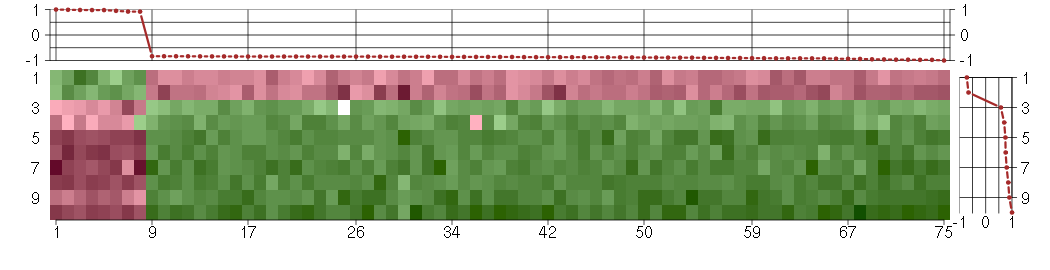

Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

DNA replication
The process whereby new strands of DNA are synthesized. The template for replication can either be an existing DNA molecule or RNA.
cell cycle checkpoint
The cell cycle regulatory process by which progression through the cycle can be halted until conditions are suitable for the cell to proceed to the next stage.
DNA replication checkpoint
A signal transduction based surveillance mechanism that prevents the initiation of mitosis until DNA replication is complete, thereby ensuring that progeny inherit a full complement of the genome.
M phase of mitotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the mitotic cell cycle during which mitosis takes place.
microtubule cytoskeleton organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising microtubules and their associated proteins.
mitotic cell cycle
Progression through the phases of the mitotic cell cycle, the most common eukaryotic cell cycle, which canonically comprises four successive phases called G1, S, G2, and M and includes replication of the genome and the subsequent segregation of chromosomes into daughter cells. In some variant cell cycles nuclear replication or nuclear division may not be followed by cell division, or G1 and G2 phases may be absent.
M phase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the cell cycle comprising nuclear division.
nuclear division
A process by which a cell nucleus is divided into two nuclei, with DNA and other nuclear contents distributed between the daughter nuclei.
DNA synthesis during DNA repair
Synthesis of DNA that proceeds from the broken 3' single-strand DNA end uses the homologous intact duplex as the template.
metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways, including anabolism and catabolism, by which living organisms transform chemical substances. Metabolic processes typically transform small molecules, but also include macromolecular processes such as DNA repair and replication, and protein synthesis and degradation.
regulation of cell cycle
Any process that modulates the rate or extent of progression through the cell cycle.
cytoskeleton organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
DNA metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid, one of the two main types of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from one, or more commonly, two, strands of linked deoxyribonucleotides.
DNA-dependent DNA replication
The process whereby new strands of DNA are synthesized, using parental DNA as a template for the DNA-dependent DNA polymerases that synthesize the new strands.
DNA replication initiation
The process by which DNA replication is started; this involves the separation of a stretch of the DNA double helix, the recruitment of DNA polymerases and the initiation of polymerase action.
regulation of DNA replication
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of DNA replication.
DNA repair
The process of restoring DNA after damage. Genomes are subject to damage by chemical and physical agents in the environment (e.g. UV and ionizing radiations, chemical mutagens, fungal and bacterial toxins, etc.) and by free radicals or alkylating agents endogenously generated in metabolism. DNA is also damaged because of errors during its replication. A variety of different DNA repair pathways have been reported that include direct reversal, base excision repair, nucleotide excision repair, photoreactivation, bypass, double-strand break repair pathway, and mismatch repair pathway.
transport
The directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells, or within a multicellular organism.
response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
response to DNA damage stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to its DNA from environmental insults or errors during metabolism.
organelle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an organelle within a cell. An organelle is an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
microtubule-based process
Any cellular process that depends upon or alters the microtubule cytoskeleton, that part of the cytoskeleton comprising microtubules and their associated proteins.
microtubule-based movement
Movement of organelles, other microtubules and other particles along microtubules, mediated by motor proteins.
cell cycle
The progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events. Canonically, the cell cycle comprises the replication and segregation of genetic material followed by the division of the cell, but in endocycles or syncytial cells nuclear replication or nuclear division may not be followed by cell division.
spindle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of the spindle, the array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during DNA segregation and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
mitosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides; the process involves condensation of chromosomal DNA into a highly compacted form. Canonically, mitosis produces two daughter nuclei whose chromosome complement is identical to that of the mother cell.
mitotic cell cycle checkpoint
A signal transduction-based surveillance mechanism that ensures accurate chromosome replication and segregation by preventing progression through a mitotic cell cycle until conditions are suitable for the cell to proceed to the next stage.
regulation of mitotic cell cycle
Any process that modulates the rate or extent of progress through the mitotic cell cycle.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
negative regulation of DNA replication
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of DNA replication.
cell proliferation
The multiplication or reproduction of cells, resulting in the expansion of a cell population.
biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
negative regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the rate of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
negative regulation of metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
negative regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of cell cycle process
Any process that modulates a cellular process that is involved in the progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
negative regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
cellular component organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a cellular component.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
cell cycle process
A cellular process that is involved in the progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
cell cycle phase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through one of the biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
regulation of DNA replication initiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of initiation of DNA replication; the process by which DNA becomes competent to replicate. In eukaryotes, replication competence is established in early G1 and lost during the ensuing S phase.
cytoskeleton-dependent intracellular transport
The directed movement of substances along cytoskeletal elements such as microfilaments or microtubules within a cell.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
negative regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
negative regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
DNA integrity checkpoint
Any cell cycle checkpoint that delays or arrests cell cycle progression in response to changes in DNA structure.
negative regulation of DNA replication initiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of initiation of DNA replication.
regulation of S phase
A cell cycle process that modulates the rate or extent of the progression through the S phase of the cell cycle.
cellular response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating the organism is under stress. The stress is usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
cellular response to DNA damage stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to its DNA from environmental insults or errors during metabolism.
macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins.
biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature e.g. polysaccharides and proteins.
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
primary metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving those compounds which are formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
negative regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
intracellular transport
The directed movement of substances within a cell.
organelle fission
The creation of two or more organelles by division of one organelle.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of DNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving DNA.
negative regulation of DNA metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving DNA.
localization
Any process by which a cell, a substance, or a cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in a specific location.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
cell division
The process resulting in the physical partitioning and separation of a cell into daughter cells.
S phase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through S phase, the part of the cell cycle during which DNA synthesis takes place.
interphase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through interphase, the stage of cell cycle between successive rounds of chromosome segregation. Canonically, interphase is the stage of the cell cycle during which the biochemical and physiologic functions of the cell are performed and replication of chromatin occurs.
interphase of mitotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through interphase, the stage of cell cycle between successive rounds of mitosis. Canonically, interphase is the stage of the cell cycle during which the biochemical and physiologic functions of the cell are performed and replication of chromatin occurs.
cellular localization
Any process by which a substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in, a specific location within or in the membrane of a cell.
establishment of localization in cell
The directed movement of a substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location within, or in the membrane of, a cell.
cellular response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biological regulation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any biological process, quality or function.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cellular metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
negative regulation of metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
regulation of metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
negative regulation of biological process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
regulation of cellular process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
cellular response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
establishment of localization
The directed movement of a cell, substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location.
cellular localization
Any process by which a substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, is transported to, and/or maintained in, a specific location within or in the membrane of a cell.
regulation of biological process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a biological process. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule.
negative regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the rate of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
negative regulation of metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism.
macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
negative regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
negative regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
cellular biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, as carried out by individual cells.
nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
cell cycle process
A cellular process that is involved in the progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
negative regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cell cycle
Any process that modulates the rate or extent of progression through the cell cycle.
regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
negative regulation of cellular process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cellular process, any of those that are carried out at the cellular level, but are not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
establishment of localization in cell
The directed movement of a substance or cellular entity, such as a protein complex or organelle, to a specific location within, or in the membrane of, a cell.
cellular response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating the organism is under stress. The stress is usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
intracellular transport
The directed movement of substances within a cell.
