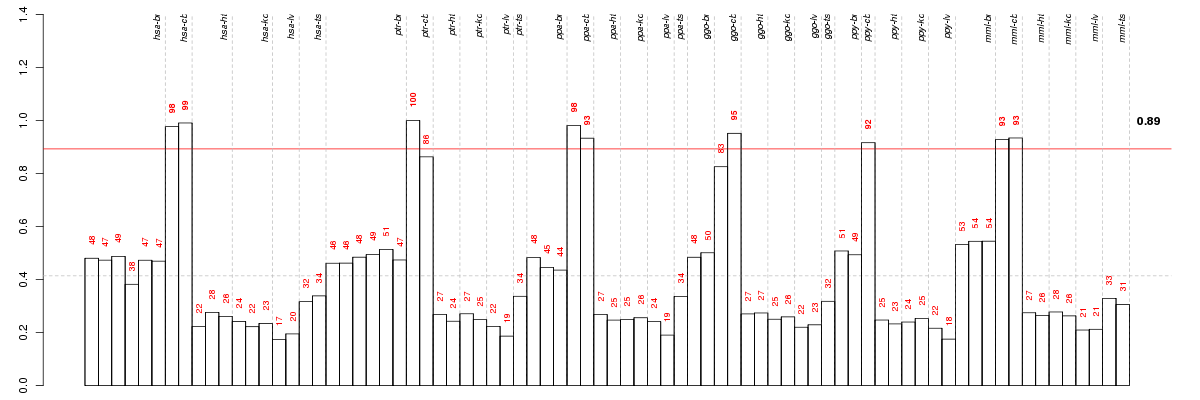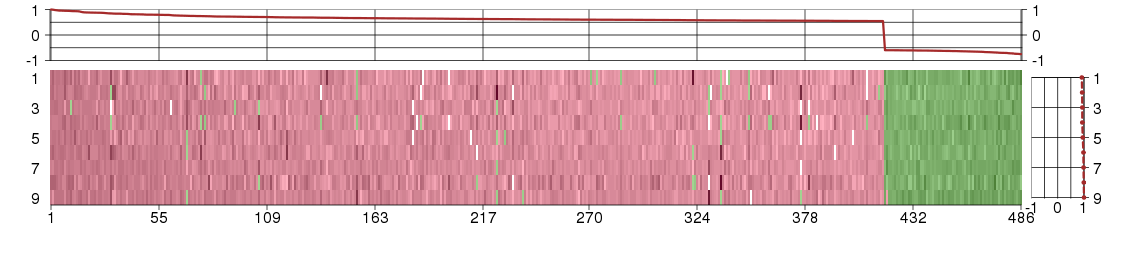

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

chromosome organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level that results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of chromosomes, structures composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins that carries hereditary information.
metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
cell activation
A change in the morphology or behavior of a cell resulting from exposure to an activating factor such as a cellular or soluble ligand.
cell activation involved in immune response
A change in the morphology or behavior of a cell resulting from exposure to an activating factor such as a cellular or soluble ligand, leading to the initiation or perpetuation of an immune response.
lymphocyte activation involved in immune response
A change in morphology and behavior of a lymphocyte resulting from exposure to a specific antigen, mitogen, cytokine, chemokine, cellular ligand, or soluble factor, leading to the initiation or perpetuation of an immune response.
T cell activation involved in immune response
The change in morphology and behavior of a mature or immature T cell resulting from exposure to a mitogen, cytokine, chemokine, cellular ligand, or an antigen for which it is specific, leading to the initiation or perpetuation of an immune response.
alpha-beta T cell activation involved in immune response
The change in morphology and behavior of an alpha-beta T cell resulting from exposure to a mitogen, cytokine, chemokine, cellular ligand, or an antigen for which it is specific, leading to the initiation or perpetuation of an immune response.
T cell differentiation involved in immune response
The process whereby an antigenically nave T cell acquires the specialized features of an effector, regulatory, or memory T cell as part of an immune response. Effector T cells include cells which provide T cell help or exhibit cytotoxicity towards other cells.
alpha-beta T cell differentiation involved in immune response
The process whereby an antigenically nave alpha-beta T cell acquires the specialized features of an effector, regulatory, or memory T cell during an immune response. Effector T cells include cells which provide T cell help or exhibit cytotoxicity towards other cells.
leukocyte activation involved in immune response
A change in morphology and behavior of a leukocyte resulting from exposure to a specific antigen, mitogen, cytokine, cellular ligand, or soluble factor, leading to the initiation or perpetuation of an immune response.
immune system process
Any process involved in the development or functioning of the immune system, an organismal system for calibrated responses to potential internal or invasive threats.
immune system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system whose objective is to provide calibrated responses by an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat, over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
leukocyte differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized hemopoietic precursor cell acquires the specialized features of a plasmacytoid dendritic cell or any cell of the myeloid leukocyte or lymphocyte lineages.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
chromatin organization
Any process that results in the specification, formation or maintenance of the physical structure of eukaryotic chromatin.
transcription
The cellular synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
transcription, DNA-dependent
The cellular synthesis of RNA on a template of DNA.
regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-dependent transcription.
nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds; includes nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, assimilatory/dissimilatory nitrate reduction and the interconversion of nitrogenous organic matter and ammonium.
transport
The directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells, or within a multicellular organism by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
ion transport
The directed movement of charged atoms or small charged molecules into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
cation transport
The directed movement of cations, atoms or small molecules with a net positive charge, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
potassium ion transport
The directed movement of potassium ions (K+) into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
metal ion transport
The directed movement of metal ions, any metal ion with an electric charge, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
organelle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an organelle within a cell. An organelle is an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
cell surface receptor linked signaling pathway
Any series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of an extracellular ligand to a receptor on the surface of the target cell.
enzyme linked receptor protein signaling pathway
Any series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of an extracellular ligand to a receptor on the surface of the target cell, where the receptor possesses catalytic activity or is closely associated with an enzyme such as a protein kinase.
transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway
The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinase binding to its physiological ligand.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of nervous tissue over time, from its formation to its mature state.
central nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the central nervous system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The central nervous system is the core nervous system that serves an integrating and coordinating function. In vertebrates it consists of the brain, spinal cord and spinal nerves. In those invertebrates with a central nervous system it typically consists of a brain, cerebral ganglia and a nerve cord.
brain development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the brain over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Brain development begins with patterning events in the neural tube and ends with the mature structure that is the center of thought and emotion. The brain is responsible for the coordination and control of bodily activities and the interpretation of information from the senses (sight, hearing, smell, etc.).
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
negative regulation of metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
gene expression
The process by which a gene's sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
regulation of gene expression
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
negative regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
posttranscriptional regulation of gene expression
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression after the production of an RNA transcript.
negative regulation of gene expression
Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
monovalent inorganic cation transport
The directed movement of inorganic cations with a valency of one into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. Inorganic cations are atoms or small molecules with a positive charge which do not contain carbon in covalent linkage.
cellular component organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a cellular component.
RNA metabolic process
The cellular chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage.
posttranscriptional gene silencing
The inactivation of gene expression by a posttranscriptional mechanism.
gene silencing
Any transcriptional or post-transcriptional process carried out at the cellular level that results in long-term gene inactivation.
chromatin modification
The alteration of DNA or protein in chromatin, which may result in changing the chromatin structure.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
signaling pathway
The series of molecular events whereby information is sent from one location to another within a living organism or between living organisms.
signaling process
Any biological process involved in the generation, transmission, reception, or interpretation of a signal. A signal is an entity used to transmit or convey information.
signaling
The entirety of a process whereby information is transmitted. This process begins with the initiation of the signal and ends when a response has been triggered.
signal transmission
The process whereby a signal is released and/or conveyed from one location to another.
hemopoiesis
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the myeloid and lymphoid derived organ/tissue systems of the blood and other parts of the body over time, from formation to the mature structure. The site of hemopoiesis is variable during development, but occurs primarily in bone marrow or kidney in many adult vertebrates.
lymphocyte differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized precursor cell acquires specialized features of B cells, T cells, or natural killer cells.
cell differentiation
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state.
T cell differentiation
The process by which a precursor cell type acquires characteristics of a more mature T-cell. A T cell is a type of lymphocyte whose definin characteristic is the expression of a T cell receptor complex.
gene silencing by RNA
Any process by which RNA molecules inactivate expression of target genes.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
RNA biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage. Includes polymerization of ribonucleotide monomers.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
posttranscriptional gene silencing by RNA
Any process of posttranscriptional gene inactivation (silencing) mediated by small RNA molecules that may trigger mRNA degradation or negatively regulate translation.
regulation of gene expression, epigenetic
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression; the process is mitotically or meiotically heritable, or is stably self-propagated in the cytoplasm of a resting cell, and does not entail a change in DNA sequence.
T cell activation
The change in morphology and behavior of a mature or immature T cell resulting from exposure to a mitogen, cytokine, chemokine, cellular ligand, or an antigen for which it is specific.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
leukocyte activation
A change in morphology and behavior of a leukocyte resulting from exposure to a specific antigen, mitogen, cytokine, cellular ligand, or soluble factor.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
alpha-beta T cell activation
The change in morphology and behavior of an alpha-beta T cell resulting from exposure to a mitogen, cytokine, chemokine, cellular ligand, or an antigen for which it is specific.
alpha-beta T cell differentiation
The process whereby a precursor cell type acquires the specialized features of an alpha-beta T cell.
lymphocyte activation
A change in morphology and behavior of a lymphocyte resulting from exposure to a specific antigen, mitogen, cytokine, chemokine, cellular ligand, or soluble factor.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
hemopoietic or lymphoid organ development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of any organ involved in hemopoiesis or lymphoid cell activation over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Such development includes differentiation of resident cell types (stromal cells) and of migratory cell types dependent on the unique microenvironment afforded by the organ for their proper differentiation.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nitrogen or nitrogenous compounds.
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of primary metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism involving those compounds formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleic acids.
all
NA
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
organelle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an organelle within a cell. An organelle is an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
signaling process
Any biological process involved in the generation, transmission, reception, or interpretation of a signal. A signal is an entity used to transmit or convey information.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
negative regulation of metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
negative regulation of metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nitrogen or nitrogenous compounds.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
negative regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
regulation of primary metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism involving those compounds formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cell activation involved in immune response
A change in the morphology or behavior of a cell resulting from exposure to an activating factor such as a cellular or soluble ligand, leading to the initiation or perpetuation of an immune response.
leukocyte activation
A change in morphology and behavior of a leukocyte resulting from exposure to a specific antigen, mitogen, cytokine, cellular ligand, or soluble factor.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
negative regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of gene expression
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
negative regulation of gene expression
Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
leukocyte activation involved in immune response
A change in morphology and behavior of a leukocyte resulting from exposure to a specific antigen, mitogen, cytokine, cellular ligand, or soluble factor, leading to the initiation or perpetuation of an immune response.
lymphocyte activation involved in immune response
A change in morphology and behavior of a lymphocyte resulting from exposure to a specific antigen, mitogen, cytokine, chemokine, cellular ligand, or soluble factor, leading to the initiation or perpetuation of an immune response.
posttranscriptional gene silencing by RNA
Any process of posttranscriptional gene inactivation (silencing) mediated by small RNA molecules that may trigger mRNA degradation or negatively regulate translation.
immune system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system whose objective is to provide calibrated responses by an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat, over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
hemopoietic or lymphoid organ development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of any organ involved in hemopoiesis or lymphoid cell activation over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Such development includes differentiation of resident cell types (stromal cells) and of migratory cell types dependent on the unique microenvironment afforded by the organ for their proper differentiation.
regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
transcription
The cellular synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
gene silencing
Any transcriptional or post-transcriptional process carried out at the cellular level that results in long-term gene inactivation.
negative regulation of gene expression
Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
transcription, DNA-dependent
The cellular synthesis of RNA on a template of DNA.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
RNA biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage. Includes polymerization of ribonucleotide monomers.
regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
transcription
The cellular synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
RNA metabolic process
The cellular chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage.
leukocyte differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized hemopoietic precursor cell acquires the specialized features of a plasmacytoid dendritic cell or any cell of the myeloid leukocyte or lymphocyte lineages.
T cell activation involved in immune response
The change in morphology and behavior of a mature or immature T cell resulting from exposure to a mitogen, cytokine, chemokine, cellular ligand, or an antigen for which it is specific, leading to the initiation or perpetuation of an immune response.
T cell differentiation
The process by which a precursor cell type acquires characteristics of a more mature T-cell. A T cell is a type of lymphocyte whose definin characteristic is the expression of a T cell receptor complex.
lymphocyte differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized precursor cell acquires specialized features of B cells, T cells, or natural killer cells.
central nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the central nervous system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The central nervous system is the core nervous system that serves an integrating and coordinating function. In vertebrates it consists of the brain, spinal cord and spinal nerves. In those invertebrates with a central nervous system it typically consists of a brain, cerebral ganglia and a nerve cord.
brain development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the brain over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Brain development begins with patterning events in the neural tube and ends with the mature structure that is the center of thought and emotion. The brain is responsible for the coordination and control of bodily activities and the interpretation of information from the senses (sight, hearing, smell, etc.).
regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-dependent transcription.
regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-dependent transcription.
posttranscriptional gene silencing
The inactivation of gene expression by a posttranscriptional mechanism.
posttranscriptional gene silencing
The inactivation of gene expression by a posttranscriptional mechanism.
T cell differentiation involved in immune response
The process whereby an antigenically nave T cell acquires the specialized features of an effector, regulatory, or memory T cell as part of an immune response. Effector T cells include cells which provide T cell help or exhibit cytotoxicity towards other cells.
alpha-beta T cell activation involved in immune response
The change in morphology and behavior of an alpha-beta T cell resulting from exposure to a mitogen, cytokine, chemokine, cellular ligand, or an antigen for which it is specific, leading to the initiation or perpetuation of an immune response.
alpha-beta T cell differentiation
The process whereby a precursor cell type acquires the specialized features of an alpha-beta T cell.
potassium ion transport
The directed movement of potassium ions (K+) into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
alpha-beta T cell differentiation involved in immune response
The process whereby an antigenically nave alpha-beta T cell acquires the specialized features of an effector, regulatory, or memory T cell during an immune response. Effector T cells include cells which provide T cell help or exhibit cytotoxicity towards other cells.
alpha-beta T cell differentiation involved in immune response
The process whereby an antigenically nave alpha-beta T cell acquires the specialized features of an effector, regulatory, or memory T cell during an immune response. Effector T cells include cells which provide T cell help or exhibit cytotoxicity towards other cells.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
integral to membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer. When used to describe a protein, indicates that all or part of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
nucleus
A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent.
voltage-gated potassium channel complex
A protein complex that forms a transmembrane channel through which potassium ions may cross a cell membrane in response to changes in membrane potential.
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
ion channel complex
A protein complex that spans a membrane and forms a water-filled channel across the phospholipid bilayer allowing selective ion transport down its electrochemical gradient.
cation channel complex
An ion channel complex through which cations pass.
potassium channel complex
An ion channel complex through which potassium ions pass.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, and prokaryotic structures such as anammoxosomes and pirellulosomes. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
protein complex
Any macromolecular complex composed of two or more polypeptide subunits, which may or may not be identical. Protein complexes may have other associated non-protein prosthetic groups, such as nucleotides, metal ions or other small molecules.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
synapse
The junction between a nerve fiber of one neuron and another neuron or muscle fiber or glial cell; the site of interneuronal communication. As the nerve fiber approaches the synapse it enlarges into a specialized structure, the presynaptic nerve ending, which contains mitochondria and synaptic vesicles. At the tip of the nerve ending is the presynaptic membrane; facing it, and separated from it by a minute cleft (the synaptic cleft) is a specialized area of membrane on the receiving cell, known as the postsynaptic membrane. In response to the arrival of nerve impulses, the presynaptic nerve ending secretes molecules of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. These diffuse across the cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
ion channel complex
A protein complex that spans a membrane and forms a water-filled channel across the phospholipid bilayer allowing selective ion transport down its electrochemical gradient.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
ion channel complex
A protein complex that spans a membrane and forms a water-filled channel across the phospholipid bilayer allowing selective ion transport down its electrochemical gradient.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
voltage-gated potassium channel complex
A protein complex that forms a transmembrane channel through which potassium ions may cross a cell membrane in response to changes in membrane potential.
voltage-gated potassium channel complex
A protein complex that forms a transmembrane channel through which potassium ions may cross a cell membrane in response to changes in membrane potential.

protein binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any protein or protein complex (a complex of two or more proteins that may include other nonprotein molecules).
molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
nucleic acid binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any nucleic acid.
DNA binding
Any molecular function by which a gene product interacts selectively with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid).
sequence-specific DNA binding transcription factor activity
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a specific DNA sequence in order to modulate transcription. The transcription factor may or may not also interact selectively with a protein or macromolecular complex.
transcription cofactor activity
The function that links a sequence-specific transcription factor to the core RNA polymerase II complex but does not bind DNA itself.
transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
ion channel activity
Catalysis of facilitated diffusion of an ion (by an energy-independent process) by passage through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel without evidence for a carrier-mediated mechanism.
voltage-gated ion channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a voltage-gated channel. An ion is an atom or group of atoms carrying an electric charge by virtue of having gained or lost one or more electrons.
voltage-gated potassium channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a potassium ion by a voltage-gated channel.
cation channel activity
Catalysis of the energy-independent passage of cations across a lipid bilayer down a concentration gradient.
potassium channel activity
Catalysis of facilitated diffusion of a potassium ion (by an energy-independent process) involving passage through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel without evidence for a carrier-mediated mechanism.
transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a substance from one side of a membrane to the other.
binding
The selective, non-covalent, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
metal ion binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any metal ion.
transcription factor binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a transcription factor, any protein required to initiate or regulate transcription.
zinc ion binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with zinc (Zn) ions.
cation transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of cation from one side of the membrane to the other.
ion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of an ion from one side of a membrane to the other.
channel activity
Catalysis of energy-independent facilitated diffusion, mediated by passage of a solute through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel. Stereospecificity is not exhibited but this transport may be specific for a particular molecular species or class of molecules.
passive transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute from one side of the membrane to the other, down the solute's concentration gradient.
voltage-gated channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a solute by a channel whose open state is dependent on the voltage across the membrane in which it is embedded.
gated channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a solute by a channel that opens in response to a specific stimulus.
substrate-specific channel activity
Catalysis of energy-independent facilitated diffusion, mediated by passage of a specific solute through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel. Stereospecificity is not exhibited but this transport may be specific for a particular molecular species or class of molecules.
voltage-gated cation channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a cation by a voltage-gated channel. A cation is a positively charged ion.
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
substrate-specific transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of a specific substance or group of related substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
transcription regulator activity
Plays a role in regulating transcription; may bind a promoter or enhancer DNA sequence or interact with a DNA-binding transcription factor.
ion binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with ions, charged atoms or groups of atoms.
cation binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with cations, charged atoms or groups of atoms with a net positive charge.
sequence-specific DNA binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with DNA of a specific nucleotide composition, e.g. GC-rich DNA binding, or with a specific sequence motif or type of DNA e.g. promotor binding or rDNA binding.
transition metal ion binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a transition metal ions; a transition metal is an element whose atom has an incomplete d-subshell of extranuclear electrons, or which gives rise to a cation or cations with an incomplete d-subshell. Transition metals often have more than one valency state. Biologically relevant transition metals include vanadium, manganese, iron, copper, cobalt, nickel, molybdenum and silver.
all
NA
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
transcription cofactor activity
The function that links a sequence-specific transcription factor to the core RNA polymerase II complex but does not bind DNA itself.
substrate-specific channel activity
Catalysis of energy-independent facilitated diffusion, mediated by passage of a specific solute through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel. Stereospecificity is not exhibited but this transport may be specific for a particular molecular species or class of molecules.
ion channel activity
Catalysis of facilitated diffusion of an ion (by an energy-independent process) by passage through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel without evidence for a carrier-mediated mechanism.
cation channel activity
Catalysis of the energy-independent passage of cations across a lipid bilayer down a concentration gradient.
voltage-gated ion channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a voltage-gated channel. An ion is an atom or group of atoms carrying an electric charge by virtue of having gained or lost one or more electrons.
voltage-gated cation channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a cation by a voltage-gated channel. A cation is a positively charged ion.
voltage-gated potassium channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a potassium ion by a voltage-gated channel.
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00601 | 5.241e-03 | 0.5746 | 5 | 19 | Glycosphingolipid biosynthesis - lacto and neolacto series |
| 04010 | 3.261e-02 | 6.502 | 15 | 215 | MAPK signaling pathway |
| 05200 | 4.576e-02 | 8.165 | 17 | 270 | Pathways in cancer |
| 00603 | 4.643e-02 | 0.3024 | 3 | 10 | Glycosphingolipid biosynthesis - globo series |
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-129/129-5p | 1.791e-04 | 13.54 | 37 | 275 |
