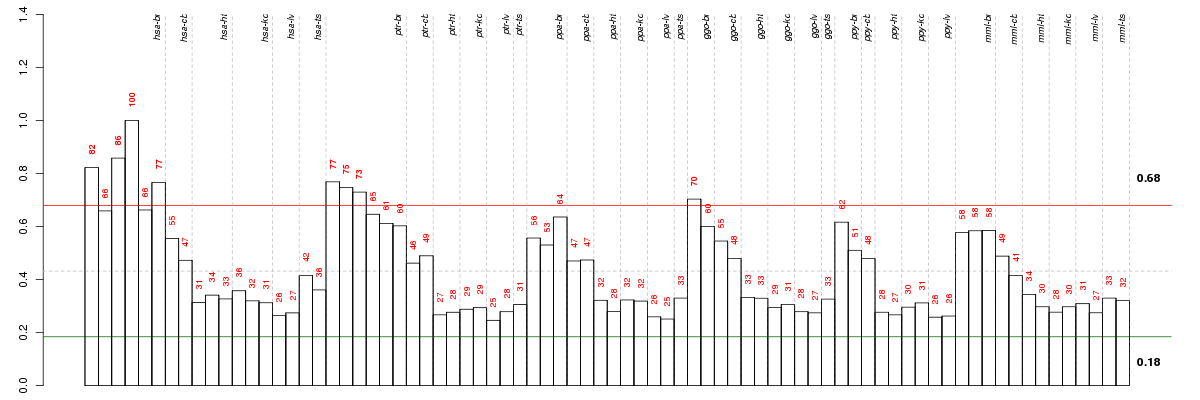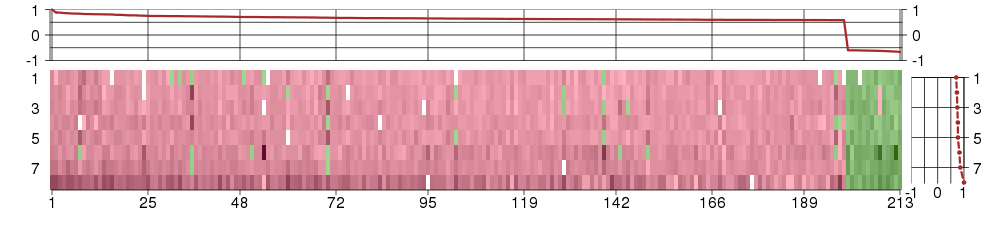

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

regulation of action potential
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of action potential creation, propagation or termination. An action potential is a spike of membrane depolarization and repolarization that travels along the membrane of a cell.
cell fate specification
The process involved in the specification of cell identity. Once specification has taken place, a cell will be committed to differentiate down a specific pathway if left in its normal environment.
system process
A multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system. An organ system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a biological objective.
cellular ion homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of ions at the level of a cell.
cell communication
Any process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
ensheathment of neurons
The process whereby glial cells envelop neuronal cell bodies and/or axons to form an insulating layer. This can take the form of myelinating or non-myelinating ensheathment.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of nervous tissue over time, from its formation to its mature state.
neurological system process
A organ system process carried out by any of the organs or tissues of neurological system.
central nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the central nervous system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The central nervous system is the core nervous system that serves an integrating and coordinating function. In vertebrates it consists of the brain, spinal cord and spinal nerves. In those invertebrates with a central nervous system it typically consists of a brain, cerebral ganglia and a nerve cord.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
axon ensheathment
Any process by which the axon of a neuron is insulated, and that insulation maintained, thereby preventing dispersion of the electrical signal.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
glial cell differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the specialized features of a glial cell.
transmission of nerve impulse
The neurological system process by which a signal is transmitted through the nervous system by synaptic transmission and the sequential electrochemical polarization and depolarization that travels across the membrane of a nerve cell (neuron) in response to stimulation.
regulation of action potential in neuron
The process that modulates the membrane potential involved in the propagation of a signal in a neuron.
cellular homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state at the level of the cell.
spinal cord development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the spinal cord over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The spinal cord primarily conducts sensory and motor nerve impulses between the brain and the peripheral nervous tissues.
cell differentiation in spinal cord
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells of the spinal cord. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate.
spinal cord oligodendrocyte cell differentiation
The process whereby neuroepithelial cells in the neural tube acquire specialized structural and/or functional features of oligodendrocytes. Oligodendrocytes are non-neuronal cells. The primary function of oligodendrocytes is the myelination of nerve axons in the central nervous system. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate.
spinal cord oligodendrocyte cell fate specification
The process whereby a cell becomes capable of differentiating autonomously into an oligodendrocyte in an environment that is neutral with respect to the developmental pathway.
oligodendrocyte cell fate specification
The process whereby a cell becomes capable of differentiating autonomously into an oligodendrocyte in an environment that is neutral with respect to the developmental pathway. Upon specification, the cell fate can be reversed.
oligodendrocyte cell fate commitment
The process whereby the developmental fate of a cell becomes restricted such that it will develop into an oligodendrocyte.
glial cell fate specification
The process whereby a cell becomes capable of differentiating autonomously into a glial cell in an environment that is neutral with respect to the developmental pathway. Upon specification, the cell fate can be reversed.
glial cell fate commitment
The process whereby the developmental fate of a cell becomes restricted such that it will develop into a glial cell.
neurogenesis
Generation of cells within the nervous system.
signaling process
Any biological process involved in the generation, transmission, reception, or interpretation of a signal. A signal is an entity used to transmit or convey information.
signaling
The entirety of a process whereby information is transmitted. This process begins with the initiation of the signal and ends when a response has been triggered.
signal transmission
The process whereby a signal is released and/or conveyed from one location to another.
cell differentiation
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
gliogenesis
The process by which glial cells are generated. This includes the production of glial progenitors and their differentiation into mature glia.
regulation of membrane potential
Any process that modulates the establishment or extent of a membrane potential, the electric potential existing across any membrane arising from charges in the membrane itself and from the charges present in the media on either side of the membrane.
myelination
The process by which myelin sheaths are formed and maintained around neurons. Oligodendrocytes in the brain and spinal cord and Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system wrap axons with compact layers of their plasma membrane. Adjacent myelin segments are separated by a non-myelinated stretch of axon called a node of Ranvier.
homeostatic process
Any biological process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state.
cell fate commitment
The commitment of cells to specific cell fates and their capacity to differentiate into particular kinds of cells. Positional information is established through protein signals that emanate from a localized source within a cell (the initial one-cell zygote) or within a developmental field.
ion homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of ions within an organism or cell.
oligodendrocyte differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the specialized features of an oligodendrocyte. An oligodendrocyte is a type of glial cell involved in myelinating the axons of neurons in the central nervous system.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
chemical homeostasis
Any biological process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of a chemical.
cellular chemical homeostasis
Any biological process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of a chemical at the level of the cell.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of biological quality
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological quality. A biological quality is a measurable attribute of an organism or part of an organism, such as size, mass, shape, color, etc.
all
NA
signaling process
Any biological process involved in the generation, transmission, reception, or interpretation of a signal. A signal is an entity used to transmit or convey information.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
transmission of nerve impulse
The neurological system process by which a signal is transmitted through the nervous system by synaptic transmission and the sequential electrochemical polarization and depolarization that travels across the membrane of a nerve cell (neuron) in response to stimulation.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
cell fate commitment
The commitment of cells to specific cell fates and their capacity to differentiate into particular kinds of cells. Positional information is established through protein signals that emanate from a localized source within a cell (the initial one-cell zygote) or within a developmental field.
cell fate specification
The process involved in the specification of cell identity. Once specification has taken place, a cell will be committed to differentiate down a specific pathway if left in its normal environment.
transmission of nerve impulse
The neurological system process by which a signal is transmitted through the nervous system by synaptic transmission and the sequential electrochemical polarization and depolarization that travels across the membrane of a nerve cell (neuron) in response to stimulation.
cell differentiation in spinal cord
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells of the spinal cord. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate.
cellular homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state at the level of the cell.
ensheathment of neurons
The process whereby glial cells envelop neuronal cell bodies and/or axons to form an insulating layer. This can take the form of myelinating or non-myelinating ensheathment.
glial cell fate commitment
The process whereby the developmental fate of a cell becomes restricted such that it will develop into a glial cell.
glial cell fate specification
The process whereby a cell becomes capable of differentiating autonomously into a glial cell in an environment that is neutral with respect to the developmental pathway. Upon specification, the cell fate can be reversed.
ensheathment of neurons
The process whereby glial cells envelop neuronal cell bodies and/or axons to form an insulating layer. This can take the form of myelinating or non-myelinating ensheathment.
central nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the central nervous system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The central nervous system is the core nervous system that serves an integrating and coordinating function. In vertebrates it consists of the brain, spinal cord and spinal nerves. In those invertebrates with a central nervous system it typically consists of a brain, cerebral ganglia and a nerve cord.
neurogenesis
Generation of cells within the nervous system.
spinal cord development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the spinal cord over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The spinal cord primarily conducts sensory and motor nerve impulses between the brain and the peripheral nervous tissues.
oligodendrocyte differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the specialized features of an oligodendrocyte. An oligodendrocyte is a type of glial cell involved in myelinating the axons of neurons in the central nervous system.
cellular chemical homeostasis
Any biological process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of a chemical at the level of the cell.
spinal cord oligodendrocyte cell differentiation
The process whereby neuroepithelial cells in the neural tube acquire specialized structural and/or functional features of oligodendrocytes. Oligodendrocytes are non-neuronal cells. The primary function of oligodendrocytes is the myelination of nerve axons in the central nervous system. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate.
oligodendrocyte cell fate commitment
The process whereby the developmental fate of a cell becomes restricted such that it will develop into an oligodendrocyte.
spinal cord oligodendrocyte cell fate specification
The process whereby a cell becomes capable of differentiating autonomously into an oligodendrocyte in an environment that is neutral with respect to the developmental pathway.
glial cell differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the specialized features of a glial cell.
oligodendrocyte cell fate specification
The process whereby a cell becomes capable of differentiating autonomously into an oligodendrocyte in an environment that is neutral with respect to the developmental pathway. Upon specification, the cell fate can be reversed.
cellular ion homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of ions at the level of a cell.
regulation of action potential in neuron
The process that modulates the membrane potential involved in the propagation of a signal in a neuron.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
integral to membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer. When used to describe a protein, indicates that all or part of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
proteinaceous extracellular matrix
A layer consisting mainly of proteins (especially collagen) and glycosaminoglycans (mostly as proteoglycans) that forms a sheet underlying or overlying cells such as endothelial and epithelial cells. The proteins are secreted by cells in the vicinity. An example of this component is found in Mus musculus.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
extracellular matrix
A structure lying external to one or more cells, which provides structural support for cells or tissues; may be completely external to the cell (as in animals) or be part of the cell (as in plants).
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
myelin sheath
An electrically insulating fatty layer that surrounds the axons of many neurons. It is an outgrowth of glial cells: Schwann cells supply the myelin for peripheral neurons while oligodendrocytes supply it to those of the central nervous system.
compact myelin
The portion of the myelin sheath in which layers of cell membrane are tightly juxtaposed, completely excluding cytoplasm. The juxtaposed cytoplasmic surfaces form the major dense line, while the juxtaposed extracellular surfaces form the interperiod line visible in electron micrographs.
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
all
NA
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
compact myelin
The portion of the myelin sheath in which layers of cell membrane are tightly juxtaposed, completely excluding cytoplasm. The juxtaposed cytoplasmic surfaces form the major dense line, while the juxtaposed extracellular surfaces form the interperiod line visible in electron micrographs.

AATKapoptosis-associated tyrosine kinase (ENSG00000181409), score: 0.61 ABCA2ATP-binding cassette, sub-family A (ABC1), member 2 (ENSG00000107331), score: 0.73 ABHD12abhydrolase domain containing 12 (ENSG00000100997), score: 0.59 ACTR1AARP1 actin-related protein 1 homolog A, centractin alpha (yeast) (ENSG00000138107), score: 0.6 ADAMTS14ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 14 (ENSG00000138316), score: 0.82 ADAMTS4ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 4 (ENSG00000158859), score: 0.59 ADAMTS8ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 8 (ENSG00000134917), score: 0.61 ADCK1aarF domain containing kinase 1 (ENSG00000063761), score: 0.59 AGPAT41-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase 4 (lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase, delta) (ENSG00000026652), score: 0.66 AK5adenylate kinase 5 (ENSG00000154027), score: 0.59 ANLNanillin, actin binding protein (ENSG00000011426), score: 0.67 ANO4anoctamin 4 (ENSG00000151572), score: 0.63 APLP1amyloid beta (A4) precursor-like protein 1 (ENSG00000105290), score: 0.59 ARHGAP22Rho GTPase activating protein 22 (ENSG00000128805), score: 0.65 ARHGAP29Rho GTPase activating protein 29 (ENSG00000137962), score: -0.67 ARRDC2arrestin domain containing 2 (ENSG00000105643), score: 0.59 ASPRV1aspartic peptidase, retroviral-like 1 (ENSG00000244617), score: 0.58 ATP10BATPase, class V, type 10B (ENSG00000118322), score: 0.76 BACE1beta-site APP-cleaving enzyme 1 (ENSG00000186318), score: 0.62 BCAS1breast carcinoma amplified sequence 1 (ENSG00000064787), score: 0.64 C11orf9chromosome 11 open reading frame 9 (ENSG00000124920), score: 0.78 C12orf76chromosome 12 open reading frame 76 (ENSG00000174456), score: 0.59 C1orf198chromosome 1 open reading frame 198 (ENSG00000119280), score: 0.73 C22orf9chromosome 22 open reading frame 9 (ENSG00000100364), score: 0.73 C2orf82chromosome 2 open reading frame 82 (ENSG00000182600), score: 0.63 C6orf1chromosome 6 open reading frame 1 (ENSG00000186577), score: 0.61 CAPN3calpain 3, (p94) (ENSG00000092529), score: 0.69 CAPN9calpain 9 (ENSG00000135773), score: 0.71 CCT8chaperonin containing TCP1, subunit 8 (theta) (ENSG00000156261), score: -0.62 CD22CD22 molecule (ENSG00000012124), score: 0.88 CD2APCD2-associated protein (ENSG00000198087), score: -0.6 CDH20cadherin 20, type 2 (ENSG00000101542), score: 0.6 CDHR1cadherin-related family member 1 (ENSG00000148600), score: 0.62 CDK2cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (ENSG00000123374), score: -0.61 CDK2AP1cyclin-dependent kinase 2 associated protein 1 (ENSG00000111328), score: 0.59 CERCAMcerebral endothelial cell adhesion molecule (ENSG00000167123), score: 0.74 CHADLchondroadherin-like (ENSG00000100399), score: 0.77 CHRM1cholinergic receptor, muscarinic 1 (ENSG00000168539), score: 0.59 CHST6carbohydrate (N-acetylglucosamine 6-O) sulfotransferase 6 (ENSG00000183196), score: 0.65 CLCA4chloride channel accessory 4 (ENSG00000016602), score: 0.81 CLDN11claudin 11 (ENSG00000013297), score: 0.66 CLDND1claudin domain containing 1 (ENSG00000080822), score: 0.74 CLN8ceroid-lipofuscinosis, neuronal 8 (epilepsy, progressive with mental retardation) (ENSG00000182372), score: 0.64 CMTM5CKLF-like MARVEL transmembrane domain containing 5 (ENSG00000166091), score: 0.74 CNP2',3'-cyclic nucleotide 3' phosphodiesterase (ENSG00000173786), score: 0.86 CNTN2contactin 2 (axonal) (ENSG00000184144), score: 0.62 COL11A2collagen, type XI, alpha 2 (ENSG00000204248), score: 0.59 COL16A1collagen, type XVI, alpha 1 (ENSG00000084636), score: 0.63 COL20A1collagen, type XX, alpha 1 (ENSG00000101203), score: 0.58 COL9A2collagen, type IX, alpha 2 (ENSG00000049089), score: 0.67 CPNE2copine II (ENSG00000140848), score: 0.72 CSRP1cysteine and glycine-rich protein 1 (ENSG00000159176), score: 0.61 DAAM2dishevelled associated activator of morphogenesis 2 (ENSG00000146122), score: 0.79 DMBT1deleted in malignant brain tumors 1 (ENSG00000187908), score: 0.69 DNAJC7DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 7 (ENSG00000168259), score: 0.61 DNMBPdynamin binding protein (ENSG00000107554), score: -0.65 DOHHdeoxyhypusine hydroxylase/monooxygenase (ENSG00000129932), score: 0.67 DSCAML1Down syndrome cell adhesion molecule like 1 (ENSG00000177103), score: 0.63 DUOXA1dual oxidase maturation factor 1 (ENSG00000140254), score: 0.58 E2F1E2F transcription factor 1 (ENSG00000101412), score: 0.59 EDIL3EGF-like repeats and discoidin I-like domains 3 (ENSG00000164176), score: 0.64 EFSembryonal Fyn-associated substrate (ENSG00000100842), score: 0.7 EIF4EBP2eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E binding protein 2 (ENSG00000148730), score: -0.63 ELOVL1elongation of very long chain fatty acids (FEN1/Elo2, SUR4/Elo3, yeast)-like 1 (ENSG00000066322), score: 0.75 EML2echinoderm microtubule associated protein like 2 (ENSG00000125746), score: 0.74 ENDOD1endonuclease domain containing 1 (ENSG00000149218), score: 0.66 ENPP2ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 2 (ENSG00000136960), score: 0.72 ERMNermin, ERM-like protein (ENSG00000136541), score: 0.7 EVI2Aecotropic viral integration site 2A (ENSG00000126860), score: 0.77 FA2Hfatty acid 2-hydroxylase (ENSG00000103089), score: 0.82 FAM102Afamily with sequence similarity 102, member A (ENSG00000167106), score: 0.66 FAM108B1family with sequence similarity 108, member B1 (ENSG00000107362), score: 0.66 FAM124Afamily with sequence similarity 124A (ENSG00000150510), score: 0.81 FAM125Bfamily with sequence similarity 125, member B (ENSG00000196814), score: 0.65 FAM13Cfamily with sequence similarity 13, member C (ENSG00000148541), score: 0.59 FCHO1FCH domain only 1 (ENSG00000130475), score: 0.62 FEZF2FEZ family zinc finger 2 (ENSG00000153266), score: 0.63 FFAR1free fatty acid receptor 1 (ENSG00000126266), score: 0.84 FGF22fibroblast growth factor 22 (ENSG00000070388), score: 0.71 FNBP1Lformin binding protein 1-like (ENSG00000137942), score: -0.63 FSCN1fascin homolog 1, actin-bundling protein (Strongylocentrotus purpuratus) (ENSG00000075618), score: 0.66 GAB2GRB2-associated binding protein 2 (ENSG00000033327), score: 0.69 GAL3ST1galactose-3-O-sulfotransferase 1 (ENSG00000128242), score: 0.64 GALNT6UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 6 (GalNAc-T6) (ENSG00000139629), score: 0.85 GIPC1GIPC PDZ domain containing family, member 1 (ENSG00000123159), score: 0.62 GJD4gap junction protein, delta 4, 40.1kDa (ENSG00000177291), score: 0.65 GLDNgliomedin (ENSG00000186417), score: 0.81 GLT25D2glycosyltransferase 25 domain containing 2 (ENSG00000198756), score: 0.59 GOLGA7golgin A7 (ENSG00000147533), score: 0.62 GPR123G protein-coupled receptor 123 (ENSG00000197177), score: 0.62 GPR37G protein-coupled receptor 37 (endothelin receptor type B-like) (ENSG00000170775), score: 0.72 GPR78G protein-coupled receptor 78 (ENSG00000155269), score: 0.7 GPRC5BG protein-coupled receptor, family C, group 5, member B (ENSG00000167191), score: 0.59 GRID1glutamate receptor, ionotropic, delta 1 (ENSG00000182771), score: 0.62 GRM3glutamate receptor, metabotropic 3 (ENSG00000198822), score: 0.62 HS3ST4heparan sulfate (glucosamine) 3-O-sulfotransferase 4 (ENSG00000182601), score: 0.59 IFNA2interferon, alpha 2 (ENSG00000188379), score: 0.68 IL1RAPL1interleukin 1 receptor accessory protein-like 1 (ENSG00000169306), score: 0.61 ITPK1inositol 1,3,4-triphosphate 5/6 kinase (ENSG00000100605), score: 0.62 JAK1Janus kinase 1 (ENSG00000162434), score: -0.61 JAM3junctional adhesion molecule 3 (ENSG00000166086), score: 0.61 KCNF1potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily F, member 1 (ENSG00000162975), score: 0.58 KCNH8potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily H (eag-related), member 8 (ENSG00000183960), score: 0.88 KLF11Kruppel-like factor 11 (ENSG00000172059), score: -0.61 KLHL32kelch-like 32 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000186231), score: 0.6 KREMEN2kringle containing transmembrane protein 2 (ENSG00000131650), score: 0.76 LGI3leucine-rich repeat LGI family, member 3 (ENSG00000168481), score: 0.61 LGR5leucine-rich repeat-containing G protein-coupled receptor 5 (ENSG00000139292), score: 0.74 LNX2ligand of numb-protein X 2 (ENSG00000139517), score: -0.6 LOC100294412similar to KIAA0655 protein (ENSG00000130787), score: 0.64 LPPR3lipid phosphate phosphatase-related protein type 3 (ENSG00000129951), score: 0.6 LRIT2leucine-rich repeat, immunoglobulin-like and transmembrane domains 2 (ENSG00000204033), score: 0.62 LYPD5LY6/PLAUR domain containing 5 (ENSG00000159871), score: 0.62 MAGmyelin associated glycoprotein (ENSG00000105695), score: 0.75 MARCKSL1MARCKS-like 1 (ENSG00000175130), score: 0.69 MAST3microtubule associated serine/threonine kinase 3 (ENSG00000099308), score: 0.59 MATN1matrilin 1, cartilage matrix protein (ENSG00000162510), score: 0.66 MID1IP1MID1 interacting protein 1 (gastrulation specific G12 homolog (zebrafish)) (ENSG00000165175), score: 0.59 MKRN3makorin ring finger protein 3 (ENSG00000179455), score: 0.69 MOGmyelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (ENSG00000204655), score: 0.72 MYO9Bmyosin IXB (ENSG00000099331), score: 0.62 NANOS3nanos homolog 3 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000187556), score: 0.59 NIPA1non imprinted in Prader-Willi/Angelman syndrome 1 (ENSG00000170113), score: 0.66 NIPAL4NIPA-like domain containing 4 (ENSG00000172548), score: 1 NKX2-2NK2 homeobox 2 (ENSG00000125820), score: 0.74 NPC1Niemann-Pick disease, type C1 (ENSG00000141458), score: 0.81 NTNG2netrin G2 (ENSG00000196358), score: 0.64 NTSR2neurotensin receptor 2 (ENSG00000169006), score: 0.59 OLIG2oligodendrocyte lineage transcription factor 2 (ENSG00000205927), score: 0.71 OPALINoligodendrocytic myelin paranodal and inner loop protein (ENSG00000197430), score: 0.73 OR2T6olfactory receptor, family 2, subfamily T, member 6 (ENSG00000198104), score: 0.73 P2RX7purinergic receptor P2X, ligand-gated ion channel, 7 (ENSG00000089041), score: 0.71 PACS2phosphofurin acidic cluster sorting protein 2 (ENSG00000179364), score: 0.64 PAQR6progestin and adipoQ receptor family member VI (ENSG00000160781), score: 0.7 PGM2phosphoglucomutase 2 (ENSG00000169299), score: -0.61 PHLDA3pleckstrin homology-like domain, family A, member 3 (ENSG00000174307), score: 0.6 PHLPP1PH domain and leucine rich repeat protein phosphatase 1 (ENSG00000081913), score: 0.64 PIP4K2Aphosphatidylinositol-5-phosphate 4-kinase, type II, alpha (ENSG00000150867), score: 0.77 PKMYT1protein kinase, membrane associated tyrosine/threonine 1 (ENSG00000127564), score: 0.6 PLEKHB1pleckstrin homology domain containing, family B (evectins) member 1 (ENSG00000021300), score: 0.63 PLEKHG3pleckstrin homology domain containing, family G (with RhoGef domain) member 3 (ENSG00000126822), score: 0.64 PLEKHH1pleckstrin homology domain containing, family H (with MyTH4 domain) member 1 (ENSG00000054690), score: 0.66 PLLPplasmolipin (ENSG00000102934), score: 0.66 PLP1proteolipid protein 1 (ENSG00000123560), score: 0.64 PLXNB3plexin B3 (ENSG00000198753), score: 0.7 PMP2peripheral myelin protein 2 (ENSG00000147588), score: 0.68 PMP22peripheral myelin protein 22 (ENSG00000109099), score: 0.6 PNCKpregnancy up-regulated non-ubiquitously expressed CaM kinase (ENSG00000130822), score: 0.59 PPP1R14Aprotein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 14A (ENSG00000167641), score: 0.71 PRAF2PRA1 domain family, member 2 (ENSG00000243279), score: 0.66 PREX1phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate-dependent Rac exchange factor 1 (ENSG00000124126), score: 0.71 PRKCQprotein kinase C, theta (ENSG00000065675), score: 0.69 PRPF18PRP18 pre-mRNA processing factor 18 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000165630), score: -0.65 PRR18proline rich 18 (ENSG00000176381), score: 0.84 PRR5Lproline rich 5 like (ENSG00000135362), score: 0.67 PRR7proline rich 7 (synaptic) (ENSG00000131188), score: 0.64 PSRC1proline/serine-rich coiled-coil 1 (ENSG00000134222), score: 0.67 PTK2PTK2 protein tyrosine kinase 2 (ENSG00000169398), score: 0.74 PTPRHprotein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, H (ENSG00000080031), score: 0.72 PXKPX domain containing serine/threonine kinase (ENSG00000168297), score: 0.66 RAB40BRAB40B, member RAS oncogene family (ENSG00000141542), score: 0.63 RALGDSral guanine nucleotide dissociation stimulator (ENSG00000160271), score: 0.62 RAPGEF5Rap guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 5 (ENSG00000136237), score: 0.65 RASAL1RAS protein activator like 1 (GAP1 like) (ENSG00000111344), score: 0.62 RBP3retinol binding protein 3, interstitial (ENSG00000107618), score: 0.58 RHOGras homolog gene family, member G (rho G) (ENSG00000177105), score: 0.62 RNF220ring finger protein 220 (ENSG00000187147), score: 0.67 ROM1retinal outer segment membrane protein 1 (ENSG00000149489), score: 0.62 RTBDNretbindin (ENSG00000132026), score: 0.59 SAMD4Bsterile alpha motif domain containing 4B (ENSG00000179134), score: 0.62 SEC14L5SEC14-like 5 (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000103184), score: 0.68 SEMA4Dsema domain, immunoglobulin domain (Ig), transmembrane domain (TM) and short cytoplasmic domain, (semaphorin) 4D (ENSG00000187764), score: 0.63 SEMA6Asema domain, transmembrane domain (TM), and cytoplasmic domain, (semaphorin) 6A (ENSG00000092421), score: 0.65 SH3GLB2SH3-domain GRB2-like endophilin B2 (ENSG00000148341), score: 0.65 SH3TC2SH3 domain and tetratricopeptide repeats 2 (ENSG00000169247), score: 0.69 SHC4SHC (Src homology 2 domain containing) family, member 4 (ENSG00000185634), score: 0.59 SIRT2sirtuin 2 (ENSG00000068903), score: 0.84 SLAIN1SLAIN motif family, member 1 (ENSG00000139737), score: 0.66 SLC31A2solute carrier family 31 (copper transporters), member 2 (ENSG00000136867), score: 0.68 SLC44A1solute carrier family 44, member 1 (ENSG00000070214), score: 0.66 SLC5A11solute carrier family 5 (sodium/glucose cotransporter), member 11 (ENSG00000158865), score: 0.79 SLC6A9solute carrier family 6 (neurotransmitter transporter, glycine), member 9 (ENSG00000196517), score: 0.64 SLCO1A2solute carrier organic anion transporter family, member 1A2 (ENSG00000084453), score: 0.61 SMEK1SMEK homolog 1, suppressor of mek1 (Dictyostelium) (ENSG00000100796), score: -0.6 SOHLH1spermatogenesis and oogenesis specific basic helix-loop-helix 1 (ENSG00000165643), score: 0.61 SOX10SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 10 (ENSG00000100146), score: 0.73 SOX8SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 8 (ENSG00000005513), score: 0.75 SP3Sp3 transcription factor (ENSG00000172845), score: -0.62 SSTsomatostatin (ENSG00000157005), score: 0.61 STK32Cserine/threonine kinase 32C (ENSG00000165752), score: 0.59 STOML1stomatin (EPB72)-like 1 (ENSG00000067221), score: 0.62 TBCBtubulin folding cofactor B (ENSG00000105254), score: 0.65 THEMISthymocyte selection associated (ENSG00000172673), score: 0.59 TJAP1tight junction associated protein 1 (peripheral) (ENSG00000137221), score: 0.81 TMC6transmembrane channel-like 6 (ENSG00000141524), score: 0.63 TMEM144transmembrane protein 144 (ENSG00000164124), score: 0.82 TMEM151Atransmembrane protein 151A (ENSG00000179292), score: 0.69 TMEM160transmembrane protein 160 (ENSG00000130748), score: 0.59 TMEM184Btransmembrane protein 184B (ENSG00000198792), score: 0.6 TNFRSF13Ctumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 13C (ENSG00000159958), score: 0.62 TP53INP2tumor protein p53 inducible nuclear protein 2 (ENSG00000078804), score: 0.7 TREM2triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (ENSG00000095970), score: 0.62 TRMT61AtRNA methyltransferase 61 homolog A (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000166166), score: 0.59 TSPAN15tetraspanin 15 (ENSG00000099282), score: 0.61 UGT8UDP glycosyltransferase 8 (ENSG00000174607), score: 0.7 UNC5Cunc-5 homolog C (C. elegans) (ENSG00000182168), score: 0.6 VAMP1vesicle-associated membrane protein 1 (synaptobrevin 1) (ENSG00000139190), score: 0.6 VSTM2BV-set and transmembrane domain containing 2B (ENSG00000187135), score: 0.63 ZCCHC24zinc finger, CCHC domain containing 24 (ENSG00000165424), score: 0.61 ZEB2zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 2 (ENSG00000169554), score: 0.6 ZFP57zinc finger protein 57 homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000204644), score: 0.71 ZNF536zinc finger protein 536 (ENSG00000198597), score: 0.62
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ggo_br_m_ca1 | ggo | br | m | _ |
| ptr_br_m5_ca1 | ptr | br | m | 5 |
| ptr_br_m2_ca1 | ptr | br | m | 2 |
| hsa_br_f_ca1 | hsa | br | f | _ |
| ptr_br_m3_ca1 | ptr | br | m | 3 |
| hsa_br_m7_ca1 | hsa | br | m | 7 |
| hsa_br_m3_ca1 | hsa | br | m | 3 |
| hsa_br_m6_ca1 | hsa | br | m | 6 |