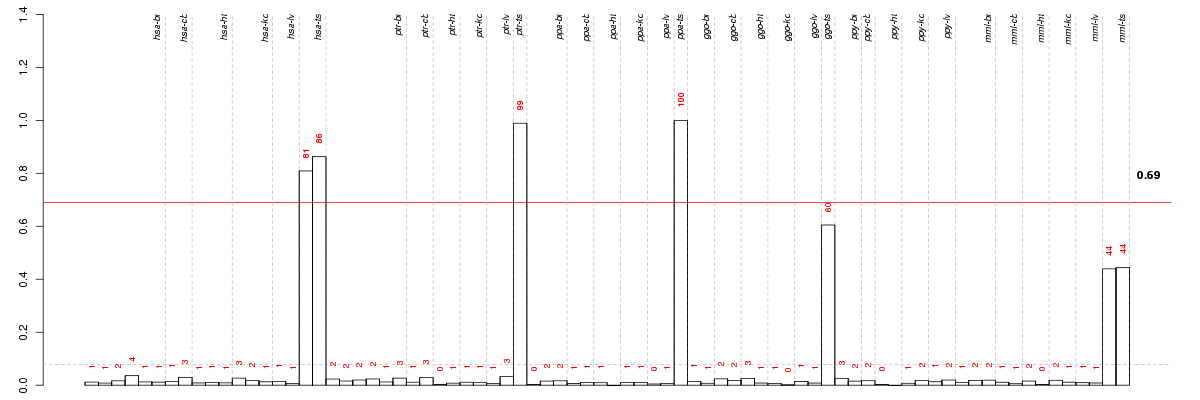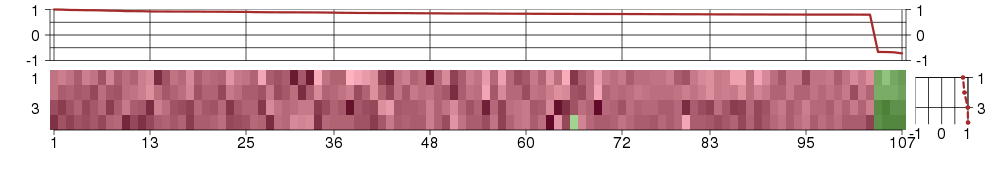

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

reproduction
The production by an organism of new individuals that contain some portion of their genetic material inherited from that organism.
metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
reproductive developmental process
A developmental process by which a progressive change in the state of some part of an organism specifically contributes to its ability to form offspring.
system process
A multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system. An organ system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a biological objective.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
transcription
The cellular synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
transcription, DNA-dependent
The cellular synthesis of RNA on a template of DNA.
regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-dependent transcription.
nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds; includes nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, assimilatory/dissimilatory nitrate reduction and the interconversion of nitrogenous organic matter and ammonium.
neurological system process
A organ system process carried out by any of the organs or tissues of neurological system.
sex differentiation
The establishment of the sex of an organism by physical differentiation.
sensory perception
The series of events required for an organism to receive a sensory stimulus, convert it to a molecular signal, and recognize and characterize the signal. This is a neurological process.
visual perception
The series of events required for an organism to receive a visual stimulus, convert it to a molecular signal, and recognize and characterize the signal. Visual stimuli are detected in the form of photons and are processed to form an image.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
gene expression
The process by which a gene's sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
regulation of gene expression
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
RNA metabolic process
The cellular chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
RNA biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage. Includes polymerization of ribonucleotide monomers.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
sensory perception of light stimulus
The series of events required for an organism to receive a sensory light stimulus, convert it to a molecular signal, and recognize and characterize the signal. This is a neurological process.
regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nitrogen or nitrogenous compounds.
regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of primary metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism involving those compounds formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleic acids.
all
NA
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
reproductive developmental process
A developmental process by which a progressive change in the state of some part of an organism specifically contributes to its ability to form offspring.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nitrogen or nitrogenous compounds.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving various organic and inorganic nitrogenous compounds, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
regulation of primary metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism involving those compounds formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular metabolic process involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of gene expression
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any cellular process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
transcription
The cellular synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
transcription, DNA-dependent
The cellular synthesis of RNA on a template of DNA.
regulation of transcription
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
RNA biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage. Includes polymerization of ribonucleotide monomers.
regulation of RNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA.
transcription
The cellular synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA.
RNA metabolic process
The cellular chemical reactions and pathways involving RNA, ribonucleic acid, one of the two main type of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from ribonucleotides joined in 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage.
regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-dependent transcription.
regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-dependent transcription.


molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
nucleic acid binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any nucleic acid.
DNA binding
Any molecular function by which a gene product interacts selectively with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid).
sequence-specific DNA binding transcription factor activity
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a specific DNA sequence in order to modulate transcription. The transcription factor may or may not also interact selectively with a protein or macromolecular complex.
binding
The selective, non-covalent, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
sequence-specific DNA binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with DNA of a specific nucleotide composition, e.g. GC-rich DNA binding, or with a specific sequence motif or type of DNA e.g. promotor binding or rDNA binding.
all
NA
AANATaralkylamine N-acetyltransferase (ENSG00000129673), score: 0.86 ACTL8actin-like 8 (ENSG00000117148), score: 0.85 AIPL1aryl hydrocarbon receptor interacting protein-like 1 (ENSG00000129221), score: 0.92 AURKCaurora kinase C (ENSG00000105146), score: 0.8 BMP15bone morphogenetic protein 15 (ENSG00000130385), score: 0.95 C17orf50chromosome 17 open reading frame 50 (ENSG00000154768), score: 0.85 C17orf66chromosome 17 open reading frame 66 (ENSG00000172653), score: 0.8 C19orf45chromosome 19 open reading frame 45 (ENSG00000198723), score: 0.8 C20orf151chromosome 20 open reading frame 151 (ENSG00000130701), score: 0.81 C4orf40chromosome 4 open reading frame 40 (ENSG00000187533), score: 0.83 C5orf47chromosome 5 open reading frame 47 (ENSG00000185056), score: 0.82 CAPN1calpain 1, (mu/I) large subunit (ENSG00000014216), score: -0.67 CATSPER4cation channel, sperm associated 4 (ENSG00000188782), score: 0.81 CDC20Bcell division cycle 20 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000164287), score: 0.81 CDC45cell division cycle 45 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000093009), score: 0.81 CDCA3cell division cycle associated 3 (ENSG00000111665), score: 0.8 COL2A1collagen, type II, alpha 1 (ENSG00000139219), score: 0.8 CSNK2A2casein kinase 2, alpha prime polypeptide (ENSG00000070770), score: 0.82 DEFB121defensin, beta 121 (ENSG00000204548), score: 0.89 DKK4dickkopf homolog 4 (Xenopus laevis) (ENSG00000104371), score: 0.84 DMBX1diencephalon/mesencephalon homeobox 1 (ENSG00000197587), score: 0.92 DMRT3doublesex and mab-3 related transcription factor 3 (ENSG00000064218), score: 0.91 DMRTB1DMRT-like family B with proline-rich C-terminal, 1 (ENSG00000143006), score: 0.82 DMRTC2DMRT-like family C2 (ENSG00000142025), score: 0.8 DRG1developmentally regulated GTP binding protein 1 (ENSG00000185721), score: 0.84 DSG4desmoglein 4 (ENSG00000175065), score: 0.81 ESX1ESX homeobox 1 (ENSG00000123576), score: 0.83 EVX1even-skipped homeobox 1 (ENSG00000106038), score: 0.94 FAM47Bfamily with sequence similarity 47, member B (ENSG00000189132), score: 0.83 FAM47Cfamily with sequence similarity 47, member C (ENSG00000198173), score: 0.8 FAM55Afamily with sequence similarity 55, member A (ENSG00000095110), score: 0.97 FGF4fibroblast growth factor 4 (ENSG00000075388), score: 1 FOXN4forkhead box N4 (ENSG00000139445), score: 0.85 FOXR1forkhead box R1 (ENSG00000176302), score: 0.8 G6PC2glucose-6-phosphatase, catalytic, 2 (ENSG00000152254), score: 0.99 GAB4GRB2-associated binding protein family, member 4 (ENSG00000215568), score: 0.92 GJA8gap junction protein, alpha 8, 50kDa (ENSG00000121634), score: 0.91 GLRA4glycine receptor, alpha 4 (ENSG00000188828), score: 0.8 HDAC8histone deacetylase 8 (ENSG00000147099), score: -0.72 HOXC13homeobox C13 (ENSG00000123364), score: 0.83 IL13interleukin 13 (ENSG00000169194), score: 0.88 IL3interleukin 3 (colony-stimulating factor, multiple) (ENSG00000164399), score: 0.89 KCNV2potassium channel, subfamily V, member 2 (ENSG00000168263), score: 0.96 KELKell blood group, metallo-endopeptidase (ENSG00000197993), score: 0.81 KLK12kallikrein-related peptidase 12 (ENSG00000186474), score: 0.93 KLK13kallikrein-related peptidase 13 (ENSG00000167759), score: 0.97 KRT26keratin 26 (ENSG00000186393), score: 0.9 LALBAlactalbumin, alpha- (ENSG00000167531), score: 0.85 LAMP3lysosomal-associated membrane protein 3 (ENSG00000078081), score: 0.98 LHX8LIM homeobox 8 (ENSG00000162624), score: 0.98 LIM2lens intrinsic membrane protein 2, 19kDa (ENSG00000105370), score: 0.89 LIN28Alin-28 homolog A (C. elegans) (ENSG00000131914), score: 0.8 LOC100287738hypothetical protein LOC100287738 (ENSG00000139656), score: 0.84 LOC100292575similar to melanoma antigen family C, 2 (ENSG00000046774), score: 0.9 LOXHD1lipoxygenase homology domains 1 (ENSG00000167210), score: 0.86 LRIT1leucine-rich repeat, immunoglobulin-like and transmembrane domains 1 (ENSG00000148602), score: 0.93 LUZP4leucine zipper protein 4 (ENSG00000102021), score: 0.83 MAGEA1melanoma antigen family A, 1 (directs expression of antigen MZ2-E) (ENSG00000198681), score: 0.89 MAGEA11melanoma antigen family A, 11 (ENSG00000185247), score: 0.92 MAGEA4melanoma antigen family A, 4 (ENSG00000147381), score: 0.82 MAGEB2melanoma antigen family B, 2 (ENSG00000099399), score: 0.84 MEP1Ameprin A, alpha (PABA peptide hydrolase) (ENSG00000112818), score: 0.88 MMP20matrix metallopeptidase 20 (ENSG00000137674), score: 0.86 MS4A6Emembrane-spanning 4-domains, subfamily A, member 6E (ENSG00000166926), score: 0.91 NANOS2nanos homolog 2 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000188425), score: 0.89 NKX2-4NK2 homeobox 4 (ENSG00000125816), score: 0.87 NLRP7NLR family, pyrin domain containing 7 (ENSG00000167634), score: 0.91 OOEPoocyte expressed protein homolog (dog) (ENSG00000203907), score: 0.84 OPN5opsin 5 (ENSG00000124818), score: 0.95 OR6F1olfactory receptor, family 6, subfamily F, member 1 (ENSG00000169214), score: 0.84 PADI1peptidyl arginine deiminase, type I (ENSG00000142623), score: 0.84 PAGE1P antigen family, member 1 (prostate associated) (ENSG00000068985), score: 0.83 PASD1PAS domain containing 1 (ENSG00000166049), score: 0.89 PAX4paired box 4 (ENSG00000106331), score: 0.85 PDE6Aphosphodiesterase 6A, cGMP-specific, rod, alpha (ENSG00000132915), score: 0.91 PDZD11PDZ domain containing 11 (ENSG00000120509), score: -0.66 PHOX2Apaired-like homeobox 2a (ENSG00000165462), score: 0.86 PITX1paired-like homeodomain 1 (ENSG00000069011), score: 0.86 POM121L2POM121 membrane glycoprotein-like 2 (ENSG00000158553), score: 0.82 PROKR1prokineticin receptor 1 (ENSG00000169618), score: 0.8 PRPHperipherin (ENSG00000135406), score: 0.8 RAG2recombination activating gene 2 (ENSG00000175097), score: 0.81 RNF113Bring finger protein 113B (ENSG00000139797), score: 0.84 RSPH6Aradial spoke head 6 homolog A (Chlamydomonas) (ENSG00000104941), score: 0.82 RXFP2relaxin/insulin-like family peptide receptor 2 (ENSG00000133105), score: 0.82 SAGS-antigen; retina and pineal gland (arrestin) (ENSG00000130561), score: 0.81 SPDYE4speedy homolog E4 (Xenopus laevis) (ENSG00000183318), score: 0.82 SPO11SPO11 meiotic protein covalently bound to DSB homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000054796), score: 0.82 SPRR4small proline-rich protein 4 (ENSG00000184148), score: 0.86 SULT6B1sulfotransferase family, cytosolic, 6B, member 1 (ENSG00000138068), score: 0.87 SYCNsyncollin (ENSG00000179751), score: 0.92 TEX19testis expressed 19 (ENSG00000182459), score: 0.92 TGM4transglutaminase 4 (prostate) (ENSG00000163810), score: 0.83 TP63tumor protein p63 (ENSG00000073282), score: 0.82 TPD52L3tumor protein D52-like 3 (ENSG00000170777), score: 0.83 TREML2triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-like 2 (ENSG00000112195), score: 0.86 TRIM31tripartite motif-containing 31 (ENSG00000204616), score: 0.81 WDR93WD repeat domain 93 (ENSG00000140527), score: 0.8 WFDC11WAP four-disulfide core domain 11 (ENSG00000180083), score: 0.81 ZADH2zinc binding alcohol dehydrogenase domain containing 2 (ENSG00000180011), score: -0.68 ZFP42zinc finger protein 42 homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000179059), score: 0.88 ZNF474zinc finger protein 474 (ENSG00000164185), score: 0.82 ZSCAN5Azinc finger and SCAN domain containing 5A (ENSG00000131848), score: 0.8 ZSCAN5Czinc finger and SCAN domain containing 5C (ENSG00000204532), score: 0.83
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa_ts_m1_ca1 | hsa | ts | m | 1 |
| hsa_ts_m2_ca1 | hsa | ts | m | 2 |
| ptr_ts_m_ca1 | ptr | ts | m | _ |
| ppa_ts_m_ca1 | ppa | ts | m | _ |