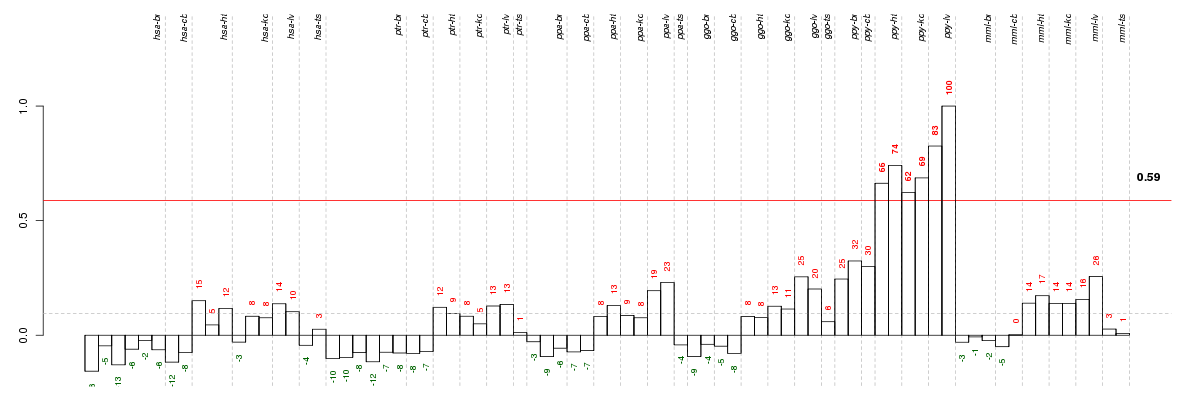

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
cytokine production
The appearance of a cytokine due to biosynthesis or secretion following a cellular stimulus, resulting in an increase in its intracellular or extracellular levels.
regulation of cytokine production
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of production of a cytokine.
positive regulation of cytokine production
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of production of a cytokine.
cell killing
Any process in an organism that results in the killing of its own cells or those of another organism, including in some cases the death of the other organism. Killing here refers to the induction of death in one cell by another cell, not cell-autonomous death due to internal or other environmental conditions.
immune system process
Any process involved in the development or functioning of the immune system, an organismal system for calibrated responses to potential internal or invasive threats.
antigen processing and presentation of peptide or polysaccharide antigen via MHC class II
The process by which an antigen-presenting cell expresses antigen (peptide or polysaccharide) on its cell surface in association with an MHC class II protein complex.
defense response
Reactions, triggered in response to the presence of a foreign body or the occurrence of an injury, which result in restriction of damage to the organism attacked or prevention/recovery from the infection caused by the attack.
defense response to bacterium
Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a bacterium that act to protect the cell or organism.
signal transduction
The process whereby an activated receptor conveys information down the signaling pathway, resulting in a change in the function or state of a cell.
response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
intracellular protein kinase cascade
A series of reactions that occur within the cell, mediated by protein kinases, which occurs as a result of a single trigger reaction or compound.
JAK-STAT cascade
Any process by which STAT proteins (Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription) are activated by members of the JAK (janus activated kinase) family of tyrosine kinases, following the binding of cytokines to their cognate receptor. Once activated, STATs dimerize and translocate to the nucleus and modulate the expression of target genes.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
defense response to Gram-negative bacterium
Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a Gram-negative bacterium that act to protect the cell or organism.
response to biotic stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a biotic stimulus, a stimulus caused or produced by a living organism.
response to other organism
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from another living organism.
response to bacterium
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a bacterium.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
antigen processing and presentation
The process by which an antigen-presenting cell expresses antigen (peptide or lipid) on its cell surface in association with an MHC protein complex.
signal transmission via phosphorylation event
The process whereby a signal is conveyed via the transfer of one or more phosphate groups.
signaling pathway
The series of molecular events whereby information is sent from one location to another within a living organism or between living organisms.
intracellular signaling pathway
The series of molecular events whereby information is sent from one location to another within a cell.
signaling process
Any biological process involved in the generation, transmission, reception, or interpretation of a signal. A signal is an entity used to transmit or convey information.
signaling
The entirety of a process whereby information is transmitted. This process begins with the initiation of the signal and ends when a response has been triggered.
signal transmission
The process whereby a signal is released and/or conveyed from one location to another.
symbiosis, encompassing mutualism through parasitism
An interaction between two organisms living together in more or less intimate association. The term host is usually used for the larger (macro) of the two members of a symbiosis. The smaller (micro) member is called the symbiont organism. Microscopic symbionts are often referred to as endosymbionts. The various forms of symbiosis include parasitism, in which the association is disadvantageous or destructive to one of the organisms; mutualism, in which the association is advantageous, or often necessary to one or both and not harmful to either; and commensalism, in which one member of the association benefits while the other is not affected. However, mutualism, parasitism, and commensalism are often not discrete categories of interactions and should rather be perceived as a continuum of interaction ranging from parasitism to mutualism. In fact, the direction of a symbiotic interaction can change during the lifetime of the symbionts due to developmental changes as well as changes in the biotic/abiotic environment in which the interaction occurs.
killing of cells of another organism
Any process in an organism that results in the killing of cells of another organism, including in some cases the death of the other organism. Killing here refers to the induction of death in one cell by another cell, not cell-autonomous death due to internal or other environmental conditions.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
intracellular signal transduction
The process whereby a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell.
cytokine biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of cytokines, any of a group of proteins that function to control the survival, growth and differentiation of tissues and cells, and which have autocrine and paracrine activity.
cytokine metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving cytokines, any of a group of proteins or glycoproteins that function to control the survival, growth and differentiation of tissues and cells, and which have autocrine and paracrine activity.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
interspecies interaction between organisms
Any process by which an organism has an effect on an organism of a different species.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
positive regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of an organismal process, any of the processes pertinent to the function of an organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
interaction with symbiont
An interaction between two organisms living together in more or less intimate association. The term symbiont is used for the smaller (macro) of the two members of a symbiosis; the various forms of symbiosis include parasitism, commensalism and mutualism.
multi-organism process
Any process by which an organism has an effect on another organism of the same or different species.
modification of morphology or physiology of other organism involved in symbiotic interaction
The process by which an organism effects a change in the structure or processes of a second organism, where the two organisms are in a symbiotic interaction.
disruption of cells of other organism involved in symbiotic interaction
A process by which an organism has a negative effect on the functioning of the second organism's cells, where the two organisms are in a symbiotic interaction.
modification by host of symbiont morphology or physiology
The process by which an organism effects a change in the structure or processes of a symbiont organism. The symbiont is defined as the smaller of the organisms involved in a symbiotic interaction.
disruption by host of symbiont cells
Any process by which an organism has a negative effect on the functioning of the symbiont's cells. The symbiont is defined as the smaller of the organisms involved in a symbiotic interaction.
killing by host of symbiont cells
Any process mediated by an organism that results in the death of cells in the symbiont organism. The symbiont is defined as the smaller of the organisms involved in a symbiotic interaction.
killing of cells in other organism involved in symbiotic interaction
Any process mediated by an organism that results in the death of cells in a second organism, where the two organisms are in a symbiotic interaction.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of biological quality
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological quality. A biological quality is a measurable attribute of an organism or part of an organism, such as size, mass, shape, color, etc.
all
NA
signaling process
Any biological process involved in the generation, transmission, reception, or interpretation of a signal. A signal is an entity used to transmit or convey information.
positive regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of an organismal process, any of the processes pertinent to the function of an organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
killing of cells of another organism
Any process in an organism that results in the killing of cells of another organism, including in some cases the death of the other organism. Killing here refers to the induction of death in one cell by another cell, not cell-autonomous death due to internal or other environmental conditions.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
signal transduction
The process whereby an activated receptor conveys information down the signaling pathway, resulting in a change in the function or state of a cell.
regulation of cytokine production
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of production of a cytokine.
positive regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of an organismal process, any of the processes pertinent to the function of an organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
positive regulation of cytokine production
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of production of a cytokine.
response to other organism
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from another living organism.
cytokine biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of cytokines, any of a group of proteins that function to control the survival, growth and differentiation of tissues and cells, and which have autocrine and paracrine activity.
intracellular signal transduction
The process whereby a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell.
positive regulation of cytokine production
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of production of a cytokine.
defense response to bacterium
Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a bacterium that act to protect the cell or organism.
interaction with symbiont
An interaction between two organisms living together in more or less intimate association. The term symbiont is used for the smaller (macro) of the two members of a symbiosis; the various forms of symbiosis include parasitism, commensalism and mutualism.
modification of morphology or physiology of other organism involved in symbiotic interaction
The process by which an organism effects a change in the structure or processes of a second organism, where the two organisms are in a symbiotic interaction.
modification by host of symbiont morphology or physiology
The process by which an organism effects a change in the structure or processes of a symbiont organism. The symbiont is defined as the smaller of the organisms involved in a symbiotic interaction.
intracellular protein kinase cascade
A series of reactions that occur within the cell, mediated by protein kinases, which occurs as a result of a single trigger reaction or compound.
disruption by host of symbiont cells
Any process by which an organism has a negative effect on the functioning of the symbiont's cells. The symbiont is defined as the smaller of the organisms involved in a symbiotic interaction.
killing of cells in other organism involved in symbiotic interaction
Any process mediated by an organism that results in the death of cells in a second organism, where the two organisms are in a symbiotic interaction.
killing by host of symbiont cells
Any process mediated by an organism that results in the death of cells in the symbiont organism. The symbiont is defined as the smaller of the organisms involved in a symbiotic interaction.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
organellar ribosome
A ribosome contained within a subcellular membrane-bounded organelle.
organellar small ribosomal subunit
The smaller of the two subunits of an organellar ribosome.
lytic vacuole
A vacuole that is maintained at an acidic pH and which contains degradative enzymes, including a wide variety of acid hydrolases.
ribonucleoprotein complex
A macromolecular complex containing both protein and RNA molecules.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
MHC class II protein complex
A transmembrane protein complex composed of an MHC class II alpha and MHC class II beta chain, and with or without a bound peptide or polysaccharide antigen.
lysosome
A small lytic vacuole that has cell cycle-independent morphology and is found in most animal cells and that contains a variety of hydrolases, most of which have their maximal activities in the pH range 5-6. The contained enzymes display latency if properly isolated. About 40 different lysosomal hydrolases are known and lysosomes have a great variety of morphologies and functions.
mitochondrion
A semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration.
vacuole
A closed structure, found only in eukaryotic cells, that is completely surrounded by unit membrane and contains liquid material. Cells contain one or several vacuoles, that may have different functions from each other. Vacuoles have a diverse array of functions. They can act as a storage organelle for nutrients or waste products, as a degradative compartment, as a cost-effective way of increasing cell size, and as a homeostatic regulator controlling both turgor pressure and pH of the cytosol.
integral to membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer. When used to describe a protein, indicates that all or part of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
endoplasmic reticulum
The irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae. The ER takes two forms, rough (or granular), with ribosomes adhering to the outer surface, and smooth (with no ribosomes attached).
ribosome
An intracellular organelle, about 200 A in diameter, consisting of RNA and protein. It is the site of protein biosynthesis resulting from translation of messenger RNA (mRNA). It consists of two subunits, one large and one small, each containing only protein and RNA. Both the ribosome and its subunits are characterized by their sedimentation coefficients, expressed in Svedberg units (symbol: S). Hence, the prokaryotic ribosome (70S) comprises a large (50S) subunit and a small (30S) subunit, while the eukaryotic ribosome (80S) comprises a large (60S) subunit and a small (40S) subunit. Two sites on the ribosomal large subunit are involved in translation, namely the aminoacyl site (A site) and peptidyl site (P site). Ribosomes from prokaryotes, eukaryotes, mitochondria, and chloroplasts have characteristically distinct ribosomal proteins.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cytoplasm
All of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
mitochondrial matrix
The gel-like material, with considerable fine structure, that lies in the matrix space, or lumen, of a mitochondrion. It contains the enzymes of the tricarboxylic acid cycle and, in some organisms, the enzymes concerned with fatty acid oxidation.
mitochondrial ribosome
A ribosome found in the mitochondrion of a eukaryotic cell; contains a characteristic set of proteins distinct from those of cytosolic ribosomes.
mitochondrial small ribosomal subunit
The smaller of the two subunits of a mitochondrial ribosome.
lysosomal membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding the lysosome and separating its contents from the cell cytoplasm.
vacuolar membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding the vacuole and separating its contents from the cytoplasm of the cell.
endoplasmic reticulum membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding the endoplasmic reticulum.
endomembrane system
A collection of membranous structures involved in transport within the cell. The main components of the endomembrane system are endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, vesicles, cell membrane and nuclear envelope. Members of the endomembrane system pass materials through each other or though the use of vesicles.
small ribosomal subunit
The smaller of the two subunits of a ribosome.
integral to endoplasmic reticulum membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of an endoplasmic reticulum membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intrinsic to endoplasmic reticulum membrane
Located in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intrinsic to organelle membrane
Located in an organelle membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
integral to organelle membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of an organelle membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
membrane-enclosed lumen
The enclosed volume within a sealed membrane or between two sealed membranes. Encompasses the volume enclosed by the membranes of a particular organelle, e.g. endoplasmic reticulum lumen, or the space between the two lipid bilayers of a double membrane surrounding an organelle, e.g. nuclear envelope lumen.
mitochondrial lumen
The volume enclosed by the mitochondrial inner membrane.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
ribosomal subunit
Either of the two ribonucleoprotein complexes that associate to form a ribosome.
nuclear membrane-endoplasmic reticulum network
The continuous network of membranes encompassing the outer nuclear membrane and the endoplasmic reticulum.
MHC protein complex
A transmembrane protein complex composed of an MHC alpha chain and, in most cases, either an MHC class II beta chain or an invariant beta2-microglobin chain, and with or without a bound peptide, lipid, or polysaccharide antigen.
MHC class I peptide loading complex
A large, multisubunit complex which consists of the MHC class I-beta 2 microglobulin dimer, the transporter associated with antigen presentation (TAP), tapasin (an MHC-encoded membrane protein), the chaperone calreticulin and the thiol oxidoreductase ERp57. Functions in the assembly of peptides with newly synthesized MHC class I molecules.
TAP complex
A heterodimer composed of the subunits TAP1 and TAP2 (transporter associated with antigen presentation). Functions in the transport of antigenic peptides from the cytosol to the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, and prokaryotic structures such as anammoxosomes and pirellulosomes. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
organelle lumen
The internal volume enclosed by the membranes of a particular organelle; includes the volume enclosed by a single organelle membrane, e.g. endoplasmic reticulum lumen, or the volume enclosed by the innermost of the two lipid bilayers of an organelle envelope, e.g. nuclear lumen.
protein complex
Any macromolecular complex composed of two or more polypeptide subunits, which may or may not be identical. Protein complexes may have other associated non-protein prosthetic groups, such as nucleotides, metal ions or other small molecules.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
mitochondrial part
Any constituent part of a mitochondrion, a semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration.
endoplasmic reticulum part
Any constituent part of the endoplasmic reticulum, the irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae.
vacuolar part
Any constituent part of a vacuole, a closed structure, found only in eukaryotic cells, that is completely surrounded by unit membrane and contains liquid material.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
intracellular organelle lumen
An organelle lumen that is part of an intracellular organelle.
subsynaptic reticulum
An elaborate tubulolamellar membrane system that underlies the postsynaptic cell membrane.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
organelle lumen
The internal volume enclosed by the membranes of a particular organelle; includes the volume enclosed by a single organelle membrane, e.g. endoplasmic reticulum lumen, or the volume enclosed by the innermost of the two lipid bilayers of an organelle envelope, e.g. nuclear lumen.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
intrinsic to organelle membrane
Located in an organelle membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
ribosomal subunit
Either of the two ribonucleoprotein complexes that associate to form a ribosome.
intracellular organelle lumen
An organelle lumen that is part of an intracellular organelle.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
nuclear membrane-endoplasmic reticulum network
The continuous network of membranes encompassing the outer nuclear membrane and the endoplasmic reticulum.
ribonucleoprotein complex
A macromolecular complex containing both protein and RNA molecules.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
endoplasmic reticulum membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding the endoplasmic reticulum.
nuclear membrane-endoplasmic reticulum network
The continuous network of membranes encompassing the outer nuclear membrane and the endoplasmic reticulum.
organellar ribosome
A ribosome contained within a subcellular membrane-bounded organelle.
ribosomal subunit
Either of the two ribonucleoprotein complexes that associate to form a ribosome.
TAP complex
A heterodimer composed of the subunits TAP1 and TAP2 (transporter associated with antigen presentation). Functions in the transport of antigenic peptides from the cytosol to the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum.
ribosome
An intracellular organelle, about 200 A in diameter, consisting of RNA and protein. It is the site of protein biosynthesis resulting from translation of messenger RNA (mRNA). It consists of two subunits, one large and one small, each containing only protein and RNA. Both the ribosome and its subunits are characterized by their sedimentation coefficients, expressed in Svedberg units (symbol: S). Hence, the prokaryotic ribosome (70S) comprises a large (50S) subunit and a small (30S) subunit, while the eukaryotic ribosome (80S) comprises a large (60S) subunit and a small (40S) subunit. Two sites on the ribosomal large subunit are involved in translation, namely the aminoacyl site (A site) and peptidyl site (P site). Ribosomes from prokaryotes, eukaryotes, mitochondria, and chloroplasts have characteristically distinct ribosomal proteins.
mitochondrial small ribosomal subunit
The smaller of the two subunits of a mitochondrial ribosome.
intrinsic to endoplasmic reticulum membrane
Located in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
mitochondrial ribosome
A ribosome found in the mitochondrion of a eukaryotic cell; contains a characteristic set of proteins distinct from those of cytosolic ribosomes.
mitochondrial small ribosomal subunit
The smaller of the two subunits of a mitochondrial ribosome.
mitochondrial lumen
The volume enclosed by the mitochondrial inner membrane.
endoplasmic reticulum membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding the endoplasmic reticulum.
intrinsic to endoplasmic reticulum membrane
Located in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
MHC class I peptide loading complex
A large, multisubunit complex which consists of the MHC class I-beta 2 microglobulin dimer, the transporter associated with antigen presentation (TAP), tapasin (an MHC-encoded membrane protein), the chaperone calreticulin and the thiol oxidoreductase ERp57. Functions in the assembly of peptides with newly synthesized MHC class I molecules.
TAP complex
A heterodimer composed of the subunits TAP1 and TAP2 (transporter associated with antigen presentation). Functions in the transport of antigenic peptides from the cytosol to the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum.
vacuolar membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding the vacuole and separating its contents from the cytoplasm of the cell.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
endoplasmic reticulum membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding the endoplasmic reticulum.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
mitochondrion
A semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration.
vacuole
A closed structure, found only in eukaryotic cells, that is completely surrounded by unit membrane and contains liquid material. Cells contain one or several vacuoles, that may have different functions from each other. Vacuoles have a diverse array of functions. They can act as a storage organelle for nutrients or waste products, as a degradative compartment, as a cost-effective way of increasing cell size, and as a homeostatic regulator controlling both turgor pressure and pH of the cytosol.
endoplasmic reticulum
The irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae. The ER takes two forms, rough (or granular), with ribosomes adhering to the outer surface, and smooth (with no ribosomes attached).
ribosome
An intracellular organelle, about 200 A in diameter, consisting of RNA and protein. It is the site of protein biosynthesis resulting from translation of messenger RNA (mRNA). It consists of two subunits, one large and one small, each containing only protein and RNA. Both the ribosome and its subunits are characterized by their sedimentation coefficients, expressed in Svedberg units (symbol: S). Hence, the prokaryotic ribosome (70S) comprises a large (50S) subunit and a small (30S) subunit, while the eukaryotic ribosome (80S) comprises a large (60S) subunit and a small (40S) subunit. Two sites on the ribosomal large subunit are involved in translation, namely the aminoacyl site (A site) and peptidyl site (P site). Ribosomes from prokaryotes, eukaryotes, mitochondria, and chloroplasts have characteristically distinct ribosomal proteins.
ribosomal subunit
Either of the two ribonucleoprotein complexes that associate to form a ribosome.
mitochondrial part
Any constituent part of a mitochondrion, a semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration.
endoplasmic reticulum part
Any constituent part of the endoplasmic reticulum, the irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae.
vacuolar part
Any constituent part of a vacuole, a closed structure, found only in eukaryotic cells, that is completely surrounded by unit membrane and contains liquid material.
subsynaptic reticulum
An elaborate tubulolamellar membrane system that underlies the postsynaptic cell membrane.
intrinsic to organelle membrane
Located in an organelle membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
MHC protein complex
A transmembrane protein complex composed of an MHC alpha chain and, in most cases, either an MHC class II beta chain or an invariant beta2-microglobin chain, and with or without a bound peptide, lipid, or polysaccharide antigen.
mitochondrial matrix
The gel-like material, with considerable fine structure, that lies in the matrix space, or lumen, of a mitochondrion. It contains the enzymes of the tricarboxylic acid cycle and, in some organisms, the enzymes concerned with fatty acid oxidation.
organellar small ribosomal subunit
The smaller of the two subunits of an organellar ribosome.
mitochondrial part
Any constituent part of a mitochondrion, a semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration.
vacuolar part
Any constituent part of a vacuole, a closed structure, found only in eukaryotic cells, that is completely surrounded by unit membrane and contains liquid material.
endoplasmic reticulum part
Any constituent part of the endoplasmic reticulum, the irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae.
endoplasmic reticulum part
Any constituent part of the endoplasmic reticulum, the irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae.
integral to endoplasmic reticulum membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of an endoplasmic reticulum membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
mitochondrial ribosome
A ribosome found in the mitochondrion of a eukaryotic cell; contains a characteristic set of proteins distinct from those of cytosolic ribosomes.
integral to organelle membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of an organelle membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
MHC class I peptide loading complex
A large, multisubunit complex which consists of the MHC class I-beta 2 microglobulin dimer, the transporter associated with antigen presentation (TAP), tapasin (an MHC-encoded membrane protein), the chaperone calreticulin and the thiol oxidoreductase ERp57. Functions in the assembly of peptides with newly synthesized MHC class I molecules.
lysosomal membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding the lysosome and separating its contents from the cell cytoplasm.

protein binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any protein or protein complex (a complex of two or more proteins that may include other nonprotein molecules).
molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
nucleic acid binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any nucleic acid.
RNA binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with an RNA molecule or a portion thereof.
ATPase activity, coupled
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate to directly drive some other reaction, for example ion transport across a membrane.
catalytic activity
Catalysis of a biochemical reaction at physiological temperatures. In biologically catalyzed reactions, the reactants are known as substrates, and the catalysts are naturally occurring macromolecular substances known as enzymes. Enzymes possess specific binding sites for substrates, and are usually composed wholly or largely of protein, but RNA that has catalytic activity (ribozyme) is often also regarded as enzymatic.
ATPase activity, coupled to transmembrane movement of substances
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate to directly drive the active transport of a substance across a membrane.
nucleoside-triphosphatase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: a nucleoside triphosphate + H2O = nucleoside diphosphate + phosphate.
transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a substance from one side of a membrane to the other.
binding
The selective, non-covalent, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
ATPase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate. May or may not be coupled to another reaction.
peptide transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of peptides, compounds of two or more amino acids where the alpha carboxyl group of one is bound to the alpha amino group of another, into, out of, within or between cells.
primary active transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute from one side of the membrane to the other, up the solute's concentration gradient, by binding the solute and undergoing a series of conformational changes. Transport works equally well in either direction and is powered by a primary energy source. Primary energy sources known to be coupled to transport are chemical, electrical and solar sources.
P-P-bond-hydrolysis-driven transmembrane transporter activity
Primary active transport of a solute across a membrane, driven by the hydrolysis of the diphosphate bond of inorganic pyrophosphate, ATP, or another nucleoside triphosphate. The transport protein may or may not be transiently phosphorylated, but the substrate is not phosphorylated. Primary active transport is catalysis of the transport of a solute across a membrane, up the solute's concentration gradient, by binding the solute and undergoing a series of conformational changes. Transport works equally well in either direction and is driven by a primary energy source.
peptide-transporting ATPase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O + peptide(in) = ADP + phosphate + peptide(out). Peptides exported include alpha-hemolysin, cyclolysin, colicin V and siderophores from Gram-negative bacteria, and bacteriocin, subtilin, competence factor and pediocin from Gram-positive bacteria.
pyrophosphatase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of a pyrophosphate bond between two phosphate groups, leaving one phosphate on each of the two fragments.
hydrolase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of various bonds, e.g. C-O, C-N, C-C, phosphoric anhydride bonds, etc. Hydrolase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 3.
hydrolase activity, acting on acid anhydrides
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of any acid anhydride.
hydrolase activity, acting on acid anhydrides, in phosphorus-containing anhydrides
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of any acid anhydride which contains phosphorus.
hydrolase activity, acting on acid anhydrides, catalyzing transmembrane movement of substances
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of an acid anhydride to directly drive the transport of a substance across a membrane.
active transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a specific substance or related group of substances from one side of a membrane to the other, up the solute's concentration gradient. The transporter binds the solute and undergoes a series of conformational changes. Transport works equally well in either direction.
substrate-specific transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of a specific substance or group of related substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
ATPase activity, coupled to movement of substances
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate to directly drive the transport of a substance.
TAP binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with TAP protein, transporter associated with antigen processing protein. TAP protein is a heterodimeric peptide transporter consisting of the subunits TAP1 and TAP2.
TAP1 binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with the TAP1 subunit of TAP (transporter associated with antigen processing) protein.
all
NA
hydrolase activity, acting on acid anhydrides, catalyzing transmembrane movement of substances
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of an acid anhydride to directly drive the transport of a substance across a membrane.
peptide-transporting ATPase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O + peptide(in) = ADP + phosphate + peptide(out). Peptides exported include alpha-hemolysin, cyclolysin, colicin V and siderophores from Gram-negative bacteria, and bacteriocin, subtilin, competence factor and pediocin from Gram-positive bacteria.
ATPase activity, coupled to transmembrane movement of substances
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate to directly drive the active transport of a substance across a membrane.
ATPase activity, coupled to transmembrane movement of substances
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate to directly drive the active transport of a substance across a membrane.
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 05322 | 6.155e-12 | 2.088 | 19 | 52 | Systemic lupus erythematosus |
| 04612 | 4.188e-05 | 1.766 | 11 | 44 | Antigen processing and presentation |
| 05332 | 1.166e-04 | 0.9635 | 8 | 24 | Graft-versus-host disease |
| 05330 | 1.026e-03 | 0.9635 | 7 | 24 | Allograft rejection |
| 04940 | 2.133e-03 | 1.084 | 7 | 27 | Type I diabetes mellitus |
| 04672 | 2.535e-03 | 1.485 | 8 | 37 | Intestinal immune network for IgA production |
| 05320 | 2.648e-03 | 1.124 | 7 | 28 | Autoimmune thyroid disease |
| 05416 | 3.013e-03 | 1.526 | 8 | 38 | Viral myocarditis |
| 05310 | 3.667e-03 | 0.8431 | 6 | 21 | Asthma |
| 05140 | 4.380e-03 | 2.047 | 9 | 51 | Leishmaniasis |
| 04621 | 1.215e-02 | 1.927 | 8 | 48 | NOD-like receptor signaling pathway |
ABCA7ATP-binding cassette, sub-family A (ABC1), member 7 (ENSG00000064687), score: 0.53 ABCB9ATP-binding cassette, sub-family B (MDR/TAP), member 9 (ENSG00000150967), score: -0.61 ABHD12Babhydrolase domain containing 12B (ENSG00000131969), score: 0.71 ABI3BPABI family, member 3 (NESH) binding protein (ENSG00000154175), score: 0.54 ACCN4amiloride-sensitive cation channel 4, pituitary (ENSG00000072182), score: 0.61 ACOT13acyl-CoA thioesterase 13 (ENSG00000112304), score: 0.62 ACSBG1acyl-CoA synthetase bubblegum family member 1 (ENSG00000103740), score: -0.79 ADAMDEC1ADAM-like, decysin 1 (ENSG00000134028), score: 0.53 ADCK2aarF domain containing kinase 2 (ENSG00000133597), score: 0.96 AGERadvanced glycosylation end product-specific receptor (ENSG00000204305), score: 0.63 AK3adenylate kinase 3 (ENSG00000147853), score: 0.53 ALAS2aminolevulinate, delta-, synthase 2 (ENSG00000158578), score: 0.67 ALX3ALX homeobox 3 (ENSG00000156150), score: -0.59 AMBRA1autophagy/beclin-1 regulator 1 (ENSG00000110497), score: -0.61 API5apoptosis inhibitor 5 (ENSG00000166181), score: -0.99 ARF5ADP-ribosylation factor 5 (ENSG00000004059), score: -0.59 ARF6ADP-ribosylation factor 6 (ENSG00000165527), score: 0.53 ARHGEF11Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 11 (ENSG00000132694), score: -0.56 ARHGEF38Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 38 (ENSG00000138784), score: 0.54 ARL1ADP-ribosylation factor-like 1 (ENSG00000120805), score: 0.64 ARNTaryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (ENSG00000143437), score: 0.63 ARPC4actin related protein 2/3 complex, subunit 4, 20kDa (ENSG00000214021), score: -0.59 ARR3arrestin 3, retinal (X-arrestin) (ENSG00000120500), score: 0.63 ARV1ARV1 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000173409), score: -0.63 ATRIPATR interacting protein (ENSG00000164053), score: 0.92 ATXN1ataxin 1 (ENSG00000124788), score: -0.77 AVILadvillin (ENSG00000135407), score: 0.81 AZU1azurocidin 1 (ENSG00000172232), score: 0.66 B3GALT4UDP-Gal:betaGlcNAc beta 1,3-galactosyltransferase, polypeptide 4 (ENSG00000235863), score: -0.69 BCL3B-cell CLL/lymphoma 3 (ENSG00000069399), score: 0.54 BEST1bestrophin 1 (ENSG00000167995), score: -0.76 BIRC2baculoviral IAP repeat-containing 2 (ENSG00000110330), score: 0.61 BIRC3baculoviral IAP repeat-containing 3 (ENSG00000023445), score: 0.66 BPIL1bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein-like 1 (ENSG00000078898), score: 0.75 BPIL3bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein-like 3 (ENSG00000167104), score: 0.63 BRD2bromodomain containing 2 (ENSG00000204256), score: -1 BRD4bromodomain containing 4 (ENSG00000141867), score: -0.56 BST1bone marrow stromal cell antigen 1 (ENSG00000109743), score: 0.6 BTLAB and T lymphocyte associated (ENSG00000186265), score: 0.57 C12orf51chromosome 12 open reading frame 51 (ENSG00000173064), score: -0.55 C12orf52chromosome 12 open reading frame 52 (ENSG00000139405), score: -0.65 C15orf23chromosome 15 open reading frame 23 (ENSG00000128944), score: -0.61 C16orf45chromosome 16 open reading frame 45 (ENSG00000166780), score: -0.59 C16orf48chromosome 16 open reading frame 48 (ENSG00000124074), score: -0.55 C16orf57chromosome 16 open reading frame 57 (ENSG00000103005), score: -0.66 C16orf61chromosome 16 open reading frame 61 (ENSG00000103121), score: 0.82 C16orf7chromosome 16 open reading frame 7 (ENSG00000075399), score: -0.71 C16orf79chromosome 16 open reading frame 79 (ENSG00000182685), score: -0.69 C17orf67chromosome 17 open reading frame 67 (ENSG00000214226), score: 0.73 C17orf76chromosome 17 open reading frame 76 (ENSG00000181350), score: -0.61 C17orf99chromosome 17 open reading frame 99 (ENSG00000187997), score: 0.62 C19orf54chromosome 19 open reading frame 54 (ENSG00000188493), score: 0.54 C1orf192chromosome 1 open reading frame 192 (ENSG00000188931), score: -0.67 C1orf27chromosome 1 open reading frame 27 (ENSG00000157181), score: 0.66 C1orf56chromosome 1 open reading frame 56 (ENSG00000143443), score: -0.61 C1orf83chromosome 1 open reading frame 83 (ENSG00000116205), score: 0.56 C1QTNF5C1q and tumor necrosis factor related protein 5 (ENSG00000235718), score: 0.62 C20orf70chromosome 20 open reading frame 70 (ENSG00000131050), score: 0.73 C21orf2chromosome 21 open reading frame 2 (ENSG00000160226), score: -0.66 C2CD4BC2 calcium-dependent domain containing 4B (ENSG00000205502), score: 0.7 C2orf66chromosome 2 open reading frame 66 (ENSG00000187944), score: 0.86 C3orf18chromosome 3 open reading frame 18 (ENSG00000088543), score: -0.62 C3orf37chromosome 3 open reading frame 37 (ENSG00000183624), score: -0.6 C3orf75chromosome 3 open reading frame 75 (ENSG00000163832), score: -0.77 C4orf29chromosome 4 open reading frame 29 (ENSG00000164074), score: 0.64 C5orf13chromosome 5 open reading frame 13 (ENSG00000134986), score: -0.76 C6orf126chromosome 6 open reading frame 126 (ENSG00000196748), score: 0.88 CA1carbonic anhydrase I (ENSG00000133742), score: 0.93 CABP7calcium binding protein 7 (ENSG00000100314), score: -0.65 CAMPcathelicidin antimicrobial peptide (ENSG00000164047), score: 0.64 CARD17caspase recruitment domain family, member 17 (ENSG00000137752), score: 0.59 CASP4caspase 4, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase (ENSG00000196954), score: 0.65 CBX7chromobox homolog 7 (ENSG00000100307), score: -0.6 CBY1chibby homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000100211), score: 0.53 CCDC134coiled-coil domain containing 134 (ENSG00000100147), score: 0.55 CCDC152coiled-coil domain containing 152 (ENSG00000198865), score: -0.62 CCDC153coiled-coil domain containing 153 (ENSG00000204313), score: 0.55 CCDC3coiled-coil domain containing 3 (ENSG00000151468), score: -0.58 CCDC42Bcoiled-coil domain containing 42B (ENSG00000186710), score: -0.59 CCDC92coiled-coil domain containing 92 (ENSG00000119242), score: -0.77 CCHCR1coiled-coil alpha-helical rod protein 1 (ENSG00000204536), score: -0.71 CCL7chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 7 (ENSG00000108688), score: 0.61 CCNG1cyclin G1 (ENSG00000113328), score: 0.61 CCRL2chemokine (C-C motif) receptor-like 2 (ENSG00000121797), score: 0.54 CCT6Achaperonin containing TCP1, subunit 6A (zeta 1) (ENSG00000146731), score: 0.52 CD1CCD1c molecule (ENSG00000158481), score: 0.55 CD209CD209 molecule (ENSG00000090659), score: 0.66 CD58CD58 molecule (ENSG00000116815), score: 0.54 CD80CD80 molecule (ENSG00000121594), score: 0.72 CDH17cadherin 17, LI cadherin (liver-intestine) (ENSG00000079112), score: 0.54 CEBPECCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP), epsilon (ENSG00000092067), score: 0.96 CENPNcentromere protein N (ENSG00000166451), score: -0.64 CENPOcentromere protein O (ENSG00000138092), score: -0.7 CFDP1craniofacial development protein 1 (ENSG00000153774), score: 0.54 CGREF1cell growth regulator with EF-hand domain 1 (ENSG00000138028), score: -0.57 CHSY1chondroitin sulfate synthase 1 (ENSG00000131873), score: 0.65 CICcapicua homolog (Drosophila) (ENSG00000079432), score: -0.6 CKAP4cytoskeleton-associated protein 4 (ENSG00000136026), score: 0.59 CLEC5AC-type lectin domain family 5, member A (ENSG00000090269), score: 0.99 CMTM6CKLF-like MARVEL transmembrane domain containing 6 (ENSG00000091317), score: 0.55 COLEC10collectin sub-family member 10 (C-type lectin) (ENSG00000184374), score: 0.57 COMMD3COMM domain containing 3 (ENSG00000148444), score: 0.6 COMMD6COMM domain containing 6 (ENSG00000188243), score: 0.57 COQ2coenzyme Q2 homolog, prenyltransferase (yeast) (ENSG00000173085), score: 0.57 CPPED1calcineurin-like phosphoesterase domain containing 1 (ENSG00000103381), score: 0.55 CREB3L4cAMP responsive element binding protein 3-like 4 (ENSG00000143578), score: 0.57 CRELD2cysteine-rich with EGF-like domains 2 (ENSG00000184164), score: 0.54 CRISP3cysteine-rich secretory protein 3 (ENSG00000096006), score: 0.56 CSF2colony stimulating factor 2 (granulocyte-macrophage) (ENSG00000164400), score: 0.57 CTBSchitobiase, di-N-acetyl- (ENSG00000117151), score: 0.65 CTNNBIP1catenin, beta interacting protein 1 (ENSG00000178585), score: -0.57 CTSGcathepsin G (ENSG00000100448), score: 0.61 CTSKcathepsin K (ENSG00000143387), score: 0.82 CXCR6chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 6 (ENSG00000172215), score: 0.65 CYB561D1cytochrome b-561 domain containing 1 (ENSG00000174151), score: -0.68 CYTIPcytohesin 1 interacting protein (ENSG00000115165), score: 0.57 DAXXdeath-domain associated protein (ENSG00000204209), score: -0.95 DBF4BDBF4 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000161692), score: -0.61 DCAF17DDB1 and CUL4 associated factor 17 (ENSG00000115827), score: -0.66 DCTDdCMP deaminase (ENSG00000129187), score: 0.54 DDIT4DNA-damage-inducible transcript 4 (ENSG00000168209), score: 0.68 DDX18DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 18 (ENSG00000088205), score: 0.57 DDX41DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 41 (ENSG00000183258), score: -0.57 DDX5DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 5 (ENSG00000108654), score: 0.58 DDX60LDEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 60-like (ENSG00000181381), score: 0.64 DEAF1deformed epidermal autoregulatory factor 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000177030), score: -0.58 DEF8differentially expressed in FDCP 8 homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000140995), score: -0.58 DHRS9dehydrogenase/reductase (SDR family) member 9 (ENSG00000073737), score: 0.63 DNAJC3DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 3 (ENSG00000102580), score: 0.61 DNAL1dynein, axonemal, light chain 1 (ENSG00000119661), score: 0.6 DOC2Adouble C2-like domains, alpha (ENSG00000149927), score: -0.85 DONSONdownstream neighbor of SON (ENSG00000159147), score: -0.65 DSCR3Down syndrome critical region gene 3 (ENSG00000157538), score: 0.52 DZIP1DAZ interacting protein 1 (ENSG00000134874), score: -0.56 ECH1enoyl CoA hydratase 1, peroxisomal (ENSG00000104823), score: 0.6 ECHDC1enoyl CoA hydratase domain containing 1 (ENSG00000093144), score: 0.59 EDA2Rectodysplasin A2 receptor (ENSG00000131080), score: 0.53 EGLN1egl nine homolog 1 (C. elegans) (ENSG00000135766), score: 0.53 EIF2AK3eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2-alpha kinase 3 (ENSG00000172071), score: 0.61 EIF2B5eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2B, subunit 5 epsilon, 82kDa (ENSG00000145191), score: 0.55 EIF2S1eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2, subunit 1 alpha, 35kDa (ENSG00000134001), score: 0.57 ELANEelastase, neutrophil expressed (ENSG00000197561), score: 0.64 EMG1EMG1 nucleolar protein homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000126749), score: 0.66 EMR3egf-like module containing, mucin-like, hormone receptor-like 3 (ENSG00000131355), score: 0.53 ENY2enhancer of yellow 2 homolog (Drosophila) (ENSG00000120533), score: 0.58 ERP44endoplasmic reticulum protein 44 (ENSG00000023318), score: 0.53 EXOC7exocyst complex component 7 (ENSG00000182473), score: -0.58 EXOSC3exosome component 3 (ENSG00000107371), score: 0.71 EXTL2exostoses (multiple)-like 2 (ENSG00000162694), score: -0.6 FAM134Cfamily with sequence similarity 134, member C (ENSG00000141699), score: -0.55 FAM162Afamily with sequence similarity 162, member A (ENSG00000114023), score: 0.62 FAM166Afamily with sequence similarity 166, member A (ENSG00000188163), score: -0.9 FAM173Bfamily with sequence similarity 173, member B (ENSG00000150756), score: 0.64 FAM174Bfamily with sequence similarity 174, member B (ENSG00000185442), score: -0.61 FAM36Afamily with sequence similarity 36, member A (ENSG00000203667), score: 0.69 FAM59Afamily with sequence similarity 59, member A (ENSG00000141441), score: -0.56 FAM83Afamily with sequence similarity 83, member A (ENSG00000147689), score: 0.58 FBXO21F-box protein 21 (ENSG00000135108), score: -0.74 FGF2fibroblast growth factor 2 (basic) (ENSG00000138685), score: -0.88 FGL2fibrinogen-like 2 (ENSG00000127951), score: 0.52 FRMD8FERM domain containing 8 (ENSG00000126391), score: -0.79 GADD45Bgrowth arrest and DNA-damage-inducible, beta (ENSG00000099860), score: 0.56 GFM2G elongation factor, mitochondrial 2 (ENSG00000164347), score: 0.65 GHRHgrowth hormone releasing hormone (ENSG00000118702), score: 0.93 GJC3gap junction protein, gamma 3, 30.2kDa (ENSG00000176402), score: 0.57 GLI4GLI family zinc finger 4 (ENSG00000181638), score: -0.65 GLIPR1GLI pathogenesis-related 1 (ENSG00000139278), score: 0.66 GLTPglycolipid transfer protein (ENSG00000139433), score: -0.63 GNGT1guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), gamma transducing activity polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000127928), score: 0.84 GPR107G protein-coupled receptor 107 (ENSG00000148358), score: -0.7 GPR97G protein-coupled receptor 97 (ENSG00000182885), score: 0.62 GPRC5DG protein-coupled receptor, family C, group 5, member D (ENSG00000111291), score: 0.55 GRAMD3GRAM domain containing 3 (ENSG00000155324), score: 0.57 GTF2E1general transcription factor IIE, polypeptide 1, alpha 56kDa (ENSG00000153767), score: 0.56 GTF3C1general transcription factor IIIC, polypeptide 1, alpha 220kDa (ENSG00000077235), score: -0.64 GZMKgranzyme K (granzyme 3; tryptase II) (ENSG00000113088), score: 0.73 HARS2histidyl-tRNA synthetase 2, mitochondrial (putative) (ENSG00000112855), score: 0.65 HCCSholocytochrome c synthase (ENSG00000004961), score: 0.54 HIST1H1Bhistone cluster 1, H1b (ENSG00000184357), score: 0.76 HIST1H3Ahistone cluster 1, H3a (ENSG00000112727), score: 0.71 HLA-DMAmajor histocompatibility complex, class II, DM alpha (ENSG00000204257), score: -0.67 HLA-DMBmajor histocompatibility complex, class II, DM beta (ENSG00000242574), score: -0.62 HLA-DOBmajor histocompatibility complex, class II, DO beta (ENSG00000204267), score: -0.82 HLA-DPA1major histocompatibility complex, class II, DP alpha 1 (ENSG00000231389), score: -0.74 HLA-DPB1major histocompatibility complex, class II, DP beta 1 (ENSG00000223865), score: -0.77 HLA-DRAmajor histocompatibility complex, class II, DR alpha (ENSG00000204287), score: -0.78 HNRNPH3heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein H3 (2H9) (ENSG00000096746), score: 0.61 HPSEheparanase (ENSG00000173083), score: 0.7 HSD17B8hydroxysteroid (17-beta) dehydrogenase 8 (ENSG00000204228), score: -0.75 HSH2Dhematopoietic SH2 domain containing (ENSG00000196684), score: 0.55 HSPA5heat shock 70kDa protein 5 (glucose-regulated protein, 78kDa) (ENSG00000044574), score: 0.68 HTATIP2HIV-1 Tat interactive protein 2, 30kDa (ENSG00000109854), score: -0.61 HTThuntingtin (ENSG00000197386), score: -0.72 IBSPintegrin-binding sialoprotein (ENSG00000029559), score: 0.56 IFNAR1interferon (alpha, beta and omega) receptor 1 (ENSG00000142166), score: 0.56 IL18interleukin 18 (interferon-gamma-inducing factor) (ENSG00000150782), score: 0.55 IL6interleukin 6 (interferon, beta 2) (ENSG00000136244), score: 0.56 IRAK4interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 (ENSG00000198001), score: 0.55 IRF2interferon regulatory factor 2 (ENSG00000168310), score: 0.57 IRF4interferon regulatory factor 4 (ENSG00000137265), score: 0.66 ITSN2intersectin 2 (ENSG00000198399), score: 0.57 JMJD6jumonji domain containing 6 (ENSG00000070495), score: 0.64 KCNE4potassium voltage-gated channel, Isk-related family, member 4 (ENSG00000152049), score: 0.56 KIAA0146KIAA0146 (ENSG00000164808), score: 0.62 KIAA0195KIAA0195 (ENSG00000177728), score: -0.69 KIAA0564KIAA0564 (ENSG00000102763), score: 0.59 KIAA0892KIAA0892 (ENSG00000129933), score: -0.66 KRT27keratin 27 (ENSG00000171446), score: 0.8 LAX1lymphocyte transmembrane adaptor 1 (ENSG00000122188), score: 0.59 LGTNligatin (ENSG00000143486), score: 0.55 LIFleukemia inhibitory factor (cholinergic differentiation factor) (ENSG00000128342), score: 0.65 LNP1leukemia NUP98 fusion partner 1 (ENSG00000206535), score: -0.56 LONP2lon peptidase 2, peroxisomal (ENSG00000102910), score: 0.64 LOXL3lysyl oxidase-like 3 (ENSG00000115318), score: -0.7 LOXL4lysyl oxidase-like 4 (ENSG00000138131), score: 0.62 LPCAT2lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 2 (ENSG00000087253), score: 0.61 LRRC23leucine rich repeat containing 23 (ENSG00000010626), score: -0.6 LSM14BLSM14B, SCD6 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000149657), score: -0.57 LTBlymphotoxin beta (TNF superfamily, member 3) (ENSG00000227507), score: 0.62 LYG2lysozyme G-like 2 (ENSG00000185674), score: 0.81 LYSMD3LysM, putative peptidoglycan-binding, domain containing 3 (ENSG00000176018), score: 0.56 MAGOHBmago-nashi homolog B (Drosophila) (ENSG00000111196), score: 0.65 MANFmesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor (ENSG00000145050), score: 0.54 MAP3K8mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 8 (ENSG00000107968), score: 0.56 MAPK10mitogen-activated protein kinase 10 (ENSG00000109339), score: -0.63 MAPK12mitogen-activated protein kinase 12 (ENSG00000188130), score: -0.77 MED17mediator complex subunit 17 (ENSG00000042429), score: 0.67 MED28mediator complex subunit 28 (ENSG00000118579), score: 0.55 MED6mediator complex subunit 6 (ENSG00000133997), score: -0.61 MEF2Bmyocyte enhancer factor 2B (ENSG00000064489), score: -0.68 MEMO1mediator of cell motility 1 (ENSG00000162961), score: 0.58 MESDC2mesoderm development candidate 2 (ENSG00000117899), score: 0.76 MFSD8major facilitator superfamily domain containing 8 (ENSG00000164073), score: 0.58 MINAMYC induced nuclear antigen (ENSG00000170854), score: 0.68 MITD1MIT, microtubule interacting and transport, domain containing 1 (ENSG00000158411), score: 0.65 MLANAmelan-A (ENSG00000120215), score: 0.97 MLST8MTOR associated protein, LST8 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000167965), score: -0.57 MMABmethylmalonic aciduria (cobalamin deficiency) cblB type (ENSG00000139428), score: 0.66 MMP8matrix metallopeptidase 8 (neutrophil collagenase) (ENSG00000118113), score: 0.72 MRPL36mitochondrial ribosomal protein L36 (ENSG00000171421), score: -0.66 MRPL44mitochondrial ribosomal protein L44 (ENSG00000135900), score: 0.53 MRPL9mitochondrial ribosomal protein L9 (ENSG00000143436), score: 0.64 MRPS14mitochondrial ribosomal protein S14 (ENSG00000120333), score: 0.55 MRPS16mitochondrial ribosomal protein S16 (ENSG00000182180), score: 0.6 MRPS17mitochondrial ribosomal protein S17 (ENSG00000239789), score: 0.55 MRPS33mitochondrial ribosomal protein S33 (ENSG00000090263), score: 0.6 MRPS35mitochondrial ribosomal protein S35 (ENSG00000061794), score: 0.52 MSMBmicroseminoprotein, beta- (ENSG00000138294), score: 0.76 MTERFD2MTERF domain containing 2 (ENSG00000122085), score: 0.54 MTHFD2Lmethylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (NADP+ dependent) 2-like (ENSG00000163738), score: 0.65 MYBPHmyosin binding protein H (ENSG00000133055), score: 0.61 MYH2myosin, heavy chain 2, skeletal muscle, adult (ENSG00000125414), score: 0.53 MYO7Amyosin VIIA (ENSG00000137474), score: 0.53 MYSM1Myb-like, SWIRM and MPN domains 1 (ENSG00000162601), score: 0.55 NAGKN-acetylglucosamine kinase (ENSG00000124357), score: 0.61 NAT10N-acetyltransferase 10 (GCN5-related) (ENSG00000135372), score: -0.65 NBEAL1neurobeachin-like 1 (ENSG00000144426), score: 0.7 NDUFB9NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 beta subcomplex, 9, 22kDa (ENSG00000147684), score: -0.64 NF2neurofibromin 2 (merlin) (ENSG00000186575), score: -0.56 NFIL3nuclear factor, interleukin 3 regulated (ENSG00000165030), score: 0.62 NLRP12NLR family, pyrin domain containing 12 (ENSG00000142405), score: 0.66 NQO1NAD(P)H dehydrogenase, quinone 1 (ENSG00000181019), score: 0.58 NRLneural retina leucine zipper (ENSG00000129535), score: -0.62 NT5C3L5'-nucleotidase, cytosolic III-like (ENSG00000141698), score: -0.72 NXF1nuclear RNA export factor 1 (ENSG00000162231), score: 0.56 OFD1oral-facial-digital syndrome 1 (ENSG00000046651), score: 0.58 OLFM2olfactomedin 2 (ENSG00000105088), score: -0.56 OSBP2oxysterol binding protein 2 (ENSG00000184792), score: -0.58 P2RY2purinergic receptor P2Y, G-protein coupled, 2 (ENSG00000175591), score: 0.57 PAPD7PAP associated domain containing 7 (ENSG00000112941), score: -0.61 PAPSS23'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate synthase 2 (ENSG00000198682), score: 0.53 PARP3poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase family, member 3 (ENSG00000041880), score: 0.56 PARP6poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase family, member 6 (ENSG00000137817), score: -0.6 PCCBpropionyl CoA carboxylase, beta polypeptide (ENSG00000114054), score: 0.52 PCGF3polycomb group ring finger 3 (ENSG00000185619), score: -0.6 PCTPphosphatidylcholine transfer protein (ENSG00000141179), score: 0.53 PCYT1Aphosphate cytidylyltransferase 1, choline, alpha (ENSG00000161217), score: 0.59 PDCD1LG2programmed cell death 1 ligand 2 (ENSG00000197646), score: 0.58 PDCD4programmed cell death 4 (neoplastic transformation inhibitor) (ENSG00000150593), score: 0.65 PDIA3protein disulfide isomerase family A, member 3 (ENSG00000167004), score: 0.53 PELI3pellino homolog 3 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000174516), score: -0.56 PFDN6prefoldin subunit 6 (ENSG00000204220), score: -0.98 PHF23PHD finger protein 23 (ENSG00000040633), score: 1 PIGUphosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis, class U (ENSG00000101464), score: -0.62 PIM2pim-2 oncogene (ENSG00000102096), score: 0.56 PLA2G16phospholipase A2, group XVI (ENSG00000176485), score: 0.61 PLA2G2Aphospholipase A2, group IIA (platelets, synovial fluid) (ENSG00000188257), score: 0.62 PLA2G2Fphospholipase A2, group IIF (ENSG00000158786), score: 0.62 PLAC8placenta-specific 8 (ENSG00000145287), score: 0.69 PM20D2peptidase M20 domain containing 2 (ENSG00000146281), score: 0.62 PODNpodocan (ENSG00000174348), score: 0.66 POLE4polymerase (DNA-directed), epsilon 4 (p12 subunit) (ENSG00000115350), score: 0.66 POLR2Fpolymerase (RNA) II (DNA directed) polypeptide F (ENSG00000100142), score: -0.67 POLR2Ipolymerase (RNA) II (DNA directed) polypeptide I, 14.5kDa (ENSG00000105258), score: -0.68 POLR3Bpolymerase (RNA) III (DNA directed) polypeptide B (ENSG00000013503), score: 0.52 POP5processing of precursor 5, ribonuclease P/MRP subunit (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000167272), score: 0.53 POU2F3POU class 2 homeobox 3 (ENSG00000137709), score: 0.69 PPA1pyrophosphatase (inorganic) 1 (ENSG00000180817), score: -0.56 PPAPDC1Bphosphatidic acid phosphatase type 2 domain containing 1B (ENSG00000147535), score: 0.61 PPBPpro-platelet basic protein (chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 7) (ENSG00000163736), score: 0.79 PPP2R2Dprotein phosphatase 2, regulatory subunit B, delta (ENSG00000175470), score: -0.57 PRDM1PR domain containing 1, with ZNF domain (ENSG00000057657), score: 0.6 PRICKLE4prickle homolog 4 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000124593), score: -0.58 PRKAR1Bprotein kinase, cAMP-dependent, regulatory, type I, beta (ENSG00000188191), score: -0.61 PRLprolactin (ENSG00000172179), score: 0.94 PRMT3protein arginine methyltransferase 3 (ENSG00000185238), score: 0.57 PROSCproline synthetase co-transcribed homolog (bacterial) (ENSG00000147471), score: 0.52 PRRT2proline-rich transmembrane protein 2 (ENSG00000167371), score: -0.57 PRSS53protease, serine, 53 (ENSG00000151006), score: 0.66 PSMB8proteasome (prosome, macropain) subunit, beta type, 8 (large multifunctional peptidase 7) (ENSG00000204264), score: -0.64 PSMB9proteasome (prosome, macropain) subunit, beta type, 9 (large multifunctional peptidase 2) (ENSG00000240065), score: -0.7 PSTPIP2proline-serine-threonine phosphatase interacting protein 2 (ENSG00000152229), score: 0.54 PTCD3Pentatricopeptide repeat domain 3 (ENSG00000132300), score: 0.78 PTGIRprostaglandin I2 (prostacyclin) receptor (IP) (ENSG00000160013), score: 0.55 PTGR2prostaglandin reductase 2 (ENSG00000140043), score: 0.69 PTGS2prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 (prostaglandin G/H synthase and cyclooxygenase) (ENSG00000073756), score: 0.53 PYROXD1pyridine nucleotide-disulphide oxidoreductase domain 1 (ENSG00000121350), score: 0.55 QSOX2quiescin Q6 sulfhydryl oxidase 2 (ENSG00000165661), score: -0.55 R3HDMLR3H domain containing-like (ENSG00000101074), score: 0.73 RAB40ARAB40A, member RAS oncogene family (ENSG00000172476), score: 0.65 RABEP2rabaptin, RAB GTPase binding effector protein 2 (ENSG00000177548), score: 0.53 RABGGTBRab geranylgeranyltransferase, beta subunit (ENSG00000137955), score: 0.6 RAD54BRAD54 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000197275), score: 0.55 RAG1recombination activating gene 1 (ENSG00000166349), score: 0.54 RAP1GDS1RAP1, GTP-GDP dissociation stimulator 1 (ENSG00000138698), score: -0.56 RAPGEF1Rap guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 1 (ENSG00000107263), score: -0.59 RARSarginyl-tRNA synthetase (ENSG00000113643), score: 0.61 RBMS1RNA binding motif, single stranded interacting protein 1 (ENSG00000153250), score: 0.53 RBMS3RNA binding motif, single stranded interacting protein 3 (ENSG00000144642), score: 0.56 RFC2replication factor C (activator 1) 2, 40kDa (ENSG00000049541), score: 0.64 RFC5replication factor C (activator 1) 5, 36.5kDa (ENSG00000111445), score: -0.58 RFX8regulatory factor X, 8 (ENSG00000196460), score: 0.59 RG9MTD1RNA (guanine-9-) methyltransferase domain containing 1 (ENSG00000174173), score: 0.53 RGL2ral guanine nucleotide dissociation stimulator-like 2 (ENSG00000237441), score: -0.96 RGS18regulator of G-protein signaling 18 (ENSG00000150681), score: 0.55 RGS2regulator of G-protein signaling 2, 24kDa (ENSG00000116741), score: 0.61 RING1ring finger protein 1 (ENSG00000204227), score: -1 RNASE7ribonuclease, RNase A family, 7 (ENSG00000165799), score: 0.55 RNLSrenalase, FAD-dependent amine oxidase (ENSG00000184719), score: 0.68 RNMTRNA (guanine-7-) methyltransferase (ENSG00000101654), score: -0.77 RPL37ribosomal protein L37 (ENSG00000145592), score: -0.89 RPUSD3RNA pseudouridylate synthase domain containing 3 (ENSG00000156990), score: -0.59 RRP15ribosomal RNA processing 15 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000067533), score: 0.67 RRP9ribosomal RNA processing 9, small subunit (SSU) processome component, homolog (yeast) (ENSG00000114767), score: 0.54 RXRBretinoid X receptor, beta (ENSG00000204231), score: -0.98 S100A12S100 calcium binding protein A12 (ENSG00000163221), score: 0.62 SAP18Sin3A-associated protein, 18kDa (ENSG00000150459), score: 0.8 SAP30BPSAP30 binding protein (ENSG00000161526), score: 0.59 SCARF1scavenger receptor class F, member 1 (ENSG00000074660), score: 0.65 SCGB3A2secretoglobin, family 3A, member 2 (ENSG00000164265), score: 0.81 SCO1SCO cytochrome oxidase deficient homolog 1 (yeast) (ENSG00000133028), score: 0.55 SCPEP1serine carboxypeptidase 1 (ENSG00000121064), score: 0.62 SCYL1SCY1-like 1 (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000142186), score: 0.99 SDCBPsyndecan binding protein (syntenin) (ENSG00000137575), score: 0.6 SEC22CSEC22 vesicle trafficking protein homolog C (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000093183), score: -0.6 SELPselectin P (granule membrane protein 140kDa, antigen CD62) (ENSG00000174175), score: 0.53 SERBP1SERPINE1 mRNA binding protein 1 (ENSG00000142864), score: 0.66 SERGEFsecretion regulating guanine nucleotide exchange factor (ENSG00000129158), score: -0.59 SERPINE1serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade E (nexin, plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1), member 1 (ENSG00000106366), score: 0.57 SFXN2sideroflexin 2 (ENSG00000156398), score: 0.54 SIK1salt-inducible kinase 1 (ENSG00000142178), score: 0.58 SIKE1suppressor of IKBKE 1 (ENSG00000052723), score: 0.58 SLAMF7SLAM family member 7 (ENSG00000026751), score: 0.55 SLC11A2solute carrier family 11 (proton-coupled divalent metal ion transporters), member 2 (ENSG00000110911), score: 0.55 SLC16A3solute carrier family 16, member 3 (monocarboxylic acid transporter 4) (ENSG00000141526), score: 0.56 SLC30A5solute carrier family 30 (zinc transporter), member 5 (ENSG00000145740), score: 0.63 SLC39A7solute carrier family 39 (zinc transporter), member 7 (ENSG00000112473), score: -0.97 SMNDC1survival motor neuron domain containing 1 (ENSG00000119953), score: 0.64 SNRNP48small nuclear ribonucleoprotein 48kDa (U11/U12) (ENSG00000168566), score: 0.68 SOD1superoxide dismutase 1, soluble (ENSG00000142168), score: 0.55 SPON2spondin 2, extracellular matrix protein (ENSG00000159674), score: 0.6 SPTA1spectrin, alpha, erythrocytic 1 (elliptocytosis 2) (ENSG00000163554), score: 0.52 SRFBP1serum response factor binding protein 1 (ENSG00000151304), score: 0.74 SRP19signal recognition particle 19kDa (ENSG00000153037), score: 0.59 SRSF3serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 3 (ENSG00000112081), score: 0.62 SRSF7serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 7 (ENSG00000115875), score: 0.55 SSBP1single-stranded DNA binding protein 1 (ENSG00000106028), score: 0.55 STAT3signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (acute-phase response factor) (ENSG00000168610), score: 0.56 STX11syntaxin 11 (ENSG00000135604), score: 0.55 SUPV3L1suppressor of var1, 3-like 1 (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000156502), score: 0.65 SUV39H1suppressor of variegation 3-9 homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000101945), score: -0.56 SYF2SYF2 homolog, RNA splicing factor (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000117614), score: 0.57 TAP1transporter 1, ATP-binding cassette, sub-family B (MDR/TAP) (ENSG00000168394), score: -0.76 TAPBPTAP binding protein (tapasin) (ENSG00000231925), score: -0.93 TBC1D14TBC1 domain family, member 14 (ENSG00000132405), score: -0.63 TBC1D8BTBC1 domain family, member 8B (with GRAM domain) (ENSG00000133138), score: 0.58 TC2Ntandem C2 domains, nuclear (ENSG00000165929), score: 0.6 TCF19transcription factor 19 (ENSG00000137310), score: -0.6 TCTE3t-complex-associated-testis-expressed 3 (ENSG00000184786), score: 0.57 TCTEX1D1Tctex1 domain containing 1 (ENSG00000152760), score: 0.61 TEFthyrotrophic embryonic factor (ENSG00000167074), score: -0.64 TFF1trefoil factor 1 (ENSG00000160182), score: 0.87 THRAP3thyroid hormone receptor associated protein 3 (ENSG00000054118), score: 0.53 THTPAthiamine triphosphatase (ENSG00000157306), score: -0.57 THUMPD3THUMP domain containing 3 (ENSG00000134077), score: -0.79 TIAL1TIA1 cytotoxic granule-associated RNA binding protein-like 1 (ENSG00000151923), score: 0.58 TIAM2T-cell lymphoma invasion and metastasis 2 (ENSG00000146426), score: -0.62 TIGITT cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains (ENSG00000181847), score: 0.72 TLCD2TLC domain containing 2 (ENSG00000185561), score: 0.56 TM9SF3transmembrane 9 superfamily member 3 (ENSG00000077147), score: 0.56 TMC3transmembrane channel-like 3 (ENSG00000188869), score: 0.77 TMCO1transmembrane and coiled-coil domains 1 (ENSG00000143183), score: 0.67 TMCO4transmembrane and coiled-coil domains 4 (ENSG00000162542), score: 0.53 TMEM120Btransmembrane protein 120B (ENSG00000188735), score: -0.6 TMEM131transmembrane protein 131 (ENSG00000075568), score: -0.7 TMEM149transmembrane protein 149 (ENSG00000126246), score: 0.65 TMEM80transmembrane protein 80 (ENSG00000177042), score: -0.72 TOB1transducer of ERBB2, 1 (ENSG00000141232), score: 0.59 TRAT1T cell receptor associated transmembrane adaptor 1 (ENSG00000163519), score: 0.75 TRDMT1tRNA aspartic acid methyltransferase 1 (ENSG00000107614), score: 0.55 TREM1triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 1 (ENSG00000124731), score: 0.57 TRIM26tripartite motif-containing 26 (ENSG00000234127), score: -0.95 TRIM5tripartite motif-containing 5 (ENSG00000132256), score: 0.59 TRIT1tRNA isopentenyltransferase 1 (ENSG00000043514), score: 0.56 TRUB2TruB pseudouridine (psi) synthase homolog 2 (E. coli) (ENSG00000167112), score: 0.56 TTC14tetratricopeptide repeat domain 14 (ENSG00000163728), score: 0.54 TTC17tetratricopeptide repeat domain 17 (ENSG00000052841), score: 0.53 TTLL11tubulin tyrosine ligase-like family, member 11 (ENSG00000175764), score: -0.58 TUSC2tumor suppressor candidate 2 (ENSG00000114383), score: -0.58 TXNDC12thioredoxin domain containing 12 (endoplasmic reticulum) (ENSG00000117862), score: 0.58 UBE2Bubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2B (RAD6 homolog) (ENSG00000119048), score: 0.6 UBE2G1ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2G 1 (UBC7 homolog, yeast) (ENSG00000132388), score: 0.63 UBE2Iubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2I (UBC9 homolog, yeast) (ENSG00000103275), score: -0.59 URB1URB1 ribosome biogenesis 1 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000142207), score: -0.62 UTP14AUTP14, U3 small nucleolar ribonucleoprotein, homolog A (yeast) (ENSG00000156697), score: 0.6 VAMP7vesicle-associated membrane protein 7 (ENSG00000124333), score: 0.57 VASH1vasohibin 1 (ENSG00000071246), score: -0.66 VMO1vitelline membrane outer layer 1 homolog (chicken) (ENSG00000182853), score: 0.52 VNN2vanin 2 (ENSG00000112303), score: 0.77 VPS37Dvacuolar protein sorting 37 homolog D (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000176428), score: -0.55 VPS52vacuolar protein sorting 52 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000223501), score: -0.99 WBP5WW domain binding protein 5 (ENSG00000185222), score: 0.64 WDR46WD repeat domain 46 (ENSG00000227057), score: -0.98 WDR83WD repeat domain 83 (ENSG00000123154), score: -0.59 WISP1WNT1 inducible signaling pathway protein 1 (ENSG00000104415), score: 0.59 WRBtryptophan rich basic protein (ENSG00000182093), score: -0.68 XPNPEP1X-prolyl aminopeptidase (aminopeptidase P) 1, soluble (ENSG00000108039), score: 0.52 YIPF4Yip1 domain family, member 4 (ENSG00000119820), score: 0.55 ZBTB22zinc finger and BTB domain containing 22 (ENSG00000236104), score: -0.93 ZBTB24zinc finger and BTB domain containing 24 (ENSG00000112365), score: -0.56 ZC3H3zinc finger CCCH-type containing 3 (ENSG00000014164), score: -0.56 ZCCHC14zinc finger, CCHC domain containing 14 (ENSG00000140948), score: -0.59 ZCCHC4zinc finger, CCHC domain containing 4 (ENSG00000168228), score: 0.53 ZDHHC8zinc finger, DHHC-type containing 8 (ENSG00000099904), score: -0.7 ZNF232zinc finger protein 232 (ENSG00000167840), score: 0.65 ZNF275zinc finger protein 275 (ENSG00000063587), score: -0.66 ZNF324zinc finger protein 324 (ENSG00000083812), score: -0.59 ZNF343zinc finger protein 343 (ENSG00000088876), score: -0.57 ZNF394zinc finger protein 394 (ENSG00000160908), score: 0.72 ZNF398zinc finger protein 398 (ENSG00000197024), score: -0.56 ZNF434zinc finger protein 434 (ENSG00000140987), score: -0.63 ZNF575zinc finger protein 575 (ENSG00000176472), score: -0.63 ZNF582zinc finger protein 582 (ENSG00000018869), score: 0.54 ZNF584zinc finger protein 584 (ENSG00000171574), score: -0.72 ZNF589zinc finger protein 589 (ENSG00000164048), score: -0.77 ZNF629zinc finger protein 629 (ENSG00000102870), score: -0.72 ZNF652zinc finger protein 652 (ENSG00000198740), score: 0.53 ZNF707zinc finger protein 707 (ENSG00000181135), score: -0.58 ZNF786zinc finger protein 786 (ENSG00000197362), score: -0.56 ZNRD1zinc ribbon domain containing 1 (ENSG00000066379), score: -0.9 ZZEF1zinc finger, ZZ-type with EF-hand domain 1 (ENSG00000074755), score: -0.58
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ppy_kd_m_ca1 | ppy | kd | m | _ |
| ppy_ht_m_ca1 | ppy | ht | m | _ |
| ppy_kd_f_ca1 | ppy | kd | f | _ |
| ppy_ht_f_ca1 | ppy | ht | f | _ |
| ppy_lv_m_ca1 | ppy | lv | m | _ |
| ppy_lv_f_ca1 | ppy | lv | f | _ |