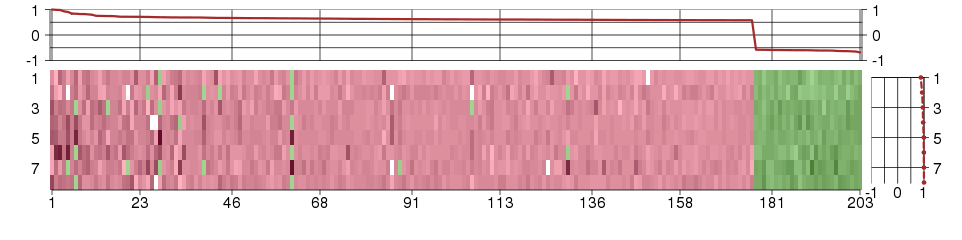

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
system process
A multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system. An organ system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a biological objective.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
transcription
The cellular synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
transcription, DNA-dependent
The cellular synthesis of RNA on a template of DNA.
regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-dependent transcription.
regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter.
transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter
The synthesis of RNA from a DNA template by RNA polymerase II (Pol II), originating at a Pol II-specific promoter. Includes transcription of messenger RNA (mRNA) and certain small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs).
nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds; includes nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, assimilatory/dissimilatory nitrate reduction and the interconversion of nitrogenous organic matter and ammonium.
transport
The directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells, or within a multicellular organism by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
ion transport
The directed movement of charged atoms or small charged molecules into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
cation transport
The directed movement of cations, atoms or small molecules with a net positive charge, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
potassium ion transport
The directed movement of potassium ions (K+) into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
metal ion transport
The directed movement of metal ions, any metal ion with an electric charge, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
cell communication
Any process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
cell surface receptor linked signaling pathway
Any series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of an extracellular ligand to a receptor on the surface of the target cell.
G-protein coupled receptor protein signaling pathway
The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a G-protein coupled receptor binding to its physiological ligand.
cell-cell signaling
Any process that mediates the transfer of information from one cell to another.
synaptic transmission
The process of communication from a neuron to a target (neuron, muscle, or secretory cell) across a synapse.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of nervous tissue over time, from its formation to its mature state.
neurological system process
A organ system process carried out by any of the organs or tissues of neurological system.
central nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the central nervous system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The central nervous system is the core nervous system that serves an integrating and coordinating function. In vertebrates it consists of the brain, spinal cord and spinal nerves. In those invertebrates with a central nervous system it typically consists of a brain, cerebral ganglia and a nerve cord.
brain development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the brain over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Brain development begins with patterning events in the neural tube and ends with the mature structure that is the center of thought and emotion. The brain is responsible for the coordination and control of bodily activities and the interpretation of information from the senses (sight, hearing, smell, etc.).
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
glial cell differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the specialized features of a glial cell.
gene expression
The process by which a gene's sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
regulation of gene expression
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
regulation of gene-specific transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the specifically regulated synthesis of RNA from DNA encoding a specific gene or set of genes by RNA polymerase II (Pol II), originating at a Pol II-specific promoter.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
negative regulation of cell development
Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
regulation of gliogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gliogenesis, the formation of mature glia.
negative regulation of gliogenesis
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of gliogenesis, the formation of mature glia.
monovalent inorganic cation transport
The directed movement of inorganic cations with a valency of one into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. Inorganic cations are atoms or small molecules with a positive charge which do not contain carbon in covalent linkage.
RNA metabolic process
The cellular chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
transmission of nerve impulse
The neurological system process by which a signal is transmitted through the nervous system by synaptic transmission and the sequential electrochemical polarization and depolarization that travels across the membrane of a nerve cell (neuron) in response to stimulation.
generation of neurons in the forebrain
The process by which nerve cells are generated in the forebrain. This includes the production of neuroblasts from and their differentiation into neurons.
forebrain neuron fate commitment
The process whereby the developmental fate of a cell becomes restricted such that it will develop into a neuron that resides in the forebrain.
forebrain neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron that will reside in the forebrain.
regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter involved in forebrain neuron fate commitment
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter that contributes to the commitment of a neuroblast to a neuronal fate. The neuron will reside in the forebrain.
cerebral cortex GABAergic interneuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a GABAergic interneuron residing in the cerebral cortex.
cerebral cortex GABAergic interneuron fate commitment
The process whereby the developmental fate of a neuroblast becomes restricted such that it will develop into a GABAergic interneuron residing in the cerebral cortex.
cerebral cortex neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron residing in the cerebral cortex.
commitment of multipotent stem cells to the neuronal lineage in the forebrain
The initial commitment of cells whereby the developmental fate of a cell becomes restricted such that it will develop into some type of neuron in the forebrain.
central nervous system neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron whose cell body resides in the central nervous system.
neurogenesis
Generation of cells within the nervous system.
signaling pathway
The series of molecular events whereby information is sent from one location to another within a living organism or between living organisms.
signaling process
Any biological process involved in the generation, transmission, reception, or interpretation of a signal. A signal is an entity used to transmit or convey information.
signaling
The entirety of a process whereby information is transmitted. This process begins with the initiation of the signal and ends when a response has been triggered.
signal transmission
The process whereby a signal is released and/or conveyed from one location to another.
cell differentiation
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state.
neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron.
forebrain development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the forebrain over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The forebrain is the anterior of the three primary divisions of the developing chordate brain or the corresponding part of the adult brain (in vertebrates, includes especially the cerebral hemispheres, the thalamus, and the hypothalamus and especially in higher vertebrates is the main control center for sensory and associative information processing, visceral functions, and voluntary motor functions).
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
gene-specific transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter
The specifically regulated synthesis of RNA from DNA encoding a specific gene or set of genes by RNA polymerase II (Pol II), originating at a Pol II-specific promoter. In addition to RNA polymerase II and the general transcription factors, specific transcription requires one or more specific factors that bind to specific DNA sequences or interact with the general transcription machinery.
regulation of gene-specific transcription
Any process that modulates the DNA-dependent transcription of a specific gene or genes.
RNA biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage. Includes polymerization of ribonucleotide monomers.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
gliogenesis
The process by which glial cells are generated. This includes the production of glial progenitors and their differentiation into mature glia.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
cell fate commitment
The commitment of cells to specific cell fates and their capacity to differentiate into particular kinds of cells. Positional information is established through protein signals that emanate from a localized source within a cell (the initial one-cell zygote) or within a developmental field.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
negative regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
regulation of glial cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of glia cell differentiation.
negative regulation of glial cell differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of glia cell differentiation.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
neuron fate commitment
The process whereby the developmental fate of a cell becomes restricted such that it will develop into a neuron.
generation of neurons
The process by which nerve cells are generated. This includes the production of neuroblasts and their differentiation into neurons.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
negative regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of developmental process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
negative regulation of developmental process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nitrogen or nitrogenous compounds.
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
regulation of nervous system development
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of nervous system development, the origin and formation of nervous tissue.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of cell development
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of primary metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism involving those compounds formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleic acids.
regulation of multicellular organismal development
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of multicellular organismal development.
all
NA
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
signaling process
Any biological process involved in the generation, transmission, reception, or interpretation of a signal. A signal is an entity used to transmit or convey information.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
negative regulation of developmental process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of developmental process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nitrogen or nitrogenous compounds.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
regulation of primary metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism involving those compounds formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cell-cell signaling
Any process that mediates the transfer of information from one cell to another.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
transmission of nerve impulse
The neurological system process by which a signal is transmitted through the nervous system by synaptic transmission and the sequential electrochemical polarization and depolarization that travels across the membrane of a nerve cell (neuron) in response to stimulation.
regulation of multicellular organismal development
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of multicellular organismal development.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
negative regulation of developmental process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of multicellular organismal development
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of multicellular organismal development.
negative regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of gene expression
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
synaptic transmission
The process of communication from a neuron to a target (neuron, muscle, or secretory cell) across a synapse.
cell fate commitment
The commitment of cells to specific cell fates and their capacity to differentiate into particular kinds of cells. Positional information is established through protein signals that emanate from a localized source within a cell (the initial one-cell zygote) or within a developmental field.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
negative regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
negative regulation of cell development
Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
negative regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
regulation of cell development
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
transmission of nerve impulse
The neurological system process by which a signal is transmitted through the nervous system by synaptic transmission and the sequential electrochemical polarization and depolarization that travels across the membrane of a nerve cell (neuron) in response to stimulation.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
transcription
The cellular synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
transcription, DNA-dependent
The cellular synthesis of RNA on a template of DNA.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
RNA biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage. Includes polymerization of ribonucleotide monomers.
regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
transcription
The cellular synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
RNA metabolic process
The cellular chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage.
negative regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
neuron fate commitment
The process whereby the developmental fate of a cell becomes restricted such that it will develop into a neuron.
negative regulation of cell development
Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
central nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the central nervous system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The central nervous system is the core nervous system that serves an integrating and coordinating function. In vertebrates it consists of the brain, spinal cord and spinal nerves. In those invertebrates with a central nervous system it typically consists of a brain, cerebral ganglia and a nerve cord.
neurogenesis
Generation of cells within the nervous system.
regulation of nervous system development
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of nervous system development, the origin and formation of nervous tissue.
brain development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the brain over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Brain development begins with patterning events in the neural tube and ends with the mature structure that is the center of thought and emotion. The brain is responsible for the coordination and control of bodily activities and the interpretation of information from the senses (sight, hearing, smell, etc.).
central nervous system neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron whose cell body resides in the central nervous system.
regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
forebrain development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the forebrain over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The forebrain is the anterior of the three primary divisions of the developing chordate brain or the corresponding part of the adult brain (in vertebrates, includes especially the cerebral hemispheres, the thalamus, and the hypothalamus and especially in higher vertebrates is the main control center for sensory and associative information processing, visceral functions, and voluntary motor functions).
regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-dependent transcription.
regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-dependent transcription.
negative regulation of glial cell differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of glia cell differentiation.
glial cell differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the specialized features of a glial cell.
negative regulation of gliogenesis
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of gliogenesis, the formation of mature glia.
generation of neurons in the forebrain
The process by which nerve cells are generated in the forebrain. This includes the production of neuroblasts from and their differentiation into neurons.
neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron.
regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
regulation of gliogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gliogenesis, the formation of mature glia.
negative regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
forebrain neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron that will reside in the forebrain.
cerebral cortex neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron residing in the cerebral cortex.
forebrain neuron fate commitment
The process whereby the developmental fate of a cell becomes restricted such that it will develop into a neuron that resides in the forebrain.
cerebral cortex GABAergic interneuron fate commitment
The process whereby the developmental fate of a neuroblast becomes restricted such that it will develop into a GABAergic interneuron residing in the cerebral cortex.
potassium ion transport
The directed movement of potassium ions (K+) into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter.
regulation of gene-specific transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the specifically regulated synthesis of RNA from DNA encoding a specific gene or set of genes by RNA polymerase II (Pol II), originating at a Pol II-specific promoter.
negative regulation of glial cell differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of glia cell differentiation.
negative regulation of gliogenesis
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of gliogenesis, the formation of mature glia.
regulation of glial cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of glia cell differentiation.
regulation of gene-specific transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the specifically regulated synthesis of RNA from DNA encoding a specific gene or set of genes by RNA polymerase II (Pol II), originating at a Pol II-specific promoter.
regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter involved in forebrain neuron fate commitment
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter that contributes to the commitment of a neuroblast to a neuronal fate. The neuron will reside in the forebrain.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
integral to membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer. When used to describe a protein, indicates that all or part of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
voltage-gated potassium channel complex
A protein complex that forms a transmembrane channel through which potassium ions may cross a cell membrane in response to changes in membrane potential.
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
ion channel complex
A protein complex that spans a membrane and forms a water-filled channel across the phospholipid bilayer allowing selective ion transport down its electrochemical gradient.
cation channel complex
An ion channel complex through which cations pass.
potassium channel complex
An ion channel complex through which potassium ions pass.
protein complex
Any macromolecular complex composed of two or more polypeptide subunits, which may or may not be identical. Protein complexes may have other associated non-protein prosthetic groups, such as nucleotides, metal ions or other small molecules.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
ion channel complex
A protein complex that spans a membrane and forms a water-filled channel across the phospholipid bilayer allowing selective ion transport down its electrochemical gradient.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
ion channel complex
A protein complex that spans a membrane and forms a water-filled channel across the phospholipid bilayer allowing selective ion transport down its electrochemical gradient.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
voltage-gated potassium channel complex
A protein complex that forms a transmembrane channel through which potassium ions may cross a cell membrane in response to changes in membrane potential.
voltage-gated potassium channel complex
A protein complex that forms a transmembrane channel through which potassium ions may cross a cell membrane in response to changes in membrane potential.

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
catalytic activity
Catalysis of a biochemical reaction at physiological temperatures. In biologically catalyzed reactions, the reactants are known as substrates, and the catalysts are naturally occurring macromolecular substances known as enzymes. Enzymes possess specific binding sites for substrates, and are usually composed wholly or largely of protein, but RNA that has catalytic activity (ribozyme) is often also regarded as enzymatic.
protein kinase activity
Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction: a protein + ATP = a phosphoprotein + ADP.
protein serine/threonine kinase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein serine/threonine = ADP + protein serine/threonine phosphate.
calmodulin-dependent protein kinase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein serine/threonine = ADP + protein serine/threonine phosphate, dependent on the presence of calcium-bound calmodulin.
transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
ion channel activity
Catalysis of facilitated diffusion of an ion (by an energy-independent process) by passage through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel without evidence for a carrier-mediated mechanism.
voltage-gated ion channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a voltage-gated channel. An ion is an atom or group of atoms carrying an electric charge by virtue of having gained or lost one or more electrons.
voltage-gated potassium channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a potassium ion by a voltage-gated channel.
cation channel activity
Catalysis of the energy-independent passage of cations across a lipid bilayer down a concentration gradient.
potassium channel activity
Catalysis of facilitated diffusion of a potassium ion (by an energy-independent process) involving passage through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel without evidence for a carrier-mediated mechanism.
transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a substance from one side of a membrane to the other.
cation transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of cation from one side of the membrane to the other.
ion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of an ion from one side of a membrane to the other.
channel activity
Catalysis of energy-independent facilitated diffusion, mediated by passage of a solute through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel. Stereospecificity is not exhibited but this transport may be specific for a particular molecular species or class of molecules.
kinase activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a substrate molecule.
transferase activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a group, e.g. a methyl group, glycosyl group, acyl group, phosphorus-containing, or other groups, from one compound (generally regarded as the donor) to another compound (generally regarded as the acceptor). Transferase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 2.
transferase activity, transferring phosphorus-containing groups
Catalysis of the transfer of a phosphorus-containing group from one compound (donor) to another (acceptor).
phosphotransferase activity, alcohol group as acceptor
Catalysis of the transfer of a phosphorus-containing group from one compound (donor) to an alcohol group (acceptor).
passive transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute from one side of the membrane to the other, down the solute's concentration gradient.
voltage-gated channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a solute by a channel whose open state is dependent on the voltage across the membrane in which it is embedded.
gated channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a solute by a channel that opens in response to a specific stimulus.
substrate-specific channel activity
Catalysis of energy-independent facilitated diffusion, mediated by passage of a specific solute through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel. Stereospecificity is not exhibited but this transport may be specific for a particular molecular species or class of molecules.
voltage-gated cation channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a cation by a voltage-gated channel. A cation is a positively charged ion.
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
substrate-specific transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of a specific substance or group of related substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
all
NA
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
protein kinase activity
Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction: a protein + ATP = a phosphoprotein + ADP.
substrate-specific channel activity
Catalysis of energy-independent facilitated diffusion, mediated by passage of a specific solute through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel. Stereospecificity is not exhibited but this transport may be specific for a particular molecular species or class of molecules.
ion channel activity
Catalysis of facilitated diffusion of an ion (by an energy-independent process) by passage through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel without evidence for a carrier-mediated mechanism.
cation channel activity
Catalysis of the energy-independent passage of cations across a lipid bilayer down a concentration gradient.
voltage-gated ion channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a voltage-gated channel. An ion is an atom or group of atoms carrying an electric charge by virtue of having gained or lost one or more electrons.
voltage-gated cation channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a cation by a voltage-gated channel. A cation is a positively charged ion.
voltage-gated potassium channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a potassium ion by a voltage-gated channel.
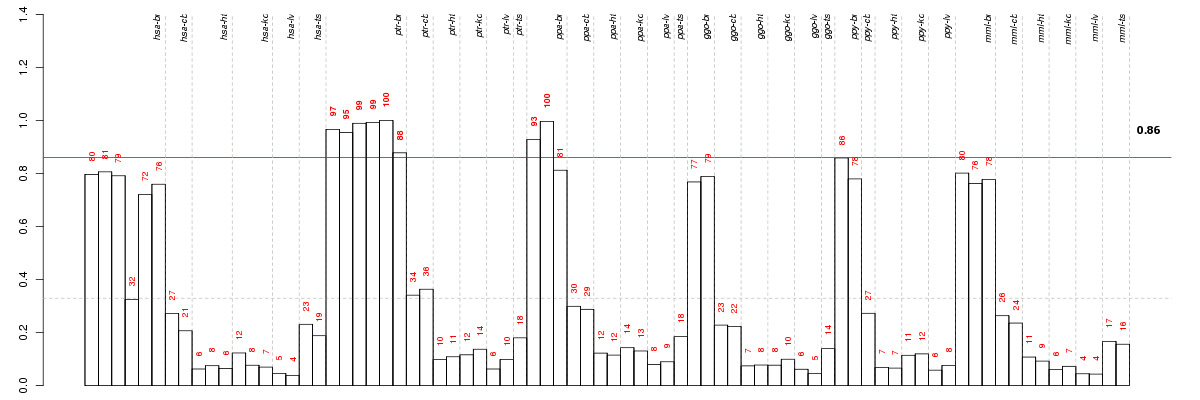
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 04080 | 6.492e-03 | 2.685 | 10 | 206 | Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction |
| 04020 | 4.187e-02 | 1.89 | 7 | 145 | Calcium signaling pathway |
AATFapoptosis antagonizing transcription factor (ENSG00000108270), score: -0.63 ALOX15Barachidonate 15-lipoxygenase, type B (ENSG00000179593), score: 0.7 ANGPT4angiopoietin 4 (ENSG00000101280), score: 0.74 ANO3anoctamin 3 (ENSG00000134343), score: 0.58 ARCactivity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein (ENSG00000198576), score: 0.59 ARPP19cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein, 19kDa (ENSG00000128989), score: 0.66 ASTLastacin-like metallo-endopeptidase (M12 family) (ENSG00000188886), score: 0.99 BASP1brain abundant, membrane attached signal protein 1 (ENSG00000176788), score: 0.59 BCL11AB-cell CLL/lymphoma 11A (zinc finger protein) (ENSG00000119866), score: 0.61 BCL11BB-cell CLL/lymphoma 11B (zinc finger protein) (ENSG00000127152), score: 0.64 BCL2L10BCL2-like 10 (apoptosis facilitator) (ENSG00000137875), score: 0.84 C12orf49chromosome 12 open reading frame 49 (ENSG00000111412), score: 0.58 C12orf76chromosome 12 open reading frame 76 (ENSG00000174456), score: 0.58 C13orf39chromosome 13 open reading frame 39 (ENSG00000139780), score: 0.69 C16orf59chromosome 16 open reading frame 59 (ENSG00000162062), score: 0.61 C16orf73chromosome 16 open reading frame 73 (ENSG00000162039), score: 0.63 C19orf62chromosome 19 open reading frame 62 (ENSG00000105393), score: 0.66 C1orf128chromosome 1 open reading frame 128 (ENSG00000057757), score: 0.6 C1orf187chromosome 1 open reading frame 187 (ENSG00000162490), score: 0.82 C1orf89chromosome 1 open reading frame 89 (ENSG00000132881), score: 0.73 C20orf103chromosome 20 open reading frame 103 (ENSG00000125869), score: 0.61 C2orf80chromosome 2 open reading frame 80 (ENSG00000188674), score: 0.69 C2orf89chromosome 2 open reading frame 89 (ENSG00000186854), score: 0.72 C6orf221chromosome 6 open reading frame 221 (ENSG00000203908), score: 0.67 C7orf52chromosome 7 open reading frame 52 (ENSG00000167011), score: 0.71 C9orf91chromosome 9 open reading frame 91 (ENSG00000157693), score: 0.66 CA7carbonic anhydrase VII (ENSG00000168748), score: 0.64 CACNG3calcium channel, voltage-dependent, gamma subunit 3 (ENSG00000006116), score: 0.61 CAMK1Gcalcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IG (ENSG00000008118), score: 0.65 CAMK2Acalcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II alpha (ENSG00000070808), score: 0.6 CAMKK1calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 1, alpha (ENSG00000004660), score: 0.58 CARD8caspase recruitment domain family, member 8 (ENSG00000105483), score: -0.68 CBLN2cerebellin 2 precursor (ENSG00000141668), score: 0.69 CCKBRcholecystokinin B receptor (ENSG00000110148), score: 0.61 CCNI2cyclin I family, member 2 (ENSG00000205089), score: 0.59 CCR6chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 6 (ENSG00000112486), score: 0.75 CDH12cadherin 12, type 2 (N-cadherin 2) (ENSG00000154162), score: 0.67 CHGAchromogranin A (parathyroid secretory protein 1) (ENSG00000100604), score: 0.66 CHRM1cholinergic receptor, muscarinic 1 (ENSG00000168539), score: 0.62 CIDEAcell death-inducing DFFA-like effector a (ENSG00000176194), score: 0.58 CPOcarboxypeptidase O (ENSG00000144410), score: 0.64 CREG2cellular repressor of E1A-stimulated genes 2 (ENSG00000175874), score: 0.69 CRHcorticotropin releasing hormone (ENSG00000147571), score: 0.59 CSMD3CUB and Sushi multiple domains 3 (ENSG00000164796), score: 0.58 CYP46A1cytochrome P450, family 46, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000036530), score: 0.6 DCAF8DDB1 and CUL4 associated factor 8 (ENSG00000132716), score: 0.71 DCXdoublecortin (ENSG00000077279), score: 0.67 DDX42DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 42 (ENSG00000198231), score: 0.6 DDX59DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 59 (ENSG00000118197), score: -0.61 DENND3DENN/MADD domain containing 3 (ENSG00000105339), score: 0.69 DGKBdiacylglycerol kinase, beta 90kDa (ENSG00000136267), score: 0.59 DLX1distal-less homeobox 1 (ENSG00000144355), score: 0.6 DLX2distal-less homeobox 2 (ENSG00000115844), score: 0.63 DLX5distal-less homeobox 5 (ENSG00000105880), score: 0.6 DNAJC7DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 7 (ENSG00000168259), score: 0.66 DPF1D4, zinc and double PHD fingers family 1 (ENSG00000011332), score: 0.58 DPP10dipeptidyl-peptidase 10 (non-functional) (ENSG00000175497), score: 0.61 DRP2dystrophin related protein 2 (ENSG00000102385), score: 0.58 DUOXA1dual oxidase maturation factor 1 (ENSG00000140254), score: 0.63 ELFN2extracellular leucine-rich repeat and fibronectin type III domain containing 2 (ENSG00000166897), score: 0.58 ELOVL3elongation of very long chain fatty acids (FEN1/Elo2, SUR4/Elo3, yeast)-like 3 (ENSG00000119915), score: 0.75 ENC1ectodermal-neural cortex 1 (with BTB-like domain) (ENSG00000171617), score: 0.62 EPHX4epoxide hydrolase 4 (ENSG00000172031), score: 0.62 ERBB2v-erb-b2 erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene homolog 2, neuro/glioblastoma derived oncogene homolog (avian) (ENSG00000141736), score: -0.58 FAM19A1family with sequence similarity 19 (chemokine (C-C motif)-like), member A1 (ENSG00000183662), score: 0.62 FAM19A2family with sequence similarity 19 (chemokine (C-C motif)-like), member A2 (ENSG00000198673), score: 0.58 FAM49Afamily with sequence similarity 49, member A (ENSG00000197872), score: 0.58 FAM5Bfamily with sequence similarity 5, member B (ENSG00000198797), score: 0.63 FBLN7fibulin 7 (ENSG00000144152), score: 0.61 FBXW12F-box and WD repeat domain containing 12 (ENSG00000164049), score: 0.8 FCRLBFc receptor-like B (ENSG00000162746), score: 0.65 FEZF2FEZ family zinc finger 2 (ENSG00000153266), score: 0.68 FFAR1free fatty acid receptor 1 (ENSG00000126266), score: 0.68 FLNBfilamin B, beta (ENSG00000136068), score: -0.63 GABPAGA binding protein transcription factor, alpha subunit 60kDa (ENSG00000154727), score: -0.62 GABRA4gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, alpha 4 (ENSG00000109158), score: 0.6 GALNT8UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 8 (GalNAc-T8) (ENSG00000130035), score: 0.93 GALR2galanin receptor 2 (ENSG00000182687), score: 0.71 GCGglucagon (ENSG00000115263), score: 0.83 GJD4gap junction protein, delta 4, 40.1kDa (ENSG00000177291), score: 0.66 GPR26G protein-coupled receptor 26 (ENSG00000154478), score: 0.63 GSG1LGSG1-like (ENSG00000169181), score: 0.58 HEATR2HEAT repeat containing 2 (ENSG00000164818), score: -0.6 HEMK1HemK methyltransferase family member 1 (ENSG00000114735), score: -0.58 HS3ST2heparan sulfate (glucosamine) 3-O-sulfotransferase 2 (ENSG00000122254), score: 0.71 HS3ST4heparan sulfate (glucosamine) 3-O-sulfotransferase 4 (ENSG00000182601), score: 0.6 HTR2A5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 2A (ENSG00000102468), score: 0.64 IFNW1interferon, omega 1 (ENSG00000177047), score: 0.7 IGFL1IGF-like family member 1 (ENSG00000188293), score: 0.72 KCNB1potassium voltage-gated channel, Shab-related subfamily, member 1 (ENSG00000158445), score: 0.59 KCNC2potassium voltage-gated channel, Shaw-related subfamily, member 2 (ENSG00000166006), score: 0.66 KCNH3potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily H (eag-related), member 3 (ENSG00000135519), score: 0.59 KCNN1potassium intermediate/small conductance calcium-activated channel, subfamily N, member 1 (ENSG00000105642), score: 0.6 KCNN4potassium intermediate/small conductance calcium-activated channel, subfamily N, member 4 (ENSG00000104783), score: 0.74 KCNQ3potassium voltage-gated channel, KQT-like subfamily, member 3 (ENSG00000184156), score: 0.65 KCNQ4potassium voltage-gated channel, KQT-like subfamily, member 4 (ENSG00000117013), score: 0.64 KCNQ5potassium voltage-gated channel, KQT-like subfamily, member 5 (ENSG00000185760), score: 0.65 KCNS1potassium voltage-gated channel, delayed-rectifier, subfamily S, member 1 (ENSG00000124134), score: 0.61 KCNS2potassium voltage-gated channel, delayed-rectifier, subfamily S, member 2 (ENSG00000156486), score: 0.63 KCNV1potassium channel, subfamily V, member 1 (ENSG00000164794), score: 0.58 KIAA0748KIAA0748 (ENSG00000135426), score: 0.69 KLF11Kruppel-like factor 11 (ENSG00000172059), score: -0.58 KRT83keratin 83 (ENSG00000170523), score: 0.6 LATS2LATS, large tumor suppressor, homolog 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000150457), score: -0.61 LIX1LLix1 homolog (mouse)-like (ENSG00000152022), score: -0.6 LMO1LIM domain only 1 (rhombotin 1) (ENSG00000166407), score: 0.59 LMO4LIM domain only 4 (ENSG00000143013), score: 0.61 LNX2ligand of numb-protein X 2 (ENSG00000139517), score: -0.59 LOC100292920similar to mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription, subunit 18 homolog (ENSG00000130772), score: -0.64 LOC401097Similar to LOC166075 (ENSG00000180044), score: 0.6 LPPR3lipid phosphate phosphatase-related protein type 3 (ENSG00000129951), score: 0.59 LRTM2leucine-rich repeats and transmembrane domains 2 (ENSG00000166159), score: 0.61 LSM6LSM6 homolog, U6 small nuclear RNA associated (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000164167), score: -0.61 LY6Dlymphocyte antigen 6 complex, locus D (ENSG00000167656), score: 0.72 LY6Hlymphocyte antigen 6 complex, locus H (ENSG00000176956), score: 0.58 MAS1MAS1 oncogene (ENSG00000130368), score: 0.71 MATKmegakaryocyte-associated tyrosine kinase (ENSG00000007264), score: 0.61 MCF2MCF.2 cell line derived transforming sequence (ENSG00000101977), score: 0.58 MCHR2melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 2 (ENSG00000152034), score: 0.65 MGAT5Bmannosyl (alpha-1,6-)-glycoprotein beta-1,6-N-acetyl-glucosaminyltransferase, isozyme B (ENSG00000167889), score: 0.58 MKL2MKL/myocardin-like 2 (ENSG00000186260), score: 0.59 MMP17matrix metallopeptidase 17 (membrane-inserted) (ENSG00000198598), score: 0.62 MMP3matrix metallopeptidase 3 (stromelysin 1, progelatinase) (ENSG00000149968), score: 0.6 MTRF1mitochondrial translational release factor 1 (ENSG00000120662), score: -0.59 NCALDneurocalcin delta (ENSG00000104490), score: 0.62 NECAB1N-terminal EF-hand calcium binding protein 1 (ENSG00000123119), score: 0.66 NETO1neuropilin (NRP) and tolloid (TLL)-like 1 (ENSG00000166342), score: 0.61 NEUROD6neurogenic differentiation 6 (ENSG00000164600), score: 0.59 NOGnoggin (ENSG00000183691), score: 0.58 NPAS1neuronal PAS domain protein 1 (ENSG00000130751), score: 0.67 NPBWR2neuropeptides B/W receptor 2 (ENSG00000125522), score: 0.82 NPVFneuropeptide VF precursor (ENSG00000105954), score: 0.65 NRG3neuregulin 3 (ENSG00000185737), score: 0.65 NRSN1neurensin 1 (ENSG00000152954), score: 0.61 OPN1SWopsin 1 (cone pigments), short-wave-sensitive (ENSG00000128617), score: 0.64 OTOL1otolin 1 homolog (zebrafish) (ENSG00000182447), score: 1 OTOSotospiralin (ENSG00000178602), score: 0.81 PANX3pannexin 3 (ENSG00000154143), score: 0.9 PCOLCEprocollagen C-endopeptidase enhancer (ENSG00000106333), score: -0.61 PCSK1proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 1 (ENSG00000175426), score: 0.62 PDE8Bphosphodiesterase 8B (ENSG00000113231), score: 0.59 PGM2L1phosphoglucomutase 2-like 1 (ENSG00000165434), score: 0.63 PIP5KL1phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase-like 1 (ENSG00000167103), score: 0.61 PKMYT1protein kinase, membrane associated tyrosine/threonine 1 (ENSG00000127564), score: 0.61 PLEKHG4Bpleckstrin homology domain containing, family G (with RhoGef domain) member 4B (ENSG00000153404), score: 0.59 PNCKpregnancy up-regulated non-ubiquitously expressed CaM kinase (ENSG00000130822), score: 0.6 PNOCprepronociceptin (ENSG00000168081), score: 0.64 PRKCAprotein kinase C, alpha (ENSG00000154229), score: 0.58 PTH2Rparathyroid hormone 2 receptor (ENSG00000144407), score: 0.6 PTPN5protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 