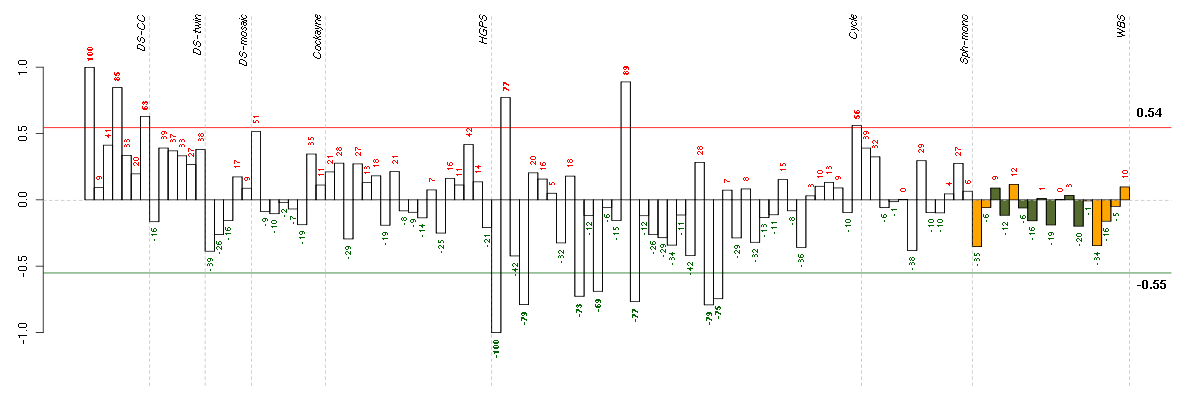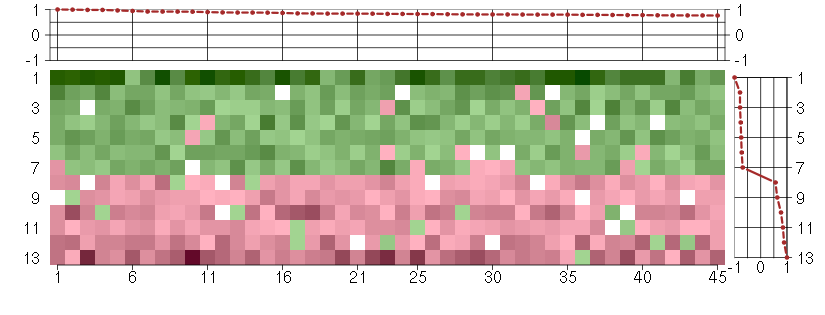

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

immune system process
Any process involved in the development or functioning of the immune system, an organismal system for calibrated responses to potential internal or invasive threats.
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
all
This term is the most general term possible
immune response
Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat.

Golgi membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding any of the compartments of the Golgi apparatus.
intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane
Double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
integral to membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of a membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer. When used to describe a protein, indicates that all or part of the peptide sequence is embedded in the membrane.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
cytoplasm
All of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
Golgi apparatus
A compound membranous cytoplasmic organelle of eukaryotic cells, consisting of flattened, ribosome-free vesicles arranged in a more or less regular stack. The Golgi apparatus differs from the endoplasmic reticulum in often having slightly thicker membranes, appearing in sections as a characteristic shallow semicircle so that the convex side (cis or entry face) abuts the endoplasmic reticulum, secretory vesicles emerging from the concave side (trans or exit face). In vertebrate cells there is usually one such organelle, while in invertebrates and plants, where they are known usually as dictyosomes, there may be several scattered in the cytoplasm. The Golgi apparatus processes proteins produced on the ribosomes of the rough endoplasmic reticulum; such processing includes modification of the core oligosaccharides of glycoproteins, and the sorting and packaging of proteins for transport to a variety of cellular locations. Three different regions of the Golgi are now recognized both in terms of structure and function: cis, in the vicinity of the cis face, trans, in the vicinity of the trans face, and medial, lying between the cis and trans regions.
endomembrane system
A collection of membranous structures involved in transport within the cell. The main components of the endomembrane system are endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, vesicles, cell membrane and nuclear envelope. Members of the endomembrane system pass materials through each other or though the use of vesicles.
integral to Golgi membrane
Located such that some or all of the gene product itself penetrates at least one phospholipid bilayer of the Golgi complex membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
intrinsic to membrane
Located in a membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intrinsic to Golgi membrane
Located in the Golgi membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intrinsic to organelle membrane
Located in an organelle membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
integral to organelle membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of an organelle membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
Golgi apparatus part
Any constituent part of the Golgi apparatus, a compound membranous cytoplasmic organelle of eukaryotic cells, consisting of flattened, ribosome-free vesicles arranged in a more or less regular stack.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
intrinsic to organelle membrane
Located in an organelle membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
organelle membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding an organelle.
membrane part
Any constituent part of a membrane, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins.
Golgi membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding any of the compartments of the Golgi apparatus.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
intrinsic to Golgi membrane
Located in the Golgi membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
Golgi membrane
The lipid bilayer surrounding any of the compartments of the Golgi apparatus.
intrinsic to Golgi membrane
Located in the Golgi membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
cytoplasmic part
Any constituent part of the cytoplasm, all of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures.
Golgi apparatus
A compound membranous cytoplasmic organelle of eukaryotic cells, consisting of flattened, ribosome-free vesicles arranged in a more or less regular stack. The Golgi apparatus differs from the endoplasmic reticulum in often having slightly thicker membranes, appearing in sections as a characteristic shallow semicircle so that the convex side (cis or entry face) abuts the endoplasmic reticulum, secretory vesicles emerging from the concave side (trans or exit face). In vertebrate cells there is usually one such organelle, while in invertebrates and plants, where they are known usually as dictyosomes, there may be several scattered in the cytoplasm. The Golgi apparatus processes proteins produced on the ribosomes of the rough endoplasmic reticulum; such processing includes modification of the core oligosaccharides of glycoproteins, and the sorting and packaging of proteins for transport to a variety of cellular locations. Three different regions of the Golgi are now recognized both in terms of structure and function: cis, in the vicinity of the cis face, trans, in the vicinity of the trans face, and medial, lying between the cis and trans regions.
Golgi apparatus part
Any constituent part of the Golgi apparatus, a compound membranous cytoplasmic organelle of eukaryotic cells, consisting of flattened, ribosome-free vesicles arranged in a more or less regular stack.
intrinsic to organelle membrane
Located in an organelle membrane such that some covalently attached portion of the gene product, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached moiety such as a GPI anchor, spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane.
Golgi apparatus part
Any constituent part of the Golgi apparatus, a compound membranous cytoplasmic organelle of eukaryotic cells, consisting of flattened, ribosome-free vesicles arranged in a more or less regular stack.
integral to Golgi membrane
Located such that some or all of the gene product itself penetrates at least one phospholipid bilayer of the Golgi complex membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.
integral to organelle membrane
Penetrating at least one phospholipid bilayer of an organelle membrane. May also refer to the state of being buried in the bilayer with no exposure outside the bilayer.

protein binding
Interacting selectively with any protein or protein complex (a complex of two or more proteins that may include other nonprotein molecules).
molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
MAP-kinase scaffold activity
Functions as a physical support for the assembly of a multiprotein mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) complex. MAPK scaffold proteins have binding sites for MAPK pathway kinases as well as for upstream signaling proteins.
structural molecule activity
The action of a molecule that contributes to the structural integrity of a complex or assembly within or outside a cell.
binding
The selective, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
receptor signaling complex scaffold activity
Functions to provide a physical support for the assembly of a multiprotein receptor signaling complex.
protein complex scaffold
Functions to provide a physical support for the assembly of a multiprotein complex.
all
This term is the most general term possible
protein complex scaffold
Functions to provide a physical support for the assembly of a multiprotein complex.
ABCG4ATP-binding cassette, sub-family G (WHITE), member 4 (207593_at), score: 0.76 ADAMTS7ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 7 (220705_s_at), score: 0.85 ADORA1adenosine A1 receptor (216220_s_at), score: 0.92 ADRA1Dadrenergic, alpha-1D-, receptor (210961_s_at), score: 0.8 AZGP1alpha-2-glycoprotein 1, zinc-binding (217014_s_at), score: 0.77 C7orf28Achromosome 7 open reading frame 28A (201974_s_at), score: 0.84 CATSPER2cation channel, sperm associated 2 (217588_at), score: 0.81 CCDC9coiled-coil domain containing 9 (206257_at), score: 0.88 COL11A2collagen, type XI, alpha 2 (216993_s_at), score: 0.83 CYBBcytochrome b-245, beta polypeptide (203923_s_at), score: 0.98 CYP3A4cytochrome P450, family 3, subfamily A, polypeptide 4 (205998_x_at), score: 0.88 DMBT1deleted in malignant brain tumors 1 (208250_s_at), score: 0.85 EDAectodysplasin A (211130_x_at), score: 1 ETNK2ethanolamine kinase 2 (219268_at), score: 0.77 F11coagulation factor XI (206610_s_at), score: 0.88 FBRSfibrosin (218255_s_at), score: 0.78 FKBP10FK506 binding protein 10, 65 kDa (219249_s_at), score: 0.99 HAB1B1 for mucin (215778_x_at), score: 0.94 HAND1heart and neural crest derivatives expressed 1 (220138_at), score: 0.78 HAO2hydroxyacid oxidase 2 (long chain) (220801_s_at), score: 0.8 INE1inactivation escape 1 (non-protein coding) (207252_at), score: 0.81 ITGALintegrin, alpha L (antigen CD11A (p180), lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1; alpha polypeptide) (213475_s_at), score: 0.77 LILRA5leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor, subfamily A (with TM domain), member 5 (215838_at), score: 0.84 LILRB3leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor, subfamily B (with TM and ITIM domains), member 3 (211133_x_at), score: 0.78 LOC80054hypothetical LOC80054 (220465_at), score: 0.86 LRRN2leucine rich repeat neuronal 2 (216164_at), score: 0.84 MAPK8IP1mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 interacting protein 1 (213013_at), score: 0.81 MAPK8IP2mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 interacting protein 2 (205050_s_at), score: 0.81 MFNGMFNG O-fucosylpeptide 3-beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (204153_s_at), score: 0.8 MOBPmyelin-associated oligodendrocyte basic protein (210193_at), score: 0.9 MYL4myosin, light chain 4, alkali; atrial, embryonic (210088_x_at), score: 0.92 MYO1Amyosin IA (211916_s_at), score: 0.82 OR1E2olfactory receptor, family 1, subfamily E, member 2 (208587_s_at), score: 0.83 PIPOXpipecolic acid oxidase (221605_s_at), score: 0.92 PRSS7protease, serine, 7 (enterokinase) (217269_s_at), score: 0.98 PYHIN1pyrin and HIN domain family, member 1 (216748_at), score: 0.89 RPGRIP1retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator interacting protein 1 (206608_s_at), score: 0.79 S100A14S100 calcium binding protein A14 (218677_at), score: 0.8 SLC26A10solute carrier family 26, member 10 (214951_at), score: 0.84 ST6GAL1ST6 beta-galactosamide alpha-2,6-sialyltranferase 1 (201998_at), score: 0.81 ST8SIA3ST8 alpha-N-acetyl-neuraminide alpha-2,8-sialyltransferase 3 (208064_s_at), score: 0.82 TMSB4Ythymosin beta 4, Y-linked (206769_at), score: 0.96 TNK1tyrosine kinase, non-receptor, 1 (217149_x_at), score: 0.77 TULP2tubby like protein 2 (206733_at), score: 0.79 VGFVGF nerve growth factor inducible (205586_x_at), score: 0.91
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485651.cel | 1 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486111.cel | 24 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485711.cel | 4 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485951.cel | 16 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486131.cel | 25 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485831.cel | 10 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485871.cel | 12 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486431.cel | 40 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| t21d 08-03.CEL | 7 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | Down | DS-CC 7 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485671.cel | 2 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| t21a 08-03.CEL | 4 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | Down | DS-CC 4 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485931.cel | 15 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| ctrl a 08-03.CEL | 1 | 1 | DS-CC | hgu133a | none | DS-CC 1 |