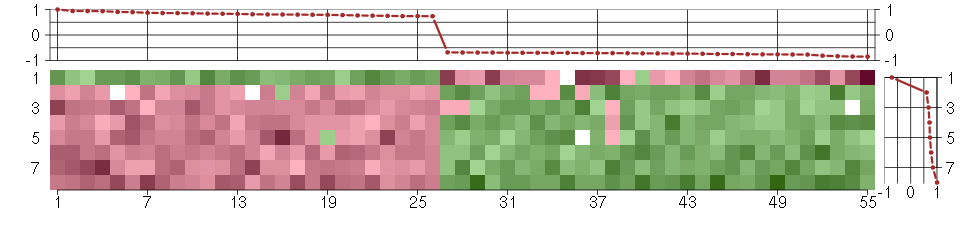

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
signal transduction
The cascade of processes by which a signal interacts with a receptor, causing a change in the level or activity of a second messenger or other downstream target, and ultimately effecting a change in the functioning of the cell.
protein modification process
The covalent alteration of one or more amino acids occurring in proteins, peptides and nascent polypeptides (co-translational, post-translational modifications). Includes the modification of charged tRNAs that are destined to occur in a protein (pre-translation modification).
protein amino acid phosphorylation
The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein.
phosphorus metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving the nonmetallic element phosphorus or compounds that contain phosphorus, usually in the form of a phosphate group (PO4).
phosphate metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving the phosphate group, the anion or salt of any phosphoric acid.
cell communication
Any process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
cell surface receptor linked signal transduction
Any series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of an extracellular ligand to a receptor on the surface of the target cell.
enzyme linked receptor protein signaling pathway
Any series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of an extracellular ligand to a receptor on the surface of the target cell, where the receptor possesses catalytic activity or is closely associated with an enzyme such as a protein kinase.
transmembrane receptor protein serine/threonine kinase signaling pathway
The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a transmembrane receptor serine/threonine kinase binding to its physiological ligand.
transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway
The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a transforming growth factor beta receptor binding to one of its physiological ligands.
common-partner SMAD protein phosphorylation
The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a common-partner SMAD protein. A common partner SMAD protein binds to pathway-restricted SMAD proteins forming a complex that translocates to the nucleus.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
phosphorylation
The process of introducing a phosphate group into a molecule, usually with the formation of a phosphoric ester, a phosphoric anhydride or a phosphoric amide.
protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general. Includes protein modification.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins.
biopolymer modification
The covalent alteration of one or more monomeric units in a polypeptide, polynucleotide, polysaccharide, or other biological polymer, resulting in a change in its properties.
post-translational protein modification
The covalent alteration of one or more amino acids occurring in a protein after the protein has been completely translated and released from the ribosome.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general, occurring at the level of an individual cell. Includes protein modification.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
signal transduction
The cascade of processes by which a signal interacts with a receptor, causing a change in the level or activity of a second messenger or other downstream target, and ultimately effecting a change in the functioning of the cell.
protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general. Includes protein modification.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular protein metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving a specific protein, rather than of proteins in general, occurring at the level of an individual cell. Includes protein modification.
protein modification process
The covalent alteration of one or more amino acids occurring in proteins, peptides and nascent polypeptides (co-translational, post-translational modifications). Includes the modification of charged tRNAs that are destined to occur in a protein (pre-translation modification).
protein amino acid phosphorylation
The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein.
common-partner SMAD protein phosphorylation
The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a common-partner SMAD protein. A common partner SMAD protein binds to pathway-restricted SMAD proteins forming a complex that translocates to the nucleus.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cytoplasm
All of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
endocytic vesicle
A membrane-bounded intracellular vesicle formed by invagination of the plasma membrane around an extracellular substance.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
vesicle
Any small, fluid-filled, spherical organelle enclosed by membrane or protein.
membrane-bounded vesicle
Any small, fluid-filled, spherical organelle enclosed by a lipid bilayer.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle
A membrane-bounded vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
cytoplasmic vesicle
A vesicle formed of membrane or protein, found in the cytoplasm of a cell.

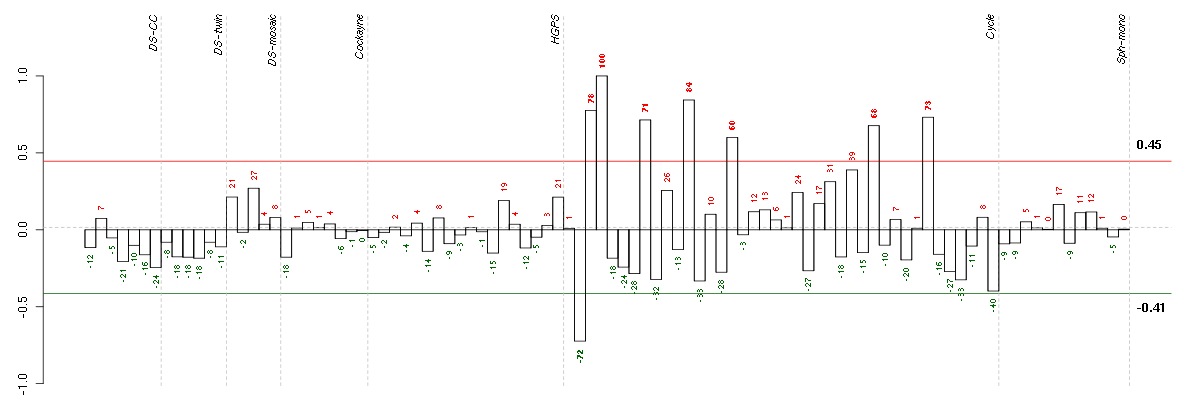
ABCA7ATP-binding cassette, sub-family A (ABC1), member 7 (219577_s_at), score: -0.85 ADAMTS7ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 7 (220705_s_at), score: -0.69 ALDH1L1aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 family, member L1 (215798_at), score: -0.75 ALDH3A1aldehyde dehydrogenase 3 family, memberA1 (205623_at), score: -0.69 BIRC3baculoviral IAP repeat-containing 3 (210538_s_at), score: 0.75 C7orf58chromosome 7 open reading frame 58 (220032_at), score: 0.83 CALB2calbindin 2 (205428_s_at), score: -0.71 CD79BCD79b molecule, immunoglobulin-associated beta (205297_s_at), score: -0.84 CDC42EP4CDC42 effector protein (Rho GTPase binding) 4 (218062_x_at), score: 0.74 CMAHcytidine monophosphate-N-acetylneuraminic acid hydroxylase (CMP-N-acetylneuraminate monooxygenase) pseudogene (205518_s_at), score: 0.81 DMBT1deleted in malignant brain tumors 1 (208250_s_at), score: -0.71 EMCNendomucin (219436_s_at), score: 0.93 FKBP10FK506 binding protein 10, 65 kDa (219249_s_at), score: -0.71 FLJ21075hypothetical protein FLJ21075 (221172_at), score: -0.72 FLRT3fibronectin leucine rich transmembrane protein 3 (219250_s_at), score: 0.79 GABARAPL1GABA(A) receptor-associated protein like 1 (208868_s_at), score: -0.7 GABARAPL3GABA(A) receptors associated protein like 3 (pseudogene) (211458_s_at), score: -0.72 GBA3glucosidase, beta, acid 3 (cytosolic) (219954_s_at), score: -0.81 GFOD1glucose-fructose oxidoreductase domain containing 1 (219821_s_at), score: -0.7 GPR56G protein-coupled receptor 56 (212070_at), score: 0.85 HAB1B1 for mucin (215778_x_at), score: -0.73 HGFhepatocyte growth factor (hepapoietin A; scatter factor) (209960_at), score: 0.9 HIST1H4Ghistone cluster 1, H4g (208551_at), score: -0.71 HMGA1high mobility group AT-hook 1 (210457_x_at), score: 0.79 IGHG1immunoglobulin heavy constant gamma 1 (G1m marker) (211693_at), score: -0.76 IL9Rinterleukin 9 receptor (217212_s_at), score: -0.77 INAinternexin neuronal intermediate filament protein, alpha (204465_s_at), score: 0.84 JUPjunction plakoglobin (201015_s_at), score: 0.86 KCTD15potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 15 (218553_s_at), score: -0.77 KIF26Bkinesin family member 26B (220002_at), score: -0.74 LRP2low density lipoprotein-related protein 2 (205710_at), score: 0.8 MEOX1mesenchyme homeobox 1 (205619_s_at), score: -0.75 MPP1membrane protein, palmitoylated 1, 55kDa (202974_at), score: 0.74 MTMR11myotubularin related protein 11 (205076_s_at), score: 0.83 NDPNorrie disease (pseudoglioma) (206022_at), score: 0.91 NOL10nucleolar protein 10 (218591_s_at), score: -0.73 OLFML2Bolfactomedin-like 2B (213125_at), score: 1 PDE5Aphosphodiesterase 5A, cGMP-specific (206757_at), score: 0.86 PMLpromyelocytic leukemia (206503_x_at), score: 0.74 PNMAL1PNMA-like 1 (218824_at), score: 0.76 PPP1R13Bprotein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 13B (216347_s_at), score: -0.83 PTPN6protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 6 (206687_s_at), score: -0.76 PXNpaxillin (211823_s_at), score: 0.77 RASGRP3RAS guanyl releasing protein 3 (calcium and DAG-regulated) (205801_s_at), score: 0.94 REG3Aregenerating islet-derived 3 alpha (205815_at), score: -0.75 SDPRserum deprivation response (phosphatidylserine binding protein) (218711_s_at), score: 0.94 SLC26A10solute carrier family 26, member 10 (214951_at), score: -0.7 SNAP25synaptosomal-associated protein, 25kDa (202508_s_at), score: 0.8 SNTG1syntrophin, gamma 1 (220405_at), score: 0.87 SPATA1spermatogenesis associated 1 (221057_at), score: -0.69 SYT1synaptotagmin I (203999_at), score: 0.81 TAL1T-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia 1 (206283_s_at), score: -0.7 TGFBR2transforming growth factor, beta receptor II (70/80kDa) (207334_s_at), score: 0.78 TMPRSS6transmembrane protease, serine 6 (214955_at), score: -0.68 TRA@T cell receptor alpha locus (216540_at), score: -0.7
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485671.cel | 2 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485951.cel | 16 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486211.cel | 29 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485791.cel | 8 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486311.cel | 34 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485691.cel | 3 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485871.cel | 12 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485711.cel | 4 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |