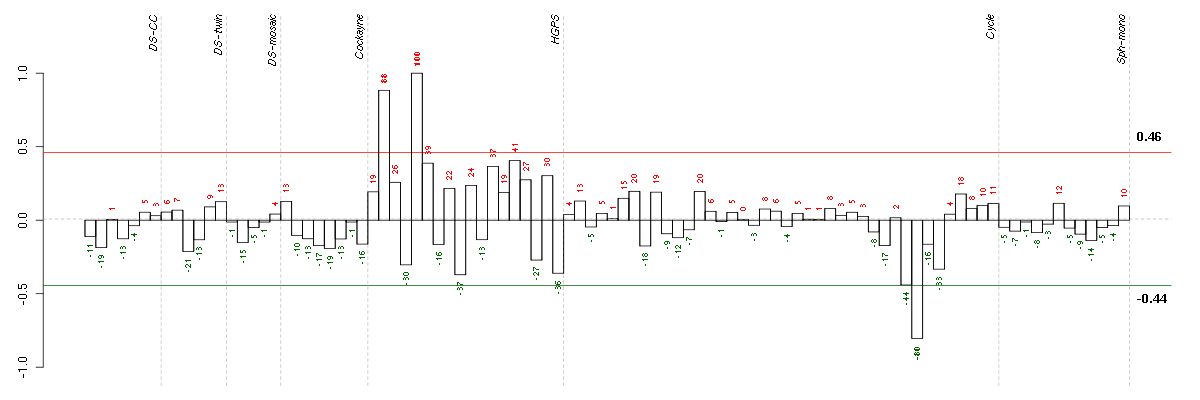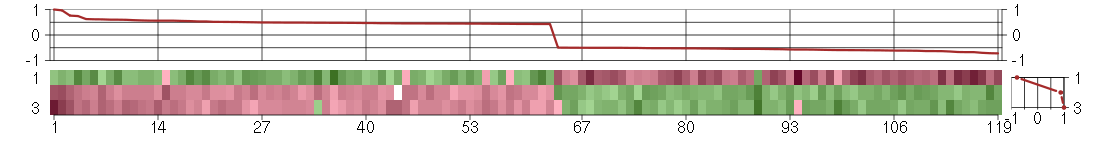

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

skeletal system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the skeleton over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The skeleton is the bony framework of the body in vertebrates (endoskeleton) or the hard outer envelope of insects (exoskeleton or dermoskeleton).
metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
organic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving organic acids, any acidic compound containing carbon in covalent linkage.
lipid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving lipids, compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent. Includes fatty acids; neutral fats, other fatty-acid esters, and soaps; long-chain (fatty) alcohols and waxes; sphingoids and other long-chain bases; glycolipids, phospholipids and sphingolipids; and carotenes, polyprenols, sterols, terpenes and other isoprenoids.
fatty acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving fatty acids, aliphatic monocarboxylic acids liberated from naturally occurring fats and oils by hydrolysis.
icosanoid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving icosanoids, any of a group of C20 polyunsaturated fatty acids.
prostanoid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving prostanoids, any compound based on or derived from the prostanoate structure.
prostaglandin metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving prostaglandins, any of a group of biologically active metabolites which contain a cyclopentane ring due to the formation of a bond between two carbons of a fatty acid. They have a wide range of biological activities.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
embryonic development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an embryo from its formation until the end of its embryonic life stage. The end of the embryonic stage is organism-specific. For example, for mammals, the process would begin with zygote formation and end with birth. For insects, the process would begin at zygote formation and end with larval hatching. For plant zygotic embryos, this would be from zygote formation to the end of seed dormancy. For plant vegetative embryos, this would be from the initial determination of the cell or group of cells to form an embryo until the point when the embryo becomes independent of the parent plant.
organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis of an organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
embryonic development ending in birth or egg hatching
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an embryo over time, from zygote formation until the end of the embryonic life stage. The end of the embryonic life stage is organism-specific and may be somewhat arbitrary; for mammals it is usually considered to be birth, for insects the hatching of the first instar larva from the eggshell.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
carboxylic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving carboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one or more carboxyl (COOH) groups or anions (COO-).
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
monocarboxylic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving monocarboxylic acids, any organic acid containing one carboxyl (COOH) group or anion (COO-).
chordate embryonic development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the embryo over time, from zygote formation through a stage including a notochord and neural tube until birth or egg hatching.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular lipid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving lipids, as carried out by individual cells.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
embryonic morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized during the embryonic phase. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. The embryonic phase begins with zygote formation. The end of the embryonic phase is organism-specific. For example, it would be at birth for mammals, larval hatching for insects and seed dormancy in plants.
embryonic skeletal system morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of the skeleton are generated and organized during the embryonic phase. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
skeletal system morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of the skeleton are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
embryonic skeletal system development
The process, occurring during the embryonic phase, whose specific outcome is the progression of the skeleton over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
embryonic development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an embryo from its formation until the end of its embryonic life stage. The end of the embryonic stage is organism-specific. For example, for mammals, the process would begin with zygote formation and end with birth. For insects, the process would begin at zygote formation and end with larval hatching. For plant zygotic embryos, this would be from zygote formation to the end of seed dormancy. For plant vegetative embryos, this would be from the initial determination of the cell or group of cells to form an embryo until the point when the embryo becomes independent of the parent plant.
embryonic morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized during the embryonic phase. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. The embryonic phase begins with zygote formation. The end of the embryonic phase is organism-specific. For example, it would be at birth for mammals, larval hatching for insects and seed dormancy in plants.
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
cellular lipid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving lipids, as carried out by individual cells.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis of an organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
skeletal system morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of the skeleton are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
embryonic skeletal system morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of the skeleton are generated and organized during the embryonic phase. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
embryonic skeletal system development
The process, occurring during the embryonic phase, whose specific outcome is the progression of the skeleton over time, from its formation to the mature structure.
fatty acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving fatty acids, aliphatic monocarboxylic acids liberated from naturally occurring fats and oils by hydrolysis.
embryonic skeletal system morphogenesis
The process by which the anatomical structures of the skeleton are generated and organized during the embryonic phase. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.


ABCA1ATP-binding cassette, sub-family A (ABC1), member 1 (203504_s_at), score: -0.52 ABCA8ATP-binding cassette, sub-family A (ABC1), member 8 (204719_at), score: -0.53 ABCB6ATP-binding cassette, sub-family B (MDR/TAP), member 6 (203192_at), score: -0.65 ACTC1actin, alpha, cardiac muscle 1 (205132_at), score: 0.74 ADH1Balcohol dehydrogenase 1B (class I), beta polypeptide (209612_s_at), score: -0.57 AKR1C2aldo-keto reductase family 1, member C2 (dihydrodiol dehydrogenase 2; bile acid binding protein; 3-alpha hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, type III) (209699_x_at), score: -0.5 AKR1C3aldo-keto reductase family 1, member C3 (3-alpha hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, type II) (209160_at), score: -0.72 ANGPTL2angiopoietin-like 2 (213004_at), score: -0.61 APOL6apolipoprotein L, 6 (219716_at), score: -0.49 ARL4CADP-ribosylation factor-like 4C (202207_at), score: -0.6 BAGEB melanoma antigen (207712_at), score: 0.46 BDKRB1bradykinin receptor B1 (207510_at), score: 0.56 C1orf38chromosome 1 open reading frame 38 (210785_s_at), score: -0.6 C1orf54chromosome 1 open reading frame 54 (219506_at), score: -0.51 C5orf23chromosome 5 open reading frame 23 (219054_at), score: 0.56 CDH2cadherin 2, type 1, N-cadherin (neuronal) (203441_s_at), score: 0.49 CGBchorionic gonadotropin, beta polypeptide (205387_s_at), score: 0.58 CHN1chimerin (chimaerin) 1 (212624_s_at), score: 0.45 CLEC3BC-type lectin domain family 3, member B (205200_at), score: -0.6 COL21A1collagen, type XXI, alpha 1 (208096_s_at), score: -0.67 COMPcartilage oligomeric matrix protein (205713_s_at), score: 0.51 CYP3A43cytochrome P450, family 3, subfamily A, polypeptide 43 (211440_x_at), score: -0.52 DEPDC6DEP domain containing 6 (218858_at), score: -0.5 DLX2distal-less homeobox 2 (207147_at), score: 0.48 DPH5DPH5 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (219590_x_at), score: -0.52 EHHADHenoyl-Coenzyme A, hydratase/3-hydroxyacyl Coenzyme A dehydrogenase (205222_at), score: 0.45 ELL2elongation factor, RNA polymerase II, 2 (214446_at), score: 0.49 F3coagulation factor III (thromboplastin, tissue factor) (204363_at), score: 0.6 GAAglucosidase, alpha; acid (202812_at), score: -0.52 GABRA5gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, alpha 5 (206456_at), score: 0.46 GALNT12UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 12 (GalNAc-T12) (218885_s_at), score: -0.55 GPRC5BG protein-coupled receptor, family C, group 5, member B (203632_s_at), score: -0.5 GRAMD1BGRAM domain containing 1B (212906_at), score: 0.57 GRAMD1CGRAM domain containing 1C (219313_at), score: 0.55 GRAMD3GRAM domain containing 3 (218706_s_at), score: 0.44 GTF2A1Lgeneral transcription factor IIA, 1-like (213413_at), score: -0.56 HERC3hect domain and RLD 3 (206183_s_at), score: 0.51 HOXB7homeobox B7 (204779_s_at), score: 0.43 HS1BP3HCLS1 binding protein 3 (219020_at), score: -0.5 HS3ST3A1heparan sulfate (glucosamine) 3-O-sulfotransferase 3A1 (219985_at), score: 0.44 IL7Rinterleukin 7 receptor (205798_at), score: 0.62 ITGA3integrin, alpha 3 (antigen CD49C, alpha 3 subunit of VLA-3 receptor) (201474_s_at), score: 0.46 KCND3potassium voltage-gated channel, Shal-related subfamily, member 3 (213832_at), score: -0.53 KIAA0802KIAA0802 (213358_at), score: -0.52 KIAA1462KIAA1462 (213316_at), score: -0.54 KITv-kit Hardy-Zuckerman 4 feline sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (205051_s_at), score: -0.54 KRT34keratin 34 (206969_at), score: 0.47 KRTAP1-1keratin associated protein 1-1 (220976_s_at), score: 0.97 LIMK2LIM domain kinase 2 (202193_at), score: 0.45 LOC730092RRN3 RNA polymerase I transcription factor homolog (S. cerevisiae) pseudogene (214712_at), score: 0.56 LPIN1lipin 1 (212274_at), score: -0.53 LRRC32leucine rich repeat containing 32 (203835_at), score: -0.61 LRRFIP2leucine rich repeat (in FLII) interacting protein 2 (220610_s_at), score: 0.45 MAN1C1mannosidase, alpha, class 1C, member 1 (218918_at), score: -0.5 MBPmyelin basic protein (210136_at), score: -0.7 MEF2Bmyocyte enhancer factor 2B (209926_at), score: 0.53 MEF2Cmyocyte enhancer factor 2C (209199_s_at), score: 0.49 MGPmatrix Gla protein (202291_s_at), score: -0.57 MMP1matrix metallopeptidase 1 (interstitial collagenase) (204475_at), score: -0.54 MT1Mmetallothionein 1M (217546_at), score: 0.45 MYL10myosin, light chain 10, regulatory (221659_s_at), score: 0.49 NMIN-myc (and STAT) interactor (203964_at), score: -0.5 NPC2Niemann-Pick disease, type C2 (200701_at), score: -0.71 NPR3natriuretic peptide receptor C/guanylate cyclase C (atrionatriuretic peptide receptor C) (219789_at), score: 0.48 NRG1neuregulin 1 (206343_s_at), score: 0.47 NUCKS1nuclear casein kinase and cyclin-dependent kinase substrate 1 (222027_at), score: 0.48 OSR2odd-skipped related 2 (Drosophila) (213568_at), score: -0.57 PARP12poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase family, member 12 (218543_s_at), score: -0.5 PDE4Bphosphodiesterase 4B, cAMP-specific (phosphodiesterase E4 dunce homolog, Drosophila) (203708_at), score: 0.48 PDGFRLplatelet-derived growth factor receptor-like (205226_at), score: -0.61 PFKFB36-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 3 (202464_s_at), score: 0.51 PLCB4phospholipase C, beta 4 (203896_s_at), score: 0.43 PMP22peripheral myelin protein 22 (210139_s_at), score: -0.63 PODXLpodocalyxin-like (201578_at), score: 0.48 POLR1Dpolymerase (RNA) I polypeptide D, 16kDa (218258_at), score: -0.51 PPLperiplakin (203407_at), score: -0.5 PPME1protein phosphatase methylesterase 1 (217841_s_at), score: 0.44 PROCRprotein C receptor, endothelial (EPCR) (203650_at), score: -0.59 PROS1protein S (alpha) (207808_s_at), score: -0.52 PRPS1phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase 1 (209440_at), score: 0.45 PSMD12proteasome (prosome, macropain) 26S subunit, non-ATPase, 12 (202353_s_at), score: 0.43 PTGER3prostaglandin E receptor 3 (subtype EP3) (213933_at), score: 0.61 PTGER4prostaglandin E receptor 4 (subtype EP4) (204897_at), score: -0.54 PTGISprostaglandin I2 (prostacyclin) synthase (208131_s_at), score: -0.58 PTGS2prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 (prostaglandin G/H synthase and cyclooxygenase) (204748_at), score: 0.5 PTPLBprotein tyrosine phosphatase-like (proline instead of catalytic arginine), member b (212640_at), score: 0.6 PVRL3poliovirus receptor-related 3 (213325_at), score: 0.49 RARBretinoic acid receptor, beta (205080_at), score: 0.56 RCAN3RCAN family member 3 (219864_s_at), score: 0.45 ROR1receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 1 (205805_s_at), score: -0.54 RPH3ALrabphilin 3A-like (without C2 domains) (221614_s_at), score: 0.47 SALL1sal-like 1 (Drosophila) (206893_at), score: 0.51 SELPLGselectin P ligand (209879_at), score: 0.48 SERPINB7serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade B (ovalbumin), member 7 (206421_s_at), score: 0.63 SIX2SIX homeobox 2 (206510_at), score: -0.67 SLAMF1signaling lymphocytic activation molecule family member 1 (206181_at), score: -0.51 SLC16A3solute carrier family 16, member 3 (monocarboxylic acid transporter 4) (202855_s_at), score: 0.46 SLC27A3solute carrier family 27 (fatty acid transporter), member 3 (222217_s_at), score: -0.67 SLC39A8solute carrier family 39 (zinc transporter), member 8 (209267_s_at), score: -0.55 SLC6A9solute carrier family 6 (neurotransmitter transporter, glycine), member 9 (207043_s_at), score: -0.63 SLC9A8solute carrier family 9 (sodium/hydrogen exchanger), member 8 (212947_at), score: -0.61 SOCS2suppressor of cytokine signaling 2 (203373_at), score: 0.55 SSFA2sperm specific antigen 2 (202506_at), score: 0.45 STMN2stathmin-like 2 (203000_at), score: 0.6 SYNPOsynaptopodin (202796_at), score: -0.63 TBC1D2BTBC1 domain family, member 2B (212796_s_at), score: -0.59 TMEM159transmembrane protein 159 (213272_s_at), score: -0.62 TMEM30Atransmembrane protein 30A (217743_s_at), score: 0.49 TNFRSF10Dtumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 10d, decoy with truncated death domain (210654_at), score: 0.45 TNFRSF6Btumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 6b, decoy (206467_x_at), score: 1 TNXAtenascin XA pseudogene (213451_x_at), score: -0.59 TNXBtenascin XB (216333_x_at), score: -0.57 TRAF4TNF receptor-associated factor 4 (202871_at), score: 0.43 UBA6ubiquitin-like modifier activating enzyme 6 (218340_s_at), score: 0.5 UCP2uncoupling protein 2 (mitochondrial, proton carrier) (208998_at), score: 0.76 ULBP2UL16 binding protein 2 (221291_at), score: 0.43 ZNF185zinc finger protein 185 (LIM domain) (203585_at), score: 0.45 ZNF423zinc finger protein 423 (214761_at), score: -0.59 ZNF654zinc finger protein 654 (219239_s_at), score: 0.53
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486291.cel | 33 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690215.cel | 2 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG11513 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690248.cel | 5 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG11513 |