ABCC8ATP-binding cassette, sub-family C (CFTR/MRP), member 8 (ENSG00000006071), score: 0.55 ACHEacetylcholinesterase (ENSG00000087085), score: 0.56 ACVR2Bactivin A receptor, type IIB (ENSG00000114739), score: 0.59 ADAM22ADAM metallopeptidase domain 22 (ENSG00000008277), score: 0.6 ADARB1adenosine deaminase, RNA-specific, B1 (ENSG00000197381), score: 0.67 AFF2AF4/FMR2 family, member 2 (ENSG00000155966), score: 0.64 AGPAT21-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase 2 (lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase, beta) (ENSG00000169692), score: -0.6 AKAP13A kinase (PRKA) anchor protein 13 (ENSG00000170776), score: -0.62 AKNAAT-hook transcription factor (ENSG00000106948), score: -0.6 AMIGO3adhesion molecule with Ig-like domain 3 (ENSG00000176020), score: 0.57 ANKLE1ankyrin repeat and LEM domain containing 1 (ENSG00000160117), score: 0.64 ANKRD6ankyrin repeat domain 6 (ENSG00000135299), score: 0.55 ANKS6ankyrin repeat and sterile alpha motif domain containing 6 (ENSG00000165138), score: 0.62 ANXA11annexin A11 (ENSG00000122359), score: -0.67 ARID1BAT rich interactive domain 1B (SWI1-like) (ENSG00000049618), score: 0.61 ARMC8armadillo repeat containing 8 (ENSG00000114098), score: 0.66 ARPC2actin related protein 2/3 complex, subunit 2, 34kDa (ENSG00000163466), score: -0.74 ARVCFarmadillo repeat gene deleted in velocardiofacial syndrome (ENSG00000099889), score: 0.64 ATF7activating transcription factor 7 (ENSG00000170653), score: 0.63 ATP2A3ATPase, Ca++ transporting, ubiquitous (ENSG00000074370), score: 0.6 B3GALTLbeta 1,3-galactosyltransferase-like (ENSG00000187676), score: -0.65 B3GNT2UDP-GlcNAc:betaGal beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 2 (ENSG00000170340), score: -0.61 B4GALT6UDP-Gal:betaGlcNAc beta 1,4- galactosyltransferase, polypeptide 6 (ENSG00000118276), score: 0.55 BACH2BTB and CNC homology 1, basic leucine zipper transcription factor 2 (ENSG00000112182), score: 0.56 BAHCC1BAH domain and coiled-coil containing 1 (ENSG00000171282), score: 0.69 BARHL1BarH-like homeobox 1 (ENSG00000125492), score: 0.99 BARHL2BarH-like homeobox 2 (ENSG00000143032), score: 0.95 BCL6B-cell CLL/lymphoma 6 (ENSG00000113916), score: 0.6 BICD1bicaudal D homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000151746), score: 0.68 BLOC1S1biogenesis of lysosomal organelles complex-1, subunit 1 (ENSG00000135441), score: -0.6 BPTFbromodomain PHD finger transcription factor (ENSG00000171634), score: 0.62 BRWD3bromodomain and WD repeat domain containing 3 (ENSG00000165288), score: 0.57 BTBD3BTB (POZ) domain containing 3 (ENSG00000132640), score: 0.55 BTG3BTG family, member 3 (ENSG00000154640), score: -0.67 BTN2A1butyrophilin, subfamily 2, member A1 (ENSG00000112763), score: 0.69 C11orf30chromosome 11 open reading frame 30 (ENSG00000158636), score: 0.57 C15orf27chromosome 15 open reading frame 27 (ENSG00000169758), score: 0.76 C16orf11chromosome 16 open reading frame 11 (ENSG00000161992), score: 0.71 C17orf28chromosome 17 open reading frame 28 (ENSG00000167861), score: 0.58 C17orf68chromosome 17 open reading frame 68 (ENSG00000178971), score: 0.59 C1orf127chromosome 1 open reading frame 127 (ENSG00000175262), score: 0.69 C20orf117chromosome 20 open reading frame 117 (ENSG00000149639), score: 0.79 C5orf24chromosome 5 open reading frame 24 (ENSG00000181904), score: 0.58 C6orf115chromosome 6 open reading frame 115 (ENSG00000146386), score: -0.7 C7orf16chromosome 7 open reading frame 16 (ENSG00000106341), score: 0.78 C8orf79chromosome 8 open reading frame 79 (ENSG00000170941), score: 0.79 CA10carbonic anhydrase X (ENSG00000154975), score: 0.57 CA8carbonic anhydrase VIII (ENSG00000178538), score: 0.72 CACNA1Acalcium channel, voltage-dependent, P/Q type, alpha 1A subunit (ENSG00000141837), score: 0.68 CACNA1Gcalcium channel, voltage-dependent, T type, alpha 1G subunit (ENSG00000006283), score: 0.56 CACNA2D2calcium channel, voltage-dependent, alpha 2/delta subunit 2 (ENSG00000007402), score: 0.57 CACNB4calcium channel, voltage-dependent, beta 4 subunit (ENSG00000182389), score: 0.6 CAMK4calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV (ENSG00000152495), score: 0.57 CAMKK2calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2, beta (ENSG00000110931), score: 0.59 CAP1CAP, adenylate cyclase-associated protein 1 (yeast) (ENSG00000131236), score: -0.62 CAPNS1calpain, small subunit 1 (ENSG00000126247), score: -0.61 CBLN1cerebellin 1 precursor (ENSG00000102924), score: 0.88 CBLN3cerebellin 3 precursor (ENSG00000139899), score: 0.86 CCDC109Acoiled-coil domain containing 109A (ENSG00000156026), score: 0.71 CCDC120coiled-coil domain containing 120 (ENSG00000147144), score: 0.55 CCDC78coiled-coil domain containing 78 (ENSG00000162004), score: 0.57 CCNG2cyclin G2 (ENSG00000138764), score: 0.59 CCNJLcyclin J-like (ENSG00000135083), score: 0.64 CDAN1congenital dyserythropoietic anemia, type I (ENSG00000140326), score: 0.56 CDC14BCDC14 cell division cycle 14 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000081377), score: -0.6 CDC25Bcell division cycle 25 homolog B (S. pombe) (ENSG00000101224), score: 0.61 CDC42BPGCDC42 binding protein kinase gamma (DMPK-like) (ENSG00000171219), score: 0.63 CDH15cadherin 15, type 1, M-cadherin (myotubule) (ENSG00000129910), score: 1 CDH23cadherin-related 23 (ENSG00000107736), score: 0.64 CDH24cadherin 24, type 2 (ENSG00000139880), score: 0.62 CDH7cadherin 7, type 2 (ENSG00000081138), score: 0.81 CDKN1Bcyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B (p27, Kip1) (ENSG00000111276), score: 0.58 CDONCdon homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000064309), score: 0.79 CDR2Lcerebellar degeneration-related protein 2-like (ENSG00000109089), score: 0.65 CECR2cat eye syndrome chromosome region, candidate 2 (ENSG00000099954), score: 0.72 CELF1CUGBP, Elav-like family member 1 (ENSG00000149187), score: 0.61 CERKLceramide kinase-like (ENSG00000188452), score: 0.82 CHD7chromodomain helicase DNA binding protein 7 (ENSG00000171316), score: 0.89 CHD9chromodomain helicase DNA binding protein 9 (ENSG00000177200), score: 0.6 CHGBchromogranin B (secretogranin 1) (ENSG00000089199), score: 0.6 CHN2chimerin (chimaerin) 2 (ENSG00000106069), score: 0.72 CHRNA3cholinergic receptor, nicotinic, alpha 3 (ENSG00000080644), score: 0.76 CLK4CDC-like kinase 4 (ENSG00000113240), score: 0.55 CLVS2clavesin 2 (ENSG00000146352), score: 0.65 CNOT2CCR4-NOT transcription complex, subunit 2 (ENSG00000111596), score: 0.72 CNPY1canopy 1 homolog (zebrafish) (ENSG00000146910), score: 0.94 CNR1cannabinoid receptor 1 (brain) (ENSG00000118432), score: 0.55 CNTN6contactin 6 (ENSG00000134115), score: 0.75 COL13A1collagen, type XIII, alpha 1 (ENSG00000197467), score: 0.74 COL27A1collagen, type XXVII, alpha 1 (ENSG00000196739), score: 0.63 COL5A2collagen, type V, alpha 2 (ENSG00000204262), score: -0.64 CORO2Acoronin, actin binding protein, 2A (ENSG00000106789), score: 0.67 CPLX4complexin 4 (ENSG00000166569), score: 0.58 CRAMP1LCrm, cramped-like (Drosophila) (ENSG00000007545), score: 0.56 CREB3L2cAMP responsive element binding protein 3-like 2 (ENSG00000182158), score: -0.66 CREBBPCREB binding protein (ENSG00000005339), score: 0.56 CRTAMcytotoxic and regulatory T cell molecule (ENSG00000109943), score: 0.98 CTCFCCCTC-binding factor (zinc finger protein) (ENSG00000102974), score: 0.66 CTNNB1catenin (cadherin-associated protein), beta 1, 88kDa (ENSG00000168036), score: 0.6 CYFIP1cytoplasmic FMR1 interacting protein 1 (ENSG00000068793), score: -0.61 DAB1disabled homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000173406), score: 0.57 DAB2IPDAB2 interacting protein (ENSG00000136848), score: 0.67 DCLRE1BDNA cross-link repair 1B (ENSG00000118655), score: 0.6 DCP1ADCP1 decapping enzyme homolog A (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000162290), score: 0.59 DDX26BDEAD/H (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp/His) box polypeptide 26B (ENSG00000165359), score: 0.62 DGCR8DiGeorge syndrome critical region gene 8 (ENSG00000128191), score: 0.66 DGKDdiacylglycerol kinase, delta 130kDa (ENSG00000077044), score: 0.64 DGKGdiacylglycerol kinase, gamma 90kDa (ENSG00000058866), score: 0.62 DHRS13dehydrogenase/reductase (SDR family) member 13 (ENSG00000167536), score: 0.69 DIP2BDIP2 disco-interacting protein 2 homolog B (Drosophila) (ENSG00000066084), score: 0.63 DISP2dispatched homolog 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000140323), score: 0.6 DIXDC1DIX domain containing 1 (ENSG00000150764), score: 0.55 DNASE1L2deoxyribonuclease I-like 2 (ENSG00000167968), score: 0.62 DNM3dynamin 3 (ENSG00000197959), score: 0.57 DNMT3ADNA (cytosine-5-)-methyltransferase 3 alpha (ENSG00000119772), score: 0.68 DOPEY2dopey family member 2 (ENSG00000142197), score: 0.69 DPF3D4, zinc and double PHD fingers, family 3 (ENSG00000205683), score: 0.65 DUOX1dual oxidase 1 (ENSG00000137857), score: 0.69 DYSFdysferlin, limb girdle muscular dystrophy 2B (autosomal recessive) (ENSG00000135636), score: -0.64 EBF1early B-cell factor 1 (ENSG00000164330), score: 0.59 ECE1endothelin converting enzyme 1 (ENSG00000117298), score: -0.72 ECE2endothelin converting enzyme 2 (ENSG00000145194), score: 0.57 EIF2C1eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2C, 1 (ENSG00000092847), score: 0.6 ELAVL3ELAV (embryonic lethal, abnormal vision, Drosophila)-like 3 (Hu antigen C) (ENSG00000196361), score: 0.55 ELMO2engulfment and cell motility 2 (ENSG00000062598), score: 0.63 EN2engrailed homeobox 2 (ENSG00000164778), score: 0.95 EOMESeomesodermin (ENSG00000163508), score: 0.93 EP300E1A binding protein p300 (ENSG00000100393), score: 0.61 EPB41erythrocyte membrane protein band 4.1 (elliptocytosis 1, RH-linked) (ENSG00000159023), score: 0.63 EPC1enhancer of polycomb homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000120616), score: 0.66 EPC2enhancer of polycomb homolog 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000135999), score: 0.6 EPHB1EPH receptor B1 (ENSG00000154928), score: 0.69 EPXeosinophil peroxidase (ENSG00000121053), score: 0.62 ERBB2IPerbb2 interacting protein (ENSG00000112851), score: -0.64 ERFEts2 repressor factor (ENSG00000105722), score: -0.65 ETV6ets variant 6 (ENSG00000139083), score: -0.74 EXPH5exophilin 5 (ENSG00000110723), score: 0.88 EZRezrin (ENSG00000092820), score: -0.72 FABP7fatty acid binding protein 7, brain (ENSG00000164434), score: 0.56 FAM110Bfamily with sequence similarity 110, member B (ENSG00000169122), score: 0.57 FAM123Cfamily with sequence similarity 123C (ENSG00000178171), score: 0.57 FAM63Bfamily with sequence similarity 63, member B (ENSG00000128923), score: 0.59 FANCBFanconi anemia, complementation group B (ENSG00000181544), score: 0.7 FAT2FAT tumor suppressor homolog 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000086570), score: 0.96 FBXO31F-box protein 31 (ENSG00000103264), score: 0.56 FGF17fibroblast growth factor 17 (ENSG00000158815), score: 0.65 FGF20fibroblast growth factor 20 (ENSG00000078579), score: 0.62 FGF3fibroblast growth factor 3 (ENSG00000186895), score: 0.57 FGF5fibroblast growth factor 5 (ENSG00000138675), score: 0.84 FGFR1fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (ENSG00000077782), score: 0.63 FHDC1FH2 domain containing 1 (ENSG00000137460), score: 0.68 FKBP5FK506 binding protein 5 (ENSG00000096060), score: -0.65 FLT3fms-related tyrosine kinase 3 (ENSG00000122025), score: 0.69 FOXN2forkhead box N2 (ENSG00000170802), score: 0.68 FOXO3forkhead box O3 (ENSG00000118689), score: 0.68 FSTL5follistatin-like 5 (ENSG00000168843), score: 0.81 FUBP1far upstream element (FUSE) binding protein 1 (ENSG00000162613), score: 0.56 FUT1fucosyltransferase 1 (galactoside 2-alpha-L-fucosyltransferase, H blood group) (ENSG00000174951), score: 0.62 FUT9fucosyltransferase 9 (alpha (1,3) fucosyltransferase) (ENSG00000172461), score: 0.61 FZD7frizzled homolog 7 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000155760), score: 0.72 GALNT12UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 12 (GalNAc-T12) (ENSG00000119514), score: 0.64 GALNT7UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 7 (GalNAc-T7) (ENSG00000109586), score: 0.74 GDNFglial cell derived neurotrophic factor (ENSG00000168621), score: 0.56 GFOD2glucose-fructose oxidoreductase domain containing 2 (ENSG00000141098), score: 0.56 GIGYF1GRB10 interacting GYF protein 1 (ENSG00000146830), score: 0.56 GIT2G protein-coupled receptor kinase interacting ArfGAP 2 (ENSG00000139436), score: 0.63 GLCEglucuronic acid epimerase (ENSG00000138604), score: 0.73 GLI1GLI family zinc finger 1 (ENSG00000111087), score: 0.57 GLRA2glycine receptor, alpha 2 (ENSG00000101958), score: 0.66 GNB3guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), beta polypeptide 3 (ENSG00000111664), score: 0.71 GNG13guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), gamma 13 (ENSG00000127588), score: 0.7 GPATCH8G patch domain containing 8 (ENSG00000186566), score: 0.72 GPR148G protein-coupled receptor 148 (ENSG00000173302), score: 0.62 GPR158G protein-coupled receptor 158 (ENSG00000151025), score: 0.61 GPR179G protein-coupled receptor 179 (ENSG00000188888), score: 0.68 GPRIN3GPRIN family member 3 (ENSG00000185477), score: 0.8 GRB14growth factor receptor-bound protein 14 (ENSG00000115290), score: -0.6 GRIA4glutamate receptor, ionotrophic, AMPA 4 (ENSG00000152578), score: 0.6 GRID2glutamate receptor, ionotropic, delta 2 (ENSG00000152208), score: 0.81 GRID2IPglutamate receptor, ionotropic, delta 2 (Grid2) interacting protein (ENSG00000215045), score: 0.91 GRIN2Cglutamate receptor, ionotropic, N-methyl D-aspartate 2C (ENSG00000161509), score: 0.77 GRM1glutamate receptor, metabotropic 1 (ENSG00000152822), score: 0.71 GRM4glutamate receptor, metabotropic 4 (ENSG00000124493), score: 0.93 HINFPhistone H4 transcription factor (ENSG00000172273), score: 0.7 HIPK1homeodomain interacting protein kinase 1 (ENSG00000163349), score: 0.67 HPCAL1hippocalcin-like 1 (ENSG00000115756), score: 0.62 HPDL4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase-like (ENSG00000186603), score: 0.65 HS3ST1heparan sulfate (glucosamine) 3-O-sulfotransferase 1 (ENSG00000002587), score: 0.59 HTR5A5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 5A (ENSG00000157219), score: 0.64 IFFO2intermediate filament family orphan 2 (ENSG00000169991), score: 0.72 IGFBP2insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2, 36kDa (ENSG00000115457), score: -0.72 IL16interleukin 16 (lymphocyte chemoattractant factor) (ENSG00000172349), score: 0.87 ING3inhibitor of growth family, member 3 (ENSG00000071243), score: 0.59 INO80INO80 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000128908), score: 0.65 IP6K2inositol hexakisphosphate kinase 2 (ENSG00000068745), score: 0.69 ITGA2Bintegrin, alpha 2b (platelet glycoprotein IIb of IIb/IIIa complex, antigen CD41) (ENSG00000005961), score: 0.55 JARID2jumonji, AT rich interactive domain 2 (ENSG00000008083), score: 0.59 JMJD1Cjumonji domain containing 1C (ENSG00000171988), score: 0.67 KCNA1potassium voltage-gated channel, shaker-related subfamily, member 1 (episodic ataxia with myokymia) (ENSG00000111262), score: 0.58 KCNAB3potassium voltage-gated channel, shaker-related subfamily, beta member 3 (ENSG00000170049), score: 0.63 KCNC1potassium voltage-gated channel, Shaw-related subfamily, member 1 (ENSG00000129159), score: 0.63 KCND1potassium voltage-gated channel, Shal-related subfamily, member 1 (ENSG00000102057), score: 0.73 KCND3potassium voltage-gated channel, Shal-related subfamily, member 3 (ENSG00000171385), score: 0.56 KCNJ6potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 6 (ENSG00000157542), score: 0.57 KCNK10potassium channel, subfamily K, member 10 (ENSG00000100433), score: 0.69 KCNK9potassium channel, subfamily K, member 9 (ENSG00000169427), score: 0.76 KCNRGpotassium channel regulator (ENSG00000198553), score: 0.57 KCTD2potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 2 (ENSG00000180901), score: 0.6 KCTD6potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 6 (ENSG00000168301), score: 0.55 KCTD8potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 8 (ENSG00000183783), score: 0.63 KDM2Alysine (K)-specific demethylase 2A (ENSG00000173120), score: 0.59 KDM4Clysine (K)-specific demethylase 4C (ENSG00000107077), score: 0.8 KIAA0182KIAA0182 (ENSG00000131149), score: 0.66 KIAA0240KIAA0240 (ENSG00000112624), score: 0.65 KIAA0247KIAA0247 (ENSG00000100647), score: 0.63 KIAA0802KIAA0802 (ENSG00000168502), score: 0.81 KIAA0895KIAA0895 (ENSG00000164542), score: 0.56 KIAA0907KIAA0907 (ENSG00000132680), score: 0.59 KIAA0922KIAA0922 (ENSG00000121210), score: -0.6 KIAA1217KIAA1217 (ENSG00000120549), score: -0.75 KIAA1244KIAA1244 (ENSG00000112379), score: 0.56 KIAA1614KIAA1614 (ENSG00000135835), score: 0.6 KIFC3kinesin family member C3 (ENSG00000140859), score: -0.66 KLHDC8Akelch domain containing 8A (ENSG00000162873), score: 0.64 KLHL3kelch-like 3 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000146021), score: 0.57 KLHL33kelch-like 33 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000185271), score: 0.63 LAS1LLAS1-like (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000001497), score: 0.56 LATS1LATS, large tumor suppressor, homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000131023), score: 0.63 LBHlimb bud and heart development homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000213626), score: -0.61 LBX1ladybird homeobox 1 (ENSG00000138136), score: 0.84 LDB2LIM domain binding 2 (ENSG00000169744), score: -0.74 LDLRAD3low density lipoprotein receptor class A domain containing 3 (ENSG00000179241), score: 0.58 LDLRAP1low density lipoprotein receptor adaptor protein 1 (ENSG00000157978), score: 0.69 LHX5LIM homeobox 5 (ENSG00000089116), score: 0.95 LMO7LIM domain 7 (ENSG00000136153), score: -0.61 LOC100131509similar to inward rectifying K+ channel negative regulator Kir2.2v (ENSG00000184185), score: 0.7 LOC100294337hypothetical protein LOC100294337 (ENSG00000120071), score: 0.6 LOC146429putative solute carrier family 22 member ENSG00000182157 (ENSG00000182157), score: 0.88 LONRF3LON peptidase N-terminal domain and ring finger 3 (ENSG00000175556), score: 0.59 LRCH1leucine-rich repeats and calponin homology (CH) domain containing 1 (ENSG00000136141), score: 0.76 LRRC16Bleucine rich repeat containing 16B (ENSG00000186648), score: 0.68 LRRC26leucine rich repeat containing 26 (ENSG00000184709), score: 0.69 LRRC38leucine rich repeat containing 38 (ENSG00000162494), score: 0.64 LRRC3Bleucine rich repeat containing 3B (ENSG00000179796), score: 0.68 LTBP4latent transforming growth factor beta binding protein 4 (ENSG00000090006), score: -0.63 MAB21L1mab-21-like 1 (C. elegans) (ENSG00000180660), score: 0.97 MAFBv-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog B (avian) (ENSG00000204103), score: -0.63 MAML1mastermind-like 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000161021), score: 0.75 MAML3mastermind-like 3 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000196782), score: 0.88 MAMSTRMEF2 activating motif and SAP domain containing transcriptional regulator (ENSG00000176909), score: 0.62 MAN2A1mannosidase, alpha, class 2A, member 1 (ENSG00000112893), score: -0.6 MAP3K12mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 12 (ENSG00000139625), score: 0.63 MAP3K9mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 9 (ENSG00000006432), score: 0.59 MAPKBP1mitogen-activated protein kinase binding protein 1 (ENSG00000137802), score: 0.6 MARK3MAP/microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 3 (ENSG00000075413), score: 0.58 MAST4microtubule associated serine/threonine kinase family member 4 (ENSG00000069020), score: -0.6 MAXMYC associated factor X (ENSG00000125952), score: 0.73 MCTP1multiple C2 domains, transmembrane 1 (ENSG00000175471), score: 0.57 MDGA1MAM domain containing glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor 1 (ENSG00000112139), score: 0.89 MED13Lmediator complex subunit 13-like (ENSG00000123066), score: 0.61 MEIS1Meis homeobox 1 (ENSG00000143995), score: 0.69 MICAL3microtubule associated monoxygenase, calponin and LIM domain containing 3 (ENSG00000243156), score: 0.63 MIER3mesoderm induction early response 1, family member 3 (ENSG00000155545), score: 0.55 MIXL1Mix1 homeobox-like 1 (Xenopus laevis) (ENSG00000185155), score: 0.56 MLLmyeloid/lymphoid or mixed-lineage leukemia (trithorax homolog, Drosophila) (ENSG00000118058), score: 0.7 MMP24matrix metallopeptidase 24 (membrane-inserted) (ENSG00000125966), score: 0.67 MOV10Mov10, Moloney leukemia virus 10, homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000155363), score: -0.6 MPP3membrane protein, palmitoylated 3 (MAGUK p55 subfamily member 3) (ENSG00000161647), score: 0.68 MPP4membrane protein, palmitoylated 4 (MAGUK p55 subfamily member 4) (ENSG00000082126), score: 0.58 MREGmelanoregulin (ENSG00000118242), score: 0.6 MRPL33mitochondrial ribosomal protein L33 (ENSG00000158019), score: -0.69 MSCmusculin (ENSG00000178860), score: -0.61 MXD4MAX dimerization protein 4 (ENSG00000123933), score: 0.6 MYO1Emyosin IE (ENSG00000157483), score: -0.65 MYOGmyogenin (myogenic factor 4) (ENSG00000122180), score: 0.56 MYST3MYST histone acetyltransferase (monocytic leukemia) 3 (ENSG00000083168), score: 0.59 MYT1myelin transcription factor 1 (ENSG00000196132), score: 0.79 NAB2NGFI-A binding protein 2 (EGR1 binding protein 2) (ENSG00000166886), score: 0.62 NCOA6nuclear receptor coactivator 6 (ENSG00000198646), score: 0.55 NEUROD2neurogenic differentiation 2 (ENSG00000171532), score: 0.58 NFKBIDnuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, delta (ENSG00000167604), score: 0.56 NHLH1nescient helix loop helix 1 (ENSG00000171786), score: 0.75 NHLH2nescient helix loop helix 2 (ENSG00000177551), score: 0.84 NIPAL3NIPA-like domain containing 3 (ENSG00000001461), score: 0.55 NKAIN1Na+/K+ transporting ATPase interacting 1 (ENSG00000084628), score: 0.72 NKX6-3NK6 homeobox 3 (ENSG00000165066), score: 0.81 NPC2Niemann-Pick disease, type C2 (ENSG00000119655), score: -0.63 NPFFneuropeptide FF-amide peptide precursor (ENSG00000139574), score: 0.59 NPM3nucleophosmin/nucleoplasmin 3 (ENSG00000107833), score: -0.7 NPR2natriuretic peptide receptor B/guanylate cyclase B (atrionatriuretic peptide receptor B) (ENSG00000159899), score: 0.62 NR1D2nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group D, member 2 (ENSG00000174738), score: 0.56 NR2C2nuclear receptor subfamily 2, group C, member 2 (ENSG00000177463), score: 0.58 NRG2neuregulin 2 (ENSG00000158458), score: 0.71 NRIP2nuclear receptor interacting protein 2 (ENSG00000053702), score: 0.65 NRP1neuropilin 1 (ENSG00000099250), score: -0.64 NYNRINNYN domain and retroviral integrase containing (ENSG00000205978), score: 0.65 ODZ1odz, odd Oz/ten-m homolog 1(Drosophila) (ENSG00000009694), score: 0.81 OGFRL1opioid growth factor receptor-like 1 (ENSG00000119900), score: 0.68 OLFML3olfactomedin-like 3 (ENSG00000116774), score: -0.6 OR2H2olfactory receptor, family 2, subfamily H, member 2 (ENSG00000204657), score: 0.55 ORAI2ORAI calcium release-activated calcium modulator 2 (ENSG00000160991), score: 0.55 OSBPL2oxysterol binding protein-like 2 (ENSG00000130703), score: 0.71 OTX2orthodenticle homeobox 2 (ENSG00000165588), score: 0.94 PAG1phosphoprotein associated with glycosphingolipid microdomains 1 (ENSG00000076641), score: 0.61 PAK7p21 protein (Cdc42/Rac)-activated kinase 7 (ENSG00000101349), score: 0.6 PAPLiron/zinc purple acid phosphatase-like protein (ENSG00000183760), score: 0.66 PARP12poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase family, member 12 (ENSG00000059378), score: -0.62 PAX6paired box 6 (ENSG00000007372), score: 0.77 PAXIP1PAX interacting (with transcription-activation domain) protein 1 (ENSG00000157212), score: 0.79 PCBP3poly(rC) binding protein 3 (ENSG00000183570), score: 0.65 PCBP4poly(rC) binding protein 4 (ENSG00000090097), score: 0.65 PCIF1PDX1 C-terminal inhibiting factor 1 (ENSG00000100982), score: 0.56 PCP2Purkinje cell protein 2 (ENSG00000174788), score: 0.55 PDE8Aphosphodiesterase 8A (ENSG00000073417), score: -0.7 PDZD7PDZ domain containing 7 (ENSG00000186862), score: 0.55 PHF12PHD finger protein 12 (ENSG00000109118), score: 0.58 PHF2PHD finger protein 2 (ENSG00000197724), score: 0.66 PHIPpleckstrin homology domain interacting protein (ENSG00000146247), score: 0.59 PISDphosphatidylserine decarboxylase (ENSG00000241878), score: 0.74 PKDCCprotein kinase domain containing, cytoplasmic homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000162878), score: -0.6 PKIBprotein kinase (cAMP-dependent, catalytic) inhibitor beta (ENSG00000135549), score: 0.87 PLCB4phospholipase C, beta 4 (ENSG00000101333), score: 0.72 PLCXD3phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C, X domain containing 3 (ENSG00000182836), score: 0.56 PLD5phospholipase D family, member 5 (ENSG00000180287), score: 0.65 PLEKHA2pleckstrin homology domain containing, family A (phosphoinositide binding specific) member 2 (ENSG00000169499), score: -0.63 PLEKHG5pleckstrin homology domain containing, family G (with RhoGef domain) member 5 (ENSG00000171680), score: 0.63 PLK2polo-like kinase 2 (ENSG00000145632), score: -0.67 PLXNA3plexin A3 (ENSG00000130827), score: 0.65 PLXND1plexin D1 (ENSG00000004399), score: -0.62 POGZpogo transposable element with ZNF domain (ENSG00000143442), score: 0.66 POLBpolymerase (DNA directed), beta (ENSG00000070501), score: 0.58 POLE4polymerase (DNA-directed), epsilon 4 (p12 subunit) (ENSG00000115350), score: -0.62 PPFIA4protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, f polypeptide (PTPRF), interacting protein (liprin), alpha 4 (ENSG00000143847), score: 0.63 PPM1Hprotein phosphatase, Mg2+/Mn2+ dependent, 1H (ENSG00000111110), score: 0.58 PRDM10PR domain containing 10 (ENSG00000170325), score: 0.8 PSD4pleckstrin and Sec7 domain containing 4 (ENSG00000125637), score: -0.6 PTCH1patched 1 (ENSG00000185920), score: 0.8 PTCHD1patched domain containing 1 (ENSG00000165186), score: 0.85 PTPN4protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 4 (megakaryocyte) (ENSG00000088179), score: 0.66 PTPRRprotein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, R (ENSG00000153233), score: 0.57 PVALBparvalbumin (ENSG00000100362), score: 0.56 PWWP2APWWP domain containing 2A (ENSG00000170234), score: 0.79 PYDC1PYD (pyrin domain) containing 1 (ENSG00000169900), score: 0.57 PYGO1pygopus homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000171016), score: 0.74 QSOX2quiescin Q6 sulfhydryl oxidase 2 (ENSG00000165661), score: 0.64 RAB37RAB37, member RAS oncogene family (ENSG00000172794), score: 0.65 RAB39RAB39, member RAS oncogene family (ENSG00000179331), score: 0.56 RAB3IL1RAB3A interacting protein (rabin3)-like 1 (ENSG00000167994), score: -0.63 RAP2BRAP2B, member of RAS oncogene family (ENSG00000181467), score: -0.7 RASGEF1CRasGEF domain family, member 1C (ENSG00000146090), score: 0.55 RBM9RNA binding motif protein 9 (ENSG00000100320), score: 0.55 RCAN3RCAN family member 3 (ENSG00000117602), score: 0.8 RELBv-rel reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog B (ENSG00000104856), score: -0.62 REV3LREV3-like, catalytic subunit of DNA polymerase zeta (yeast) (ENSG00000009413), score: 0.71 RFTN1raftlin, lipid raft linker 1 (ENSG00000131378), score: -0.69 RFX7regulatory factor X, 7 (ENSG00000181827), score: 0.59 RGS8regulator of G-protein signaling 8 (ENSG00000135824), score: 0.62 RIMS1regulating synaptic membrane exocytosis 1 (ENSG00000079841), score: 0.6 RIPK2receptor-interacting serine-threonine kinase 2 (ENSG00000104312), score: -0.6 RIPPLY2ripply2 homolog (zebrafish) (ENSG00000203877), score: 0.55 RIT2Ras-like without CAAX 2 (ENSG00000152214), score: 0.61 RMND5Arequired for meiotic nuclear division 5 homolog A (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000153561), score: 0.71 RNF112ring finger protein 112 (ENSG00000128482), score: 0.58 RNF144Aring finger protein 144A (ENSG00000151692), score: 0.57 RNF146ring finger protein 146 (ENSG00000118518), score: 0.63 RNF182ring finger protein 182 (ENSG00000180537), score: 0.61 RPS6KA5ribosomal protein S6 kinase, 90kDa, polypeptide 5 (ENSG00000100784), score: 0.6 RUNX1T1runt-related transcription factor 1; translocated to, 1 (cyclin D-related) (ENSG00000079102), score: 0.6 S100A10S100 calcium binding protein A10 (ENSG00000197747), score: -0.61 SART3squamous cell carcinoma antigen recognized by T cells 3 (ENSG00000075856), score: 0.69 SBK1SH3-binding domain kinase 1 (ENSG00000188322), score: 0.61 SEL1L3sel-1 suppressor of lin-12-like 3 (C. elegans) (ENSG00000091490), score: 0.74 SETD5SET domain containing 5 (ENSG00000168137), score: 0.83 SEZ6seizure related 6 homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000063015), score: 0.56 SF3B3splicing factor 3b, subunit 3, 130kDa (ENSG00000189091), score: 0.65 SGK223homolog of rat pragma of Rnd2 (ENSG00000182319), score: 0.66 SH3RF1SH3 domain containing ring finger 1 (ENSG00000154447), score: -0.62 SHBSrc homology 2 domain containing adaptor protein B (ENSG00000107338), score: -0.68 SHFSrc homology 2 domain containing F (ENSG00000138606), score: 0.67 SHKBP1SH3KBP1 binding protein 1 (ENSG00000160410), score: -0.62 SHPRHSNF2 histone linker PHD RING helicase (ENSG00000146414), score: 0.63 SIDT1SID1 transmembrane family, member 1 (ENSG00000072858), score: 0.55 SKIv-ski sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (avian) (ENSG00000157933), score: 0.75 SKOR1SKI family transcriptional corepressor 1 (ENSG00000188779), score: 0.71 SLC1A6solute carrier family 1 (high affinity aspartate/glutamate transporter), member 6 (ENSG00000105143), score: 0.67 SLC26A5solute carrier family 26, member 5 (prestin) (ENSG00000170615), score: 0.84 SLC35F4solute carrier family 35, member F4 (ENSG00000151812), score: 0.94 SLC36A1solute carrier family 36 (proton/amino acid symporter), member 1 (ENSG00000123643), score: 0.61 SLC6A5solute carrier family 6 (neurotransmitter transporter, glycine), member 5 (ENSG00000165970), score: 0.71 SLC9A5solute carrier family 9 (sodium/hydrogen exchanger), member 5 (ENSG00000135740), score: 0.6 SNED1sushi, nidogen and EGF-like domains 1 (ENSG00000162804), score: 0.68 SNRKSNF related kinase (ENSG00000163788), score: 0.8 SNX25sorting nexin 25 (ENSG00000109762), score: 0.63 SOCS5suppressor of cytokine signaling 5 (ENSG00000171150), score: 0.7 SP4Sp4 transcription factor (ENSG00000105866), score: 0.76 SPHKAPSPHK1 interactor, AKAP domain containing (ENSG00000153820), score: 0.66 SPINK6serine peptidase inhibitor, Kazal type 6 (ENSG00000178172), score: 0.85 SPOPspeckle-type POZ protein (ENSG00000121067), score: 0.61 SPTBspectrin, beta, erythrocytic (ENSG00000070182), score: 0.55 SPTBN5spectrin, beta, non-erythrocytic 5 (ENSG00000137877), score: 0.83 SRRM4serine/arginine repetitive matrix 4 (ENSG00000139767), score: 0.6 SSH1slingshot homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000084112), score: 0.56 ST3GAL4ST3 beta-galactoside alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase 4 (ENSG00000110080), score: -0.62 ST8SIA1ST8 alpha-N-acetyl-neuraminide alpha-2,8-sialyltransferase 1 (ENSG00000111728), score: 0.6 ST8SIA5ST8 alpha-N-acetyl-neuraminide alpha-2,8-sialyltransferase 5 (ENSG00000101638), score: 0.58 STACSH3 and cysteine rich domain (ENSG00000144681), score: 0.55 STARD13StAR-related lipid transfer (START) domain containing 13 (ENSG00000133121), score: -0.61 STAT5Bsignal transducer and activator of transcription 5B (ENSG00000173757), score: 0.62 STAT6signal transducer and activator of transcription 6, interleukin-4 induced (ENSG00000166888), score: -0.7 STK32Aserine/threonine kinase 32A (ENSG00000169302), score: 0.55 SYNE1spectrin repeat containing, nuclear envelope 1 (ENSG00000131018), score: 0.64 SYT12synaptotagmin XII (ENSG00000173227), score: 0.56 SYT2synaptotagmin II (ENSG00000143858), score: 0.71 SYT4synaptotagmin IV (ENSG00000132872), score: 0.6 TAF10TAF10 RNA polymerase II, TATA box binding protein (TBP)-associated factor, 30kDa (ENSG00000166337), score: -0.66 TBC1D9TBC1 domain family, member 9 (with GRAM domain) (ENSG00000109436), score: 0.59 TET3tet oncogene family member 3 (ENSG00000187605), score: 0.61 TFAP2Etranscription factor AP-2 epsilon (activating enhancer binding protein 2 epsilon) (ENSG00000116819), score: 0.57 TGM1transglutaminase 1 (K polypeptide epidermal type I, protein-glutamine-gamma-glutamyltransferase) (ENSG00000092295), score: 0.6 TIAM1T-cell lymphoma invasion and metastasis 1 (ENSG00000156299), score: 0.8 TIMP4TIMP metallopeptidase inhibitor 4 (ENSG00000157150), score: 0.61 TLL1tolloid-like 1 (ENSG00000038295), score: 0.95 TMC2transmembrane channel-like 2 (ENSG00000149488), score: 0.66 TMEM145transmembrane protein 145 (ENSG00000167619), score: 0.62 TMEM163transmembrane protein 163 (ENSG00000152128), score: 0.59 TMEM178transmembrane protein 178 (ENSG00000152154), score: 0.56 TMEM63Ctransmembrane protein 63C (ENSG00000165548), score: 0.61 TNCtenascin C (ENSG00000041982), score: -0.6 TNFAIP2tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 2 (ENSG00000185215), score: -0.6 TNFRSF25tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 25 (ENSG00000215788), score: 0.69 TNK1tyrosine kinase, non-receptor, 1 (ENSG00000174292), score: 0.57 TNRC6Atrinucleotide repeat containing 6A (ENSG00000090905), score: 0.6 TP73tumor protein p73 (ENSG00000078900), score: 0.72 TRANK1tetratricopeptide repeat and ankyrin repeat containing 1 (ENSG00000168016), score: 0.58 TRIM11tripartite motif-containing 11 (ENSG00000154370), score: 0.72 TRIM17tripartite motif-containing 17 (ENSG00000162931), score: 0.61 TRIM3tripartite motif-containing 3 (ENSG00000110171), score: 0.6 TRIM32tripartite motif-containing 32 (ENSG00000119401), score: 0.61 TRIM62tripartite motif-containing 62 (ENSG00000116525), score: 0.66 TRIM67tripartite motif-containing 67 (ENSG00000119283), score: 0.88 TRIM7tripartite motif-containing 7 (ENSG00000146054), score: 0.64 TRIM72tripartite motif-containing 72 (ENSG00000177238), score: 0.57 TRPC3transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily C, member 3 (ENSG00000138741), score: 0.65 TSEN34tRNA splicing endonuclease 34 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000170892), score: -0.65 UBASH3Bubiquitin associated and SH3 domain containing B (ENSG00000154127), score: 0.84 UPF0639UPF0639 protein (ENSG00000175985), score: 0.73 USP3ubiquitin specific peptidase 3 (ENSG00000140455), score: 0.56 USTuronyl-2-sulfotransferase (ENSG00000111962), score: 0.65 VANGL2vang-like 2 (van gogh, Drosophila) (ENSG00000162738), score: 0.57 VAT1Lvesicle amine transport protein 1 homolog (T. californica)-like (ENSG00000171724), score: 0.65 VAX2ventral anterior homeobox 2 (ENSG00000116035), score: 0.7 VSX1visual system homeobox 1 (ENSG00000100987), score: 0.74 WACWW domain containing adaptor with coiled-coil (ENSG00000095787), score: 0.65 WDR76WD repeat domain 76 (ENSG00000092470), score: 0.61 WHSC1L1Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome candidate 1-like 1 (ENSG00000147548), score: 0.61 WSCD1WSC domain containing 1 (ENSG00000179314), score: 0.55 WSCD2WSC domain containing 2 (ENSG00000075035), score: 0.66 WWC2WW and C2 domain containing 2 (ENSG00000151718), score: -0.61 XKR6XK, Kell blood group complex subunit-related family, member 6 (ENSG00000171044), score: 0.61 XKR7XK, Kell blood group complex subunit-related family, member 7 (ENSG00000101321), score: 0.87 YTHDC1YTH domain containing 1 (ENSG00000083896), score: 0.57 ZBTB34zinc finger and BTB domain containing 34 (ENSG00000177125), score: 0.6 ZFHX3zinc finger homeobox 3 (ENSG00000140836), score: -0.68 ZFP112zinc finger protein 112 homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000062370), score: 0.65 ZFP30zinc finger protein 30 homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000120784), score: 0.58 ZFPM2zinc finger protein, multitype 2 (ENSG00000169946), score: 0.72 ZFYVE28zinc finger, FYVE domain containing 28 (ENSG00000159733), score: 0.6 ZIC2Zic family member 2 (odd-paired homolog, Drosophila) (ENSG00000043355), score: 0.83 ZIC4Zic family member 4 (ENSG00000174963), score: 0.96 ZIC5Zic family member 5 (odd-paired homolog, Drosophila) (ENSG00000139800), score: 0.81 ZNF157zinc finger protein 157 (ENSG00000147117), score: 0.87 ZNF219zinc finger protein 219 (ENSG00000165804), score: 0.59 ZNF238zinc finger protein 238 (ENSG00000179456), score: 0.72 ZNF273zinc finger protein 273 (ENSG00000198039), score: 0.66 ZNF296zinc finger protein 296 (ENSG00000170684), score: 0.75 ZNF304zinc finger protein 304 (ENSG00000131845), score: 0.67 ZNF333zinc finger protein 333 (ENSG00000160961), score: 0.56 ZNF34zinc finger protein 34 (ENSG00000196378), score: 0.57 ZNF37Azinc finger protein 37A (ENSG00000075407), score: 0.59 ZNF382zinc finger protein 382 (ENSG00000161298), score: 0.67 ZNF445zinc finger protein 445 (ENSG00000185219), score: 0.6 ZNF521zinc finger protein 521 (ENSG00000198795), score: 0.85 ZNF620zinc finger protein 620 (ENSG00000177842), score: 0.57 ZNF671zinc finger protein 671 (ENSG00000083814), score: 0.68 ZNF862zinc finger protein 862 (ENSG00000106479), score: 0.59
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ppy_cb_f_ca1 | ppy | cb | f | _ |
| mml_cb_m_ca1 | mml | cb | m | _ |
| ppa_cb_f_ca1 | ppa | cb | f | _ |
| mml_cb_f_ca1 | mml | cb | f | _ |
| ggo_cb_f_ca1 | ggo | cb | f | _ |
| hsa_cb_m_ca1 | hsa | cb | m | _ |
| ppa_cb_m_ca1 | ppa | cb | m | _ |
| hsa_cb_f_ca1 | hsa | cb | f | _ |
| ptr_cb_m_ca1 | ptr | cb | m | _ |