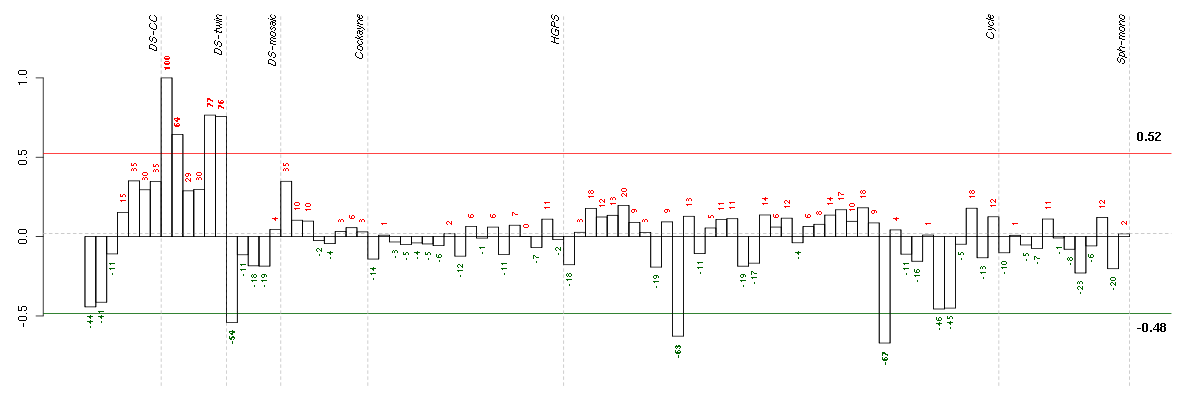

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

skeletal system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the skeleton over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The skeleton is the bony framework of the body in vertebrates (endoskeleton) or the hard outer envelope of insects (exoskeleton or dermoskeleton).
ossification
The formation of bone or of a bony substance, or the conversion of fibrous tissue or of cartilage into bone or a bony substance.
angiogenesis
Blood vessel formation when new vessels emerge from the proliferation of pre-existing blood vessels.
metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
blood vessel development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the blood vessel over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The blood vessel is the vasculature carrying blood.
osteoblast differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the specialized features of an osteoblast, the mesodermal cell that gives rise to bone.
cell activation
A change in the morphology or behavior of a cell resulting from exposure to an activating factor such as a cellular or soluble ligand.
vasculature development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the vasculature over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
immune system process
Any process involved in the development or functioning of the immune system, an organismal system for calibrated responses to potential internal or invasive threats.
antigen processing and presentation of peptide antigen via MHC class I
The process by which an antigen-presenting cell expresses a peptide antigen on its cell surface in association with an MHC class I protein complex. Class I here refers to classical class I molecules.
system process
A multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system. An organ system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a biological objective.
defense response
Reactions, triggered in response to the presence of a foreign body or the occurrence of an injury, which result in restriction of damage to the organism attacked or prevention/recovery from the infection caused by the attack.
blood coagulation
The sequential process by which the multiple coagulation factors of the blood interact, ultimately resulting in the formation of an insoluble fibrin clot; it may be divided into three stages: stage 1, the formation of intrinsic and extrinsic prothrombin converting principle; stage 2, the formation of thrombin; stage 3, the formation of stable fibrin polymers.
apoptosis
A form of programmed cell death characterized by rounding-up of the cell, retraction of pseudopodes, reduction of cellular volume (pyknosis), chromatin condensation, nuclear fragmentation (karyorrhexis), classically little or no ultrastructural modifications of cytoplasmic organelles, plasma membrane blebbing (but maintenance of its integrity until the final stages of the process) and engulfment by resident phagocytes. Apoptosis is usually induced by external or internal signals that trigger the activity of proteolytic caspases, whose actions dismantle the cell and result in cell death.
signal transduction
The cascade of processes by which a signal interacts with a receptor, causing a change in the level or activity of a second messenger or other downstream target, and ultimately effecting a change in the functioning of the cell.
protein modification process
The covalent alteration of one or more amino acids occurring in proteins, peptides and nascent polypeptides (co-translational, post-translational modifications). Includes the modification of charged tRNAs that are destined to occur in a protein (pre-translation modification).
cell motion
Any process involved in the controlled movement of a cell.
chemotaxis
The directed movement of a motile cell or organism, or the directed growth of a cell guided by a specific chemical concentration gradient. Movement may be towards a higher concentration (positive chemotaxis) or towards a lower concentration (negative chemotaxis).
response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
inflammatory response
The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages.
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
cell communication
Any process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
cell surface receptor linked signal transduction
Any series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of an extracellular ligand to a receptor on the surface of the target cell.
enzyme linked receptor protein signaling pathway
Any series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of an extracellular ligand to a receptor on the surface of the target cell, where the receptor possesses catalytic activity or is closely associated with an enzyme such as a protein kinase.
intracellular signaling cascade
A series of reactions within the cell that occur as a result of a single trigger reaction or compound.
protein kinase cascade
A series of reactions, mediated by protein kinases, which occurs as a result of a single trigger reaction or compound.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis of an organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
tissue development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a tissue over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
hemostasis
The stopping of bleeding (loss of body fluid) or the arrest of the circulation to an organ or part.
behavior
The specific actions or reactions of an organism in response to external or internal stimuli. Patterned activity of a whole organism in a manner dependent upon some combination of that organism's internal state and external conditions.
locomotory behavior
The specific movement from place to place of an organism in response to external or internal stimuli. Locomotion of a whole organism in a manner dependent upon some combination of that organism's internal state and external conditions.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cell death
The specific activation or halting of processes within a cell so that its vital functions markedly cease, rather than simply deteriorating gradually over time, which culminates in cell death.
programmed cell death
Cell death resulting from activation of endogenous cellular processes.
cell proliferation
The multiplication or reproduction of cells, resulting in the expansion of a cell population.
positive regulation of cell proliferation
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of cell proliferation.
response to external stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an external stimulus.
response to wounding
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to the organism.
positive regulation of metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
regulation of signal transduction
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction.
positive regulation of signal transduction
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction.
negative regulation of signal transduction
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of protein kinase cascade
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of a series of reactions, mediated by protein kinases, which occurs as a result of a single trigger reaction or compound.
regulation of cell communication
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell communication. Cell communication is the process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
positive regulation of cell communication
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell communication. Cell communication is the process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
negative regulation of cell communication
Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of cell communication. Cell communication is the process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
positive regulation of protein kinase cascade
Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of a series of reactions, mediated by protein kinases, which occurs as a result of a single trigger reaction or compound.
death
A permanent cessation of all vital functions: the end of life; can be applied to a whole organism or to a part of an organism.
cell migration
The orderly movement of cells from one site to another, often during the development of a multicellular organism or multicellular structure.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general. Includes protein modification.
antigen processing and presentation
The process by which an antigen-presenting cell expresses antigen (peptide or lipid) on its cell surface in association with an MHC protein complex.
cell differentiation
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate.
regulation of ossification
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of bone formation.
respiratory tube development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the respiratory tube over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The respiratory tube is assumed to mean any tube in the respiratory tract.
lung development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the lung over time, from its formation to the mature structure. In all air-breathing vertebrates the lungs are developed from the ventral wall of the oesophagus as a pouch which divides into two sacs. In amphibians and many reptiles the lungs retain very nearly this primitive sac-like character, but in the higher forms the connection with the esophagus becomes elongated into the windpipe and the inner walls of the sacs become more and more divided, until, in the mammals, the air spaces become minutely divided into tubes ending in small air cells, in the walls of which the blood circulates in a fine network of capillaries. In mammals the lungs are more or less divided into lobes, and each lung occupies a separate cavity in the thorax.
regulation of cell migration
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of protein modification process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the covalent alteration of one or more amino acid residues within a protein.
positive regulation of protein modification process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the covalent alteration of one or more amino acid residues within a protein.
regulation of cellular protein metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein, occurring at the level of an individual cell.
positive regulation of cellular protein metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein, occurring at the level of an individual cell.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of localization
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location.
regulation of tissue remodeling
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of tissue remodeling.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
tube development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a tube over time, from its initial formation to a mature structure. Epithelial and endothelial tubes transport gases, liquids and cells from one site to another and form the basic structure of many organs and tissues including lung and trachea, kidney, the mammary gland, the vascular system and the gastrointestinal and urinary-genital tracts.
locomotion
Self-propelled movement of a cell or organism from one location to another.
regulation of locomotion
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of locomotion of a cell or organism.
wound healing
The series of events that restore integrity to a damaged tissue, following an injury.
regulation of cell proliferation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell proliferation.
response to chemical stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a chemical stimulus.
taxis
The directed movement of a motile cell or organism in response to an external stimulus.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins.
biopolymer modification
The covalent alteration of one or more monomeric units in a polypeptide, polynucleotide, polysaccharide, or other biological polymer, resulting in a change in its properties.
regulation of system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a system process, a multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general, occurring at the level of an individual cell. Includes protein modification.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
positive regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
regulation of osteoblast differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of osteoblast differentiation.
positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of osteoblast differentiation.
bone remodeling
The continuous turnover of bone matrix and mineral that involves first, an increase in resorption (osteoclastic activity) and later, reactive bone formation (osteoblastic activity). The process of bone remodeling takes place in the adult skeleton at discrete foci. The process ensures the mechanical integrity of the skeleton throughout life and plays an important role in calcium homeostasis. An imbalance in the regulation of bone resorption and bone formation results in many of the metabolic bone diseases, such as osteoporosis.
regulation of bone remodeling
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of bone remodeling, the processes of bone formation and resorption that combine to maintain skeletal integrity.
antigen processing and presentation of peptide antigen
The process by which an antigen-presenting cell expresses peptide antigen in association with an MHC protein complex on its cell surface, including proteolysis and transport steps for the peptide antigen both prior to and following assembly with the MHC protein complex. The peptide antigen is typically, but not always, processed from an endogenous or exogenous protein.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
blood vessel morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of blood vessels are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. The blood vessel is the vasculature carrying blood.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
anatomical structure formation
The process pertaining to the initial formation of an anatomical structure from unspecified parts. This process begins with the specific processes that contribute to the appearance of the discrete structure and ends when the structural rudiment is recognizable. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
tissue remodeling
The reorganization or renovation of existing tissues. This process can either change the characteristics of a tissue such as in blood vessel remodeling, or result in the dynamic equilibrium of a tissue such as in bone remodeling.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
cell motility
Any process involved in the controlled movement of a cell that results in translocation of the cell from one place to another.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of developmental process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
coagulation
The process by which a fluid solution, or part of it, changes into a solid or semisolid mass.
regulation of body fluid levels
Any process that modulates the levels of body fluids.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
leukocyte migration
The movement of leukocytes within or between different tissues and organs of the body.
positive regulation of developmental process
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
cartilage development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cartilage over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cartilage is a connective tissue dominated by extracellular matrix containing collagen type II and large amounts of proteoglycan, particularly chondroitin sulfate.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
positive regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of an organismal process, any of the processes pertinent to the function of an organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
negative regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of an organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of an organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
regulation of protein metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein.
positive regulation of protein metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein.
regulation of cell motion
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the movement of a cell.
localization of cell
Any process by which a cell is transported to, and/or maintained in, a specific location.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
bone development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of bone over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Bone is the hard skeletal connective tissue consisting of both mineral and cellular components.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of biological quality
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological quality. A biological quality is a measurable attribute of an organism or part of an organism, such as size, mass, shape, color, etc.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
positive regulation of metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
positive regulation of developmental process
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
positive regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of an organismal process, any of the processes pertinent to the function of an organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
negative regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of an organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of an organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
regulation of locomotion
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of locomotion of a cell or organism.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of developmental process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
regulation of localization
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
positive regulation of metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
cell motility
Any process involved in the controlled movement of a cell that results in translocation of the cell from one place to another.
positive regulation of cell proliferation
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of cell proliferation.
positive regulation of cell communication
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell communication. Cell communication is the process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
negative regulation of cell communication
Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of cell communication. Cell communication is the process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
signal transduction
The cascade of processes by which a signal interacts with a receptor, causing a change in the level or activity of a second messenger or other downstream target, and ultimately effecting a change in the functioning of the cell.
regulation of cell communication
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell communication. Cell communication is the process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cell proliferation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell proliferation.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of cell motion
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the movement of a cell.
regulation of tissue remodeling
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of tissue remodeling.
regulation of system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a system process, a multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system.
positive regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of an organismal process, any of the processes pertinent to the function of an organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
negative regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of an organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of an organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
anatomical structure formation
The process pertaining to the initial formation of an anatomical structure from unspecified parts. This process begins with the specific processes that contribute to the appearance of the discrete structure and ends when the structural rudiment is recognizable. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
cell death
The specific activation or halting of processes within a cell so that its vital functions markedly cease, rather than simply deteriorating gradually over time, which culminates in cell death.
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
tube development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a tube over time, from its initial formation to a mature structure. Epithelial and endothelial tubes transport gases, liquids and cells from one site to another and form the basic structure of many organs and tissues including lung and trachea, kidney, the mammary gland, the vascular system and the gastrointestinal and urinary-genital tracts.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
regulation of ossification
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of bone formation.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
positive regulation of developmental process
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
positive regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
regulation of cell motion
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the movement of a cell.
response to wounding
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to the organism.
taxis
The directed movement of a motile cell or organism in response to an external stimulus.
chemotaxis
The directed movement of a motile cell or organism, or the directed growth of a cell guided by a specific chemical concentration gradient. Movement may be towards a higher concentration (positive chemotaxis) or towards a lower concentration (negative chemotaxis).
cell motion
Any process involved in the controlled movement of a cell.
regulation of body fluid levels
Any process that modulates the levels of body fluids.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general. Includes protein modification.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
regulation of protein metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein.
positive regulation of protein metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein.
regulation of cell migration
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration.
regulation of signal transduction
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction.
positive regulation of cell communication
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell communication. Cell communication is the process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
negative regulation of cell communication
Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of cell communication. Cell communication is the process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
positive regulation of signal transduction
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction.
negative regulation of signal transduction
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction.
positive regulation of cell proliferation
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of cell proliferation.
osteoblast differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the specialized features of an osteoblast, the mesodermal cell that gives rise to bone.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
positive regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
positive regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
regulation of bone remodeling
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of bone remodeling, the processes of bone formation and resorption that combine to maintain skeletal integrity.
blood coagulation
The sequential process by which the multiple coagulation factors of the blood interact, ultimately resulting in the formation of an insoluble fibrin clot; it may be divided into three stages: stage 1, the formation of intrinsic and extrinsic prothrombin converting principle; stage 2, the formation of thrombin; stage 3, the formation of stable fibrin polymers.
regulation of osteoblast differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of osteoblast differentiation.
positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of osteoblast differentiation.
regulation of osteoblast differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of osteoblast differentiation.
organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis of an organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
tissue development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a tissue over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
respiratory tube development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the respiratory tube over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The respiratory tube is assumed to mean any tube in the respiratory tract.
ossification
The formation of bone or of a bony substance, or the conversion of fibrous tissue or of cartilage into bone or a bony substance.
regulation of cell migration
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration.
leukocyte migration
The movement of leukocytes within or between different tissues and organs of the body.
inflammatory response
The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages.
taxis
The directed movement of a motile cell or organism in response to an external stimulus.
positive regulation of cellular protein metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein, occurring at the level of an individual cell.
positive regulation of cellular protein metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein, occurring at the level of an individual cell.
regulation of cellular protein metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein, occurring at the level of an individual cell.
positive regulation of protein metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein.
cellular protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general, occurring at the level of an individual cell. Includes protein modification.
protein modification process
The covalent alteration of one or more amino acids occurring in proteins, peptides and nascent polypeptides (co-translational, post-translational modifications). Includes the modification of charged tRNAs that are destined to occur in a protein (pre-translation modification).
regulation of cellular protein metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein, occurring at the level of an individual cell.
positive regulation of cellular protein metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein, occurring at the level of an individual cell.
positive regulation of signal transduction
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction.
negative regulation of signal transduction
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction.
positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of osteoblast differentiation.
lung development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the lung over time, from its formation to the mature structure. In all air-breathing vertebrates the lungs are developed from the ventral wall of the oesophagus as a pouch which divides into two sacs. In amphibians and many reptiles the lungs retain very nearly this primitive sac-like character, but in the higher forms the connection with the esophagus becomes elongated into the windpipe and the inner walls of the sacs become more and more divided, until, in the mammals, the air spaces become minutely divided into tubes ending in small air cells, in the walls of which the blood circulates in a fine network of capillaries. In mammals the lungs are more or less divided into lobes, and each lung occupies a separate cavity in the thorax.
cartilage development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cartilage over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cartilage is a connective tissue dominated by extracellular matrix containing collagen type II and large amounts of proteoglycan, particularly chondroitin sulfate.
bone development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of bone over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Bone is the hard skeletal connective tissue consisting of both mineral and cellular components.
regulation of ossification
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of bone formation.
angiogenesis
Blood vessel formation when new vessels emerge from the proliferation of pre-existing blood vessels.
blood coagulation
The sequential process by which the multiple coagulation factors of the blood interact, ultimately resulting in the formation of an insoluble fibrin clot; it may be divided into three stages: stage 1, the formation of intrinsic and extrinsic prothrombin converting principle; stage 2, the formation of thrombin; stage 3, the formation of stable fibrin polymers.
positive regulation of protein modification process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the covalent alteration of one or more amino acid residues within a protein.
regulation of protein modification process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the covalent alteration of one or more amino acid residues within a protein.
positive regulation of protein modification process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the covalent alteration of one or more amino acid residues within a protein.
regulation of protein kinase cascade
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of a series of reactions, mediated by protein kinases, which occurs as a result of a single trigger reaction or compound.
positive regulation of protein kinase cascade
Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of a series of reactions, mediated by protein kinases, which occurs as a result of a single trigger reaction or compound.
positive regulation of protein kinase cascade
Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of a series of reactions, mediated by protein kinases, which occurs as a result of a single trigger reaction or compound.
blood vessel morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of blood vessels are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. The blood vessel is the vasculature carrying blood.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
MHC class I protein complex
A transmembrane protein complex composed of a MHC class I alpha chain and an invariant beta2-microglobin chain, and with or without a bound peptide antigen. Class I here refers to classical class I molecules.
extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
extracellular space
That part of a multicellular organism outside the cells proper, usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
MHC protein complex
A transmembrane protein complex composed of an MHC alpha chain and, in most cases, either an MHC class II beta chain or an invariant beta2-microglobin chain, and with or without a bound peptide, lipid, or polysaccharide antigen.
protein complex
Any macromolecular complex composed of two or more polypeptide subunits, which may or may not be identical. Protein complexes may have other associated non-protein prosthetic groups, such as nucleotides, metal ions or carbohydrate groups.
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
all
This term is the most general term possible
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
MHC protein complex
A transmembrane protein complex composed of an MHC alpha chain and, in most cases, either an MHC class II beta chain or an invariant beta2-microglobin chain, and with or without a bound peptide, lipid, or polysaccharide antigen.

protein binding
Interacting selectively with any protein or protein complex (a complex of two or more proteins that may include other nonprotein molecules).
molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
receptor binding
Interacting selectively with one or more specific sites on a receptor molecule, a macromolecule that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function.
signal transducer activity
Mediates the transfer of a signal from the outside to the inside of a cell by means other than the introduction of the signal molecule itself into the cell.
receptor activity
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell activity.
transmembrane receptor activity
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell activity, and spanning to the membrane of either the cell or an organelle.
cytokine activity
Functions to control the survival, growth, differentiation and effector function of tissues and cells.
binding
The selective, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
growth factor activity
The function that stimulates a cell to grow or proliferate. Most growth factors have other actions besides the induction of cell growth or proliferation.
MHC class I receptor activity
Combining with an MHC class I protein complex to initiate a change in cellular activity. Class I here refers to classical class I molecules.
molecular transducer activity
The molecular function that accepts an input of one form and creates an output of a different form.
all
This term is the most general term possible
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 04060 | 1.591e-04 | 6.417 | 21 | 115 | Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction |
| 04610 | 5.283e-03 | 1.842 | 9 | 33 | Complement and coagulation cascades |
| 05332 | 4.122e-02 | 1.172 | 6 | 21 | Graft-versus-host disease |
| 04630 | 4.589e-02 | 4.855 | 13 | 87 | Jak-STAT signaling pathway |
| 04010 | 4.864e-02 | 10.21 | 21 | 183 | MAPK signaling pathway |
ABLIM3actin binding LIM protein family, member 3 (205730_s_at), score: -0.28 ACBD3acyl-Coenzyme A binding domain containing 3 (202323_s_at), score: -0.32 ACSL1acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 1 (201963_at), score: -0.3 ACVR1activin A receptor, type I (203935_at), score: -0.33 ADIPOR2adiponectin receptor 2 (201346_at), score: -0.43 ADRA2Aadrenergic, alpha-2A-, receptor (209869_at), score: -0.44 AJAP1adherens junctions associated protein 1 (206460_at), score: -0.51 AKIRIN1akirin 1 (217893_s_at), score: -0.29 ANGPTL4angiopoietin-like 4 (221009_s_at), score: -0.9 ANK2ankyrin 2, neuronal (202920_at), score: -0.46 ANKLE2ankyrin repeat and LEM domain containing 2 (212201_at), score: -0.3 AQP3aquaporin 3 (Gill blood group) (39248_at), score: -0.46 ARID5AAT rich interactive domain 5A (MRF1-like) (213138_at), score: -0.45 ASAP2ArfGAP with SH3 domain, ankyrin repeat and PH domain 2 (206414_s_at), score: -0.35 ATP13A3ATPase type 13A3 (219558_at), score: -0.57 ATP2A2ATPase, Ca++ transporting, cardiac muscle, slow twitch 2 (212361_s_at), score: -0.3 ATP6V0A1ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal V0 subunit a1 (205095_s_at), score: -0.33 B3GNT2UDP-GlcNAc:betaGal beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 2 (219326_s_at), score: -0.49 B4GALT5UDP-Gal:betaGlcNAc beta 1,4- galactosyltransferase, polypeptide 5 (221484_at), score: -0.4 BBS1Bardet-Biedl syndrome 1 (218471_s_at), score: -0.32 BCKDHBbranched chain keto acid dehydrogenase E1, beta polypeptide (210653_s_at), score: -0.3 BCL7AB-cell CLL/lymphoma 7A (203795_s_at), score: -0.44 BHLHE40basic helix-loop-helix family, member e40 (201170_s_at), score: -0.44 BMP2bone morphogenetic protein 2 (205289_at), score: -0.52 BMP6bone morphogenetic protein 6 (206176_at), score: -0.35 BMPR2bone morphogenetic protein receptor, type II (serine/threonine kinase) (210214_s_at), score: -0.57 BTN3A1butyrophilin, subfamily 3, member A1 (209770_at), score: -0.3 C14orf1chromosome 14 open reading frame 1 (217188_s_at), score: -0.31 C17orf71chromosome 17 open reading frame 71 (218514_at), score: -0.29 C17orf91chromosome 17 open reading frame 91 (214696_at), score: -0.66 C19orf28chromosome 19 open reading frame 28 (220178_at), score: -0.42 C1Rcomplement component 1, r subcomponent (212067_s_at), score: -0.6 C1RLcomplement component 1, r subcomponent-like (218983_at), score: -0.28 C1Scomplement component 1, s subcomponent (208747_s_at), score: -0.39 C21orf45chromosome 21 open reading frame 45 (219004_s_at), score: 0.87 C4orf18chromosome 4 open reading frame 18 (219872_at), score: -0.41 C6orf145chromosome 6 open reading frame 145 (212923_s_at), score: -0.32 CADPS2Ca++-dependent secretion activator 2 (219572_at), score: -0.4 CASP1caspase 1, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase (interleukin 1, beta, convertase) (211368_s_at), score: -0.36 CASP4caspase 4, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase (209310_s_at), score: -0.37 CBFBcore-binding factor, beta subunit (206788_s_at), score: -0.39 CBLBCas-Br-M (murine) ecotropic retroviral transforming sequence b (209682_at), score: -0.48 CCL2chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 (216598_s_at), score: -0.58 CCRL1chemokine (C-C motif) receptor-like 1 (220351_at), score: -0.3 CD302CD302 molecule (203799_at), score: -0.53 CD55CD55 molecule, decay accelerating factor for complement (Cromer blood group) (201925_s_at), score: -0.48 CD58CD58 molecule (211744_s_at), score: -0.31 CDC14BCDC14 cell division cycle 14 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (208022_s_at), score: -0.33 CDC42SE1CDC42 small effector 1 (218157_x_at), score: -0.3 CDV3CDV3 homolog (mouse) (213548_s_at), score: -0.36 CDYLchromodomain protein, Y-like (203100_s_at), score: -0.33 CHIC2cysteine-rich hydrophobic domain 2 (219492_at), score: -0.42 CHMP1Bchromatin modifying protein 1B (218178_s_at), score: -0.37 CHST11carbohydrate (chondroitin 4) sulfotransferase 11 (219634_at), score: -0.32 CLCF1cardiotrophin-like cytokine factor 1 (219500_at), score: -0.33 CLIP1CAP-GLY domain containing linker protein 1 (210716_s_at), score: -0.29 CLIP3CAP-GLY domain containing linker protein 3 (212358_at), score: -0.28 COL14A1collagen, type XIV, alpha 1 (212865_s_at), score: -0.33 COL15A1collagen, type XV, alpha 1 (203477_at), score: -0.75 COQ10Bcoenzyme Q10 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (219397_at), score: -0.38 CORINcorin, serine peptidase (220356_at), score: -0.46 CPA3carboxypeptidase A3 (mast cell) (205624_at), score: -0.35 CREG1cellular repressor of E1A-stimulated genes 1 (201200_at), score: -0.57 CRISPLD2cysteine-rich secretory protein LCCL domain containing 2 (221541_at), score: -0.32 CSGALNACT2chondroitin sulfate N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 2 (222235_s_at), score: -0.46 CSRNP2cysteine-serine-rich nuclear protein 2 (221260_s_at), score: -0.35 CST3cystatin C (201360_at), score: -0.36 CTSAcathepsin A (200661_at), score: -0.32 CTSDcathepsin D (200766_at), score: -0.29 CTSOcathepsin O (203758_at), score: -0.44 CXCL3chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 3 (207850_at), score: -0.49 CXCL6chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 6 (granulocyte chemotactic protein 2) (206336_at), score: -0.29 CYP51A1cytochrome P450, family 51, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 (216607_s_at), score: -0.54 DCNdecorin (211896_s_at), score: -0.44 DCP1ADCP1 decapping enzyme homolog A (S. cerevisiae) (218508_at), score: -0.29 DDX3YDEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 3, Y-linked (205000_at), score: -0.45 DGKDdiacylglycerol kinase, delta 130kDa (208072_s_at), score: -0.46 DHCR77-dehydrocholesterol reductase (201790_s_at), score: -0.31 DKK2dickkopf homolog 2 (Xenopus laevis) (219908_at), score: -0.44 DNASE2deoxyribonuclease II, lysosomal (214992_s_at), score: -0.42 DNMBPdynamin binding protein (212838_at), score: -0.3 DOCK9dedicator of cytokinesis 9 (212538_at), score: -0.55 DPP4dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 (211478_s_at), score: -0.5 DRAMdamage-regulated autophagy modulator (218627_at), score: -0.4 DSCR3Down syndrome critical region gene 3 (203635_at), score: -0.31 DUSP14dual specificity phosphatase 14 (203367_at), score: -0.32 DUSP3dual specificity phosphatase 3 (201536_at), score: -0.41 DUSP5dual specificity phosphatase 5 (209457_at), score: -0.33 ECM1extracellular matrix protein 1 (209365_s_at), score: -0.33 EDN1endothelin 1 (218995_s_at), score: -0.36 EFHD1EF-hand domain family, member D1 (209343_at), score: -0.36 EGR2early growth response 2 (Krox-20 homolog, Drosophila) (205249_at), score: -0.47 EGR3early growth response 3 (206115_at), score: -0.48 ENTPD7ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 7 (220153_at), score: -0.48 EPHA2EPH receptor A2 (203499_at), score: -0.3 EPHB3EPH receptor B3 (1438_at), score: 0.91 ERAP1endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 (214012_at), score: -0.4 F10coagulation factor X (205620_at), score: -0.57 F3coagulation factor III (thromboplastin, tissue factor) (204363_at), score: -0.47 FABP3fatty acid binding protein 3, muscle and heart (mammary-derived growth inhibitor) (214285_at), score: -0.28 FADS3fatty acid desaturase 3 (216080_s_at), score: -0.38 FAM108B1family with sequence similarity 108, member B1 (220285_at), score: -0.39 FAM13Bfamily with sequence similarity 13, member B (218518_at), score: -0.29 FBXW7F-box and WD repeat domain containing 7 (218751_s_at), score: -0.36 FCGRTFc fragment of IgG, receptor, transporter, alpha (218831_s_at), score: -0.29 FEM1Bfem-1 homolog b (C. elegans) (212367_at), score: -0.37 FGF1fibroblast growth factor 1 (acidic) (205117_at), score: -0.55 FGF2fibroblast growth factor 2 (basic) (204421_s_at), score: -0.39 FGF7fibroblast growth factor 7 (keratinocyte growth factor) (205782_at), score: -0.66 FHOD1formin homology 2 domain containing 1 (218530_at), score: -0.33 FOSBFBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog B (202768_at), score: -0.64 GABARAPL1GABA(A) receptor-associated protein like 1 (208868_s_at), score: -0.44 GABARAPL3GABA(A) receptors associated protein like 3 (pseudogene) (211458_s_at), score: -0.34 GADD45Agrowth arrest and DNA-damage-inducible, alpha (203725_at), score: -0.38 GAP43growth associated protein 43 (204471_at), score: 1 GCH1GTP cyclohydrolase 1 (204224_s_at), score: -0.45 GDF5growth differentiation factor 5 (206614_at), score: 0.91 GEMGTP binding protein overexpressed in skeletal muscle (204472_at), score: -0.68 GFPT2glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate transaminase 2 (205100_at), score: -0.29 GNA13guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), alpha 13 (206917_at), score: -0.29 GNPTABN-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate transferase, alpha and beta subunits (212959_s_at), score: -0.56 GNSglucosamine (N-acetyl)-6-sulfatase (203676_at), score: -0.29 GPNMBglycoprotein (transmembrane) nmb (201141_at), score: -0.78 GPR183G protein-coupled receptor 183 (205419_at), score: -0.58 GPR37G protein-coupled receptor 37 (endothelin receptor type B-like) (209631_s_at), score: -0.44 GRAMD3GRAM domain containing 3 (218706_s_at), score: -0.5 GRIK2glutamate receptor, ionotropic, kainate 2 (213845_at), score: -0.31 GRNgranulin (211284_s_at), score: -0.42 GSTM1glutathione S-transferase mu 1 (204550_x_at), score: -0.39 GSTT1glutathione S-transferase theta 1 (203815_at), score: -0.32 HBEGFheparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (203821_at), score: -0.7 HHEXhematopoietically expressed homeobox (215933_s_at), score: -0.29 HIPK3homeodomain interacting protein kinase 3 (210148_at), score: -0.52 HIST1H2AChistone cluster 1, H2ac (215071_s_at), score: -0.29 HIVEP1human immunodeficiency virus type I enhancer binding protein 1 (204512_at), score: -0.46 HIVEP2human immunodeficiency virus type I enhancer binding protein 2 (212642_s_at), score: -0.4 HK2hexokinase 2 (202934_at), score: -0.61 HLA-Amajor histocompatibility complex, class I, A (213932_x_at), score: -0.34 HLA-Amajor histocompatibility complex, class I, A (217436_x_at), score: -0.36 HLA-Bmajor histocompatibility complex, class I, B (211911_x_at), score: -0.36 HLA-Cmajor histocompatibility complex, class I, C (211799_x_at), score: -0.56 HLA-Emajor histocompatibility complex, class I, E (200904_at), score: -0.55 HLA-Fmajor histocompatibility complex, class I, F (204806_x_at), score: -0.48 HLXH2.0-like homeobox (214438_at), score: -0.58 HMGB3L1high-mobility group box 3-like 1 (216548_x_at), score: 0.91 HMOX1heme oxygenase (decycling) 1 (203665_at), score: -0.53 HOXB6homeobox B6 (205366_s_at), score: -0.42 HOXB7homeobox B7 (204779_s_at), score: -0.36 HSPA12Aheat shock 70kDa protein 12A (214434_at), score: -0.31 HTR2A5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 2A (207135_at), score: -0.52 ICAM1intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (202638_s_at), score: -0.59 IDI1isopentenyl-diphosphate delta isomerase 1 (204615_x_at), score: -0.51 IDSiduronate 2-sulfatase (202439_s_at), score: -0.37 IDUAiduronidase, alpha-L- (205059_s_at), score: -0.3 IGFBP5insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 (203424_s_at), score: -0.34 IGFBP7insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 (201162_at), score: -0.39 IL11interleukin 11 (206924_at), score: -0.57 IL1RAPinterleukin 1 receptor accessory protein (205227_at), score: -0.55 IL1RL1interleukin 1 receptor-like 1 (207526_s_at), score: -0.45 IL23Ainterleukin 23, alpha subunit p19 (211796_s_at), score: -0.31 IL6interleukin 6 (interferon, beta 2) (205207_at), score: -0.76 IL6STinterleukin 6 signal transducer (gp130, oncostatin M receptor) (211000_s_at), score: -0.34 IL8interleukin 8 (211506_s_at), score: -0.65 INPP1inositol polyphosphate-1-phosphatase (202794_at), score: -0.33 INSIG1insulin induced gene 1 (201627_s_at), score: -0.48 ITGA1integrin, alpha 1 (214660_at), score: -0.53 ITGA4integrin, alpha 4 (antigen CD49D, alpha 4 subunit of VLA-4 receptor) (205885_s_at), score: -0.29 ITPR3inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor, type 3 (201189_s_at), score: -0.31 JARID2jumonji, AT rich interactive domain 2 (203297_s_at), score: -0.54 JHDM1Djumonji C domain containing histone demethylase 1 homolog D (S. cerevisiae) (221778_at), score: -0.54 JMJD3jumonji domain containing 3, histone lysine demethylase (213146_at), score: -0.6 JMJD6jumonji domain containing 6 (212722_s_at), score: -0.45 JUNDjun D proto-oncogene (203751_x_at), score: -0.46 KHDRBS3KH domain containing, RNA binding, signal transduction associated 3 (209781_s_at), score: -0.34 KIAA0247KIAA0247 (202181_at), score: -0.51 KIAA1024KIAA1024 (215081_at), score: -0.31 KIAA1644KIAA1644 (52837_at), score: -0.45 KLHL21kelch-like 21 (Drosophila) (203068_at), score: -0.5 KPNA4karyopherin alpha 4 (importin alpha 3) (209653_at), score: -0.29 LAMA5laminin, alpha 5 (210150_s_at), score: -0.3 LBHlimb bud and heart development homolog (mouse) (221011_s_at), score: -0.4 LDLRlow density lipoprotein receptor (202068_s_at), score: -0.31 LGALS3BPlectin, galactoside-binding, soluble, 3 binding protein (200923_at), score: -0.34 LHFPlipoma HMGIC fusion partner (218656_s_at), score: -0.45 LIFleukemia inhibitory factor (cholinergic differentiation factor) (205266_at), score: -0.74 LIMS1LIM and senescent cell antigen-like domains 1 (207198_s_at), score: -0.43 LITAFlipopolysaccharide-induced TNF factor (200706_s_at), score: -0.31 LMBRD1LMBR1 domain containing 1 (218191_s_at), score: -0.54 LMCD1LIM and cysteine-rich domains 1 (218574_s_at), score: -0.68 LOC100128809similar to hCG2045829 (215707_s_at), score: -0.33 LOH3CR2Aloss of heterozygosity, 3, chromosomal region 2, gene A (220244_at), score: -0.36 LRIG1leucine-rich repeats and immunoglobulin-like domains 1 (211596_s_at), score: -0.45 LRRC2leucine rich repeat containing 2 (219949_at), score: -0.29 LUZP1leucine zipper protein 1 (221832_s_at), score: -0.3 LY96lymphocyte antigen 96 (206584_at), score: -0.29 MAFv-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog (avian) (209348_s_at), score: -0.38 MAGI2membrane associated guanylate kinase, WW and PDZ domain containing 2 (209737_at), score: -0.49 MAN1C1mannosidase, alpha, class 1C, member 1 (218918_at), score: -0.63 MAN2B2mannosidase, alpha, class 2B, member 2 (214703_s_at), score: -0.29 MANBAmannosidase, beta A, lysosomal (203778_at), score: -0.31 MAP1Smicrotubule-associated protein 1S (218522_s_at), score: -0.3 MAP2K3mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 3 (207667_s_at), score: -0.61 MAP3K2mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 2 (221695_s_at), score: -0.34 MAP3K4mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 4 (216199_s_at), score: -0.49 MAP3K7IP1mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 7 interacting protein 1 (203901_at), score: 0.89 MAP3K7IP2mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 7 interacting protein 2 (210284_s_at), score: -0.39 MARCH2membrane-associated ring finger (C3HC4) 2 (210075_at), score: -0.28 MAXMYC associated factor X (210734_x_at), score: -0.31 MEF2Amyocyte enhancer factor 2A (214684_at), score: -0.28 MEIS1Meis homeobox 1 (204069_at), score: -0.41 MEIS3P1Meis homeobox 3 pseudogene 1 (214077_x_at), score: -0.52 MFAP4microfibrillar-associated protein 4 (212713_at), score: -0.57 MSCmusculin (activated B-cell factor-1) (209928_s_at), score: -0.33 MTSS1metastasis suppressor 1 (203037_s_at), score: -0.62 MYO1Dmyosin ID (212338_at), score: -0.34 NAB1NGFI-A binding protein 1 (EGR1 binding protein 1) (208047_s_at), score: -0.37 NAMPTnicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (217738_at), score: -0.53 NDRG1N-myc downstream regulated 1 (200632_s_at), score: -0.33 NEDD9neural precursor cell expressed, developmentally down-regulated 9 (202149_at), score: -0.41 NFATC1nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic, calcineurin-dependent 1 (210162_s_at), score: -0.79 NFIL3nuclear factor, interleukin 3 regulated (203574_at), score: -0.48 NFKB1nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 1 (209239_at), score: -0.62 NFKB2nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 2 (p49/p100) (207535_s_at), score: -0.29 NID1nidogen 1 (202008_s_at), score: -0.43 NINJ1ninjurin 1 (203045_at), score: -0.52 NPnucleoside phosphorylase (201695_s_at), score: -0.39 NPC1Niemann-Pick disease, type C1 (202679_at), score: -0.45 NPC2Niemann-Pick disease, type C2 (200701_at), score: -0.49 NR3C1nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group C, member 1 (glucocorticoid receptor) (201866_s_at), score: -0.48 NR4A1nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 1 (202340_x_at), score: -0.47 NR4A3nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 3 (209959_at), score: -0.74 OLFML2Aolfactomedin-like 2A (213075_at), score: -0.44 OS9osteosarcoma amplified 9, endoplasmic reticulum associated protein (200714_x_at), score: -0.31 OSMRoncostatin M receptor (205729_at), score: -0.34 OSTM1osteopetrosis associated transmembrane protein 1 (218196_at), score: -0.31 P2RX4purinergic receptor P2X, ligand-gated ion channel, 4 (204088_at), score: -0.33 PANX1pannexin 1 (204715_at), score: -0.33 PCDH7protocadherin 7 (205534_at), score: -0.32 PDGFAplatelet-derived growth factor alpha polypeptide (205463_s_at), score: -0.62 PDGFDplatelet derived growth factor D (219304_s_at), score: -0.59 PDLIM3PDZ and LIM domain 3 (209621_s_at), score: -0.39 PHTF2putative homeodomain transcription factor 2 (217097_s_at), score: -0.33 PIK3CDphosphoinositide-3-kinase, catalytic, delta polypeptide (203879_at), score: -0.57 PIONpigeon homolog (Drosophila) (222150_s_at), score: -0.38 PKP2plakophilin 2 (207717_s_at), score: -0.33 PLAURplasminogen activator, urokinase receptor (211924_s_at), score: -0.38 PLK3polo-like kinase 3 (Drosophila) (204958_at), score: -0.4 PLSCR4phospholipid scramblase 4 (218901_at), score: -0.42 PMEPA1prostate transmembrane protein, androgen induced 1 (217875_s_at), score: -0.86 POLR1Cpolymerase (RNA) I polypeptide C, 30kDa (207515_s_at), score: -0.38 PPAP2Aphosphatidic acid phosphatase type 2A (209147_s_at), score: -0.42 PPARDperoxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta (37152_at), score: -0.52 PPLperiplakin (203407_at), score: -0.37 PPP1R13Lprotein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 13 like (218849_s_at), score: -0.3 PPP1R15Aprotein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 15A (202014_at), score: -0.3 PRELPproline/arginine-rich end leucine-rich repeat protein (204223_at), score: -0.3 PROS1protein S (alpha) (207808_s_at), score: -0.37 PSAPprosaposin (200866_s_at), score: -0.29 PTGDSprostaglandin D2 synthase 21kDa (brain) (212187_x_at), score: -0.42 PTHLHparathyroid hormone-like hormone (211756_at), score: -0.36 PTPN1protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 1 (202716_at), score: -0.3 PTPN12protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 12 (216915_s_at), score: -0.31 PTPREprotein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, E (221840_at), score: -0.33 RAB33ARAB33A, member RAS oncogene family (206039_at), score: -0.38 RABGEF1RAB guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 1 (218310_at), score: -0.32 RABGGTBRab geranylgeranyltransferase, beta subunit (209180_at), score: -0.4 RAMP1receptor (G protein-coupled) activity modifying protein 1 (204916_at), score: -0.29 RANBP2RAN binding protein 2 (201711_x_at), score: -0.43 RAPGEF2Rap guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 2 (203097_s_at), score: -0.43 RCAN1regulator of calcineurin 1 (215253_s_at), score: -0.3 RCAN2regulator of calcineurin 2 (203498_at), score: -0.49 RCL1RNA terminal phosphate cyclase-like 1 (218544_s_at), score: -0.45 RGPD5RANBP2-like and GRIP domain containing 5 (210676_x_at), score: -0.43 RGS2regulator of G-protein signaling 2, 24kDa (202388_at), score: -0.69 RGS3regulator of G-protein signaling 3 (203823_at), score: -0.33 RGS4regulator of G-protein signaling 4 (204338_s_at), score: -0.3 RIOK3RIO kinase 3 (yeast) (202129_s_at), score: -0.29 RNASET2ribonuclease T2 (217983_s_at), score: -0.32 RNF103ring finger protein 103 (202636_at), score: -0.39 RNF25ring finger protein 25 (218861_at), score: -0.29 RPS4Y1ribosomal protein S4, Y-linked 1 (201909_at), score: -0.43 RRADRas-related associated with diabetes (204802_at), score: -0.64 RUNX1runt-related transcription factor 1 (209360_s_at), score: -0.64 RWDD2ARWD domain containing 2A (213555_at), score: -0.28 SAT1spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase 1 (213988_s_at), score: -0.41 SCARB1scavenger receptor class B, member 1 (201819_at), score: -0.39 SCARB2scavenger receptor class B, member 2 (201647_s_at), score: -0.3 SCPEP1serine carboxypeptidase 1 (218217_at), score: -0.29 SEMA5Asema domain, seven thrombospondin repeats (type 1 and type 1-like), transmembrane domain (TM) and short cytoplasmic domain, (semaphorin) 5A (205405_at), score: -0.3 SENP5SUMO1/sentrin specific peptidase 5 (213184_at), score: -0.32 SERPINB2serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade B (ovalbumin), member 2 (204614_at), score: -0.49 SETXsenataxin (201964_at), score: -0.37 SFRS5splicing factor, arginine/serine-rich 5 (212266_s_at), score: -0.37 SGK1serum/glucocorticoid regulated kinase 1 (201739_at), score: -0.35 SGPP1sphingosine-1-phosphate phosphatase 1 (221268_s_at), score: -0.31 SH3BGRLSH3 domain binding glutamic acid-rich protein like (201311_s_at), score: -0.3 SHBSrc homology 2 domain containing adaptor protein B (204657_s_at), score: -0.4 SKILSKI-like oncogene (206675_s_at), score: -0.45 SLC10A3solute carrier family 10 (sodium/bile acid cotransporter family), member 3 (204928_s_at), score: -0.34 SLC19A2solute carrier family 19 (thiamine transporter), member 2 (209681_at), score: -0.63 SLC1A1solute carrier family 1 (neuronal/epithelial high affinity glutamate transporter, system Xag), member 1 (213664_at), score: -0.3 SLC20A2solute carrier family 20 (phosphate transporter), member 2 (202744_at), score: -0.35 SLC2A3P1solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 3 pseudogene 1 (221751_at), score: -0.3 SLC39A8solute carrier family 39 (zinc transporter), member 8 (209267_s_at), score: -0.36 SLC46A3solute carrier family 46, member 3 (214719_at), score: -0.3 SLCO3A1solute carrier organic anion transporter family, member 3A1 (219229_at), score: -0.34 SMAD7SMAD family member 7 (204790_at), score: -0.29 SMOXspermine oxidase (210357_s_at), score: -0.66 SMURF1SMAD specific E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1 (212666_at), score: -0.4 SOCS2suppressor of cytokine signaling 2 (203373_at), score: -0.37 SOD3superoxide dismutase 3, extracellular (205236_x_at), score: -0.3 SOX4SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 4 (201417_at), score: -0.55 SOX9SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 9 (202935_s_at), score: -0.49 SPATA2Lspermatogenesis associated 2-like (214965_at), score: -0.43 SPHK1sphingosine kinase 1 (219257_s_at), score: -0.34 SPRED2sprouty-related, EVH1 domain containing 2 (212458_at), score: -0.61 SPRY2sprouty homolog 2 (Drosophila) (204011_at), score: -0.58 SPRY4sprouty homolog 4 (Drosophila) (221489_s_at), score: -0.62 SPSB1splA/ryanodine receptor domain and SOCS box containing 1 (219677_at), score: -0.34 SQLEsqualene epoxidase (213562_s_at), score: -0.5 SRFserum response factor (c-fos serum response element-binding transcription factor) (202401_s_at), score: -0.55 ST3GAL1ST3 beta-galactoside alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase 1 (208322_s_at), score: -0.51 STBD1starch binding domain 1 (203986_at), score: -0.49 STK38Lserine/threonine kinase 38 like (212572_at), score: -0.7 SULF1sulfatase 1 (212353_at), score: -0.47 SVEP1sushi, von Willebrand factor type A, EGF and pentraxin domain containing 1 (213247_at), score: -0.54 TBX3T-box 3 (219682_s_at), score: -0.57 TEX2testis expressed 2 (218099_at), score: -0.35 TFPItissue factor pathway inhibitor (lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor) (209676_at), score: -0.3 TGFBR1transforming growth factor, beta receptor 1 (206943_at), score: -0.57 TGM2transglutaminase 2 (C polypeptide, protein-glutamine-gamma-glutamyltransferase) (201042_at), score: -0.33 THBDthrombomodulin (203887_s_at), score: -0.57 TICAM1toll-like receptor adaptor molecule 1 (213191_at), score: -0.38 TK1thymidine kinase 1, soluble (202338_at), score: 0.88 TM2D1TM2 domain containing 1 (211703_s_at), score: -0.53 TM6SF1transmembrane 6 superfamily member 1 (219892_at), score: -0.49 TMEM39Atransmembrane protein 39A (218615_s_at), score: -0.45 TMEM41Btransmembrane protein 41B (212623_at), score: -0.63 TMEM51transmembrane protein 51 (218815_s_at), score: -0.34 TMEM87Atransmembrane protein 87A (212204_at), score: -0.31 TNFAIP2tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 2 (202510_s_at), score: -0.48 TNFAIP3tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 3 (202644_s_at), score: -0.36 TNFAIP6tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 6 (206026_s_at), score: -0.39 TNFAIP8tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 8 (210260_s_at), score: -0.4 TNFRSF11Btumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 11b (204933_s_at), score: -0.35 TNFSF4tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 4 (207426_s_at), score: -0.6 TNS3tensin 3 (217853_at), score: -0.44 TNXBtenascin XB (216333_x_at), score: -0.3 TOM1target of myb1 (chicken) (202807_s_at), score: -0.34 TP53BP2tumor protein p53 binding protein, 2 (203120_at), score: -0.53 TP53I11tumor protein p53 inducible protein 11 (214667_s_at), score: -0.37 TPD52L1tumor protein D52-like 1 (203786_s_at), score: -0.37 TPP1tripeptidyl peptidase I (200742_s_at), score: -0.61 TPST1tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase 1 (204140_at), score: -0.49 TPST2tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase 2 (204079_at), score: -0.32 TRAF3TNF receptor-associated factor 3 (221571_at), score: -0.37 TRAPPC10trafficking protein particle complex 10 (209412_at), score: -0.31 TRIB1tribbles homolog 1 (Drosophila) (202241_at), score: -0.7 TRIM22tripartite motif-containing 22 (213293_s_at), score: -0.42 TRIM32tripartite motif-containing 32 (203846_at), score: -0.37 TTC17tetratricopeptide repeat domain 17 (218972_at), score: -0.36 TTPALtocopherol (alpha) transfer protein-like (219633_at), score: -0.31 UBA7ubiquitin-like modifier activating enzyme 7 (203281_s_at), score: -0.36 UTP3UTP3, small subunit (SSU) processome component, homolog (S. cerevisiae) (209486_at), score: -0.38 VCLvinculin (200930_s_at), score: -0.38 VDRvitamin D (1,25- dihydroxyvitamin D3) receptor (204255_s_at), score: -0.38 VEGFAvascular endothelial growth factor A (211527_x_at), score: -0.75 VPS37Bvacuolar protein sorting 37 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (221704_s_at), score: -0.3 WEE1WEE1 homolog (S. pombe) (212533_at), score: 0.92 WTAPWilms tumor 1 associated protein (210285_x_at), score: -0.35 WWTR1WW domain containing transcription regulator 1 (202132_at), score: -0.47 YIPF6Yip1 domain family, member 6 (212341_at), score: -0.33 YPEL5yippee-like 5 (Drosophila) (217783_s_at), score: -0.28 YRDCyrdC domain containing (E. coli) (218647_s_at), score: -0.58 ZFP36L2zinc finger protein 36, C3H type-like 2 (201367_s_at), score: 0.92 ZKSCAN3zinc finger with KRAB and SCAN domains 3 (211773_s_at), score: 0.91 ZMYM6zinc finger, MYM-type 6 (219924_s_at), score: -0.36 ZNF143zinc finger protein 143 (221873_at), score: -0.58 ZNF282zinc finger protein 282 (212892_at), score: -0.33 ZNF35zinc finger protein 35 (206096_at), score: -0.6 ZNF672zinc finger protein 672 (218068_s_at), score: -0.53
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486231.cel | 30 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485851.cel | 11 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| 46A.CEL | 1 | 3 | DS-mosaic | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-mosaic 1 |
| 2Twin.CEL | 2 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-twin 2 |
| 6Twin.CEL | 6 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-twin 6 |
| 5CTwin.CEL | 5 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | Down | DS-twin 5 |
| 1Twin.CEL | 1 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | Down | DS-twin 1 |