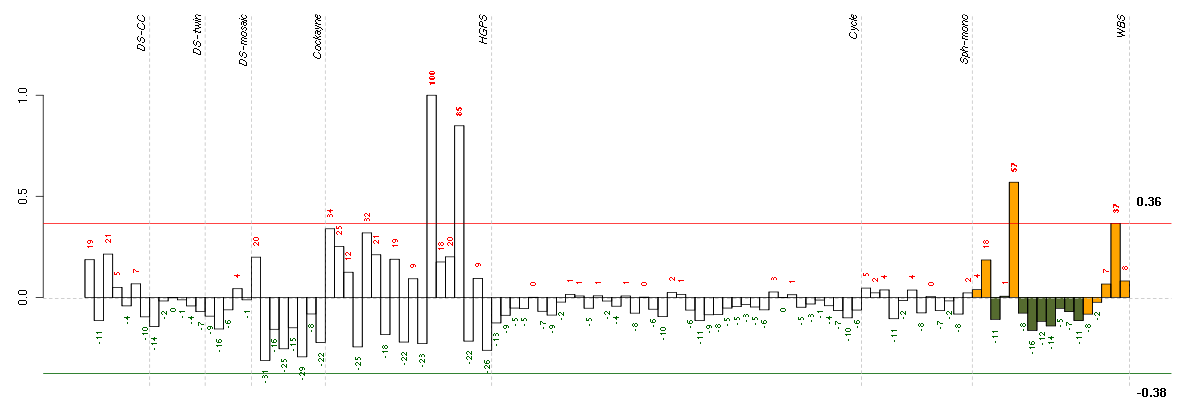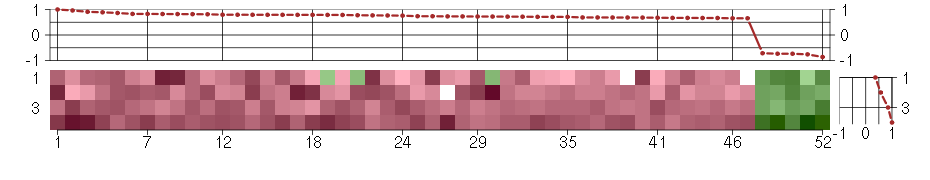

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

generation of a signal involved in cell-cell signaling
The cellular process by which a physical entity or change in state, a signal, is created that originates in one cell and is used to transfer information to another cell. This process begins with the initial formation of the signal and ends with the mature form and placement of the signal.
secretion
The controlled release of a substance by a cell, a group of cells, or a tissue.
transport
The directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells, or within a multicellular organism.
cell communication
Any process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
cell-cell signaling
Any process that mediates the transfer of information from one cell to another.
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
hormone transport
The directed movement of hormones into, out of, within or between cells.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of cell communication
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell communication. Cell communication is the process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
regulation of hormone levels
Any process that modulates the levels of hormone within an organism or a tissue. A hormone is any substance formed in very small amounts in one specialized organ or group of cells and carried (sometimes in the bloodstream) to another organ or group of cells in the same organism, upon which it has a specific regulatory action.
positive regulation of follicle-stimulating hormone secretion
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of follicle-stimulating hormone.
negative regulation of follicle-stimulating hormone secretion
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of follicle-stimulating hormone.
positive regulation of hormone secretion
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of a hormone from a cell or group of cells.
gonadotropin secretion
The regulated release of a gonadotropin, any hormone that stimulates the gonads, especially follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone.
regulation of gonadotropin secretion
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of a gonadotropin.
negative regulation of gonadotropin secretion
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of a gonadotropin.
positive regulation of gonadotropin secretion
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of a gonadotropin.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of localization
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location.
hormone secretion
The regulated release of hormones, substances with a specific regulatory effect on a particular organ or group of cells.
regulation of follicle-stimulating hormone secretion
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of follicle-stimulating hormone.
regulation of hormone secretion
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of a hormone from a cell or group of cells.
follicle-stimulating hormone secretion
The regulated release of follicle-stimulating hormone, a gonadotropic glycoprotein hormone secreted by the anterior pituitary.
