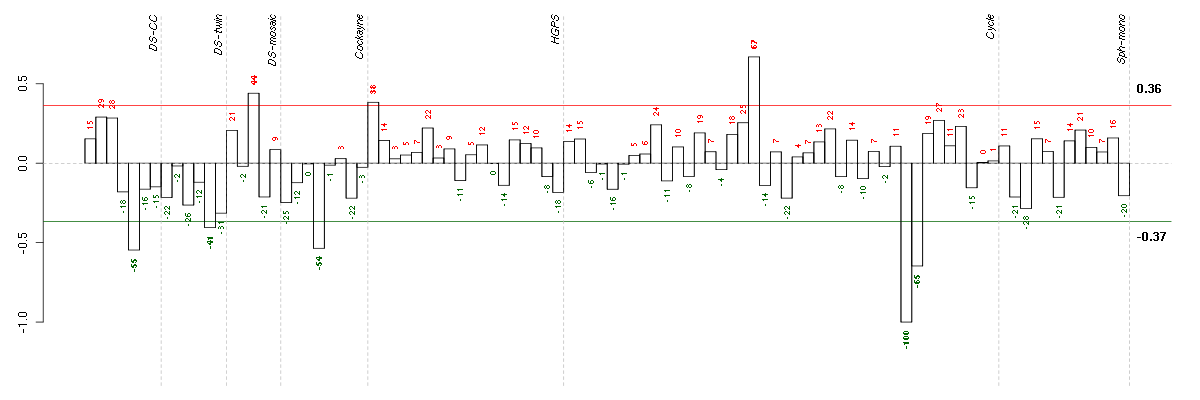

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of nervous tissue over time, from its formation to its mature state.
central nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the central nervous system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The central nervous system is the core nervous system that serves an integrating and coordinating function. In vertebrates it consists of the brain, spinal cord and spinal nerves. In those invertebrates with a central nervous system it typically consists of a brain, cerebral ganglia and a nerve cord.
brain development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the brain over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The brain is one of the two components of the central nervous system and is the center of thought and emotion. It is responsible for the coordination and control of bodily activities and the interpretation of information from the senses (sight, hearing, smell, etc.).
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
glial cell differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the specialized features of a glial cell.
negative regulation of cell development
Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
regulation of gliogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gliogenesis, the formation of mature glia.
negative regulation of gliogenesis
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of gliogenesis, the formation of mature glia.
cerebral cortex neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron residing in the cerebral cortex.
neurogenesis
Generation of cells within the nervous system.
cell differentiation
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate.
neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron.
forebrain development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the forebrain over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The forebrain is the anterior of the three primary divisions of the developing chordate brain or the corresponding part of the adult brain (in vertebrates, includes especially the cerebral hemispheres, the thalamus, and the hypothalamus and especially in higher vertebrates is the main control center for sensory and associative information processing, visceral functions, and voluntary motor functions).
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
gliogenesis
The process by which glial cells are generated. This includes the production of glial progenitors and their differentiation into mature glia.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
negative regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
regulation of glial cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of glia cell differentiation.
negative regulation of glial cell differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of glia cell differentiation.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
generation of neurons
The process by which nerve cells are generated. This includes the production of neuroblasts and their differentiation into neurons.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
negative regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of developmental process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
negative regulation of developmental process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
regulation of nervous system development
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of nervous system development, the origin and formation of nervous tissue.
regulation of cell development
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
all
This term is the most general term possible
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
negative regulation of developmental process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of developmental process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
negative regulation of developmental process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of nervous system development
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of nervous system development, the origin and formation of nervous tissue.
negative regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
negative regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
negative regulation of cell development
Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
negative regulation of cell development
Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
negative regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
negative regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
regulation of cell development
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
glial cell differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the specialized features of a glial cell.
negative regulation of gliogenesis
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of gliogenesis, the formation of mature glia.
neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron.
regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
regulation of gliogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gliogenesis, the formation of mature glia.
negative regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
cerebral cortex neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron residing in the cerebral cortex.
central nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the central nervous system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The central nervous system is the core nervous system that serves an integrating and coordinating function. In vertebrates it consists of the brain, spinal cord and spinal nerves. In those invertebrates with a central nervous system it typically consists of a brain, cerebral ganglia and a nerve cord.
neurogenesis
Generation of cells within the nervous system.
regulation of nervous system development
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of nervous system development, the origin and formation of nervous tissue.
brain development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the brain over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The brain is one of the two components of the central nervous system and is the center of thought and emotion. It is responsible for the coordination and control of bodily activities and the interpretation of information from the senses (sight, hearing, smell, etc.).
forebrain development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the forebrain over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The forebrain is the anterior of the three primary divisions of the developing chordate brain or the corresponding part of the adult brain (in vertebrates, includes especially the cerebral hemispheres, the thalamus, and the hypothalamus and especially in higher vertebrates is the main control center for sensory and associative information processing, visceral functions, and voluntary motor functions).
negative regulation of glial cell differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of glia cell differentiation.
negative regulation of gliogenesis
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of gliogenesis, the formation of mature glia.
regulation of glial cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of glia cell differentiation.
negative regulation of glial cell differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of glia cell differentiation.


CLCF1cardiotrophin-like cytokine factor 1 (219500_at), score: 0.82 CLDN11claudin 11 (206908_s_at), score: -0.87 DDIT3DNA-damage-inducible transcript 3 (209383_at), score: -0.91 DLX2distal-less homeobox 2 (207147_at), score: 1 GALgalanin prepropeptide (214240_at), score: 0.68 ID3inhibitor of DNA binding 3, dominant negative helix-loop-helix protein (207826_s_at), score: 0.73 ID4inhibitor of DNA binding 4, dominant negative helix-loop-helix protein (209291_at), score: 0.72 KLF10Kruppel-like factor 10 (202393_s_at), score: 0.84 NPTX1neuronal pentraxin I (204684_at), score: 0.72 QPRTquinolinate phosphoribosyltransferase (204044_at), score: -0.84 SLC22A4solute carrier family 22 (organic cation/ergothioneine transporter), member 4 (205896_at), score: 0.74 SMAD7SMAD family member 7 (204790_at), score: 0.89 THUMPD2THUMP domain containing 2 (219248_at), score: 0.7
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486271.cel | 32 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486291.cel | 33 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| t21b 08-03.CEL | 5 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | Down | DS-CC 5 |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949704.cel | 4 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | CS | eGFP |
| 5CTwin.CEL | 5 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | Down | DS-twin 5 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690199.cel | 1 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM0316B |
| 46C.CEL | 3 | 3 | DS-mosaic | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-mosaic 3 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485991.cel | 18 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |