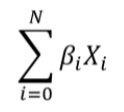Difference between revisions of "Polygenic Risk Scores"
Sbprm2021 3 (talk | contribs) |
Sbprm2021 3 (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
==<big>Introduction</big>== | ==<big>Introduction</big>== | ||
| + | [[File:PRS.png|thumb|PRS Formula]] | ||
| + | |||
=Definition= | =Definition= | ||
| + | |||
Polygenic Risk Score or PRS is the calculation of a risk score from the subject's genome with the weighted sum of the SNPs to estimate the risk that the subject will develop a certain disease or trait according to the changes linked to the phenotype studied. There are two main factors that we use to calculate the PRS: the allelic dosage (Xi), which represents the number of copies of the main effect allele and can be 0, 1 or 2. And the other factor is the effect size (βi), which measures the strength of the relationship of a trait with the allelic dosage at a position i on a numeric scale. | Polygenic Risk Score or PRS is the calculation of a risk score from the subject's genome with the weighted sum of the SNPs to estimate the risk that the subject will develop a certain disease or trait according to the changes linked to the phenotype studied. There are two main factors that we use to calculate the PRS: the allelic dosage (Xi), which represents the number of copies of the main effect allele and can be 0, 1 or 2. And the other factor is the effect size (βi), which measures the strength of the relationship of a trait with the allelic dosage at a position i on a numeric scale. | ||
| − | |||
=Jura & UK Biobank= | =Jura & UK Biobank= | ||
Revision as of 16:12, 4 June 2021
- Project name: Polygenetic Risk Score (PRS)
- Tutor: Alex Button (alexanderluke.button_AT_unil.ch)
- Slides: File:Polygenetic Risk Score.pdf
Introduction
Definition
Polygenic Risk Score or PRS is the calculation of a risk score from the subject's genome with the weighted sum of the SNPs to estimate the risk that the subject will develop a certain disease or trait according to the changes linked to the phenotype studied. There are two main factors that we use to calculate the PRS: the allelic dosage (Xi), which represents the number of copies of the main effect allele and can be 0, 1 or 2. And the other factor is the effect size (βi), which measures the strength of the relationship of a trait with the allelic dosage at a position i on a numeric scale.
Jura & UK Biobank
In order to have data, we used Jura, which is a cluster for analysis of sensitive data and is primarily used by the CHUV. We need to have authorization to use Jura, but like that we can have real subject’s data.And there are data coming from the UK Biobank, which is a large-scale biomedical database and research resource, containing genetic and health information from half a million UK participants that is enabling new scientific discoveries to be made that improve public health.