negative regulation of hormone secretion
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of a hormone from a cell or group of cells.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
anatomical structure development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an anatomical structure from an initial condition to its mature state. This process begins with the formation of the structure and ends with the mature structure, whatever form that may be including its natural destruction. An anatomical structure is any biological entity that occupies space and is distinguished from its surroundings. Anatomical structures can be macroscopic such as a carpel, or microscopic such as an acrosome.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of secretion
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the controlled release of a substance from a cell or group of cells.
positive regulation of secretion
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the controlled release of a substance from a cell or group of cells.
negative regulation of secretion
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the controlled release of a substance from a cell or group of cells.
regulation of transport
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
positive regulation of transport
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
negative regulation of transport
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
regulation of biological quality
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological quality. A biological quality is a measurable attribute of an organism or part of an organism, such as size, mass, shape, color, etc.
all
This term is the most general term possible
multicellular organismal development
The biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of localization
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cell communication
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell communication. Cell communication is the process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
system development
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organismal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of organs or tissues that work together to carry out a given biological process.
regulation of transport
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
positive regulation of transport
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
negative regulation of transport
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
positive regulation of hormone secretion
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of a hormone from a cell or group of cells.
negative regulation of hormone secretion
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of a hormone from a cell or group of cells.
generation of a signal involved in cell-cell signaling
The cellular process by which a physical entity or change in state, a signal, is created that originates in one cell and is used to transfer information to another cell. This process begins with the initial formation of the signal and ends with the mature form and placement of the signal.
regulation of hormone secretion
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of a hormone from a cell or group of cells.
organ development
Development of a tissue or tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Development pertains to the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a structure over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions.
positive regulation of hormone secretion
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of a hormone from a cell or group of cells.
negative regulation of hormone secretion
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of a hormone from a cell or group of cells.
positive regulation of transport
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
negative regulation of transport
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells.
hormone secretion
The regulated release of hormones, substances with a specific regulatory effect on a particular organ or group of cells.
regulation of secretion
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the controlled release of a substance from a cell or group of cells.
positive regulation of secretion
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the controlled release of a substance from a cell or group of cells.
negative regulation of secretion
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the controlled release of a substance from a cell or group of cells.
hormone secretion
The regulated release of hormones, substances with a specific regulatory effect on a particular organ or group of cells.
hormone transport
The directed movement of hormones into, out of, within or between cells.
negative regulation of gonadotropin secretion
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of a gonadotropin.
positive regulation of gonadotropin secretion
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of a gonadotropin.
positive regulation of hormone secretion
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of a hormone from a cell or group of cells.
regulation of gonadotropin secretion
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of a gonadotropin.
negative regulation of hormone secretion
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of a hormone from a cell or group of cells.
regulation of hormone secretion
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of a hormone from a cell or group of cells.
positive regulation of secretion
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the controlled release of a substance from a cell or group of cells.
negative regulation of secretion
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the controlled release of a substance from a cell or group of cells.
negative regulation of gonadotropin secretion
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of a gonadotropin.
positive regulation of gonadotropin secretion
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of a gonadotropin.
positive regulation of follicle-stimulating hormone secretion
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of follicle-stimulating hormone.
negative regulation of follicle-stimulating hormone secretion
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of follicle-stimulating hormone.
regulation of follicle-stimulating hormone secretion
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of follicle-stimulating hormone.
positive regulation of follicle-stimulating hormone secretion
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of follicle-stimulating hormone.
negative regulation of follicle-stimulating hormone secretion
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of follicle-stimulating hormone.

extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
all
This term is the most general term possible

ADAMTS5ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 5 (219935_at), score: 0.71 BSCL2Bernardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy 2 (seipin) (208906_at), score: 0.74 C20orf39chromosome 20 open reading frame 39 (219310_at), score: 0.72 C4orf31chromosome 4 open reading frame 31 (219747_at), score: 0.89 CD24CD24 molecule (209771_x_at), score: 0.79 CGBchorionic gonadotropin, beta polypeptide (205387_s_at), score: 0.96 CH25Hcholesterol 25-hydroxylase (206932_at), score: 0.72 CKBcreatine kinase, brain (200884_at), score: 0.81 CLEC2BC-type lectin domain family 2, member B (209732_at), score: 0.79 CLPBClpB caseinolytic peptidase B homolog (E. coli) (221845_s_at), score: 0.67 COL8A2collagen, type VIII, alpha 2 (221900_at), score: 0.82 COMPcartilage oligomeric matrix protein (205713_s_at), score: 0.71 CST6cystatin E/M (206595_at), score: 0.77 CYP1B1cytochrome P450, family 1, subfamily B, polypeptide 1 (202436_s_at), score: -0.73 ETFBelectron-transfer-flavoprotein, beta polypeptide (202942_at), score: 0.67 FAM46Afamily with sequence similarity 46, member A (221766_s_at), score: 0.77 GABRA5gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, alpha 5 (206456_at), score: 0.79 GAS2L1growth arrest-specific 2 like 1 (31874_at), score: 0.71 GATA6GATA binding protein 6 (210002_at), score: -0.72 GFRA1GDNF family receptor alpha 1 (205696_s_at), score: 0.82 GLT25D2glycosyltransferase 25 domain containing 2 (209883_at), score: 0.82 HOXA11homeobox A11 (213823_at), score: 0.83 IER3immediate early response 3 (201631_s_at), score: -0.86 INHBAinhibin, beta A (210511_s_at), score: -0.76 INHBBinhibin, beta B (205258_at), score: 0.83 IRX5iroquois homeobox 5 (210239_at), score: 0.79 KRT14keratin 14 (209351_at), score: 0.72 LAPTM5lysosomal multispanning membrane protein 5 (201721_s_at), score: 0.68 MAFv-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog (avian) (209348_s_at), score: 0.79 MAPKAPK3mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 3 (202788_at), score: 0.76 MEGF6multiple EGF-like-domains 6 (213942_at), score: 0.73 MXRA5matrix-remodelling associated 5 (209596_at), score: 0.69 NBL1neuroblastoma, suppression of tumorigenicity 1 (37005_at), score: 0.8 NCAM1neural cell adhesion molecule 1 (212843_at), score: 0.91 NTF3neurotrophin 3 (206706_at), score: 0.69 PLAC8placenta-specific 8 (219014_at), score: 1 PPP2R2Bprotein phosphatase 2 (formerly 2A), regulatory subunit B, beta isoform (213849_s_at), score: 0.74 PSG2pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 2 (208134_x_at), score: 0.86 PSG6pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 6 (209738_x_at), score: 0.67 RUNX3runt-related transcription factor 3 (204198_s_at), score: 0.79 SALL1sal-like 1 (Drosophila) (206893_at), score: 0.66 SLC10A3solute carrier family 10 (sodium/bile acid cotransporter family), member 3 (204928_s_at), score: 0.67 SLC16A5solute carrier family 16, member 5 (monocarboxylic acid transporter 6) (206600_s_at), score: 0.79 ST6GALNAC5ST6 (alpha-N-acetyl-neuraminyl-2,3-beta-galactosyl-1,3)-N-acetylgalactosaminide alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase 5 (220979_s_at), score: 0.69 SVILsupervillin (202565_s_at), score: -0.74 TACSTD2tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (202286_s_at), score: 0.73 TBX5T-box 5 (207155_at), score: 0.66 TIMP2TIMP metallopeptidase inhibitor 2 (203167_at), score: 0.79 TRHDEthyrotropin-releasing hormone degrading enzyme (219937_at), score: 0.68 TSPAN13tetraspanin 13 (217979_at), score: 0.69 UNC5Bunc-5 homolog B (C. elegans) (213100_at), score: 0.78 WNT5Bwingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 5B (221029_s_at), score: 0.72
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F348_WBS.CEL | 16 | 8 | WBS | hgu133plus2 | WBS | WBS 1 |
| 4319_WBS.CEL | 5 | 8 | WBS | hgu133plus2 | WBS | WBS 1 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690416.cel | 15 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM0316B |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690360.cel | 12 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM0316B |