5 (striatum-enriched) (ENSG00000110786), score: 0.59 RASL10ARAS-like, family 10, member A (ENSG00000100276), score: 0.65 RAX2retina and anterior neural fold homeobox 2 (ENSG00000173976), score: 0.98 RGS4regulator of G-protein signaling 4 (ENSG00000117152), score: 0.65 RIMBP2RIMS binding protein 2 (ENSG00000060709), score: 0.58 RP2retinitis pigmentosa 2 (X-linked recessive) (ENSG00000102218), score: -0.6 RPRMreprimo, TP53 dependent G2 arrest mediator candidate (ENSG00000177519), score: 0.66 RPRMLreprimo-like (ENSG00000179673), score: 0.6 RTBDNretbindin (ENSG00000132026), score: 0.65 S100A5S100 calcium binding protein A5 (ENSG00000196420), score: 0.7 SAGE1sarcoma antigen 1 (ENSG00000181433), score: 0.61 SARSseryl-tRNA synthetase (ENSG00000031698), score: 0.58 SATB2SATB homeobox 2 (ENSG00000119042), score: 0.62 SCGB1A1secretoglobin, family 1A, member 1 (uteroglobin) (ENSG00000149021), score: 0.67 SCN3Bsodium channel, voltage-gated, type III, beta (ENSG00000166257), score: 0.63 SDCCAG8serologically defined colon cancer antigen 8 (ENSG00000054282), score: 0.62 SERPINI1serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade I (neuroserpin), member 1 (ENSG00000163536), score: 0.62 SH2D5SH2 domain containing 5 (ENSG00000189410), score: 0.62 SH3D19SH3 domain containing 19 (ENSG00000109686), score: -0.6 SLC12A4solute carrier family 12 (potassium/chloride transporters), member 4 (ENSG00000124067), score: -0.59 SLC17A8solute carrier family 17 (sodium-dependent inorganic phosphate cotransporter), member 8 (ENSG00000179520), score: 0.69 SLC6A20solute carrier family 6 (proline IMINO transporter), member 20 (ENSG00000163817), score: 0.62 SMAD4SMAD family member 4 (ENSG00000141646), score: -0.6 SP1Sp1 transcription factor (ENSG00000185591), score: -0.61 SSTsomatostatin (ENSG00000157005), score: 0.59 STK32Cserine/threonine kinase 32C (ENSG00000165752), score: 0.58 STYK1serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase 1 (ENSG00000060140), score: 0.63 SV2Csynaptic vesicle glycoprotein 2C (ENSG00000122012), score: 0.59 SYTL2synaptotagmin-like 2 (ENSG00000137501), score: 0.62 TAB1TGF-beta activated kinase 1/MAP3K7 binding protein 1 (ENSG00000100324), score: 0.74 TACR3tachykinin receptor 3 (ENSG00000169836), score: 0.69 TBC1D2BTBC1 domain family, member 2B (ENSG00000167202), score: -0.59 TBR1T-box, brain, 1 (ENSG00000136535), score: 0.63 THYN1thymocyte nuclear protein 1 (ENSG00000151500), score: 0.6 TJP2tight junction protein 2 (zona occludens 2) (ENSG00000119139), score: -0.58 TMEM155transmembrane protein 155 (ENSG00000164112), score: 0.67 TMEM196transmembrane protein 196 (ENSG00000173452), score: 0.61 TREM2triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (ENSG00000095970), score: 0.59 TRPM2transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily M, member 2 (ENSG00000142185), score: 0.64 TSPAN18tetraspanin 18 (ENSG00000157570), score: -0.65 TTC23tetratricopeptide repeat domain 23 (ENSG00000103852), score: -0.59 VGFVGF nerve growth factor inducible (ENSG00000128564), score: 0.68 VPS41vacuolar protein sorting 41 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000006715), score: 0.6 VSTM2AV-set and transmembrane domain containing 2A (ENSG00000170419), score: 0.61 WNT10Bwingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 10B (ENSG00000169884), score: 0.63 YARStyrosyl-tRNA synthetase (ENSG00000134684), score: 0.59 ZBTB10zinc finger and BTB domain containing 10 (ENSG00000205189), score: -0.63 ZDHHC18zinc finger, DHHC-type containing 18 (ENSG00000204160), score: 0.6 ZFR2zinc finger RNA binding protein 2 (ENSG00000105278), score: 0.61 ZMAT4zinc finger, matrin type 4 (ENSG00000165061), score: 0.69 ZNF274zinc finger protein 274 (ENSG00000171606), score: -0.59
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ptr_br_f_ca1 | ptr | br | f | _ |
| ppa_br_m_ca1 | ppa | br | m | _ |
| ptr_br_m2_ca1 | ptr | br | m | 2 |
| ptr_br_m3_ca1 | ptr | br | m | 3 |
| ptr_br_m5_ca1 | ptr | br | m | 5 |
| ptr_br_m1_ca1 | ptr | br | m | 1 |
| ppa_br_f1_ca1 | ppa | br | f | 1 |
| ptr_br_m4_ca1 | ptr | br | m | 4 |