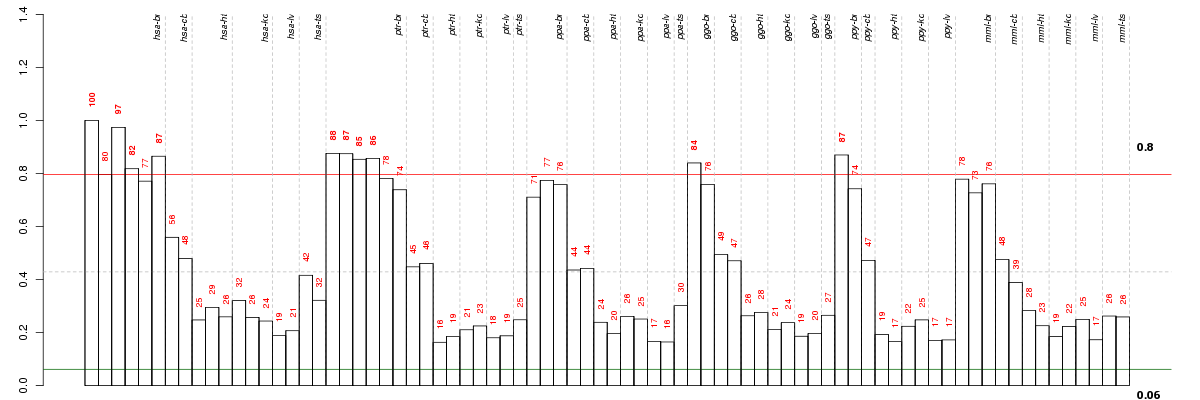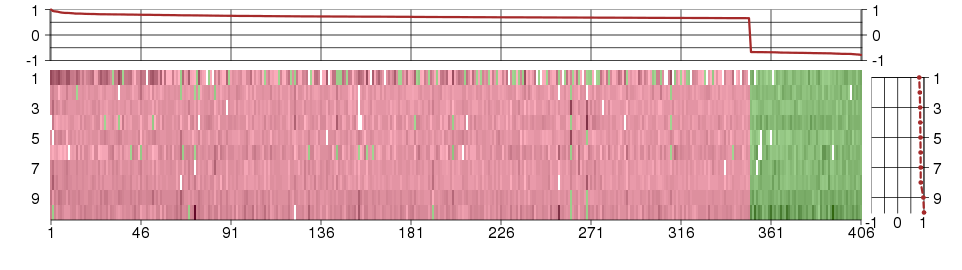

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

two-component signal transduction system (phosphorelay)
A conserved series of molecular signals found in prokaryotes and eukaryotes; involves autophosphorylation of a histidine kinase and the transfer of the phosphate group to an aspartate that then acts as a phospho-donor to response regulator proteins.
cell morphogenesis
The developmental process by which the size or shape of a cell is generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation
The change in form (cell shape and size) that occurs when relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history.
regulation of action potential
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of action potential creation, propagation or termination. An action potential is a spike of membrane depolarization and repolarization that travels along the membrane of a cell.
system process
A multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system. An organ system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a biological objective.
transport
The directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells, or within a multicellular organism by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
ion transport
The directed movement of charged atoms or small charged molecules into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
cation transport
The directed movement of cations, atoms or small molecules with a net positive charge, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
potassium ion transport
The directed movement of potassium ions (K+) into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
metal ion transport
The directed movement of metal ions, any metal ion with an electric charge, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
cellular ion homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of ions at the level of a cell.
cell communication
Any process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
cell surface receptor linked signaling pathway
Any series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of an extracellular ligand to a receptor on the surface of the target cell.
G-protein coupled receptor protein signaling pathway
The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a G-protein coupled receptor binding to its physiological ligand.
cell-cell signaling
Any process that mediates the transfer of information from one cell to another.
synaptic transmission
The process of communication from a neuron to a target (neuron, muscle, or secretory cell) across a synapse.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of nervous tissue over time, from its formation to its mature state.
neurological system process
A organ system process carried out by any of the organs or tissues of neurological system.
axonogenesis
Generation of a long process of a neuron, that carries efferent (outgoing) action potentials from the cell body towards target cells.
central nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the central nervous system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The central nervous system is the core nervous system that serves an integrating and coordinating function. In vertebrates it consists of the brain, spinal cord and spinal nerves. In those invertebrates with a central nervous system it typically consists of a brain, cerebral ganglia and a nerve cord.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
glial cell differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the specialized features of a glial cell.
monovalent inorganic cation transport
The directed movement of inorganic cations with a valency of one into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. Inorganic cations are atoms or small molecules with a positive charge which do not contain carbon in covalent linkage.
cellular component organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a cellular component.
transmission of nerve impulse
The neurological system process by which a signal is transmitted through the nervous system by synaptic transmission and the sequential electrochemical polarization and depolarization that travels across the membrane of a nerve cell (neuron) in response to stimulation.
regulation of action potential in neuron
The process that modulates the membrane potential involved in the propagation of a signal in a neuron.
cellular homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state at the level of the cell.
neurogenesis
Generation of cells within the nervous system.
signaling pathway
The series of molecular events whereby information is sent from one location to another within a living organism or between living organisms.
signaling process
Any biological process involved in the generation, transmission, reception, or interpretation of a signal. A signal is an entity used to transmit or convey information.
signaling
The entirety of a process whereby information is transmitted. This process begins with the initiation of the signal and ends when a response has been triggered.
signal transmission
The process whereby a signal is released and/or conveyed from one location to another.
cell projection organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
cell differentiation
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state.
neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron.
neuron projection development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites).
regulation of neurological system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a neurophysiological process, an organ system process carried out by any of the organs or tissues of neurological system.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
cellular component morphogenesis
The process by which cellular structures, including whole cells or cell parts, are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
cell part morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a cell part are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
gliogenesis
The process by which glial cells are generated. This includes the production of glial progenitors and their differentiation into mature glia.
regulation of membrane potential
Any process that modulates the establishment or extent of a membrane potential, the electric potential existing across any membrane arising from charges in the membrane itself and from the charges present in the media on either side of the membrane.
homeostatic process
Any biological process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state.
regulation of system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a system process, a multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system.
ion homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of ions within an organism or cell.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
neuron development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron over time, from initial commitment of the cell to a specific fate, to the fully functional differentiated cell.
cell morphogenesis involved in neuron differentiation
The process by which the structures of a neuron are generated and organized. This process occurs while the initially relatively unspecialized cell is acquiring the specialized features of a neuron.
generation of neurons
The process by which nerve cells are generated. This includes the production of neuroblasts and their differentiation into neurons.
oligodendrocyte differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the specialized features of an oligodendrocyte. An oligodendrocyte is a type of glial cell involved in myelinating the axons of neurons in the central nervous system.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
neuron projection morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a neuron projection are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
cell projection morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a cell projection are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
chemical homeostasis
Any biological process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of a chemical.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
cellular chemical homeostasis
Any biological process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of a chemical at the level of the cell.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of biological quality
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological quality. A biological quality is a measurable attribute of an organism or part of an organism, such as size, mass, shape, color, etc.
all
NA
cell projection organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
signaling process
Any biological process involved in the generation, transmission, reception, or interpretation of a signal. A signal is an entity used to transmit or convey information.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
cell-cell signaling
Any process that mediates the transfer of information from one cell to another.
cellular component morphogenesis
The process by which cellular structures, including whole cells or cell parts, are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
transmission of nerve impulse
The neurological system process by which a signal is transmitted through the nervous system by synaptic transmission and the sequential electrochemical polarization and depolarization that travels across the membrane of a nerve cell (neuron) in response to stimulation.
regulation of system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a system process, a multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system.
cellular component morphogenesis
The process by which cellular structures, including whole cells or cell parts, are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
synaptic transmission
The process of communication from a neuron to a target (neuron, muscle, or secretory cell) across a synapse.
neuron projection morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a neuron projection are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation
The change in form (cell shape and size) that occurs when relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history.
cell projection morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a cell projection are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
cell projection morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of a cell projection are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
transmission of nerve impulse
The neurological system process by which a signal is transmitted through the nervous system by synaptic transmission and the sequential electrochemical polarization and depolarization that travels across the membrane of a nerve cell (neuron) in response to stimulation.
regulation of neurological system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a neurophysiological process, an organ system process carried out by any of the organs or tissues of neurological system.
cellular homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state at the level of the cell.
neuron development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron over time, from initial commitment of the cell to a specific fate, to the fully functional differentiated cell.
neuron projection development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites).
cell morphogenesis involved in neuron differentiation
The process by which the structures of a neuron are generated and organized. This process occurs while the initially relatively unspecialized cell is acquiring the specialized features of a neuron.
central nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the central nervous system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The central nervous system is the core nervous system that serves an integrating and coordinating function. In vertebrates it consists of the brain, spinal cord and spinal nerves. In those invertebrates with a central nervous system it typically consists of a brain, cerebral ganglia and a nerve cord.
neurogenesis
Generation of cells within the nervous system.
oligodendrocyte differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the specialized features of an oligodendrocyte. An oligodendrocyte is a type of glial cell involved in myelinating the axons of neurons in the central nervous system.
cellular chemical homeostasis
Any biological process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of a chemical at the level of the cell.
glial cell differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the specialized features of a glial cell.
neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron.
axonogenesis
Generation of a long process of a neuron, that carries efferent (outgoing) action potentials from the cell body towards target cells.
potassium ion transport
The directed movement of potassium ions (K+) into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
cellular ion homeostasis
Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady-state of ions at the level of a cell.
regulation of action potential in neuron
The process that modulates the membrane potential involved in the propagation of a signal in a neuron.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
integral to membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer. When used to describe a protein, indicates that all or part of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cytoplasm
All of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
synaptic vesicle
A secretory organelle, some 50 nm in diameter, of presynaptic nerve terminals; accumulates in high concentrations of neurotransmitters and is secreted these into the synaptic cleft by fusion with the 'active zone' of the presynaptic plasma membrane.
voltage-gated potassium channel complex
A protein complex that forms a transmembrane channel through which potassium ions may cross a cell membrane in response to changes in membrane potential.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
cell junction
A plasma membrane part that forms a specialized region of connection between two cells or between a cell and the extracellular matrix. At a cell junction, anchoring proteins extend through the plasma membrane to link cytoskeletal proteins in one cell to cytoskeletal proteins in neighboring cells or to proteins in the extracellular matrix.
coated vesicle
Small membrane-bounded organelle formed by pinching off of a coated region of membrane. Some coats are made of clathrin, whereas others are made from other proteins.
clathrin-coated vesicle
A vesicle with a coat formed of clathrin connected to the membrane via one of the clathrin adaptor complexes.
axon
The long process of a neuron that conducts nerve impulses, usually away from the cell body to the terminals and varicosities, which are sites of storage and release of neurotransmitter.
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
vesicle
Any small, fluid-filled, spherical organelle enclosed by membrane or protein.
membrane-bounded vesicle
Any small, fluid-filled, spherical organelle enclosed by a lipid bilayer.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
axon part
A part of an axon, a cell projection of a neuron.
ion channel complex
A protein complex that spans a membrane and forms a water-filled channel across the phospholipid bilayer allowing selective ion transport down its electrochemical gradient.
cation channel complex
An ion channel complex through which cations pass.
potassium channel complex
An ion channel complex through which potassium ions pass.
cell projection
A prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
neuron projection
A prolongation or process extending from a nerve cell, e.g. an axon or dendrite.
myelin sheath
An electrically insulating fatty layer that surrounds the axons of many neurons. It is an outgrowth of glial cells: Schwann cells supply the myelin for peripheral neurons while oligodendrocytes supply it to those of the central nervous system.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, and prokaryotic structures such as anammoxosomes and pirellulosomes. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
protein complex
Any macromolecular complex composed of two or more polypeptide subunits, which may or may not be identical. Protein complexes may have other associated non-protein prosthetic groups, such as nucleotides, metal ions or other small molecules.
axon terminus
Terminal inflated portion of the axon, containing the specialized apparatus necessary to release neurotransmitters. The axon terminus is considered to be the whole region of thickening and the terminal button is a specialized region of it.
neuron projection terminus
The specialized, terminal region of a neuron projection such as an axon or a dendrite.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
synapse part
Any constituent part of a synapse, the junction between a nerve fiber of one neuron and another neuron or muscle fiber or glial cell.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell projection part
Any constituent part of a cell projection, a prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
synapse
The junction between a nerve fiber of one neuron and another neuron or muscle fiber or glial cell; the site of interneuronal communication. As the nerve fiber approaches the synapse it enlarges into a specialized structure, the presynaptic nerve ending, which contains mitochondria and synaptic vesicles. At the tip of the nerve ending is the presynaptic membrane; facing it, and separated from it by a minute cleft (the synaptic cleft) is a specialized area of membrane on the receiving cell, known as the postsynaptic membrane. In response to the arrival of nerve impulses, the presynaptic nerve ending secretes molecules of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. These diffuse across the cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
synapse part
Any constituent part of a synapse, the junction between a nerve fiber of one neuron and another neuron or muscle fiber or glial cell.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
cell projection part
Any constituent part of a cell projection, a prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
ion channel complex
A protein complex that spans a membrane and forms a water-filled channel across the phospholipid bilayer allowing selective ion transport down its electrochemical gradient.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
neuron projection terminus
The specialized, terminal region of a neuron projection such as an axon or a dendrite.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
axon terminus
Terminal inflated portion of the axon, containing the specialized apparatus necessary to release neurotransmitters. The axon terminus is considered to be the whole region of thickening and the terminal button is a specialized region of it.
axon part
A part of an axon, a cell projection of a neuron.
ion channel complex
A protein complex that spans a membrane and forms a water-filled channel across the phospholipid bilayer allowing selective ion transport down its electrochemical gradient.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
voltage-gated potassium channel complex
A protein complex that forms a transmembrane channel through which potassium ions may cross a cell membrane in response to changes in membrane potential.
voltage-gated potassium channel complex
A protein complex that forms a transmembrane channel through which potassium ions may cross a cell membrane in response to changes in membrane potential.
synaptic vesicle
A secretory organelle, some 50 nm in diameter, of presynaptic nerve terminals; accumulates in high concentrations of neurotransmitters and is secreted these into the synaptic cleft by fusion with the 'active zone' of the presynaptic plasma membrane.

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
catalytic activity
Catalysis of a biochemical reaction at physiological temperatures. In biologically catalyzed reactions, the reactants are known as substrates, and the catalysts are naturally occurring macromolecular substances known as enzymes. Enzymes possess specific binding sites for substrates, and are usually composed wholly or largely of protein, but RNA that has catalytic activity (ribozyme) is often also regarded as enzymatic.
protein kinase activity
Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction: a protein + ATP = a phosphoprotein + ADP.
protein tyrosine kinase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate.
transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein-L-tyrosine = ADP + a protein-L-tyrosine phosphate, to initiate a change in cell activity.
signal transducer activity
Mediates the transfer of a signal from the outside to the inside of a cell by means other than the introduction of the signal molecule itself into the cell.
receptor activity
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell activity.
transmembrane receptor activity
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell activity, and spanning to the membrane of either the cell or an organelle.
ephrin receptor activity
Combining with an ephrin to initiate a change in cell activity.
transmembrane-ephrin receptor activity
NA
transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
ion channel activity
Catalysis of facilitated diffusion of an ion (by an energy-independent process) by passage through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel without evidence for a carrier-mediated mechanism.
voltage-gated ion channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a voltage-gated channel. An ion is an atom or group of atoms carrying an electric charge by virtue of having gained or lost one or more electrons.
voltage-gated potassium channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a potassium ion by a voltage-gated channel.
cation channel activity
Catalysis of the energy-independent passage of cations across a lipid bilayer down a concentration gradient.
potassium channel activity
Catalysis of facilitated diffusion of a potassium ion (by an energy-independent process) involving passage through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel without evidence for a carrier-mediated mechanism.
transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a substance from one side of a membrane to the other.
UDP-glycosyltransferase activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a glycosyl group from a UDP-sugar to a small hydrophobic molecule.
cation transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of cation from one side of the membrane to the other.
galactosyltransferase activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a galactosyl group to an acceptor molecule, typically another carbohydrate or a lipid.
ion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of an ion from one side of a membrane to the other.
channel activity
Catalysis of energy-independent facilitated diffusion, mediated by passage of a solute through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel. Stereospecificity is not exhibited but this transport may be specific for a particular molecular species or class of molecules.
kinase activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a substrate molecule.
transferase activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a group, e.g. a methyl group, glycosyl group, acyl group, phosphorus-containing, or other groups, from one compound (generally regarded as the donor) to another compound (generally regarded as the acceptor). Transferase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 2.
transferase activity, transferring glycosyl groups
Catalysis of the transfer of a glycosyl group from one compound (donor) to another (acceptor).
transferase activity, transferring hexosyl groups
Catalysis of the transfer of a hexosyl group from one compound (donor) to another (acceptor).
transferase activity, transferring phosphorus-containing groups
Catalysis of the transfer of a phosphorus-containing group from one compound (donor) to another (acceptor).
phosphotransferase activity, alcohol group as acceptor
Catalysis of the transfer of a phosphorus-containing group from one compound (donor) to an alcohol group (acceptor).
transmembrane receptor protein kinase activity
NA
passive transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute from one side of the membrane to the other, down the solute's concentration gradient.
voltage-gated channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a solute by a channel whose open state is dependent on the voltage across the membrane in which it is embedded.
gated channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a solute by a channel that opens in response to a specific stimulus.
substrate-specific channel activity
Catalysis of energy-independent facilitated diffusion, mediated by passage of a specific solute through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel. Stereospecificity is not exhibited but this transport may be specific for a particular molecular species or class of molecules.
voltage-gated cation channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a cation by a voltage-gated channel. A cation is a positively charged ion.
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
substrate-specific transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of a specific substance or group of related substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
UDP-galactosyltransferase activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a galactose group from UDP-galactose to an acceptor molecule.
molecular transducer activity
The molecular function that accepts an input of one form and creates an output of a different form.
all
NA
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
protein kinase activity
Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction: a protein + ATP = a phosphoprotein + ADP.
substrate-specific channel activity
Catalysis of energy-independent facilitated diffusion, mediated by passage of a specific solute through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel. Stereospecificity is not exhibited but this transport may be specific for a particular molecular species or class of molecules.
ion channel activity
Catalysis of facilitated diffusion of an ion (by an energy-independent process) by passage through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel without evidence for a carrier-mediated mechanism.
UDP-galactosyltransferase activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a galactose group from UDP-galactose to an acceptor molecule.
transmembrane receptor protein kinase activity
NA
cation channel activity
Catalysis of the energy-independent passage of cations across a lipid bilayer down a concentration gradient.
transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein-L-tyrosine = ADP + a protein-L-tyrosine phosphate, to initiate a change in cell activity.
voltage-gated ion channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a voltage-gated channel. An ion is an atom or group of atoms carrying an electric charge by virtue of having gained or lost one or more electrons.
voltage-gated cation channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a cation by a voltage-gated channel. A cation is a positively charged ion.
voltage-gated potassium channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a potassium ion by a voltage-gated channel.