negative regulation of biosynthetic process
Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the rate of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
negative regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
negative regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
negative regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
negative regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
negative regulation of cellular metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways by which individual cells transform chemical substances.
regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
negative regulation of macromolecule metabolic process
Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving macromolecules, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature e.g. polysaccharides and proteins.
cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass, carried out by individual cells.
cellular biopolymer metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
negative regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of mitotic cell cycle
Any process that modulates the rate or extent of progress through the mitotic cell cycle.
regulation of cell cycle process
Any process that modulates a cellular process that is involved in the progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events.
cellular response to DNA damage stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to its DNA from environmental insults or errors during metabolism.
negative regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process
Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a macromolecule, any molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass.
cellular biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
regulation of DNA replication
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of DNA replication.
negative regulation of cellular biosynthetic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances, carried out by individual cells.
negative regulation of DNA replication
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of DNA replication.
negative regulation of DNA replication
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of DNA replication.
negative regulation of DNA metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving DNA.
negative regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids.
regulation of DNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving DNA.
regulation of DNA replication
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of DNA replication.
negative regulation of DNA metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving DNA.
DNA metabolic process
The chemical reactions and pathways involving DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid, one of the two main types of nucleic acid, consisting of a long, unbranched macromolecule formed from one, or more commonly, two, strands of linked deoxyribonucleotides.
cellular biopolymer biosynthetic process
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of biopolymers, long, repeating chains of monomers found in nature, such as polysaccharides and proteins, as carried out by individual cells.
regulation of DNA metabolic process
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving DNA.
negative regulation of DNA metabolic process
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving DNA.
mitosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides; the process involves condensation of chromosomal DNA into a highly compacted form. Canonically, mitosis produces two daughter nuclei whose chromosome complement is identical to that of the mother cell.
mitotic cell cycle checkpoint
A signal transduction-based surveillance mechanism that ensures accurate chromosome replication and segregation by preventing progression through a mitotic cell cycle until conditions are suitable for the cell to proceed to the next stage.
microtubule cytoskeleton organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising microtubules and their associated proteins.
M phase of mitotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through M phase, the part of the mitotic cell cycle during which mitosis takes place.
spindle organization
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of the spindle, the array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during DNA segregation and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
regulation of S phase
A cell cycle process that modulates the rate or extent of the progression through the S phase of the cell cycle.
S phase
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through S phase, the part of the cell cycle during which DNA synthesis takes place.
interphase of mitotic cell cycle
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through interphase, the stage of cell cycle between successive rounds of mitosis. Canonically, interphase is the stage of the cell cycle during which the biochemical and physiologic functions of the cell are performed and replication of chromatin occurs.
DNA repair
The process of restoring DNA after damage. Genomes are subject to damage by chemical and physical agents in the environment (e.g. UV and ionizing radiations, chemical mutagens, fungal and bacterial toxins, etc.) and by free radicals or alkylating agents endogenously generated in metabolism. DNA is also damaged because of errors during its replication. A variety of different DNA repair pathways have been reported that include direct reversal, base excision repair, nucleotide excision repair, photoreactivation, bypass, double-strand break repair pathway, and mismatch repair pathway.
microtubule-based movement
Movement of organelles, other microtubules and other particles along microtubules, mediated by motor proteins.
negative regulation of DNA replication
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of DNA replication.
DNA replication
The process whereby new strands of DNA are synthesized. The template for replication can either be an existing DNA molecule or RNA.
regulation of DNA replication
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of DNA replication.
negative regulation of DNA replication
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of DNA replication.
regulation of DNA replication initiation
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of initiation of DNA replication; the process by which DNA becomes competent to replicate. In eukaryotes, replication competence is established in early G1 and lost during the ensuing S phase.
negative regulation of DNA replication initiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of initiation of DNA replication.
DNA synthesis during DNA repair
Synthesis of DNA that proceeds from the broken 3' single-strand DNA end uses the homologous intact duplex as the template.
mitosis
A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides; the process involves condensation of chromosomal DNA into a highly compacted form. Canonically, mitosis produces two daughter nuclei whose chromosome complement is identical to that of the mother cell.
negative regulation of DNA replication initiation
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of initiation of DNA replication.
DNA replication checkpoint
A signal transduction based surveillance mechanism that prevents the initiation of mitosis until DNA replication is complete, thereby ensuring that progeny inherit a full complement of the genome.
DNA replication initiation
The process by which DNA replication is started; this involves the separation of a stretch of the DNA double helix, the recruitment of DNA polymerases and the initiation of polymerase action.

nuclear chromosome
A chromosome found in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell.
condensed chromosome
A highly compacted molecule of DNA and associated proteins resulting in a cytologically distinct structure.
intracellular
The living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
chromosome, centromeric region
The region of a chromosome that includes the centromere and associated proteins. In monocentric chromosomes, this region corresponds to a single area of the chromosome, whereas in holocentric chromosomes, it is evenly distributed along the chromosome.
kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of DNA and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
condensed chromosome kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of a condensed chromosome and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
condensed chromosome, centromeric region
The region of a condensed chromosome that includes the centromere and associated proteins, including the kinetochore. In monocentric chromosomes, this region corresponds to a single area of the chromosome, whereas in holocentric chromosomes, it is evenly distributed along the chromosome.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Includes the plasma membrane and any external encapsulating structures such as the cell wall and cell envelope.
nucleus
A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent.
nucleoplasm
That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus.
replication fork
The Y-shaped region of a replicating DNA molecule, resulting from the separation of the DNA strands and in which the synthesis of new strands takes place. Also includes associated protein complexes.
chromosome
A structure composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins (e.g. histones) that carries hereditary information.
spindle
The array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during mitosis or meiosis and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
cytoskeleton
Any of the various filamentous elements that form the internal framework of cells, and typically remain after treatment of the cells with mild detergent to remove membrane constituents and soluble components of the cytoplasm. The term embraces intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, the microtrabecular lattice, and other structures characterized by a polymeric filamentous nature and long-range order within the cell. The various elements of the cytoskeleton not only serve in the maintenance of cellular shape but also have roles in other cellular functions, including cellular movement, cell division, endocytosis, and movement of organelles.
kinesin complex
Any complex that includes a dimer of molecules from the kinesin superfamily, a group of related proteins that contain an extended region of predicted alpha-helical coiled coil in the main chain that likely produces dimerization. The native complexes of several kinesin family members have also been shown to contain additional peptides, often designated light chains as all of the noncatalytic subunits that are currently known are smaller than the chain that contains the motor unit. Kinesin complexes generally possess a force-generating enzymatic activity, or motor, which converts the free energy of the gamma phosphate bond of ATP into mechanical work.
microtubule
Any of the long, generally straight, hollow tubes of internal diameter 12-15 nm and external diameter 24 nm found in a wide variety of eukaryotic cells; each consists (usually) of 13 protofilaments of polymeric tubulin, staggered in such a manner that the tubulin monomers are arranged in a helical pattern on the microtubular surface, and with the alpha/beta axes of the tubulin subunits parallel to the long axis of the tubule; exist in equilibrium with pool of tubulin monomers and can be rapidly assembled or disassembled in response to physiological stimuli; concerned with force generation, e.g. in the spindle.
microtubule associated complex
Any multimeric complex connected to a microtubule.
spindle microtubule
Any microtubule that is part of a mitotic or meiotic spindle; anchored at one spindle pole.
microtubule cytoskeleton
The part of the cytoskeleton (the internal framework of a cell) composed of microtubules and associated proteins.
membrane-enclosed lumen
The enclosed volume within a sealed membrane or between two sealed membranes. Encompasses the volume enclosed by the membranes of a particular organelle, e.g. endoplasmic reticulum lumen, or the space between the two lipid bilayers of a double membrane surrounding an organelle, e.g. nuclear envelope lumen.
nuclear lumen
The volume enclosed by the nuclear inner membrane.
macromolecular complex
A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which the constituent parts function together.
organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
organelle lumen
The internal volume enclosed by the membranes of a particular organelle; includes the volume enclosed by a single organelle membrane, e.g. endoplasmic reticulum lumen, or the volume enclosed by the innermost of the two lipid bilayers of an organelle envelope, e.g. nuclear lumen.
protein complex
Any macromolecular complex composed of two or more polypeptide subunits, which may or may not be identical. Protein complexes may have other associated non-protein prosthetic groups, such as nucleotides, metal ions or carbohydrate groups.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
chromosomal part
Any constituent part of a chromosome, a structure composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins (e.g. histones) that carries hereditary information.
nuclear part
Any constituent part of the nucleus, a membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
nuclear chromosome part
Any constituent part of a nuclear chromosome, a chromosome found in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell.
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
intracellular organelle lumen
An organelle lumen that is part of an intracellular organelle.
all
This term is the most general term possible
cell part
Any constituent part of a cell, the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
organelle part
Any constituent part of an organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, but excludes the plasma membrane.
organelle lumen
The internal volume enclosed by the membranes of a particular organelle; includes the volume enclosed by a single organelle membrane, e.g. endoplasmic reticulum lumen, or the volume enclosed by the innermost of the two lipid bilayers of an organelle envelope, e.g. nuclear lumen.
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, not bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes ribosomes, the cytoskeleton and chromosomes.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle lumen
An organelle lumen that is part of an intracellular organelle.
intracellular part
Any constituent part of the living contents of a cell; the matter contained within (but not including) the plasma membrane, usually taken to exclude large vacuoles and masses of secretory or ingested material. In eukaryotes it includes the nucleus and cytoplasm.
intracellular organelle
Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. Excludes the plasma membrane.
intracellular organelle part
A constituent part of an intracellular organelle, an organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, occurring within the cell. Includes constituent parts of the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, vesicles, ribosomes and the cytoskeleton but excludes the plasma membrane.
kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of DNA and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of DNA and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
nuclear lumen
The volume enclosed by the nuclear inner membrane.
nuclear chromosome part
Any constituent part of a nuclear chromosome, a chromosome found in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell.
spindle
The array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during mitosis or meiosis and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
microtubule associated complex
Any multimeric complex connected to a microtubule.
nucleoplasm
That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus.
nuclear part
Any constituent part of the nucleus, a membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated.
nuclear chromosome
A chromosome found in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell.
chromosomal part
Any constituent part of a chromosome, a structure composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins (e.g. histones) that carries hereditary information.
cytoskeletal part
Any constituent part of the cytoskeleton, a cellular scaffolding or skeleton that maintains cell shape, enables some cell motion (using structures such as flagella and cilia), and plays important roles in both intra-cellular transport (e.g. the movement of vesicles and organelles) and cellular division. Includes constituent parts of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, and the microtrabecular lattice.
kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of DNA and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.
nuclear chromosome part
Any constituent part of a nuclear chromosome, a chromosome found in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell.
spindle microtubule
Any microtubule that is part of a mitotic or meiotic spindle; anchored at one spindle pole.
condensed chromosome, centromeric region
The region of a condensed chromosome that includes the centromere and associated proteins, including the kinetochore. In monocentric chromosomes, this region corresponds to a single area of the chromosome, whereas in holocentric chromosomes, it is evenly distributed along the chromosome.
spindle
The array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during mitosis or meiosis and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart.
microtubule
Any of the long, generally straight, hollow tubes of internal diameter 12-15 nm and external diameter 24 nm found in a wide variety of eukaryotic cells; each consists (usually) of 13 protofilaments of polymeric tubulin, staggered in such a manner that the tubulin monomers are arranged in a helical pattern on the microtubular surface, and with the alpha/beta axes of the tubulin subunits parallel to the long axis of the tubule; exist in equilibrium with pool of tubulin monomers and can be rapidly assembled or disassembled in response to physiological stimuli; concerned with force generation, e.g. in the spindle.
microtubule associated complex
Any multimeric complex connected to a microtubule.
condensed chromosome kinetochore
A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of a condensed chromosome and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules.

nucleotide binding
Interacting selectively with a nucleotide, any compound consisting of a nucleoside that is esterified with (ortho)phosphate or an oligophosphate at any hydroxyl group on the ribose or deoxyribose moiety.
molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
motor activity
Catalysis of movement along a polymeric molecule such as a microfilament or microtubule, coupled to the hydrolysis of a nucleoside triphosphate.
microtubule motor activity
Catalysis of movement along a microtubule, coupled to the hydrolysis of a nucleoside triphosphate (usually ATP).
catalytic activity
Catalysis of a biochemical reaction at physiological temperatures. In biologically catalyzed reactions, the reactants are known as substrates, and the catalysts are naturally occurring macromolecular substances known as enzymes. Enzymes possess specific binding sites for substrates, and are usually composed wholly or largely of protein, but RNA that has catalytic activity (ribozyme) is often also regarded as enzymatic.
DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: deoxynucleoside triphosphate + DNA(n) = diphosphate + DNA(n+1); the synthesis of DNA from deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates in the presence of a DNA template and primer.
nucleoside-triphosphatase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: a nucleoside triphosphate + H2O = nucleoside diphosphate + phosphate.
binding
The selective, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
ATP binding
Interacting selectively with ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator.
pyrophosphatase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of a pyrophosphate bond between two phosphate groups, leaving one phosphate on each of the two fragments.
transferase activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a group, e.g. a methyl group, glycosyl group, acyl group, phosphorus-containing, or other groups, from one compound (generally regarded as the donor) to another compound (generally regarded as the acceptor). Transferase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 2.
transferase activity, transferring phosphorus-containing groups
Catalysis of the transfer of a phosphorus-containing group from one compound (donor) to another (acceptor).
nucleotidyltransferase activity
Catalysis of the transfer of a nucleotidyl group to a reactant.
hydrolase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of various bonds, e.g. C-O, C-N, C-C, phosphoric anhydride bonds, etc. Hydrolase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 3.
hydrolase activity, acting on acid anhydrides
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of any acid anhydride.
hydrolase activity, acting on acid anhydrides, in phosphorus-containing anhydrides
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of any acid anhydride which contains phosphorus.
purine nucleotide binding
Interacting selectively with purine nucleotides, any compound consisting of a purine nucleoside esterified with (ortho)phosphate.
adenyl nucleotide binding
Interacting selectively with adenyl nucleotides, any compound consisting of adenosine esterified with (ortho)phosphate.
ribonucleotide binding
Interacting selectively with a ribonucleotide, any compound consisting of a ribonucleoside that is esterified with (ortho)phosphate or an oligophosphate at any hydroxyl group on the ribose moiety.
purine ribonucleotide binding
Interacting selectively with a purine ribonucleotide, any compound consisting of a purine ribonucleoside that is esterified with (ortho)phosphate or an oligophosphate at any hydroxyl group on the ribose moiety.
adenyl ribonucleotide binding
Interacting selectively with an adenyl ribonucleotide, any compound consisting of adenosine esterified with (ortho)phosphate or an oligophosphate at any hydroxyl group on the ribose moiety.
DNA polymerase activity
Catalysis of the reaction: deoxynucleoside triphosphate + DNA(n) = diphosphate + DNA(n+1); the synthesis of DNA from deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates in the presence of a nucleic acid template and primer.
all
This term is the most general term possible
purine ribonucleotide binding
Interacting selectively with a purine ribonucleotide, any compound consisting of a purine ribonucleoside that is esterified with (ortho)phosphate or an oligophosphate at any hydroxyl group on the ribose moiety.
adenyl ribonucleotide binding
Interacting selectively with an adenyl ribonucleotide, any compound consisting of adenosine esterified with (ortho)phosphate or an oligophosphate at any hydroxyl group on the ribose moiety.
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
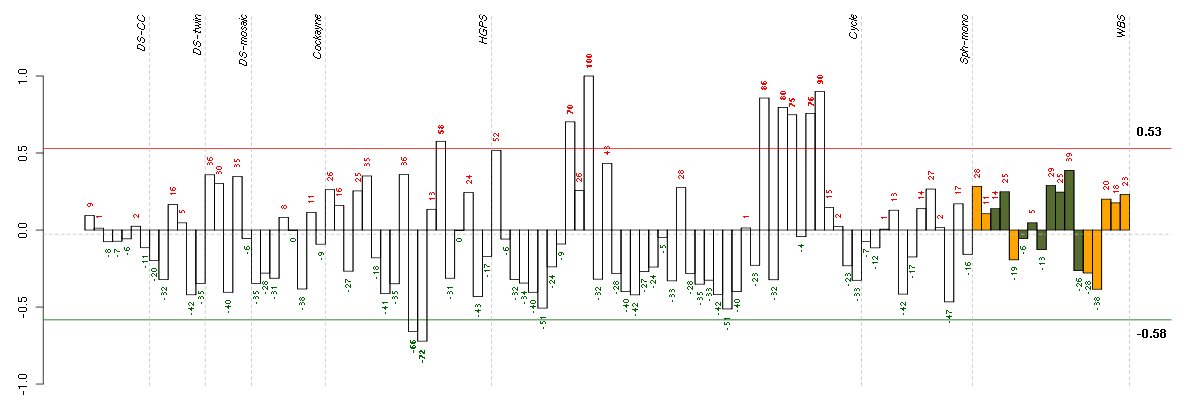
| 04110 | 2.095e-06 | 0.9347 | 10 | 98 | Cell cycle |
| 03030 | 1.432e-03 | 0.3147 | 5 | 33 | DNA replication |
| 00100 | 5.429e-03 | 0.2194 | 4 | 23 | Biosynthesis of steroids |
ASF1BASF1 anti-silencing function 1 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (218115_at), score: -0.88 AURKBaurora kinase B (209464_at), score: -0.85 BARD1BRCA1 associated RING domain 1 (205345_at), score: -0.9 BUB1budding uninhibited by benzimidazoles 1 homolog (yeast) (209642_at), score: -0.84 C18orf24chromosome 18 open reading frame 24 (217640_x_at), score: -0.91 C1orf135chromosome 1 open reading frame 135 (220011_at), score: -0.83 C21orf45chromosome 21 open reading frame 45 (219004_s_at), score: -0.92 CCNE2cyclin E2 (205034_at), score: -0.86 CDC45LCDC45 cell division cycle 45-like (S. cerevisiae) (204126_s_at), score: -0.88 CDC6cell division cycle 6 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (203967_at), score: -0.86 CDC7cell division cycle 7 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (204510_at), score: -0.94 CDCA4cell division cycle associated 4 (218399_s_at), score: -0.84 CDCA8cell division cycle associated 8 (221520_s_at), score: -0.84 CDK2cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (204252_at), score: -0.88 CDT1chromatin licensing and DNA replication factor 1 (209832_s_at), score: -0.83 CENPEcentromere protein E, 312kDa (205046_at), score: -0.84 CENPIcentromere protein I (214804_at), score: -0.92 CHAF1Achromatin assembly factor 1, subunit A (p150) (214426_x_at), score: -0.87 CKAP2cytoskeleton associated protein 2 (218252_at), score: -0.84 DHCR77-dehydrocholesterol reductase (201790_s_at), score: 0.95 DLEU2Ldeleted in lymphocytic leukemia 2-like (215629_s_at), score: -0.85 DSN1DSN1, MIND kinetochore complex component, homolog (S. cerevisiae) (219512_at), score: -0.96 E2F8E2F transcription factor 8 (219990_at), score: -0.86 ERCC6Lexcision repair cross-complementing rodent repair deficiency, complementation group 6-like (219650_at), score: -0.92 EXO1exonuclease 1 (204603_at), score: -0.84 EZH2enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (Drosophila) (203358_s_at), score: -1 FABP3fatty acid binding protein 3, muscle and heart (mammary-derived growth inhibitor) (214285_at), score: 1 FANCGFanconi anemia, complementation group G (203564_at), score: -0.88 GINS1GINS complex subunit 1 (Psf1 homolog) (206102_at), score: -0.9 GINS2GINS complex subunit 2 (Psf2 homolog) (221521_s_at), score: -0.88 GINS3GINS complex subunit 3 (Psf3 homolog) (45633_at), score: -0.89 GINS4GINS complex subunit 4 (Sld5 homolog) (211767_at), score: -0.85 GTSE1G-2 and S-phase expressed 1 (204318_s_at), score: -0.86 HELLShelicase, lymphoid-specific (220085_at), score: -0.91 HJURPHolliday junction recognition protein (218726_at), score: -0.87 INSIG1insulin induced gene 1 (201627_s_at), score: 0.98 KIF11kinesin family member 11 (204444_at), score: -0.85 KIF14kinesin family member 14 (206364_at), score: -0.84 KIF15kinesin family member 15 (219306_at), score: -0.87 KIF18Bkinesin family member 18B (222039_at), score: -0.97 KIF2Ckinesin family member 2C (209408_at), score: -0.83 KIF4Akinesin family member 4A (218355_at), score: -0.87 KNTC1kinetochore associated 1 (206316_s_at), score: -0.92 LMNB1lamin B1 (203276_at), score: -0.85 LSSlanosterol synthase (2,3-oxidosqualene-lanosterol cyclase) (211019_s_at), score: 0.92 MAD2L1MAD2 mitotic arrest deficient-like 1 (yeast) (203362_s_at), score: -0.86 MCM10minichromosome maintenance complex component 10 (220651_s_at), score: -0.98 MKI67antigen identified by monoclonal antibody Ki-67 (212022_s_at), score: -0.86 NCAPGnon-SMC condensin I complex, subunit G (218663_at), score: -0.84 NCAPHnon-SMC condensin I complex, subunit H (212949_at), score: -0.83 OIP5Opa interacting protein 5 (213599_at), score: -0.85 ORC6Lorigin recognition complex, subunit 6 like (yeast) (219105_x_at), score: -0.95 PKMYT1protein kinase, membrane associated tyrosine/threonine 1 (204267_x_at), score: -0.85 PLXNC1plexin C1 (213241_at), score: 0.92 POLA1polymerase (DNA directed), alpha 1, catalytic subunit (204835_at), score: -0.97 POLD1polymerase (DNA directed), delta 1, catalytic subunit 125kDa (203422_at), score: -0.85 POLE2polymerase (DNA directed), epsilon 2 (p59 subunit) (205909_at), score: -0.89 POLQpolymerase (DNA directed), theta (219510_at), score: -0.85 PRIM1primase, DNA, polypeptide 1 (49kDa) (205053_at), score: -0.91 PSMC3IPPSMC3 interacting protein (213951_s_at), score: -0.89 RAD54BRAD54 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) (219494_at), score: -0.9 RBL1retinoblastoma-like 1 (p107) (205296_at), score: -0.84 RFC3replication factor C (activator 1) 3, 38kDa (204127_at), score: -0.93 RFWD3ring finger and WD repeat domain 3 (218564_at), score: -0.85 SC4MOLsterol-C4-methyl oxidase-like (209146_at), score: 0.98 SCDstearoyl-CoA desaturase (delta-9-desaturase) (200832_s_at), score: 0.98 SPAG5sperm associated antigen 5 (203145_at), score: -0.87 SPC25SPC25, NDC80 kinetochore complex component, homolog (S. cerevisiae) (209891_at), score: -0.87 SQLEsqualene epoxidase (213562_s_at), score: 0.99 STILSCL/TAL1 interrupting locus (205339_at), score: -0.9 TACC3transforming, acidic coiled-coil containing protein 3 (218308_at), score: -0.85 TIMELESStimeless homolog (Drosophila) (203046_s_at), score: -0.85 TMEM194Atransmembrane protein 194A (212621_at), score: -0.98 TTKTTK protein kinase (204822_at), score: -0.93 WDR76WD repeat domain 76 (205519_at), score: -0.87
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690352.cel | 11 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG11498 |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690344.cel | 10 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | none | GM00038C |
| E-GEOD-3860-raw-cel-1561690376.cel | 13 | 5 | HGPS | hgu133a | HGPS | AG11513 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485811.cel | 9 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486291.cel | 33 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486331.cel | 35 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486271.cel | 32 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486231.cel | 30 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486351.cel | 36 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485851.cel | 11 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |