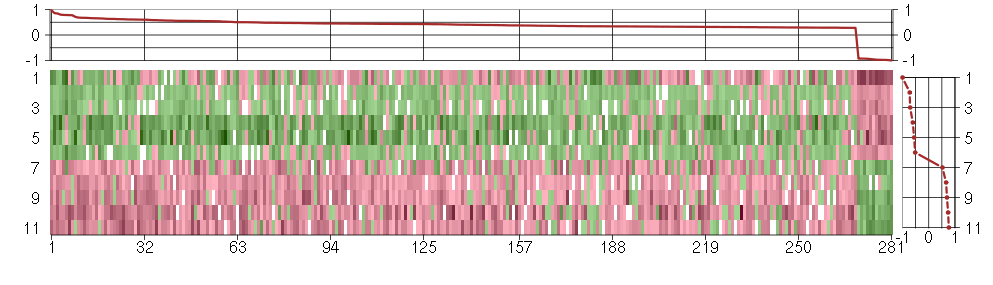

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

reproduction
The production by an organism of new individuals that contain some portion of their genetic material inherited from that organism.
signal transduction
The cascade of processes by which a signal interacts with a receptor, causing a change in the level or activity of a second messenger or other downstream target, and ultimately effecting a change in the functioning of the cell.
response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
cell communication
Any process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
cell surface receptor linked signal transduction
Any series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of an extracellular ligand to a receptor on the surface of the target cell.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis of an organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
female pregnancy
The set of physiological processes that allow an embryo or foetus to develop within the body of a female animal. It covers the time from fertilization of a female ovum by a male spermatozoon until birth.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
response to external stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an external stimulus.
response to wounding
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to the organism.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
wound healing
The series of events that restore integrity to a damaged tissue, following an injury.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
multi-organism process
Any process by which an organism has an effect on another organism of the same or different species.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
all
This term is the most general term possible
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
female pregnancy
The set of physiological processes that allow an embryo or foetus to develop within the body of a female animal. It covers the time from fertilization of a female ovum by a male spermatozoon until birth.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
signal transduction
The cascade of processes by which a signal interacts with a receptor, causing a change in the level or activity of a second messenger or other downstream target, and ultimately effecting a change in the functioning of the cell.
anatomical structure morphogenesis
The process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
response to wounding
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to the organism.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
organ morphogenesis
Morphogenesis of an organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process by which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.

plasma membrane
The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
integral to membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer. When used to describe a protein, indicates that all or part of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
proteinaceous extracellular matrix
A layer consisting mainly of proteins (especially collagen) and glycosaminoglycans (mostly as proteoglycans) that forms a sheet underlying or overlying cells such as endothelial and epithelial cells. The proteins are secreted by cells in the vicinity.
extracellular space
That part of a multicellular organism outside the cells proper, usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cell surface
The external part of the cell wall and/or plasma membrane.
dystrophin-associated glycoprotein complex
A multiprotein complex that forms a strong mechanical link between the cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix; typical of, but not confined to, muscle cells. The complex is composed of transmembrane, cytoplasmic, and extracellular proteins, including dystrophin, sarcoglycans, dystroglycan, dystrobrevins, syntrophins, sarcospan, caveolin-3, and NO synthase.
dystroglycan complex
A protein complex that includes alpha- and beta-dystroglycan, which are alternative products of the same gene; the laminin-binding component of the dystrophin-associated glycoprotein complex, providing a link between the subsarcolemmal cytoskeleton (in muscle cells) and the extracellular matrix. Alpha-dystroglycan is an extracellular protein binding to alpha-laminin and to beta-dystroglycan; beta-dystroglycan is a transmembrane protein which binds alpha-dystroglycan and dystrophin.
sarcoglycan complex
A protein complex formed of four sarcoglycans plus sarcospan; there are six known sarcoglycans: alpha-, beta-, gamma-, delta-, epsilon- and zeta-sarcoglycan; all are N-glycosylated single-pass transmembrane proteins. The sarcoglycan-sarcospan complex is a subcomplex of the dystrophin glycoprotein complex, and is fixed to the dystrophin axis by a lateral association with the dystroglycan complex.
extracellular matrix
A structure lying external to one or more cells, which provides structural support for cells or tissues; may be completely external to the cell (as in animals) or be part of the cell (as in plants).
