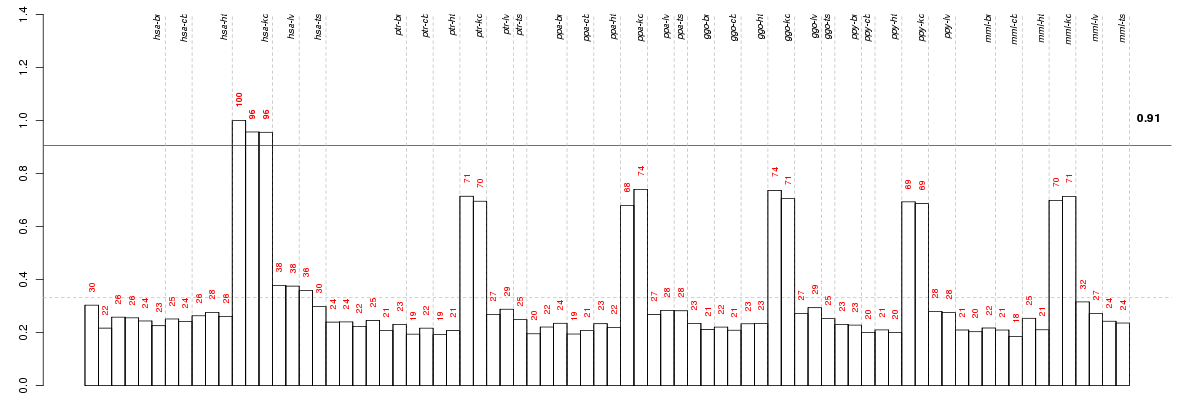

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

renal system process involved in regulation of blood volume
A slow mechanism of blood pressure regulation that responds to changes in pressure resulting from fluid and salt intake by modulating the quantity of blood in the circulatory system.
system process
A multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system. An organ system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a biological objective.
circulatory system process
A organ system process carried out by any of the organs or tissues of the circulatory system. The circulatory system is an organ system that moves extracellular fluids to and from tissue within a multicellular organism.
renal system process
A organ system process carried out by any of the organs or tissues of the renal system. The renal system is responsible for fluid volume regulation and detoxification in an organism.
renal system process involved in regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure
Renal process that modulates the force with which blood travels through the circulatory system. The process is controlled by a balance of processes that increase pressure and decrease pressure.
regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure
The process that modulates the force with which blood travels through the systemic arterial circulatory system. The process is controlled by a balance of processes that increase pressure and decrease pressure.
renal water transport
The directed movement of water (H2O) by the kidney.
secretion
The controlled release of a substance by a cell, a group of cells, or a tissue.
transport
The directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells, or within a multicellular organism by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
ion transport
The directed movement of charged atoms or small charged molecules into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
cation transport
The directed movement of cations, atoms or small molecules with a net positive charge, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
sodium ion transport
The directed movement of sodium ions (Na+) into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
anion transport
The directed movement of anions, atoms or small molecules with a net negative charge, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
metal ion transport
The directed movement of metal ions, any metal ion with an electric charge, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
water transport
The directed movement of water (H2O) into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
excretion
The elimination by an organism of the waste products that arise as a result of metabolic activity. These products include water, carbon dioxide (CO2), and nitrogenous compounds.
blood circulation
The flow of blood through the body of an animal, enabling the transport of nutrients to the tissues and the removal of waste products.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
regulation of blood pressure
Any process that modulates the force with which blood travels through the circulatory system. The process is controlled by a balance of processes that increase pressure and decrease pressure.
carbohydrate transport
The directed movement of carbohydrate into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. Carbohydrates are any of a group of organic compounds based of the general formula Cx(H2O)y.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
monovalent inorganic cation transport
The directed movement of inorganic cations with a valency of one into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. Inorganic cations are atoms or small molecules with a positive charge which do not contain carbon in covalent linkage.
organic cation transport
The directed movement of organic cations into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. Organic cations are atoms or small molecules with a positive charge which contain carbon in covalent linkage.
ammonium transport
The directed movement of ammonium into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. Ammonium is the cation NH4+ which is formed from N2 by root-nodule bacteria in leguminous plants and is an excretory product in ammonotelic animals.
polyol transport
The directed movement of polyols, any polyhydric alcohol, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
glycerol transport
The directed movement of glycerol into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. Glycerol is 1,2,3-propanetriol, a sweet, hygroscopic, viscous liquid, widely distributed in nature as a constituent of many lipids.
organic alcohol transport
The directed movement of organic alcohols into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. An organic alcohol is any carbon-containing compound containing a hydroxyl group.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
fluid transport
The directed movement of substances that are in liquid form in normal living conditions into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.
regulation of body fluid levels
Any process that modulates the levels of body fluids.
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
transmembrane transport
The process whereby a solute is transported from one side of a membrane to the other. This process includes the actual movement of the solute, and any regulation and preparatory steps, such as reduction of the solute.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of biological quality
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological quality. A biological quality is a measurable attribute of an organism or part of an organism, such as size, mass, shape, color, etc.
all
NA
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
transmembrane transport
The process whereby a solute is transported from one side of a membrane to the other. This process includes the actual movement of the solute, and any regulation and preparatory steps, such as reduction of the solute.
regulation of body fluid levels
Any process that modulates the levels of body fluids.
renal water transport
The directed movement of water (H2O) by the kidney.
excretion
The elimination by an organism of the waste products that arise as a result of metabolic activity. These products include water, carbon dioxide (CO2), and nitrogenous compounds.
regulation of blood pressure
Any process that modulates the force with which blood travels through the circulatory system. The process is controlled by a balance of processes that increase pressure and decrease pressure.
renal system process involved in regulation of blood volume
A slow mechanism of blood pressure regulation that responds to changes in pressure resulting from fluid and salt intake by modulating the quantity of blood in the circulatory system.
glycerol transport
The directed movement of glycerol into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. Glycerol is 1,2,3-propanetriol, a sweet, hygroscopic, viscous liquid, widely distributed in nature as a constituent of many lipids.
renal water transport
The directed movement of water (H2O) by the kidney.
renal system process involved in regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure
Renal process that modulates the force with which blood travels through the circulatory system. The process is controlled by a balance of processes that increase pressure and decrease pressure.
sodium ion transport
The directed movement of sodium ions (Na+) into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex
A large protein complex that catalyzes the synthesis or hydrolysis of ATP by a rotational mechanism, coupled to the transport of protons across a membrane. The complex comprises a membrane sector (F0, V0, or A0) that carries out proton transport and a cytoplasmic compartment sector (F1, V1, or A1) that catalyzes ATP synthesis or hydrolysis. Two major types have been characterized: V-type ATPases couple ATP hydrolysis to the transport of protons across a concentration gradient, whereas F-type ATPases, also known as ATP synthases, normally run in the reverse direction to utilize energy from a proton concentration or electrochemical gradient to synthesize ATP. A third type, A-type ATPases have been found in archaea, and are closely related to eukaryotic V-type ATPases but are reversible.
intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
vacuole
A closed structure, found only in eukaryotic cells, that is completely surrounded by unit membrane and contains liquid material. Cells contain one or several vacuoles, that may have different functions from each other. Vacuoles have a diverse array of functions. They can act as a storage organelle for nutrients or waste products, as a degradative compartment, as a cost-effective way of increasing cell size, and as a homeostatic regulator controlling both turgor pressure and pH of the cytosol.
integral to membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer. When used to describe a protein, indicates that all or part of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cytoplasm
All of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
vacuolar membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding the vacuole and separating its contents from the cytoplasm of the cell.
brush border
Dense covering of microvilli on the apical surface of epithelial cells in tissues such as the intestine, kidney, and choroid plexus; the microvilli aid absorption by increasing the surface area of the cell.
basolateral plasma membrane
The region of the plasma membrane that includes the basal end and sides of the cell. Often used in reference to animal polarized epithelial membranes, where the basal membrane is the part attached to the extracellular matrix, or in plant cells, where the basal membrane is defined with respect to the zygotic axis.
apical plasma membrane
The region of the plasma membrane located at the apical end of the cell.
vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex
A proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex found in the vacuolar membrane, where it acts as a proton pump to mediate acidification of the vacuolar lumen.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
cell projection membrane
The portion of the plasma membrane surrounding a cell surface projection.
brush border membrane
The portion of the plasma membrane surrounding the brush border.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex
A proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex that couples ATP hydrolysis to the transport of protons across a concentration gradient. The resulting transmembrane electrochemical potential of H+ is used to drive a variety of (i) secondary active transport systems via H+-dependent symporters and antiporters and (ii) channel-mediated transport systems. The complex comprises a membrane sector (V0) that carries out proton transport and a cytoplasmic compartment sector (V1) that catalyzes ATP hydrolysis. V-type ATPases are found in the membranes of organelles such as vacuoles, endosomes, and lysosomes, and in the plasma membrane.
cell projection
A prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, and prokaryotic structures such as anammoxosomes and pirellulosomes. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
protein complex
Any macromolecular complex composed of two or more polypeptide subunits, which may or may not be identical. Protein complexes may have other associated non-protein prosthetic groups, such as nucleotides, metal ions or other small molecules.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
vacuolar part
Any constituent part of a vacuole, a closed structure, found only in eukaryotic cells, that is completely surrounded by unit membrane and contains liquid material.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell projection part
Any constituent part of a cell projection, a prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
apical part of cell
The region of a polarized cell that forms a tip or is distal to a base. For example, in a polarized epithelial cell, the apical region has an exposed surface and lies opposite to the basal lamina that separates the epithelium from other tissue.
all
NA
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
cell projection part
Any constituent part of a cell projection, a prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex
A large protein complex that catalyzes the synthesis or hydrolysis of ATP by a rotational mechanism, coupled to the transport of protons across a membrane. The complex comprises a membrane sector (F0, V0, or A0) that carries out proton transport and a cytoplasmic compartment sector (F1, V1, or A1) that catalyzes ATP synthesis or hydrolysis. Two major types have been characterized: V-type ATPases couple ATP hydrolysis to the transport of protons across a concentration gradient, whereas F-type ATPases, also known as ATP synthases, normally run in the reverse direction to utilize energy from a proton concentration or electrochemical gradient to synthesize ATP. A third type, A-type ATPases have been found in archaea, and are closely related to eukaryotic V-type ATPases but are reversible.
vacuolar membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding the vacuole and separating its contents from the cytoplasm of the cell.
vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex
A proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex found in the vacuolar membrane, where it acts as a proton pump to mediate acidification of the vacuolar lumen.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
vacuole
A closed structure, found only in eukaryotic cells, that is completely surrounded by unit membrane and contains liquid material. Cells contain one or several vacuoles, that may have different functions from each other. Vacuoles have a diverse array of functions. They can act as a storage organelle for nutrients or waste products, as a degradative compartment, as a cost-effective way of increasing cell size, and as a homeostatic regulator controlling both turgor pressure and pH of the cytosol.
vacuolar part
Any constituent part of a vacuole, a closed structure, found only in eukaryotic cells, that is completely surrounded by unit membrane and contains liquid material.
apical plasma membrane
The region of the plasma membrane located at the apical end of the cell.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
cell projection membrane
The portion of the plasma membrane surrounding a cell surface projection.
brush border membrane
The portion of the plasma membrane surrounding the brush border.
vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex
A proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex found in the vacuolar membrane, where it acts as a proton pump to mediate acidification of the vacuolar lumen.
vacuolar part
Any constituent part of a vacuole, a closed structure, found only in eukaryotic cells, that is completely surrounded by unit membrane and contains liquid material.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.

protein binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any protein or protein complex (a complex of two or more proteins that may include other nonprotein molecules).
molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
catalytic activity
Catalysis of a biochemical reaction at physiological temperatures. In biologically catalyzed reactions, the reactants are known as substrates, and the catalysts are naturally occurring macromolecular substances known as enzymes. Enzymes possess specific binding sites for substrates, and are usually composed wholly or largely of protein, but RNA that has catalytic activity (ribozyme) is often also regarded as enzymatic.
metal ion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of metal ions from one side of a membrane to the other.
dipeptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of a dipeptide.
peptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of a peptide bond. A peptide bond is a covalent bond formed when the carbon atom from the carboxyl group of one amino acid shares electrons with the nitrogen atom from the amino group of a second amino acid.
phospholipase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of a glycerophospholipid.
sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: sphingomyelin + H2O = N-acylsphingosine + choline phosphate.
transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
ion channel activity
Catalysis of facilitated diffusion of an ion (by an energy-independent process) by passage through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel without evidence for a carrier-mediated mechanism.
cation channel activity
Catalysis of the energy-independent passage of cations across a lipid bilayer down a concentration gradient.
sodium channel activity
Catalysis of facilitated diffusion of a sodium ion (by an energy-independent process) involving passage through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel without evidence for a carrier-mediated mechanism.
transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a substance from one side of a membrane to the other.
secondary active transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute from one side of a membrane to the other, up its concentration gradient. The transporter binds the solute and undergoes a series of conformational changes. Transport works equally well in either direction and is driven by a chemiosmotic source of energy. Chemiosmotic sources of energy include uniport, symport or antiport.
inorganic anion exchanger activity
NA
binding
The selective, non-covalent, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
phosphoric diester hydrolase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of a phosphodiester to give a phosphomonoester and a free hydroxyl group.
cytoskeletal protein binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with any protein component of any cytoskeleton (actin, microtubule, or intermediate filament cytoskeleton).
exopeptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of a peptide bond not more than three residues from the N- or C-terminus of a polypeptide chain, in a reaction that requires a free N-terminal amino group, C-terminal carboxyl group or both.
cation transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of cation from one side of the membrane to the other.
anion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a negatively charged ion from one side of a membrane to the other.
peptidase activity, acting on L-amino acid peptides
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of peptide bonds formed between L-amino acids.
ion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of an ion from one side of a membrane to the other.
monovalent inorganic cation transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a inorganic cations with a valency of one from one side of a membrane to the other. Inorganic cations are atoms or small molecules with a positive charge that do not contain carbon in covalent linkage.
potassium ion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of potassium ions (K+) from one side of a membrane to the other.
polyol transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a polyol from one side of the membrane to the other. A polyol is any polyhydric alcohol.
glycerol transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of glycerol from one side of the membrane to the other. Glycerol is 1,2,3-propanetriol, a sweet, hygroscopic, viscous liquid, widely distributed in nature as a constituent of many lipids.
channel activity
Catalysis of energy-independent facilitated diffusion, mediated by passage of a solute through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel. Stereospecificity is not exhibited but this transport may be specific for a particular molecular species or class of molecules.
ligand-gated ion channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a channel that opens when a specific ligand has been bound by the channel complex or one of its constituent parts.
amiloride-sensitive sodium channel activity
NA
symporter activity
Enables the active transport of a solute across a membrane by a mechanism whereby two or more species are transported together in the same direction in a tightly coupled process not directly linked to a form of energy other than chemiosmotic energy.
antiporter activity
Enables the active transport of a solute across a membrane by a mechanism whereby two or more species are transported in opposite directions in a tightly coupled process not directly linked to a form of energy other than chemiosmotic energy.
solute:solute antiporter activity
Catalysis of the reaction: solute A(out) + solute B(in) = solute A(in) + solute B(out).
anion:anion antiporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: anion A(out) + anion B(in) = anion A(in) + anion B(out).
anion exchanger activity
NA
alcohol transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of an alcohol from one side of the membrane to the other. An alcohol is any carbon compound that contains a hydroxyl group.
lipase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of a lipid or phospholipid.
hydrolase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of various bonds, e.g. C-O, C-N, C-C, phosphoric anhydride bonds, etc. Hydrolase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 3.
hydrolase activity, acting on ester bonds
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of any ester bond.
passive transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute from one side of the membrane to the other, down the solute's concentration gradient.
active transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a specific substance or related group of substances from one side of a membrane to the other, up the solute's concentration gradient. The transporter binds the solute and undergoes a series of conformational changes. Transport works equally well in either direction.
ligand-gated channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a solute by a channel that opens when a specific ligand has been bound by the channel complex or one of its constituent parts.
gated channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of a solute by a channel that opens in response to a specific stimulus.
substrate-specific channel activity
Catalysis of energy-independent facilitated diffusion, mediated by passage of a specific solute through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel. Stereospecificity is not exhibited but this transport may be specific for a particular molecular species or class of molecules.
inorganic cation transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of inorganic cations from one side of a membrane to the other. Inorganic cations are atoms or small molecules with a positive charge that do not contain carbon in covalent linkage.
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
substrate-specific transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of a specific substance or group of related substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
ankyrin binding
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with ankyrin, a 200 kDa cytoskeletal protein that attaches other cytoskeletal proteins to integral membrane proteins.
phosphoric ester hydrolase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: RPO-R' + H2O = RPOOH + R'H. This reaction is the hydrolysis of any phosphoric ester bond, any ester formed from orthophosphoric acid, O=P(OH)3.
ammonia transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the directed movement of ammonia from one side of the membrane to the other.
all
NA
substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity
Enables the transfer of a specific substance or group of related substances from one side of a membrane to the other.
substrate-specific channel activity
Catalysis of energy-independent facilitated diffusion, mediated by passage of a specific solute through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel. Stereospecificity is not exhibited but this transport may be specific for a particular molecular species or class of molecules.
ion channel activity
Catalysis of facilitated diffusion of an ion (by an energy-independent process) by passage through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel without evidence for a carrier-mediated mechanism.
sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: sphingomyelin + H2O = N-acylsphingosine + choline phosphate.
cation channel activity
Catalysis of the energy-independent passage of cations across a lipid bilayer down a concentration gradient.
ligand-gated ion channel activity
Catalysis of the transmembrane transfer of an ion by a channel that opens when a specific ligand has been bound by the channel complex or one of its constituent parts.
anion:anion antiporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: anion A(out) + anion B(in) = anion A(in) + anion B(out).
amiloride-sensitive sodium channel activity
NA
potassium ion transmembrane transporter activity
Catalysis of the transfer of potassium ions (K+) from one side of a membrane to the other.
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 04966 | 7.076e-04 | 0.3504 | 5 | 21 | Collecting duct acid secretion |
| 04960 | 5.062e-03 | 0.5506 | 5 | 33 | Aldosterone-regulated sodium reabsorption |
ACAD10acyl-CoA dehydrogenase family, member 10 (ENSG00000111271), score: 0.46 ACOT11acyl-CoA thioesterase 11 (ENSG00000162390), score: 0.49 ACPPacid phosphatase, prostate (ENSG00000014257), score: 0.58 ALDH3B1aldehyde dehydrogenase 3 family, member B1 (ENSG00000006534), score: 0.58 ANO10anoctamin 10 (ENSG00000160746), score: 0.49 AP1M2adaptor-related protein complex 1, mu 2 subunit (ENSG00000129354), score: 0.5 APCDD1Ladenomatosis polyposis coli down-regulated 1-like (ENSG00000198768), score: 0.6 APEHN-acylaminoacyl-peptide hydrolase (ENSG00000164062), score: 0.46 APEX2APEX nuclease (apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease) 2 (ENSG00000169188), score: 0.55 AQP2aquaporin 2 (collecting duct) (ENSG00000167580), score: 0.58 AQP3aquaporin 3 (Gill blood group) (ENSG00000165272), score: 0.5 ARG2arginase, type II (ENSG00000081181), score: 0.48 ARSEarylsulfatase E (chondrodysplasia punctata 1) (ENSG00000157399), score: 0.48 ATP12AATPase, H+/K+ transporting, nongastric, alpha polypeptide (ENSG00000075673), score: 0.71 ATP4BATPase, H+/K+ exchanging, beta polypeptide (ENSG00000186009), score: 0.47 ATP6V0A4ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal V0 subunit a4 (ENSG00000105929), score: 0.48 ATP6V0D2ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 38kDa, V0 subunit d2 (ENSG00000147614), score: 0.46 ATP6V1B1ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 56/58kDa, V1 subunit B1 (ENSG00000116039), score: 0.51 B3GNT3UDP-GlcNAc:betaGal beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 3 (ENSG00000179913), score: 0.87 B4GALNT2beta-1,4-N-acetyl-galactosaminyl transferase 2 (ENSG00000167080), score: 0.57 BARX2BARX homeobox 2 (ENSG00000043039), score: 0.46 BSNDBartter syndrome, infantile, with sensorineural deafness (Barttin) (ENSG00000162399), score: 0.47 C12orf59chromosome 12 open reading frame 59 (ENSG00000165685), score: 0.48 C14orf45chromosome 14 open reading frame 45 (ENSG00000119636), score: 0.47 C19orf21chromosome 19 open reading frame 21 (ENSG00000099812), score: 0.5 C19orf33chromosome 19 open reading frame 33 (ENSG00000167644), score: 0.46 C1orf106chromosome 1 open reading frame 106 (ENSG00000163362), score: 0.48 C1orf186chromosome 1 open reading frame 186 (ENSG00000196533), score: 1 C1orf52chromosome 1 open reading frame 52 (ENSG00000162642), score: -0.47 C22orf28chromosome 22 open reading frame 28 (ENSG00000100220), score: 0.48 C2orf24chromosome 2 open reading frame 24 (ENSG00000115649), score: 0.49 C2orf49chromosome 2 open reading frame 49 (ENSG00000135974), score: -0.49 C2orf54chromosome 2 open reading frame 54 (ENSG00000172478), score: 0.52 C5orf32chromosome 5 open reading frame 32 (ENSG00000120306), score: 0.48 C9orf71chromosome 9 open reading frame 71 (ENSG00000181778), score: 0.47 CA12carbonic anhydrase XII (ENSG00000074410), score: 0.5 CALCAcalcitonin-related polypeptide alpha (ENSG00000110680), score: 0.54 CASRcalcium-sensing receptor (ENSG00000036828), score: 0.47 CCNT2cyclin T2 (ENSG00000082258), score: -0.56 CDH16cadherin 16, KSP-cadherin (ENSG00000166589), score: 0.53 CDHR2cadherin-related family member 2 (ENSG00000074276), score: 0.56 CDHR5cadherin-related family member 5 (ENSG00000099834), score: 0.49 CHORDC1cysteine and histidine-rich domain (CHORD)-containing 1 (ENSG00000110172), score: -0.54 CHP2calcineurin B homologous protein 2 (ENSG00000166869), score: 0.65 CIRH1Acirrhosis, autosomal recessive 1A (cirhin) (ENSG00000141076), score: 0.47 CLCC1chloride channel CLIC-like 1 (ENSG00000121940), score: -0.48 CLCNKAchloride channel Ka (ENSG00000186510), score: 0.5 CLDN19claudin 19 (ENSG00000164007), score: 0.57 CLDN4claudin 4 (ENSG00000189143), score: 0.46 CLDN8claudin 8 (ENSG00000156284), score: 0.48 CLN6ceroid-lipofuscinosis, neuronal 6, late infantile, variant (ENSG00000128973), score: 0.48 CLRN3clarin 3 (ENSG00000180745), score: 0.47 CNDP2CNDP dipeptidase 2 (metallopeptidase M20 family) (ENSG00000133313), score: 0.48 COQ4coenzyme Q4 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000167113), score: 0.51 CRYAAcrystallin, alpha A (ENSG00000160202), score: 0.51 CRYBB3crystallin, beta B3 (ENSG00000100053), score: 0.56 CTRCchymotrypsin C (caldecrin) (ENSG00000162438), score: 0.56 CUBNcubilin (intrinsic factor-cobalamin receptor) (ENSG00000107611), score: 0.5 CWH43cell wall biogenesis 43 C-terminal homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ENSG00000109182), score: 0.55 CYP27B1cytochrome P450, family 27, subfamily B, polypeptide 1 (ENSG00000111012), score: 0.65 DEPDC6DEP domain containing 6 (ENSG00000155792), score: 0.46 DLEC1deleted in lung and esophageal cancer 1 (ENSG00000008226), score: 0.48 DNAJC11DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 11 (ENSG00000007923), score: 0.53 DPEP1dipeptidase 1 (renal) (ENSG00000015413), score: 0.46 DUSP23dual specificity phosphatase 23 (ENSG00000158716), score: 0.48 EEF1Geukaryotic translation elongation factor 1 gamma (ENSG00000149016), score: 0.5 EIF3Keukaryotic translation initiation factor 3, subunit K (ENSG00000178982), score: 0.5 ELF5E74-like factor 5 (ets domain transcription factor) (ENSG00000135374), score: 0.45 ENAMenamelin (ENSG00000132464), score: 0.45 ENPP7ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 7 (ENSG00000182156), score: 0.55 ERP27endoplasmic reticulum protein 27 (ENSG00000139055), score: 0.73 EVPLenvoplakin (ENSG00000167880), score: 0.49 FAM150Bfamily with sequence similarity 150, member B (ENSG00000189292), score: 0.51 FAM151Afamily with sequence similarity 151, member A (ENSG00000162391), score: 0.57 FAM3Dfamily with sequence similarity 3, member D (ENSG00000198643), score: 0.49 FBN3fibrillin 3 (ENSG00000142449), score: 0.47 FBXO17F-box protein 17 (ENSG00000104835), score: 0.45 FCAMRFc receptor, IgA, IgM, high affinity (ENSG00000162897), score: 0.54 FMO1flavin containing monooxygenase 1 (ENSG00000010932), score: 0.47 FOLR1folate receptor 1 (adult) (ENSG00000110195), score: 0.58 FOXI1forkhead box I1 (ENSG00000168269), score: 0.46 FUT3fucosyltransferase 3 (galactoside 3(4)-L-fucosyltransferase, Lewis blood group) (ENSG00000171124), score: 0.72 FUT6fucosyltransferase 6 (alpha (1,3) fucosyltransferase) (ENSG00000156413), score: 0.5 FXYD2FXYD domain containing ion transport regulator 2 (ENSG00000137731), score: 0.47 FXYD3FXYD domain containing ion transport regulator 3 (ENSG00000089356), score: 0.45 GALNT14UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 14 (GalNAc-T14) (ENSG00000158089), score: 0.47 GCM1glial cells missing homolog 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000137270), score: 0.47 GGT6gamma-glutamyltransferase 6 (ENSG00000167741), score: 0.73 GHDCGH3 domain containing (ENSG00000167925), score: 0.49 GLIS2GLIS family zinc finger 2 (ENSG00000126603), score: 0.48 GNPDA1glucosamine-6-phosphate deaminase 1 (ENSG00000113552), score: 0.54 GPR114G protein-coupled receptor 114 (ENSG00000159618), score: 0.82 HDAC6histone deacetylase 6 (ENSG00000094631), score: 0.46 HEPACAM2HEPACAM family member 2 (ENSG00000188175), score: 0.5 HEXAhexosaminidase A (alpha polypeptide) (ENSG00000213614), score: 0.52 HHLA2HERV-H LTR-associating 2 (ENSG00000114455), score: 0.67 HOXA11homeobox A11 (ENSG00000005073), score: 0.47 HOXA7homeobox A7 (ENSG00000122592), score: 0.47 HOXC10homeobox C10 (ENSG00000180818), score: 0.53 HOXC5homeobox C5 (ENSG00000172789), score: 0.46 HOXD10homeobox D10 (ENSG00000128710), score: 0.46 ICMTisoprenylcysteine carboxyl methyltransferase (ENSG00000116237), score: 0.5 IL17RBinterleukin 17 receptor B (ENSG00000056736), score: 0.58 IL9Rinterleukin 9 receptor (ENSG00000124334), score: 0.56 ILDR1immunoglobulin-like domain containing receptor 1 (ENSG00000145103), score: 0.51 INMTindolethylamine N-methyltransferase (ENSG00000106125), score: 0.63 INTS2integrator complex subunit 2 (ENSG00000108506), score: -0.5 ITM2Bintegral membrane protein 2B (ENSG00000136156), score: 0.49 KCNE3potassium voltage-gated channel, Isk-related family, member 3 (ENSG00000175538), score: 0.67 KCNH6potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily H (eag-related), member 6 (ENSG00000173826), score: 0.82 KCNJ1potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 1 (ENSG00000151704), score: 0.48 KCNK5potassium channel, subfamily K, member 5 (ENSG00000164626), score: 0.48 KIAA0100KIAA0100 (ENSG00000007202), score: 0.52 KIAA1191KIAA1191 (ENSG00000122203), score: 0.52 KLklotho (ENSG00000133116), score: 0.47 KRT7keratin 7 (ENSG00000135480), score: 0.47 LGALS2lectin, galactoside-binding, soluble, 2 (ENSG00000100079), score: 0.5 LMX1BLIM homeobox transcription factor 1, beta (ENSG00000136944), score: 0.49 LYG1lysozyme G-like 1 (ENSG00000144214), score: 0.62 MCATmalonyl CoA:ACP acyltransferase (mitochondrial) (ENSG00000100294), score: 0.52 MCCD1mitochondrial coiled-coil domain 1 (ENSG00000204511), score: 0.69 MED30mediator complex subunit 30 (ENSG00000164758), score: -0.47 METTL1methyltransferase like 1 (ENSG00000037897), score: 0.5 MIFmacrophage migration inhibitory factor (glycosylation-inhibiting factor) (ENSG00000133460), score: 0.45 MIOXmyo-inositol oxygenase (ENSG00000100253), score: 0.49 MTNR1Amelatonin receptor 1A (ENSG00000168412), score: 0.5 MUC1mucin 1, cell surface associated (ENSG00000185499), score: 0.48 MUC13mucin 13, cell surface associated (ENSG00000173702), score: 0.7 MUC20mucin 20, cell surface associated (ENSG00000176945), score: 0.52 NCCRP1non-specific cytotoxic cell receptor protein 1 homolog (zebrafish) (ENSG00000188505), score: 0.76 NOX4NADPH oxidase 4 (ENSG00000086991), score: 0.55 NPHS2nephrosis 2, idiopathic, steroid-resistant (podocin) (ENSG00000116218), score: 0.48 OGG18-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase (ENSG00000114026), score: 0.46 OLFM4olfactomedin 4 (ENSG00000102837), score: 0.49 PABPC1Lpoly(A) binding protein, cytoplasmic 1-like (ENSG00000101104), score: 0.5 PAK4p21 protein (Cdc42/Rac)-activated kinase 4 (ENSG00000130669), score: 0.46 PAPPApregnancy-associated plasma protein A, pappalysin 1 (ENSG00000182752), score: 0.48 PAPPA2pappalysin 2 (ENSG00000116183), score: 0.67 PAX2paired box 2 (ENSG00000075891), score: 0.53 PAX8paired box 8 (ENSG00000125618), score: 0.49 PDZK1IP1PDZK1 interacting protein 1 (ENSG00000162366), score: 0.53 PEPDpeptidase D (ENSG00000124299), score: 0.53 PLA2G15phospholipase A2, group XV (ENSG00000103066), score: 0.45 PLA2G4Fphospholipase A2, group IVF (ENSG00000168907), score: 0.51 PLEKHJ1pleckstrin homology domain containing, family J member 1 (ENSG00000104886), score: 0.51 PRCPprolylcarboxypeptidase (angiotensinase C) (ENSG00000137509), score: 0.48 PRDM14PR domain containing 14 (ENSG00000147596), score: 0.49 PRKAB1protein kinase, AMP-activated, beta 1 non-catalytic subunit (ENSG00000111725), score: 0.53 PRLRprolactin receptor (ENSG00000113494), score: 0.53 PRR13proline rich 13 (ENSG00000205352), score: 0.5 PRR15proline rich 15 (ENSG00000176532), score: 0.5 PRR15Lproline rich 15-like (ENSG00000167183), score: 0.46 PRSS8protease, serine, 8 (ENSG00000052344), score: 0.52 PRXperiaxin (ENSG00000105227), score: 0.55 PSMD9proteasome (prosome, macropain) 26S subunit, non-ATPase, 9 (ENSG00000110801), score: 0.49 PTH1Rparathyroid hormone 1 receptor (ENSG00000160801), score: 0.53 PTH2Rparathyroid hormone 2 receptor (ENSG00000144407), score: 0.58 PTPN1protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 1 (ENSG00000196396), score: 0.5 RAB25RAB25, member RAS oncogene family (ENSG00000132698), score: 0.48 RASSF10Ras association (RalGDS/AF-6) domain family (N-terminal) member 10 (ENSG00000189431), score: 0.46 RASSF6Ras association (RalGDS/AF-6) domain family member 6 (ENSG00000169435), score: 0.47 RBP2retinol binding protein 2, cellular (ENSG00000114113), score: 0.82 RDH12retinol dehydrogenase 12 (all-trans/9-cis/11-cis) (ENSG00000139988), score: 0.48 RDH8retinol dehydrogenase 8 (all-trans) (ENSG00000080511), score: 0.57 REG3Aregenerating islet-derived 3 alpha (ENSG00000172016), score: 0.54 RENrenin (ENSG00000143839), score: 0.57 RENBPrenin binding protein (ENSG00000102032), score: 0.5 RHBGRh family, B glycoprotein (gene/pseudogene) (ENSG00000132677), score: 0.47 RHCGRh family, C glycoprotein (ENSG00000140519), score: 0.49 RNPEParginyl aminopeptidase (aminopeptidase B) (ENSG00000176393), score: 0.47 S100A2S100 calcium binding protein A2 (ENSG00000196754), score: 0.6 SCINscinderin (ENSG00000006747), score: 0.46 SCNN1Asodium channel, nonvoltage-gated 1 alpha (ENSG00000111319), score: 0.48 SCNN1Bsodium channel, nonvoltage-gated 1, beta (ENSG00000168447), score: 0.54 SCNN1Gsodium channel, nonvoltage-gated 1, gamma (ENSG00000166828), score: 0.48 SCRN2secernin 2 (ENSG00000141295), score: 0.48 SERPINB7serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade B (ovalbumin), member 7 (ENSG00000166396), score: 0.46 SHISA3shisa homolog 3 (Xenopus laevis) (ENSG00000178343), score: 0.56 SLC12A3solute carrier family 12 (sodium/chloride transporters), member 3 (ENSG00000070915), score: 0.52 SLC15A1solute carrier family 15 (oligopeptide transporter), member 1 (ENSG00000088386), score: 0.54 SLC19A1solute carrier family 19 (folate transporter), member 1 (ENSG00000173638), score: 0.49 SLC22A11solute carrier family 22 (organic anion/urate transporter), member 11 (ENSG00000168065), score: 0.49 SLC22A12solute carrier family 22 (organic anion/urate transporter), member 12 (ENSG00000197891), score: 0.5 SLC22A13solute carrier family 22 (organic anion transporter), member 13 (ENSG00000172940), score: 0.7 SLC22A6solute carrier family 22 (organic anion transporter), member 6 (ENSG00000197901), score: 0.48 SLC22A8solute carrier family 22 (organic anion transporter), member 8 (ENSG00000149452), score: 0.55 SLC28A2solute carrier family 28 (sodium-coupled nucleoside transporter), member 2 (ENSG00000137860), score: 0.48 SLC2A9solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 9 (ENSG00000109667), score: 0.47 SLC30A2solute carrier family 30 (zinc transporter), member 2 (ENSG00000158014), score: 0.58 SLC34A1solute carrier family 34 (sodium phosphate), member 1 (ENSG00000131183), score: 0.49 SLC34A3solute carrier family 34 (sodium phosphate), member 3 (ENSG00000198569), score: 0.49 SLC39A4solute carrier family 39 (zinc transporter), member 4 (ENSG00000147804), score: 0.57 SLC39A5solute carrier family 39 (metal ion transporter), member 5 (ENSG00000139540), score: 0.58 SLC3A2solute carrier family 3 (activators of dibasic and neutral amino acid transport), member 2 (ENSG00000168003), score: 0.46 SLC44A4solute carrier family 44, member 4 (ENSG00000204385), score: 0.54 SLC47A2solute carrier family 47, member 2 (ENSG00000180638), score: 0.46 SLC4A1solute carrier family 4, anion exchanger, member 1 (erythrocyte membrane protein band 3, Diego blood group) (ENSG00000004939), score: 0.52 SLC4A9solute carrier family 4, sodium bicarbonate cotransporter, member 9 (ENSG00000113073), score: 0.46 SLC5A10solute carrier family 5 (sodium/glucose cotransporter), member 10 (ENSG00000154025), score: 0.57 SLC5A12solute carrier family 5 (sodium/glucose cotransporter), member 12 (ENSG00000148942), score: 0.52 SLC5A2solute carrier family 5 (sodium/glucose cotransporter), member 2 (ENSG00000140675), score: 0.52 SLC5A8solute carrier family 5 (iodide transporter), member 8 (ENSG00000139357), score: 0.57 SLC6A19solute carrier family 6 (neutral amino acid transporter), member 19 (ENSG00000174358), score: 0.57 SLC7A7solute carrier family 7 (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system), member 7 (ENSG00000155465), score: 0.5 SLC9A4solute carrier family 9 (sodium/hydrogen exchanger), member 4 (ENSG00000180251), score: 0.57 SMPD1sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase 1, acid lysosomal (ENSG00000166311), score: 0.5 SMPDL3Bsphingomyelin phosphodiesterase, acid-like 3B (ENSG00000130768), score: 0.64 SOSTsclerostin (ENSG00000167941), score: 0.57 ST14suppression of tumorigenicity 14 (colon carcinoma) (ENSG00000149418), score: 0.49 STRA6stimulated by retinoic acid gene 6 homolog (mouse) (ENSG00000137868), score: 0.47 SUCLG1succinate-CoA ligase, alpha subunit (ENSG00000163541), score: 0.5 SUSD2sushi domain containing 2 (ENSG00000099994), score: 0.66 TACSTD2tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (ENSG00000184292), score: 0.58 TDGF1teratocarcinoma-derived growth factor 1 (ENSG00000241186), score: 0.47 TFCP2L1transcription factor CP2-like 1 (ENSG00000115112), score: 0.52 TH1LTH1-like (Drosophila) (ENSG00000101158), score: 0.46 TM7SF3transmembrane 7 superfamily member 3 (ENSG00000064115), score: 0.5 TMC4transmembrane channel-like 4 (ENSG00000167608), score: 0.58 TMED4transmembrane emp24 protein transport domain containing 4 (ENSG00000158604), score: 0.61 TMEM115transmembrane protein 115 (ENSG00000126062), score: 0.46 TMEM150Btransmembrane protein 150B (ENSG00000180061), score: 0.67 TMEM171transmembrane protein 171 (ENSG00000157111), score: 0.52 TMEM174transmembrane protein 174 (ENSG00000164325), score: 0.51 TMEM72transmembrane protein 72 (ENSG00000187783), score: 0.53 TMEM79transmembrane protein 79 (ENSG00000163472), score: 0.63 TMEM86Atransmembrane protein 86A (ENSG00000151117), score: 0.48 TMPRSS4transmembrane protease, serine 4 (ENSG00000137648), score: 0.63 TRIM10tripartite motif-containing 10 (ENSG00000204613), score: 0.8 TRIM15tripartite motif-containing 15 (ENSG00000204610), score: 0.82 TRIM6-TRIM34TRIM6-TRIM34 readthrough (ENSG00000242885), score: 0.47 TRIP6thyroid hormone receptor interactor 6 (ENSG00000087077), score: 0.5 TRPC7transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily C, member 7 (ENSG00000069018), score: 0.86 TSPAN33tetraspanin 33 (ENSG00000158457), score: 0.52 TSPO2translocator protein 2 (ENSG00000112212), score: 0.58 TTC22tetratricopeptide repeat domain 22 (ENSG00000006555), score: 0.55 TUBAL3tubulin, alpha-like 3 (ENSG00000178462), score: 0.83 UMODuromodulin (ENSG00000169344), score: 0.47 UNC5CLunc-5 homolog C (C. elegans)-like (ENSG00000124602), score: 0.51 UPK1Buroplakin 1B (ENSG00000114638), score: 0.46 USH1CUsher syndrome 1C (autosomal recessive, severe) (ENSG00000006611), score: 0.49 VDRvitamin D (1,25- dihydroxyvitamin D3) receptor (ENSG00000111424), score: 0.47 VGLL1vestigial like 1 (Drosophila) (ENSG00000102243), score: 0.66 WDR72WD repeat domain 72 (ENSG00000166415), score: 0.49 WDR91WD repeat domain 91 (ENSG00000105875), score: 0.48 XPNPEP2X-prolyl aminopeptidase (aminopeptidase P) 2, membrane-bound (ENSG00000122121), score: 0.55 ZNF518Bzinc finger protein 518B (ENSG00000178163), score: -0.49 ZNF599zinc finger protein 599 (ENSG00000153896), score: 0.47
| Id | species | tissue | sex | individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa_kd_f_ca1 | hsa | kd | f | _ |
| hsa_kd_m2_ca1 | hsa | kd | m | 2 |
| hsa_kd_m1_ca1 | hsa | kd | m | 1 |