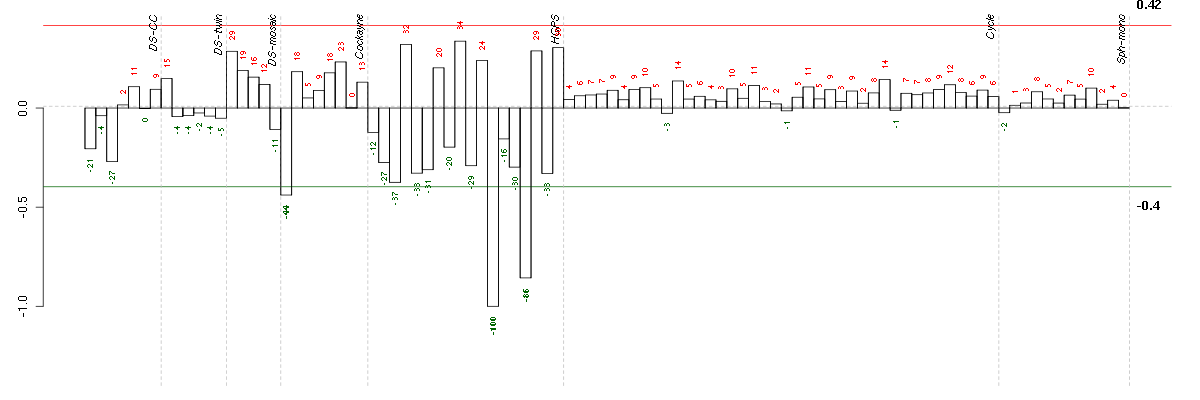

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

reproduction
The production by an organism of new individuals that contain some portion of their genetic material inherited from that organism.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
female pregnancy
The set of physiological processes that allow an embryo or foetus to develop within the body of a female animal. It covers the time from fertilization of a female ovum by a male spermatozoon until birth.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
cell differentiation
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
multi-organism process
Any process by which an organism has an effect on another organism of the same or different species.
all
This term is the most general term possible
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
female pregnancy
The set of physiological processes that allow an embryo or foetus to develop within the body of a female animal. It covers the time from fertilization of a female ovum by a male spermatozoon until birth.
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
integral to membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer. When used to describe a protein, indicates that all or part of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
proteinaceous extracellular matrix
A layer consisting mainly of proteins (especially collagen) and glycosaminoglycans (mostly as proteoglycans) that forms a sheet underlying or overlying cells such as endothelial and epithelial cells. The proteins are secreted by cells in the vicinity.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
extracellular matrix
A structure lying external to one or more cells, which provides structural support for cells or tissues; may be completely external to the cell (as in animals) or be part of the cell (as in plants).
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
all
This term is the most general term possible
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.

protein binding
Interacting selectively with any protein or protein complex (a complex of two or more proteins that may include other nonprotein molecules).
molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
receptor binding
Interacting selectively with one or more specific sites on a receptor molecule, a macromolecule that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function.
binding
The selective, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
growth factor activity
The function that stimulates a cell to grow or proliferate. Most growth factors have other actions besides the induction of cell growth or proliferation.
all
This term is the most general term possible
ACADSacyl-Coenzyme A dehydrogenase, C-2 to C-3 short chain (202366_at), score: -0.63 ADAMTS5ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 5 (219935_at), score: -0.67 ADCY7adenylate cyclase 7 (203741_s_at), score: -0.55 AHRaryl hydrocarbon receptor (202820_at), score: 0.63 AMPHamphiphysin (205257_s_at), score: -0.57 C13orf15chromosome 13 open reading frame 15 (218723_s_at), score: -0.55 C4orf31chromosome 4 open reading frame 31 (219747_at), score: -0.86 CDC42cell division cycle 42 (GTP binding protein, 25kDa) (208727_s_at), score: -0.55 CGBchorionic gonadotropin, beta polypeptide (205387_s_at), score: -1 CH25Hcholesterol 25-hydroxylase (206932_at), score: -0.65 CLEC2BC-type lectin domain family 2, member B (209732_at), score: -0.88 COL10A1collagen, type X, alpha 1 (217428_s_at), score: -0.73 CYP1B1cytochrome P450, family 1, subfamily B, polypeptide 1 (202436_s_at), score: 0.59 CYP26B1cytochrome P450, family 26, subfamily B, polypeptide 1 (219825_at), score: -0.62 DBNDD2dysbindin (dystrobrevin binding protein 1) domain containing 2 (218094_s_at), score: 0.6 DOK5docking protein 5 (214844_s_at), score: 0.76 DPTdermatopontin (213068_at), score: -0.68 EMP2epithelial membrane protein 2 (204975_at), score: -0.56 EMX2empty spiracles homeobox 2 (221950_at), score: -0.69 ENPP1ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 1 (205066_s_at), score: -0.65 ERAP1endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 (214012_at), score: 0.58 EVI2Aecotropic viral integration site 2A (204774_at), score: -0.54 FGF13fibroblast growth factor 13 (205110_s_at), score: -0.7 GABRA5gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, alpha 5 (206456_at), score: -0.55 GALNT3UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 3 (GalNAc-T3) (203397_s_at), score: 0.61 GATA6GATA binding protein 6 (210002_at), score: 0.62 GLI2GLI family zinc finger 2 (207034_s_at), score: 0.63 GLT25D2glycosyltransferase 25 domain containing 2 (209883_at), score: -0.73 GPR177G protein-coupled receptor 177 (221958_s_at), score: 0.6 GRAMD4GRAM domain containing 4 (212856_at), score: -0.57 HOXA11homeobox A11 (213823_at), score: -0.63 HOXA9homeobox A9 (214651_s_at), score: -0.59 HOXB6homeobox B6 (205366_s_at), score: -0.59 IER3immediate early response 3 (201631_s_at), score: 0.57 IL11RAinterleukin 11 receptor, alpha (204773_at), score: -0.63 IL1R1interleukin 1 receptor, type I (202948_at), score: -0.55 INHBAinhibin, beta A (210511_s_at), score: 0.56 INHBBinhibin, beta B (205258_at), score: -0.62 INPP4Binositol polyphosphate-4-phosphatase, type II, 105kDa (205376_at), score: -0.57 IRX5iroquois homeobox 5 (210239_at), score: -0.77 JAG1jagged 1 (Alagille syndrome) (216268_s_at), score: 0.61 JAM2junctional adhesion molecule 2 (219213_at), score: -0.62 LAPTM5lysosomal multispanning membrane protein 5 (201721_s_at), score: -0.76 LGALS3BPlectin, galactoside-binding, soluble, 3 binding protein (200923_at), score: 0.67 LRRC15leucine rich repeat containing 15 (213909_at), score: -0.64 LRRC17leucine rich repeat containing 17 (205381_at), score: 0.63 LTBP1latent transforming growth factor beta binding protein 1 (202728_s_at), score: 0.66 MANSC1MANSC domain containing 1 (220945_x_at), score: 0.54 MAPKAPK3mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 3 (202788_at), score: -0.68 ME3malic enzyme 3, NADP(+)-dependent, mitochondrial (204663_at), score: 0.54 MEGF6multiple EGF-like-domains 6 (213942_at), score: -0.66 METmet proto-oncogene (hepatocyte growth factor receptor) (211599_x_at), score: -0.64 MGC87042similar to Six transmembrane epithelial antigen of prostate (217553_at), score: -0.61 MMP3matrix metallopeptidase 3 (stromelysin 1, progelatinase) (205828_at), score: -0.69 MXRA5matrix-remodelling associated 5 (209596_at), score: -0.59 NBL1neuroblastoma, suppression of tumorigenicity 1 (37005_at), score: -0.59 NCAM1neural cell adhesion molecule 1 (212843_at), score: -0.8 NR2F2nuclear receptor subfamily 2, group F, member 2 (215073_s_at), score: 0.58 NRG1neuregulin 1 (206343_s_at), score: -0.58 NRXN3neurexin 3 (205795_at), score: 0.57 NTF3neurotrophin 3 (206706_at), score: -0.67 OSBPL10oxysterol binding protein-like 10 (219073_s_at), score: 0.55 OSR2odd-skipped related 2 (Drosophila) (213568_at), score: -0.56 PLAC8placenta-specific 8 (219014_at), score: -0.74 PNMA2paraneoplastic antigen MA2 (209598_at), score: 0.6 PPP2R2Bprotein phosphatase 2 (formerly 2A), regulatory subunit B, beta isoform (213849_s_at), score: -0.74 PRR7proline rich 7 (synaptic) (219742_at), score: -0.56 PSG2pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 2 (208134_x_at), score: -0.71 PSG4pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 4 (208191_x_at), score: -0.6 PSG5pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 5 (204830_x_at), score: -0.62 PSG6pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 6 (209738_x_at), score: -0.68 PSG7pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 7 (205602_x_at), score: -0.67 PSG9pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 9 (209594_x_at), score: -0.65 PTPRBprotein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, B (205846_at), score: -0.58 PTPRRprotein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, R (210675_s_at), score: -0.54 RASIP1Ras interacting protein 1 (220027_s_at), score: -0.6 RELNreelin (205923_at), score: 0.61 RGS4regulator of G-protein signaling 4 (204338_s_at), score: 0.63 RPS6KA5ribosomal protein S6 kinase, 90kDa, polypeptide 5 (204633_s_at), score: -0.6 RUNX3runt-related transcription factor 3 (204198_s_at), score: -0.74 SALL1sal-like 1 (Drosophila) (206893_at), score: -0.59 SCN9Asodium channel, voltage-gated, type IX, alpha subunit (206950_at), score: 0.59 SCRG1scrapie responsive protein 1 (205475_at), score: 0.56 SLC12A7solute carrier family 12 (potassium/chloride transporters), member 7 (218066_at), score: 0.56 SLC16A5solute carrier family 16, member 5 (monocarboxylic acid transporter 6) (206600_s_at), score: -0.65 SOBPsine oculis binding protein homolog (Drosophila) (218974_at), score: 0.59 SOCS2suppressor of cytokine signaling 2 (203373_at), score: -0.57 SPATS2spermatogenesis associated, serine-rich 2 (218324_s_at), score: 0.54 ST6GALNAC5ST6 (alpha-N-acetyl-neuraminyl-2,3-beta-galactosyl-1,3)-N-acetylgalactosaminide alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase 5 (220979_s_at), score: -0.72 SVILsupervillin (202565_s_at), score: 0.57 TACSTD2tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (202286_s_at), score: -0.65 TBX5T-box 5 (207155_at), score: -0.56 TCF7L1transcription factor 7-like 1 (T-cell specific, HMG-box) (221016_s_at), score: 0.68 TNFAIP3tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 3 (202644_s_at), score: 0.63 TSPAN13tetraspanin 13 (217979_at), score: -0.55 TSPAN4tetraspanin 4 (209264_s_at), score: -0.58 TWIST1twist homolog 1 (Drosophila) (213943_at), score: -0.6 WNT5Bwingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 5B (221029_s_at), score: -0.6
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690360.cel | 12 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM0316B |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690416.cel | 15 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM0316B |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949557.cel | 1 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | CS | eGFP |