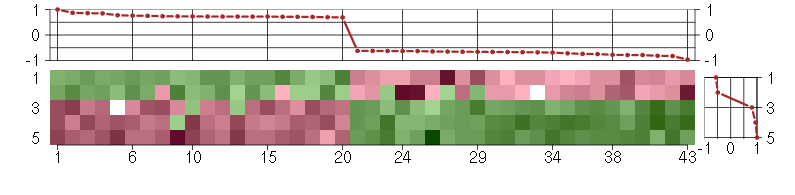

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
genetic imprinting
Heritable alterations in the activity of a gene that depend on whether it passed through the paternal or the maternal germline, but that are not encoded by DNA itself.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
gene expression
The process by which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
regulation of gene expression
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
regulation of gene expression, epigenetic
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression; the process is mitotically or meiotically heritable, or is stably self-propagated in the cytoplasm of a resting cell, and does not entail a change in DNA sequence.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of gene expression
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product or products (proteins or RNA). This includes the production of an RNA transcript as well as any processing to produce a mature RNA product or an mRNA (for protein-coding genes) and the translation of that mRNA into protein. Some protein processing events may be included when they are required to form an active form of a product from an inactive precursor form.
genetic imprinting
Heritable alterations in the activity of a gene that depend on whether it passed through the paternal or the maternal germline, but that are not encoded by DNA itself.


protein binding
Interacting selectively with any protein or protein complex (a complex of two or more proteins that may include other nonprotein molecules).
molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
receptor binding
Interacting selectively with one or more specific sites on a receptor molecule, a macromolecule that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function.
binding
The selective, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
growth factor activity
The function that stimulates a cell to grow or proliferate. Most growth factors have other actions besides the induction of cell growth or proliferation.
all
This term is the most general term possible
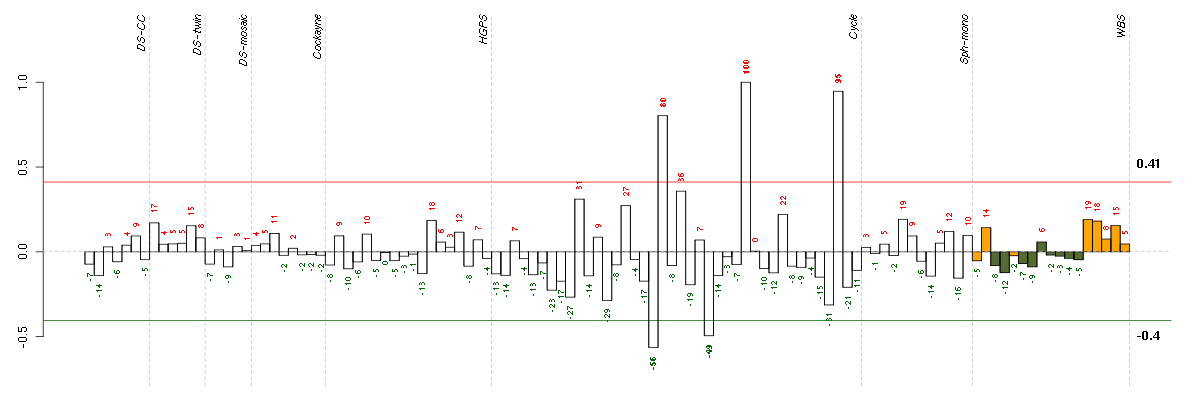
ANXA10annexin A10 (210143_at), score: -0.78 ARL17ADP-ribosylation factor-like 17 (210435_at), score: -0.65 ATP6V0E1ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 9kDa, V0 subunit e1 (214244_s_at), score: 0.72 B3GNTL1UDP-GlcNAc:betaGal beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase-like 1 (213589_s_at), score: 0.87 C9orf114chromosome 9 open reading frame 114 (218565_at), score: 0.77 CD320CD320 molecule (218529_at), score: 0.85 CLCF1cardiotrophin-like cytokine factor 1 (219500_at), score: -0.65 CLEC3BC-type lectin domain family 3, member B (205200_at), score: -0.68 COL5A3collagen, type V, alpha 3 (52255_s_at), score: -0.79 CTSZcathepsin Z (210042_s_at), score: 0.72 DIRAS3DIRAS family, GTP-binding RAS-like 3 (215506_s_at), score: -0.75 EDNRBendothelin receptor type B (204271_s_at), score: -0.79 EMCNendomucin (219436_s_at), score: 0.72 EML1echinoderm microtubule associated protein like 1 (204797_s_at), score: -0.69 EPOerythropoietin (217254_s_at), score: 0.73 EVI2Becotropic viral integration site 2B (211742_s_at), score: 0.72 GNB1Lguanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), beta polypeptide 1-like (220762_s_at), score: 0.86 GPM6Bglycoprotein M6B (209170_s_at), score: -0.72 GPRASP1G protein-coupled receptor associated sorting protein 1 (204793_at), score: 0.75 HGFhepatocyte growth factor (hepapoietin A; scatter factor) (209960_at), score: -0.63 IGF2insulin-like growth factor 2 (somatomedin A) (202409_at), score: -0.62 IL33interleukin 33 (209821_at), score: -0.83 KCTD14potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 14 (58916_at), score: 0.7 KLK13kallikrein-related peptidase 13 (205783_at), score: -0.63 KMOkynurenine 3-monooxygenase (kynurenine 3-hydroxylase) (205307_s_at), score: -0.63 LOC100128223hypothetical protein LOC100128223 (221264_s_at), score: 0.76 LOC388152hypothetical LOC388152 (220602_s_at), score: 0.69 MLPHmelanophilin (218211_s_at), score: 0.72 NEFLneurofilament, light polypeptide (221805_at), score: -0.74 NFATC2IPnuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic, calcineurin-dependent 2 interacting protein (217526_at), score: -0.67 NUDT6nudix (nucleoside diphosphate linked moiety X)-type motif 6 (220183_s_at), score: 0.71 PIGLphosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis, class L (213889_at), score: 0.72 PRKG2protein kinase, cGMP-dependent, type II (207505_at), score: -0.82 PRSS3protease, serine, 3 (207463_x_at), score: -0.67 PTGS1prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 1 (prostaglandin G/H synthase and cyclooxygenase) (215813_s_at), score: -0.62 RPL27Aribosomal protein L27a (212044_s_at), score: 0.73 SAT1spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase 1 (213988_s_at), score: -0.66 SETMARSET domain and mariner transposase fusion gene (206554_x_at), score: 0.74 SYT1synaptotagmin I (203999_at), score: -0.66 TMSB15Athymosin beta 15a (205347_s_at), score: 0.71 TPK1thiamin pyrophosphokinase 1 (221218_s_at), score: -0.97 UCP2uncoupling protein 2 (mitochondrial, proton carrier) (208998_at), score: 1 ZNF219zinc finger protein 219 (219314_s_at), score: -0.66
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485991.cel | 18 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486111.cel | 24 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486011.cel | 19 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486391.cel | 38 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486191.cel | 28 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |