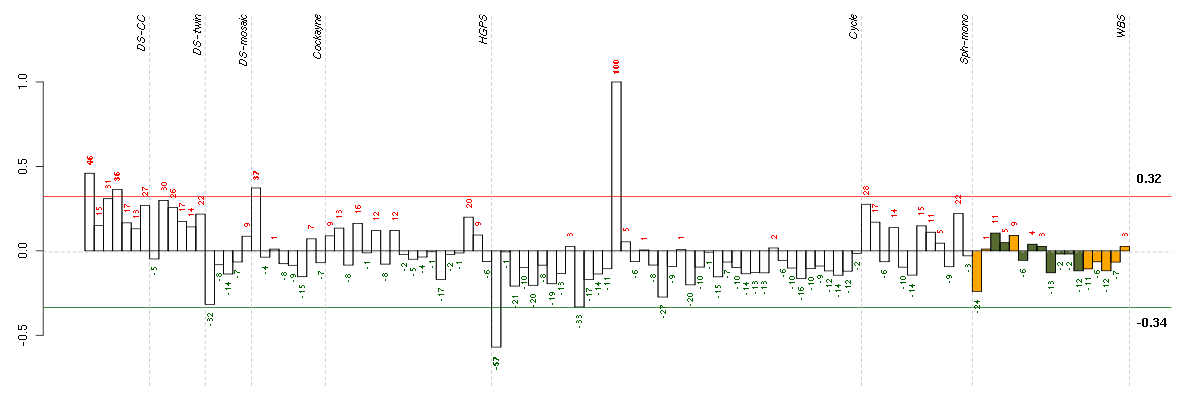

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.


intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cytoskeleton
Any of the various filamentous elements that form the internal framework of cells, and typically remain after treatment of the cells with mild detergent to remove membrane constituents and soluble components of the cytoplasm. The term embraces intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, the microtrabecular lattice, and other structures characterized by a polymeric filamentous nature and long-range order within the cell. The various elements of the cytoskeleton not only serve in the maintenance of cellular shape but also have roles in other cellular functions, including cellular movement, cell division, endocytosis, and movement of organelles.
brush border
Dense covering of microvilli on the apical surface of epithelial cells in tissues such as the intestine, kidney, and choroid plexus; the microvilli aid absorption by increasing the surface area of the cell.
actin cytoskeleton
The part of the cytoskeleton (the internal framework of a cell) composed of actin and associated proteins. Includes actin cytoskeleton-associated complexes.
myosin complex
A protein complex, formed of one or more myosin heavy chains plus associated light chains and other proteins, that functions as a molecular motor; uses the energy of ATP hydrolysis to move actin filaments or to move vesicles or other cargo on fixed actin filaments; has magnesium-ATPase activity and binds actin. Myosin classes are distinguished based on sequence features of the motor, or head, domain, but also have distinct tail regions that are believed to bind specific cargoes.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
cell projection
A prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
protein complex
Any macromolecular complex composed of two or more polypeptide subunits, which may or may not be identical. Protein complexes may have other associated non-protein prosthetic groups, such as nucleotides, metal ions or carbohydrate groups.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
myosin complex
A protein complex, formed of one or more myosin heavy chains plus associated light chains and other proteins, that functions as a molecular motor; uses the energy of ATP hydrolysis to move actin filaments or to move vesicles or other cargo on fixed actin filaments; has magnesium-ATPase activity and binds actin. Myosin classes are distinguished based on sequence features of the motor, or head, domain, but also have distinct tail regions that are believed to bind specific cargoes.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
myosin complex
A protein complex, formed of one or more myosin heavy chains plus associated light chains and other proteins, that functions as a molecular motor; uses the energy of ATP hydrolysis to move actin filaments or to move vesicles or other cargo on fixed actin filaments; has magnesium-ATPase activity and binds actin. Myosin classes are distinguished based on sequence features of the motor, or head, domain, but also have distinct tail regions that are believed to bind specific cargoes.

ACSL6acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 6 (211207_s_at), score: 0.89 ADAMDEC1ADAM-like, decysin 1 (206134_at), score: 0.86 ADAMTS9ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 9 (220287_at), score: 0.84 CDH19cadherin 19, type 2 (206898_at), score: 1 CEACAM6carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (non-specific cross reacting antigen) (211657_at), score: 0.73 CHN2chimerin (chimaerin) 2 (207486_x_at), score: 0.84 CYCSP52cytochrome c, somatic pseudogene 52 (217206_at), score: 0.78 DHRS9dehydrogenase/reductase (SDR family) member 9 (219799_s_at), score: 0.79 DTNBdystrobrevin, beta (215295_at), score: 0.88 ERBB4v-erb-a erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene homolog 4 (avian) (214053_at), score: 0.73 HCG8HLA complex group 8 (215985_at), score: 0.74 ICA1islet cell autoantigen 1, 69kDa (211740_at), score: 0.83 KCNIP1Kv channel interacting protein 1 (221307_at), score: 0.75 KCNJ16potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 16 (219564_at), score: 0.79 LHX3LIM homeobox 3 (221670_s_at), score: 0.78 LOC100132247similar to Uncharacterized protein KIAA0220 (215002_at), score: 0.87 LOC93432maltase-glucoamylase-like pseudogene (216666_at), score: 0.86 MAP3K9mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 9 (213927_at), score: 0.77 MYBPC1myosin binding protein C, slow type (214087_s_at), score: 0.75 MYO1Amyosin IA (211916_s_at), score: 0.94 MYO5Cmyosin VC (218966_at), score: 0.87 N4BP3Nedd4 binding protein 3 (214775_at), score: 0.78 NTRK2neurotrophic tyrosine kinase, receptor, type 2 (207152_at), score: 0.78 PCDH11Yprotocadherin 11 Y-linked (211227_s_at), score: 0.83 PDE3Aphosphodiesterase 3A, cGMP-inhibited (206388_at), score: 0.91 PRLprolactin (205445_at), score: 0.84 PRSS7protease, serine, 7 (enterokinase) (217269_s_at), score: 0.76 RP11-35N6.1plasticity related gene 3 (219732_at), score: 0.88 SLC6A14solute carrier family 6 (amino acid transporter), member 14 (219795_at), score: 0.77 TAAR2trace amine associated receptor 2 (221394_at), score: 0.92 TLR1toll-like receptor 1 (210176_at), score: 0.87 TSPY1testis specific protein, Y-linked 1 (216374_at), score: 0.76 VGFVGF nerve growth factor inducible (205586_x_at), score: 0.77
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485651.cel | 1 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| t21a 08-03.CEL | 4 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | Down | DS-CC 4 |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949557.cel | 1 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | CS | eGFP |
| ctrl a 08-03.CEL | 1 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | none | DS-CC 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485911.cel | 14 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |