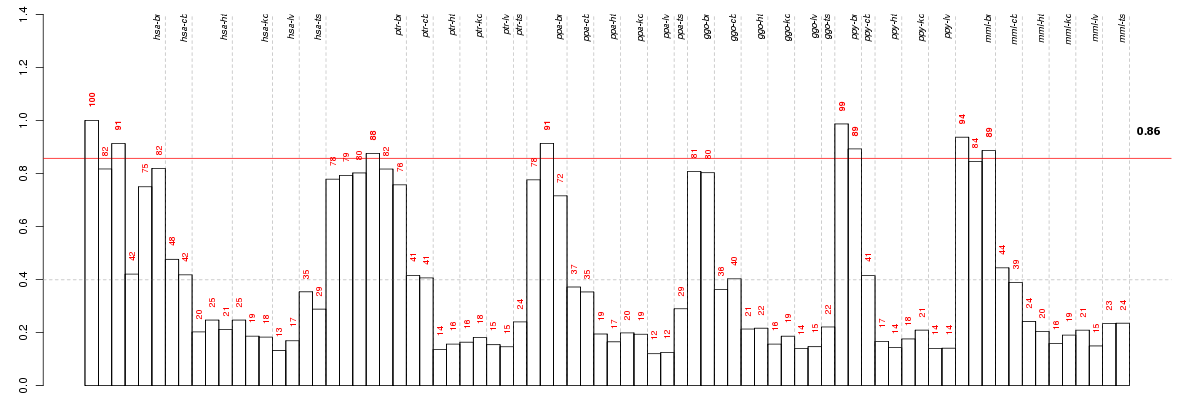

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

cell morphogenesis
The developmental process by which the size or shape of a cell is generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation
The change in form (cell shape and size) that occurs when relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history.
metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
cell growth
The process by which a cell irreversibly increases in size over time by accretion and biosynthetic production of matter similar to that already present.
system process
A multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system. An organ system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a biological objective.
signal transduction
The process whereby an activated receptor conveys information down the signaling pathway, resulting in a change in the function or state of a cell.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of nucleotide metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleotides.
purine nucleotide metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a purine nucleotide, a compound consisting of nucleoside (a purine base linked to a deoxyribose or ribose sugar) esterified with a phosphate moiety at either the 3' or 5'-hydroxyl group of its glycose moiety.
purine nucleotide biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a purine nucleotide, a compound consisting of nucleoside (a purine base linked to a deoxyribose or ribose sugar) esterified with a phosphate moiety at either the 3' or 5'-hydroxyl group of its glycose moiety.
cAMP biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of the nucleotide cAMP (cyclic AMP, adenosine 3',5'-cyclophosphate).
nucleoside phosphate metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any phosphorylated nucleoside.
nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds; includes nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, assimilatory/dissimilatory nitrate reduction and the interconversion of nitrogenous organic matter and ammonium.
transport
The directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells, or within a multicellular organism by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
ion transport
The directed movement of charged atoms or small charged molecules into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
cation transport
The directed movement of cations, atoms or small molecules with a net positive charge, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
potassium ion transport
The directed movement of potassium ions (K+) into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
metal ion transport
The directed movement of metal ions, any metal ion with an electric charge, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
cellular component movement
The directed, self-propelled movement of a cellular component without the involvement of an external agent such as a transporter or a pore.
growth
The increase in size or mass of an entire organism, a part of an organism or a cell.
cell communication
Any process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
cell surface receptor linked signaling pathway
Any series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of an extracellular ligand to a receptor on the surface of the target cell.
G-protein coupled receptor protein signaling pathway
The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a G-protein coupled receptor binding to its physiological ligand.
G-protein signaling, coupled to cyclic nucleotide second messenger
The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a G-protein coupled receptor binding to its physiological ligand, followed by modulation of a nucleotide cyclase activity and a subsequent change in the concentration of a cyclic nucleotide.
activation of phospholipase C activity by G-protein coupled receptor protein signaling pathway coupled to IP3 second messenger
The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a G-protein coupled receptor binding to its physiological ligand, followed by the activation of phospholipase C and the subsequent release of inositol trisphosphate.
activation of phospholipase C activity
The initiation of the activity of the inactive enzyme phospolipase C as the result of a series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a G-protein coupled receptor binding to its physiological ligand.
serotonin receptor signaling pathway
The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a serotonin receptor binding to one of its physiological ligands.
cell-cell signaling
Any process that mediates the transfer of information from one cell to another.
synaptic transmission
The process of communication from a neuron to a target (neuron, muscle, or secretory cell) across a synapse.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of nervous tissue over time, from its formation to its mature state.
neurological system process
A organ system process carried out by any of the organs or tissues of neurological system.
axonogenesis
Generation of a long process of a neuron, that carries efferent (outgoing) action potentials from the cell body towards target cells.
axon guidance
The process by which the migration of an axon growth cone is directed to a specific target site in response to a combination of attractive and repulsive cues.
central nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the central nervous system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The central nervous system is the core nervous system that serves an integrating and coordinating function. In vertebrates it consists of the brain, spinal cord and spinal nerves. In those invertebrates with a central nervous system it typically consists of a brain, cerebral ganglia and a nerve cord.
brain development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the brain over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Brain development begins with patterning events in the neural tube and ends with the mature structure that is the center of thought and emotion. The brain is responsible for the coordination and control of bodily activities and the interpretation of information from the senses (sight, hearing, smell, etc.).
sensory perception
The series of events required for an organism to receive a sensory stimulus, convert it to a molecular signal, and recognize and characterize the signal. This is a neurological process.
behavior
The specific actions or reactions of an organism in response to external or internal stimuli. Patterned activity of a whole organism in a manner dependent upon some combination of that organism's internal state and external conditions.
learning or memory
The acquisition and processing of information and/or the storage and retrieval of this information over time.
learning
Any process in an organism in which a relatively long-lasting adaptive behavioral change occurs as the result of experience.
feeding behavior
Behavior associated with the intake of food.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
associative learning
Learning by associating a stimulus (the cause) with a particular outcome (the effect).
regulation of cell size
Any process that modulates the size of a cell.
cAMP metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving the nucleotide cAMP (cyclic AMP, adenosine 3',5'-cyclophosphate).
biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones.
nucleotide metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a nucleotide, a nucleoside that is esterified with (ortho)phosphate or an oligophosphate at any hydroxyl group on the glycose moiety; may be mono-, di- or triphosphate; this definition includes cyclic nucleotides (nucleoside cyclic phosphates).
nucleoside monophosphate metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a nucleoside monophosphate, a glycosamine consisting of a base linked to a deoxyribose or ribose sugar esterified with phosphate on its glycose moiety.
nucleoside monophosphate biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a nucleoside monophosphate, a glycosamine consisting of a base linked to a deoxyribose or ribose sugar esterified with phosphate on its glycose moiety.
nucleotide biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of nucleotides, any nucleoside that is esterified with (ortho)phosphate or an oligophosphate at any hydroxyl group on the glycose moiety; may be mono-, di- or triphosphate; this definition includes cyclic-nucleotides (nucleoside cyclic phosphates).
cyclic nucleotide metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a cyclic nucleotide, a nucleotide in which the phosphate group is in diester linkage to two positions on the sugar residue.
cyclic nucleotide biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a cyclic nucleotide, a nucleotide in which the phosphate group is in diester linkage to two positions on the sugar residue.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of phospholipase activity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of phospholipase activity, the hydrolysis of a phospholipid.
positive regulation of phospholipase activity
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of phospholipase activity, the hydrolysis of a phospholipid.
regulation of cell communication
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell communication. Cell communication is the process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
negative regulation of cell development
Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
regulation of cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell morphogenesis contributing to cell differentiation. Cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation is the change in form (cell shape and size) that occurs when relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history.
positive regulation of phospholipase C activity
Any process that increases the rate of phospholipase C activity.
regulation of neuron projection development
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of neuron projection development. Neuron projection development is the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites).
monovalent inorganic cation transport
The directed movement of inorganic cations with a valency of one into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. Inorganic cations are atoms or small molecules with a positive charge which do not contain carbon in covalent linkage.
cellular component organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a cellular component.
dendrite development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the dendrite over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A dendrite is a freely branching protoplasmic process of a nerve cell.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
transmission of nerve impulse
The neurological system process by which a signal is transmitted through the nervous system by synaptic transmission and the sequential electrochemical polarization and depolarization that travels across the membrane of a nerve cell (neuron) in response to stimulation.
sensory perception of pain
The series of events required for an organism to receive a painful stimulus, convert it to a molecular signal, and recognize and characterize the signal. Pain is medically defined as the physical sensation of discomfort or distress caused by injury or illness, so can hence be described as a harmful stimulus which signals current (or impending) tissue damage. Pain may come from extremes of temperature, mechanical damage, electricity or from noxious chemical substances. This is a neurological process.
second-messenger-mediated signaling
A series of molecular signals in which an ion or small molecule is formed or released into the cytosol, thereby helping relay the signal within the cell.
cyclic-nucleotide-mediated signaling
A series of molecular signals in which a cell uses a cyclic nucleotide to convert an extracellular signal into a response.
phosphoinositide-mediated signaling
A series of molecular signals in which a cell uses a phosphoinositide to convert an extracellular signal into a response.
generation of neurons in the forebrain
The process by which nerve cells are generated in the forebrain. This includes the production of neuroblasts from and their differentiation into neurons.
forebrain neuron fate commitment
The process whereby the developmental fate of a cell becomes restricted such that it will develop into a neuron that resides in the forebrain.
forebrain neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron that will reside in the forebrain.
central nervous system neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron whose cell body resides in the central nervous system.
neurogenesis
Generation of cells within the nervous system.
regulation of anatomical structure morphogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of anatomical structure morphogenesis.
regulation of cell morphogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell morphogenesis. Cell morphogenesis is the developmental process by which the shape of a cell is generated and organized.
signaling pathway
The series of molecular events whereby information is sent from one location to another within a living organism or between living organisms.
intracellular signaling pathway
The series of molecular events whereby information is sent from one location to another within a cell.
signaling process
Any biological process involved in the generation, transmission, reception, or interpretation of a signal. A signal is an entity used to transmit or convey information.
signaling
The entirety of a process whereby information is transmitted. This process begins with the initiation of the signal and ends when a response has been triggered.
signal transmission
The process whereby a signal is released and/or conveyed from one location to another.
cell projection organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
cell differentiation
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state.
neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron.
regulation of cyclic nucleotide metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving cyclic nucleotides.
regulation of cyclic nucleotide biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of cyclic nucleotides.
regulation of nucleotide biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of nucleotides.
regulation of cAMP metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving the nucleotide cAMP (cyclic AMP, adenosine 3',5'-cyclophosphate).
regulation of cAMP biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of the nucleotide cAMP (cyclic AMP, adenosine 3',5'-cyclophosphate).
forebrain development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the forebrain over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The forebrain is the anterior of the three primary divisions of the developing chordate brain or the corresponding part of the adult brain (in vertebrates, includes especially the cerebral hemispheres, the thalamus, and the hypothalamus and especially in higher vertebrates is the main control center for sensory and associative information processing, visceral functions, and voluntary motor functions).
neuron projection development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites).
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of cell projection organization
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a process involved in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cell projections.
regulation of neurological system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a neurophysiological process, an organ system process carried out by any of the organs or tissues of neurological system.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of cellular component size
A process that modulates the size of a cellular component.
cellular component morphogenesis
The process by which cellular structures, including whole cells or cell parts, are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
cell part morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a cell part are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
nucleobase, nucleoside and nucleotide biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of nucleobases, nucleosides and nucleotides.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
intracellular signal transduction
The process whereby a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell.
positive regulation of catalytic activity
Any process that activates or increases the activity of an enzyme.
regulation of system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a system process, a multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system.
positive regulation of molecular function
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of a molecular function, an elemental biological activity occurring at the molecular level, such as catalysis or binding.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular nitrogen compound biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds.
small molecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
small molecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
cell fate commitment
The commitment of cells to specific cell fates and their capacity to differentiate into particular kinds of cells. Positional information is established through protein signals that emanate from a localized source within a cell (the initial one-cell zygote) or within a developmental field.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
negative regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
regulation of neuron differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neuron differentiation.
heterocycle metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving heterocyclic compounds, those with a cyclic molecular structure and at least two different atoms in the ring (or rings).
regulation of synaptic plasticity
A process that modulates synaptic plasticity, the ability of synapses to change as circumstances require. They may alter function, such as increasing or decreasing their sensitivity, or they may increase or decrease in actual numbers.
regulation of neuronal synaptic plasticity
A process that modulates neuronal synaptic plasticity, the ability of neuronal synapses to change as circumstances require. They may alter function, such as increasing or decreasing their sensitivity, or they may increase or decrease in actual numbers.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
developmental cell growth
The growth of a cell, where growth contributes to the progression of the cell over time from one condition to another.
developmental growth
The increase in size or mass of an entire organism, a part of an organism or a cell, where the increase in size or mass has the specific outcome of the progression of the organism over time from one condition to another.
neuron fate commitment
The process whereby the developmental fate of a cell becomes restricted such that it will develop into a neuron.
neuron development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron over time, from initial commitment of the cell to a specific fate, to the fully functional differentiated cell.
cell morphogenesis involved in neuron differentiation
The process by which the structures of a neuron are generated and organized. This process occurs while the initially relatively unspecialized cell is acquiring the specialized features of a neuron.
axon extension
Long distance growth of a single process.
generation of neurons
The process by which nerve cells are generated. This includes the production of neuroblasts and their differentiation into neurons.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
neuron projection morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a neuron projection are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites.
dendrite morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a dendrite are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. A dendrite is a freely branching protoplasmic process of a nerve cell.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
cell projection morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a cell projection are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
negative regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
regulation of axonogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of axonogenesis, the generation of an axon, the long process of a neuron.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of catalytic activity
Any process that modulates the activity of an enzyme.
regulation of developmental process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of synaptic transmission
Any process that modulates the frequency or rate of synaptic transmission, the process of communication from a neuron to a target (neuron, muscle, or secretory cell) across a synapse.
cognition
The operation of the mind by which an organism becomes aware of objects of thought or perception; it includes the mental activities associated with thinking, learning, and memory.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
negative regulation of developmental process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of cellular component organization
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a process involved in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cell structures, including the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nitrogen or nitrogenous compounds.
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
regulation of hydrolase activity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of hydrolase activity, the catalysis of the hydrolysis of various bonds, e.g. C-O, C-N, C-C, phosphoric anhydride bonds, etc. Hydrolase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 3.
positive regulation of hydrolase activity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of hydrolase activity, the catalysis of the hydrolysis of various bonds.
regulation of nervous system development
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of nervous system development, the origin and formation of nervous tissue.
regulation of transmission of nerve impulse
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transmission of a nerve impulse, the sequential electrochemical polarization and depolarization that travels across the membrane of a neuron in response to stimulation.
nucleobase, nucleoside and nucleotide metabolic process
The cellular chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides and nucleotides.
regulation of lipase activity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of lipase activity, the hydrolysis of a lipid or phospholipid.
positive regulation of lipase activity
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of lipase activity, the hydrolysis of a lipid or phospholipid.
regulation of cell development
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of biological quality
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological quality. A biological quality is a measurable attribute of an organism or part of an organism, such as size, mass, shape, color, etc.
regulation of molecular function
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a molecular function, an elemental biological activity occurring at the molecular level, such as catalysis or binding.
regulation of primary metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism involving those compounds formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
regulation of anatomical structure size
Any process that modulates the size of an anatomical structure.
regulation of multicellular organismal development
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of multicellular organismal development.
all
NA
cell growth
The process by which a cell irreversibly increases in size over time by accretion and biosynthetic production of matter similar to that already present.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cell projection organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
signaling process
Any biological process involved in the generation, transmission, reception, or interpretation of a signal. A signal is an entity used to transmit or convey information.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
developmental growth
The increase in size or mass of an entire organism, a part of an organism or a cell, where the increase in size or mass has the specific outcome of the progression of the organism over time from one condition to another.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
negative regulation of developmental process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of developmental process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of cellular component organization
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a process involved in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cell structures, including the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nitrogen or nitrogenous compounds.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of primary metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism involving those compounds formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
small molecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of small molecules, any monomeric molecule of small relative molecular mass.
developmental cell growth
The growth of a cell, where growth contributes to the progression of the cell over time from one condition to another.
cell-cell signaling
Any process that mediates the transfer of information from one cell to another.
cellular component morphogenesis
The process by which cellular structures, including whole cells or cell parts, are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
regulation of cell communication
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell communication. Cell communication is the process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cell projection organization
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a process involved in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cell projections.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of cell morphogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell morphogenesis. Cell morphogenesis is the developmental process by which the shape of a cell is generated and organized.
regulation of cell projection organization
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a process involved in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cell projections.
signal transduction
The process whereby an activated receptor conveys information down the signaling pathway, resulting in a change in the function or state of a cell.
transmission of nerve impulse
The neurological system process by which a signal is transmitted through the nervous system by synaptic transmission and the sequential electrochemical polarization and depolarization that travels across the membrane of a nerve cell (neuron) in response to stimulation.
regulation of system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a system process, a multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system.
regulation of multicellular organismal development
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of multicellular organismal development.
cellular component morphogenesis
The process by which cellular structures, including whole cells or cell parts, are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
regulation of anatomical structure morphogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of anatomical structure morphogenesis.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
negative regulation of developmental process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of multicellular organismal development
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of multicellular organismal development.
negative regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
regulation of catalytic activity
Any process that modulates the activity of an enzyme.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular nitrogen compound biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
nucleobase, nucleoside and nucleotide metabolic process
The cellular chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides and nucleotides.
nucleobase, nucleoside and nucleotide biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of nucleobases, nucleosides and nucleotides.
synaptic transmission
The process of communication from a neuron to a target (neuron, muscle, or secretory cell) across a synapse.
regulation of transmission of nerve impulse
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transmission of a nerve impulse, the sequential electrochemical polarization and depolarization that travels across the membrane of a neuron in response to stimulation.
dendrite development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the dendrite over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A dendrite is a freely branching protoplasmic process of a nerve cell.
regulation of neuron projection development
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of neuron projection development. Neuron projection development is the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites).
neuron projection morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a neuron projection are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites.
cell fate commitment
The commitment of cells to specific cell fates and their capacity to differentiate into particular kinds of cells. Positional information is established through protein signals that emanate from a localized source within a cell (the initial one-cell zygote) or within a developmental field.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
negative regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
negative regulation of cell development
Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
developmental cell growth
The growth of a cell, where growth contributes to the progression of the cell over time from one condition to another.
negative regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
regulation of cell development
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
cell growth
The process by which a cell irreversibly increases in size over time by accretion and biosynthetic production of matter similar to that already present.
cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation
The change in form (cell shape and size) that occurs when relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history.
regulation of cell morphogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell morphogenesis. Cell morphogenesis is the developmental process by which the shape of a cell is generated and organized.
cell projection morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a cell projection are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
cell projection morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a cell projection are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
intracellular signal transduction
The process whereby a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell.
transmission of nerve impulse
The neurological system process by which a signal is transmitted through the nervous system by synaptic transmission and the sequential electrochemical polarization and depolarization that travels across the membrane of a nerve cell (neuron) in response to stimulation.
regulation of neurological system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a neurophysiological process, an organ system process carried out by any of the organs or tissues of neurological system.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
regulation of cell morphogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell morphogenesis. Cell morphogenesis is the developmental process by which the shape of a cell is generated and organized.
regulation of cellular component size
A process that modulates the size of a cellular component.
positive regulation of catalytic activity
Any process that activates or increases the activity of an enzyme.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
positive regulation of hydrolase activity
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of hydrolase activity, the catalysis of the hydrolysis of various bonds.
nucleobase, nucleoside and nucleotide biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of nucleobases, nucleosides and nucleotides.
regulation of synaptic transmission
Any process that modulates the frequency or rate of synaptic transmission, the process of communication from a neuron to a target (neuron, muscle, or secretory cell) across a synapse.
dendrite morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a dendrite are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. A dendrite is a freely branching protoplasmic process of a nerve cell.
negative regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
neuron fate commitment
The process whereby the developmental fate of a cell becomes restricted such that it will develop into a neuron.
neuron development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron over time, from initial commitment of the cell to a specific fate, to the fully functional differentiated cell.
regulation of cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell morphogenesis contributing to cell differentiation. Cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation is the change in form (cell shape and size) that occurs when relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history.
neuron projection development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites).
cell morphogenesis involved in neuron differentiation
The process by which the structures of a neuron are generated and organized. This process occurs while the initially relatively unspecialized cell is acquiring the specialized features of a neuron.
negative regulation of cell development
Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
regulation of cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell morphogenesis contributing to cell differentiation. Cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation is the change in form (cell shape and size) that occurs when relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history.
regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
regulation of axonogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of axonogenesis, the generation of an axon, the long process of a neuron.
regulation of synaptic plasticity
A process that modulates synaptic plasticity, the ability of synapses to change as circumstances require. They may alter function, such as increasing or decreasing their sensitivity, or they may increase or decrease in actual numbers.
regulation of transmission of nerve impulse
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transmission of a nerve impulse, the sequential electrochemical polarization and depolarization that travels across the membrane of a neuron in response to stimulation.
learning or memory
The acquisition and processing of information and/or the storage and retrieval of this information over time.
central nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the central nervous system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The central nervous system is the core nervous system that serves an integrating and coordinating function. In vertebrates it consists of the brain, spinal cord and spinal nerves. In those invertebrates with a central nervous system it typically consists of a brain, cerebral ganglia and a nerve cord.
neurogenesis
Generation of cells within the nervous system.
regulation of nervous system development
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of nervous system development, the origin and formation of nervous tissue.
brain development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the brain over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Brain development begins with patterning events in the neural tube and ends with the mature structure that is the center of thought and emotion. The brain is responsible for the coordination and control of bodily activities and the interpretation of information from the senses (sight, hearing, smell, etc.).
central nervous system neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron whose cell body resides in the central nervous system.
regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
forebrain development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the forebrain over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The forebrain is the anterior of the three primary divisions of the developing chordate brain or the corresponding part of the adult brain (in vertebrates, includes especially the cerebral hemispheres, the thalamus, and the hypothalamus and especially in higher vertebrates is the main control center for sensory and associative information processing, visceral functions, and voluntary motor functions).
regulation of nucleotide biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of nucleotides.
purine nucleotide biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a purine nucleotide, a compound consisting of nucleoside (a purine base linked to a deoxyribose or ribose sugar) esterified with a phosphate moiety at either the 3' or 5'-hydroxyl group of its glycose moiety.
regulation of nucleotide biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of nucleotides.
positive regulation of lipase activity
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of lipase activity, the hydrolysis of a lipid or phospholipid.
cAMP biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of the nucleotide cAMP (cyclic AMP, adenosine 3',5'-cyclophosphate).
regulation of nucleotide metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleotides.
purine nucleotide metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a purine nucleotide, a compound consisting of nucleoside (a purine base linked to a deoxyribose or ribose sugar) esterified with a phosphate moiety at either the 3' or 5'-hydroxyl group of its glycose moiety.
nucleotide biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of nucleotides, any nucleoside that is esterified with (ortho)phosphate or an oligophosphate at any hydroxyl group on the glycose moiety; may be mono-, di- or triphosphate; this definition includes cyclic-nucleotides (nucleoside cyclic phosphates).
axon guidance
The process by which the migration of an axon growth cone is directed to a specific target site in response to a combination of attractive and repulsive cues.
axon extension
Long distance growth of a single process.
regulation of axonogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of axonogenesis, the generation of an axon, the long process of a neuron.
generation of neurons in the forebrain
The process by which nerve cells are generated in the forebrain. This includes the production of neuroblasts from and their differentiation into neurons.
neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron.
regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
regulation of neuron differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neuron differentiation.
negative regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
forebrain neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron that will reside in the forebrain.
regulation of neuron projection development
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of neuron projection development. Neuron projection development is the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites).
axonogenesis
Generation of a long process of a neuron, that carries efferent (outgoing) action potentials from the cell body towards target cells.
dendrite morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a dendrite are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. A dendrite is a freely branching protoplasmic process of a nerve cell.
forebrain neuron fate commitment
The process whereby the developmental fate of a cell becomes restricted such that it will develop into a neuron that resides in the forebrain.
potassium ion transport
The directed movement of potassium ions (K+) into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
regulation of cyclic nucleotide biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of cyclic nucleotides.
regulation of cAMP metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving the nucleotide cAMP (cyclic AMP, adenosine 3',5'-cyclophosphate).
positive regulation of phospholipase activity
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of phospholipase activity, the hydrolysis of a phospholipid.
regulation of cAMP biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of the nucleotide cAMP (cyclic AMP, adenosine 3',5'-cyclophosphate).
regulation of cAMP biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of the nucleotide cAMP (cyclic AMP, adenosine 3',5'-cyclophosphate).
nucleoside monophosphate biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a nucleoside monophosphate, a glycosamine consisting of a base linked to a deoxyribose or ribose sugar esterified with phosphate on its glycose moiety.
G-protein signaling, coupled to cyclic nucleotide second messenger
The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a G-protein coupled receptor binding to its physiological ligand, followed by modulation of a nucleotide cyclase activity and a subsequent change in the concentration of a cyclic nucleotide.
activation of phospholipase C activity by G-protein coupled receptor protein signaling pathway coupled to IP3 second messenger
The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a G-protein coupled receptor binding to its physiological ligand, followed by the activation of phospholipase C and the subsequent release of inositol trisphosphate.
cAMP biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of the nucleotide cAMP (cyclic AMP, adenosine 3',5'-cyclophosphate).
regulation of cyclic nucleotide biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of cyclic nucleotides.
cAMP metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving the nucleotide cAMP (cyclic AMP, adenosine 3',5'-cyclophosphate).
cyclic nucleotide biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a cyclic nucleotide, a nucleotide in which the phosphate group is in diester linkage to two positions on the sugar residue.
regulation of cyclic nucleotide metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving cyclic nucleotides.
activation of phospholipase C activity by G-protein coupled receptor protein signaling pathway coupled to IP3 second messenger
The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a G-protein coupled receptor binding to its physiological ligand, followed by the activation of phospholipase C and the subsequent release of inositol trisphosphate.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
integral to membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer. When used to describe a protein, indicates that all or part of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cytoskeleton
Any of the various filamentous elements that form the internal framework of cells, and typically remain after treatment of the cells with mild detergent to remove membrane constituents and soluble components of the cytoplasm. The term embraces intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, the microtrabecular lattice, and other structures characterized by a polymeric filamentous nature and long-range order within the cell. The various elements of the cytoskeleton not only serve in the maintenance of cellular shape but also have roles in other cellular functions, including cellular movement, cell division, endocytosis, and movement of organelles.
voltage-gated potassium channel complex
A protein complex that forms a transmembrane channel through which potassium ions may cross a cell membrane in response to changes in membrane potential.
postsynaptic density
The post synaptic density is a region that lies adjacent to the cytoplasmic face of the postsynaptic membrane at excitatory synapse. It forms a disc that consists of a range of proteins with different functions, some of which contact the cytoplasmic domains of ion channels in the postsynaptic membrane. The proteins making up the disc include receptors, and structural proteins linked to the actin cytoskeleton. They also include signalling machinery, such as protein kinases and phosphatases.
cell junction
A plasma membrane part that forms a specialized region of connection between two cells or between a cell and the extracellular matrix. At a cell junction, anchoring proteins extend through the plasma membrane to link cytoskeletal proteins in one cell to cytoskeletal proteins in neighboring cells or to proteins in the extracellular matrix.
axon
The long process of a neuron that conducts nerve impulses, usually away from the cell body to the terminals and varicosities, which are sites of storage and release of neurotransmitter.
dendrite
A neuron projection that has a short, tapering, often branched, morphology, receives and integrates signals from other neurons or from sensory stimuli, and conducts a nerve impulse towards the axon or the cell body. In most neurons, the impulse is conveyed from dendrites to axon via the cell body, but in some types of unipolar neuron, the impulse does not travel via the cell body.
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
asymmetric synapse
A type of synapse occurring between an axon and a dendritic spine or dendritic shaft. Asymmetric synapses, the most abundant synapse type in the central nervous system, involve axons that contain predominantly spherical vesicles and contain a thickened postsynaptic density.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
axon part
A part of an axon, a cell projection of a neuron.
ion channel complex
A protein complex that spans a membrane and forms a water-filled channel across the phospholipid bilayer allowing selective ion transport down its electrochemical gradient.
cation channel complex
An ion channel complex through which cations pass.
potassium channel complex
An ion channel complex through which potassium ions pass.
presynaptic membrane
A specialized area of membrane of the axon terminal that faces the plasma membrane of the neuron or muscle fiber with which the axon terminal establishes a synaptic junction; many synaptic junctions exhibit structural presynaptic characteristics, such as conical, electron-dense internal protrusions, that distinguish it from the remainder of the axon plasma membrane.
cell projection
A prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
neuron projection
A prolongation or process extending from a nerve cell, e.g. an axon or dendrite.
neuronal cell body
The portion of a neuron that includes the nucleus, but excludes all cell projections such as axons and dendrites.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, and prokaryotic structures such as anammoxosomes and pirellulosomes. Excludes the plasma membrane.
non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
protein complex
Any macromolecular complex composed of two or more polypeptide subunits, which may or may not be identical. Protein complexes may have other associated non-protein prosthetic groups, such as nucleotides, metal ions or other small molecules.
cell body
The portion of a cell bearing surface projections such as axons, dendrites, cilia, or flagella that includes the nucleus, but excludes all cell projections.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
synapse part
Any constituent part of a synapse, the junction between a nerve fiber of one neuron and another neuron or muscle fiber or glial cell.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell projection part
Any constituent part of a cell projection, a prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
synapse
The junction between a nerve fiber of one neuron and another neuron or muscle fiber or glial cell; the site of interneuronal communication. As the nerve fiber approaches the synapse it enlarges into a specialized structure, the presynaptic nerve ending, which contains mitochondria and synaptic vesicles. At the tip of the nerve ending is the presynaptic membrane; facing it, and separated from it by a minute cleft (the synaptic cleft) is a specialized area of membrane on the receiving cell, known as the postsynaptic membrane. In response to the arrival of nerve impulses, the presynaptic nerve ending secretes molecules of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. These diffuse across the cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane.
postsynaptic membrane
A specialized area of membrane facing the presynaptic membrane on the tip of the nerve ending and separated from it by a minute cleft (the synaptic cleft). Neurotransmitters across the synaptic cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
synapse part
Any constituent part of a synapse, the junction between a nerve fiber of one neuron and another neuron or muscle fiber or glial cell.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
presynaptic membrane
A specialized area of membrane of the axon terminal that faces the plasma membrane of the neuron or muscle fiber with which the axon terminal establishes a synaptic junction; many synaptic junctions exhibit structural presynaptic characteristics, such as conical, electron-dense internal protrusions, that distinguish it from the remainder of the axon plasma membrane.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
postsynaptic membrane
A specialized area of membrane facing the presynaptic membrane on the tip of the nerve ending and separated from it by a minute cleft (the synaptic cleft). Neurotransmitters across the synaptic cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane.
cell projection part
Any constituent part of a cell projection, a prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
ion channel complex
A protein complex that spans a membrane and forms a water-filled channel across the phospholipid bilayer allowing selective ion transport down its electrochemical gradient.
postsynaptic density
The post synaptic density is a region that lies adjacent to the cytoplasmic face of the postsynaptic membrane at excitatory synapse. It forms a disc that consists of a range of proteins with different functions, some of which contact the cytoplasmic domains of ion channels in the postsynaptic membrane. The proteins making up the disc include receptors, and structural proteins linked to the actin cytoskeleton. They also include signalling machinery, such as protein kinases and phosphatases.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
axon part
A part of an axon, a cell projection of a neuron.
ion channel complex
A protein complex that spans a membrane and forms a water-filled channel across the phospholipid bilayer allowing selective ion transport down its electrochemical gradient.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
voltage-gated potassium channel complex
A protein complex that forms a transmembrane channel through which potassium ions may cross a cell membrane in response to changes in membrane potential.
voltage-gated potassium channel complex
A protein complex that forms a transmembrane channel through which potassium ions may cross a cell membrane in response to changes in membrane potential.

protein binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any protein or protein complex (a complex of two or more proteins that may include other nonprotein molecules).
peptide receptor activity
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular peptide to initiate a change in cell activity.
molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
catalytic activity
Catalysis of a biochemical reaction at physiological temperatures. In biologically catalyzed reactions, the reactants are known as substrates, and the catalysts are naturally occurring macromolecular substances known as enzymes. Enzymes possess specific binding sites for substrates, and are usually composed wholly or largely of protein, but RNA that has catalytic activity (ribozyme) is often also regarded as enzymatic.
receptor binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with one or more specific sites on a receptor molecule, a macromolecule that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function.
protein kinase activity
Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction: a protein + ATP = a phosphoprotein + ADP.
protein serine/threonine kinase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein serine/threonine = ADP + protein serine/threonine phosphate.
calmodulin-dependent protein kinase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein serine/threonine = ADP + protein serine/threonine phosphate, dependent on the presence of calcium-bound calmodulin.
protein tyrosine kinase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate.
transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein-L-tyrosine = ADP + a protein-L-tyrosine phosphate, to initiate a change in cell activity.
signal transducer activity
Mediates the transfer of a signal from the outside to the inside of a cell by means other than the introduction of the signal molecule itself into the cell.
receptor activity
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell activity.
transmembrane receptor activity
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell activity, and spanning to the membrane of either the cell or an organelle.
G-protein coupled receptor activity
A receptor that binds an extracellular ligand and transmits the signal to a heterotrimeric G-protein complex. These receptors are characteristically seven-transmembrane receptors and are made up of hetero- or homodimers.
serotonin receptor activity
Combining with the biogenic amine serotonin, a neurotransmitter and hormone found in vertebrates, invertebrates and plants, to initiate a change in cell activity.
ephrin receptor activity
Combining with an ephrin to initiate a change in cell activity.
transmembrane-ephrin receptor activity
NA
hormone activity
The action characteristic of a hormone, any substance formed in very small amounts in one specialized organ or group of cells and carried (sometimes in the bloodstream) to another organ or group of cells in the same organism, upon which it has a specific regulatory action. The term was originally applied to agents with a stimulatory physiological action in vertebrate animals (as opposed to a chalone, which has a depressant action). Usage is now extended to regulatory compounds in lower animals and plants, and to synthetic substances having comparable effects; all bind receptors and trigger some biological process.
neuropeptide hormone activity
The action characteristic of a neuropeptide hormone, any peptide hormone that acts in the central nervous system. A neuropeptide is any of several types of molecules found in brain tissue, composed of short chains of amino acids; they include endorphins, enkephalins, vasopressin, and others. They are often localized in axon terminals at synapses and are classified as putative neurotransmitters, although some are also hormones.
transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
ion channel activity
Catalysis of facilitated diffusion of an ion (by an energy-independent process) by passage through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel without evidence for a carrier-mediated mechanism.
extracellular ligand-gated ion channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a channel that opens when a specific extracellular ligand has been bound by the channel complex or one of its constituent parts.
voltage-gated ion channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a voltage-gated channel. An ion is an atom or group of atoms carrying an electric charge by virtue of having gained or lost one or more electrons.
voltage-gated potassium channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a potassium ion by a voltage-gated channel.
delayed rectifier potassium channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a potassium ion by a delayed rectifying voltage-gated channel. A delayed rectifying current-voltage relation is one where channel activation kinetics are time-dependent, and activation is slow.
cation channel activity
Catalysis of the energy-independent passage of cations across a lipid bilayer down a concentration gradient.
potassium channel activity
Catalysis of facilitated diffusion of a potassium ion (by an energy-independent process) involving passage through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel without evidence for a carrier-mediated mechanism.
transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a substance from one side of a membrane to the other.
binding
The selective, non-covalent, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
neuropeptide receptor activity
Combining with a neuropeptide to initiate a change in cell activity.
G-protein coupled amine receptor activity
A receptor that binds an extracellular amine and transmits the signal to a heterotrimeric G-protein complex. These receptors are characteristically seven-transmembrane receptors and are made up of hetero- or homodimers.
cation transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of cation from one side of the membrane to the other.
peptide receptor activity, G-protein coupled
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular peptide to initiate a G-protein mediated change in cell activity. A G-protein is a signal transduction molecule that alternates between an inactive GDP-bound and an active GTP-bound state.
ion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of an ion from one side of a membrane to the other.
channel activity
Catalysis of energy-independent facilitated diffusion, mediated by passage of a solute through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel. Stereospecificity is not exhibited but this transport may be specific for a particular molecular species or class of molecules.
ligand-gated ion channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a channel that opens when a specific ligand has been bound by the channel complex or one of its constituent parts.
kinase activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a substrate molecule.
transferase activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a group, e.g. a methyl group, glycosyl group, acyl group, phosphorus-containing, or other groups, from one compound (generally regarded as the donor) to another compound (generally regarded as the acceptor). Transferase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 2.
transferase activity, transferring phosphorus-containing groups
Catalysis of the transfer of a phosphorus-containing group from one compound (donor) to another (acceptor).
phosphotransferase activity, alcohol group as acceptor
Catalysis of the transfer of a phosphorus-containing group from one compound (donor) to an alcohol group (acceptor).
peptide hormone binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any peptide with hormonal activity in animals.
transmembrane receptor protein kinase activity
NA
passive transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute from one side of the membrane to the other, down the solute's concentration gradient.
voltage-gated channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a solute by a channel whose open state is dependent on the voltage across the membrane in which it is embedded.
ligand-gated channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a solute by a channel that opens when a specific ligand has been bound by the channel complex or one of its constituent parts.
gated channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a solute by a channel that opens in response to a specific stimulus.
substrate-specific channel activity
Catalysis of energy-independent facilitated diffusion, mediated by passage of a specific solute through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel. Stereospecificity is not exhibited but this transport may be specific for a particular molecular species or class of molecules.
voltage-gated cation channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a cation by a voltage-gated channel. A cation is a positively charged ion.
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
substrate-specific transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of a specific substance or group of related substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
neurotransmitter receptor activity
Combining with a neurotransmitter to initiate a change in cell activity.
neurotransmitter binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a neurotransmitter, any chemical substance that is capable of transmitting (or inhibiting the transmission of) a nerve impulse from a neuron to another cell.
peptide binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with peptides, any of a group of organic compounds comprising two or more amino acids linked by peptide bonds.
hormone binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any hormone, naturally occurring substances secreted by specialized cells that affect the metabolism or behavior of other cells possessing functional receptors for the hormone.
neuropeptide binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently and stoichiometrically with neuropeptides, peptides with direct synaptic effects (peptide neurotransmitters) or indirect modulatory effects on the nervous system (peptide neuromodulators).
amine binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group.
serotonin binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine), a monoamine neurotransmitter occurring in the peripheral and central nervous systems, also having hormonal properties.
molecular transducer activity
The molecular function that accepts an input of one form and creates an output of a different form.
all
NA
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
peptide hormone binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any peptide with hormonal activity in animals.
neuropeptide receptor activity
Combining with a neuropeptide to initiate a change in cell activity.
peptide receptor activity
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular peptide to initiate a change in cell activity.
neurotransmitter receptor activity
Combining with a neurotransmitter to initiate a change in cell activity.
protein kinase activity
Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction: a protein + ATP = a phosphoprotein + ADP.
substrate-specific channel activity
Catalysis of energy-independent facilitated diffusion, mediated by passage of a specific solute through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel. Stereospecificity is not exhibited but this transport may be specific for a particular molecular species or class of molecules.
ion channel activity
Catalysis of facilitated diffusion of an ion (by an energy-independent process) by passage through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel without evidence for a carrier-mediated mechanism.
neuropeptide receptor activity
Combining with a neuropeptide to initiate a change in cell activity.
transmembrane receptor protein kinase activity
NA
cation channel activity
Catalysis of the energy-independent passage of cations across a lipid bilayer down a concentration gradient.
peptide receptor activity, G-protein coupled
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular peptide to initiate a G-protein mediated change in cell activity. A G-protein is a signal transduction molecule that alternates between an inactive GDP-bound and an active GTP-bound state.
transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein-L-tyrosine = ADP + a protein-L-tyrosine phosphate, to initiate a change in cell activity.
voltage-gated ion channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a voltage-gated channel. An ion is an atom or group of atoms carrying an electric charge by virtue of having gained or lost one or more electrons.
ligand-gated ion channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a channel that opens when a specific ligand has been bound by the channel complex or one of its constituent parts.
voltage-gated cation channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a cation by a voltage-gated channel. A cation is a positively charged ion.
voltage-gated potassium channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a potassium ion by a voltage-gated channel.
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 04080 | 1.747e-10 | 7.679 | 32 | 206 | Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction |
| 04360 | 9.088e-08 | 3.952 | 20 | 106 | Axon guidance |
| 04020 | 7.479e-07 | 5.405 | 22 | 145 | Calcium signaling pathway |
| 04916 | 1.207e-03 | 3.02 | 12 | 81 | Melanogenesis |
| 04720 | 3.499e-03 | 1.976 | 9 | 53 | Long-term potentiation |
| 05214 | 4.503e-03 | 2.05 | 9 | 55 | Glioma |
| 04540 | 7.060e-03 | 2.199 | 9 | 59 | Gap junction |
| 04971 | 7.842e-03 | 2.237 | 9 | 60 | Gastric acid secretion |
| 04070 | 1.581e-02 | 2.498 | 9 | 67 | Phosphatidylinositol signaling system |
| 04970 | 2.861e-02 | 2.237 | 8 | 60 | Salivary secretion |
| 00534 | 4.957e-02 | 0.6337 | 4 | 17 | Glycosaminoglycan biosynthesis - heparan sulfate |
ABHD12abhydrolase domain containing 12 (ENSG00000100997), score: 0.65 ABLIM2actin binding LIM protein family, member 2 (ENSG00000163995), score: 0.66 ADAMTS10ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 10 (ENSG00000142303), score: 0.64 ADAMTS8ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 8 (ENSG00000134917), score: 0.82 ADCYAP1adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide 1 (pituitary) (ENSG00000141433), score: 0.72 ADRA1Dadrenergic, alpha-1D-, receptor (ENSG00000171873), score: 0.87 ADRB3adrenergic, beta-3-, receptor (ENSG00000188778), score: 0.65 ADRBK1adrenergic, beta, receptor kinase 1 (ENSG00000173020), score: 0.67 AGAP3ArfGAP with GTPase domain, ankyrin repeat and PH domain 3 (ENSG00000133612), score: 0.66 AK5adenylate kinase 5 (ENSG00000154027), score: 0.72 ALKanaplastic lymphoma receptor tyrosine kinase (ENSG00000171094), score: 0.65 AMZ1archaelysin family metallopeptidase 1 (ENSG00000174945), score: 0.68 ANKRD33Bankyrin repeat domain 33B (ENSG00000164236), score: 0.65 ANO3anoctamin 3 (ENSG00000134343), score: 0.67 ARCactivity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein (ENSG00000198576), score: 0.86 ARFIP1ADP-ribosylation factor interacting protein 1 (ENSG00000164144), score: -0.72 ASB6ankyrin repeat and SOCS box-containing 6 (ENSG00000148331), score: 0.78 ASCC1activating signal cointegrator 1 complex subunit 1 (ENSG00000138303), score: -0.67 ATP13A2ATPase type 13A2 (ENSG00000159363), score: 0.65 ATP6V0CATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 16kDa, V0 subunit c (ENSG00000185883), score: 0.66 ATRNL1attractin-like 1 (ENSG00000107518), score: 0.65 B3GAT1beta-1,3-glucuronyltransferase 1 (glucuronosyltransferase P) (ENSG00000109956), score: 0.66 B3GNT1UDP-GlcNAc:betaGal beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 1 (ENSG00000174684), score: 0.64 B3GNT4UDP-GlcNAc:betaGal beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 4 (ENSG00000176383), score: 0.73 B4GALT2UDP-Gal:betaGlcNAc beta 1,4- galactosyltransferase, polypeptide 2 (ENSG00000117411), score: 0.65 BAI1brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor 1 (ENSG00000181790), score: 0.74 BAI2brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor 2 (ENSG00000121753), score: 0.68 BAP1BRCA1 associated protein-1 (ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase) (ENSG00000163930), score: 0.65 BCL11AB-cell CLL/lymphoma 11A (zinc finger protein) (ENSG00000119866), score: 0.69 BCL11BB-cell CLL/lymphoma 11B (zinc finger protein) (ENSG00000127152), score: 0.76 BCRbreakpoint cluster region (ENSG00000186716), score: 0.64 BEANbrain expressed, associated with Nedd4 (ENSG00000166546), score: 0.74 BTBD9BTB (POZ) domain containing 9 (ENSG00000183826), score: 0.73 BZRAP1benzodiazapine receptor (peripheral) associated protein 1 (ENSG00000005379), score: 0.68 C11orf41chromosome 11 open reading frame 41 (ENSG00000110427), score: 0.65 C11orf87chromosome 11 open reading frame 87 (ENSG00000185742), score: 0.74 C12orf41chromosome 12 open reading frame 41 (ENSG00000139620), score: -0.67 C13orf36chromosome 13 open reading frame 36 (ENSG00000180440), score: 0.84 C19orf26chromosome 19 open reading frame 26 (ENSG00000099625), score: 0.75 C1orf93chromosome 1 open reading frame 93 (ENSG00000157870), score: 0.66 C1orf95chromosome 1 open reading frame 95 (ENSG00000203685), score: 0.77 C1QL2complement component 1, q subcomponent-like 2 (ENSG00000144119), score: 0.79 C1QTNF4C1q and tumor necrosis factor related protein 4 (ENSG00000172247), score: 0.72 C20orf103chromosome 20 open reading frame 103 (ENSG00000125869), score: 0.68 C20orf72chromosome 20 open reading frame 72 (ENSG00000125871), score: -0.65 C2CD2LC2CD2-like (ENSG00000172375), score: 0.65 C2orf55chromosome 2 open reading frame 55 (ENSG00000196872), score: 0.7 C2orf80chromosome 2 open reading frame 80 (ENSG00000188674), score: 0.64 C4orf44chromosome 4 open reading frame 44 (ENSG00000188981), score: 0.74 C5orf40chromosome 5 open reading frame 40 (ENSG00000172568), score: 0.77 C6orf1chromosome 6 open reading frame 1 (ENSG00000186577), score: 0.66 C6orf222chromosome 6 open reading frame 222 (ENSG00000189325), score: 0.7 C6orf72chromosome 6 open reading frame 72 (ENSG00000055211), score: -0.77 C8orf46chromosome 8 open reading frame 46 (ENSG00000169085), score: 0.64 CA7carbonic anhydrase VII (ENSG00000168748), score: 0.65 CACNA1Ecalcium channel, voltage-dependent, R type, alpha 1E subunit (ENSG00000198216), score: 0.68 CACNG3calcium channel, voltage-dependent, gamma subunit 3 (ENSG00000006116), score: 0.77 CALHM1calcium homeostasis modulator 1 (ENSG00000185933), score: 0.68 CALM1calmodulin 1 (phosphorylase kinase, delta) (ENSG00000160014), score: 0.69 CALYcalcyon neuron-specific vesicular protein (ENSG00000130643), score: 0.7 CAMK1calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase I (ENSG00000134072), score: 0.66 CAMK1Gcalcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IG (ENSG00000008118), score: 0.73 CAMK2Acalcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II alpha (ENSG00000070808), score: 0.76 CAMKK1calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 1, alpha (ENSG00000004660), score: 0.67 CARTPTCART prepropeptide (ENSG00000164326), score: 0.73 CBLN2cerebellin 2 precursor (ENSG00000141668), score: 0.7 CBLN4cerebellin 4 precursor (ENSG00000054803), score: 0.79 CCDC85Acoiled-coil domain containing 85A (ENSG00000055813), score: 0.64 CCKBRcholecystokinin B receptor (ENSG00000110148), score: 0.67 CD2APCD2-associated protein (ENSG00000198087), score: -0.66 CD46CD46 molecule, complement regulatory protein (ENSG00000117335), score: -0.65 CDH4cadherin 4, type 1, R-cadherin (retinal) (ENSG00000179242), score: 0.79 CDH8cadherin 8, type 2 (ENSG00000150394), score: 0.76 CDH9cadherin 9, type 2 (T1-cadherin) (ENSG00000113100), score: 0.68 CDK5R2cyclin-dependent kinase 5, regulatory subunit 2 (p39) (ENSG00000171450), score: 0.65 CDKN2Dcyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2D (p19, inhibits CDK4) (ENSG00000129355), score: 0.73 CELF5CUGBP, Elav-like family member 5 (ENSG00000161082), score: 0.69 CELSR2cadherin, EGF LAG seven-pass G-type receptor 2 (flamingo homolog, Drosophila) (ENSG00000143126), score: 0.65 CHD1chromodomain helicase DNA binding protein 1 (ENSG00000153922), score: -0.66 CHGAchromogranin A (parathyroid secretory protein 1) (ENSG00000100604), score: 0.69 CHRM1cholinergic receptor, muscarinic 1 (ENSG00000168539), score: 0.79 CHRM3cholinergic receptor, muscarinic 3 (ENSG00000133019), score: 0.78 CHRNB2cholinergic receptor, nicotinic, beta 2 (neuronal) (ENSG00000160716), score: 0.68 CHST1carbohydrate (keratan sulfate Gal-6) sulfotransferase 1 (ENSG00000175264), score: 0.78 CHST8carbohydrate (N-acetylgalactosamine 4-0) sulfotransferase 8 (ENSG00000124302), score: 0.7 CNTN3contactin 3 (plasmacytoma associated) (ENSG00000113805), score: 0.65 CNTNAP5contactin associated protein-like 5 (ENSG00000155052), score: 0.79 COBLcordon-bleu homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000106078), score: 0.64 COPB1coatomer protein complex, subunit beta 1 (ENSG00000129083), score: -0.7 CORO1Acoronin, actin binding protein, 1A (ENSG00000102879), score: 0.67 CPNE5copine V (ENSG00000124772), score: 0.7 CPNE6copine VI (neuronal) (ENSG00000100884), score: 0.74 CREG2cellular repressor of E1A-stimulated genes 2 (ENSG00000175874), score: 0.65 CRHcorticotropin releasing hormone (ENSG00000147571), score: 0.68 CRYGAcrystallin, gamma A (ENSG00000168582), score: 0.83 CSMD2CUB and Sushi multiple domains 2 (ENSG00000121904), score: 0.65 CYP46A1cytochrome P450, family 46, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000036530), score: 0.74 DAGLAdiacylglycerol lipase, alpha (ENSG00000134780), score: 0.73 DCLK1doublecortin-like kinase 1 (ENSG00000133083), score: 0.64 DDNdendrin (ENSG00000181418), score: 0.73 DENND4CDENN/MADD domain containing 4C (ENSG00000137145), score: -0.75 DGCR2DiGeorge syndrome critical region gene 2 (ENSG00000070413), score: 0.69 DGKBdiacylglycerol kinase, beta 90kDa (ENSG00000136267), score: 0.7 DGKZdiacylglycerol kinase, zeta 104kDa (ENSG00000149091), score: 0.76 DHX29DEAH (Asp-Glu-Ala-His) box polypeptide 29 (ENSG00000067248), score: -0.67 DLGAP2discs, large (Drosophila) homolog-associated protein 2 (ENSG00000198010), score: 0.68 DLK2delta-like 2 homolog (Drosophila) (ENSG00000171462), score: 0.65 DLX1distal-less homeobox 1 (ENSG00000144355), score: 0.77 DLX2distal-less homeobox 2 (ENSG00000115844), score: 0.77 DLX5distal-less homeobox 5 (ENSG00000105880), score: 0.72 DRP2dystrophin related protein 2 (ENSG00000102385), score: 0.7 DSCAMDown syndrome cell adhesion molecule (ENSG00000171587), score: 0.72 DUSP14dual specificity phosphatase 14 (ENSG00000161326), score: 0.73 EFNA3ephrin-A3 (ENSG00000143590), score: 0.76 EFNB3ephrin-B3 (ENSG00000108947), score: 0.76 EGR2early growth response 2 (ENSG00000122877), score: 0.65 EGR3early growth response 3 (ENSG00000179388), score: 0.83 EGR4early growth response 4 (ENSG00000135625), score: 0.68 ELFN2extracellular leucine-rich repeat and fibronectin type III domain containing 2 (ENSG00000166897), score: 0.75 ELMOD2ELMO/CED-12 domain containing 2 (ENSG00000179387), score: -0.82 ENC1ectodermal-neural cortex 1 (with BTB-like domain) (ENSG00000171617), score: 0.75 EPHA4EPH receptor A4 (ENSG00000116106), score: 0.66 EPHA5EPH receptor A5 (ENSG00000145242), score: 0.75 EPHB6EPH receptor B6 (ENSG00000106123), score: 0.69 EPHX4epoxide hydrolase 4 (ENSG00000172031), score: 0.74 ERI1exoribonuclease 1 (ENSG00000104626), score: -0.67 EVLEnah/Vasp-like (ENSG00000196405), score: 0.65 EXTL1exostoses (multiple)-like 1 (ENSG00000158008), score: 0.69 FAM19A1family with sequence similarity 19 (chemokine (C-C motif)-like), member A1 (ENSG00000183662), score: 0.82 FAM43Bfamily with sequence similarity 43, member B (ENSG00000183114), score: 0.66 FAM49Afamily with sequence similarity 49, member A (ENSG00000197872), score: 0.66 FAM5Bfamily with sequence similarity 5, member B (ENSG00000198797), score: 0.73 FBXL16F-box and leucine-rich repeat protein 16 (ENSG00000127585), score: 0.64 FBXL18F-box and leucine-rich repeat protein 18 (ENSG00000155034), score: 0.72 FBXL5F-box and leucine-rich repeat protein 5 (ENSG00000118564), score: -0.81 FBXO8F-box protein 8 (ENSG00000164117), score: -0.7 FCHO2FCH domain only 2 (ENSG00000157107), score: -0.64 FERD3LFer3-like (Drosophila) (ENSG00000146618), score: 0.89 FEZF2FEZ family zinc finger 2 (ENSG00000153266), score: 0.78 FGF10fibroblast growth factor 10 (ENSG00000070193), score: 0.68 FIBCD1fibrinogen C domain containing 1 (ENSG00000130720), score: 0.66 FLRT1fibronectin leucine rich transmembrane protein 1 (ENSG00000126500), score: 0.66 FLRT2fibronectin leucine rich transmembrane protein 2 (ENSG00000185070), score: 0.64 FOXG1forkhead box G1 (ENSG00000176165), score: 0.72 FREM3FRAS1 related extracellular matrix 3 (ENSG00000183090), score: 0.66 FRMPD4FERM and PDZ domain containing 4 (ENSG00000169933), score: 0.68 FSCN1fascin homolog 1, actin-bundling protein (Strongylocentrotus purpuratus) (ENSG00000075618), score: 0.73 GABRA4gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, alpha 4 (ENSG00000109158), score: 0.64 GABRQgamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor, theta (ENSG00000147402), score: 0.95 GALNTL6UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase-like 6 (ENSG00000174473), score: 0.65 GDAP1L1ganglioside-induced differentiation-associated protein 1-like 1 (ENSG00000124194), score: 0.65 GGA3golgi-associated, gamma adaptin ear containing, ARF binding protein 3 (ENSG00000125447), score: 0.65 GJD2gap junction protein, delta 2, 36kDa (ENSG00000159248), score: 0.7 GLRA3glycine receptor, alpha 3 (ENSG00000145451), score: 0.66 GNAI3guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), alpha inhibiting activity polypeptide 3 (ENSG00000065135), score: -0.64 GNB1guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), beta polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000078369), score: 0.68 GNG4guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), gamma 4 (ENSG00000168243), score: 0.69 GOLGA4golgin A4 (ENSG00000144674), score: -0.69 GP5glycoprotein V (platelet) (ENSG00000178732), score: 0.7 GPR123G protein-coupled receptor 123 (ENSG00000197177), score: 0.84 GPR150G protein-coupled receptor 150 (ENSG00000178015), score: 0.87 GPR153G protein-coupled receptor 153 (ENSG00000158292), score: 0.68 GPR26G protein-coupled receptor 26 (ENSG00000154478), score: 0.82 GPR45G protein-coupled receptor 45 (ENSG00000135973), score: 0.84 GPR61G protein-coupled receptor 61 (ENSG00000156097), score: 0.66 GPR78G protein-coupled receptor 78 (ENSG00000155269), score: 0.65 GRIA3glutamate receptor, ionotrophic, AMPA 3 (ENSG00000125675), score: 0.64 GRIK4glutamate receptor, ionotropic, kainate 4 (ENSG00000149403), score: 0.68 GRIN1glutamate receptor, ionotropic, N-methyl D-aspartate 1 (ENSG00000176884), score: 0.64 GRIN2Bglutamate receptor, ionotropic, N-methyl D-aspartate 2B (ENSG00000150086), score: 0.75 GRM2glutamate receptor, metabotropic 2 (ENSG00000164082), score: 0.72 GSG1LGSG1-like (ENSG00000169181), score: 0.74 GSK3Aglycogen synthase kinase 3 alpha (ENSG00000105723), score: 0.71 HAT1histone acetyltransferase 1 (ENSG00000128708), score: -0.77 HBP1HMG-box transcription factor 1 (ENSG00000105856), score: -0.71 HCRTR2hypocretin (orexin) receptor 2 (ENSG00000137252), score: 0.69 HELQhelicase, POLQ-like (ENSG00000163312), score: -0.67 HHIPL1HHIP-like 1 (ENSG00000182218), score: 0.65 HOPXHOP homeobox (ENSG00000171476), score: 0.7 HRH1histamine receptor H1 (ENSG00000196639), score: 0.7 HS3ST2heparan sulfate (glucosamine) 3-O-sulfotransferase 2 (ENSG00000122254), score: 0.76 HS3ST4heparan sulfate (glucosamine) 3-O-sulfotransferase 4 (ENSG00000182601), score: 0.66 HSD11B1Lhydroxysteroid (11-beta) dehydrogenase 1-like (ENSG00000167733), score: 0.68 HSPBP1HSPA (heat shock 70kDa) binding protein, cytoplasmic cochaperone 1 (ENSG00000133265), score: 0.77 HTR1A5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 1A (ENSG00000178394), score: 0.95 HTR1B5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 1B (ENSG00000135312), score: 0.7 HTR1E5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 1E (ENSG00000168830), score: 0.77 HTR2A5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 2A (ENSG00000102468), score: 0.78 HTR2C5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 2C (ENSG00000147246), score: 0.81 HTR3B5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 3B (ENSG00000149305), score: 0.65 HTR45-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 4 (ENSG00000164270), score: 0.83 HTR65-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 6 (ENSG00000158748), score: 0.99 IDEinsulin-degrading enzyme (ENSG00000119912), score: -0.65 IL1RAPL2interleukin 1 receptor accessory protein-like 2 (ENSG00000189108), score: 0.67 IL34interleukin 34 (ENSG00000157368), score: 0.71 INSM2insulinoma-associated 2 (ENSG00000168348), score: 0.66 IQSEC1IQ motif and Sec7 domain 1 (ENSG00000144711), score: 0.68 ISLR2immunoglobulin superfamily containing leucine-rich repeat 2 (ENSG00000167178), score: 0.67 ITPK1inositol 1,3,4-triphosphate 5/6 kinase (ENSG00000100605), score: 0.65 ITPKAinositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase A (ENSG00000137825), score: 0.7 IWS1IWS1 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000163166), score: -0.66 KCNA3potassium voltage-gated channel, shaker-related subfamily, member 3 (ENSG00000177272), score: 0.72 KCNA4potassium voltage-gated channel, shaker-related subfamily, member 4 (ENSG00000182255), score: 0.76 KCNA6potassium voltage-gated channel, shaker-related subfamily, member 6 (ENSG00000151079), score: 0.74 KCNAB2potassium voltage-gated channel, shaker-related subfamily, beta member 2 (ENSG00000069424), score: 0.64 KCNB2potassium voltage-gated channel, Shab-related subfamily, member 2 (ENSG00000182674), score: 0.75 KCNC2potassium voltage-gated channel, Shaw-related subfamily, member 2 (ENSG00000166006), score: 0.72 KCNC4potassium voltage-gated channel, Shaw-related subfamily, member 4 (ENSG00000116396), score: 0.64 KCNF1potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily F, member 1 (ENSG00000162975), score: 0.8 KCNG1potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily G, member 1 (ENSG00000026559), score: 0.85 KCNG2potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily G, member 2 (ENSG00000178342), score: 0.71 KCNG3potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily G, member 3 (ENSG00000171126), score: 0.83 KCNH3potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily H (eag-related), member 3 (ENSG00000135519), score: 0.79 KCNH4potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily H (eag-related), member 4 (ENSG00000089558), score: 0.85 KCNN1potassium intermediate/small conductance calcium-activated channel, subfamily N, member 1 (ENSG00000105642), score: 0.73 KCNQ3potassium voltage-gated channel, KQT-like subfamily, member 3 (ENSG00000184156), score: 0.72 KCNQ5potassium voltage-gated channel, KQT-like subfamily, member 5 (ENSG00000185760), score: 0.71 KCNS1potassium voltage-gated channel, delayed-rectifier, subfamily S, member 1 (ENSG00000124134), score: 0.78 KCNS2potassium voltage-gated channel, delayed-rectifier, subfamily S, member 2 (ENSG00000156486), score: 0.8 KCNV1potassium channel, subfamily V, member 1 (ENSG00000164794), score: 0.82 KCTD16potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 16 (ENSG00000183775), score: 0.72 KCTD17potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 17 (ENSG00000100379), score: 0.64 KCTD4potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 4 (ENSG00000180332), score: 0.74 KIAA0284KIAA0284 (ENSG00000099814), score: 0.66 KIAA0748KIAA0748 (ENSG00000135426), score: 0.72 KIRREL3kin of IRRE like 3 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000149571), score: 0.68 KISS1RKISS1 receptor (ENSG00000116014), score: 0.91 KLHL2kelch-like 2, Mayven (Drosophila) (ENSG00000109466), score: 0.64 KLHL29kelch-like 29 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000119771), score: 0.69 KRT10keratin 10 (ENSG00000186395), score: -0.66 KRT83keratin 83 (ENSG00000170523), score: 0.64 LBRlamin B receptor (ENSG00000143815), score: -0.67 LECT1leukocyte cell derived chemotaxin 1 (ENSG00000136110), score: 0.64 LGR4leucine-rich repeat-containing G protein-coupled receptor 4 (ENSG00000205213), score: -0.65 LHX2LIM homeobox 2 (ENSG00000106689), score: 0.69 LIMA1LIM domain and actin binding 1 (ENSG00000050405), score: -0.66 LMO4LIM domain only 4 (ENSG00000143013), score: 0.73 LMTK2lemur tyrosine kinase 2 (ENSG00000164715), score: 0.7 LNX1ligand of numb-protein X 1 (ENSG00000072201), score: 0.64 LOC100132308solute carrier family 29 (nucleoside transporters), member 4 pseudogene (ENSG00000164638), score: 0.75 LOC401097Similar to LOC166075 (ENSG00000180044), score: 0.66 LPPR3lipid phosphate phosphatase-related protein type 3 (ENSG00000129951), score: 0.85 LPPR4lipid phosphate phosphatase-related protein type 4 (ENSG00000117600), score: 0.78 LPPR5lipid phosphate phosphatase-related protein type 5 (ENSG00000117598), score: 0.76 LRFN1leucine rich repeat and fibronectin type III domain containing 1 (ENSG00000128011), score: 0.66 LRFN2leucine rich repeat and fibronectin type III domain containing 2 (ENSG00000156564), score: 0.85 LRFN3leucine rich repeat and fibronectin type III domain containing 3 (ENSG00000126243), score: 0.77 LRFN5leucine rich repeat and fibronectin type III domain containing 5 (ENSG00000165379), score: 0.69 LRRC4Cleucine rich repeat containing 4C (ENSG00000148948), score: 0.66 LRRC55leucine rich repeat containing 55 (ENSG00000183908), score: 0.67 LRRC7leucine rich repeat containing 7 (ENSG00000033122), score: 0.65 LRTM2leucine-rich repeats and transmembrane domains 2 (ENSG00000166159), score: 0.84 LY6Hlymphocyte antigen 6 complex, locus H (ENSG00000176956), score: 0.72 LZICleucine zipper and CTNNBIP1 domain containing (ENSG00000162441), score: -0.77 MAFGv-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog G (avian) (ENSG00000197063), score: 0.74 MAMLD1mastermind-like domain containing 1 (ENSG00000013619), score: 0.7 MANEALmannosidase, endo-alpha-like (ENSG00000185090), score: 0.65 MAP1Smicrotubule-associated protein 1S (ENSG00000130479), score: 0.69 MAPK1mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 (ENSG00000100030), score: 0.66 MAPK3mitogen-activated protein kinase 3 (ENSG00000102882), score: 0.82 MARCH1membrane-associated ring finger (C3HC4) 1 (ENSG00000145416), score: 0.69 MARCH4membrane-associated ring finger (C3HC4) 4 (ENSG00000144583), score: 0.72 MARCH7membrane-associated ring finger (C3HC4) 7 (ENSG00000136536), score: -0.66 MARK2MAP/microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 2 (ENSG00000072518), score: 0.67 MAS1MAS1 oncogene (ENSG00000130368), score: 0.66 MAST3microtubule associated serine/threonine kinase 3 (ENSG00000099308), score: 0.76 MATKmegakaryocyte-associated tyrosine kinase (ENSG00000007264), score: 0.75 MC4Rmelanocortin 4 receptor (ENSG00000166603), score: 0.77 MED29mediator complex subunit 29 (ENSG00000063322), score: 0.76 MEF2Cmyocyte enhancer factor 2C (ENSG00000081189), score: 0.69 MEPEmatrix extracellular phosphoglycoprotein (ENSG00000152595), score: 0.66 MGAT5Bmannosyl (alpha-1,6-)-glycoprotein beta-1,6-N-acetyl-glucosaminyltransferase, isozyme B (ENSG00000167889), score: 0.75 MGST2microsomal glutathione S-transferase 2 (ENSG00000085871), score: -0.65 MKL1megakaryoblastic leukemia (translocation) 1 (ENSG00000196588), score: 0.71 MKL2MKL/myocardin-like 2 (ENSG00000186260), score: 0.72 MMDmonocyte to macrophage differentiation-associated (ENSG00000108960), score: 0.66 MMP17matrix metallopeptidase 17 (membrane-inserted) (ENSG00000198598), score: 0.83 MTERFD3MTERF domain containing 3 (ENSG00000120832), score: -0.71 MYNNmyoneurin (ENSG00000085274), score: -0.66 MYO16myosin XVI (ENSG00000041515), score: 0.68 MYPOPMyb-related transcription factor, partner of profilin (ENSG00000176182), score: 0.7 N4BP2L2NEDD4 binding protein 2-like 2 (ENSG00000139617), score: -0.67 NAA38N(alpha)-acetyltransferase 38, NatC auxiliary subunit (ENSG00000128534), score: -0.7 NAGPAN-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphodiester alpha-N-acetylglucosaminidase (ENSG00000103174), score: 0.71 NCALDneurocalcin delta (ENSG00000104490), score: 0.68 NCANneurocan (ENSG00000130287), score: 0.67 NCDNneurochondrin (ENSG00000020129), score: 0.67 NDEL1nudE nuclear distribution gene E homolog (A. nidulans)-like 1 (ENSG00000166579), score: 0.74 NELFnasal embryonic LHRH factor (ENSG00000165802), score: 0.73 NETO1neuropilin (NRP) and tolloid (TLL)-like 1 (ENSG00000166342), score: 0.74 NEUROD6neurogenic differentiation 6 (ENSG00000164600), score: 0.71 NFATC3nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic, calcineurin-dependent 3 (ENSG00000072736), score: -0.7 NFE2L2nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (ENSG00000116044), score: -0.66 NGBneuroglobin (ENSG00000165553), score: 0.76 NGEFneuronal guanine nucleotide exchange factor (ENSG00000066248), score: 0.66 NKX2-1NK2 homeobox 1 (ENSG00000136352), score: 0.66 NLKnemo-like kinase (ENSG00000087095), score: 0.67 NOGnoggin (ENSG00000183691), score: 0.72 NOVA2neuro-oncological ventral antigen 2 (ENSG00000104967), score: 0.7 NPAS1neuronal PAS domain protein 1 (ENSG00000130751), score: 0.85 NPAS4neuronal PAS domain protein 4 (ENSG00000174576), score: 0.78 NPBWR1neuropeptides B/W receptor 1 (ENSG00000183729), score: 0.73 NPY2Rneuropeptide Y receptor Y2 (ENSG00000185149), score: 0.66 NRG3neuregulin 3 (ENSG00000185737), score: 0.71 NRSN1neurensin 1 (ENSG00000152954), score: 0.64 NTN3netrin 3 (ENSG00000162068), score: 0.69 NTNG2netrin G2 (ENSG00000196358), score: 0.72 NTSR1neurotensin receptor 1 (high affinity) (ENSG00000101188), score: 0.84 NUMBLnumb homolog (Drosophila)-like (ENSG00000105245), score: 0.72 NUP107nucleoporin 107kDa (ENSG00000111581), score: -0.67 OLFM1olfactomedin 1 (ENSG00000130558), score: 0.65 OPN4opsin 4 (ENSG00000122375), score: 0.77 OPRD1opioid receptor, delta 1 (ENSG00000116329), score: 0.94 OR2AG2olfactory receptor, family 2, subfamily AG, member 2 (ENSG00000188124), score: 0.79 OSBPL9oxysterol binding protein-like 9 (ENSG00000117859), score: -0.71 OTX1orthodenticle homeobox 1 (ENSG00000115507), score: 0.75 PCDH10protocadherin 10 (ENSG00000138650), score: 0.67 PCDH19protocadherin 19 (ENSG00000165194), score: 0.84 PCDH20protocadherin 20 (ENSG00000197991), score: 0.73 PCDH8protocadherin 8 (ENSG00000136099), score: 0.88 PCSK1proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 1 (ENSG00000175426), score: 0.75 PCSK2proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 2 (ENSG00000125851), score: 0.65 PDE1Bphosphodiesterase 1B, calmodulin-dependent (ENSG00000123360), score: 0.68 PDE2Aphosphodiesterase 2A, cGMP-stimulated (ENSG00000186642), score: 0.74 PDE8Bphosphodiesterase 8B (ENSG00000113231), score: 0.7 PDYNprodynorphin (ENSG00000101327), score: 0.85 PHACTR4phosphatase and actin regulator 4 (ENSG00000204138), score: -0.66 PIK3R2phosphoinositide-3-kinase, regulatory subunit 2 (beta) (ENSG00000105647), score: 0.66 PIN1peptidylprolyl cis/trans isomerase, NIMA-interacting 1 (ENSG00000127445), score: 0.71 PIP5KL1phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase-like 1 (ENSG00000167103), score: 0.69 PITPNM2phosphatidylinositol transfer protein, membrane-associated 2 (ENSG00000090975), score: 0.72 PKN2protein kinase N2 (ENSG00000065243), score: -0.75 PLD3phospholipase D family, member 3 (ENSG00000105223), score: 0.79 PLXNA1plexin A1 (ENSG00000114554), score: 0.76 PLXNA4plexin A4 (ENSG00000221866), score: 0.71 PNCKpregnancy up-regulated non-ubiquitously expressed CaM kinase (ENSG00000130822), score: 0.71 PNMAL2PNMA-like 2 (ENSG00000204851), score: 0.67 PNOCprepronociceptin (ENSG00000168081), score: 0.75 PPME1protein phosphatase methylesterase 1 (ENSG00000214517), score: 0.65 PPP6R3protein phosphatase 6, regulatory subunit 3 (ENSG00000110075), score: -0.71 PRAF2PRA1 domain family, member 2 (ENSG00000243279), score: 0.7 PRDM11PR domain containing 11 (ENSG00000019485), score: 0.69 PRDM8PR domain containing 8 (ENSG00000152784), score: 0.72 PRICKLE2prickle homolog 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000163637), score: 0.67 PRKCGprotein kinase C, gamma (ENSG00000126583), score: 0.66 PRKG2protein kinase, cGMP-dependent, type II (ENSG00000138669), score: 0.65 PRLHRprolactin releasing hormone receptor (ENSG00000119973), score: 0.84 PROKR2prokineticin receptor 2 (ENSG00000101292), score: 1 PRPF19PRP19/PSO4 pre-mRNA processing factor 19 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000110107), score: 0.65 PRR7proline rich 7 (synaptic) (ENSG00000131188), score: 0.78 PRRG3proline rich Gla (G-carboxyglutamic acid) 3 (transmembrane) (ENSG00000130032), score: 0.78 PSDpleckstrin and Sec7 domain containing (ENSG00000059915), score: 0.66 PSRC1proline/serine-rich coiled-coil 1 (ENSG00000134222), score: 0.67 PTCHD2patched domain containing 2 (ENSG00000204624), score: 0.7 PTHLHparathyroid hormone-like hormone (ENSG00000087494), score: 0.67 PTPN5protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 5 (striatum-enriched) (ENSG00000110786), score: 0.72 PTPRAprotein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, A (ENSG00000132670), score: 0.73 PTPRNprotein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, N (ENSG00000054356), score: 0.68 PTPRSprotein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, S (ENSG00000105426), score: 0.65 R3HDM1R3H domain containing 1 (ENSG00000048991), score: 0.66 R3HDM2R3H domain containing 2 (ENSG00000179912), score: 0.65 RAB3BRAB3B, member RAS oncogene family (ENSG00000169213), score: 0.7 RASAL1RAS protein activator like 1 (GAP1 like) (ENSG00000111344), score: 0.66 RASD2RASD family, member 2 (ENSG00000100302), score: 0.67 RASL10ARAS-like, family 10, member A (ENSG00000100276), score: 0.79 RGS4regulator of G-protein signaling 4 (ENSG00000117152), score: 0.7 RHBDD2rhomboid domain containing 2 (ENSG00000005486), score: 0.72 RIMBP2RIMS binding protein 2 (ENSG00000060709), score: 0.73 RIN1Ras and Rab interactor 1 (ENSG00000174791), score: 0.7 RNF24ring finger protein 24 (ENSG00000101236), score: 0.69 RNF44ring finger protein 44 (ENSG00000146083), score: 0.67 ROCK1Rho-associated, coiled-coil containing protein kinase 1 (ENSG00000067900), score: -0.8 RORBRAR-related orphan receptor B (ENSG00000198963), score: 0.66 RPRMreprimo, TP53 dependent G2 arrest mediator candidate (ENSG00000177519), score: 0.72 RPRMLreprimo-like (ENSG00000179673), score: 0.66 RTBDNretbindin (ENSG00000132026), score: 0.72 RTN2reticulon 2 (ENSG00000125744), score: 0.65 RTN4RL1reticulon 4 receptor-like 1 (ENSG00000185924), score: 0.76 RXFP3relaxin/insulin-like family peptide receptor 3 (ENSG00000182631), score: 0.76 RYKRYK receptor-like tyrosine kinase (ENSG00000163785), score: -0.64 SARSseryl-tRNA synthetase (ENSG00000031698), score: 0.65 SATB2SATB homeobox 2 (ENSG00000119042), score: 0.72 SCN3Bsodium channel, voltage-gated, type III, beta (ENSG00000166257), score: 0.71 SEMA4Fsema domain, immunoglobulin domain (Ig), transmembrane domain (TM) and short cytoplasmic domain, (semaphorin) 4F (ENSG00000135622), score: 0.64 SGSM2small G protein signaling modulator 2 (ENSG00000141258), score: 0.74 SGSM3small G protein signaling modulator 3 (ENSG00000100359), score: 0.72 SH2D5SH2 domain containing 5 (ENSG00000189410), score: 0.76 SHANK1SH3 and multiple ankyrin repeat domains 1 (ENSG00000161681), score: 0.65 SHC3SHC (Src homology 2 domain containing) transforming protein 3 (ENSG00000148082), score: 0.76 SIKE1suppressor of IKBKE 1 (ENSG00000052723), score: -0.69 SIN3BSIN3 homolog B, transcription regulator (yeast) (ENSG00000127511), score: 0.72 SLC10A4solute carrier family 10 (sodium/bile acid cotransporter family), member 4 (ENSG00000145248), score: 0.73 SLC24A4solute carrier family 24 (sodium/potassium/calcium exchanger), member 4 (ENSG00000140090), score: 0.7 SLC25A22solute carrier family 25 (mitochondrial carrier: glutamate), member 22 (ENSG00000177542), score: 0.65 SLC2A6solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 6 (ENSG00000160326), score: 0.68 SLC32A1solute carrier family 32 (GABA vesicular transporter), member 1 (ENSG00000101438), score: 0.67 SLC35E4solute carrier family 35, member E4 (ENSG00000100036), score: 0.75 SLC39A10solute carrier family 39 (zinc transporter), member 10 (ENSG00000196950), score: 0.64 SLC6A7solute carrier family 6 (neurotransmitter transporter, L-proline), member 7 (ENSG00000011083), score: 0.7 SLC7A3solute carrier family 7 (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system), member 3 (ENSG00000165349), score: 0.78 SLC8A3solute carrier family 8 (sodium/calcium exchanger), member 3 (ENSG00000100678), score: 0.69 SLIT1slit homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000187122), score: 0.81 SLITRK1SLIT and NTRK-like family, member 1 (ENSG00000178235), score: 0.7 SLITRK5SLIT and NTRK-like family, member 5 (ENSG00000165300), score: 0.67 SMAP2small ArfGAP2 (ENSG00000084070), score: 0.67 SNNstannin (ENSG00000184602), score: 0.65 SP1Sp1 transcription factor (ENSG00000185591), score: -0.72 SPATA2Lspermatogenesis associated 2-like (ENSG00000158792), score: 0.71 SPDEFSAM pointed domain containing ets transcription factor (ENSG00000124664), score: 0.67 SPRED3sprouty-related, EVH1 domain containing 3 (ENSG00000188766), score: 0.83 SPRYD3SPRY domain containing 3 (ENSG00000167778), score: 0.65 SSTsomatostatin (ENSG00000157005), score: 0.78 ST6GALNAC5ST6 (alpha-N-acetyl-neuraminyl-2,3-beta-galactosyl-1,3)-N-acetylgalactosaminide alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase 5 (ENSG00000117069), score: 0.79 STK32Cserine/threonine kinase 32C (ENSG00000165752), score: 0.74 STOML1stomatin (EPB72)-like 1 (ENSG00000067221), score: 0.69 STX1Asyntaxin 1A (brain) (ENSG00000106089), score: 0.7 STYK1serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase 1 (ENSG00000060140), score: 0.74 SYNGAP1synaptic Ras GTPase activating protein 1 (ENSG00000197283), score: 0.72 SYT17synaptotagmin XVII (ENSG00000103528), score: 0.7 SYT5synaptotagmin V (ENSG00000129990), score: 0.72 TACR1tachykinin receptor 1 (ENSG00000115353), score: 0.64 TBR1T-box, brain, 1 (ENSG00000136535), score: 0.75 TCEB3transcription elongation factor B (SIII), polypeptide 3 (110kDa, elongin A) (ENSG00000011007), score: -0.69 TCERG1Ltranscription elongation regulator 1-like (ENSG00000176769), score: 0.7 TGFBR1transforming growth factor, beta receptor 1 (ENSG00000106799), score: -0.73 TJP2tight junction protein 2 (zona occludens 2) (ENSG00000119139), score: -0.67 TMEFF2transmembrane protein with EGF-like and two follistatin-like domains 2 (ENSG00000144339), score: 0.64 TMEM132Dtransmembrane protein 132D (ENSG00000151952), score: 0.8 TMEM151Atransmembrane protein 151A (ENSG00000179292), score: 0.69 TMEM155transmembrane protein 155 (ENSG00000164112), score: 0.7 TMEM179transmembrane protein 179 (ENSG00000189203), score: 0.7 TMEM198transmembrane protein 198 (ENSG00000188760), score: 0.68 TNPO2transportin 2 (ENSG00000105576), score: 0.7 TOLLIPtoll interacting protein (ENSG00000078902), score: 0.7 TPRKBTP53RK binding protein (ENSG00000144034), score: -0.65 TRIP11thyroid hormone receptor interactor 11 (ENSG00000100815), score: -0.69 TRPM2transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily M, member 2 (ENSG00000142185), score: 0.72 TSHZ3teashirt zinc finger homeobox 3 (ENSG00000121297), score: 0.74 TUBA4Atubulin, alpha 4a (ENSG00000127824), score: 0.65 TUSC2tumor suppressor candidate 2 (ENSG00000114383), score: 0.68 UFSP2UFM1-specific peptidase 2 (ENSG00000109775), score: -0.67 UNC5Aunc-5 homolog A (C. elegans) (ENSG00000113763), score: 0.67 UNC5Dunc-5 homolog D (C. elegans) (ENSG00000156687), score: 0.65 USP3ubiquitin specific peptidase 3 (ENSG00000140455), score: -0.66 VGFVGF nerve growth factor inducible (ENSG00000128564), score: 0.74 VIPvasoactive intestinal peptide (ENSG00000146469), score: 0.68 VPS54vacuolar protein sorting 54 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000143952), score: -0.68 VSTM2AV-set and transmembrane domain containing 2A (ENSG00000170419), score: 0.74 VSTM2BV-set and transmembrane domain containing 2B (ENSG00000187135), score: 0.75 VSTM2LV-set and transmembrane domain containing 2 like (ENSG00000132821), score: 0.71 VWC2Lvon Willebrand factor C domain-containing protein 2-like (ENSG00000174453), score: 0.75 WDR7WD repeat domain 7 (ENSG00000091157), score: 0.65 WNT1wingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 1 (ENSG00000125084), score: 0.97 WNT10Bwingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 10B (ENSG00000169884), score: 0.79 WNT16wingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 16 (ENSG00000002745), score: 0.81 WNT7Awingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 7A (ENSG00000154764), score: 0.71 XKR4XK, Kell blood group complex subunit-related family, member 4 (ENSG00000206579), score: 0.81 XYLT1xylosyltransferase I (ENSG00000103489), score: 0.74 YES1v-yes-1 Yamaguchi sarcoma viral oncogene homolog 1 (ENSG00000176105), score: -0.66 YWHAGtyrosine 3-monooxygenase/tryptophan 5-monooxygenase activation protein, gamma polypeptide (ENSG00000170027), score: 0.71 YWHAHtyrosine 3-monooxygenase/tryptophan 5-monooxygenase activation protein, eta polypeptide (ENSG00000128245), score: 0.66 ZDHHC22zinc finger, DHHC-type containing 22 (ENSG00000177108), score: 0.73 ZFAND6zinc finger, AN1-type domain 6 (ENSG00000086666), score: -0.66 ZNF831zinc finger protein 831 (ENSG00000124203), score: 0.86
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ptr_br_m1_ca1 | ptr | br | m | 1 |
| mml_br_f_ca1 | mml | br | f | _ |
| ppy_br_f_ca1 | ppy | br | f | _ |
| hsa_br_m3_ca1 | hsa | br | m | 3 |
| ppa_br_f1_ca1 | ppa | br | f | 1 |
| mml_br_m2_ca1 | mml | br | m | 2 |
| ppy_br_m_ca1 | ppy | br | m | _ |
| hsa_br_m7_ca1 | hsa | br | m | 7 |