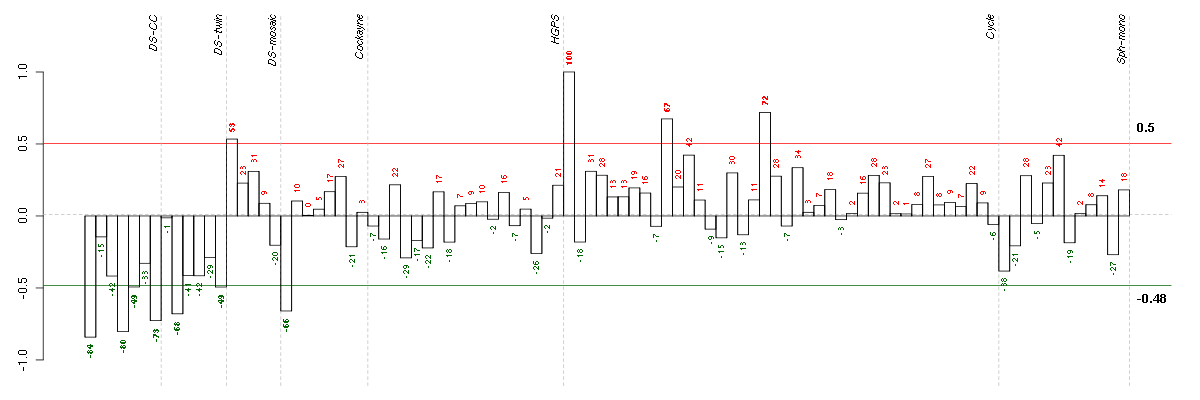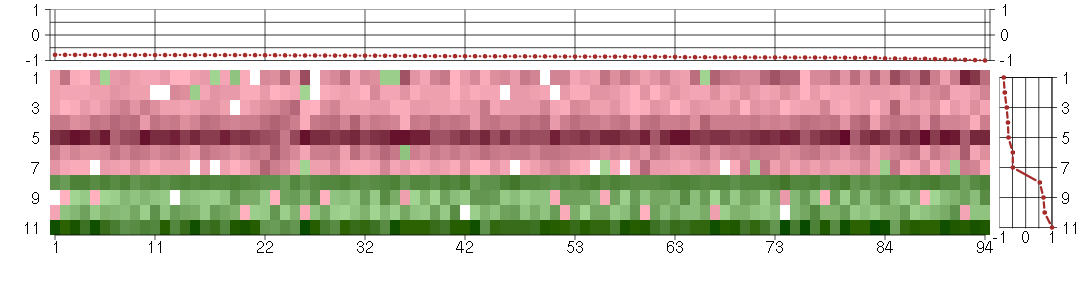

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

regulation of DNA recombination
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of DNA recombination, a process by which a new genotype is formed by reassortment of genes resulting in gene combinations different from those that were present in the parents.
metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
cell activation
A change in the morphology or behavior of a cell resulting from exposure to an activating factor such as a cellular or soluble ligand.
somatic diversification of immune receptors
The somatic process allowing for the production of immune receptors whose specificity is not encoded in the germline genomic sequences.
somatic recombination of immunoglobulin genes during immune response
The process by which immunoglobulin genes are formed through recombination of the germline genetic elements, also known as immunoglobulin gene segments, within a single locus following the induction of an immune response.
somatic diversification of immunoglobulins during immune response
The somatic process by means of which sequence diversity of immunoglobulins is generated after the induction of an immune response.
adaptive immune response
An immune response based on directed amplification of specific receptors for antigen produced through a somatic diversification process, and allowing for enhanced response to subsequent exposures to the same antigen (immunological memory).
immune effector process
Any process of the immune system that occurs as part of an immune response.
immune system process
Any process involved in the development or functioning of the immune system, an organismal system for calibrated responses to potential internal or invasive threats.
immunoglobulin production
The appearance of immunoglobulin due to biosynthesis or secretion following a cellular stimulus, resulting in an increase in its intracellular or extracellular levels.
immunoglobulin production during immune response
The appearance of immunoglobulin due to biosynthesis or secretion following a cellular stimulus during an immune response, resulting in an increase in its intracellular or extracellular levels.
production of molecular mediator of immune response
The synthesis or release of any molecular mediator of the immune response following an immunological stimulus, resulting in an increase in its intracellular or extracellular levels.
leukocyte mediated immunity
Any process involved in the carrying out of an immune response by a leukocyte.
lymphocyte mediated immunity
Any process involved in the carrying out of an immune response by a lymphocyte.
adaptive immune response based on somatic recombination of immune receptors built from immunoglobulin superfamily domains
An immune response based on directed amplification of specific receptors for antigen produced through a somatic diversification process that includes somatic recombination of germline gene segments encoding immunoglobulin superfamily domains, and allowing for enhanced responses upon subsequent exposures to the same antigen (immunological memory). Recombined receptors for antigen encoded by immunoglobulin superfamily domains include T cell receptors and immunoglobulins (antibodies).
immune system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system whose objective is to provide calibrated responses by an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat, over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
somatic diversification of immune receptors via germline recombination within a single locus
The process by which immune receptor genes are diversified through recombination of the germline genetic elements within a single genetic locus.
regulation of immunoglobulin production
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of immunoglobulin production.
regulation of immune system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
positive regulation of immune system process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
regulation of leukocyte activation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte activation.
positive regulation of leukocyte activation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte activation.
regulation of immune effector process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune effector process.
regulation of production of molecular mediator of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of the production of molecular mediator of immune response.
regulation of leukocyte mediated immunity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte mediated immunity.
regulation of lymphocyte mediated immunity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of lymphocyte mediated immunity.
regulation of B cell mediated immunity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of B cell mediated immunity.
regulation of adaptive immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an adaptive immune response.
regulation of adaptive immune response based on somatic recombination of immune receptors built from immunoglobulin superfamily domains
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an adaptive immune response based on somatic recombination of immune receptors built from immunoglobulin superfamily domains.
regulation of immunoglobulin mediated immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immunoglobulin mediated immune response.
system process
A multicellular organismal process carried out by any of the organs or tissues in an organ system. An organ system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a biological objective.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
DNA metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid, one of the two main types of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from one, or more commonly, two, strands of linked deoxyribonucleotides.
DNA recombination
Any process by which a new genotype is formed by reassortment of genes resulting in gene combinations different from those that were present in the parents. In eukaryotes genetic recombination can occur by chromosome assortment, intrachromosomal recombination, or nonreciprocal interchromosomal recombination. Intrachromosomal recombination occurs by crossing over. In bacteria it may occur by genetic transformation, conjugation, transduction, or F-duction.
transport
The directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells, or within a multicellular organism.
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
neurological system process
A organ system process carried out by any of the organs or tissues of neurological system.
sensory perception
The series of events required for an organism to receive a sensory stimulus, convert it to a molecular signal, and recognize and characterize the signal.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
positive regulation of metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
peptide transport
The directed movement of peptides, compounds of two or more amino acids where the alpha carboxyl group of one is bound to the alpha amino group of another, into, out of, within or between cells.
immunoglobulin mediated immune response
An immune response mediated by immunoglobulins, whether cell-bound or in solution.
positive regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
somatic cell DNA recombination
Recombination occurring within or between DNA molecules in somatic cells.
somatic diversification of immunoglobulins
The somatic process by means of which sequence diversity of immunoglobulins is generated.
somatic recombination of immunoglobulin gene segments
The process by which immunoglobulin genes are formed through recombination of the germline genetic elements, as known as immunoglobulin gene segments, within a single locus.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
B cell mediated immunity
Any process involved with the carrying out of an immune response by a B cell, through, for instance, the production of antibodies or cytokines, or antigen presentation to T cells.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
B cell activation
The change in morphology and behavior of a mature or immature B cell resulting from exposure to a mitogen, cytokine, chemokine, cellular ligand, or an antigen for which it is specific.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
isotype switching
The switching of activated B cells from IgM biosynthesis to biosynthesis of other isotypes of immunoglobulin, accomplished through a recombination process involving an intrachromosomal deletion involving switch regions that reside 5' of each constant region gene segment in the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus.
regulation of isotype switching
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of isotype switching.
leukocyte activation
A change in morphology and behavior of a leukocyte resulting from exposure to a specific antigen, mitogen, cytokine, cellular ligand, or soluble factor.
positive regulation of isotype switching
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of isotype switching.
positive regulation of DNA recombination
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of DNA recombination.
lymphocyte activation
A change in morphology and behavior of a lymphocyte resulting from exposure to a specific antigen, mitogen, cytokine, chemokine, cellular ligand, or soluble factor.
isotype switching to IgG isotypes
The switching of activated B cells from IgM biosynthesis to biosynthesis of an IgG isotype, accomplished through a recombination process involving an intrachromosomal deletion between switch regions that reside 5' of the IgM and one of the IgG constant region gene segments in the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus.
regulation of isotype switching to IgG isotypes
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of isotype switching to IgG isotypes.
positive regulation of isotype switching to IgG isotypes
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of isotype switching to IgG isotypes.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
regulation of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of developmental process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of B cell activation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of B cell activation.
regulation of cell activation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell activation, the change in the morphology or behavior of a cell resulting from exposure to an activating factor such as a cellular or soluble ligand.
positive regulation of cell activation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of activation.
positive regulation of B cell activation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of B cell activation.
cognition
The operation of the mind by which an organism becomes aware of objects of thought or perception; it includes the mental activities associated with thinking, learning, and memory.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of DNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving DNA.
positive regulation of DNA metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving DNA.
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
regulation of lymphocyte activation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of lymphocyte activation.
positive regulation of lymphocyte activation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of lymphocyte activation.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
positive regulation of immune system process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
positive regulation of metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of immune system process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of developmental process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of multicellular organismal process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a multicellular organismal process, the processes pertinent to the function of a multicellular organism above the cellular level; includes the integrated processes of tissues and organs.
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
regulation of response to stimulus
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a response to a stimulus. Response to stimulus is a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
positive regulation of metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
somatic diversification of immune receptors
The somatic process allowing for the production of immune receptors whose specificity is not encoded in the germline genomic sequences.
positive regulation of immune system process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune system process.
immune effector process
Any process of the immune system that occurs as part of an immune response.
regulation of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
regulation of leukocyte activation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte activation.
positive regulation of leukocyte activation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte activation.
leukocyte activation
A change in morphology and behavior of a leukocyte resulting from exposure to a specific antigen, mitogen, cytokine, cellular ligand, or soluble factor.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of cell activation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of activation.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of cell activation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell activation, the change in the morphology or behavior of a cell resulting from exposure to an activating factor such as a cellular or soluble ligand.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
regulation of isotype switching
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of isotype switching.
regulation of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the immune response, the immunological reaction of an organism to an immunogenic stimulus.
positive regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
positive regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
somatic recombination of immunoglobulin gene segments
The process by which immunoglobulin genes are formed through recombination of the germline genetic elements, as known as immunoglobulin gene segments, within a single locus.
regulation of production of molecular mediator of immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of the production of molecular mediator of immune response.
regulation of leukocyte mediated immunity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte mediated immunity.
positive regulation of leukocyte activation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte activation.
regulation of immune effector process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune effector process.
regulation of adaptive immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an adaptive immune response.
regulation of lymphocyte activation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of lymphocyte activation.
positive regulation of lymphocyte activation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of lymphocyte activation.
regulation of leukocyte activation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte activation.
positive regulation of cell activation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of activation.
positive regulation of leukocyte activation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of leukocyte activation.
immune system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system whose objective is to provide calibrated responses by an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat, over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
positive regulation of DNA metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving DNA.
positive regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of DNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving DNA.
positive regulation of DNA metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving DNA.
DNA metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid, one of the two main types of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from one, or more commonly, two, strands of linked deoxyribonucleotides.
regulation of DNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving DNA.
positive regulation of DNA metabolic process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving DNA.
somatic recombination of immunoglobulin genes during immune response
The process by which immunoglobulin genes are formed through recombination of the germline genetic elements, also known as immunoglobulin gene segments, within a single locus following the induction of an immune response.
somatic diversification of immunoglobulins
The somatic process by means of which sequence diversity of immunoglobulins is generated.
regulation of immunoglobulin production
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of immunoglobulin production.
regulation of lymphocyte mediated immunity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of lymphocyte mediated immunity.
positive regulation of lymphocyte activation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of lymphocyte activation.
regulation of adaptive immune response based on somatic recombination of immune receptors built from immunoglobulin superfamily domains
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an adaptive immune response based on somatic recombination of immune receptors built from immunoglobulin superfamily domains.
B cell mediated immunity
Any process involved with the carrying out of an immune response by a B cell, through, for instance, the production of antibodies or cytokines, or antigen presentation to T cells.
regulation of B cell activation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of B cell activation.
positive regulation of B cell activation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of B cell activation.
positive regulation of isotype switching to IgG isotypes
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of isotype switching to IgG isotypes.
positive regulation of isotype switching
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of isotype switching.
regulation of isotype switching
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of isotype switching.
positive regulation of DNA recombination
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of DNA recombination.
regulation of DNA recombination
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of DNA recombination, a process by which a new genotype is formed by reassortment of genes resulting in gene combinations different from those that were present in the parents.
positive regulation of DNA recombination
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of DNA recombination.
isotype switching
The switching of activated B cells from IgM biosynthesis to biosynthesis of other isotypes of immunoglobulin, accomplished through a recombination process involving an intrachromosomal deletion involving switch regions that reside 5' of each constant region gene segment in the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus.
somatic diversification of immunoglobulins during immune response
The somatic process by means of which sequence diversity of immunoglobulins is generated after the induction of an immune response.
regulation of isotype switching
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of isotype switching.
regulation of B cell mediated immunity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of B cell mediated immunity.
regulation of isotype switching
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of isotype switching.
positive regulation of B cell activation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of B cell activation.
regulation of B cell mediated immunity
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of B cell mediated immunity.
positive regulation of isotype switching
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of isotype switching.
regulation of isotype switching
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of isotype switching.
positive regulation of isotype switching
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of isotype switching.
somatic diversification of immune receptors via germline recombination within a single locus
The process by which immune receptor genes are diversified through recombination of the germline genetic elements within a single genetic locus.
immunoglobulin production during immune response
The appearance of immunoglobulin due to biosynthesis or secretion following a cellular stimulus during an immune response, resulting in an increase in its intracellular or extracellular levels.
regulation of immunoglobulin mediated immune response
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of an immunoglobulin mediated immune response.
regulation of isotype switching to IgG isotypes
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of isotype switching to IgG isotypes.
positive regulation of isotype switching to IgG isotypes
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of isotype switching to IgG isotypes.
regulation of isotype switching
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of isotype switching.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
integral to membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer. When used to describe a protein, indicates that all or part of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
signal transducer activity
Mediates the transfer of a signal from the outside to the inside of a cell by means other than the introduction of the signal molecule itself into the cell.
receptor activity
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell activity.
transmembrane receptor activity
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell activity, and spanning to the membrane of either the cell or an organelle.
G-protein coupled receptor activity
A receptor that binds an extracellular ligand and transmits the signal to a heterotrimeric G-protein complex. These receptors are characteristically seven-transmembrane receptors and are made up of hetero- or homodimers.
binding
The selective, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
neurotransmitter receptor activity
Combining with a neurotransmitter to initiate a change in cell activity.
neurotransmitter binding
Interacting selectively with a neurotransmitter, any chemical substance that is capable of transmitting (or inhibiting the transmission of) a nerve impulse from a neuron to another cell.
molecular transducer activity
The molecular function that accepts an input of one form and creates an output of a different form.
all
This term is the most general term possible
neurotransmitter receptor activity
Combining with a neurotransmitter to initiate a change in cell activity.
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 04080 | 4.122e-02 | 0.7545 | 5 | 78 | Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction |
A1CFAPOBEC1 complementation factor (220951_s_at), score: -0.81 ADAMTS9ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 9 (220287_at), score: -0.85 ADAMTSL4ADAMTS-like 4 (220578_at), score: -0.78 AGMATagmatine ureohydrolase (agmatinase) (219792_at), score: -0.87 AIPL1aryl hydrocarbon receptor interacting protein-like 1 (219977_at), score: -0.78 APOMapolipoprotein M (205682_x_at), score: -0.84 BEND5BEN domain containing 5 (219670_at), score: -0.78 BMP10bone morphogenetic protein 10 (208292_at), score: -0.78 BRS3bombesin-like receptor 3 (207369_at), score: -0.78 BTNL3butyrophilin-like 3 (217207_s_at), score: -0.88 C1orf61chromosome 1 open reading frame 61 (205103_at), score: -0.85 C2orf54chromosome 2 open reading frame 54 (220149_at), score: -0.78 C7orf28Achromosome 7 open reading frame 28A (201974_s_at), score: -0.88 C8orf17chromosome 8 open reading frame 17 (208266_at), score: -0.81 C8orf60chromosome 8 open reading frame 60 (220712_at), score: -0.83 CA4carbonic anhydrase IV (206209_s_at), score: -0.82 CASZ1castor zinc finger 1 (220015_at), score: -0.83 CEACAM5carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 5 (201884_at), score: -0.85 CEACAM6carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (non-specific cross reacting antigen) (211657_at), score: -0.95 CHD2chromodomain helicase DNA binding protein 2 (203461_at), score: -0.84 CHN2chimerin (chimaerin) 2 (207486_x_at), score: -0.79 CHST4carbohydrate (N-acetylglucosamine 6-O) sulfotransferase 4 (220446_s_at), score: -0.81 CLDN10claudin 10 (205328_at), score: -0.88 CLDN18claudin 18 (214135_at), score: -0.83 CLEC4MC-type lectin domain family 4, member M (207995_s_at), score: -0.88 CNKSR2connector enhancer of kinase suppressor of Ras 2 (206731_at), score: -0.85 COL11A2collagen, type XI, alpha 2 (216993_s_at), score: -0.81 CSN2casein beta (207951_at), score: -0.89 CTSEcathepsin E (205927_s_at), score: -0.8 DAOD-amino-acid oxidase (206878_at), score: -0.79 DNASE1L3deoxyribonuclease I-like 3 (205554_s_at), score: -0.86 DRD5dopamine receptor D5 (208486_at), score: -0.9 EDARectodysplasin A receptor (220048_at), score: -0.79 ELNelastin (212670_at), score: -0.78 FAM38Bfamily with sequence similarity 38, member B (219602_s_at), score: -0.92 FAM75A3family with sequence similarity 75, member A3 (215935_at), score: -0.83 GABRR2gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor, rho 2 (208217_at), score: -0.79 GNRHRgonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor (216341_s_at), score: -0.85 GPR12G protein-coupled receptor 12 (214558_at), score: -0.85 GRHL2grainyhead-like 2 (Drosophila) (219388_at), score: -0.81 HAO2hydroxyacid oxidase 2 (long chain) (220801_s_at), score: -0.82 HOXD4homeobox D4 (205522_at), score: -0.79 IFNGinterferon, gamma (210354_at), score: -0.79 ITIH2inter-alpha (globulin) inhibitor H2 (204987_at), score: -0.79 ITKIL2-inducible T-cell kinase (211339_s_at), score: -0.82 KCNJ16potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 16 (219564_at), score: -0.84 KLF1Kruppel-like factor 1 (erythroid) (210504_at), score: -0.89 KMOkynurenine 3-monooxygenase (kynurenine 3-hydroxylase) (205307_s_at), score: -0.78 KRT2keratin 2 (207908_at), score: -0.83 LHX3LIM homeobox 3 (221670_s_at), score: -0.96 LOC100188945cell division cycle associated 4 pseudogene (215109_at), score: -0.88 LOC389906similar to Serine/threonine-protein kinase PRKX (Protein kinase PKX1) (59433_at), score: -0.88 MBmyoglobin (204179_at), score: -0.9 MEP1Bmeprin A, beta (207251_at), score: -0.83 MFNGMFNG O-fucosylpeptide 3-beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (204153_s_at), score: -0.92 MMRN2multimerin 2 (219091_s_at), score: -0.93 MOBPmyelin-associated oligodendrocyte basic protein (210193_at), score: -0.9 MSTP9macrophage stimulating, pseudogene 9 (213382_at), score: -0.88 MUC3Amucin 3A, cell surface associated (217117_x_at), score: -0.8 MYL4myosin, light chain 4, alkali; atrial, embryonic (210088_x_at), score: -0.83 MYO1Amyosin IA (211916_s_at), score: -0.8 N4BP3Nedd4 binding protein 3 (214775_at), score: -0.84 NINninein (GSK3B interacting protein) (219285_s_at), score: -0.79 NOTCH4Notch homolog 4 (Drosophila) (205247_at), score: -0.79 NRN1neuritin 1 (218625_at), score: -0.88 NTNG1netrin G1 (206713_at), score: -0.85 NTRK2neurotrophic tyrosine kinase, receptor, type 2 (207152_at), score: -0.79 OCLMoculomedin (208274_at), score: -0.8 OR7E24olfactory receptor, family 7, subfamily E, member 24 (215463_at), score: -0.93 PECAM1platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule (208982_at), score: -0.94 PLUNCpalate, lung and nasal epithelium associated (220542_s_at), score: -0.83 PRSS7protease, serine, 7 (enterokinase) (217269_s_at), score: -0.98 PYHIN1pyrin and HIN domain family, member 1 (216748_at), score: -0.85 RETret proto-oncogene (205879_x_at), score: -0.85 ROS1c-ros oncogene 1 , receptor tyrosine kinase (207569_at), score: -0.81 RP11-35N6.1plasticity related gene 3 (219732_at), score: -0.89 RPGRIP1retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator interacting protein 1 (206608_s_at), score: -0.93 RRHretinal pigment epithelium-derived rhodopsin homolog (208314_at), score: -0.79 S100A14S100 calcium binding protein A14 (218677_at), score: -0.88 SCN10Asodium channel, voltage-gated, type X, alpha subunit (208578_at), score: -0.78 SEMA6Dsema domain, transmembrane domain (TM), and cytoplasmic domain, (semaphorin) 6D (220574_at), score: -0.87 SLC10A1solute carrier family 10 (sodium/bile acid cotransporter family), member 1 (207185_at), score: -0.84 SLC10A2solute carrier family 10 (sodium/bile acid cotransporter family), member 2 (207095_at), score: -0.78 SLC15A1solute carrier family 15 (oligopeptide transporter), member 1 (211349_at), score: -0.83 SLC1A7solute carrier family 1 (glutamate transporter), member 7 (210923_at), score: -0.79 TACR1tachykinin receptor 1 (208048_at), score: -0.87 TAS2R9taste receptor, type 2, member 9 (221461_at), score: -0.85 TBX21T-box 21 (220684_at), score: -0.85 TBX6T-box 6 (207684_at), score: -0.87 TP63tumor protein p63 (209863_s_at), score: -0.88 TRA@T cell receptor alpha locus (216540_at), score: -1 TRIM10tripartite motif-containing 10 (56748_at), score: -0.79 VGFVGF nerve growth factor inducible (205586_x_at), score: -0.97
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ctrl a 08-03.CEL | 1 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | none | DS-CC 1 |
| t21a 08-03.CEL | 4 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | Down | DS-CC 4 |
| t21d 08-03.CEL | 7 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | Down | DS-CC 7 |
| 2Twin.CEL | 2 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-twin 2 |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949557.cel | 1 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | CS | eGFP |
| 6Twin.CEL | 6 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-twin 6 |
| t21b 08-03.CEL | 5 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | Down | DS-CC 5 |
| 46A.CEL | 1 | 3 | DS-mosaic | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-mosaic 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485831.cel | 10 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486011.cel | 19 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485651.cel | 1 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |