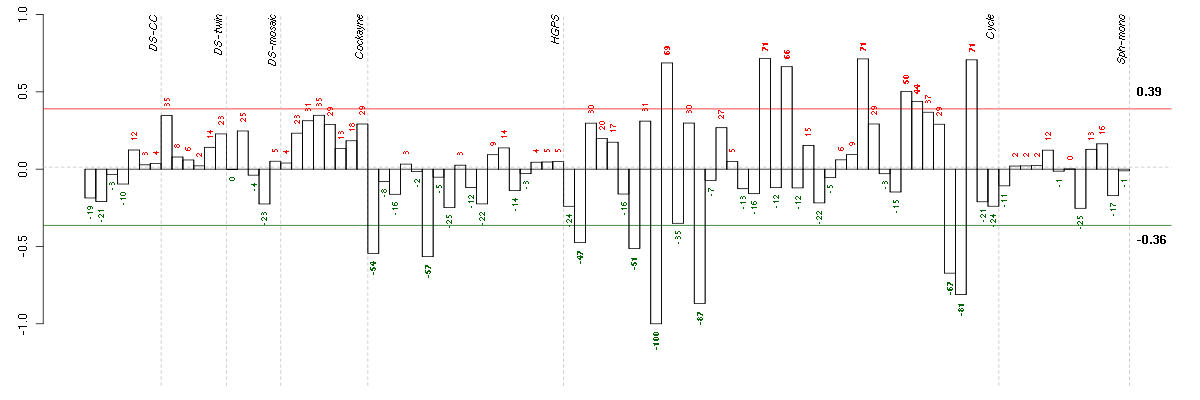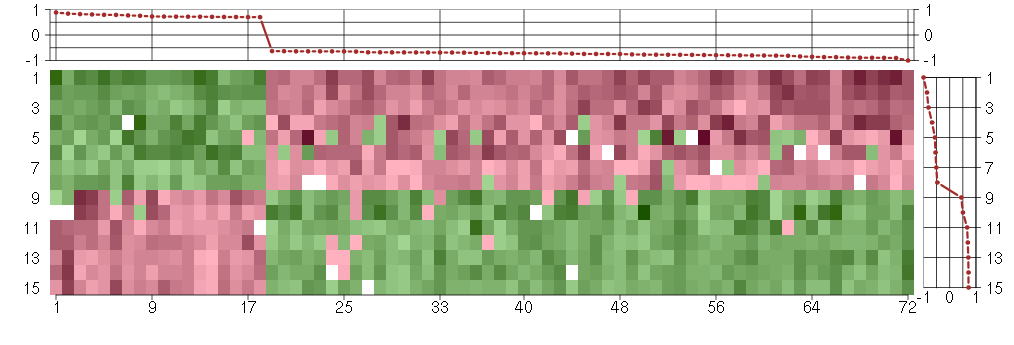

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
collagen catabolic process
The proteolytic chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of collagen in the extracellular matrix, usually carried out by proteases secreted by nearby cells.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
collagen metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving collagen, any of a group of fibrous proteins of very high tensile strength that form the main component of connective tissue in animals. Collagen is highly enriched in glycine (some regions are 33% glycine) and proline, occurring predominantly as 3-hydroxyproline (about 20%).
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
multicellular organismal metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways in multicellular organisms that occur at the tissue, organ, or organismal level. These processes, unlike cellular metabolism, can include transport of substances between cells when that transport is required.
multicellular organismal catabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of substances in multicellular organisms that occur at the tissue, organ, or organismal level. These processes, unlike cellular metabolism, can include transport of substances between cells when that transport is required.
multicellular organismal macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, large molecules including proteins, nucleic acids and carbohydrates, in multicellular organisms occurring at the tissue, organ, or organismal level.
all
This term is the most general term possible
multicellular organismal metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways in multicellular organisms that occur at the tissue, organ, or organismal level. These processes, unlike cellular metabolism, can include transport of substances between cells when that transport is required.
multicellular organismal macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, large molecules including proteins, nucleic acids and carbohydrates, in multicellular organisms occurring at the tissue, organ, or organismal level.
collagen catabolic process
The proteolytic chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of collagen in the extracellular matrix, usually carried out by proteases secreted by nearby cells.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
intermediate filament
A cytoskeletal structure that forms a distinct elongated structure, characteristically 10 nm in diameter, that occurs in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. Intermediate filaments form a fibrous system, composed of chemically heterogeneous subunits and involved in mechanically integrating the various components of the cytoplasmic space. Intermediate filaments may be divided into five chemically distinct classes: Type I, acidic keratins; Type II, basic keratins; Type III, including desmin, vimentin and others; Type IV, neurofilaments and related filaments; and Type V, lamins.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
extracellular space
That part of a multicellular organism outside the cells proper, usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cytoskeleton
Any of the various filamentous elements that form the internal framework of cells, and typically remain after treatment of the cells with mild detergent to remove membrane constituents and soluble components of the cytoplasm. The term embraces intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, the microtrabecular lattice, and other structures characterized by a polymeric filamentous nature and long-range order within the cell. The various elements of the cytoskeleton not only serve in the maintenance of cellular shape but also have roles in other cellular functions, including cellular movement, cell division, endocytosis, and movement of organelles.
neurofilament
A type of intermediate filament found in the core of neuronal axons. Neurofilaments are heteropolymers composed of three type IV polypeptides: NF-L, NF-M, and NF-H (for low, middle, and high molecular weight). Neurofilaments are responsible for the radial growth of an axon and determine axonal diameter.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
intermediate filament cytoskeleton
Cytoskeletal structure made from intermediate filaments, typically organized in the cytosol as an extended system that stretches from the nuclear envelope to the plasma membrane. Some intermediate filaments run parallel to the cell surface, while others traverse the cytosol; together they form an internal framework that helps support the shape and resilience of the cell.
neurofilament cytoskeleton
Intermediate filament cytoskeletal structure that is made up of neurofilaments. Neurofilaments are specialized intermediate filaments found in neurons.
all
This term is the most general term possible
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
intermediate filament
A cytoskeletal structure that forms a distinct elongated structure, characteristically 10 nm in diameter, that occurs in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. Intermediate filaments form a fibrous system, composed of chemically heterogeneous subunits and involved in mechanically integrating the various components of the cytoplasmic space. Intermediate filaments may be divided into five chemically distinct classes: Type I, acidic keratins; Type II, basic keratins; Type III, including desmin, vimentin and others; Type IV, neurofilaments and related filaments; and Type V, lamins.
neurofilament
A type of intermediate filament found in the core of neuronal axons. Neurofilaments are heteropolymers composed of three type IV polypeptides: NF-L, NF-M, and NF-H (for low, middle, and high molecular weight). Neurofilaments are responsible for the radial growth of an axon and determine axonal diameter.

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
catalytic activity
Catalysis of a biochemical reaction at physiological temperatures. In biologically catalyzed reactions, the reactants are known as substrates, and the catalysts are naturally occurring macromolecular substances known as enzymes. Enzymes possess specific binding sites for substrates, and are usually composed wholly or largely of protein, but RNA that has catalytic activity (ribozyme) is often also regarded as enzymatic.
prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: arachidonate + donor-H2 + 2 O2 = prostaglandin H2 + acceptor + H2O.
oxidoreductase activity
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction, a reversible chemical reaction in which the oxidation state of an atom or atoms within a molecule is altered. One substrate acts as a hydrogen or electron donor and becomes oxidized, while the other acts as hydrogen or electron acceptor and becomes reduced.
oxidoreductase activity, acting on paired donors, with incorporation or reduction of molecular oxygen
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which hydrogen or electrons are transferred from each of two donors, and molecular oxygen is reduced or incorporated into a donor.
all
This term is the most general term possible
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 04080 | 1.183e-03 | 0.7835 | 7 | 78 | Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction |
ADAM19ADAM metallopeptidase domain 19 (meltrin beta) (209765_at), score: -0.64 ADORA2Badenosine A2b receptor (205891_at), score: 0.79 AHI1Abelson helper integration site 1 (221569_at), score: -0.87 AIM1absent in melanoma 1 (212543_at), score: 0.71 AJAP1adherens junctions associated protein 1 (206460_at), score: -0.63 ANXA10annexin A10 (210143_at), score: -0.84 ARNT2aryl-hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator 2 (202986_at), score: 0.72 BMP6bone morphogenetic protein 6 (206176_at), score: -0.89 C14orf45chromosome 14 open reading frame 45 (220173_at), score: -0.65 C2CD2C2 calcium-dependent domain containing 2 (212875_s_at), score: -0.68 C2CD2LC2CD2-like (204757_s_at), score: -0.64 C5orf23chromosome 5 open reading frame 23 (219054_at), score: -0.69 CALB2calbindin 2 (205428_s_at), score: -0.79 CCDC28Acoiled-coil domain containing 28A (209479_at), score: 0.73 CD55CD55 molecule, decay accelerating factor for complement (Cromer blood group) (201925_s_at), score: -0.72 CDCP1CUB domain containing protein 1 (218451_at), score: -0.71 CST6cystatin E/M (206595_at), score: -0.8 CXCL6chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 6 (granulocyte chemotactic protein 2) (206336_at), score: -0.76 DEPDC6DEP domain containing 6 (218858_at), score: 0.81 DIRAS3DIRAS family, GTP-binding RAS-like 3 (215506_s_at), score: -0.87 DNAJB9DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily B, member 9 (202843_at), score: -0.85 DUSP4dual specificity phosphatase 4 (204014_at), score: -0.74 DZIP3DAZ interacting protein 3, zinc finger (213186_at), score: 0.72 ESM1endothelial cell-specific molecule 1 (208394_x_at), score: -0.88 ESRRAestrogen-related receptor alpha (1487_at), score: -0.71 FERMT1fermitin family homolog 1 (Drosophila) (218796_at), score: -0.79 FICDFIC domain containing (219910_at), score: -0.69 FNBP1formin binding protein 1 (212288_at), score: 0.71 GKglycerol kinase (207387_s_at), score: -0.89 GK3Pglycerol kinase 3 pseudogene (215966_x_at), score: -0.9 GPR177G protein-coupled receptor 177 (221958_s_at), score: -0.74 GRB14growth factor receptor-bound protein 14 (206204_at), score: -0.8 GTF2A1Lgeneral transcription factor IIA, 1-like (213413_at), score: 0.82 HTR2A5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 2A (207135_at), score: -0.79 IL11interleukin 11 (206924_at), score: -0.68 IL13RA2interleukin 13 receptor, alpha 2 (206172_at), score: -0.8 IL33interleukin 33 (209821_at), score: -1 KAL1Kallmann syndrome 1 sequence (205206_at), score: -0.81 LRP8low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 8, apolipoprotein e receptor (205282_at), score: -0.72 MMP10matrix metallopeptidase 10 (stromelysin 2) (205680_at), score: -0.78 MMP16matrix metallopeptidase 16 (membrane-inserted) (207012_at), score: -0.68 NCALDneurocalcin delta (211685_s_at), score: -0.9 NEFLneurofilament, light polypeptide (221805_at), score: -0.69 NEFMneurofilament, medium polypeptide (205113_at), score: -0.77 NPTX1neuronal pentraxin I (204684_at), score: -0.77 NR5A2nuclear receptor subfamily 5, group A, member 2 (208343_s_at), score: -0.64 NTMneurotrimin (222020_s_at), score: -0.71 OPCMLopioid binding protein/cell adhesion molecule-like (214111_at), score: -0.74 P2RX5purinergic receptor P2X, ligand-gated ion channel, 5 (210448_s_at), score: -0.69 PCDH9protocadherin 9 (219737_s_at), score: -0.82 PIGLphosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis, class L (213889_at), score: 0.71 PRSS2protease, serine, 2 (trypsin 2) (205402_x_at), score: -0.7 PRSS3protease, serine, 3 (213421_x_at), score: -0.78 PTGS1prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 1 (prostaglandin G/H synthase and cyclooxygenase) (215813_s_at), score: -0.72 PTGS2prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 (prostaglandin G/H synthase and cyclooxygenase) (204748_at), score: -0.68 PTHLHparathyroid hormone-like hormone (211756_at), score: -0.75 PTPRBprotein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, B (205846_at), score: -0.7 RFX5regulatory factor X, 5 (influences HLA class II expression) (202963_at), score: 0.75 RNF44ring finger protein 44 (203286_at), score: 0.7 S1PR1sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 (204642_at), score: -0.63 SLC38A4solute carrier family 38, member 4 (220786_s_at), score: 0.79 SLC4A7solute carrier family 4, sodium bicarbonate cotransporter, member 7 (209884_s_at), score: -0.68 SMAD3SMAD family member 3 (218284_at), score: 0.72 SSTR1somatostatin receptor 1 (208482_at), score: -0.64 TFDP2transcription factor Dp-2 (E2F dimerization partner 2) (203588_s_at), score: 0.88 TGFAtransforming growth factor, alpha (205016_at), score: -0.77 THYN1thymocyte nuclear protein 1 (218491_s_at), score: 0.72 TMEM2transmembrane protein 2 (218113_at), score: -0.73 TP53tumor protein p53 (201746_at), score: 0.77 TSPAN13tetraspanin 13 (217979_at), score: -0.64 UCP2uncoupling protein 2 (mitochondrial, proton carrier) (208998_at), score: 0.84 VWA5Avon Willebrand factor A domain containing 5A (210102_at), score: 0.7
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485811.cel | 9 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485891.cel | 13 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486371.cel | 37 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486351.cel | 36 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690256.cel | 6 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GMO8398C |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690199.cel | 1 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM0316B |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485771.cel | 7 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485671.cel | 2 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486291.cel | 33 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486271.cel | 32 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486051.cel | 21 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485831.cel | 10 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486391.cel | 38 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486191.cel | 28 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486011.cel | 19 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |