
Under-expression is coded with green,
over-expression with red color.

response to stress
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a disturbance in organismal or cellular homeostasis, usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation).
cell communication
Any process that mediates interactions between a cell and its surroundings. Encompasses interactions such as signaling or attachment between one cell and another cell, between a cell and an extracellular matrix, or between a cell and any other aspect of its environment.
cell-cell signaling
Any process that mediates the transfer of information from one cell to another.
biological_process
Any process specifically pertinent to the functioning of integrated living units: cells, tissues, organs, and organisms. A process is a collection of molecular events with a defined beginning and end.
response to external stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an external stimulus.
response to wounding
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to the organism.
cellular process
Any process that is carried out at the cellular level, but not necessarily restricted to a single cell. For example, cell communication occurs among more than one cell, but occurs at the cellular level.
response to stimulus
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus.
all
This term is the most general term possible
response to wounding
A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to the organism.

extracellular region
The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
cellular_component
The part of a cell or its extracellular environment in which a gene product is located. A gene product may be located in one or more parts of a cell and its location may be as specific as a particular macromolecular complex, that is, a stable, persistent association of macromolecules that function together.
extracellular space
That part of a multicellular organism outside the cells proper, usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid.
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.
all
This term is the most general term possible
extracellular region part
Any constituent part of the extracellular region, the space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers constituent parts of the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite.

protein binding
Interacting selectively with any protein or protein complex (a complex of two or more proteins that may include other nonprotein molecules).
G-protein-coupled receptor binding
Interacting selectively with a G-protein-coupled receptor.
molecular_function
Elemental activities, such as catalysis or binding, describing the actions of a gene product at the molecular level. A given gene product may exhibit one or more molecular functions.
serine-type endopeptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of internal, alpha-peptide bonds in a polypeptide chain by a catalytic mechanism that involves a catalytic triad consisting of a serine nucleophile that is activated by a proton relay involving an acidic residue (e.g. aspartate or glutamate) and a basic residue (usually histidine).
catalytic activity
Catalysis of a biochemical reaction at physiological temperatures. In biologically catalyzed reactions, the reactants are known as substrates, and the catalysts are naturally occurring macromolecular substances known as enzymes. Enzymes possess specific binding sites for substrates, and are usually composed wholly or largely of protein, but RNA that has catalytic activity (ribozyme) is often also regarded as enzymatic.
endopeptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of internal, alpha-peptide bonds in a polypeptide chain.
serine-type peptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of peptide bonds in a polypeptide chain by a catalytic mechanism that involves a catalytic triad consisting of a serine nucleophile that is activated by a proton relay involving an acidic residue (e.g. aspartate or glutamate) and a basic residue (usually histidine).
peptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of a peptide bond. A peptide bond is a covalent bond formed when the carbon atom from the carboxyl group of one amino acid shares electrons with the nitrogen atom from the amino group of a second amino acid.
receptor binding
Interacting selectively with one or more specific sites on a receptor molecule, a macromolecule that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function.
cytokine activity
Functions to control the survival, growth, differentiation and effector function of tissues and cells.
binding
The selective, often stoichiometric, interaction of a molecule with one or more specific sites on another molecule.
chemokine activity
The function of a family of chemotactic pro-inflammatory activation-inducible cytokines acting primarily upon hemopoietic cells in immunoregulatory processes; all chemokines possess a number of conserved cysteine residues involved in intramolecular disulfide bond formation.
peptidase activity, acting on L-amino acid peptides
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of peptide bonds formed between L-amino acids.
hydrolase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of various bonds, e.g. C-O, C-N, C-C, phosphoric anhydride bonds, etc. Hydrolase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 3.
serine hydrolase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of a substrate by a catalytic mechanism that involves a catalytic triad consisting of a serine nucleophile that is activated by a proton relay involving an acidic residue (e.g. aspartate or glutamate) and a basic residue (usually histidine).
chemokine receptor binding
Interacting selectively with any chemokine receptor.
all
This term is the most general term possible
serine-type peptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of peptide bonds in a polypeptide chain by a catalytic mechanism that involves a catalytic triad consisting of a serine nucleophile that is activated by a proton relay involving an acidic residue (e.g. aspartate or glutamate) and a basic residue (usually histidine).
