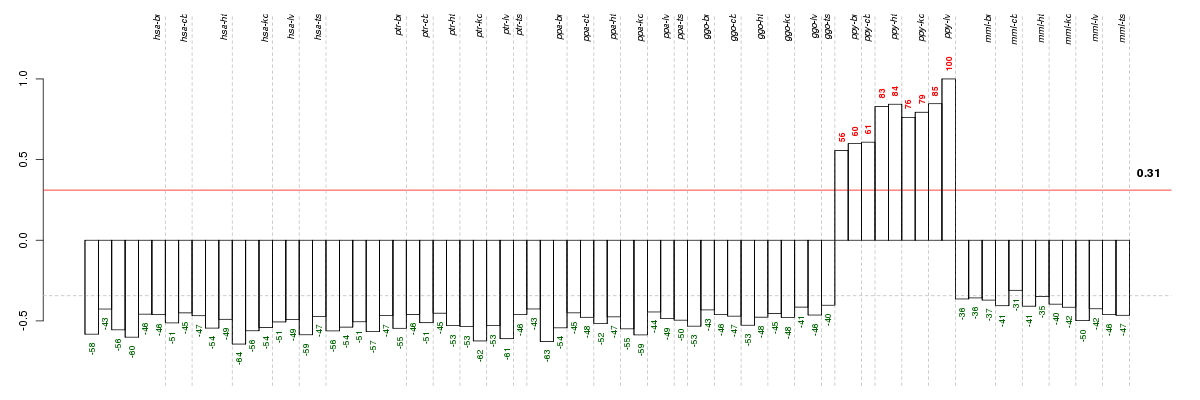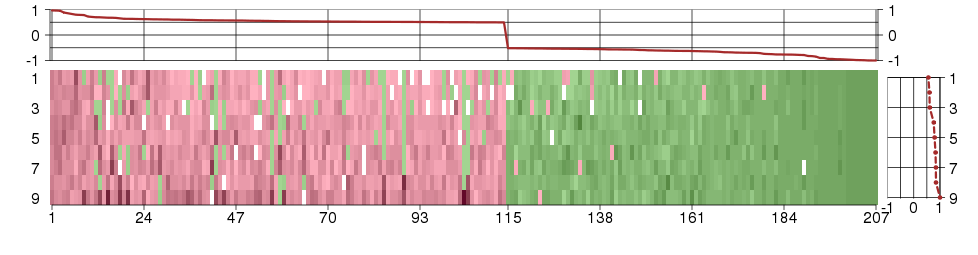

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

immune system process
Any process involved in the development or functioning of the immune system, an organismal system for calibrated responses to potential internal or invasive threats.
antigen processing and presentation of peptide antigen via MHC class I
The process by which an antigen-presenting cell expresses a peptide antigen on its cell surface in association with an MHC class I protein complex. Class I here refers to classical class I molecules.
antigen processing and presentation of endogenous peptide antigen
The process by which an antigen-presenting cell expresses a peptide antigen of endogenous origin on its cell surface in association with an MHC protein complex. The peptide is typically a fragment of a larger endogenous protein which has been degraded within the cell.
antigen processing and presentation of peptide or polysaccharide antigen via MHC class II
The process by which an antigen-presenting cell expresses antigen (peptide or polysaccharide) on its cell surface in association with an MHC class II protein complex.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
antigen processing and presentation
The process by which an antigen-presenting cell expresses antigen (peptide or lipid) on its cell surface in association with an MHC protein complex.
antigen processing and presentation of endogenous antigen
The process by which an antigen-presenting cell expresses antigen (peptide or lipid) of endogenous origin on its cell surface in association with an MHC protein complex.
antigen processing and presentation of endogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I
The process by which an antigen-presenting cell expresses a peptide antigen of endogenous origin on its cell surface in association with an MHC class I protein complex. The peptide antigen is typically, but not always, processed from a whole protein. Class I here refers to classical class I molecules.
antigen processing and presentation of peptide antigen
The process by which an antigen-presenting cell expresses peptide antigen in association with an MHC protein complex on its cell surface, including proteolysis and transport steps for the peptide antigen both prior to and following assembly with the MHC protein complex. The peptide antigen is typically, but not always, processed from an endogenous or exogenous protein.
all
NA
antigen processing and presentation of endogenous peptide antigen
The process by which an antigen-presenting cell expresses a peptide antigen of endogenous origin on its cell surface in association with an MHC protein complex. The peptide is typically a fragment of a larger endogenous protein which has been degraded within the cell.
antigen processing and presentation of endogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I
The process by which an antigen-presenting cell expresses a peptide antigen of endogenous origin on its cell surface in association with an MHC class I protein complex. The peptide antigen is typically, but not always, processed from a whole protein. Class I here refers to classical class I molecules.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
MHC class II protein complex
A transmembrane protein complex composed of an MHC class II alpha and MHC class II beta chain, and with or without a bound peptide or polysaccharide antigen.
integral to membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer. When used to describe a protein, indicates that all or part of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
endoplasmic reticulum
The irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae. The ER takes two forms, rough (or granular), with ribosomes adhering to the outer surface, and smooth (with no ribosomes attached).
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cytoplasm
All of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
endoplasmic reticulum membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding the endoplasmic reticulum.
endomembrane system
A collection of membranous structures involved in transport within the cell. The main components of the endomembrane system are endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, vesicles, cell membrane and nuclear envelope. Members of the endomembrane system pass materials through each other or though the use of vesicles.
integral to endoplasmic reticulum membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of an endoplasmic reticulum membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intrinsic to endoplasmic reticulum membrane
Located in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intrinsic to organelle membrane
Located in an organelle membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
integral to organelle membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of an organelle membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
nuclear membrane-endoplasmic reticulum network
The continuous network of membranes encompassing the outer nuclear membrane and the endoplasmic reticulum.
MHC protein complex
A transmembrane protein complex composed of an MHC alpha chain and, in most cases, either an MHC class II beta chain or an invariant beta2-microglobin chain, and with or without a bound peptide, lipid, or polysaccharide antigen.
MHC class I peptide loading complex
A large, multisubunit complex which consists of the MHC class I-beta 2 microglobulin dimer, the transporter associated with antigen presentation (TAP), tapasin (an MHC-encoded membrane protein), the chaperone calreticulin and the thiol oxidoreductase ERp57. Functions in the assembly of peptides with newly synthesized MHC class I molecules.
TAP complex
A heterodimer composed of the subunits TAP1 and TAP2 (transporter associated with antigen presentation). Functions in the transport of antigenic peptides from the cytosol to the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, and prokaryotic structures such as anammoxosomes and pirellulosomes. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
protein complex
Any macromolecular complex composed of two or more polypeptide subunits, which may or may not be identical. Protein complexes may have other associated non-protein prosthetic groups, such as nucleotides, metal ions or other small molecules.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
endoplasmic reticulum part
Any constituent part of the endoplasmic reticulum, the irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
subsynaptic reticulum
An elaborate tubulolamellar membrane system that underlies the postsynaptic cell membrane.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
intrinsic to organelle membrane
Located in an organelle membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
nuclear membrane-endoplasmic reticulum network
The continuous network of membranes encompassing the outer nuclear membrane and the endoplasmic reticulum.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
endoplasmic reticulum membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding the endoplasmic reticulum.
nuclear membrane-endoplasmic reticulum network
The continuous network of membranes encompassing the outer nuclear membrane and the endoplasmic reticulum.
TAP complex
A heterodimer composed of the subunits TAP1 and TAP2 (transporter associated with antigen presentation). Functions in the transport of antigenic peptides from the cytosol to the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum.
intrinsic to endoplasmic reticulum membrane
Located in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
endoplasmic reticulum membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding the endoplasmic reticulum.
intrinsic to endoplasmic reticulum membrane
Located in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
MHC class I peptide loading complex
A large, multisubunit complex which consists of the MHC class I-beta 2 microglobulin dimer, the transporter associated with antigen presentation (TAP), tapasin (an MHC-encoded membrane protein), the chaperone calreticulin and the thiol oxidoreductase ERp57. Functions in the assembly of peptides with newly synthesized MHC class I molecules.
TAP complex
A heterodimer composed of the subunits TAP1 and TAP2 (transporter associated with antigen presentation). Functions in the transport of antigenic peptides from the cytosol to the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
endoplasmic reticulum membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding the endoplasmic reticulum.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
endoplasmic reticulum
The irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae. The ER takes two forms, rough (or granular), with ribosomes adhering to the outer surface, and smooth (with no ribosomes attached).
endoplasmic reticulum part
Any constituent part of the endoplasmic reticulum, the irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae.
subsynaptic reticulum
An elaborate tubulolamellar membrane system that underlies the postsynaptic cell membrane.
intrinsic to organelle membrane
Located in an organelle membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
MHC protein complex
A transmembrane protein complex composed of an MHC alpha chain and, in most cases, either an MHC class II beta chain or an invariant beta2-microglobin chain, and with or without a bound peptide, lipid, or polysaccharide antigen.
endoplasmic reticulum part
Any constituent part of the endoplasmic reticulum, the irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae.
endoplasmic reticulum part
Any constituent part of the endoplasmic reticulum, the irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae.
integral to endoplasmic reticulum membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of an endoplasmic reticulum membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
integral to organelle membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of an organelle membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
MHC class I peptide loading complex
A large, multisubunit complex which consists of the MHC class I-beta 2 microglobulin dimer, the transporter associated with antigen presentation (TAP), tapasin (an MHC-encoded membrane protein), the chaperone calreticulin and the thiol oxidoreductase ERp57. Functions in the assembly of peptides with newly synthesized MHC class I molecules.

protein binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any protein or protein complex (a complex of two or more proteins that may include other nonprotein molecules).
molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
ATPase activity, coupled
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate to directly drive some other reaction, for example ion transport across a membrane.
catalytic activity
Catalysis of a biochemical reaction at physiological temperatures. In biologically catalyzed reactions, the reactants are known as substrates, and the catalysts are naturally occurring macromolecular substances known as enzymes. Enzymes possess specific binding sites for substrates, and are usually composed wholly or largely of protein, but RNA that has catalytic activity (ribozyme) is often also regarded as enzymatic.
ATPase activity, coupled to transmembrane movement of substances
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate to directly drive the active transport of a substance across a membrane.
nucleoside-triphosphatase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: a nucleoside triphosphate + H2O = nucleoside diphosphate + phosphate.
protein-lysine 6-oxidase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: peptidyl-L-lysyl-peptide + H2O + O2 = peptidyl-allysyl-peptide + NH3 + hydrogen peroxide.
signal transducer activity
Mediates the transfer of a signal from the outside to the inside of a cell by means other than the introduction of the signal molecule itself into the cell.
receptor activity
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell activity.
transmembrane receptor activity
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell activity, and spanning to the membrane of either the cell or an organelle.
MHC class II receptor activity
Combining with an MHC class II protein complex to initiate a change in cellular activity.
transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a substance from one side of a membrane to the other.
binding
The selective, non-covalent, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
oxidoreductase activity
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction, a reversible chemical reaction in which the oxidation state of an atom or atoms within a molecule is altered. One substrate acts as a hydrogen or electron donor and becomes oxidized, while the other acts as hydrogen or electron acceptor and becomes reduced.
ATPase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate. May or may not be coupled to another reaction.
peptide transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of peptides, compounds of two or more amino acids where the alpha carboxyl group of one is bound to the alpha amino group of another, into, out of, within or between cells.
primary active transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute from one side of the membrane to the other, up the solute's concentration gradient, by binding the solute and undergoing a series of conformational changes. Transport works equally well in either direction and is powered by a primary energy source. Primary energy sources known to be coupled to transport are chemical, electrical and solar sources.
P-P-bond-hydrolysis-driven transmembrane transporter activity
Primary active transport of a solute across a membrane, driven by the hydrolysis of the diphosphate bond of inorganic pyrophosphate, ATP, or another nucleoside triphosphate. The transport protein may or may not be transiently phosphorylated, but the substrate is not phosphorylated. Primary active transport is catalysis of the transport of a solute across a membrane, up the solute's concentration gradient, by binding the solute and undergoing a series of conformational changes. Transport works equally well in either direction and is driven by a primary energy source.
peptide antigen-transporting ATPase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: peptide antigen(in) + ATP = peptide antigen(out) + ADP + phosphate.
peptide-transporting ATPase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O + peptide(in) = ADP + phosphate + peptide(out). Peptides exported include alpha-hemolysin, cyclolysin, colicin V and siderophores from Gram-negative bacteria, and bacteriocin, subtilin, competence factor and pediocin from Gram-positive bacteria.
pyrophosphatase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of a pyrophosphate bond between two phosphate groups, leaving one phosphate on each of the two fragments.
oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-NH2 group of donors
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which a CH-NH2 group acts as a hydrogen or electron donor and reduces a hydrogen or electron acceptor.
oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-NH2 group of donors, oxygen as acceptor
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which a CH-NH2 group acts as a hydrogen or electron donor and reduces an oxygen molecule.
hydrolase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of various bonds, e.g. C-O, C-N, C-C, phosphoric anhydride bonds, etc. Hydrolase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 3.
hydrolase activity, acting on acid anhydrides
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of any acid anhydride.
hydrolase activity, acting on acid anhydrides, in phosphorus-containing anhydrides
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of any acid anhydride which contains phosphorus.
hydrolase activity, acting on acid anhydrides, catalyzing transmembrane movement of substances
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of an acid anhydride to directly drive the transport of a substance across a membrane.
active transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a specific substance or related group of substances from one side of a membrane to the other, up the solute's concentration gradient. The transporter binds the solute and undergoes a series of conformational changes. Transport works equally well in either direction.
substrate-specific transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of a specific substance or group of related substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
ATPase activity, coupled to movement of substances
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate to directly drive the transport of a substance.
TAP binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with TAP protein, transporter associated with antigen processing protein. TAP protein is a heterodimeric peptide transporter consisting of the subunits TAP1 and TAP2.
TAP1 binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with the TAP1 subunit of TAP (transporter associated with antigen processing) protein.
TAP2 binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with the TAP2 subunit of TAP (transporter associated with antigen processing) protein.
molecular transducer activity
The molecular function that accepts an input of one form and creates an output of a different form.
all
NA
hydrolase activity, acting on acid anhydrides, catalyzing transmembrane movement of substances
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of an acid anhydride to directly drive the transport of a substance across a membrane.
peptide-transporting ATPase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O + peptide(in) = ADP + phosphate + peptide(out). Peptides exported include alpha-hemolysin, cyclolysin, colicin V and siderophores from Gram-negative bacteria, and bacteriocin, subtilin, competence factor and pediocin from Gram-positive bacteria.
ATPase activity, coupled to transmembrane movement of substances
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate to directly drive the active transport of a substance across a membrane.
ATPase activity, coupled to transmembrane movement of substances
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate to directly drive the active transport of a substance across a membrane.
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 05322 | 1.732e-15 | 0.8811 | 17 | 52 | Systemic lupus erythematosus |
| 04612 | 2.199e-06 | 0.7456 | 9 | 44 | Antigen processing and presentation |
| 05330 | 5.473e-06 | 0.4067 | 7 | 24 | Allograft rejection |
| 05332 | 5.473e-06 | 0.4067 | 7 | 24 | Graft-versus-host disease |
| 04940 | 1.239e-05 | 0.4575 | 7 | 27 | Type I diabetes mellitus |
| 05320 | 1.603e-05 | 0.4745 | 7 | 28 | Autoimmune thyroid disease |
| 05310 | 4.641e-05 | 0.3558 | 6 | 21 | Asthma |
| 04672 | 9.929e-05 | 0.627 | 7 | 37 | Intestinal immune network for IgA production |
| 05416 | 1.169e-04 | 0.6439 | 7 | 38 | Viral myocarditis |
| 05140 | 7.134e-04 | 0.8642 | 7 | 51 | Leishmaniasis |
| 04145 | 4.111e-03 | 1.576 | 8 | 93 | Phagosome |
| 03020 | 6.339e-03 | 0.3219 | 4 | 19 | RNA polymerase |
| 04514 | 2.841e-02 | 1.728 | 7 | 102 | Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) |
ABHD12Babhydrolase domain containing 12B (ENSG00000131969), score: 0.61 ACCN4amiloride-sensitive cation channel 4, pituitary (ENSG00000072182), score: 0.61 ACSBG1acyl-CoA synthetase bubblegum family member 1 (ENSG00000103740), score: -0.64 ADCK2aarF domain containing kinase 2 (ENSG00000133597), score: 0.95 AGERadvanced glycosylation end product-specific receptor (ENSG00000204305), score: 0.58 ALAS2aminolevulinate, delta-, synthase 2 (ENSG00000158578), score: 0.62 API5apoptosis inhibitor 5 (ENSG00000166181), score: -0.95 ARL1ADP-ribosylation factor-like 1 (ENSG00000120805), score: 0.54 ARV1ARV1 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000173409), score: -0.56 ASB14ankyrin repeat and SOCS box-containing 14 (ENSG00000239388), score: 0.54 ATRIPATR interacting protein (ENSG00000164053), score: 0.85 ATXN1ataxin 1 (ENSG00000124788), score: -0.61 AVILadvillin (ENSG00000135407), score: 0.79 AZU1azurocidin 1 (ENSG00000172232), score: 0.57 B3GALT4UDP-Gal:betaGlcNAc beta 1,3-galactosyltransferase, polypeptide 4 (ENSG00000235863), score: -0.69 BEST1bestrophin 1 (ENSG00000167995), score: -0.68 BRD2bromodomain containing 2 (ENSG00000204256), score: -1 C10orf2chromosome 10 open reading frame 2 (ENSG00000107815), score: -0.57 C16orf57chromosome 16 open reading frame 57 (ENSG00000103005), score: -0.55 C16orf61chromosome 16 open reading frame 61 (ENSG00000103121), score: 0.72 C16orf7chromosome 16 open reading frame 7 (ENSG00000075399), score: -0.57 C16orf79chromosome 16 open reading frame 79 (ENSG00000182685), score: -0.64 C18orf22chromosome 18 open reading frame 22 (ENSG00000101546), score: -0.58 C1orf192chromosome 1 open reading frame 192 (ENSG00000188931), score: -0.57 C1orf27chromosome 1 open reading frame 27 (ENSG00000157181), score: 0.53 C1orf56chromosome 1 open reading frame 56 (ENSG00000143443), score: -0.61 C1QTNF5C1q and tumor necrosis factor related protein 5 (ENSG00000235718), score: 0.51 C21orf2chromosome 21 open reading frame 2 (ENSG00000160226), score: -0.54 C2orf66chromosome 2 open reading frame 66 (ENSG00000187944), score: 0.63 C2orf79chromosome 2 open reading frame 79 (ENSG00000184924), score: -0.52 C3orf75chromosome 3 open reading frame 75 (ENSG00000163832), score: -0.77 C4orf29chromosome 4 open reading frame 29 (ENSG00000164074), score: 0.5 C5orf13chromosome 5 open reading frame 13 (ENSG00000134986), score: -0.76 C6orf126chromosome 6 open reading frame 126 (ENSG00000196748), score: 0.7 C9orf95chromosome 9 open reading frame 95 (ENSG00000106733), score: 0.51 CA1carbonic anhydrase I (ENSG00000133742), score: 0.68 CCDC152coiled-coil domain containing 152 (ENSG00000198865), score: -0.66 CCDC42Bcoiled-coil domain containing 42B (ENSG00000186710), score: -0.56 CCHCR1coiled-coil alpha-helical rod protein 1 (ENSG00000204536), score: -0.71 CD101CD101 molecule (ENSG00000134256), score: 0.62 CD80CD80 molecule (ENSG00000121594), score: 0.5 CEBPECCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP), epsilon (ENSG00000092067), score: 0.69 CENPNcentromere protein N (ENSG00000166451), score: -0.65 CENPOcentromere protein O (ENSG00000138092), score: -0.62 CFDP1craniofacial development protein 1 (ENSG00000153774), score: 0.5 CKAP4cytoskeleton-associated protein 4 (ENSG00000136026), score: 0.49 CLEC5AC-type lectin domain family 5, member A (ENSG00000090269), score: 0.78 COMMD3COMM domain containing 3 (ENSG00000148444), score: 0.51 CTSKcathepsin K (ENSG00000143387), score: 0.58 CYB561D1cytochrome b-561 domain containing 1 (ENSG00000174151), score: -0.53 DAXXdeath-domain associated protein (ENSG00000204209), score: -0.96 DBF4BDBF4 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000161692), score: -0.55 DCAF17DDB1 and CUL4 associated factor 17 (ENSG00000115827), score: -0.62 DDIT4DNA-damage-inducible transcript 4 (ENSG00000168209), score: 0.49 DDX41DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 41 (ENSG00000183258), score: -0.55 DNAL1dynein, axonemal, light chain 1 (ENSG00000119661), score: 0.71 DOC2Adouble C2-like domains, alpha (ENSG00000149927), score: -0.55 DONSONdownstream neighbor of SON (ENSG00000159147), score: -0.57 ECHDC1enoyl CoA hydratase domain containing 1 (ENSG00000093144), score: 0.52 EIF2B5eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2B, subunit 5 epsilon, 82kDa (ENSG00000145191), score: 0.63 EMR3egf-like module containing, mucin-like, hormone receptor-like 3 (ENSG00000131355), score: 0.79 ERCC5excision repair cross-complementing rodent repair deficiency, complementation group 5 (ENSG00000134899), score: 0.52 EXOSC3exosome component 3 (ENSG00000107371), score: 0.6 FAM162Afamily with sequence similarity 162, member A (ENSG00000114023), score: 0.51 FAM166Afamily with sequence similarity 166, member A (ENSG00000188163), score: -0.9 FAM173Bfamily with sequence similarity 173, member B (ENSG00000150756), score: 0.58 FAM174Bfamily with sequence similarity 174, member B (ENSG00000185442), score: -0.54 FAM18B2family with sequence similarity 18, member B2 (ENSG00000239704), score: -0.52 FAM36Afamily with sequence similarity 36, member A (ENSG00000203667), score: 0.57 FGF2fibroblast growth factor 2 (basic) (ENSG00000138685), score: -0.74 FRMD8FERM domain containing 8 (ENSG00000126391), score: -0.76 GFM2G elongation factor, mitochondrial 2 (ENSG00000164347), score: 0.62 GHRHgrowth hormone releasing hormone (ENSG00000118702), score: 0.88 GLIPR1GLI pathogenesis-related 1 (ENSG00000139278), score: 0.53 GLTPglycolipid transfer protein (ENSG00000139433), score: -0.68 GNGT1guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), gamma transducing activity polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000127928), score: 0.55 GPR107G protein-coupled receptor 107 (ENSG00000148358), score: -0.63 GTF2E1general transcription factor IIE, polypeptide 1, alpha 56kDa (ENSG00000153767), score: 0.52 HARS2histidyl-tRNA synthetase 2, mitochondrial (putative) (ENSG00000112855), score: 0.63 HIST1H1Bhistone cluster 1, H1b (ENSG00000184357), score: 0.5 HIST1H3Ahistone cluster 1, H3a (ENSG00000112727), score: 0.52 HLA-DMAmajor histocompatibility complex, class II, DM alpha (ENSG00000204257), score: -0.68 HLA-DMBmajor histocompatibility complex, class II, DM beta (ENSG00000242574), score: -0.62 HLA-DOBmajor histocompatibility complex, class II, DO beta (ENSG00000204267), score: -0.82 HLA-DPA1major histocompatibility complex, class II, DP alpha 1 (ENSG00000231389), score: -0.75 HLA-DPB1major histocompatibility complex, class II, DP beta 1 (ENSG00000223865), score: -0.77 HLA-DRAmajor histocompatibility complex, class II, DR alpha (ENSG00000204287), score: -0.78 HNRNPH3heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein H3 (2H9) (ENSG00000096746), score: 0.53 HSD17B8hydroxysteroid (17-beta) dehydrogenase 8 (ENSG00000204228), score: -0.75 HTATIP2HIV-1 Tat interactive protein 2, 30kDa (ENSG00000109854), score: -0.62 IBSPintegrin-binding sialoprotein (ENSG00000029559), score: 0.58 IL34interleukin 34 (ENSG00000157368), score: 0.5 KIAA0195KIAA0195 (ENSG00000177728), score: -0.54 KIAA0892KIAA0892 (ENSG00000129933), score: -0.53 KRT27keratin 27 (ENSG00000171446), score: 0.51 LONP2lon peptidase 2, peroxisomal (ENSG00000102910), score: 0.5 LOXL3lysyl oxidase-like 3 (ENSG00000115318), score: -0.78 LOXL4lysyl oxidase-like 4 (ENSG00000138131), score: 0.5 LRRC23leucine rich repeat containing 23 (ENSG00000010626), score: -0.57 LYG2lysozyme G-like 2 (ENSG00000185674), score: 0.82 MAGOHBmago-nashi homolog B (Drosophila) (ENSG00000111196), score: 0.51 MAPK12mitogen-activated protein kinase 12 (ENSG00000188130), score: -0.59 MED17mediator complex subunit 17 (ENSG00000042429), score: 0.56 MED28mediator complex subunit 28 (ENSG00000118579), score: 0.52 MED6mediator complex subunit 6 (ENSG00000133997), score: -0.6 MEF2Bmyocyte enhancer factor 2B (ENSG00000064489), score: -0.7 MESDC2mesoderm development candidate 2 (ENSG00000117899), score: 0.6 MINAMYC induced nuclear antigen (ENSG00000170854), score: 0.57 MITD1MIT, microtubule interacting and transport, domain containing 1 (ENSG00000158411), score: 0.54 MLANAmelan-A (ENSG00000120215), score: 0.65 MMABmethylmalonic aciduria (cobalamin deficiency) cblB type (ENSG00000139428), score: 0.52 MRPL36mitochondrial ribosomal protein L36 (ENSG00000171421), score: -0.7 MRPL9mitochondrial ribosomal protein L9 (ENSG00000143436), score: 0.53 MRPS30mitochondrial ribosomal protein S30 (ENSG00000112996), score: -0.59 MRPS33mitochondrial ribosomal protein S33 (ENSG00000090263), score: 0.5 MSMBmicroseminoprotein, beta- (ENSG00000138294), score: 0.5 MYOZ3myozenin 3 (ENSG00000164591), score: 0.63 MYSM1Myb-like, SWIRM and MPN domains 1 (ENSG00000162601), score: 0.53 N4BP2L2NEDD4 binding protein 2-like 2 (ENSG00000139617), score: -0.52 NAGKN-acetylglucosamine kinase (ENSG00000124357), score: 0.56 NAT10N-acetyltransferase 10 (GCN5-related) (ENSG00000135372), score: -0.54 NDUFB9NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 beta subcomplex, 9, 22kDa (ENSG00000147684), score: -0.61 NEIL2nei endonuclease VIII-like 2 (E. coli) (ENSG00000154328), score: 0.52 NRLneural retina leucine zipper (ENSG00000129535), score: -0.52 OR1D2olfactory receptor, family 1, subfamily D, member 2 (ENSG00000184166), score: 0.54 PAPD7PAP associated domain containing 7 (ENSG00000112941), score: -0.54 PFDN6prefoldin subunit 6 (ENSG00000204220), score: -0.99 PHF23PHD finger protein 23 (ENSG00000040633), score: 0.96 PIM2pim-2 oncogene (ENSG00000102096), score: 0.53 PLA2G16phospholipase A2, group XVI (ENSG00000176485), score: 0.55 PLA2G2Fphospholipase A2, group IIF (ENSG00000158786), score: 0.53 PLEKHG2pleckstrin homology domain containing, family G (with RhoGef domain) member 2 (ENSG00000090924), score: 0.54 PLTPphospholipid transfer protein (ENSG00000100979), score: -0.54 PM20D2peptidase M20 domain containing 2 (ENSG00000146281), score: 0.51 PODNpodocan (ENSG00000174348), score: 0.51 POLR1Epolymerase (RNA) I polypeptide E, 53kDa (ENSG00000137054), score: 0.5 POLR2Fpolymerase (RNA) II (DNA directed) polypeptide F (ENSG00000100142), score: -0.7 POLR2Ipolymerase (RNA) II (DNA directed) polypeptide I, 14.5kDa (ENSG00000105258), score: -0.63 POU2F3POU class 2 homeobox 3 (ENSG00000137709), score: 0.54 PPA1pyrophosphatase (inorganic) 1 (ENSG00000180817), score: -0.53 PPBPpro-platelet basic protein (chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 7) (ENSG00000163736), score: 0.56 PRICKLE4prickle homolog 4 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000124593), score: -0.53 PRLprolactin (ENSG00000172179), score: 0.68 PRMT3protein arginine methyltransferase 3 (ENSG00000185238), score: 0.51 PRSS53protease, serine, 53 (ENSG00000151006), score: 0.53 PSMB8proteasome (prosome, macropain) subunit, beta type, 8 (large multifunctional peptidase 7) (ENSG00000204264), score: -0.65 PSMB9proteasome (prosome, macropain) subunit, beta type, 9 (large multifunctional peptidase 2) (ENSG00000240065), score: -0.7 PTCD3Pentatricopeptide repeat domain 3 (ENSG00000132300), score: 0.67 PYCR1pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase 1 (ENSG00000183010), score: 0.51 RAB40ARAB40A, member RAS oncogene family (ENSG00000172476), score: 0.57 RFX8regulatory factor X, 8 (ENSG00000196460), score: 0.69 RGL2ral guanine nucleotide dissociation stimulator-like 2 (ENSG00000237441), score: -0.97 RING1ring finger protein 1 (ENSG00000204227), score: -1 RNLSrenalase, FAD-dependent amine oxidase (ENSG00000184719), score: 0.5 RNMTRNA (guanine-7-) methyltransferase (ENSG00000101654), score: -0.69 RPL37ribosomal protein L37 (ENSG00000145592), score: -0.85 RPUSD3RNA pseudouridylate synthase domain containing 3 (ENSG00000156990), score: -0.54 RRP15ribosomal RNA processing 15 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000067533), score: 0.57 RXRBretinoid X receptor, beta (ENSG00000204231), score: -0.99 SAP18Sin3A-associated protein, 18kDa (ENSG00000150459), score: 0.59 SAP30BPSAP30 binding protein (ENSG00000161526), score: 0.57 SCGB3A2secretoglobin, family 3A, member 2 (ENSG00000164265), score: 0.51 SCYL1SCY1-like 1 (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000142186), score: 0.96 SEC22CSEC22 vesicle trafficking protein homolog C (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000093183), score: -0.55 SERBP1SERPINE1 mRNA binding protein 1 (ENSG00000142864), score: 0.51 SFT2D1SFT2 domain containing 1 (ENSG00000198818), score: -0.57 SLC39A7solute carrier family 39 (zinc transporter), member 7 (ENSG00000112473), score: -0.97 SMNDC1survival motor neuron domain containing 1 (ENSG00000119953), score: 0.56 SNRNP48small nuclear ribonucleoprotein 48kDa (U11/U12) (ENSG00000168566), score: 0.55 SRFBP1serum response factor binding protein 1 (ENSG00000151304), score: 0.6 SUPV3L1suppressor of var1, 3-like 1 (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000156502), score: 0.6 TAP1transporter 1, ATP-binding cassette, sub-family B (MDR/TAP) (ENSG00000168394), score: -0.77 TAPBPTAP binding protein (tapasin) (ENSG00000231925), score: -0.94 TCF19transcription factor 19 (ENSG00000137310), score: -0.6 TCTE3t-complex-associated-testis-expressed 3 (ENSG00000184786), score: 0.51 TCTEX1D1Tctex1 domain containing 1 (ENSG00000152760), score: 0.61 TFF1trefoil factor 1 (ENSG00000160182), score: 0.57 THUMPD3THUMP domain containing 3 (ENSG00000134077), score: -0.83 TMC3transmembrane channel-like 3 (ENSG00000188869), score: 0.52 TMCO1transmembrane and coiled-coil domains 1 (ENSG00000143183), score: 0.51 TMEM101transmembrane protein 101 (ENSG00000091947), score: -0.54 TMEM131transmembrane protein 131 (ENSG00000075568), score: -0.62 TMEM187transmembrane protein 187 (ENSG00000177854), score: -0.52 TMEM80transmembrane protein 80 (ENSG00000177042), score: -0.64 TRIM26tripartite motif-containing 26 (ENSG00000234127), score: -0.95 TRIT1tRNA isopentenyltransferase 1 (ENSG00000043514), score: 0.61 TRUB2TruB pseudouridine (psi) synthase homolog 2 (E. coli) (ENSG00000167112), score: 0.5 UBE2G1ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2G 1 (UBC7 homolog, yeast) (ENSG00000132388), score: 0.52 UTP14AUTP14, U3 small nucleolar ribonucleoprotein, homolog A (yeast) (ENSG00000156697), score: 0.57 UTP23UTP23, small subunit (SSU) processome component, homolog (yeast) (ENSG00000147679), score: 0.5 VILLvillin-like (ENSG00000136059), score: 0.5 VMO1vitelline membrane outer layer 1 homolog (chicken) (ENSG00000182853), score: 0.52 VNN2vanin 2 (ENSG00000112303), score: 0.59 VPS52vacuolar protein sorting 52 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000223501), score: -1 WBP5WW domain binding protein 5 (ENSG00000185222), score: 0.52 WDR46WD repeat domain 46 (ENSG00000227057), score: -0.98 ZBTB22zinc finger and BTB domain containing 22 (ENSG00000236104), score: -0.94 ZNF232zinc finger protein 232 (ENSG00000167840), score: 0.63 ZNF394zinc finger protein 394 (ENSG00000160908), score: 0.59 ZNF434zinc finger protein 434 (ENSG00000140987), score: -0.53 ZNF584zinc finger protein 584 (ENSG00000171574), score: -0.52 ZNF589zinc finger protein 589 (ENSG00000164048), score: -0.77 ZNF629zinc finger protein 629 (ENSG00000102870), score: -0.61 ZNF652zinc finger protein 652 (ENSG00000198740), score: 0.53 ZNF792zinc finger protein 792 (ENSG00000180884), score: 0.5 ZNRD1zinc ribbon domain containing 1 (ENSG00000066379), score: -0.9
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ppy_br_m_ca1 | ppy | br | m | _ |
| ppy_br_f_ca1 | ppy | br | f | _ |
| ppy_cb_f_ca1 | ppy | cb | f | _ |
| ppy_kd_m_ca1 | ppy | kd | m | _ |
| ppy_kd_f_ca1 | ppy | kd | f | _ |
| ppy_ht_m_ca1 | ppy | ht | m | _ |
| ppy_ht_f_ca1 | ppy | ht | f | _ |
| ppy_lv_m_ca1 | ppy | lv | m | _ |
| ppy_lv_f_ca1 | ppy | lv | f | _ |