.51 EPC1enhancer of polycomb homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000120616), score: 0.52 EPC2enhancer of polycomb homolog 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000135999), score: 0.52 EPHB1EPH receptor B1 (ENSG00000154928), score: 0.51 ESYT3extended synaptotagmin-like protein 3 (ENSG00000158220), score: 0.52 ETV6ets variant 6 (ENSG00000139083), score: -0.56 EXPH5exophilin 5 (ENSG00000110723), score: 0.64 FAM131Cfamily with sequence similarity 131, member C (ENSG00000185519), score: 0.49 FAT2FAT tumor suppressor homolog 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000086570), score: 0.7 FBXO31F-box protein 31 (ENSG00000103264), score: 0.55 FBXO5F-box protein 5 (ENSG00000112029), score: 0.51 FGF17fibroblast growth factor 17 (ENSG00000158815), score: 0.59 FGF3fibroblast growth factor 3 (ENSG00000186895), score: 0.93 FGF5fibroblast growth factor 5 (ENSG00000138675), score: 0.6 FHDC1FH2 domain containing 1 (ENSG00000137460), score: 0.59 FKBP4FK506 binding protein 4, 59kDa (ENSG00000004478), score: 0.49 FLCNfolliculin (ENSG00000154803), score: 0.57 FSTL5follistatin-like 5 (ENSG00000168843), score: 0.59 FUT9fucosyltransferase 9 (alpha (1,3) fucosyltransferase) (ENSG00000172461), score: 0.57 FZD7frizzled homolog 7 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000155760), score: 0.55 GALNT7UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 7 (GalNAc-T7) (ENSG00000109586), score: 0.5 GDNFglial cell derived neurotrophic factor (ENSG00000168621), score: 0.56 GFOD2glucose-fructose oxidoreductase domain containing 2 (ENSG00000141098), score: 0.5 GIGYF1GRB10 interacting GYF protein 1 (ENSG00000146830), score: 0.55 GLCEglucuronic acid epimerase (ENSG00000138604), score: 0.54 GNB3guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), beta polypeptide 3 (ENSG00000111664), score: 0.48 GNG13guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), gamma 13 (ENSG00000127588), score: 0.59 GPR101G protein-coupled receptor 101 (ENSG00000165370), score: 0.55 GPRIN3GPRIN family member 3 (ENSG00000185477), score: 0.67 GRID2glutamate receptor, ionotropic, delta 2 (ENSG00000152208), score: 0.6 GRID2IPglutamate receptor, ionotropic, delta 2 (Grid2) interacting protein (ENSG00000215045), score: 0.69 GRIN2Cglutamate receptor, ionotropic, N-methyl D-aspartate 2C (ENSG00000161509), score: 0.56 GRM1glutamate receptor, metabotropic 1 (ENSG00000152822), score: 0.52 GRM4glutamate receptor, metabotropic 4 (ENSG00000124493), score: 0.64 GTF2H5general transcription factor IIH, polypeptide 5 (ENSG00000185068), score: -0.54 HES7hairy and enhancer of split 7 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000179111), score: 0.61 HINFPhistone H4 transcription factor (ENSG00000172273), score: 0.64 HIPK1homeodomain interacting protein kinase 1 (ENSG00000163349), score: 0.55 HNRNPRheterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein R (ENSG00000125944), score: 0.48 HPCAL1hippocalcin-like 1 (ENSG00000115756), score: 0.5 HTR5A5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 5A (ENSG00000157219), score: 0.48 IFFO2intermediate filament family orphan 2 (ENSG00000169991), score: 0.64 IGFBP2insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2, 36kDa (ENSG00000115457), score: -0.54 IL16interleukin 16 (lymphocyte chemoattractant factor) (ENSG00000172349), score: 0.6 INCENPinner centromere protein antigens 135/155kDa (ENSG00000149503), score: 0.54 IP6K2inositol hexakisphosphate kinase 2 (ENSG00000068745), score: 0.57 JMJD1Cjumonji domain containing 1C (ENSG00000171988), score: 0.51 KCNK9potassium channel, subfamily K, member 9 (ENSG00000169427), score: 0.55 KCNRGpotassium channel regulator (ENSG00000198553), score: 0.52 KCTD2potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 2 (ENSG00000180901), score: 0.49 KCTD8potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 8 (ENSG00000183783), score: 0.49 KDM4Clysine (K)-specific demethylase 4C (ENSG00000107077), score: 0.61 KIAA0182KIAA0182 (ENSG00000131149), score: 0.55 KIAA0247KIAA0247 (ENSG00000100647), score: 0.49 KIAA0802KIAA0802 (ENSG00000168502), score: 0.59 KIAA1024KIAA1024 (ENSG00000169330), score: 0.56 KIAA1244KIAA1244 (ENSG00000112379), score: 0.48 KLHL3kelch-like 3 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000146021), score: 0.51 KRT39keratin 39 (ENSG00000196859), score: 0.53 KRT40keratin 40 (ENSG00000204889), score: 0.57 LATS1LATS, large tumor suppressor, homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000131023), score: 0.48 LBX1ladybird homeobox 1 (ENSG00000138136), score: 0.65 LDB2LIM domain binding 2 (ENSG00000169744), score: -0.54 LDLRAD3low density lipoprotein receptor class A domain containing 3 (ENSG00000179241), score: 0.49 LDLRAP1low density lipoprotein receptor adaptor protein 1 (ENSG00000157978), score: 0.51 LHX5LIM homeobox 5 (ENSG00000089116), score: 0.54 LOC100131509similar to inward rectifying K+ channel negative regulator Kir2.2v (ENSG00000184185), score: 0.51 LOC100294337hypothetical protein LOC100294337 (ENSG00000120071), score: 0.51 LOC146429putative solute carrier family 22 member ENSG00000182157 (ENSG00000182157), score: 0.73 LONRF3LON peptidase N-terminal domain and ring finger 3 (ENSG00000175556), score: 0.5 LRCH1leucine-rich repeats and calponin homology (CH) domain containing 1 (ENSG00000136141), score: 0.51 LRRC26leucine rich repeat containing 26 (ENSG00000184709), score: 0.48 MAB21L1mab-21-like 1 (C. elegans) (ENSG00000180660), score: 0.7 MAML1mastermind-like 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000161021), score: 0.58 MAML3mastermind-like 3 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000196782), score: 0.62 MAPKBP1mitogen-activated protein kinase binding protein 1 (ENSG00000137802), score: 0.48 MAXMYC associated factor X (ENSG00000125952), score: 0.67 MDGA1MAM domain containing glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor 1 (ENSG00000112139), score: 0.65 MEIS1Meis homeobox 1 (ENSG00000143995), score: 0.52 MID1midline 1 (Opitz/BBB syndrome) (ENSG00000101871), score: 0.56 MLLmyeloid/lymphoid or mixed-lineage leukemia (trithorax homolog, Drosophila) (ENSG00000118058), score: 0.56 MLL2myeloid/lymphoid or mixed-lineage leukemia 2 (ENSG00000167548), score: 0.48 MMP24matrix metallopeptidase 24 (membrane-inserted) (ENSG00000125966), score: 0.48 MPP3membrane protein, palmitoylated 3 (MAGUK p55 subfamily member 3) (ENSG00000161647), score: 0.53 MR1major histocompatibility complex, class I-related (ENSG00000153029), score: -0.53 MRPL33mitochondrial ribosomal protein L33 (ENSG00000158019), score: -0.63 MXD4MAX dimerization protein 4 (ENSG00000123933), score: 0.55 MYT1myelin transcription factor 1 (ENSG00000196132), score: 0.61 NAB2NGFI-A binding protein 2 (EGR1 binding protein 2) (ENSG00000166886), score: 0.56 NCOA5nuclear receptor coactivator 5 (ENSG00000124160), score: 0.49 NFKBIDnuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, delta (ENSG00000167604), score: 0.56 NHLH2nescient helix loop helix 2 (ENSG00000177551), score: 0.71 NKAIN1Na+/K+ transporting ATPase interacting 1 (ENSG00000084628), score: 0.58 NKX6-3NK6 homeobox 3 (ENSG00000165066), score: 0.7 NOTOnotochord homeobox (ENSG00000214513), score: 0.61 NPFFneuropeptide FF-amide peptide precursor (ENSG00000139574), score: 0.53 NPFFR1neuropeptide FF receptor 1 (ENSG00000148734), score: 0.64 NPR2natriuretic peptide receptor B/guanylate cyclase B (atrionatriuretic peptide receptor B) (ENSG00000159899), score: 0.49 NR2C2nuclear receptor subfamily 2, group C, member 2 (ENSG00000177463), score: 0.5 NRG2neuregulin 2 (ENSG00000158458), score: 0.52 NRIP2nuclear receptor interacting protein 2 (ENSG00000053702), score: 0.62 NYNRINNYN domain and retroviral integrase containing (ENSG00000205978), score: 0.61 ODZ1odz, odd Oz/ten-m homolog 1(Drosophila) (ENSG00000009694), score: 0.65 OSBPL2oxysterol binding protein-like 2 (ENSG00000130703), score: 0.54 OTX2orthodenticle homeobox 2 (ENSG00000165588), score: 0.76 PAG1phosphoprotein associated with glycosphingolipid microdomains 1 (ENSG00000076641), score: 0.53 PAPD7PAP associated domain containing 7 (ENSG00000112941), score: 0.54 PAPLiron/zinc purple acid phosphatase-like protein (ENSG00000183760), score: 0.5 PAX6paired box 6 (ENSG00000007372), score: 0.56 PAXIP1PAX interacting (with transcription-activation domain) protein 1 (ENSG00000157212), score: 0.59 PDE8Aphosphodiesterase 8A (ENSG00000073417), score: -0.61 PELI2pellino homolog 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000139946), score: 0.52 PHF11PHD finger protein 11 (ENSG00000136147), score: -0.52 PHF2PHD finger protein 2 (ENSG00000197724), score: 0.6 PHIPpleckstrin homology domain interacting protein (ENSG00000146247), score: 0.52 PISDphosphatidylserine decarboxylase (ENSG00000183530), score: 0.56 PISDphosphatidylserine decarboxylase (ENSG00000241878), score: 0.51 PKIBprotein kinase (cAMP-dependent, catalytic) inhibitor beta (ENSG00000135549), score: 0.7 PLCB4phospholipase C, beta 4 (ENSG00000101333), score: 0.48 PLK2polo-like kinase 2 (ENSG00000145632), score: -0.54 PLXNA3plexin A3 (ENSG00000130827), score: 0.49 POGZpogo transposable element with ZNF domain (ENSG00000143442), score: 0.48 POLBpolymerase (DNA directed), beta (ENSG00000070501), score: 0.53 PPM1Bprotein phosphatase, Mg2+/Mn2+ dependent, 1B (ENSG00000138032), score: 0.53 PPYR1pancreatic polypeptide receptor 1 (ENSG00000204174), score: 0.53 PQLC3PQ loop repeat containing 3 (ENSG00000162976), score: -0.55 PRDM10PR domain containing 10 (ENSG00000170325), score: 0.71 PRPF6PRP6 pre-mRNA processing factor 6 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000101161), score: 0.53 PRR12proline rich 12 (ENSG00000126464), score: 0.5 PTCH1patched 1 (ENSG00000185920), score: 0.53 PTCHD1patched domain containing 1 (ENSG00000165186), score: 0.61 PTPN4protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 4 (megakaryocyte) (ENSG00000088179), score: 0.56 PURApurine-rich element binding protein A (ENSG00000185129), score: 0.48 PWWP2APWWP domain containing 2A (ENSG00000170234), score: 0.57 PYDC1PYD (pyrin domain) containing 1 (ENSG00000169900), score: 0.67 PYGO1pygopus homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000171016), score: 0.52 QSOX2quiescin Q6 sulfhydryl oxidase 2 (ENSG00000165661), score: 0.58 RAB37RAB37, member RAS oncogene family (ENSG00000172794), score: 0.52 RAB39RAB39, member RAS oncogene family (ENSG00000179331), score: 0.66 RBM9RNA binding motif protein 9 (ENSG00000100320), score: 0.48 RBMS1RNA binding motif, single stranded interacting protein 1 (ENSG00000153250), score: -0.51 RCAN3RCAN family member 3 (ENSG00000117602), score: 0.66 REV3LREV3-like, catalytic subunit of DNA polymerase zeta (yeast) (ENSG00000009413), score: 0.57 RGS8regulator of G-protein signaling 8 (ENSG00000135824), score: 0.48 RMND5Arequired for meiotic nuclear division 5 homolog A (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000153561), score: 0.58 S100A10S100 calcium binding protein A10 (ENSG00000197747), score: -0.52 SART3squamous cell carcinoma antigen recognized by T cells 3 (ENSG00000075856), score: 0.58 SBK1SH3-binding domain kinase 1 (ENSG00000188322), score: 0.52 SCGNsecretagogin, EF-hand calcium binding protein (ENSG00000079689), score: 0.55 SEL1L3sel-1 suppressor of lin-12-like 3 (C. elegans) (ENSG00000091490), score: 0.5 SETD5SET domain containing 5 (ENSG00000168137), score: 0.6 SF3B3splicing factor 3b, subunit 3, 130kDa (ENSG00000189091), score: 0.57 SGK223homolog of rat pragma of Rnd2 (ENSG00000182319), score: 0.55 SH3PXD2BSH3 and PX domains 2B (ENSG00000174705), score: 0.48 SHBSrc homology 2 domain containing adaptor protein B (ENSG00000107338), score: -0.56 SKIv-ski sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (avian) (ENSG00000157933), score: 0.57 SKOR1SKI family transcriptional corepressor 1 (ENSG00000188779), score: 0.51 SLC1A6solute carrier family 1 (high affinity aspartate/glutamate transporter), member 6 (ENSG00000105143), score: 0.54 SLC26A5solute carrier family 26, member 5 (prestin) (ENSG00000170615), score: 0.49 SLC35F4solute carrier family 35, member F4 (ENSG00000151812), score: 0.7 SLC36A1solute carrier family 36 (proton/amino acid symporter), member 1 (ENSG00000123643), score: 0.54 SLC6A5solute carrier family 6 (neurotransmitter transporter, glycine), member 5 (ENSG00000165970), score: 0.5 SMPDL3Bsphingomyelin phosphodiesterase, acid-like 3B (ENSG00000130768), score: 0.56 SNRKSNF related kinase (ENSG00000163788), score: 0.6 SNX25sorting nexin 25 (ENSG00000109762), score: 0.49 SOCS5suppressor of cytokine signaling 5 (ENSG00000171150), score: 0.55 SP4Sp4 transcription factor (ENSG00000105866), score: 0.59 SPENspen homolog, transcriptional regulator (Drosophila) (ENSG00000065526), score: 0.49 SPHKAPSPHK1 interactor, AKAP domain containing (ENSG00000153820), score: 0.49 SPINK6serine peptidase inhibitor, Kazal type 6 (ENSG00000178172), score: 1 SPOPspeckle-type POZ protein (ENSG00000121067), score: 0.54 SPTBN5spectrin, beta, non-erythrocytic 5 (ENSG00000137877), score: 0.56 SRCAPSnf2-related CREBBP activator protein (ENSG00000080603), score: 0.48 SRRM4serine/arginine repetitive matrix 4 (ENSG00000139767), score: 0.49 STACSH3 and cysteine rich domain (ENSG00000144681), score: 0.58 STAT5Bsignal transducer and activator of transcription 5B (ENSG00000173757), score: 0.55 SURF1surfeit 1 (ENSG00000148290), score: -0.53 SYT2synaptotagmin II (ENSG00000143858), score: 0.48 TAF10TAF10 RNA polymerase II, TATA box binding protein (TBP)-associated factor, 30kDa (ENSG00000166337), score: -0.53 TBC1D20TBC1 domain family, member 20 (ENSG00000125875), score: 0.52 TBC1D9TBC1 domain family, member 9 (with GRAM domain) (ENSG00000109436), score: 0.48 TFAP2Etranscription factor AP-2 epsilon (activating enhancer binding protein 2 epsilon) (ENSG00000116819), score: 0.53 TGM1transglutaminase 1 (K polypeptide epidermal type I, protein-glutamine-gamma-glutamyltransferase) (ENSG00000092295), score: 0.65 TIAM1T-cell lymphoma invasion and metastasis 1 (ENSG00000156299), score: 0.59 TLL1tolloid-like 1 (ENSG00000038295), score: 0.66 TMC2transmembrane channel-like 2 (ENSG00000149488), score: 0.94 TNFRSF25tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 25 (ENSG00000215788), score: 0.48 TOP1MTtopoisomerase (DNA) I, mitochondrial (ENSG00000184428), score: -0.52 TP73tumor protein p73 (ENSG00000078900), score: 0.68 TPBGtrophoblast glycoprotein (ENSG00000146242), score: -0.53 TRIM11tripartite motif-containing 11 (ENSG00000154370), score: 0.57 TRIM17tripartite motif-containing 17 (ENSG00000162931), score: 0.48 TRIM32tripartite motif-containing 32 (ENSG00000119401), score: 0.57 TRIM67tripartite motif-containing 67 (ENSG00000119283), score: 0.65 TRIM7tripartite motif-containing 7 (ENSG00000146054), score: 0.5 TRIM72tripartite motif-containing 72 (ENSG00000177238), score: 0.51 TSEN34tRNA splicing endonuclease 34 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000170892), score: -0.53 TTC23tetratricopeptide repeat domain 23 (ENSG00000103852), score: -0.52 UBASH3Bubiquitin associated and SH3 domain containing B (ENSG00000154127), score: 0.58 ULK3unc-51-like kinase 3 (C. elegans) (ENSG00000140474), score: 0.51 USTuronyl-2-sulfotransferase (ENSG00000111962), score: 0.48 VAT1Lvesicle amine transport protein 1 homolog (T. californica)-like (ENSG00000171724), score: 0.49 VAX2ventral anterior homeobox 2 (ENSG00000116035), score: 0.54 VSX1visual system homeobox 1 (ENSG00000100987), score: 0.8 VWA5Avon Willebrand factor A domain containing 5A (ENSG00000110002), score: -0.6 WACWW domain containing adaptor with coiled-coil (ENSG00000095787), score: 0.53 WSCD2WSC domain containing 2 (ENSG00000075035), score: 0.51 XKR6XK, Kell blood group complex subunit-related family, member 6 (ENSG00000171044), score: 0.5 XKR7XK, Kell blood group complex subunit-related family, member 7 (ENSG00000101321), score: 0.66 YTHDF1YTH domain family, member 1 (ENSG00000149658), score: 0.54 ZBTB34zinc finger and BTB domain containing 34 (ENSG00000177125), score: 0.53 ZBTB40zinc finger and BTB domain containing 40 (ENSG00000184677), score: 0.51 ZBTB41zinc finger and BTB domain containing 41 (ENSG00000177888), score: 0.5 ZCCHC12zinc finger, CCHC domain containing 12 (ENSG00000174460), score: 0.49 ZFPM2zinc finger protein, multitype 2 (ENSG00000169946), score: 0.53 ZIC2Zic family member 2 (odd-paired homolog, Drosophila) (ENSG00000043355), score: 0.58 ZIC4Zic family member 4 (ENSG00000174963), score: 0.67 ZIC5Zic family member 5 (odd-paired homolog, Drosophila) (ENSG00000139800), score: 0.61 ZNF157zinc finger protein 157 (ENSG00000147117), score: 0.56 ZNF238zinc finger protein 238 (ENSG00000179456), score: 0.53 ZNF273zinc finger protein 273 (ENSG00000198039), score: 0.64 ZNF296zinc finger protein 296 (ENSG00000170684), score: 0.58 ZNF304zinc finger protein 304 (ENSG00000131845), score: 0.48 ZNF354Czinc finger protein 354C (ENSG00000177932), score: 0.49 ZNF37Azinc finger protein 37A (ENSG00000075407), score: 0.58 ZNF521zinc finger protein 521 (ENSG00000198795), score: 0.6 ZNF589zinc finger protein 589 (ENSG00000164048), score: 0.48 ZNF671zinc finger protein 671 (ENSG00000083814), score: 0.5 ZNF704zinc finger protein 704 (ENSG00000164684), score: 0.52 ZP2zona pellucida glycoprotein 2 (sperm receptor) (ENSG00000103310), score: 0.7
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ppa_cb_m_ca1 | ppa | cb | m | _ |
| hsa_cb_m_ca1 | hsa | cb | m | _ |
| ptr_cb_m_ca1 | ptr | cb | m | _ |
| hsa_cb_f_ca1 | hsa | cb | f | _ |