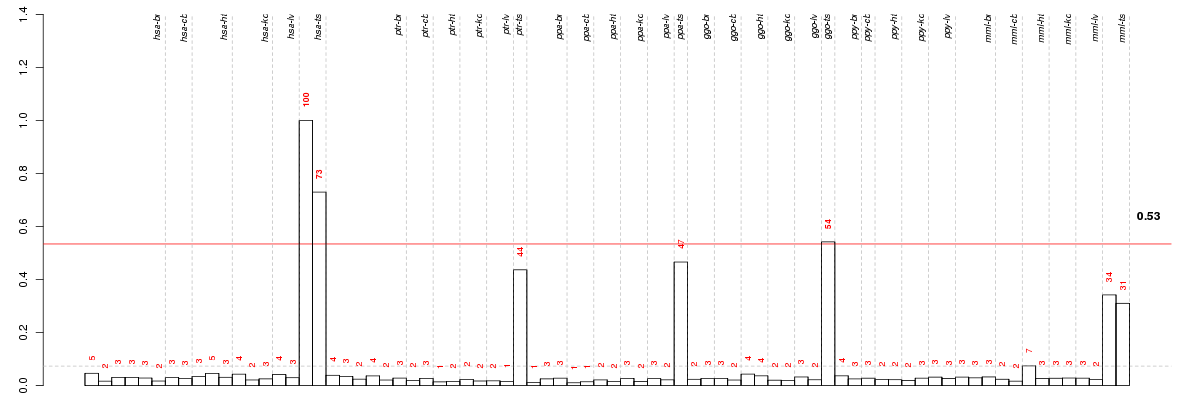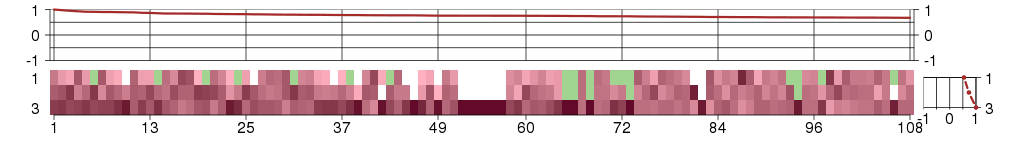

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

reproduction
The production by an organism of new individuals that contain some portion of their genetic material inherited from that organism.
metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
system process
A multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system. An organ system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a biological objective.
defense response
Reactions, triggered in response to the presence of a foreign body or the occurrence of an injury, which result in restriction of damage to the organism attacked or prevention/recovery from the infection caused by the attack.
defense response to bacterium
Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a bacterium that act to protect the cell or organism.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
transcription
The cellular synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
transcription, DNA-dependent
The cellular synthesis of RNA on a template of DNA.
regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-dependent transcription.
nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds; includes nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, assimilatory/dissimilatory nitrate reduction and the interconversion of nitrogenous organic matter and ammonium.
response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
neurological system process
A organ system process carried out by any of the organs or tissues of neurological system.
sensory perception
The series of events required for an organism to receive a sensory stimulus, convert it to a molecular signal, and recognize and characterize the signal. This is a neurological process.
sensory perception of chemical stimulus
The series of events required for an organism to receive a sensory chemical stimulus, convert it to a molecular signal, and recognize and characterize the signal. This is a neurological process.
sensory perception of smell
The series of events required for an organism to receive an olfactory stimulus, convert it to a molecular signal, and recognize and characterize the signal. Olfaction involves the detection of chemical composition of an organism's ambient medium by chemoreceptors. This is a neurological process.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
response to biotic stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a biotic stimulus, a stimulus caused or produced by a living organism.
response to other organism
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from another living organism.
response to bacterium
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a bacterium.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
gene expression
The process by which a gene's sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
regulation of gene expression
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
RNA metabolic process
The cellular chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
sexual reproduction
The regular alternation, in the life cycle of haplontic, diplontic and diplohaplontic organisms, of meiosis and fertilization which provides for the production offspring. In diplontic organisms there is a life cycle in which the products of meiosis behave directly as gametes, fusing to form a zygote from which the diploid, or sexually reproductive polyploid, adult organism will develop. In diplohaplontic organisms a haploid phase (gametophyte) exists in the life cycle between meiosis and fertilization (e.g. higher plants, many algae and Fungi); the products of meiosis are spores that develop as haploid individuals from which haploid gametes develop to form a diploid zygote; diplohaplontic organisms show an alternation of haploid and diploid generations. In haplontic organisms meiosis occurs in the zygote, giving rise to four haploid cells (e.g. many algae and protozoa), only the zygote is diploid and this may form a resistant spore, tiding organisms over hard times.
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
RNA biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage. Includes polymerization of ribonucleotide monomers.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
endocrine system development
Progression of the endocrine system over time, from its formation to a mature structure. The endocrine system is a system of hormones and ductless glands, where the glands release hormones directly into the blood, lymph or other intercellular fluid, and the hormones circulate within the body to affect distant organs. The major glands that make up the human endocrine system are the hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, parathryoids, adrenals, pineal body, and the reproductive glands which include the ovaries and testes.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nitrogen or nitrogenous compounds.
regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
multi-organism process
Any process by which an organism has an effect on another organism of the same or different species.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of primary metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism involving those compounds formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleic acids.
all
NA
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nitrogen or nitrogenous compounds.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
regulation of primary metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism involving those compounds formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
response to other organism
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from another living organism.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of gene expression
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
defense response to bacterium
Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a bacterium that act to protect the cell or organism.
regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
transcription
The cellular synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
transcription, DNA-dependent
The cellular synthesis of RNA on a template of DNA.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
RNA biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage. Includes polymerization of ribonucleotide monomers.
regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
transcription
The cellular synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
RNA metabolic process
The cellular chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage.
regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-dependent transcription.
regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-dependent transcription.

extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
all
NA

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
nucleic acid binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any nucleic acid.
DNA binding
Any molecular function by which a gene product interacts selectively with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid).
binding
The selective, non-covalent, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
sequence-specific DNA binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with DNA of a specific nucleotide composition, e.g. GC-rich DNA binding, or with a specific sequence motif or type of DNA e.g. promotor binding or rDNA binding.
all
NA
AADACL3arylacetamide deacetylase-like 3 (ENSG00000188984), score: 0.93 ABCB5ATP-binding cassette, sub-family B (MDR/TAP), member 5 (ENSG00000004846), score: 0.71 ADAM7ADAM metallopeptidase domain 7 (ENSG00000069206), score: 0.71 AMHR2anti-Mullerian hormone receptor, type II (ENSG00000135409), score: 0.8 AMPD1adenosine monophosphate deaminase 1 (ENSG00000116748), score: 0.76 BRS3bombesin-like receptor 3 (ENSG00000102239), score: 0.82 C20orf134chromosome 20 open reading frame 134 (ENSG00000182584), score: 0.68 C20orf186chromosome 20 open reading frame 186 (ENSG00000186191), score: 0.75 C6orf15chromosome 6 open reading frame 15 (ENSG00000204542), score: 0.73 CDX1caudal type homeobox 1 (ENSG00000113722), score: 0.87 CHATcholine O-acetyltransferase (ENSG00000070748), score: 0.79 CILP2cartilage intermediate layer protein 2 (ENSG00000160161), score: 0.81 CNGA2cyclic nucleotide gated channel alpha 2 (ENSG00000183862), score: 0.75 COL2A1collagen, type II, alpha 1 (ENSG00000139219), score: 0.81 CRISP1cysteine-rich secretory protein 1 (ENSG00000124812), score: 0.89 CRYGCcrystallin, gamma C (ENSG00000163254), score: 0.73 CXorf67chromosome X open reading frame 67 (ENSG00000187690), score: 0.73 CYP11A1cytochrome P450, family 11, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000140459), score: 0.73 DEFB110defensin, beta 110 (ENSG00000203970), score: 0.76 DEFB118defensin, beta 118 (ENSG00000131068), score: 0.68 DEFB121defensin, beta 121 (ENSG00000204548), score: 0.85 DEFB123defensin, beta 123 (ENSG00000180424), score: 0.69 DEFB129defensin, beta 129 (ENSG00000125903), score: 0.76 DEFB132defensin, beta 132 (ENSG00000186458), score: 0.74 DEFB133defensin, beta 133 (ENSG00000214643), score: 0.76 EDDM3Bepididymal protein 3B (ENSG00000181552), score: 0.73 ELSPBP1epididymal sperm binding protein 1 (ENSG00000169393), score: 0.78 ESR2estrogen receptor 2 (ER beta) (ENSG00000140009), score: 0.74 ESX1ESX homeobox 1 (ENSG00000123576), score: 0.75 EVX2even-skipped homeobox 2 (ENSG00000174279), score: 0.75 FAM187Bfamily with sequence similarity 187, member B (ENSG00000177558), score: 0.69 FNDC7fibronectin type III domain containing 7 (ENSG00000143107), score: 0.75 FOXE1forkhead box E1 (thyroid transcription factor 2) (ENSG00000178919), score: 0.7 FTHL17ferritin, heavy polypeptide-like 17 (ENSG00000132446), score: 0.77 GCNT7glucosaminyl (N-acetyl) transferase family member 7 (ENSG00000124091), score: 0.77 GFI1Bgrowth factor independent 1B transcription repressor (ENSG00000165702), score: 0.84 GIPgastric inhibitory polypeptide (ENSG00000159224), score: 0.91 GPX5glutathione peroxidase 5 (epididymal androgen-related protein) (ENSG00000224586), score: 0.83 HMHB1histocompatibility (minor) HB-1 (ENSG00000158497), score: 0.8 HOXC13homeobox C13 (ENSG00000123364), score: 0.77 IL13interleukin 13 (ENSG00000169194), score: 0.74 IL3interleukin 3 (colony-stimulating factor, multiple) (ENSG00000164399), score: 0.82 ISL2ISL LIM homeobox 2 (ENSG00000159556), score: 0.76 JSRP1junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum protein 1 (ENSG00000167476), score: 0.79 KPRPkeratinocyte proline-rich protein (ENSG00000203786), score: 0.69 KRT23keratin 23 (histone deacetylase inducible) (ENSG00000108244), score: 0.89 KRT9keratin 9 (ENSG00000171403), score: 0.76 LALBAlactalbumin, alpha- (ENSG00000167531), score: 0.78 LIN28Alin-28 homolog A (C. elegans) (ENSG00000131914), score: 0.71 LIPFlipase, gastric (ENSG00000182333), score: 0.78 LOC100287738hypothetical protein LOC100287738 (ENSG00000139656), score: 0.72 LOC100292575similar to melanoma antigen family C, 2 (ENSG00000046774), score: 0.72 LRRC18leucine rich repeat containing 18 (ENSG00000165383), score: 0.68 LUZP4leucine zipper protein 4 (ENSG00000102021), score: 0.79 LY6G6Flymphocyte antigen 6 complex, locus G6F (ENSG00000204424), score: 0.75 MAGEA1melanoma antigen family A, 1 (directs expression of antigen MZ2-E) (ENSG00000198681), score: 0.76 MAGEA4melanoma antigen family A, 4 (ENSG00000147381), score: 0.72 MAGEB17melanoma antigen family B, 17 (ENSG00000182798), score: 0.84 MAGEB2melanoma antigen family B, 2 (ENSG00000099399), score: 0.72 MAGEB3melanoma antigen family B, 3 (ENSG00000198798), score: 0.68 MS4A6Emembrane-spanning 4-domains, subfamily A, member 6E (ENSG00000166926), score: 0.68 MYLPFmyosin light chain, phosphorylatable, fast skeletal muscle (ENSG00000180209), score: 0.69 NANOS2nanos homolog 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000188425), score: 0.82 NLRP11NLR family, pyrin domain containing 11 (ENSG00000179873), score: 0.7 NLRP7NLR family, pyrin domain containing 7 (ENSG00000167634), score: 0.78 NOBOXNOBOX oogenesis homeobox (ENSG00000106410), score: 0.9 NOX5NADPH oxidase, EF-hand calcium binding domain 5 (ENSG00000137808), score: 0.8 NR0B1nuclear receptor subfamily 0, group B, member 1 (ENSG00000169297), score: 0.71 NR5A1nuclear receptor subfamily 5, group A, member 1 (ENSG00000136931), score: 0.72 OBP2Aodorant binding protein 2A (ENSG00000122136), score: 0.77 OR10R2olfactory receptor, family 10, subfamily R, member 2 (ENSG00000198965), score: 0.76 OR6F1olfactory receptor, family 6, subfamily F, member 1 (ENSG00000169214), score: 0.83 OR6K3olfactory receptor, family 6, subfamily K, member 3 (ENSG00000203757), score: 0.76 OR9Q2olfactory receptor, family 9, subfamily Q, member 2 (ENSG00000186513), score: 1 OSR2odd-skipped related 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000164920), score: 0.68 OTPorthopedia homeobox (ENSG00000171540), score: 0.7 PASD1PAS domain containing 1 (ENSG00000166049), score: 0.82 PATE1prostate and testis expressed 1 (ENSG00000171053), score: 0.75 PHOX2Apaired-like homeobox 2a (ENSG00000165462), score: 0.9 PITX1paired-like homeodomain 1 (ENSG00000069011), score: 0.76 PLAC1placenta-specific 1 (ENSG00000170965), score: 0.9 POU4F2POU class 4 homeobox 2 (ENSG00000151615), score: 0.97 PRDM14PR domain containing 14 (ENSG00000147596), score: 0.69 PROK1prokineticin 1 (ENSG00000143125), score: 0.84 PRPHperipherin (ENSG00000135406), score: 0.71 PSORS1C2psoriasis susceptibility 1 candidate 2 (ENSG00000204538), score: 0.8 RFX6regulatory factor X, 6 (ENSG00000185002), score: 0.69 SLC46A2solute carrier family 46, member 2 (ENSG00000119457), score: 0.68 SPINT4serine peptidase inhibitor, Kunitz type 4 (ENSG00000149651), score: 0.74 SPO11SPO11 meiotic protein covalently bound to DSB homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000054796), score: 0.68 SPOCD1SPOC domain containing 1 (ENSG00000134668), score: 0.68 SYCNsyncollin (ENSG00000179751), score: 0.79 TBX4T-box 4 (ENSG00000121075), score: 0.69 TCL1AT-cell leukemia/lymphoma 1A (ENSG00000100721), score: 0.84 TEX101testis expressed 101 (ENSG00000131126), score: 0.69 TEX13Btestis expressed 13B (ENSG00000170925), score: 0.87 TKTL1transketolase-like 1 (ENSG00000007350), score: 0.69 TMPRSS11Atransmembrane protease, serine 11A (ENSG00000187054), score: 0.72 TPD52L3tumor protein D52-like 3 (ENSG00000170777), score: 0.79 TRIM71tripartite motif-containing 71 (ENSG00000206557), score: 0.7 VGLL2vestigial like 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000170162), score: 0.77 WFDC10AWAP four-disulfide core domain 10A (ENSG00000180305), score: 0.69 WFDC8WAP four-disulfide core domain 8 (ENSG00000158901), score: 0.77 WFDC9WAP four-disulfide core domain 9 (ENSG00000180205), score: 0.77 ZIM3zinc finger, imprinted 3 (ENSG00000141946), score: 0.84
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ggo_ts_m_ca1 | ggo | ts | m | _ |
| hsa_ts_m2_ca1 | hsa | ts | m | 2 |
| hsa_ts_m1_ca1 | hsa | ts | m | 1 |