
Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

reproduction
The production by an organism of new individuals that contain some portion of their genetic material inherited from that organism.
female pregnancy
The set of physiological processes that allow an embryo or foetus to develop within the body of a female animal. It covers the time from fertilization of a female ovum by a male spermatozoon until birth.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
cell differentiation
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate.
multicellular organismal process
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function.
developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an integrated living unit: an anatomical structure (which may be a subcellular structure, cell, tissue, or organ), or organism over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
muscle cell differentiation
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a muscle cell.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
positive regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of developmental process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
positive regulation of developmental process
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of muscle cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of muscle cell differentiation.
positive regulation of muscle cell differentiation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of muscle cell differentiation.
multi-organism process
Any process by which an organism has an effect on another organism of the same or different species.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
all
This term is the most general term possible
reproductive process
A biological process that directly contributes to the process of producing new individuals by one or two organisms. The new individuals inherit some proportion of their genetic material from the parent or parents.
cellular developmental process
A biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cell over time from an initial condition to a later condition.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
positive regulation of developmental process
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
positive regulation of biological process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of developmental process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of a multicellular organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
female pregnancy
The set of physiological processes that allow an embryo or foetus to develop within the body of a female animal. It covers the time from fertilization of a female ovum by a male spermatozoon until birth.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
positive regulation of cellular process
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
positive regulation of developmental process
Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of development, the biological process whose specific outcome is the progression of an organism over time from an initial condition (e.g. a zygote, or a young adult) to a later condition (e.g. a multicellular animal or an aged adult).
positive regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation, the process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and functional features.
positive regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
positive regulation of cell differentiation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation.
regulation of muscle cell differentiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of muscle cell differentiation.
positive regulation of muscle cell differentiation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of muscle cell differentiation.
positive regulation of muscle cell differentiation
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of muscle cell differentiation.

extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
all
This term is the most general term possible

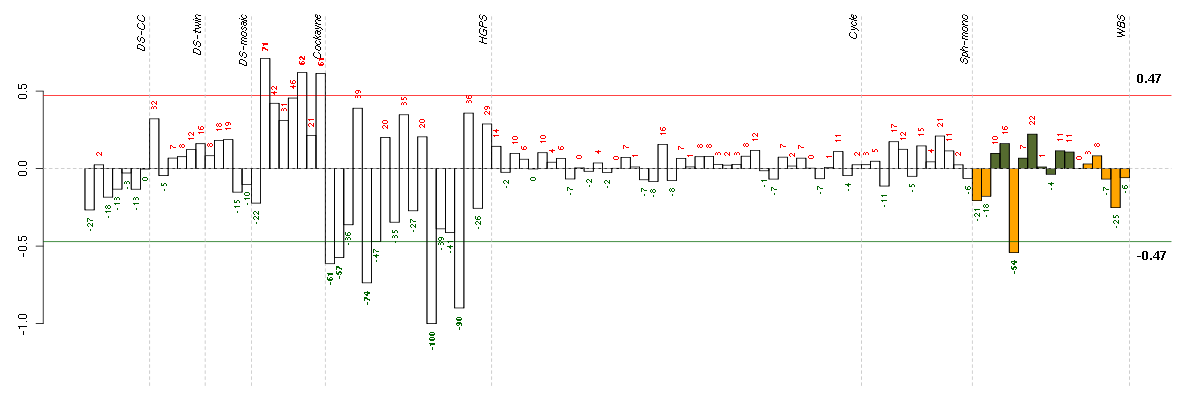
ACTC1actin, alpha, cardiac muscle 1 (205132_at), score: -0.72 C4orf31chromosome 4 open reading frame 31 (219747_at), score: -1 C5orf30chromosome 5 open reading frame 30 (221823_at), score: -0.75 CAPGcapping protein (actin filament), gelsolin-like (201850_at), score: -0.65 CGBchorionic gonadotropin, beta polypeptide (205387_s_at), score: -0.99 CKBcreatine kinase, brain (200884_at), score: -0.79 COL8A2collagen, type VIII, alpha 2 (221900_at), score: -0.73 COMPcartilage oligomeric matrix protein (205713_s_at), score: -0.9 FAM46Afamily with sequence similarity 46, member A (221766_s_at), score: -0.72 GABBR2gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) B receptor, 2 (209990_s_at), score: -0.67 GABRA5gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, alpha 5 (206456_at), score: -0.7 GLSglutaminase (203159_at), score: -0.72 HSPB7heat shock 27kDa protein family, member 7 (cardiovascular) (218934_s_at), score: -0.66 IGFBP3insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 (212143_s_at), score: -0.73 INHBBinhibin, beta B (205258_at), score: -0.72 IRX5iroquois homeobox 5 (210239_at), score: -0.74 ISLRimmunoglobulin superfamily containing leucine-rich repeat (207191_s_at), score: -0.79 KRT19keratin 19 (201650_at), score: -0.68 LBHlimb bud and heart development homolog (mouse) (221011_s_at), score: -0.77 MEGF6multiple EGF-like-domains 6 (213942_at), score: -0.8 NRG1neuregulin 1 (206343_s_at), score: -0.7 NTF3neurotrophin 3 (206706_at), score: -0.75 ODZ4odz, odd Oz/ten-m homolog 4 (Drosophila) (213273_at), score: -0.66 PODXLpodocalyxin-like (201578_at), score: -0.72 PSG2pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 2 (208134_x_at), score: -0.8 PSG5pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 5 (204830_x_at), score: -0.74 PSG6pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 6 (209738_x_at), score: -0.7 PSG9pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 9 (209594_x_at), score: -0.76 PTPRBprotein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, B (205846_at), score: -0.69 SGCDsarcoglycan, delta (35kDa dystrophin-associated glycoprotein) (213543_at), score: -0.7 SLC16A5solute carrier family 16, member 5 (monocarboxylic acid transporter 6) (206600_s_at), score: -0.71 TACSTD2tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (202286_s_at), score: -0.68 TIMP2TIMP metallopeptidase inhibitor 2 (203167_at), score: -0.81 TSPAN13tetraspanin 13 (217979_at), score: -0.73 UAP1UDP-N-acteylglucosamine pyrophosphorylase 1 (209340_at), score: -0.67 UBL3ubiquitin-like 3 (201535_at), score: -0.75 UNC5Bunc-5 homolog B (C. elegans) (213100_at), score: -0.71 WNT5Bwingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 5B (221029_s_at), score: -0.67
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690360.cel | 12 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM0316B |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690416.cel | 15 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM0316B |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690248.cel | 5 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG11513 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690199.cel | 1 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM0316B |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690215.cel | 2 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG11513 |
| 4319_WBS.CEL | 5 | 8 | WBS | hgu133plus2 | WBS | WBS 1 |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949938.cel | 8 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | none | CSB |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949750.cel | 6 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | CS | CSB |
| E-GEOD-3407-raw-cel-1437949579.cel | 2 | 4 | Cockayne | hgu133a | none | CSB |