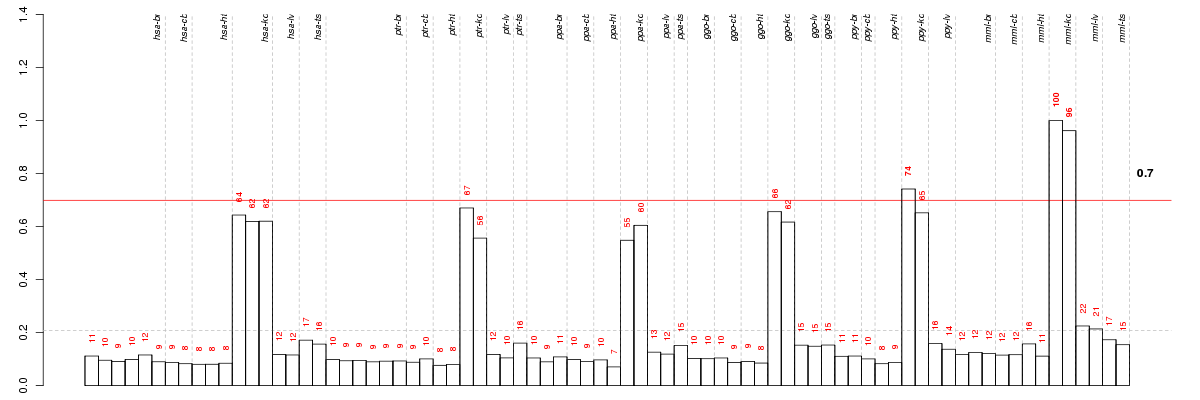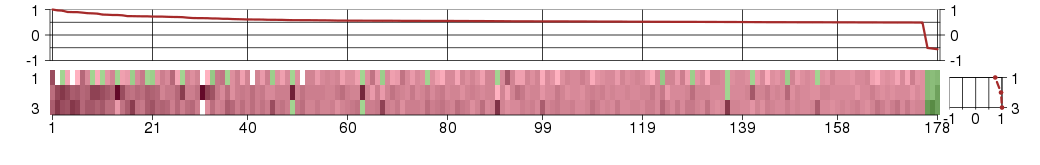

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

skeletal system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the skeleton over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The skeleton is the bony framework of the body in vertebrates (endoskeleton) or the hard outer envelope of insects (exoskeleton or dermoskeleton).
regionalization
The pattern specification process by which an axis or axes is subdivided in space to define an area or volume in which specific patterns of cell differentiation will take place or in which cells interpret a specific environment.
system process
A multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system. An organ system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a biological objective.
secretion
The controlled release of a substance by a cell, a group of cells, or a tissue.
transport
The directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells, or within a multicellular organism by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
ion transport
The directed movement of charged atoms or small charged molecules into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
cation transport
The directed movement of cations, atoms or small molecules with a net positive charge, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
sodium ion transport
The directed movement of sodium ions (Na+) into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
anion transport
The directed movement of anions, atoms or small molecules with a net negative charge, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
metal ion transport
The directed movement of metal ions, any metal ion with an electric charge, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
embryo development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an embryo from its formation until the end of its embryonic life stage. The end of the embryonic stage is organism-specific. For example, for mammals, the process would begin with zygote formation and end with birth. For insects, the process would begin at zygote formation and end with larval hatching. For plant zygotic embryos, this would be from zygote formation to the end of seed dormancy. For plant vegetative embryos, this would be from the initial determination of the cell or group of cells to form an embryo until the point when the embryo becomes independent of the parent plant.
pattern specification process
Any developmental process that results in the creation of defined areas or spaces within an organism to which cells respond and eventually are instructed to differentiate.
organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis of an organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
excretion
The elimination by an organism of the waste products that arise as a result of metabolic activity. These products include water, carbon dioxide (CO2), and nitrogenous compounds.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
embryo development ending in birth or egg hatching
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an embryo over time, from zygote formation until the end of the embryonic life stage. The end of the embryonic life stage is organism-specific and may be somewhat arbitrary; for mammals it is usually considered to be birth, for insects the hatching of the first instar larva from the eggshell.
anterior/posterior pattern formation
The regionalization process by which specific areas of cell differentiation are determined along the anterior-posterior axis. The anterior-posterior axis is defined by a line that runs from the head or mouth of an organism to the tail or opposite end of the organism.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
monovalent inorganic cation transport
The directed movement of inorganic cations with a valency of one into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. Inorganic cations are atoms or small molecules with a positive charge which do not contain carbon in covalent linkage.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
chordate embryonic development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the embryo over time, from zygote formation through a stage including a notochord and neural tube until birth or egg hatching.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
embryonic organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis, during the embryonic phase, of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
embryonic organ development
Development, taking place during the embryonic phase, of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
embryonic morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized during the embryonic phase. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. The embryonic phase begins with zygote formation. The end of the embryonic phase is organism-specific. For example, it would be at birth for mammals, larval hatching for insects and seed dormancy in plants.
embryonic skeletal system morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of the skeleton are generated and organized during the embryonic phase. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
skeletal system morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of the skeleton are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
embryonic skeletal system development
The process, occurring during the embryonic phase, whose specific outcome is the progression of the skeleton over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
transmembrane transport
The process whereby a solute is transported from one side of a membrane to the other. This process includes the actual movement of the solute, and any regulation and preparatory steps, such as reduction of the solute.
all
NA
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
embryo development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an embryo from its formation until the end of its embryonic life stage. The end of the embryonic stage is organism-specific. For example, for mammals, the process would begin with zygote formation and end with birth. For insects, the process would begin at zygote formation and end with larval hatching. For plant zygotic embryos, this would be from zygote formation to the end of seed dormancy. For plant vegetative embryos, this would be from the initial determination of the cell or group of cells to form an embryo until the point when the embryo becomes independent of the parent plant.
pattern specification process
Any developmental process that results in the creation of defined areas or spaces within an organism to which cells respond and eventually are instructed to differentiate.
embryonic morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized during the embryonic phase. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. The embryonic phase begins with zygote formation. The end of the embryonic phase is organism-specific. For example, it would be at birth for mammals, larval hatching for insects and seed dormancy in plants.
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
transmembrane transport
The process whereby a solute is transported from one side of a membrane to the other. This process includes the actual movement of the solute, and any regulation and preparatory steps, such as reduction of the solute.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
embryonic organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis, during the embryonic phase, of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
embryonic organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis, during the embryonic phase, of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis of an organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
embryonic organ development
Development, taking place during the embryonic phase, of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
excretion
The elimination by an organism of the waste products that arise as a result of metabolic activity. These products include water, carbon dioxide (CO2), and nitrogenous compounds.
skeletal system morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of the skeleton are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
embryonic skeletal system morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of the skeleton are generated and organized during the embryonic phase. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
embryonic skeletal system development
The process, occurring during the embryonic phase, whose specific outcome is the progression of the skeleton over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
embryonic skeletal system morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of the skeleton are generated and organized during the embryonic phase. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
sodium ion transport
The directed movement of sodium ions (Na+) into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
integral to membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer. When used to describe a protein, indicates that all or part of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
brush border
Dense covering of microvilli on the apical surface of epithelial cells in tissues such as the intestine, kidney, and choroid plexus; the microvilli aid absorption by increasing the surface area of the cell.
apical plasma membrane
The region of the plasma membrane located at the apical end of the cell.
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
cell projection membrane
The portion of the plasma membrane surrounding a cell surface projection.
brush border membrane
The portion of the plasma membrane surrounding the brush border.
cell projection
A prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell projection part
Any constituent part of a cell projection, a prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
apical part of cell
The region of a polarized cell that forms a tip or is distal to a base. For example, in a polarized epithelial cell, the apical region has an exposed surface and lies opposite to the basal lamina that separates the epithelium from other tissue.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
cell projection part
Any constituent part of a cell projection, a prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
apical plasma membrane
The region of the plasma membrane located at the apical end of the cell.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
cell projection membrane
The portion of the plasma membrane surrounding a cell surface projection.
brush border membrane
The portion of the plasma membrane surrounding the brush border.

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
nucleic acid binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any nucleic acid.
DNA binding
Any molecular function by which a gene product interacts selectively with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid).
sequence-specific DNA binding transcription factor activity
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a specific DNA sequence in order to modulate transcription. The transcription factor may or may not also interact selectively with a protein or macromolecular complex.
transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a substance from one side of a membrane to the other.
secondary active transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute from one side of a membrane to the other, up its concentration gradient. The transporter binds the solute and undergoes a series of conformational changes. Transport works equally well in either direction and is driven by a chemiosmotic source of energy. Chemiosmotic sources of energy include uniport, symport or antiport.
binding
The selective, non-covalent, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
cation transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of cation from one side of the membrane to the other.
anion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a negatively charged ion from one side of a membrane to the other.
ion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of an ion from one side of a membrane to the other.
inorganic anion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of inorganic anions from one side of a membrane to the other. Inorganic anions are atoms or small molecules with a negative charge which do not contain carbon in covalent linkage.
symporter activity
Enables the active transport of a solute across a membrane by a mechanism whereby two or more species are transported together in the same direction in a tightly coupled process not directly linked to a form of energy other than chemiosmotic energy.
solute:cation symporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: solute(out) + cation(out) = solute(in) + cation(in).
anion:cation symporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: anion(out) + cation(out) = anion(in) + cation(in).
antiporter activity
Enables the active transport of a solute across a membrane by a mechanism whereby two or more species are transported in opposite directions in a tightly coupled process not directly linked to a form of energy other than chemiosmotic energy.
solute:solute antiporter activity
Catalysis of the reaction: solute A(out) + solute B(in) = solute A(in) + solute B(out).
cation:chloride symporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: cation(out) + Cl-(out) = cation(in) + Cl-(in).
active transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a specific substance or related group of substances from one side of a membrane to the other, up the solute's concentration gradient. The transporter binds the solute and undergoes a series of conformational changes. Transport works equally well in either direction.
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
substrate-specific transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of a specific substance or group of related substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
sequence-specific DNA binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with DNA of a specific nucleotide composition, e.g. GC-rich DNA binding, or with a specific sequence motif or type of DNA e.g. promotor binding or rDNA binding.
all
NA
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
solute:cation symporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: solute(out) + cation(out) = solute(in) + cation(in).
anion:cation symporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: anion(out) + cation(out) = anion(in) + cation(in).
A2LD1AIG2-like domain 1 (ENSG00000134864), score: 0.56 AADATaminoadipate aminotransferase (ENSG00000109576), score: 0.55 ABCC4ATP-binding cassette, sub-family C (CFTR/MRP), member 4 (ENSG00000125257), score: 0.55 AFPalpha-fetoprotein (ENSG00000081051), score: 0.56 AGR3anterior gradient homolog 3 (Xenopus laevis) (ENSG00000173467), score: 0.9 ALOX12arachidonate 12-lipoxygenase (ENSG00000108839), score: 0.58 ANKRD37ankyrin repeat domain 37 (ENSG00000186352), score: -0.53 AP1S3adaptor-related protein complex 1, sigma 3 subunit (ENSG00000152056), score: 0.49 AQP2aquaporin 2 (collecting duct) (ENSG00000167580), score: 0.5 AQP6aquaporin 6, kidney specific (ENSG00000086159), score: 0.5 ARSFarylsulfatase F (ENSG00000062096), score: 0.56 ASPAaspartoacylase (ENSG00000108381), score: 0.52 ATP10DATPase, class V, type 10D (ENSG00000145246), score: 0.56 ATP12AATPase, H+/K+ transporting, nongastric, alpha polypeptide (ENSG00000075673), score: 0.64 ATP6V0A4ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal V0 subunit a4 (ENSG00000105929), score: 0.49 ATP6V1G3ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 13kDa, V1 subunit G3 (ENSG00000151418), score: 0.49 B4GALNT2beta-1,4-N-acetyl-galactosaminyl transferase 2 (ENSG00000167080), score: 0.53 BCAR3breast cancer anti-estrogen resistance 3 (ENSG00000137936), score: 0.5 BSNDBartter syndrome, infantile, with sensorineural deafness (Barttin) (ENSG00000162399), score: 0.54 BTCbetacellulin (ENSG00000174808), score: 0.74 C12orf59chromosome 12 open reading frame 59 (ENSG00000165685), score: 0.51 C17orf78chromosome 17 open reading frame 78 (ENSG00000167230), score: 0.84 C1orf106chromosome 1 open reading frame 106 (ENSG00000163362), score: 0.51 C1orf116chromosome 1 open reading frame 116 (ENSG00000182795), score: 0.49 CA13carbonic anhydrase XIII (ENSG00000185015), score: 0.72 CALCRcalcitonin receptor (ENSG00000004948), score: 0.68 CASRcalcium-sensing receptor (ENSG00000036828), score: 0.61 CCL23chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 23 (ENSG00000167236), score: 0.55 CD164L2CD164 sialomucin-like 2 (ENSG00000174950), score: 0.77 CDCP1CUB domain containing protein 1 (ENSG00000163814), score: 0.57 CDH16cadherin 16, KSP-cadherin (ENSG00000166589), score: 0.5 CLDN16claudin 16 (ENSG00000113946), score: 0.62 CLDN19claudin 19 (ENSG00000164007), score: 0.65 CLDN8claudin 8 (ENSG00000156284), score: 0.55 COCHcoagulation factor C homolog, cochlin (Limulus polyphemus) (ENSG00000100473), score: 0.53 COL19A1collagen, type XIX, alpha 1 (ENSG00000082293), score: 0.52 CSN2casein beta (ENSG00000135222), score: 0.78 CUBNcubilin (intrinsic factor-cobalamin receptor) (ENSG00000107611), score: 0.57 CWH43cell wall biogenesis 43 C-terminal homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000109182), score: 0.52 CYP24A1cytochrome P450, family 24, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000019186), score: 0.61 DEFB4Bdefensin, beta 4B (ENSG00000171711), score: 0.95 DHDHdihydrodiol dehydrogenase (dimeric) (ENSG00000104808), score: 0.58 DOCK8dedicator of cytokinesis 8 (ENSG00000107099), score: 0.56 EGFepidermal growth factor (ENSG00000138798), score: 0.51 ELF5E74-like factor 5 (ets domain transcription factor) (ENSG00000135374), score: 0.59 ESM1endothelial cell-specific molecule 1 (ENSG00000164283), score: 0.56 ESRP1epithelial splicing regulatory protein 1 (ENSG00000104413), score: 0.55 F2RL1coagulation factor II (thrombin) receptor-like 1 (ENSG00000164251), score: 0.51 FAM83Cfamily with sequence similarity 83, member C (ENSG00000125998), score: 0.51 FGFBP1fibroblast growth factor binding protein 1 (ENSG00000137440), score: 0.88 FMO1flavin containing monooxygenase 1 (ENSG00000010932), score: 0.55 FOXI1forkhead box I1 (ENSG00000168269), score: 0.53 FOXL1forkhead box L1 (ENSG00000176678), score: 0.49 FOXN1forkhead box N1 (ENSG00000109101), score: 0.56 GCM1glial cells missing homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000137270), score: 0.64 GDPD3glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase domain containing 3 (ENSG00000102886), score: 0.52 GFRALGDNF family receptor alpha like (ENSG00000187871), score: 0.5 GKN2gastrokine 2 (ENSG00000183607), score: 0.51 GP2glycoprotein 2 (zymogen granule membrane) (ENSG00000169347), score: 0.73 GPR172BG protein-coupled receptor 172B (ENSG00000132517), score: 0.55 GPRC6AG protein-coupled receptor, family C, group 6, member A (ENSG00000173612), score: 0.74 GRHL2grainyhead-like 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000083307), score: 0.54 GYLTL1Bglycosyltransferase-like 1B (ENSG00000165905), score: 0.56 HMX2H6 family homeobox 2 (ENSG00000188816), score: 0.54 HNF4Ghepatocyte nuclear factor 4, gamma (ENSG00000164749), score: 0.49 HOXA10homeobox A10 (ENSG00000153807), score: 0.52 HOXA2homeobox A2 (ENSG00000105996), score: 0.63 HOXA3homeobox A3 (ENSG00000105997), score: 0.53 HOXA5homeobox A5 (ENSG00000106004), score: 0.51 HOXA9homeobox A9 (ENSG00000078399), score: 0.53 HOXB5homeobox B5 (ENSG00000120075), score: 0.52 HOXB6homeobox B6 (ENSG00000108511), score: 0.53 HOXB7homeobox B7 (ENSG00000120087), score: 0.53 HOXC10homeobox C10 (ENSG00000180818), score: 0.53 HOXC6homeobox C6 (ENSG00000197757), score: 0.49 HOXC8homeobox C8 (ENSG00000037965), score: 0.55 HOXD10homeobox D10 (ENSG00000128710), score: 0.5 HOXD4homeobox D4 (ENSG00000170166), score: 0.54 HSD11B2hydroxysteroid (11-beta) dehydrogenase 2 (ENSG00000176387), score: 0.55 HTR1D5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 1D (ENSG00000179546), score: 0.79 IGFL3IGF-like family member 3 (ENSG00000188624), score: 0.56 IL12Binterleukin 12B (natural killer cell stimulatory factor 2, cytotoxic lymphocyte maturation factor 2, p40) (ENSG00000113302), score: 0.74 INSRRinsulin receptor-related receptor (ENSG00000027644), score: 0.54 IVNS1ABPinfluenza virus NS1A binding protein (ENSG00000116679), score: 0.5 KCNJ1potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 1 (ENSG00000151704), score: 0.5 KIAA1609KIAA1609 (ENSG00000140950), score: 0.52 KLklotho (ENSG00000133116), score: 0.55 KLF8Kruppel-like factor 8 (ENSG00000102349), score: 0.5 KRT3keratin 3 (ENSG00000186442), score: 0.8 LAMB4laminin, beta 4 (ENSG00000091128), score: 0.9 LRRC19leucine rich repeat containing 19 (ENSG00000184434), score: 0.59 MAT2Amethionine adenosyltransferase II, alpha (ENSG00000168906), score: 0.5 MATN3matrilin 3 (ENSG00000132031), score: 0.52 MCCD1mitochondrial coiled-coil domain 1 (ENSG00000204511), score: 0.49 MCM10minichromosome maintenance complex component 10 (ENSG00000065328), score: 0.6 MIOXmyo-inositol oxygenase (ENSG00000100253), score: 0.52 MMP13matrix metallopeptidase 13 (collagenase 3) (ENSG00000137745), score: 0.66 MOBKL2BMOB1, Mps One Binder kinase activator-like 2B (yeast) (ENSG00000120162), score: 0.52 MS4A10membrane-spanning 4-domains, subfamily A, member 10 (ENSG00000172689), score: 1 MSLNLmesothelin-like (ENSG00000162006), score: 0.7 MTMR8myotubularin related protein 8 (ENSG00000102043), score: 0.71 MTNR1Amelatonin receptor 1A (ENSG00000168412), score: 0.53 MYO3Bmyosin IIIB (ENSG00000071909), score: 0.55 NARFnuclear prelamin A recognition factor (ENSG00000141562), score: -0.56 NET1neuroepithelial cell transforming 1 (ENSG00000173848), score: 0.53 NHSNance-Horan syndrome (congenital cataracts and dental anomalies) (ENSG00000188158), score: 0.6 NRG1neuregulin 1 (ENSG00000157168), score: 0.53 OR10Q1olfactory receptor, family 10, subfamily Q, member 1 (ENSG00000180475), score: 0.73 OXGR1oxoglutarate (alpha-ketoglutarate) receptor 1 (ENSG00000165621), score: 0.67 PAPLNpapilin, proteoglycan-like sulfated glycoprotein (ENSG00000100767), score: 0.5 PAQR5progestin and adipoQ receptor family member V (ENSG00000137819), score: 0.5 PARD6Bpar-6 partitioning defective 6 homolog beta (C. elegans) (ENSG00000124171), score: 0.58 PAX2paired box 2 (ENSG00000075891), score: 0.51 PKHD1polycystic kidney and hepatic disease 1 (autosomal recessive) (ENSG00000170927), score: 0.59 PLA2G3phospholipase A2, group III (ENSG00000100078), score: 0.85 PNPLA1patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 1 (ENSG00000180316), score: 0.62 PROM2prominin 2 (ENSG00000155066), score: 0.52 PTPLAD2protein tyrosine phosphatase-like A domain containing 2 (ENSG00000188921), score: 0.72 RAB19RAB19, member RAS oncogene family (ENSG00000146955), score: 0.56 RENrenin (ENSG00000143839), score: 0.55 SCTRsecretin receptor (ENSG00000080293), score: 0.5 SFXN2sideroflexin 2 (ENSG00000156398), score: 0.49 SHISA2shisa homolog 2 (Xenopus laevis) (ENSG00000180730), score: 0.5 SIM1single-minded homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000112246), score: 0.61 SLC10A2solute carrier family 10 (sodium/bile acid cotransporter family), member 2 (ENSG00000125255), score: 0.56 SLC12A1solute carrier family 12 (sodium/potassium/chloride transporters), member 1 (ENSG00000074803), score: 0.54 SLC12A3solute carrier family 12 (sodium/chloride transporters), member 3 (ENSG00000070915), score: 0.53 SLC12A6solute carrier family 12 (potassium/chloride transporters), member 6 (ENSG00000140199), score: 0.51 SLC13A1solute carrier family 13 (sodium/sulfate symporters), member 1 (ENSG00000081800), score: 0.5 SLC15A2solute carrier family 15 (H+/peptide transporter), member 2 (ENSG00000163406), score: 0.51 SLC15A5solute carrier family 15, member 5 (ENSG00000188991), score: 0.9 SLC16A4solute carrier family 16, member 4 (monocarboxylic acid transporter 5) (ENSG00000168679), score: 0.52 SLC16A9solute carrier family 16, member 9 (monocarboxylic acid transporter 9) (ENSG00000165449), score: 0.57 SLC18A1solute carrier family 18 (vesicular monoamine), member 1 (ENSG00000036565), score: 0.58 SLC22A11solute carrier family 22 (organic anion/urate transporter), member 11 (ENSG00000168065), score: 0.53 SLC22A12solute carrier family 22 (organic anion/urate transporter), member 12 (ENSG00000197891), score: 0.51 SLC22A2solute carrier family 22 (organic cation transporter), member 2 (ENSG00000112499), score: 0.56 SLC22A4solute carrier family 22 (organic cation/ergothioneine transporter), member 4 (ENSG00000197208), score: 0.55 SLC23A3solute carrier family 23 (nucleobase transporters), member 3 (ENSG00000213901), score: 0.53 SLC25A45solute carrier family 25, member 45 (ENSG00000162241), score: 0.58 SLC26A7solute carrier family 26, member 7 (ENSG00000147606), score: 0.57 SLC34A1solute carrier family 34 (sodium phosphate), member 1 (ENSG00000131183), score: 0.52 SLC38A8solute carrier family 38, member 8 (ENSG00000166558), score: 0.5 SLC47A2solute carrier family 47, member 2 (ENSG00000180638), score: 0.5 SLC4A1solute carrier family 4, anion exchanger, member 1 (erythrocyte membrane protein band 3, Diego blood group) (ENSG00000004939), score: 0.51 SLC5A12solute carrier family 5 (sodium/glucose cotransporter), member 12 (ENSG00000148942), score: 0.5 SLC5A8solute carrier family 5 (iodide transporter), member 8 (ENSG00000139357), score: 0.66 SLC6A19solute carrier family 6 (neutral amino acid transporter), member 19 (ENSG00000174358), score: 0.55 SLC6A4solute carrier family 6 (neurotransmitter transporter, serotonin), member 4 (ENSG00000108576), score: 0.61 SLC7A13solute carrier family 7, (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system) member 13 (ENSG00000164893), score: 0.71 SLC9A4solute carrier family 9 (sodium/hydrogen exchanger), member 4 (ENSG00000180251), score: 0.53 SNX29sorting nexin 29 (ENSG00000048471), score: 0.49 SOX14SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 14 (ENSG00000168875), score: 0.66 STRA6stimulated by retinoic acid gene 6 homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000137868), score: 0.53 SULT1C2sulfotransferase family, cytosolic, 1C, member 2 (ENSG00000198203), score: 0.52 TAAR2trace amine associated receptor 2 (ENSG00000146378), score: 0.58 TAL2T-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia 2 (ENSG00000186051), score: 0.52 TCN2transcobalamin II (ENSG00000185339), score: 0.5 TFAP2Atranscription factor AP-2 alpha (activating enhancer binding protein 2 alpha) (ENSG00000137203), score: 0.49 TFAP2Btranscription factor AP-2 beta (activating enhancer binding protein 2 beta) (ENSG00000008196), score: 0.5 TFECtranscription factor EC (ENSG00000105967), score: 0.71 TINAGtubulointerstitial nephritis antigen (ENSG00000137251), score: 0.55 TMEM174transmembrane protein 174 (ENSG00000164325), score: 0.49 TMEM72transmembrane protein 72 (ENSG00000187783), score: 0.54 TMIGD1transmembrane and immunoglobulin domain containing 1 (ENSG00000182271), score: 0.86 TMPRSS13transmembrane protease, serine 13 (ENSG00000137747), score: 0.65 TNFSF15tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 15 (ENSG00000181634), score: 0.78 TRPM6transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily M, member 6 (ENSG00000119121), score: 0.49 UCMAupper zone of growth plate and cartilage matrix associated (ENSG00000165623), score: 0.54 UCN3urocortin 3 (stresscopin) (ENSG00000178473), score: 0.97 UMODuromodulin (ENSG00000169344), score: 0.53 UPK2uroplakin 2 (ENSG00000110375), score: 0.72 VDRvitamin D (1,25- dihydroxyvitamin D3) receptor (ENSG00000111424), score: 0.54 XPCxeroderma pigmentosum, complementation group C (ENSG00000154767), score: 0.55 XPNPEP2X-prolyl aminopeptidase (aminopeptidase P) 2, membrane-bound (ENSG00000122121), score: 0.5 ZBTB16zinc finger and BTB domain containing 16 (ENSG00000109906), score: -0.51
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ppy_kd_m_ca1 | ppy | kd | m | _ |
| mml_kd_f_ca1 | mml | kd | f | _ |
| mml_kd_m_ca1 | mml | kd | m | _ |