serine-type endopeptidase activity
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of internal, alpha-peptide bonds in a polypeptide chain by a catalytic mechanism that involves a catalytic triad consisting of a serine nucleophile that is activated by a proton relay involving an acidic residue (e.g. aspartate or glutamate) and a basic residue (usually histidine).
chemokine activity
The function of a family of chemotactic pro-inflammatory activation-inducible cytokines acting primarily upon hemopoietic cells in immunoregulatory processes; all chemokines possess a number of conserved cysteine residues involved in intramolecular disulfide bond formation.
| Id | Pvalue | ExpCount | Count | Size | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 04060 | 1.169e-02 | 1.208 | 7 | 122 | Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction |
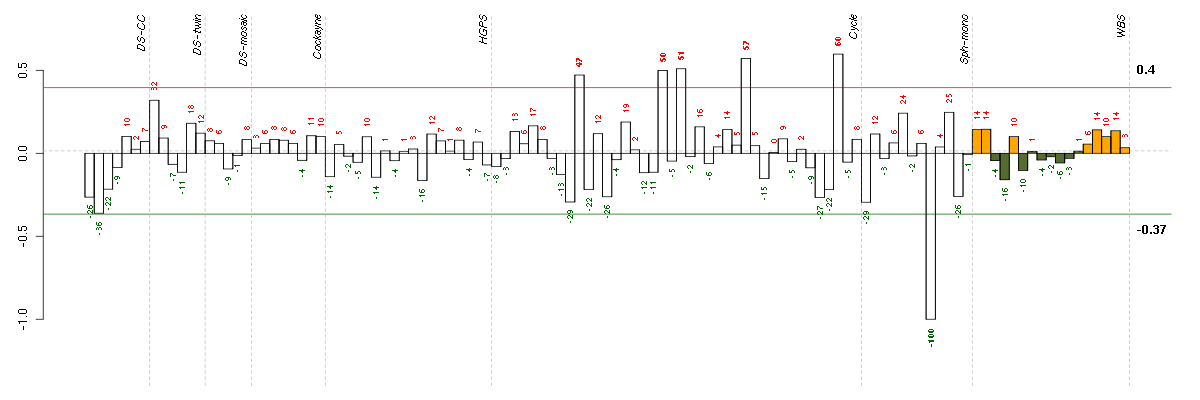
ABCG1ATP-binding cassette, sub-family G (WHITE), member 1 (204567_s_at), score: -0.64 AHI1Abelson helper integration site 1 (221569_at), score: -0.61 AREGamphiregulin (205239_at), score: -0.77 BCL11AB-cell CLL/lymphoma 11A (zinc finger protein) (219497_s_at), score: -0.58 C3complement component 3 (217767_at), score: -0.61 CAPN3calpain 3, (p94) (210944_s_at), score: -0.65 CCL11chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 11 (210133_at), score: -0.93 CCL7chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 7 (208075_s_at), score: -0.7 CCL8chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 8 (214038_at), score: -0.87 CLK1CDC-like kinase 1 (214683_s_at), score: -0.61 COL14A1collagen, type XIV, alpha 1 (212865_s_at), score: -0.59 COL5A3collagen, type V, alpha 3 (52255_s_at), score: -0.89 CPEB3cytoplasmic polyadenylation element binding protein 3 (205773_at), score: -0.62 CTSKcathepsin K (202450_s_at), score: -0.66 CTSOcathepsin O (203758_at), score: -0.58 CXCL6chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 6 (granulocyte chemotactic protein 2) (206336_at), score: -0.75 DIRAS3DIRAS family, GTP-binding RAS-like 3 (215506_s_at), score: -0.58 DNAJB9DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily B, member 9 (202843_at), score: -0.64 DOCK4dedicator of cytokinesis 4 (205003_at), score: -0.71 DPP4dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 (211478_s_at), score: -0.67 DUSP6dual specificity phosphatase 6 (208892_s_at), score: -0.6 EGR3early growth response 3 (206115_at), score: -0.67 EML1echinoderm microtubule associated protein like 1 (204797_s_at), score: -0.59 EREGepiregulin (205767_at), score: -0.64 GAP43growth associated protein 43 (204471_at), score: -0.65 GKglycerol kinase (207387_s_at), score: -0.78 GPM6Bglycoprotein M6B (209170_s_at), score: -1 GPR177G protein-coupled receptor 177 (221958_s_at), score: -0.72 HGFhepatocyte growth factor (hepapoietin A; scatter factor) (209960_at), score: -0.98 HSD11B1hydroxysteroid (11-beta) dehydrogenase 1 (205404_at), score: -0.57 IL13RA2interleukin 13 receptor, alpha 2 (206172_at), score: -0.76 IL1RNinterleukin 1 receptor antagonist (212657_s_at), score: -0.76 IL24interleukin 24 (206569_at), score: -0.88 IL33interleukin 33 (209821_at), score: -0.78 ING1inhibitor of growth family, member 1 (208415_x_at), score: -0.63 IRAK3interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 3 (213817_at), score: -0.66 LIFleukemia inhibitory factor (cholinergic differentiation factor) (205266_at), score: -0.59 MAP4K4mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase 4 (218181_s_at), score: -0.59 MAP7microtubule-associated protein 7 (202890_at), score: -0.64 MID1IP1MID1 interacting protein 1 (gastrulation specific G12 homolog (zebrafish)) (218251_at), score: -0.62 MMP10matrix metallopeptidase 10 (stromelysin 2) (205680_at), score: -0.8 MRPS6mitochondrial ribosomal protein S6 (213167_s_at), score: -0.62 NEFLneurofilament, light polypeptide (221805_at), score: -0.55 NLGN4Yneuroligin 4, Y-linked (207703_at), score: -0.57 NR4A2nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 2 (216248_s_at), score: -0.66 OLFML2Aolfactomedin-like 2A (213075_at), score: -0.8 PCSK1proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 1 (205825_at), score: -0.67 PID1phosphotyrosine interaction domain containing 1 (219093_at), score: -0.65 PLATplasminogen activator, tissue (201860_s_at), score: -0.61 PMAIP1phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate-induced protein 1 (204286_s_at), score: -0.62 PNRC2proline-rich nuclear receptor coactivator 2 (217779_s_at), score: -0.57 PRKG2protein kinase, cGMP-dependent, type II (207505_at), score: -0.66 PRSS1protease, serine, 1 (trypsin 1) (216470_x_at), score: -0.65 PRSS3protease, serine, 3 (207463_x_at), score: -0.58 PTHLHparathyroid hormone-like hormone (211756_at), score: -0.58 PTPRDprotein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, D (214043_at), score: -0.75 RGS5regulator of G-protein signaling 5 (218353_at), score: -0.69 RPS20ribosomal protein S20 (216247_at), score: -0.58 SLC1A3solute carrier family 1 (glial high affinity glutamate transporter), member 3 (202800_at), score: -0.73 SLC22A4solute carrier family 22 (organic cation/ergothioneine transporter), member 4 (205896_at), score: -0.56 SLC38A4solute carrier family 38, member 4 (220786_s_at), score: 0.7 SPRY4sprouty homolog 4 (Drosophila) (221489_s_at), score: -0.6 STRA6stimulated by retinoic acid gene 6 homolog (mouse) (221701_s_at), score: -0.64 TFDP2transcription factor Dp-2 (E2F dimerization partner 2) (203588_s_at), score: 0.75 UCP2uncoupling protein 2 (mitochondrial, proton carrier) (208998_at), score: 0.83 ZFYVE16zinc finger, FYVE domain containing 16 (203651_at), score: -0.58
| Id | sample | Experiment | ExpName | Array | Syndrome | Cell.line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-GEOD-4219-raw-cel-1311956418.cel | 13 | 7 | Sph-mono | hgu133plus2 | none | Sph-mon 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515485831.cel | 10 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486011.cel | 19 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486051.cel | 21 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486191.cel | 28 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |
| E-TABM-263-raw-cel-1515486391.cel | 38 | 6 | Cycle | hgu133a2 | none | Cycle 1 |