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
protein complex
Any macromolecular complex composed of two or more polypeptide subunits, which may or may not be identical. Protein complexes may have other associated non-protein prosthetic groups, such as nucleotides, metal ions or carbohydrate groups.
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
all
This term is the most general term possible
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
dystroglycan complex
A protein complex that includes alpha- and beta-dystroglycan, which are alternative products of the same gene; the laminin-binding component of the dystrophin-associated glycoprotein complex, providing a link between the subsarcolemmal cytoskeleton (in muscle cells) and the extracellular matrix. Alpha-dystroglycan is an extracellular protein binding to alpha-laminin and to beta-dystroglycan; beta-dystroglycan is a transmembrane protein which binds alpha-dystroglycan and dystrophin.
sarcoglycan complex
A protein complex formed of four sarcoglycans plus sarcospan; there are six known sarcoglycans: alpha-, beta-, gamma-, delta-, epsilon- and zeta-sarcoglycan; all are N-glycosylated single-pass transmembrane proteins. The sarcoglycan-sarcospan complex is a subcomplex of the dystrophin glycoprotein complex, and is fixed to the dystrophin axis by a lateral association with the dystroglycan complex.
plasma membrane part
Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins.
dystrophin-associated glycoprotein complex
A multiprotein complex that forms a strong mechanical link between the cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix; typical of, but not confined to, muscle cells. The complex is composed of transmembrane, cytoplasmic, and extracellular proteins, including dystrophin, sarcoglycans, dystroglycan, dystrobrevins, syntrophins, sarcospan, caveolin-3, and NO synthase.
dystroglycan complex
A protein complex that includes alpha- and beta-dystroglycan, which are alternative products of the same gene; the laminin-binding component of the dystrophin-associated glycoprotein complex, providing a link between the subsarcolemmal cytoskeleton (in muscle cells) and the extracellular matrix. Alpha-dystroglycan is an extracellular protein binding to alpha-laminin and to beta-dystroglycan; beta-dystroglycan is a transmembrane protein which binds alpha-dystroglycan and dystrophin.
sarcoglycan complex
A protein complex formed of four sarcoglycans plus sarcospan; there are six known sarcoglycans: alpha-, beta-, gamma-, delta-, epsilon- and zeta-sarcoglycan; all are N-glycosylated single-pass transmembrane proteins. The sarcoglycan-sarcospan complex is a subcomplex of the dystrophin glycoprotein complex, and is fixed to the dystrophin axis by a lateral association with the dystroglycan complex.
intrinsic to plasma membrane
Located in the plasma membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
integral to plasma membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a plasma membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.

molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
nucleic acid binding
Interacting selectively with any nucleic acid.
DNA binding
Interacting selectively with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid).
signal transducer activity
Mediates the transfer of a signal from the outside to the inside of a cell by means other than the introduction of the signal molecule itself into the cell.
receptor activity
Combining with an extracellular or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell activity.
binding
The selective, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
sequence-specific DNA binding
Interacting selectively with DNA of a specific nucleotide composition, e.g. GC-rich DNA binding, or with a specific sequence motif or type of DNA e.g. promotor binding or rDNA binding.
molecular transducer activity
The molecular function that accepts an input of one form and creates an output of a different form.
all
This term is the most general term possible
ACYP2acylphosphatase 2, muscle type (206833_s_at), score: 0.32 ADAMTS5ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 5 (219935_at), score: 0.49 ADARB1adenosine deaminase, RNA-specific, B1 (RED1 homolog rat) (203865_s_at), score: 0.35 ADRA2Aadrenergic, alpha-2A-, receptor (209869_at), score: 0.54 ALDOCaldolase C, fructose-bisphosphate (202022_at), score: 0.41 ANGangiogenin, ribonuclease, RNase A family, 5 (213397_x_at), score: 0.29 ANGPTL4angiopoietin-like 4 (221009_s_at), score: 0.79 ANK3ankyrin 3, node of Ranvier (ankyrin G) (206385_s_at), score: -0.93 ANTXR1anthrax toxin receptor 1 (220092_s_at), score: 0.6 APPL2adaptor protein, phosphotyrosine interaction, PH domain and leucine zipper containing 2 (218218_at), score: 0.38 ARSAarylsulfatase A (204443_at), score: 0.43 ATP9AATPase, class II, type 9A (212062_at), score: 0.33 AUTS2autism susceptibility candidate 2 (212599_at), score: 0.47 B4GALT1UDP-Gal:betaGlcNAc beta 1,4- galactosyltransferase, polypeptide 1 (201883_s_at), score: 0.36 BAALCbrain and acute leukemia, cytoplasmic (218899_s_at), score: 0.35 BACE2beta-site APP-cleaving enzyme 2 (217867_x_at), score: 0.39 BDKRB1bradykinin receptor B1 (207510_at), score: 0.29 BNIP3LBCL2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa interacting protein 3-like (221479_s_at), score: 0.34 C10orf116chromosome 10 open reading frame 116 (203571_s_at), score: 0.32 C17orf91chromosome 17 open reading frame 91 (214696_at), score: 0.44 C20orf30chromosome 20 open reading frame 30 (220477_s_at), score: 0.34 C20orf39chromosome 20 open reading frame 39 (219310_at), score: 0.3 C3orf64chromosome 3 open reading frame 64 (221935_s_at), score: 0.47 C5orf23chromosome 5 open reading frame 23 (219054_at), score: 0.54 C5orf30chromosome 5 open reading frame 30 (221823_at), score: 0.49 CAMK2N1calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II inhibitor 1 (218309_at), score: 0.55 CBFBcore-binding factor, beta subunit (206788_s_at), score: 0.47 CBLBCas-Br-M (murine) ecotropic retroviral transforming sequence b (209682_at), score: 0.46 CCRL1chemokine (C-C motif) receptor-like 1 (220351_at), score: 0.54 CD302CD302 molecule (203799_at), score: 0.36 CD55CD55 molecule, decay accelerating factor for complement (Cromer blood group) (201925_s_at), score: 0.32 CDCP1CUB domain containing protein 1 (218451_at), score: 0.4 CGBchorionic gonadotropin, beta polypeptide (205387_s_at), score: 0.34 CHD3chromodomain helicase DNA binding protein 3 (208807_s_at), score: -0.93 CHMP1Bchromatin modifying protein 1B (218178_s_at), score: 0.35 CHPFchondroitin polymerizing factor (202175_at), score: 0.43 CLEC2BC-type lectin domain family 2, member B (209732_at), score: 0.61 CLGNcalmegin (205830_at), score: 0.33 COL13A1collagen, type XIII, alpha 1 (211343_s_at), score: 0.62 COL15A1collagen, type XV, alpha 1 (203477_at), score: 0.48 COL8A2collagen, type VIII, alpha 2 (221900_at), score: 0.48 COMPcartilage oligomeric matrix protein (205713_s_at), score: 0.55 COX7A1cytochrome c oxidase subunit VIIa polypeptide 1 (muscle) (204570_at), score: 0.31 CRATcarnitine acetyltransferase (209522_s_at), score: 0.48 CRISPLD2cysteine-rich secretory protein LCCL domain containing 2 (221541_at), score: 0.42 CST3cystatin C (201360_at), score: 0.45 CST6cystatin E/M (206595_at), score: 0.4 CTSBcathepsin B (213274_s_at), score: 0.36 CTSKcathepsin K (202450_s_at), score: 0.44 CTSOcathepsin O (203758_at), score: 0.43 CYP51A1cytochrome P450, family 51, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 (216607_s_at), score: 0.57 DCLK1doublecortin-like kinase 1 (205399_at), score: 0.31 DCNdecorin (211896_s_at), score: 0.38 DDR1discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinase 1 (208779_x_at), score: 0.38 DDX3YDEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 3, Y-linked (205000_at), score: 0.35 DKK2dickkopf homolog 2 (Xenopus laevis) (219908_at), score: 0.29 DNM1dynamin 1 (215116_s_at), score: 0.28 DPTdermatopontin (213068_at), score: 0.47 DUSP14dual specificity phosphatase 14 (203367_at), score: 0.57 ECM1extracellular matrix protein 1 (209365_s_at), score: 0.71 EDEM1ER degradation enhancer, mannosidase alpha-like 1 (203279_at), score: 0.43 EGR3early growth response 3 (206115_at), score: 0.34 EIF1AYeukaryotic translation initiation factor 1A, Y-linked (204409_s_at), score: 0.55 ELF1E74-like factor 1 (ets domain transcription factor) (212418_at), score: 0.35 ELL2elongation factor, RNA polymerase II, 2 (214446_at), score: 0.34 EMX2empty spiracles homeobox 2 (221950_at), score: 0.32 ENPP1ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 1 (205066_s_at), score: 0.5 F10coagulation factor X (205620_at), score: 0.36 F3coagulation factor III (thromboplastin, tissue factor) (204363_at), score: 0.61 FAM13Bfamily with sequence similarity 13, member B (218518_at), score: 0.41 FAM46Afamily with sequence similarity 46, member A (221766_s_at), score: 0.38 FASFas (TNF receptor superfamily, member 6) (204780_s_at), score: 0.44 FBLN5fibulin 5 (203088_at), score: 0.5 FBXW7F-box and WD repeat domain containing 7 (218751_s_at), score: 0.33 FGF13fibroblast growth factor 13 (205110_s_at), score: 0.33 FGF2fibroblast growth factor 2 (basic) (204421_s_at), score: 0.55 FGF7fibroblast growth factor 7 (keratinocyte growth factor) (205782_at), score: 0.63 FHOD3formin homology 2 domain containing 3 (218980_at), score: 0.62 FKBP1AFK506 binding protein 1A, 12kDa (210186_s_at), score: 0.33 FLJ14213protor-2 (219383_at), score: 0.38 FLRT2fibronectin leucine rich transmembrane protein 2 (204359_at), score: 0.53 FOLR3folate receptor 3 (gamma) (206371_at), score: 0.43 FOSBFBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog B (202768_at), score: 0.36 GAAglucosidase, alpha; acid (202812_at), score: 0.43 GABARAPL1GABA(A) receptor-associated protein like 1 (208868_s_at), score: 0.3 GABARAPL3GABA(A) receptors associated protein like 3 (pseudogene) (211458_s_at), score: 0.42 GABBR2gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) B receptor, 2 (209990_s_at), score: 0.63 GAS6growth arrest-specific 6 (202177_at), score: 0.56 GATA2GATA binding protein 2 (209710_at), score: 0.29 GDPD5glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase domain containing 5 (32502_at), score: 0.38 GLT25D2glycosyltransferase 25 domain containing 2 (209883_at), score: 0.46 GMDSGDP-mannose 4,6-dehydratase (204875_s_at), score: -0.98 GPC4glypican 4 (204983_s_at), score: 0.41 GPERG protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1 (210640_s_at), score: 0.33 GPNMBglycoprotein (transmembrane) nmb (201141_at), score: 0.78 GPR176G protein-coupled receptor 176 (206673_at), score: 0.3 GPR37G protein-coupled receptor 37 (endothelin receptor type B-like) (209631_s_at), score: 0.3 GRAMD3GRAM domain containing 3 (218706_s_at), score: 0.58 GREM2gremlin 2, cysteine knot superfamily, homolog (Xenopus laevis) (220794_at), score: 0.4 H2BFSH2B histone family, member S (208579_x_at), score: 0.31 HAS2hyaluronan synthase 2 (206432_at), score: 0.54 HBEGFheparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (203821_at), score: 0.32 HIP1huntingtin interacting protein 1 (205425_at), score: 0.43 HIPK3homeodomain interacting protein kinase 3 (210148_at), score: 0.34 HIST1H2BKhistone cluster 1, H2bk (209806_at), score: 0.31 HIST2H2AA3histone cluster 2, H2aa3 (214290_s_at), score: 0.54 HIVEP2human immunodeficiency virus type I enhancer binding protein 2 (212642_s_at), score: 0.66 HLA-Emajor histocompatibility complex, class I, E (200904_at), score: 0.65 HMGA2high mobility group AT-hook 2 (208025_s_at), score: -0.93 HMOX1heme oxygenase (decycling) 1 (203665_at), score: 0.97 HOXB2homeobox B2 (205453_at), score: 0.45 HOXB6homeobox B6 (205366_s_at), score: 0.39 HOXB7homeobox B7 (204779_s_at), score: 0.42 HS3ST3A1heparan sulfate (glucosamine) 3-O-sulfotransferase 3A1 (219985_at), score: 0.44 HSPB7heat shock 27kDa protein family, member 7 (cardiovascular) (218934_s_at), score: 0.86 HTR2A5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 2A (207135_at), score: 0.4 IDI1isopentenyl-diphosphate delta isomerase 1 (204615_x_at), score: 0.34 IL11interleukin 11 (206924_at), score: 0.61 IL1R1interleukin 1 receptor, type I (202948_at), score: 0.29 IL1RL1interleukin 1 receptor-like 1 (207526_s_at), score: 0.34 INHBBinhibin, beta B (205258_at), score: 0.46 INSIG1insulin induced gene 1 (201627_s_at), score: 0.52 IQSEC1IQ motif and Sec7 domain 1 (203906_at), score: 0.3 IRS2insulin receptor substrate 2 (209185_s_at), score: 0.52 IRX5iroquois homeobox 5 (210239_at), score: 0.47 ISLRimmunoglobulin superfamily containing leucine-rich repeat (207191_s_at), score: 0.64 ITGA2integrin, alpha 2 (CD49B, alpha 2 subunit of VLA-2 receptor) (205032_at), score: 0.33 ITPR3inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor, type 3 (201189_s_at), score: 0.44 JARID1Djumonji, AT rich interactive domain 1D (206700_s_at), score: 0.32 JMJD3jumonji domain containing 3, histone lysine demethylase (213146_at), score: 0.35 KCNN4potassium intermediate/small conductance calcium-activated channel, subfamily N, member 4 (204401_at), score: 0.78 KIAA1024KIAA1024 (215081_at), score: 0.28 KLHL21kelch-like 21 (Drosophila) (203068_at), score: 0.37 LBHlimb bud and heart development homolog (mouse) (221011_s_at), score: 0.8 LDLRlow density lipoprotein receptor (202068_s_at), score: 0.3 LIPAlipase A, lysosomal acid, cholesterol esterase (201847_at), score: 0.31 LMBRD1LMBR1 domain containing 1 (218191_s_at), score: 0.3 LOC100128809similar to hCG2045829 (215707_s_at), score: 0.48 LRRC15leucine rich repeat containing 15 (213909_at), score: 0.84 LTBP2latent transforming growth factor beta binding protein 2 (204682_at), score: 0.55 LTBRlymphotoxin beta receptor (TNFR superfamily, member 3) (203005_at), score: 0.33 MALLmal, T-cell differentiation protein-like (209373_at), score: 0.4 MAN2B2mannosidase, alpha, class 2B, member 2 (214703_s_at), score: 0.3 MAP2K3mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 3 (207667_s_at), score: 0.34 MEGF6multiple EGF-like-domains 6 (213942_at), score: 0.37 MEIS1Meis homeobox 1 (204069_at), score: 0.45 MEIS3P1Meis homeobox 3 pseudogene 1 (214077_x_at), score: 0.44 METmet proto-oncogene (hepatocyte growth factor receptor) (211599_x_at), score: 0.3 MFAP4microfibrillar-associated protein 4 (212713_at), score: 0.5 MMP14matrix metallopeptidase 14 (membrane-inserted) (202827_s_at), score: 0.51 MMP2matrix metallopeptidase 2 (gelatinase A, 72kDa gelatinase, 72kDa type IV collagenase) (201069_at), score: 0.32 MRASmuscle RAS oncogene homolog (206538_at), score: 0.36 MRC2mannose receptor, C type 2 (37408_at), score: 0.4 MSX1msh homeobox 1 (205932_s_at), score: 0.5 MT1Mmetallothionein 1M (217546_at), score: 0.5 MTA1metastasis associated 1 (211783_s_at), score: -0.94 MXRA5matrix-remodelling associated 5 (209596_at), score: 0.45 MYCT1myc target 1 (220471_s_at), score: -0.96 MYO10myosin X (201976_s_at), score: 0.32 MYO1Dmyosin ID (212338_at), score: 0.49 NBL1neuroblastoma, suppression of tumorigenicity 1 (37005_at), score: 0.68 NDNnecdin homolog (mouse) (209550_at), score: 0.31 NET1neuroepithelial cell transforming 1 (201830_s_at), score: 0.6 NFASCneurofascin homolog (chicken) (213438_at), score: 0.42 NFATC1nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic, calcineurin-dependent 1 (210162_s_at), score: 0.34 NFIL3nuclear factor, interleukin 3 regulated (203574_at), score: 0.29 NID1nidogen 1 (202008_s_at), score: 0.36 NKX3-1NK3 homeobox 1 (209706_at), score: 0.62 NPR3natriuretic peptide receptor C/guanylate cyclase C (atrionatriuretic peptide receptor C) (219789_at), score: 0.39 NR2F2nuclear receptor subfamily 2, group F, member 2 (215073_s_at), score: -0.98 NR4A1nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 1 (202340_x_at), score: 0.29 NR4A3nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 3 (209959_at), score: 0.31 NRG1neuregulin 1 (206343_s_at), score: 0.29 NTF3neurotrophin 3 (206706_at), score: 0.42 NTMneurotrimin (222020_s_at), score: 0.29 OSBPL3oxysterol binding protein-like 3 (209626_s_at), score: 0.33 OXTRoxytocin receptor (206825_at), score: 0.35 P4HTMprolyl 4-hydroxylase, transmembrane (endoplasmic reticulum) (222125_s_at), score: 0.32 PBX1pre-B-cell leukemia homeobox 1 (212148_at), score: 0.59 PCDHG@protocadherin gamma cluster (215836_s_at), score: 0.29 PDCD1LG2programmed cell death 1 ligand 2 (220049_s_at), score: 0.37 PDE4Bphosphodiesterase 4B, cAMP-specific (phosphodiesterase E4 dunce homolog, Drosophila) (203708_at), score: 0.33 PIP4K2Aphosphatidylinositol-5-phosphate 4-kinase, type II, alpha (212829_at), score: 0.28 PITPNC1phosphatidylinositol transfer protein, cytoplasmic 1 (219155_at), score: 0.45 PKIAprotein kinase (cAMP-dependent, catalytic) inhibitor alpha (204612_at), score: 0.37 PLAURplasminogen activator, urokinase receptor (211924_s_at), score: 0.51 PMEPA1prostate transmembrane protein, androgen induced 1 (217875_s_at), score: 0.55 PPAP2Aphosphatidic acid phosphatase type 2A (209147_s_at), score: 0.66 PPICpeptidylprolyl isomerase C (cyclophilin C) (204518_s_at), score: 0.44 PPP1R13Lprotein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 13 like (218849_s_at), score: 0.44 PPP1R3Cprotein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 3C (204284_at), score: 0.48 PSG2pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 2 (208134_x_at), score: 0.45 PSG4pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 4 (208191_x_at), score: 0.43 PSG5pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 5 (204830_x_at), score: 0.67 PSG6pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 6 (209738_x_at), score: 0.63 PSG7pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 7 (205602_x_at), score: 0.32 PSG9pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 9 (209594_x_at), score: 0.66 PTGER2prostaglandin E receptor 2 (subtype EP2), 53kDa (206631_at), score: 0.4 PTGS1prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 1 (prostaglandin G/H synthase and cyclooxygenase) (215813_s_at), score: 0.47 PTHLHparathyroid hormone-like hormone (211756_at), score: 0.34 PTPRBprotein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, B (205846_at), score: 0.45 PVRL3poliovirus receptor-related 3 (213325_at), score: 0.34 R3HDM2R3H domain containing 2 (203831_at), score: 0.39 RABGEF1RAB guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 1 (218310_at), score: 0.43 RBMS1RNA binding motif, single stranded interacting protein 1 (209868_s_at), score: 0.43 RGS2regulator of G-protein signaling 2, 24kDa (202388_at), score: 0.29 RGS3regulator of G-protein signaling 3 (203823_at), score: 0.46 RNASE4ribonuclease, RNase A family, 4 (205158_at), score: 0.29 RNF128ring finger protein 128 (219263_at), score: 0.28 RPS4Y1ribosomal protein S4, Y-linked 1 (201909_at), score: 0.48 RTN3reticulon 3 (219549_s_at), score: 0.29 RUNX1runt-related transcription factor 1 (209360_s_at), score: 0.55 SAFB2scaffold attachment factor B2 (32099_at), score: -0.97 SALL1sal-like 1 (Drosophila) (206893_at), score: 0.3 SAMD4Asterile alpha motif domain containing 4A (212845_at), score: 0.43 SATB2SATB homeobox 2 (213435_at), score: 0.3 SC4MOLsterol-C4-methyl oxidase-like (209146_at), score: 0.31 SCG5secretogranin V (7B2 protein) (203889_at), score: 0.45 SDC4syndecan 4 (202071_at), score: 0.37 SERPINE2serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade E (nexin, plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1), member 2 (212190_at), score: 0.57 SFRP1secreted frizzled-related protein 1 (202036_s_at), score: 0.56 SGCBsarcoglycan, beta (43kDa dystrophin-associated glycoprotein) (205121_at), score: 0.31 SGCDsarcoglycan, delta (35kDa dystrophin-associated glycoprotein) (213543_at), score: 0.6 SGCGsarcoglycan, gamma (35kDa dystrophin-associated glycoprotein) (207302_at), score: 0.39 SIRPAsignal-regulatory protein alpha (202897_at), score: 0.58 SLC10A3solute carrier family 10 (sodium/bile acid cotransporter family), member 3 (204928_s_at), score: 0.56 SLC17A9solute carrier family 17, member 9 (219559_at), score: 0.33 SLC1A1solute carrier family 1 (neuronal/epithelial high affinity glutamate transporter, system Xag), member 1 (213664_at), score: 0.32 SLC22A18solute carrier family 22, member 18 (204981_at), score: 0.33 SLC2A10solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 10 (221024_s_at), score: 0.55 SLC30A1solute carrier family 30 (zinc transporter), member 1 (212907_at), score: 0.5 SLC4A4solute carrier family 4, sodium bicarbonate cotransporter, member 4 (203908_at), score: 0.3 SLC6A10Psolute carrier family 6 (neurotransmitter transporter, creatine), member 10 (pseudogene) (215812_s_at), score: 0.34 SLC7A11solute carrier family 7, (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system) member 11 (217678_at), score: -1 SLC7A8solute carrier family 7 (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system), member 8 (216092_s_at), score: 0.58 SLCO3A1solute carrier organic anion transporter family, member 3A1 (219229_at), score: 0.28 SMPD1sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase 1, acid lysosomal (209420_s_at), score: 0.29 SNAI1snail homolog 1 (Drosophila) (219480_at), score: 0.54 SOCS2suppressor of cytokine signaling 2 (203373_at), score: 0.68 SOX4SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 4 (201417_at), score: 0.61 SOX9SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 9 (202935_s_at), score: 0.34 SPHK1sphingosine kinase 1 (219257_s_at), score: 0.39 SPRY4sprouty homolog 4 (Drosophila) (221489_s_at), score: 0.34 ST3GAL1ST3 beta-galactoside alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase 1 (208322_s_at), score: 0.4 STC1stanniocalcin 1 (204597_x_at), score: 0.32 STMN2stathmin-like 2 (203000_at), score: 0.44 SULF1sulfatase 1 (212353_at), score: 0.65 TACSTD2tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (202286_s_at), score: 0.35 TBX3T-box 3 (219682_s_at), score: 0.44 TCOF1Treacher Collins-Franceschetti syndrome 1 (202385_s_at), score: -0.97 TERF1telomeric repeat binding factor (NIMA-interacting) 1 (203448_s_at), score: -0.98 TESK1testis-specific kinase 1 (204106_at), score: 0.44 TEX2testis expressed 2 (218099_at), score: 0.43 TFPI2tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 (209278_s_at), score: 0.28 TGFAtransforming growth factor, alpha (205016_at), score: 0.47 THBDthrombomodulin (203887_s_at), score: 0.34 TICAM1toll-like receptor adaptor molecule 1 (213191_at), score: 0.33 TIMP2TIMP metallopeptidase inhibitor 2 (203167_at), score: 0.44 TIMP3TIMP metallopeptidase inhibitor 3 (201149_s_at), score: 0.43 TM2D1TM2 domain containing 1 (211703_s_at), score: 0.42 TMBIM1transmembrane BAX inhibitor motif containing 1 (217730_at), score: 0.31 TMED7transmembrane emp24 protein transport domain containing 7 (209404_s_at), score: 0.34 TMEM158transmembrane protein 158 (213338_at), score: 0.67 TMEM22transmembrane protein 22 (219569_s_at), score: 0.44 TMEM41Btransmembrane protein 41B (212623_at), score: 0.77 TMEM47transmembrane protein 47 (209656_s_at), score: 0.45 TMEM8transmembrane protein 8 (five membrane-spanning domains) (221882_s_at), score: 0.44 TMEM87Atransmembrane protein 87A (212204_at), score: 0.31 TOM1target of myb1 (chicken) (202807_s_at), score: 0.34 TPP1tripeptidyl peptidase I (200742_s_at), score: 0.34 TPST2tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase 2 (204079_at), score: 0.32 TSPAN13tetraspanin 13 (217979_at), score: 0.45 UAP1UDP-N-acteylglucosamine pyrophosphorylase 1 (209340_at), score: 0.39 UBL3ubiquitin-like 3 (201535_at), score: 0.6 USTuronyl-2-sulfotransferase (205139_s_at), score: 0.3 VDRvitamin D (1,25- dihydroxyvitamin D3) receptor (204255_s_at), score: 0.32 WTAPWilms tumor 1 associated protein (210285_x_at), score: 0.47 ZBTB20zinc finger and BTB domain containing 20 (205383_s_at), score: 0.32 ZMIZ1zinc finger, MIZ-type containing 1 (212124_at), score: 0.31 ZNF536zinc finger protein 536 (206403_at), score: 0.45 ZNF74zinc finger protein 74 (205881_at), score: -0.93
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1Twin.CEL | 1 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | Down | DS-twin 1 |
| 5CTwin.CEL | 5 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | Down | DS-twin 5 |
| 6Twin.CEL | 6 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-twin 6 |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949579.cel | 2 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | none | CSB |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949750.cel | 6 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | CS | CSB |
| 2Twin.CEL | 2 | 2 | DS-twin | hgu133plus2 | none | DS-twin 2 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690199.cel | 1 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM0316B |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690416.cel | 15 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM0316B |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690360.cel | 12 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM0316B |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690223.cel | 3 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM00038C |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690256.cel | 6 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GMO8398C |