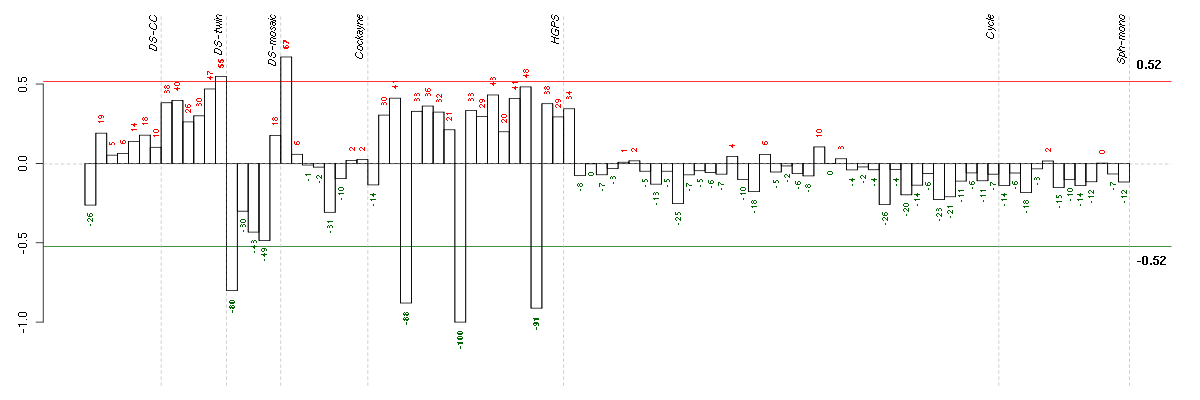

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of nervous tissue over time, from its formation to its mature state.
central nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the central nervous system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The central nervous system is the core nervous system that serves an integrating and coordinating function. In vertebrates it consists of the brain, spinal cord and spinal nerves. In those invertebrates with a central nervous system it typically consists of a brain, cerebral ganglia and a nerve cord.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
neurogenesis
Generation of cells within the nervous system.
cell differentiation
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate.
neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
cell fate commitment
The commitment of cells to specific cell fates and their capacity to differentiate into particular kinds of cells. Positional information is established through protein signals that emanate from a localized source within a cell (the initial one-cell zygote) or within a developmental field.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
negative regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
regulation of neuron differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neuron differentiation.
negative regulation of neuron differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of neuron differentiation.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
neuron fate commitment
The process whereby the developmental fate of a cell becomes restricted such that it will develop into a neuron.
generation of neurons
The process by which nerve cells are generated. This includes the production of neuroblasts and their differentiation into neurons.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of developmental process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
negative regulation of developmental process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
regulation of nervous system development
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of nervous system development, the origin and formation of nervous tissue.
regulation of cell development
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
all
This term is the most general term possible
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
negative regulation of developmental process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of developmental process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
negative regulation of developmental process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of nervous system development
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of nervous system development, the origin and formation of nervous tissue.
negative regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
cell fate commitment
The commitment of cells to specific cell fates and their capacity to differentiate into particular kinds of cells. Positional information is established through protein signals that emanate from a localized source within a cell (the initial one-cell zygote) or within a developmental field.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
negative regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
cell development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
negative regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
regulation of cell development
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the progression of the cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a specific fate.
regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
neuron differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron.
regulation of neurogenesis
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the origin and formation of neurons.
regulation of neuron differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neuron differentiation.
negative regulation of neuron differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of neuron differentiation.
neuron fate commitment
The process whereby the developmental fate of a cell becomes restricted such that it will develop into a neuron.
central nervous system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the central nervous system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The central nervous system is the core nervous system that serves an integrating and coordinating function. In vertebrates it consists of the brain, spinal cord and spinal nerves. In those invertebrates with a central nervous system it typically consists of a brain, cerebral ganglia and a nerve cord.
neurogenesis
Generation of cells within the nervous system.
regulation of nervous system development
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of nervous system development, the origin and formation of nervous tissue.
negative regulation of neuron differentiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of neuron differentiation.

extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
extracellular space
That part of a multicellular organism outside the cells proper, usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid.
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
all
This term is the most general term possible
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.

ADAM23ADAM metallopeptidase domain 23 (206046_at), score: -0.88 APOL1apolipoprotein L, 1 (209546_s_at), score: -0.66 ARID5AAT rich interactive domain 5A (MRF1-like) (213138_at), score: -0.67 ARL4CADP-ribosylation factor-like 4C (202207_at), score: -0.69 CA11carbonic anhydrase XI (209726_at), score: -0.62 CDH13cadherin 13, H-cadherin (heart) (204726_at), score: -0.71 COL4A5collagen, type IV, alpha 5 (213110_s_at), score: -0.75 CYFIP2cytoplasmic FMR1 interacting protein 2 (215785_s_at), score: -0.76 DAAM2dishevelled associated activator of morphogenesis 2 (212793_at), score: -0.77 DNAJB5DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily B, member 5 (212817_at), score: -0.71 EFHD1EF-hand domain family, member D1 (209343_at), score: -0.91 ERAP1endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 (214012_at), score: -0.68 FHOD1formin homology 2 domain containing 1 (218530_at), score: -0.79 GALNT3UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 3 (GalNAc-T3) (203397_s_at), score: -0.92 GPX3glutathione peroxidase 3 (plasma) (214091_s_at), score: -0.83 HES1hairy and enhancer of split 1, (Drosophila) (203394_s_at), score: -0.67 HNMThistamine N-methyltransferase (204112_s_at), score: -0.76 IL23Ainterleukin 23, alpha subunit p19 (211796_s_at), score: -0.63 LAMA4laminin, alpha 4 (202202_s_at), score: 0.84 LIMS2LIM and senescent cell antigen-like domains 2 (220765_s_at), score: -0.62 LMOD1leiomodin 1 (smooth muscle) (203766_s_at), score: -0.73 LPPLIM domain containing preferred translocation partner in lipoma (202822_at), score: -0.63 MAN2A2mannosidase, alpha, class 2A, member 2 (202032_s_at), score: -0.67 MLXIPMLX interacting protein (202519_at), score: -0.64 NAP1L3nucleosome assembly protein 1-like 3 (204749_at), score: 0.81 NESnestin (218678_at), score: -0.71 NOTCH1Notch homolog 1, translocation-associated (Drosophila) (218902_at), score: -0.64 NOTCH3Notch homolog 3 (Drosophila) (203238_s_at), score: -0.69 NRXN3neurexin 3 (205795_at), score: -0.9 P2RX4purinergic receptor P2X, ligand-gated ion channel, 4 (204088_at), score: -0.64 PDE4Aphosphodiesterase 4A, cAMP-specific (phosphodiesterase E2 dunce homolog, Drosophila) (204735_at), score: -0.65 PDGFAplatelet-derived growth factor alpha polypeptide (205463_s_at), score: -0.82 PDLIM3PDZ and LIM domain 3 (209621_s_at), score: -1 PLAUplasminogen activator, urokinase (211668_s_at), score: -0.64 PRSS3protease, serine, 3 (213421_x_at), score: -0.77 PSMB9proteasome (prosome, macropain) subunit, beta type, 9 (large multifunctional peptidase 2) (204279_at), score: -0.66 PTK2PTK2 protein tyrosine kinase 2 (207821_s_at), score: -0.63 PTPRZ1protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor-type, Z polypeptide 1 (204469_at), score: -0.69 RELNreelin (205923_at), score: -0.69 RTN1reticulon 1 (203485_at), score: -0.95 SCARB1scavenger receptor class B, member 1 (201819_at), score: -0.76 SCG2secretogranin II (chromogranin C) (204035_at), score: -0.64 SCN9Asodium channel, voltage-gated, type IX, alpha subunit (206950_at), score: -0.67 SIM2single-minded homolog 2 (Drosophila) (206558_at), score: -0.82 SOBPsine oculis binding protein homolog (Drosophila) (218974_at), score: -0.62 SORT1sortilin 1 (212807_s_at), score: -0.7 STAT4signal transducer and activator of transcription 4 (206118_at), score: -0.67 STBD1starch binding domain 1 (203986_at), score: -0.66 SYNMsynemin, intermediate filament protein (212730_at), score: -0.64 TEAD3TEA domain family member 3 (209454_s_at), score: -0.7 TFPItissue factor pathway inhibitor (lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor) (209676_at), score: -0.67 TNFSF4tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 4 (207426_s_at), score: -0.89 TSPAN12tetraspanin 12 (219274_at), score: -0.77 UBA7ubiquitin-like modifier activating enzyme 7 (203281_s_at), score: -0.67 ZFHX3zinc finger homeobox 3 (208033_s_at), score: -0.64
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690336.cel | 9 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG10750 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690432.cel | 16 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG10750 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690231.cel | 4 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG10750 |
| 46A.CEL | 1 | 3 | DS-mosaic | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-mosaic 1 |
| 6Twin.CEL | 6 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-twin 6 |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949557.cel | 1 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | CS | eGFP |