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00533 | 1.188e-03 | 0.4161 | 5 | 14 | Glycosaminoglycan biosynthesis - keratan sulfate |
| 04360 | 6.610e-03 | 3.15 | 11 | 106 | Axon guidance |
| 04080 | 1.990e-02 | 6.122 | 15 | 206 | Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction |
AATKapoptosis-associated tyrosine kinase (ENSG00000181409), score: 0.72 ABCA2ATP-binding cassette, sub-family A (ABC1), member 2 (ENSG00000107331), score: 0.82 ABHD12abhydrolase domain containing 12 (ENSG00000100997), score: 0.75 ACTR1AARP1 actin-related protein 1 homolog A, centractin alpha (yeast) (ENSG00000138107), score: 0.75 ADAMTS10ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 10 (ENSG00000142303), score: 0.68 ADAMTS14ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 14 (ENSG00000138316), score: 0.79 ADAMTS8ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 8 (ENSG00000134917), score: 0.8 ADORA1adenosine A1 receptor (ENSG00000163485), score: 0.67 ADRA1Dadrenergic, alpha-1D-, receptor (ENSG00000171873), score: 0.71 AGAP3ArfGAP with GTPase domain, ankyrin repeat and PH domain 3 (ENSG00000133612), score: 0.71 AGPAT41-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase 4 (lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase, delta) (ENSG00000026652), score: 0.73 AK5adenylate kinase 5 (ENSG00000154027), score: 0.74 AMZ1archaelysin family metallopeptidase 1 (ENSG00000174945), score: 0.69 ANKRD13Dankyrin repeat domain 13 family, member D (ENSG00000172932), score: 0.66 ANKRD24ankyrin repeat domain 24 (ENSG00000089847), score: 0.68 ANLNanillin, actin binding protein (ENSG00000011426), score: 0.71 ANO4anoctamin 4 (ENSG00000151572), score: 0.72 AP3M1adaptor-related protein complex 3, mu 1 subunit (ENSG00000185009), score: -0.7 APLP1amyloid beta (A4) precursor-like protein 1 (ENSG00000105290), score: 0.7 ARCactivity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein (ENSG00000198576), score: 0.72 ARHGAP22Rho GTPase activating protein 22 (ENSG00000128805), score: 0.73 ARHGAP29Rho GTPase activating protein 29 (ENSG00000137962), score: -0.79 ARRDC2arrestin domain containing 2 (ENSG00000105643), score: 0.68 ATP10BATPase, class V, type 10B (ENSG00000118322), score: 0.77 ATP6V0D1ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 38kDa, V0 subunit d1 (ENSG00000159720), score: 0.71 B3GAT1beta-1,3-glucuronyltransferase 1 (glucuronosyltransferase P) (ENSG00000109956), score: 0.71 B3GNT1UDP-GlcNAc:betaGal beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 1 (ENSG00000174684), score: 0.67 B4GALT1UDP-Gal:betaGlcNAc beta 1,4- galactosyltransferase, polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000086062), score: -0.67 B4GALT2UDP-Gal:betaGlcNAc beta 1,4- galactosyltransferase, polypeptide 2 (ENSG00000117411), score: 0.71 BACE1beta-site APP-cleaving enzyme 1 (ENSG00000186318), score: 0.69 BAI1brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor 1 (ENSG00000181790), score: 0.71 BAI2brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor 2 (ENSG00000121753), score: 0.69 BCAS1breast carcinoma amplified sequence 1 (ENSG00000064787), score: 0.72 BCCIPBRCA2 and CDKN1A interacting protein (ENSG00000107949), score: -0.72 BCL11AB-cell CLL/lymphoma 11A (zinc finger protein) (ENSG00000119866), score: 0.7 BCL11BB-cell CLL/lymphoma 11B (zinc finger protein) (ENSG00000127152), score: 0.68 C11orf9chromosome 11 open reading frame 9 (ENSG00000124920), score: 0.84 C12orf41chromosome 12 open reading frame 41 (ENSG00000139620), score: -0.67 C12orf76chromosome 12 open reading frame 76 (ENSG00000174456), score: 0.73 C13orf36chromosome 13 open reading frame 36 (ENSG00000180440), score: 0.67 C16orf13chromosome 16 open reading frame 13 (ENSG00000130731), score: 0.77 C19orf26chromosome 19 open reading frame 26 (ENSG00000099625), score: 0.69 C19orf62chromosome 19 open reading frame 62 (ENSG00000105393), score: 0.68 C1orf198chromosome 1 open reading frame 198 (ENSG00000119280), score: 0.72 C1orf216chromosome 1 open reading frame 216 (ENSG00000142686), score: 0.69 C1orf93chromosome 1 open reading frame 93 (ENSG00000157870), score: 0.67 C1orf95chromosome 1 open reading frame 95 (ENSG00000203685), score: 0.69 C1QL2complement component 1, q subcomponent-like 2 (ENSG00000144119), score: 0.75 C1QTNF4C1q and tumor necrosis factor related protein 4 (ENSG00000172247), score: 0.67 C20orf103chromosome 20 open reading frame 103 (ENSG00000125869), score: 0.7 C22orf9chromosome 22 open reading frame 9 (ENSG00000100364), score: 0.81 C2orf82chromosome 2 open reading frame 82 (ENSG00000182600), score: 0.68 C5orf30chromosome 5 open reading frame 30 (ENSG00000181751), score: 0.67 C6orf1chromosome 6 open reading frame 1 (ENSG00000186577), score: 0.77 C7orf41chromosome 7 open reading frame 41 (ENSG00000180354), score: 0.67 C8orf46chromosome 8 open reading frame 46 (ENSG00000169085), score: 0.7 C9orf16chromosome 9 open reading frame 16 (ENSG00000171159), score: 0.69 CACNG3calcium channel, voltage-dependent, gamma subunit 3 (ENSG00000006116), score: 0.69 CALHM1calcium homeostasis modulator 1 (ENSG00000185933), score: 0.77 CALYcalcyon neuron-specific vesicular protein (ENSG00000130643), score: 0.73 CAMK1Gcalcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IG (ENSG00000008118), score: 0.71 CAMK2Acalcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II alpha (ENSG00000070808), score: 0.74 CAPN9calpain 9 (ENSG00000135773), score: 0.84 CBLN2cerebellin 2 precursor (ENSG00000141668), score: 0.7 CBLN4cerebellin 4 precursor (ENSG00000054803), score: 0.67 CCDC50coiled-coil domain containing 50 (ENSG00000152492), score: -0.7 CCKBRcholecystokinin B receptor (ENSG00000110148), score: 0.68 CD22CD22 molecule (ENSG00000012124), score: 0.9 CD2APCD2-associated protein (ENSG00000198087), score: -0.77 CDH20cadherin 20, type 2 (ENSG00000101542), score: 0.71 CDH4cadherin 4, type 1, R-cadherin (retinal) (ENSG00000179242), score: 0.75 CDHR1cadherin-related family member 1 (ENSG00000148600), score: 0.75 CDK2cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (ENSG00000123374), score: -0.74 CDK5R2cyclin-dependent kinase 5, regulatory subunit 2 (p39) (ENSG00000171450), score: 0.68 CDKN2Dcyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2D (p19, inhibits CDK4) (ENSG00000129355), score: 0.69 CELSR2cadherin, EGF LAG seven-pass G-type receptor 2 (flamingo homolog, Drosophila) (ENSG00000143126), score: 0.69 CERCAMcerebral endothelial cell adhesion molecule (ENSG00000167123), score: 0.77 CHADLchondroadherin-like (ENSG00000100399), score: 0.81 CHD1chromodomain helicase DNA binding protein 1 (ENSG00000153922), score: -0.76 CHGAchromogranin A (parathyroid secretory protein 1) (ENSG00000100604), score: 0.76 CHRM1cholinergic receptor, muscarinic 1 (ENSG00000168539), score: 0.78 CHST1carbohydrate (keratan sulfate Gal-6) sulfotransferase 1 (ENSG00000175264), score: 0.74 CHST6carbohydrate (N-acetylglucosamine 6-O) sulfotransferase 6 (ENSG00000183196), score: 0.69 CHST8carbohydrate (N-acetylgalactosamine 4-0) sulfotransferase 8 (ENSG00000124302), score: 0.67 CLCA4chloride channel accessory 4 (ENSG00000016602), score: 0.81 CLDN11claudin 11 (ENSG00000013297), score: 0.71 CLDND1claudin domain containing 1 (ENSG00000080822), score: 0.71 CMTM5CKLF-like MARVEL transmembrane domain containing 5 (ENSG00000166091), score: 0.83 CNP2',3'-cyclic nucleotide 3' phosphodiesterase (ENSG00000173786), score: 0.93 CNTN2contactin 2 (axonal) (ENSG00000184144), score: 0.7 COBLcordon-bleu homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000106078), score: 0.7 COL16A1collagen, type XVI, alpha 1 (ENSG00000084636), score: 0.68 COL9A2collagen, type IX, alpha 2 (ENSG00000049089), score: 0.7 COPB1coatomer protein complex, subunit beta 1 (ENSG00000129083), score: -0.71 COPS7BCOP9 constitutive photomorphogenic homolog subunit 7B (Arabidopsis) (ENSG00000144524), score: 0.68 CPNE2copine II (ENSG00000140848), score: 0.72 CPNE5copine V (ENSG00000124772), score: 0.66 CPNE6copine VI (neuronal) (ENSG00000100884), score: 0.7 CREG2cellular repressor of E1A-stimulated genes 2 (ENSG00000175874), score: 0.72 CRHcorticotropin releasing hormone (ENSG00000147571), score: 0.69 CTR9Ctr9, Paf1/RNA polymerase II complex component, homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000198730), score: -0.67 CWC22CWC22 spliceosome-associated protein homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000163510), score: -0.68 CYP46A1cytochrome P450, family 46, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000036530), score: 0.74 DAAM2dishevelled associated activator of morphogenesis 2 (ENSG00000146122), score: 0.82 DACH2dachshund homolog 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000126733), score: 0.68 DCTN1dynactin 1 (ENSG00000204843), score: 0.66 DDNdendrin (ENSG00000181418), score: 0.67 DDX3XDEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 3, X-linked (ENSG00000215301), score: -0.68 DEAF1deformed epidermal autoregulatory factor 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000177030), score: 0.68 DGKZdiacylglycerol kinase, zeta 104kDa (ENSG00000149091), score: 0.72 DLL3delta-like 3 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000090932), score: 0.69 DLX1distal-less homeobox 1 (ENSG00000144355), score: 0.73 DNAJC7DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 7 (ENSG00000168259), score: 0.71 DNMBPdynamin binding protein (ENSG00000107554), score: -0.74 DOHHdeoxyhypusine hydroxylase/monooxygenase (ENSG00000129932), score: 0.75 DSCAMDown syndrome cell adhesion molecule (ENSG00000171587), score: 0.67 DSCAML1Down syndrome cell adhesion molecule like 1 (ENSG00000177103), score: 0.74 DTNBdystrobrevin, beta (ENSG00000138101), score: 0.72 E2F1E2F transcription factor 1 (ENSG00000101412), score: 0.71 EDIL3EGF-like repeats and discoidin I-like domains 3 (ENSG00000164176), score: 0.7 EDN3endothelin 3 (ENSG00000124205), score: 0.69 EFNA3ephrin-A3 (ENSG00000143590), score: 0.69 EFNB3ephrin-B3 (ENSG00000108947), score: 0.7 EFSembryonal Fyn-associated substrate (ENSG00000100842), score: 0.72 EIF3Eeukaryotic translation initiation factor 3, subunit E (ENSG00000104408), score: -0.74 EIF4EBP2eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E binding protein 2 (ENSG00000148730), score: -0.74 ELFN2extracellular leucine-rich repeat and fibronectin type III domain containing 2 (ENSG00000166897), score: 0.73 ELK4ELK4, ETS-domain protein (SRF accessory protein 1) (ENSG00000158711), score: -0.68 EML2echinoderm microtubule associated protein like 2 (ENSG00000125746), score: 0.85 ENC1ectodermal-neural cortex 1 (with BTB-like domain) (ENSG00000171617), score: 0.69 ENPP2ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 2 (ENSG00000136960), score: 0.72 EPHB6EPH receptor B6 (ENSG00000106123), score: 0.69 EPHX4epoxide hydrolase 4 (ENSG00000172031), score: 0.69 ERMNermin, ERM-like protein (ENSG00000136541), score: 0.76 EVI2Aecotropic viral integration site 2A (ENSG00000126860), score: 0.79 EVLEnah/Vasp-like (ENSG00000196405), score: 0.66 FA2Hfatty acid 2-hydroxylase (ENSG00000103089), score: 0.87 FAM102Afamily with sequence similarity 102, member A (ENSG00000167106), score: 0.75 FAM124Afamily with sequence similarity 124A (ENSG00000150510), score: 0.81 FAM13Cfamily with sequence similarity 13, member C (ENSG00000148541), score: 0.67 FAM5Bfamily with sequence similarity 5, member B (ENSG00000198797), score: 0.73 FBXL15F-box and leucine-rich repeat protein 15 (ENSG00000107872), score: 0.69 FBXL19F-box and leucine-rich repeat protein 19 (ENSG00000099364), score: 0.67 FCHO1FCH domain only 1 (ENSG00000130475), score: 0.72 FDX1Lferredoxin 1-like (ENSG00000167807), score: 0.68 FEZF2FEZ family zinc finger 2 (ENSG00000153266), score: 0.82 FFAR1free fatty acid receptor 1 (ENSG00000126266), score: 0.94 FGF22fibroblast growth factor 22 (ENSG00000070388), score: 0.8 FKBP8FK506 binding protein 8, 38kDa (ENSG00000105701), score: 0.71 FLRT1fibronectin leucine rich transmembrane protein 1 (ENSG00000126500), score: 0.66 FOXG1forkhead box G1 (ENSG00000176165), score: 0.7 FSCN1fascin homolog 1, actin-bundling protein (Strongylocentrotus purpuratus) (ENSG00000075618), score: 0.83 FSD1fibronectin type III and SPRY domain containing 1 (ENSG00000105255), score: 0.66 GAB2GRB2-associated binding protein 2 (ENSG00000033327), score: 0.72 GAL3ST1galactose-3-O-sulfotransferase 1 (ENSG00000128242), score: 0.69 GALNT6UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 6 (GalNAc-T6) (ENSG00000139629), score: 0.79 GIPC1GIPC PDZ domain containing family, member 1 (ENSG00000123159), score: 0.72 GJD4gap junction protein, delta 4, 40.1kDa (ENSG00000177291), score: 0.73 GLDNgliomedin (ENSG00000186417), score: 0.87 GLT25D2glycosyltransferase 25 domain containing 2 (ENSG00000198756), score: 0.67 GOLGA4golgin A4 (ENSG00000144674), score: -0.69 GPR123G protein-coupled receptor 123 (ENSG00000197177), score: 0.78 GPR150G protein-coupled receptor 150 (ENSG00000178015), score: 0.68 GPR26G protein-coupled receptor 26 (ENSG00000154478), score: 0.68 GPR37G protein-coupled receptor 37 (endothelin receptor type B-like) (ENSG00000170775), score: 0.79 GPR78G protein-coupled receptor 78 (ENSG00000155269), score: 0.77 GRID1glutamate receptor, ionotropic, delta 1 (ENSG00000182771), score: 0.75 GRIK4glutamate receptor, ionotropic, kainate 4 (ENSG00000149403), score: 0.66 GRM3glutamate receptor, metabotropic 3 (ENSG00000198822), score: 0.73 GSG1LGSG1-like (ENSG00000169181), score: 0.67 HAS1hyaluronan synthase 1 (ENSG00000105509), score: 0.7 HAT1histone acetyltransferase 1 (ENSG00000128708), score: -0.67 HS3ST2heparan sulfate (glucosamine) 3-O-sulfotransferase 2 (ENSG00000122254), score: 0.76 HS3ST4heparan sulfate (glucosamine) 3-O-sulfotransferase 4 (ENSG00000182601), score: 0.74 HSD11B1Lhydroxysteroid (11-beta) dehydrogenase 1-like (ENSG00000167733), score: 0.74 HTR1A5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 1A (ENSG00000178394), score: 0.74 HTR1E5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 1E (ENSG00000168830), score: 0.72 HTR65-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 6 (ENSG00000158748), score: 0.67 IDEinsulin-degrading enzyme (ENSG00000119912), score: -0.7 IGSF8immunoglobulin superfamily, member 8 (ENSG00000162729), score: 0.68 ITPK1inositol 1,3,4-triphosphate 5/6 kinase (ENSG00000100605), score: 0.74 KCNA6potassium voltage-gated channel, shaker-related subfamily, member 6 (ENSG00000151079), score: 0.68 KCNC2potassium voltage-gated channel, Shaw-related subfamily, member 2 (ENSG00000166006), score: 0.74 KCNF1potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily F, member 1 (ENSG00000162975), score: 0.77 KCNG1potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily G, member 1 (ENSG00000026559), score: 0.68 KCNH3potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily H (eag-related), member 3 (ENSG00000135519), score: 0.77 KCNH4potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily H (eag-related), member 4 (ENSG00000089558), score: 0.67 KCNH8potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily H (eag-related), member 8 (ENSG00000183960), score: 0.92 KCNMB4potassium large conductance calcium-activated channel, subfamily M, beta member 4 (ENSG00000135643), score: 0.67 KCNN1potassium intermediate/small conductance calcium-activated channel, subfamily N, member 1 (ENSG00000105642), score: 0.75 KCNQ4potassium voltage-gated channel, KQT-like subfamily, member 4 (ENSG00000117013), score: 0.71 KCNQ5potassium voltage-gated channel, KQT-like subfamily, member 5 (ENSG00000185760), score: 0.67 KCNS1potassium voltage-gated channel, delayed-rectifier, subfamily S, member 1 (ENSG00000124134), score: 0.7 KCNV1potassium channel, subfamily V, member 1 (ENSG00000164794), score: 0.69 KCTD17potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 17 (ENSG00000100379), score: 0.68 KCTD4potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 4 (ENSG00000180332), score: 0.75 KIAA0748KIAA0748 (ENSG00000135426), score: 0.73 KIAA1429KIAA1429 (ENSG00000164944), score: -0.69 KINKIN, antigenic determinant of recA protein homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000151657), score: -0.7 KIRREL3kin of IRRE like 3 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000149571), score: 0.71 KLF11Kruppel-like factor 11 (ENSG00000172059), score: -0.76 KLHL26kelch-like 26 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000167487), score: 0.69 KLHL32kelch-like 32 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000186231), score: 0.67 KLHL4kelch-like 4 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000102271), score: 0.68 KREMEN2kringle containing transmembrane protein 2 (ENSG00000131650), score: 0.72 KRT83keratin 83 (ENSG00000170523), score: 0.76 L3MBTL2l(3)mbt-like 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000100395), score: 0.69 LAPTM4Alysosomal protein transmembrane 4 alpha (ENSG00000068697), score: -0.7 LGI3leucine-rich repeat LGI family, member 3 (ENSG00000168481), score: 0.75 LGR5leucine-rich repeat-containing G protein-coupled receptor 5 (ENSG00000139292), score: 0.67 LHX2LIM homeobox 2 (ENSG00000106689), score: 0.68 LIMK1LIM domain kinase 1 (ENSG00000106683), score: 0.7 LMO4LIM domain only 4 (ENSG00000143013), score: 0.68 LNX2ligand of numb-protein X 2 (ENSG00000139517), score: -0.71 LOC100294412similar to KIAA0655 protein (ENSG00000130787), score: 0.66 LPPR3lipid phosphate phosphatase-related protein type 3 (ENSG00000129951), score: 0.8 LRFN2leucine rich repeat and fibronectin type III domain containing 2 (ENSG00000156564), score: 0.71 LRFN3leucine rich repeat and fibronectin type III domain containing 3 (ENSG00000126243), score: 0.75 LRRC14leucine rich repeat containing 14 (ENSG00000160959), score: 0.72 LRTM2leucine-rich repeats and transmembrane domains 2 (ENSG00000166159), score: 0.77 LY6Dlymphocyte antigen 6 complex, locus D (ENSG00000167656), score: 0.73 LY6Hlymphocyte antigen 6 complex, locus H (ENSG00000176956), score: 0.75 MADCAM1mucosal vascular addressin cell adhesion molecule 1 (ENSG00000099866), score: 0.74 MAGmyelin associated glycoprotein (ENSG00000105695), score: 0.84 MALT1mucosa associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation gene 1 (ENSG00000172175), score: -0.73 MAP1LC3Amicrotubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 alpha (ENSG00000101460), score: 0.67 MAP1Smicrotubule-associated protein 1S (ENSG00000130479), score: 0.67 MAP3K1mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 1 (ENSG00000095015), score: -0.7 MAPK3mitogen-activated protein kinase 3 (ENSG00000102882), score: 0.76 MAPK8IP3mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 interacting protein 3 (ENSG00000138834), score: 0.67 MARCH1membrane-associated ring finger (C3HC4) 1 (ENSG00000145416), score: 0.66 MARCH4membrane-associated ring finger (C3HC4) 4 (ENSG00000144583), score: 0.73 MARCKSL1MARCKS-like 1 (ENSG00000175130), score: 0.7 MAST3microtubule associated serine/threonine kinase 3 (ENSG00000099308), score: 0.77 MATKmegakaryocyte-associated tyrosine kinase (ENSG00000007264), score: 0.75 MATN1matrilin 1, cartilage matrix protein (ENSG00000162510), score: 0.73 MED15mediator complex subunit 15 (ENSG00000099917), score: 0.66 MED29mediator complex subunit 29 (ENSG00000063322), score: 0.68 MGAT5Bmannosyl (alpha-1,6-)-glycoprotein beta-1,6-N-acetyl-glucosaminyltransferase, isozyme B (ENSG00000167889), score: 0.69 MKRN3makorin ring finger protein 3 (ENSG00000179455), score: 0.79 MMP17matrix metallopeptidase 17 (membrane-inserted) (ENSG00000198598), score: 0.77 MOBKL1BMOB1, Mps One Binder kinase activator-like 1B (yeast) (ENSG00000114978), score: -0.69 MOGmyelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (ENSG00000204655), score: 0.8 MT3metallothionein 3 (ENSG00000087250), score: 0.68 MYBBP1AMYB binding protein (P160) 1a (ENSG00000132382), score: 0.7 NANOS3nanos homolog 3 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000187556), score: 0.72 NANPN-acetylneuraminic acid phosphatase (ENSG00000170191), score: -0.71 NCANneurocan (ENSG00000130287), score: 0.67 NCDNneurochondrin (ENSG00000020129), score: 0.67 NELFnasal embryonic LHRH factor (ENSG00000165802), score: 0.7 NEUROD6neurogenic differentiation 6 (ENSG00000164600), score: 0.73 NIPA1non imprinted in Prader-Willi/Angelman syndrome 1 (ENSG00000170113), score: 0.73 NIPAL4NIPA-like domain containing 4 (ENSG00000172548), score: 1 NKX2-2NK2 homeobox 2 (ENSG00000125820), score: 0.81 NLKnemo-like kinase (ENSG00000087095), score: 0.69 NPAS1neuronal PAS domain protein 1 (ENSG00000130751), score: 0.81 NPBWR1neuropeptides B/W receptor 1 (ENSG00000183729), score: 0.69 NPBWR2neuropeptides B/W receptor 2 (ENSG00000125522), score: 0.73 NPC1Niemann-Pick disease, type C1 (ENSG00000141458), score: 0.7 NRG3neuregulin 3 (ENSG00000185737), score: 0.66 NTNG2netrin G2 (ENSG00000196358), score: 0.81 NTSR2neurotensin receptor 2 (ENSG00000169006), score: 0.68 OLIG2oligodendrocyte lineage transcription factor 2 (ENSG00000205927), score: 0.8 OPALINoligodendrocytic myelin paranodal and inner loop protein (ENSG00000197430), score: 0.81 OPRD1opioid receptor, delta 1 (ENSG00000116329), score: 0.76 OR2T6olfactory receptor, family 2, subfamily T, member 6 (ENSG00000198104), score: 0.69 OXSR1oxidative-stress responsive 1 (ENSG00000172939), score: -0.7 P2RX7purinergic receptor P2X, ligand-gated ion channel, 7 (ENSG00000089041), score: 0.78 PACS2phosphofurin acidic cluster sorting protein 2 (ENSG00000179364), score: 0.7 PANX3pannexin 3 (ENSG00000154143), score: 0.68 PAQR6progestin and adipoQ receptor family member VI (ENSG00000160781), score: 0.78 PATL1protein associated with topoisomerase II homolog 1 (yeast) (ENSG00000166889), score: -0.68 PCDH10protocadherin 10 (ENSG00000138650), score: 0.68 PCDH8protocadherin 8 (ENSG00000136099), score: 0.72 PDE8Bphosphodiesterase 8B (ENSG00000113231), score: 0.68 PELI3pellino homolog 3 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000174516), score: 0.68 PEX13peroxisomal biogenesis factor 13 (ENSG00000162928), score: -0.71 PEX5Lperoxisomal biogenesis factor 5-like (ENSG00000114757), score: 0.67 PGM2phosphoglucomutase 2 (ENSG00000169299), score: -0.71 PHLDA3pleckstrin homology-like domain, family A, member 3 (ENSG00000174307), score: 0.68 PHLPP1PH domain and leucine rich repeat protein phosphatase 1 (ENSG00000081913), score: 0.68 PIN1peptidylprolyl cis/trans isomerase, NIMA-interacting 1 (ENSG00000127445), score: 0.73 PIP4K2Aphosphatidylinositol-5-phosphate 4-kinase, type II, alpha (ENSG00000150867), score: 0.81 PIP5KL1phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase-like 1 (ENSG00000167103), score: 0.81 PKMYT1protein kinase, membrane associated tyrosine/threonine 1 (ENSG00000127564), score: 0.69 PLD3phospholipase D family, member 3 (ENSG00000105223), score: 0.69 PLEKHB1pleckstrin homology domain containing, family B (evectins) member 1 (ENSG00000021300), score: 0.69 PLEKHH1pleckstrin homology domain containing, family H (with MyTH4 domain) member 1 (ENSG00000054690), score: 0.72 PLEKHM2pleckstrin homology domain containing, family M (with RUN domain) member 2 (ENSG00000116786), score: 0.66 PLLPplasmolipin (ENSG00000102934), score: 0.72 PLP1proteolipid protein 1 (ENSG00000123560), score: 0.72 PLXNB3plexin B3 (ENSG00000198753), score: 0.8 PMP2peripheral myelin protein 2 (ENSG00000147588), score: 0.7 PNCKpregnancy up-regulated non-ubiquitously expressed CaM kinase (ENSG00000130822), score: 0.77 PNMAL2PNMA-like 2 (ENSG00000204851), score: 0.72 PNPLA6patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 6 (ENSG00000032444), score: 0.72 PPP1R14Aprotein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 14A (ENSG00000167641), score: 0.73 PRAF2PRA1 domain family, member 2 (ENSG00000243279), score: 0.84 PRDM8PR domain containing 8 (ENSG00000152784), score: 0.68 PREX1phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate-dependent Rac exchange factor 1 (ENSG00000124126), score: 0.79 PRKCQprotein kinase C, theta (ENSG00000065675), score: 0.68 PRPF18PRP18 pre-mRNA processing factor 18 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000165630), score: -0.73 PRPF40APRP40 pre-mRNA processing factor 40 homolog A (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000196504), score: -0.7 PRR18proline rich 18 (ENSG00000176381), score: 0.88 PRR7proline rich 7 (synaptic) (ENSG00000131188), score: 0.83 PRRC1proline-rich coiled-coil 1 (ENSG00000164244), score: -0.74 PSDpleckstrin and Sec7 domain containing (ENSG00000059915), score: 0.66 PSRC1proline/serine-rich coiled-coil 1 (ENSG00000134222), score: 0.81 PTK2PTK2 protein tyrosine kinase 2 (ENSG00000169398), score: 0.79 PTPN5protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 5 (striatum-enriched) (ENSG00000110786), score: 0.72 PTPRHprotein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, H (ENSG00000080031), score: 0.72 RAB11BRAB11B, member RAS oncogene family (ENSG00000185236), score: 0.67 RAB40BRAB40B, member RAS oncogene family (ENSG00000141542), score: 0.74 RAB40CRAB40C, member RAS oncogene family (ENSG00000197562), score: 0.72 RALGDSral guanine nucleotide dissociation stimulator (ENSG00000160271), score: 0.7 RAPGEF5Rap guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 5 (ENSG00000136237), score: 0.7 RASAL1RAS protein activator like 1 (GAP1 like) (ENSG00000111344), score: 0.72 RASD2RASD family, member 2 (ENSG00000100302), score: 0.66 RASL10ARAS-like, family 10, member A (ENSG00000100276), score: 0.75 RGS4regulator of G-protein signaling 4 (ENSG00000117152), score: 0.67 RHBDD2rhomboid domain containing 2 (ENSG00000005486), score: 0.75 RHEBL1Ras homolog enriched in brain like 1 (ENSG00000167550), score: 0.67 RNF220ring finger protein 220 (ENSG00000187147), score: 0.79 ROCK1Rho-associated, coiled-coil containing protein kinase 1 (ENSG00000067900), score: -0.72 RP2retinitis pigmentosa 2 (X-linked recessive) (ENSG00000102218), score: -0.72 RPRMreprimo, TP53 dependent G2 arrest mediator candidate (ENSG00000177519), score: 0.76 RRM1ribonucleotide reductase M1 (ENSG00000167325), score: -0.67 RSPO2R-spondin 2 homolog (Xenopus laevis) (ENSG00000147655), score: 0.67 RTBDNretbindin (ENSG00000132026), score: 0.79 SAMD4Bsterile alpha motif domain containing 4B (ENSG00000179134), score: 0.73 SATB2SATB homeobox 2 (ENSG00000119042), score: 0.67 SBF1SET binding factor 1 (ENSG00000100241), score: 0.66 SCN3Bsodium channel, voltage-gated, type III, beta (ENSG00000166257), score: 0.71 SCYL2SCY1-like 2 (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000136021), score: -0.67 SEC14L5SEC14-like 5 (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000103184), score: 0.79 SEMA5Bsema domain, seven thrombospondin repeats (type 1 and type 1-like), transmembrane domain (TM) and short cytoplasmic domain, (semaphorin) 5B (ENSG00000082684), score: 0.68 SERPINI1serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade I (neuroserpin), member 1 (ENSG00000163536), score: 0.68 SGSM2small G protein signaling modulator 2 (ENSG00000141258), score: 0.69 SGSM3small G protein signaling modulator 3 (ENSG00000100359), score: 0.72 SH2D5SH2 domain containing 5 (ENSG00000189410), score: 0.67 SH3GLB2SH3-domain GRB2-like endophilin B2 (ENSG00000148341), score: 0.73 SIRT2sirtuin 2 (ENSG00000068903), score: 0.86 SLAIN1SLAIN motif family, member 1 (ENSG00000139737), score: 0.7 SLC10A4solute carrier family 10 (sodium/bile acid cotransporter family), member 4 (ENSG00000145248), score: 0.67 SLC2A6solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 6 (ENSG00000160326), score: 0.69 SLC35E4solute carrier family 35, member E4 (ENSG00000100036), score: 0.67 SLC5A11solute carrier family 5 (sodium/glucose cotransporter), member 11 (ENSG00000158865), score: 0.8 SLC6A9solute carrier family 6 (neurotransmitter transporter, glycine), member 9 (ENSG00000196517), score: 0.73 SLIT1slit homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000187122), score: 0.78 SLITRK1SLIT and NTRK-like family, member 1 (ENSG00000178235), score: 0.75 SMEK1SMEK homolog 1, suppressor of mek1 (Dictyostelium) (ENSG00000100796), score: -0.71 SNX2sorting nexin 2 (ENSG00000205302), score: -0.7 SOHLH1spermatogenesis and oogenesis specific basic helix-loop-helix 1 (ENSG00000165643), score: 0.74 SOX10SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 10 (ENSG00000100146), score: 0.81 SOX8SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 8 (ENSG00000005513), score: 0.86 SP3Sp3 transcription factor (ENSG00000172845), score: -0.75 SPTY2D1SPT2, Suppressor of Ty, domain containing 1 (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000179119), score: -0.67 SRSF2IPserine/arginine-rich splicing factor 2, interacting protein (ENSG00000139218), score: -0.71 SSTsomatostatin (ENSG00000157005), score: 0.79 ST6GALNAC5ST6 (alpha-N-acetyl-neuraminyl-2,3-beta-galactosyl-1,3)-N-acetylgalactosaminide alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase 5 (ENSG00000117069), score: 0.71 STK32Cserine/threonine kinase 32C (ENSG00000165752), score: 0.78 STOML1stomatin (EPB72)-like 1 (ENSG00000067221), score: 0.82 STX1Asyntaxin 1A (brain) (ENSG00000106089), score: 0.66 SYNGR3synaptogyrin 3 (ENSG00000127561), score: 0.7 SYT3synaptotagmin III (ENSG00000213023), score: 0.67 SYT5synaptotagmin V (ENSG00000129990), score: 0.71 TBCBtubulin folding cofactor B (ENSG00000105254), score: 0.73 TBR1T-box, brain, 1 (ENSG00000136535), score: 0.73 TCEB3transcription elongation factor B (SIII), polypeptide 3 (110kDa, elongin A) (ENSG00000011007), score: -0.72 TGFBR1transforming growth factor, beta receptor 1 (ENSG00000106799), score: -0.72 TJAP1tight junction associated protein 1 (peripheral) (ENSG00000137221), score: 0.86 TMEFF2transmembrane protein with EGF-like and two follistatin-like domains 2 (ENSG00000144339), score: 0.7 TMEM132Dtransmembrane protein 132D (ENSG00000151952), score: 0.67 TMEM144transmembrane protein 144 (ENSG00000164124), score: 0.81 TMEM151Atransmembrane protein 151A (ENSG00000179292), score: 0.83 TMEM155transmembrane protein 155 (ENSG00000164112), score: 0.71 TMEM160transmembrane protein 160 (ENSG00000130748), score: 0.75 TMEM184Btransmembrane protein 184B (ENSG00000198792), score: 0.73 TMEM55Btransmembrane protein 55B (ENSG00000165782), score: 0.69 TMIEtransmembrane inner ear (ENSG00000181585), score: 0.76 TMPRSS5transmembrane protease, serine 5 (ENSG00000166682), score: 0.69 TMX1thioredoxin-related transmembrane protein 1 (ENSG00000139921), score: -0.68 TNK2tyrosine kinase, non-receptor, 2 (ENSG00000061938), score: 0.7 TPPPtubulin polymerization promoting protein (ENSG00000171368), score: 0.7 TRIP11thyroid hormone receptor interactor 11 (ENSG00000100815), score: -0.68 TRMT61AtRNA methyltransferase 61 homolog A (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000166166), score: 0.69 TRPM2transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily M, member 2 (ENSG00000142185), score: 0.78 TRPM7transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily M, member 7 (ENSG00000092439), score: -0.73 UGT8UDP glycosyltransferase 8 (ENSG00000174607), score: 0.7 USP15ubiquitin specific peptidase 15 (ENSG00000135655), score: -0.69 USP3ubiquitin specific peptidase 3 (ENSG00000140455), score: -0.73 USP53ubiquitin specific peptidase 53 (ENSG00000145390), score: -0.74 VAMP1vesicle-associated membrane protein 1 (synaptobrevin 1) (ENSG00000139190), score: 0.75 VGFVGF nerve growth factor inducible (ENSG00000128564), score: 0.76 VSTM2AV-set and transmembrane domain containing 2A (ENSG00000170419), score: 0.69 VSTM2BV-set and transmembrane domain containing 2B (ENSG00000187135), score: 0.8 VSTM2LV-set and transmembrane domain containing 2 like (ENSG00000132821), score: 0.69 WEE1WEE1 homolog (S. pombe) (ENSG00000166483), score: -0.68 WNT10Bwingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 10B (ENSG00000169884), score: 0.78 WNT7Awingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 7A (ENSG00000154764), score: 0.73 XRN25'-3' exoribonuclease 2 (ENSG00000088930), score: -0.68 YME1L1YME1-like 1 (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000136758), score: -0.69 ZFP57zinc finger protein 57 homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000204644), score: 0.77 ZNF536zinc finger protein 536 (ENSG00000198597), score: 0.66
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa_br_m6_ca1 | hsa | br | m | 6 |
| ggo_br_m_ca1 | ggo | br | m | _ |
| ptr_br_m5_ca1 | ptr | br | m | 5 |
| ptr_br_m1_ca1 | ptr | br | m | 1 |
| hsa_br_f_ca1 | hsa | br | f | _ |
| ppy_br_m_ca1 | ppy | br | m | _ |
| ptr_br_m2_ca1 | ptr | br | m | 2 |
| ptr_br_m3_ca1 | ptr | br | m | 3 |
| hsa_br_m3_ca1 | hsa | br | m | 3 |
| hsa_br_m7_ca1 | hsa | br | m | 7 |