
Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

vesicle-mediated transport
The directed movement of substances, either within a vesicle or in the vesicle membrane, into, out of or within a cell.
transport
The directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells, or within a multicellular organism.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
intracellular transport
The directed movement of substances within a cell.
Golgi vesicle transport
The directed movement of substances into, out of or within the Golgi apparatus, mediated by vesicles.
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
cellular localization
Any process by which a substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in, a specific location within or in the membrane of a cell.
establishment of localization in cell
The directed movement of a substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location within, or in the membrane of, a cell.
all
This term is the most general term possible
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
cellular localization
Any process by which a substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in, a specific location within or in the membrane of a cell.
establishment of localization in cell
The directed movement of a substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location within, or in the membrane of, a cell.
vesicle-mediated transport
The directed movement of substances, either within a vesicle or in the vesicle membrane, into, out of or within a cell.
intracellular transport
The directed movement of substances within a cell.
Golgi vesicle transport
The directed movement of substances into, out of or within the Golgi apparatus, mediated by vesicles.

intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cytoplasm
All of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
vesicle
Any small, fluid-filled, spherical organelle enclosed by membrane or protein.
membrane-bounded vesicle
Any small, fluid-filled, spherical organelle enclosed by a lipid bilayer.
melanosome
A tissue-specific, membrane-bounded cytoplasmic organelle within which melanin pigments are synthesized and stored. Melanosomes are synthesized in melanocyte cells.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
pigment granule
A small, subcellular membrane-bounded vesicle containing pigment and/or pigment precursor molecules. Pigment granule biogenesis is poorly understood, as pigment granules are derived from multiple sources including the endoplasmic reticulum, coated vesicles, lysosomes, and endosomes.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
catalytic activity
Catalysis of a biochemical reaction at physiological temperatures. In biologically catalyzed reactions, the reactants are known as substrates, and the catalysts are naturally occurring macromolecular substances known as enzymes. Enzymes possess specific binding sites for substrates, and are usually composed wholly or largely of protein, but RNA that has catalytic activity (ribozyme) is often also regarded as enzymatic.
protein kinase activity
Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction: a protein + ATP = a phosphoprotein + ADP.
protein serine/threonine kinase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein serine/threonine = ADP + protein serine/threonine phosphate.
receptor signaling protein serine/threonine kinase activity
NA
signal transducer activity
Mediates the transfer of a signal from the outside to the inside of a cell by means other than the introduction of the signal molecule itself into the cell.
receptor signaling protein activity
NA
kinase activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a substrate molecule.
transferase activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a group, e.g. a methyl group, glycosyl group, acyl group, phosphorus-containing, or other groups, from one compound (generally regarded as the donor) to another compound (generally regarded as the acceptor). Transferase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 2.
transferase activity, transferring phosphorus-containing groups
Catalysis of the transfer of a phosphorus-containing group from one compound (donor) to another (acceptor).
phosphotransferase activity, alcohol group as acceptor
Catalysis of the transfer of a phosphorus-containing group from one compound (donor) to an alcohol group (acceptor).
molecular transducer activity
The molecular function that accepts an input of one form and creates an output of a different form.
all
This term is the most general term possible
protein kinase activity
Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction: a protein + ATP = a phosphoprotein + ADP.
receptor signaling protein serine/threonine kinase activity
NA
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-320/320abcd | 2.794e-03 | 4.794 | 19 | 372 |
ACLYATP citrate lyase (210337_s_at), score: 0.78 ADAM10ADAM metallopeptidase domain 10 (214895_s_at), score: 0.7 ARF1ADP-ribosylation factor 1 (208750_s_at), score: 0.75 ATP13A3ATPase type 13A3 (219558_at), score: 0.81 ATP6V1AATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 70kDa, V1 subunit A (201971_s_at), score: 0.82 C19orf6chromosome 19 open reading frame 6 (213986_s_at), score: 0.82 CALUcalumenin (214845_s_at), score: 0.91 CANXcalnexin (208853_s_at), score: 0.82 CAPRIN1cell cycle associated protein 1 (200722_s_at), score: 0.7 CBFBcore-binding factor, beta subunit (206788_s_at), score: 0.7 CD44CD44 molecule (Indian blood group) (210916_s_at), score: 0.75 CDV3CDV3 homolog (mouse) (213548_s_at), score: 0.98 CLIC4chloride intracellular channel 4 (201559_s_at), score: 0.7 COL6A1collagen, type VI, alpha 1 (212940_at), score: 0.88 COPAcoatomer protein complex, subunit alpha (214336_s_at), score: 0.98 CPDcarboxypeptidase D (201942_s_at), score: 0.96 CYP51A1cytochrome P450, family 51, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 (216607_s_at), score: 0.83 DAPK3death-associated protein kinase 3 (203890_s_at), score: 0.69 DAZAP2DAZ associated protein 2 (212595_s_at), score: 0.79 DDX3XDEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 3, X-linked (201211_s_at), score: 1 DHX9DEAH (Asp-Glu-Ala-His) box polypeptide 9 (212105_s_at), score: 0.99 EPB41L2erythrocyte membrane protein band 4.1-like 2 (201718_s_at), score: 0.74 ERLIN1ER lipid raft associated 1 (202444_s_at), score: 0.74 EXOC5exocyst complex component 5 (218748_s_at), score: 0.76 FKBP1AFK506 binding protein 1A, 12kDa (210186_s_at), score: 0.81 FN1fibronectin 1 (214701_s_at), score: 0.86 GNA13guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), alpha 13 (206917_at), score: 0.74 GNSglucosamine (N-acetyl)-6-sulfatase (203676_at), score: 0.9 GTF2Igeneral transcription factor II, i (210892_s_at), score: 0.85 HIPK3homeodomain interacting protein kinase 3 (210148_at), score: 0.71 HSPA4heat shock 70kDa protein 4 (211016_x_at), score: 0.73 KPNA4karyopherin alpha 4 (importin alpha 3) (209653_at), score: 0.85 LAMP1lysosomal-associated membrane protein 1 (201551_s_at), score: 0.72 LMAN1lectin, mannose-binding, 1 (203294_s_at), score: 0.87 MAP3K2mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 2 (221695_s_at), score: 0.85 MAP3K7mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 7 (211537_x_at), score: 0.8 MAP3K7IP2mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 7 interacting protein 2 (210284_s_at), score: 0.86 MAPK1mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 (208351_s_at), score: 0.77 MAPKAPK2mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2 (201461_s_at), score: 0.77 MAT2Amethionine adenosyltransferase II, alpha (200769_s_at), score: 0.94 MAXMYC associated factor X (210734_x_at), score: 0.89 MBNL2muscleblind-like 2 (Drosophila) (205018_s_at), score: 0.77 NID1nidogen 1 (202008_s_at), score: 0.73 NOTCH2Notch homolog 2 (Drosophila) (210756_s_at), score: 0.79 OSMRoncostatin M receptor (205729_at), score: 0.73 PAFAH1B1platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase, isoform Ib, alpha subunit 45kDa (211547_s_at), score: 0.75 PCDHGA11protocadherin gamma subfamily A, 11 (211876_x_at), score: 0.96 PCDHGA3protocadherin gamma subfamily A, 3 (216352_x_at), score: 0.87 PHTF2putative homeodomain transcription factor 2 (217097_s_at), score: 0.88 PICALMphosphatidylinositol binding clathrin assembly protein (215236_s_at), score: 0.9 PIP5K1Aphosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase, type I, alpha (211205_x_at), score: 0.75 PRPF4BPRP4 pre-mRNA processing factor 4 homolog B (yeast) (211090_s_at), score: 0.79 PRRX1paired related homeobox 1 (205991_s_at), score: 0.91 PSEN1presenilin 1 (207782_s_at), score: 0.71 PTBP1polypyrimidine tract binding protein 1 (212016_s_at), score: 0.95 PTPROprotein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, O (211600_at), score: 0.76 PXNpaxillin (211823_s_at), score: 0.76 RAB5ARAB5A, member RAS oncogene family (206113_s_at), score: 0.99 RAB5CRAB5C, member RAS oncogene family (201156_s_at), score: 0.87 RANBP2RAN binding protein 2 (201711_x_at), score: 0.76 SCAMP1secretory carrier membrane protein 1 (206667_s_at), score: 0.81 SCARB2scavenger receptor class B, member 2 (201647_s_at), score: 0.72 SEPT11septin 11 (201308_s_at), score: 0.71 SMEK1SMEK homolog 1, suppressor of mek1 (Dictyostelium) (220368_s_at), score: 0.87 SNAP23synaptosomal-associated protein, 23kDa (214544_s_at), score: 0.74 SPAG9sperm associated antigen 9 (206748_s_at), score: 0.73 SS18synovial sarcoma translocation, chromosome 18 (216684_s_at), score: 0.72 STIP1stress-induced-phosphoprotein 1 (212009_s_at), score: 0.82 SYPL1synaptophysin-like 1 (201259_s_at), score: 0.85 TAF9BTAF9B RNA polymerase II, TATA box binding protein (TBP)-associated factor, 31kDa (221618_s_at), score: 0.72 TGFBR2transforming growth factor, beta receptor II (70/80kDa) (207334_s_at), score: 0.79 TMED2transmembrane emp24 domain trafficking protein 2 (204426_at), score: 0.76 UBXN4UBX domain protein 4 (212008_at), score: 0.77 VAMP3vesicle-associated membrane protein 3 (cellubrevin) (201337_s_at), score: 0.8 WACWW domain containing adaptor with coiled-coil (219679_s_at), score: 0.94 WDR1WD repeat domain 1 (210935_s_at), score: 0.69 YIPF5Yip1 domain family, member 5 (221423_s_at), score: 0.7 YWHAZtyrosine 3-monooxygenase/tryptophan 5-monooxygenase activation protein, zeta polypeptide (200641_s_at), score: 0.75
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
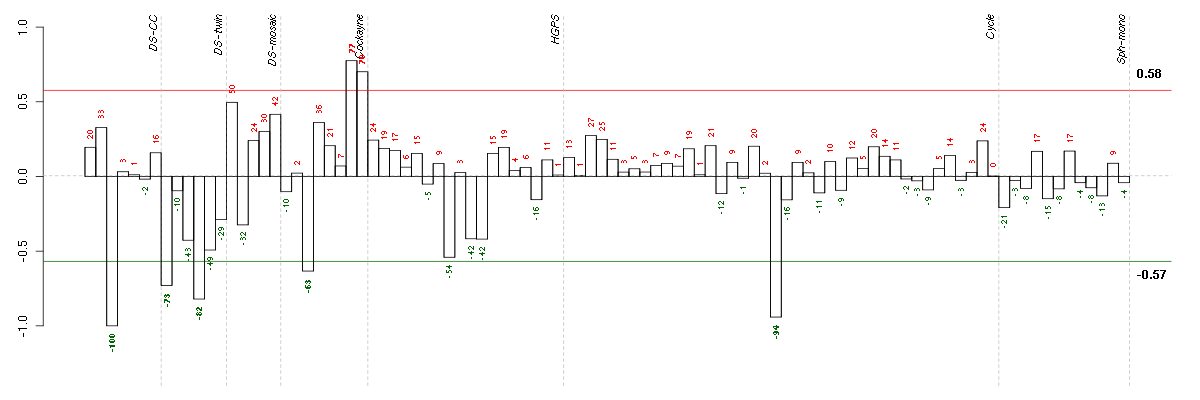
| ctrl c 08-03.CEL | 3 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | none | DS-CC 3 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486031.cel | 20 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| 4Twin.CEL | 4 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-twin 4 |
| 1Twin.CEL | 1 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | Down | DS-twin 1 |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949655.cel | 3 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | none | CSB |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949938.cel | 8 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | none | CSB |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949854.cel | 7 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | CS | eGFP |