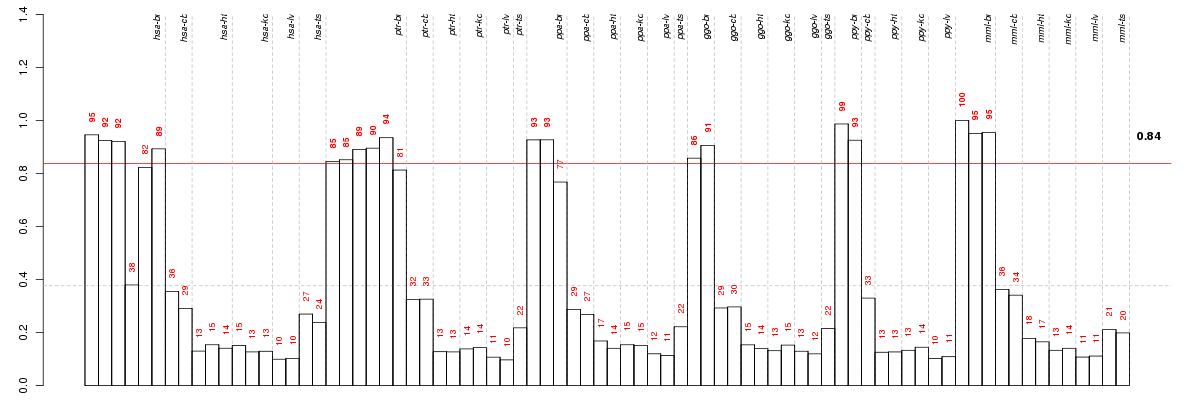

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

two-component signal transduction system (phosphorelay)
A conserved series of molecular signals found in prokaryotes and eukaryotes; involves autophosphorylation of a histidine kinase and the transfer of the phosphate group to an aspartate that then acts as a phospho-donor to response regulator proteins.
cell morphogenesis
The developmental process by which the size or shape of a cell is generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation
The change in form (cell shape and size) that occurs when relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history.
metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
system process
A multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system. An organ system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a biological objective.
signal transduction
The process whereby an activated receptor conveys information down the signaling pathway, resulting in a change in the function or state of a cell.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
purine nucleotide metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a purine nucleotide, a compound consisting of nucleoside (a purine base linked to a deoxyribose or ribose sugar) esterified with a phosphate moiety at either the 3' or 5'-hydroxyl group of its glycose moiety.
nucleoside phosphate metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any phosphorylated nucleoside.
nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds; includes nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, assimilatory/dissimilatory nitrate reduction and the interconversion of nitrogenous organic matter and ammonium.
transport
The directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells, or within a multicellular organism by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
ion transport
The directed movement of charged atoms or small charged molecules into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
cation transport
The directed movement of cations, atoms or small molecules with a net positive charge, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
potassium ion transport
The directed movement of potassium ions (K+) into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
metal ion transport
The directed movement of metal ions, any metal ion with an electric charge, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
cellular component movement
The directed, self-propelled movement of a cellular component without the involvement of an external agent such as a transporter or a pore.
cell communication
Any process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
cell surface receptor linked signaling pathway
Any series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of an extracellular ligand to a receptor on the surface of the target cell.
G-protein coupled receptor protein signaling pathway
The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a G-protein coupled receptor binding to its physiological ligand.
G-protein signaling, coupled to cyclic nucleotide second messenger
The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a G-protein coupled receptor binding to its physiological ligand, followed by modulation of a nucleotide cyclase activity and a subsequent change in the concentration of a cyclic nucleotide.
serotonin receptor signaling pathway
The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a serotonin receptor binding to one of its physiological ligands.
cell-cell signaling
Any process that mediates the transfer of information from one cell to another.
synaptic transmission
The process of communication from a neuron to a target (neuron, muscle, or secretory cell) across a synapse.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of nervous tissue over time, from its formation to its mature state.
neurological system process
A organ system process carried out by any of the organs or tissues of neurological system.
axonogenesis
Generation of a long process of a neuron, that carries efferent (outgoing) action potentials from the cell body towards target cells.
axon guidance
The process by which the migration of an axon growth cone is directed to a specific target site in response to a combination of attractive and repulsive cues.
central nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the central nervous system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The central nervous system is the core nervous system that serves an integrating and coordinating function. In vertebrates it consists of the brain, spinal cord and spinal nerves. In those invertebrates with a central nervous system it typically consists of a brain, cerebral ganglia and a nerve cord.
behavior
The specific actions or reactions of an organism in response to external or internal stimuli. Patterned activity of a whole organism in a manner dependent upon some combination of that organism's internal state and external conditions.
cell recognition
The process by which a cell in a multicellular organism interprets its surroundings.
neuron recognition
The process by which a neuronal cell in a multicellular organism interprets its surroundings.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cAMP metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving the nucleotide cAMP (cyclic AMP, adenosine 3',5'-cyclophosphate).
biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones.
nucleotide metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a nucleotide, a nucleoside that is esterified with (ortho)phosphate or an oligophosphate at any hydroxyl group on the glycose moiety; may be mono-, di- or triphosphate; this definition includes cyclic nucleotides (nucleoside cyclic phosphates).
nucleoside monophosphate metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a nucleoside monophosphate, a glycosamine consisting of a base linked to a deoxyribose or ribose sugar esterified with phosphate on its glycose moiety.
nucleoside monophosphate biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a nucleoside monophosphate, a glycosamine consisting of a base linked to a deoxyribose or ribose sugar esterified with phosphate on its glycose moiety.
nucleotide biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of nucleotides, any nucleoside that is esterified with (ortho)phosphate or an oligophosphate at any hydroxyl group on the glycose moiety; may be mono-, di- or triphosphate; this definition includes cyclic-nucleotides (nucleoside cyclic phosphates).
cyclic nucleotide metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a cyclic nucleotide, a nucleotide in which the phosphate group is in diester linkage to two positions on the sugar residue.
cyclic nucleotide biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a cyclic nucleotide, a nucleotide in which the phosphate group is in diester linkage to two positions on the sugar residue.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
monovalent inorganic cation transport
The directed movement of inorganic cations with a valency of one into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. Inorganic cations are atoms or small molecules with a positive charge which do not contain carbon in covalent linkage.
cellular component organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a cellular component.
transmission of nerve impulse
The neurological system process by which a signal is transmitted through the nervous system by synaptic transmission and the sequential electrochemical polarization and depolarization that travels across the membrane of a nerve cell (neuron) in response to stimulation.
second-messenger-mediated signaling
A series of molecular signals in which an ion or small molecule is formed or released into the cytosol, thereby helping relay the signal within the cell.
cyclic-nucleotide-mediated signaling
A series of molecular signals in which a cell uses a cyclic nucleotide to convert an extracellular signal into a response.
central nervous system neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron whose cell body resides in the central nervous system.
neurogenesis
Generation of cells within the nervous system.
signaling pathway
The series of molecular events whereby information is sent from one location to another within a living organism or between living organisms.
intracellular signaling pathway
The series of molecular events whereby information is sent from one location to another within a cell.
signaling process
Any biological process involved in the generation, transmission, reception, or interpretation of a signal. A signal is an entity used to transmit or convey information.
signaling
The entirety of a process whereby information is transmitted. This process begins with the initiation of the signal and ends when a response has been triggered.
signal transmission
The process whereby a signal is released and/or conveyed from one location to another.
cell projection organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
cell differentiation
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state.
neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron.
neuron projection development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites).
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
cellular component morphogenesis
The process by which cellular structures, including whole cells or cell parts, are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
cell part morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a cell part are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
nucleobase, nucleoside and nucleotide biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of nucleobases, nucleosides and nucleotides.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
intracellular signal transduction
The process whereby a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell.
regulation of system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a system process, a multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular nitrogen compound biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds.
small molecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
small molecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
heterocycle metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving heterocyclic compounds, those with a cyclic molecular structure and at least two different atoms in the ring (or rings).
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
neuron development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron over time, from initial commitment of the cell to a specific fate, to the fully functional differentiated cell.
cell morphogenesis involved in neuron differentiation
The process by which the structures of a neuron are generated and organized. This process occurs while the initially relatively unspecialized cell is acquiring the specialized features of a neuron.
generation of neurons
The process by which nerve cells are generated. This includes the production of neuroblasts and their differentiation into neurons.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
neuron projection morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a neuron projection are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
cell projection morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a cell projection are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
nucleobase, nucleoside and nucleotide metabolic process
The cellular chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides and nucleotides.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
all
NA
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cell projection organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
signaling process
Any biological process involved in the generation, transmission, reception, or interpretation of a signal. A signal is an entity used to transmit or convey information.
cell recognition
The process by which a cell in a multicellular organism interprets its surroundings.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
small molecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
cell-cell signaling
Any process that mediates the transfer of information from one cell to another.
cellular component morphogenesis
The process by which cellular structures, including whole cells or cell parts, are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
signal transduction
The process whereby an activated receptor conveys information down the signaling pathway, resulting in a change in the function or state of a cell.
transmission of nerve impulse
The neurological system process by which a signal is transmitted through the nervous system by synaptic transmission and the sequential electrochemical polarization and depolarization that travels across the membrane of a nerve cell (neuron) in response to stimulation.
regulation of system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a system process, a multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system.
cellular component morphogenesis
The process by which cellular structures, including whole cells or cell parts, are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
cellular nitrogen compound biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds.
nucleobase, nucleoside and nucleotide metabolic process
The cellular chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides and nucleotides.
nucleobase, nucleoside and nucleotide biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of nucleobases, nucleosides and nucleotides.
synaptic transmission
The process of communication from a neuron to a target (neuron, muscle, or secretory cell) across a synapse.
neuron projection morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a neuron projection are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation
The change in form (cell shape and size) that occurs when relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history.
cell projection morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a cell projection are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
cell projection morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a cell projection are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
intracellular signal transduction
The process whereby a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell.
transmission of nerve impulse
The neurological system process by which a signal is transmitted through the nervous system by synaptic transmission and the sequential electrochemical polarization and depolarization that travels across the membrane of a nerve cell (neuron) in response to stimulation.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
nucleobase, nucleoside and nucleotide biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of nucleobases, nucleosides and nucleotides.
neuron development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron over time, from initial commitment of the cell to a specific fate, to the fully functional differentiated cell.
neuron recognition
The process by which a neuronal cell in a multicellular organism interprets its surroundings.
neuron projection development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites).
cell morphogenesis involved in neuron differentiation
The process by which the structures of a neuron are generated and organized. This process occurs while the initially relatively unspecialized cell is acquiring the specialized features of a neuron.
central nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the central nervous system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The central nervous system is the core nervous system that serves an integrating and coordinating function. In vertebrates it consists of the brain, spinal cord and spinal nerves. In those invertebrates with a central nervous system it typically consists of a brain, cerebral ganglia and a nerve cord.
neurogenesis
Generation of cells within the nervous system.
central nervous system neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron whose cell body resides in the central nervous system.
purine nucleotide metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a purine nucleotide, a compound consisting of nucleoside (a purine base linked to a deoxyribose or ribose sugar) esterified with a phosphate moiety at either the 3' or 5'-hydroxyl group of its glycose moiety.
nucleotide biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of nucleotides, any nucleoside that is esterified with (ortho)phosphate or an oligophosphate at any hydroxyl group on the glycose moiety; may be mono-, di- or triphosphate; this definition includes cyclic-nucleotides (nucleoside cyclic phosphates).
axon guidance
The process by which the migration of an axon growth cone is directed to a specific target site in response to a combination of attractive and repulsive cues.
neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron.
axonogenesis
Generation of a long process of a neuron, that carries efferent (outgoing) action potentials from the cell body towards target cells.
potassium ion transport
The directed movement of potassium ions (K+) into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
nucleoside monophosphate biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a nucleoside monophosphate, a glycosamine consisting of a base linked to a deoxyribose or ribose sugar esterified with phosphate on its glycose moiety.
G-protein signaling, coupled to cyclic nucleotide second messenger
The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a G-protein coupled receptor binding to its physiological ligand, followed by modulation of a nucleotide cyclase activity and a subsequent change in the concentration of a cyclic nucleotide.
cAMP metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving the nucleotide cAMP (cyclic AMP, adenosine 3',5'-cyclophosphate).
cyclic nucleotide biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a cyclic nucleotide, a nucleotide in which the phosphate group is in diester linkage to two positions on the sugar residue.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
integral to membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer. When used to describe a protein, indicates that all or part of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
voltage-gated potassium channel complex
A protein complex that forms a transmembrane channel through which potassium ions may cross a cell membrane in response to changes in membrane potential.
axon
The long process of a neuron that conducts nerve impulses, usually away from the cell body to the terminals and varicosities, which are sites of storage and release of neurotransmitter.
dendrite
A neuron projection that has a short, tapering, often branched, morphology, receives and integrates signals from other neurons or from sensory stimuli, and conducts a nerve impulse towards the axon or the cell body. In most neurons, the impulse is conveyed from dendrites to axon via the cell body, but in some types of unipolar neuron, the impulse does not travel via the cell body.
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
asymmetric synapse
A type of synapse occurring between an axon and a dendritic spine or dendritic shaft. Asymmetric synapses, the most abundant synapse type in the central nervous system, involve axons that contain predominantly spherical vesicles and contain a thickened postsynaptic density.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
axon part
A part of an axon, a cell projection of a neuron.
ion channel complex
A protein complex that spans a membrane and forms a water-filled channel across the phospholipid bilayer allowing selective ion transport down its electrochemical gradient.
cation channel complex
An ion channel complex through which cations pass.
potassium channel complex
An ion channel complex through which potassium ions pass.
cell projection
A prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
neuron projection
A prolongation or process extending from a nerve cell, e.g. an axon or dendrite.
neuronal cell body
The portion of a neuron that includes the nucleus, but excludes all cell projections such as axons and dendrites.
dendritic spine
Protrusion from a dendrite. Spines are specialised subcellular compartments involved in the synaptic transmission. They are linked to the dendritic shaft by a restriction. Because of their bulb shape, they function as a biochemical and an electrical compartment. Spine remodeling is though to be involved in synaptic plasticity.
protein complex
Any macromolecular complex composed of two or more polypeptide subunits, which may or may not be identical. Protein complexes may have other associated non-protein prosthetic groups, such as nucleotides, metal ions or other small molecules.
axon terminus
Terminal inflated portion of the axon, containing the specialized apparatus necessary to release neurotransmitters. The axon terminus is considered to be the whole region of thickening and the terminal button is a specialized region of it.
cell body
The portion of a cell bearing surface projections such as axons, dendrites, cilia, or flagella that includes the nucleus, but excludes all cell projections.
neuron projection terminus
The specialized, terminal region of a neuron projection such as an axon or a dendrite.
neuron spine
A small membranous protrusion, often ending in a bulbous head and attached to the neuron by a narrow stalk or neck.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
synapse part
Any constituent part of a synapse, the junction between a nerve fiber of one neuron and another neuron or muscle fiber or glial cell.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell projection part
Any constituent part of a cell projection, a prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
synapse
The junction between a nerve fiber of one neuron and another neuron or muscle fiber or glial cell; the site of interneuronal communication. As the nerve fiber approaches the synapse it enlarges into a specialized structure, the presynaptic nerve ending, which contains mitochondria and synaptic vesicles. At the tip of the nerve ending is the presynaptic membrane; facing it, and separated from it by a minute cleft (the synaptic cleft) is a specialized area of membrane on the receiving cell, known as the postsynaptic membrane. In response to the arrival of nerve impulses, the presynaptic nerve ending secretes molecules of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. These diffuse across the cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane.
postsynaptic membrane
A specialized area of membrane facing the presynaptic membrane on the tip of the nerve ending and separated from it by a minute cleft (the synaptic cleft). Neurotransmitters across the synaptic cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
synapse part
Any constituent part of a synapse, the junction between a nerve fiber of one neuron and another neuron or muscle fiber or glial cell.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
postsynaptic membrane
A specialized area of membrane facing the presynaptic membrane on the tip of the nerve ending and separated from it by a minute cleft (the synaptic cleft). Neurotransmitters across the synaptic cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane.
cell projection part
Any constituent part of a cell projection, a prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
ion channel complex
A protein complex that spans a membrane and forms a water-filled channel across the phospholipid bilayer allowing selective ion transport down its electrochemical gradient.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
neuron projection terminus
The specialized, terminal region of a neuron projection such as an axon or a dendrite.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
axon terminus
Terminal inflated portion of the axon, containing the specialized apparatus necessary to release neurotransmitters. The axon terminus is considered to be the whole region of thickening and the terminal button is a specialized region of it.
axon part
A part of an axon, a cell projection of a neuron.
dendritic spine
Protrusion from a dendrite. Spines are specialised subcellular compartments involved in the synaptic transmission. They are linked to the dendritic shaft by a restriction. Because of their bulb shape, they function as a biochemical and an electrical compartment. Spine remodeling is though to be involved in synaptic plasticity.
dendritic spine
Protrusion from a dendrite. Spines are specialised subcellular compartments involved in the synaptic transmission. They are linked to the dendritic shaft by a restriction. Because of their bulb shape, they function as a biochemical and an electrical compartment. Spine remodeling is though to be involved in synaptic plasticity.
ion channel complex
A protein complex that spans a membrane and forms a water-filled channel across the phospholipid bilayer allowing selective ion transport down its electrochemical gradient.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
voltage-gated potassium channel complex
A protein complex that forms a transmembrane channel through which potassium ions may cross a cell membrane in response to changes in membrane potential.
voltage-gated potassium channel complex
A protein complex that forms a transmembrane channel through which potassium ions may cross a cell membrane in response to changes in membrane potential.

protein binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any protein or protein complex (a complex of two or more proteins that may include other nonprotein molecules).
molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
catalytic activity
Catalysis of a biochemical reaction at physiological temperatures. In biologically catalyzed reactions, the reactants are known as substrates, and the catalysts are naturally occurring macromolecular substances known as enzymes. Enzymes possess specific binding sites for substrates, and are usually composed wholly or largely of protein, but RNA that has catalytic activity (ribozyme) is often also regarded as enzymatic.
receptor binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with one or more specific sites on a receptor molecule, a macromolecule that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function.
inositol or phosphatidylinositol phosphodiesterase activity
NA
phosphoinositide phospholipase C activity
Catalysis of the reaction: 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate + H2O = D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate + diacylglycerol.
phospholipase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of a glycerophospholipid.
phospholipase C activity
Catalysis of the reaction: a phospholipid + H2O = 1,2-diacylglycerol + a phosphatidate.
protein kinase activity
Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction: a protein + ATP = a phosphoprotein + ADP.
protein tyrosine kinase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate.
transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein-L-tyrosine = ADP + a protein-L-tyrosine phosphate, to initiate a change in cell activity.
signal transducer activity
Mediates the transfer of a signal from the outside to the inside of a cell by means other than the introduction of the signal molecule itself into the cell.
receptor activity
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell activity.
transmembrane receptor activity
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell activity, and spanning to the membrane of either the cell or an organelle.
G-protein coupled receptor activity
A receptor that binds an extracellular ligand and transmits the signal to a heterotrimeric G-protein complex. These receptors are characteristically seven-transmembrane receptors and are made up of hetero- or homodimers.
serotonin receptor activity
Combining with the biogenic amine serotonin, a neurotransmitter and hormone found in vertebrates, invertebrates and plants, to initiate a change in cell activity.
ephrin receptor activity
Combining with an ephrin to initiate a change in cell activity.
transmembrane-ephrin receptor activity
NA
hormone activity
The action characteristic of a hormone, any substance formed in very small amounts in one specialized organ or group of cells and carried (sometimes in the bloodstream) to another organ or group of cells in the same organism, upon which it has a specific regulatory action. The term was originally applied to agents with a stimulatory physiological action in vertebrate animals (as opposed to a chalone, which has a depressant action). Usage is now extended to regulatory compounds in lower animals and plants, and to synthetic substances having comparable effects; all bind receptors and trigger some biological process.
neuropeptide hormone activity
The action characteristic of a neuropeptide hormone, any peptide hormone that acts in the central nervous system. A neuropeptide is any of several types of molecules found in brain tissue, composed of short chains of amino acids; they include endorphins, enkephalins, vasopressin, and others. They are often localized in axon terminals at synapses and are classified as putative neurotransmitters, although some are also hormones.
transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
ion channel activity
Catalysis of facilitated diffusion of an ion (by an energy-independent process) by passage through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel without evidence for a carrier-mediated mechanism.
voltage-gated ion channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a voltage-gated channel. An ion is an atom or group of atoms carrying an electric charge by virtue of having gained or lost one or more electrons.
voltage-gated potassium channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a potassium ion by a voltage-gated channel.
cation channel activity
Catalysis of the energy-independent passage of cations across a lipid bilayer down a concentration gradient.
potassium channel activity
Catalysis of facilitated diffusion of a potassium ion (by an energy-independent process) involving passage through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel without evidence for a carrier-mediated mechanism.
transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a substance from one side of a membrane to the other.
binding
The selective, non-covalent, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
phosphoric diester hydrolase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of a phosphodiester to give a phosphomonoester and a free hydroxyl group.
drug binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a drug, any naturally occurring or synthetic substance, other than a nutrient, that, when administered or applied to an organism, affects the structure or functioning of the organism; in particular, any such substance used in the diagnosis, prevention, or treatment of disease.
G-protein coupled amine receptor activity
A receptor that binds an extracellular amine and transmits the signal to a heterotrimeric G-protein complex. These receptors are characteristically seven-transmembrane receptors and are made up of hetero- or homodimers.
cation transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of cation from one side of the membrane to the other.
ion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of an ion from one side of a membrane to the other.
channel activity
Catalysis of energy-independent facilitated diffusion, mediated by passage of a solute through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel. Stereospecificity is not exhibited but this transport may be specific for a particular molecular species or class of molecules.
lipase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of a lipid or phospholipid.
kinase activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a substrate molecule.
transferase activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a group, e.g. a methyl group, glycosyl group, acyl group, phosphorus-containing, or other groups, from one compound (generally regarded as the donor) to another compound (generally regarded as the acceptor). Transferase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 2.
transferase activity, transferring phosphorus-containing groups
Catalysis of the transfer of a phosphorus-containing group from one compound (donor) to another (acceptor).
phosphotransferase activity, alcohol group as acceptor
Catalysis of the transfer of a phosphorus-containing group from one compound (donor) to an alcohol group (acceptor).
hydrolase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of various bonds, e.g. C-O, C-N, C-C, phosphoric anhydride bonds, etc. Hydrolase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 3.
hydrolase activity, acting on ester bonds
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of any ester bond.
transmembrane receptor protein kinase activity
NA
passive transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute from one side of the membrane to the other, down the solute's concentration gradient.
voltage-gated channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a solute by a channel whose open state is dependent on the voltage across the membrane in which it is embedded.
gated channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a solute by a channel that opens in response to a specific stimulus.
substrate-specific channel activity
Catalysis of energy-independent facilitated diffusion, mediated by passage of a specific solute through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel. Stereospecificity is not exhibited but this transport may be specific for a particular molecular species or class of molecules.
voltage-gated cation channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a cation by a voltage-gated channel. A cation is a positively charged ion.
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
substrate-specific transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of a specific substance or group of related substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
phosphoric ester hydrolase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: RPO-R' + H2O = RPOOH + R'H. This reaction is the hydrolysis of any phosphoric ester bond, any ester formed from orthophosphoric acid, O=P(OH)3.
amine binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group.
serotonin binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine), a monoamine neurotransmitter occurring in the peripheral and central nervous systems, also having hormonal properties.
molecular transducer activity
The molecular function that accepts an input of one form and creates an output of a different form.
all
NA
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
protein kinase activity
Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction: a protein + ATP = a phosphoprotein + ADP.
substrate-specific channel activity
Catalysis of energy-independent facilitated diffusion, mediated by passage of a specific solute through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel. Stereospecificity is not exhibited but this transport may be specific for a particular molecular species or class of molecules.
ion channel activity
Catalysis of facilitated diffusion of an ion (by an energy-independent process) by passage through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel without evidence for a carrier-mediated mechanism.
transmembrane receptor protein kinase activity
NA
phospholipase C activity
Catalysis of the reaction: a phospholipid + H2O = 1,2-diacylglycerol + a phosphatidate.
cation channel activity
Catalysis of the energy-independent passage of cations across a lipid bilayer down a concentration gradient.
transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein-L-tyrosine = ADP + a protein-L-tyrosine phosphate, to initiate a change in cell activity.
phosphoinositide phospholipase C activity
Catalysis of the reaction: 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate + H2O = D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate + diacylglycerol.
voltage-gated ion channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a voltage-gated channel. An ion is an atom or group of atoms carrying an electric charge by virtue of having gained or lost one or more electrons.
voltage-gated cation channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a cation by a voltage-gated channel. A cation is a positively charged ion.
voltage-gated potassium channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a potassium ion by a voltage-gated channel.
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 04080 | 7.038e-10 | 3.813 | 22 | 206 | Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction |
| 04020 | 8.457e-05 | 2.684 | 13 | 145 | Calcium signaling pathway |
| 04360 | 7.291e-04 | 1.962 | 10 | 106 | Axon guidance |
| 04540 | 2.708e-03 | 1.092 | 7 | 59 | Gap junction |
| 04730 | 9.852e-03 | 0.9995 | 6 | 54 | Long-term depression |
| 04971 | 1.596e-02 | 1.111 | 6 | 60 | Gastric acid secretion |
| 04720 | 4.576e-02 | 0.981 | 5 | 53 | Long-term potentiation |
ADAMTS8ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 8 (ENSG00000134917), score: 0.88 ADCYAP1adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide 1 (pituitary) (ENSG00000141433), score: 0.83 ADRA1Dadrenergic, alpha-1D-, receptor (ENSG00000171873), score: 0.92 AK5adenylate kinase 5 (ENSG00000154027), score: 0.9 ANO3anoctamin 3 (ENSG00000134343), score: 0.91 ARCactivity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein (ENSG00000198576), score: 0.91 ATRNL1attractin-like 1 (ENSG00000107518), score: 0.87 BAI1brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor 1 (ENSG00000181790), score: 0.84 BCL11AB-cell CLL/lymphoma 11A (zinc finger protein) (ENSG00000119866), score: 0.88 BCL11BB-cell CLL/lymphoma 11B (zinc finger protein) (ENSG00000127152), score: 0.92 C11orf87chromosome 11 open reading frame 87 (ENSG00000185742), score: 0.88 C13orf36chromosome 13 open reading frame 36 (ENSG00000180440), score: 0.98 C1orf95chromosome 1 open reading frame 95 (ENSG00000203685), score: 0.84 C1QL2complement component 1, q subcomponent-like 2 (ENSG00000144119), score: 0.88 C20orf103chromosome 20 open reading frame 103 (ENSG00000125869), score: 0.86 C2orf55chromosome 2 open reading frame 55 (ENSG00000196872), score: 0.81 C2orf80chromosome 2 open reading frame 80 (ENSG00000188674), score: 0.89 C5orf40chromosome 5 open reading frame 40 (ENSG00000172568), score: 0.8 C8orf46chromosome 8 open reading frame 46 (ENSG00000169085), score: 0.84 C9orf91chromosome 9 open reading frame 91 (ENSG00000157693), score: 0.82 CACNG3calcium channel, voltage-dependent, gamma subunit 3 (ENSG00000006116), score: 0.95 CALYcalcyon neuron-specific vesicular protein (ENSG00000130643), score: 0.8 CAMK1Gcalcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IG (ENSG00000008118), score: 0.9 CAMK2Acalcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II alpha (ENSG00000070808), score: 0.91 CBLN2cerebellin 2 precursor (ENSG00000141668), score: 0.94 CBLN4cerebellin 4 precursor (ENSG00000054803), score: 0.97 CCKBRcholecystokinin B receptor (ENSG00000110148), score: 0.83 CDH12cadherin 12, type 2 (N-cadherin 2) (ENSG00000154162), score: 0.91 CDH8cadherin 8, type 2 (ENSG00000150394), score: 0.95 CDH9cadherin 9, type 2 (T1-cadherin) (ENSG00000113100), score: 0.9 CDK5R2cyclin-dependent kinase 5, regulatory subunit 2 (p39) (ENSG00000171450), score: 0.8 CHGAchromogranin A (parathyroid secretory protein 1) (ENSG00000100604), score: 0.89 CHRM1cholinergic receptor, muscarinic 1 (ENSG00000168539), score: 0.95 CHRM3cholinergic receptor, muscarinic 3 (ENSG00000133019), score: 0.94 CHST1carbohydrate (keratan sulfate Gal-6) sulfotransferase 1 (ENSG00000175264), score: 0.85 CNTN3contactin 3 (plasmacytoma associated) (ENSG00000113805), score: 0.81 CNTN5contactin 5 (ENSG00000149972), score: 0.82 CNTNAP5contactin associated protein-like 5 (ENSG00000155052), score: 0.89 CPNE6copine VI (neuronal) (ENSG00000100884), score: 0.82 CREG2cellular repressor of E1A-stimulated genes 2 (ENSG00000175874), score: 0.93 CRHcorticotropin releasing hormone (ENSG00000147571), score: 0.96 CSMD3CUB and Sushi multiple domains 3 (ENSG00000164796), score: 0.88 CSRNP3cysteine-serine-rich nuclear protein 3 (ENSG00000178662), score: 0.84 CYP46A1cytochrome P450, family 46, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000036530), score: 0.87 DCLK1doublecortin-like kinase 1 (ENSG00000133083), score: 0.82 DCXdoublecortin (ENSG00000077279), score: 0.86 DDNdendrin (ENSG00000181418), score: 0.83 DGKBdiacylglycerol kinase, beta 90kDa (ENSG00000136267), score: 0.92 DGKZdiacylglycerol kinase, zeta 104kDa (ENSG00000149091), score: 0.8 DLX1distal-less homeobox 1 (ENSG00000144355), score: 0.95 DLX2distal-less homeobox 2 (ENSG00000115844), score: 0.83 DLX5distal-less homeobox 5 (ENSG00000105880), score: 0.81 DPP10dipeptidyl-peptidase 10 (non-functional) (ENSG00000175497), score: 0.88 DRP2dystrophin related protein 2 (ENSG00000102385), score: 0.88 DSCAMDown syndrome cell adhesion molecule (ENSG00000171587), score: 0.87 EFNA3ephrin-A3 (ENSG00000143590), score: 0.85 EFNB3ephrin-B3 (ENSG00000108947), score: 0.85 EGR3early growth response 3 (ENSG00000179388), score: 0.9 ELFN2extracellular leucine-rich repeat and fibronectin type III domain containing 2 (ENSG00000166897), score: 0.88 ENC1ectodermal-neural cortex 1 (with BTB-like domain) (ENSG00000171617), score: 0.94 EPHA4EPH receptor A4 (ENSG00000116106), score: 0.83 EPHA5EPH receptor A5 (ENSG00000145242), score: 0.94 EPHB6EPH receptor B6 (ENSG00000106123), score: 0.82 EPHX4epoxide hydrolase 4 (ENSG00000172031), score: 0.92 EXTL1exostoses (multiple)-like 1 (ENSG00000158008), score: 0.8 FAM19A1family with sequence similarity 19 (chemokine (C-C motif)-like), member A1 (ENSG00000183662), score: 0.98 FAM19A2family with sequence similarity 19 (chemokine (C-C motif)-like), member A2 (ENSG00000198673), score: 0.89 FAM49Afamily with sequence similarity 49, member A (ENSG00000197872), score: 0.88 FAM5Bfamily with sequence similarity 5, member B (ENSG00000198797), score: 0.89 FEZF2FEZ family zinc finger 2 (ENSG00000153266), score: 0.94 FLRT2fibronectin leucine rich transmembrane protein 2 (ENSG00000185070), score: 0.81 FOXG1forkhead box G1 (ENSG00000176165), score: 0.82 FREM3FRAS1 related extracellular matrix 3 (ENSG00000183090), score: 0.8 FRMPD4FERM and PDZ domain containing 4 (ENSG00000169933), score: 0.83 FSCN1fascin homolog 1, actin-bundling protein (Strongylocentrotus purpuratus) (ENSG00000075618), score: 0.8 GABRA4gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, alpha 4 (ENSG00000109158), score: 0.89 GJD2gap junction protein, delta 2, 36kDa (ENSG00000159248), score: 0.85 GLRA3glycine receptor, alpha 3 (ENSG00000145451), score: 0.89 GPR123G protein-coupled receptor 123 (ENSG00000197177), score: 0.85 GPR26G protein-coupled receptor 26 (ENSG00000154478), score: 0.98 GPR45G protein-coupled receptor 45 (ENSG00000135973), score: 0.84 GRIA3glutamate receptor, ionotrophic, AMPA 3 (ENSG00000125675), score: 0.85 GRIN2Bglutamate receptor, ionotropic, N-methyl D-aspartate 2B (ENSG00000150086), score: 0.83 GRM2glutamate receptor, metabotropic 2 (ENSG00000164082), score: 0.82 HOPXHOP homeobox (ENSG00000171476), score: 0.83 HRH1histamine receptor H1 (ENSG00000196639), score: 0.83 HS3ST2heparan sulfate (glucosamine) 3-O-sulfotransferase 2 (ENSG00000122254), score: 0.94 HS3ST4heparan sulfate (glucosamine) 3-O-sulfotransferase 4 (ENSG00000182601), score: 0.85 HTR1A5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 1A (ENSG00000178394), score: 0.96 HTR1B5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 1B (ENSG00000135312), score: 0.86 HTR1E5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 1E (ENSG00000168830), score: 0.87 HTR2A5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 2A (ENSG00000102468), score: 0.98 HTR2C5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 2C (ENSG00000147246), score: 0.88 HTR45-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 4 (ENSG00000164270), score: 0.83 HTR65-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 6 (ENSG00000158748), score: 0.95 KCNA4potassium voltage-gated channel, shaker-related subfamily, member 4 (ENSG00000182255), score: 0.85 KCNA6potassium voltage-gated channel, shaker-related subfamily, member 6 (ENSG00000151079), score: 0.91 KCNB1potassium voltage-gated channel, Shab-related subfamily, member 1 (ENSG00000158445), score: 0.8 KCNB2potassium voltage-gated channel, Shab-related subfamily, member 2 (ENSG00000182674), score: 0.94 KCNC2potassium voltage-gated channel, Shaw-related subfamily, member 2 (ENSG00000166006), score: 0.97 KCNF1potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily F, member 1 (ENSG00000162975), score: 0.9 KCNG1potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily G, member 1 (ENSG00000026559), score: 0.86 KCNH3potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily H (eag-related), member 3 (ENSG00000135519), score: 0.9 KCNH4potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily H (eag-related), member 4 (ENSG00000089558), score: 0.97 KCNK2potassium channel, subfamily K, member 2 (ENSG00000082482), score: 0.82 KCNN1potassium intermediate/small conductance calcium-activated channel, subfamily N, member 1 (ENSG00000105642), score: 0.85 KCNQ3potassium voltage-gated channel, KQT-like subfamily, member 3 (ENSG00000184156), score: 0.9 KCNQ5potassium voltage-gated channel, KQT-like subfamily, member 5 (ENSG00000185760), score: 0.96 KCNS1potassium voltage-gated channel, delayed-rectifier, subfamily S, member 1 (ENSG00000124134), score: 0.98 KCNS2potassium voltage-gated channel, delayed-rectifier, subfamily S, member 2 (ENSG00000156486), score: 0.98 KCNV1potassium channel, subfamily V, member 1 (ENSG00000164794), score: 0.99 KCTD16potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 16 (ENSG00000183775), score: 0.83 KCTD4potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 4 (ENSG00000180332), score: 0.9 KIAA0748KIAA0748 (ENSG00000135426), score: 0.96 LHX2LIM homeobox 2 (ENSG00000106689), score: 0.82 LMO4LIM domain only 4 (ENSG00000143013), score: 0.92 LPPR3lipid phosphate phosphatase-related protein type 3 (ENSG00000129951), score: 0.91 LPPR4lipid phosphate phosphatase-related protein type 4 (ENSG00000117600), score: 0.92 LPPR5lipid phosphate phosphatase-related protein type 5 (ENSG00000117598), score: 0.93 LRFN2leucine rich repeat and fibronectin type III domain containing 2 (ENSG00000156564), score: 0.91 LRFN5leucine rich repeat and fibronectin type III domain containing 5 (ENSG00000165379), score: 0.87 LRRC4Cleucine rich repeat containing 4C (ENSG00000148948), score: 0.84 LRRC55leucine rich repeat containing 55 (ENSG00000183908), score: 0.81 LRTM2leucine-rich repeats and transmembrane domains 2 (ENSG00000166159), score: 0.97 LY6Hlymphocyte antigen 6 complex, locus H (ENSG00000176956), score: 0.84 MAP2K1mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 (ENSG00000169032), score: 0.8 MAPK1mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 (ENSG00000100030), score: 0.84 MARCH4membrane-associated ring finger (C3HC4) 4 (ENSG00000144583), score: 0.84 MAS1MAS1 oncogene (ENSG00000130368), score: 0.94 MAST3microtubule associated serine/threonine kinase 3 (ENSG00000099308), score: 0.85 MATKmegakaryocyte-associated tyrosine kinase (ENSG00000007264), score: 0.9 MCHR2melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 2 (ENSG00000152034), score: 0.87 MDGA2MAM domain containing glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor 2 (ENSG00000139915), score: 0.81 MEF2Cmyocyte enhancer factor 2C (ENSG00000081189), score: 0.88 MGAT5Bmannosyl (alpha-1,6-)-glycoprotein beta-1,6-N-acetyl-glucosaminyltransferase, isozyme B (ENSG00000167889), score: 0.87 MKL2MKL/myocardin-like 2 (ENSG00000186260), score: 0.91 MMDmonocyte to macrophage differentiation-associated (ENSG00000108960), score: 0.81 MMP17matrix metallopeptidase 17 (membrane-inserted) (ENSG00000198598), score: 0.9 NCALDneurocalcin delta (ENSG00000104490), score: 0.91 NCANneurocan (ENSG00000130287), score: 0.83 NECAB1N-terminal EF-hand calcium binding protein 1 (ENSG00000123119), score: 0.89 NEFLneurofilament, light polypeptide (ENSG00000104725), score: 0.82 NELFnasal embryonic LHRH factor (ENSG00000165802), score: 0.8 NETO1neuropilin (NRP) and tolloid (TLL)-like 1 (ENSG00000166342), score: 0.96 NEUROD6neurogenic differentiation 6 (ENSG00000164600), score: 0.94 NGBneuroglobin (ENSG00000165553), score: 0.9 NLKnemo-like kinase (ENSG00000087095), score: 0.89 NPAS1neuronal PAS domain protein 1 (ENSG00000130751), score: 0.92 NPBWR2neuropeptides B/W receptor 2 (ENSG00000125522), score: 0.89 NPY2Rneuropeptide Y receptor Y2 (ENSG00000185149), score: 0.81 NRG3neuregulin 3 (ENSG00000185737), score: 0.94 NRSN1neurensin 1 (ENSG00000152954), score: 0.86 NSFN-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor (ENSG00000073969), score: 0.82 OPRD1opioid receptor, delta 1 (ENSG00000116329), score: 1 PCDH19protocadherin 19 (ENSG00000165194), score: 0.96 PCDH20protocadherin 20 (ENSG00000197991), score: 0.86 PCDH8protocadherin 8 (ENSG00000136099), score: 0.94 PCSK1proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 1 (ENSG00000175426), score: 0.97 PDE1Bphosphodiesterase 1B, calmodulin-dependent (ENSG00000123360), score: 0.82 PDE2Aphosphodiesterase 2A, cGMP-stimulated (ENSG00000186642), score: 0.82 PDE8Bphosphodiesterase 8B (ENSG00000113231), score: 0.89 PDYNprodynorphin (ENSG00000101327), score: 0.88 PEX5Lperoxisomal biogenesis factor 5-like (ENSG00000114757), score: 0.84 PGM2L1phosphoglucomutase 2-like 1 (ENSG00000165434), score: 0.86 PLCB1phospholipase C, beta 1 (phosphoinositide-specific) (ENSG00000182621), score: 0.84 PNCKpregnancy up-regulated non-ubiquitously expressed CaM kinase (ENSG00000130822), score: 0.84 PNMAL2PNMA-like 2 (ENSG00000204851), score: 0.83 PNOCprepronociceptin (ENSG00000168081), score: 0.93 PRDM8PR domain containing 8 (ENSG00000152784), score: 0.83 PRICKLE2prickle homolog 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000163637), score: 0.87 PRKG2protein kinase, cGMP-dependent, type II (ENSG00000138669), score: 0.82 PTPN5protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 5 (striatum-enriched) (ENSG00000110786), score: 0.88 RASL10ARAS-like, family 10, member A (ENSG00000100276), score: 0.88 RGS4regulator of G-protein signaling 4 (ENSG00000117152), score: 0.95 RHEBL1Ras homolog enriched in brain like 1 (ENSG00000167550), score: 0.82 RIMBP2RIMS binding protein 2 (ENSG00000060709), score: 0.87 RORBRAR-related orphan receptor B (ENSG00000198963), score: 0.89 RPRMreprimo, TP53 dependent G2 arrest mediator candidate (ENSG00000177519), score: 0.83 RSPO2R-spondin 2 homolog (Xenopus laevis) (ENSG00000147655), score: 0.9 RTBDNretbindin (ENSG00000132026), score: 0.82 SATB2SATB homeobox 2 (ENSG00000119042), score: 0.91 SCG2secretogranin II (ENSG00000171951), score: 0.86 SCN3Bsodium channel, voltage-gated, type III, beta (ENSG00000166257), score: 0.92 SEMA3Asema domain, immunoglobulin domain (Ig), short basic domain, secreted, (semaphorin) 3A (ENSG00000075213), score: 0.83 SERPINI1serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade I (neuroserpin), member 1 (ENSG00000163536), score: 0.87 SH2D5SH2 domain containing 5 (ENSG00000189410), score: 0.89 SHC3SHC (Src homology 2 domain containing) transforming protein 3 (ENSG00000148082), score: 0.89 SLC10A4solute carrier family 10 (sodium/bile acid cotransporter family), member 4 (ENSG00000145248), score: 0.86 SLC24A4solute carrier family 24 (sodium/potassium/calcium exchanger), member 4 (ENSG00000140090), score: 0.82 SLC39A10solute carrier family 39 (zinc transporter), member 10 (ENSG00000196950), score: 0.85 SLC8A3solute carrier family 8 (sodium/calcium exchanger), member 3 (ENSG00000100678), score: 0.8 SLIT1slit homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000187122), score: 0.94 SLITRK1SLIT and NTRK-like family, member 1 (ENSG00000178235), score: 0.89 SLITRK5SLIT and NTRK-like family, member 5 (ENSG00000165300), score: 0.84 SNTG1syntrophin, gamma 1 (ENSG00000147481), score: 0.85 SP1Sp1 transcription factor (ENSG00000185591), score: -0.83 SPRED3sprouty-related, EVH1 domain containing 3 (ENSG00000188766), score: 0.81 SSTsomatostatin (ENSG00000157005), score: 0.92 ST6GALNAC5ST6 (alpha-N-acetyl-neuraminyl-2,3-beta-galactosyl-1,3)-N-acetylgalactosaminide alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase 5 (ENSG00000117069), score: 0.93 STK32Cserine/threonine kinase 32C (ENSG00000165752), score: 0.86 STX1Asyntaxin 1A (brain) (ENSG00000106089), score: 0.81 STYK1serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase 1 (ENSG00000060140), score: 0.96 SYT5synaptotagmin V (ENSG00000129990), score: 0.85 TBR1T-box, brain, 1 (ENSG00000136535), score: 0.95 TMEM132Dtransmembrane protein 132D (ENSG00000151952), score: 0.97 TMEM155transmembrane protein 155 (ENSG00000164112), score: 0.97 TMEM196transmembrane protein 196 (ENSG00000173452), score: 0.92 TRPM2transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily M, member 2 (ENSG00000142185), score: 0.83 VGFVGF nerve growth factor inducible (ENSG00000128564), score: 0.89 VIPvasoactive intestinal peptide (ENSG00000146469), score: 0.9 VSTM2AV-set and transmembrane domain containing 2A (ENSG00000170419), score: 0.96 VSTM2BV-set and transmembrane domain containing 2B (ENSG00000187135), score: 0.81 VSTM2LV-set and transmembrane domain containing 2 like (ENSG00000132821), score: 0.83 VWC2Lvon Willebrand factor C domain-containing protein 2-like (ENSG00000174453), score: 0.91 WNT10Bwingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 10B (ENSG00000169884), score: 0.92 WNT7Awingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 7A (ENSG00000154764), score: 0.83 XKR4XK, Kell blood group complex subunit-related family, member 4 (ENSG00000206579), score: 0.81 ZDHHC22zinc finger, DHHC-type containing 22 (ENSG00000177108), score: 0.82 ZMAT4zinc finger, matrin type 4 (ENSG00000165061), score: 0.91 ZNF365zinc finger protein 365 (ENSG00000138311), score: 0.81
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ptr_br_m3_ca1 | ptr | br | m | 3 |
| ptr_br_m2_ca1 | ptr | br | m | 2 |
| ggo_br_m_ca1 | ggo | br | m | _ |
| ptr_br_m5_ca1 | ptr | br | m | 5 |
| hsa_br_f_ca1 | hsa | br | f | _ |
| ptr_br_m1_ca1 | ptr | br | m | 1 |
| ggo_br_f_ca1 | ggo | br | f | _ |
| hsa_br_m3_ca1 | hsa | br | m | 3 |
| hsa_br_m2_ca1 | hsa | br | m | 2 |
| ppy_br_f_ca1 | ppy | br | f | _ |
| ppa_br_m_ca1 | ppa | br | m | _ |
| ppa_br_f1_ca1 | ppa | br | f | 1 |
| ptr_br_m4_ca1 | ptr | br | m | 4 |
| hsa_br_m7_ca1 | hsa | br | m | 7 |
| mml_br_m1_ca1 | mml | br | m | 1 |
| mml_br_f_ca1 | mml | br | f | _ |
| ppy_br_m_ca1 | ppy | br | m | _ |
| mml_br_m2_ca1 | mml | br | m | 2 |